Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):514-527. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to use big data from elementary, middle, and high school lunches to determine the primary food groups and menu items that contribute to lunch meals through text-mining and investigate the variations in food groups and menu composition patterns across different grade levels.
Methods
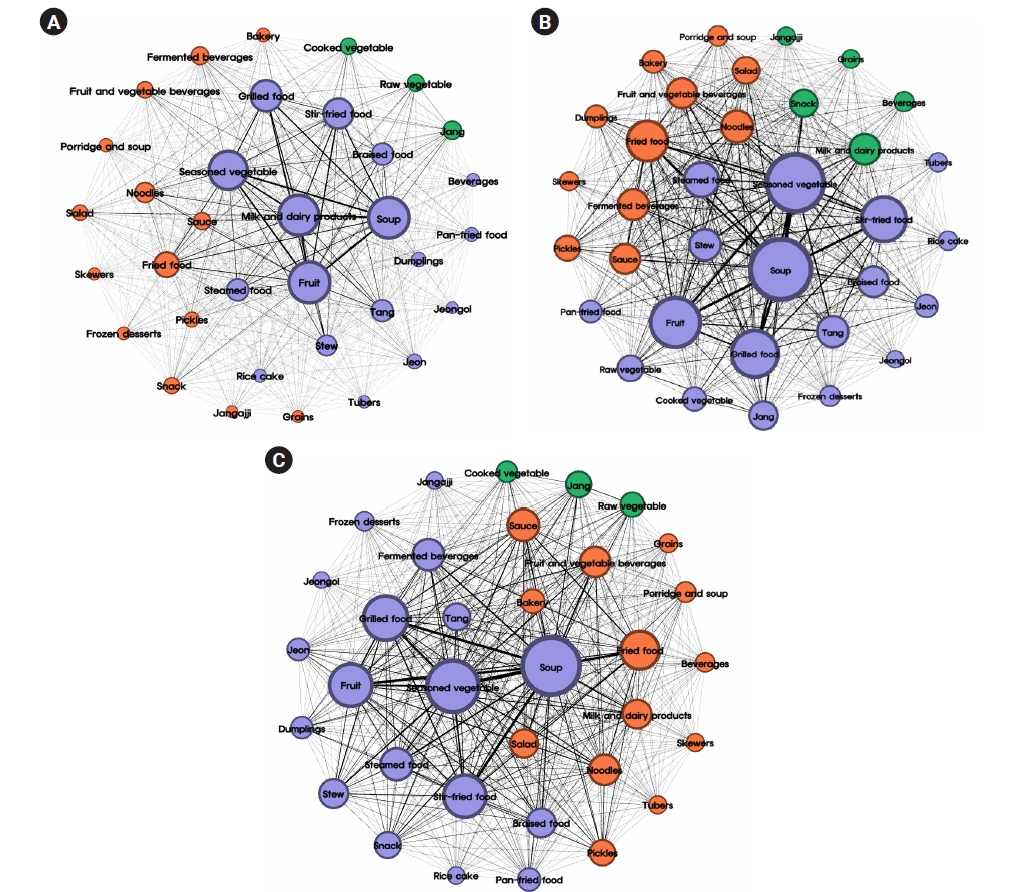
Between 2021 and 2023, a total of 7,892,456 lunch menus from 17 cities and provinces in South Korea were analyzed using big data from the National Education Information System (NEIS) system. After undergoing text preprocessing for text-mining, the collected menus were classified into 34 food groups based on primary ingredients and cooking methods, excluding the types of rice and kimchi. Subsequently, analyses of term frequency, term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF), centrality, and co-occurrence networks were performed on the food group and menu data.
Results
According to the TF-IDF, the most frequent food group across all grade levels was soup and seasoned vegetables, whereas milk was the most frequently provided menu. As the grade level increased, the frequency of grilled and fried food increased. In elementary schools, fruits exhibited the highest centrality, whereas soup had the highest centrality in middle and high schools. Co-occurrence frequency revealed that the soup-fruit combination was the most common in elementary schools, whereas soup and seasoned vegetables were most frequently paired in middle and high schools. The co-occurrence network of food groups and menus further indicated that menus regularly provided as standard meals and those frequently offered as special meals formed distinct communities.
Conclusion
This study investigated the food groups and menu provision patterns in school meals through text-mining techniques applied to large-scale school lunch. The findings may contribute in enhancing the quality of nutritional management, school foodservice, and menu composition of school meal programs.
- 957 View
- 40 Download

- [English]
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):97-113. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Since the enactment of the School Nutrition Act in 1981, school lunch programs in South Korea have grown quantitatively and qualitatively with a current student participation rate of 99.8%. Nonetheless, educational materials are needed to reduce misunderstanding and ignorance about school lunch programs. This study aimed to develop 3 educational videos that help students of various ages (kindergarteners/lower-grade elementary, upper-grade elementary, and secondary school, respectively), understand the school lunch program.
Methods
A scenario was created, was made, and the opinions on the scenario from experts in foodservice sectors were collected. A survey was conducted to students and parents to determine topics they wanted to know about school foodservice. The final videos were produced using this information and the expert opinions. The data were analyzed using SPSS 27.0 for Mac (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA); a P-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Three videos on school foodservice were developed for various age levels of students: kindergarten/lower-grade elementary, upper-grade elementary, and secondary school. Additionally, English subtitles were included for the multicultural student population. These videos, each lasting about 7 minutes, cover topics such as nutrition, hygiene, and the cultural significance of the school lunch program. The survey results showed that parents and students wanted to know the following topics about the school lunch program: “nutritionally balanced diet” (11.9%), “purchasing safe food ingredients” (10.9%), and “healthy eating habits” (9.9%).
Conclusions
The developed videos will serve as valuable educational resources on school foodservice, foster a deeper understanding of the school lunch program in parents and students, and potentially address their inquiries regarding production processes, nutrition, hygiene, cultural heritage, and health.
- 1,292 View
- 28 Download

- [Korean]
- Analysis of Surveys to Determine the Real Prices of Ingredients used in School Foodservice
- Seo-Hyun Lee, Min A Lee, Jae-Yoon Ryoo, Sanghyo Kim, Soo-Youn Kim, Hojin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):188-199. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose was to identify the ingredients that are usually surveyed for assessing real prices and to present the demand for such surveys by nutrition teachers and dietitians for ingredients used by school foodservice.
Methods
A survey was conducted online from December 2019 to January 2020. The survey questionnaire was distributed to 1,158 nutrition teachers and dietitians from elementary, middle, and high schools nationwide, and 439 (37.9% return rate) of the 1,158 were collected and used for data analysis.
Results
The ingredients which were investigated for price realities directly by schools were industrial products in 228 schools (51.8%), fruits in 169 schools (38.4%), and specialty crops in 166 schools (37.7%). Moreover, nutrition teachers and dietitians in elementary, middle, and high schools searched in different ways for the real prices of ingredients. In elementary schools, there was a high demand for price information about grains, vegetables or root and tuber crops, special crops, fruits, eggs, fishes, and organic and locally grown ingredients by the School Foodservice Support Centers. Real price information about meats, industrial products, and pickled processed products were sought from the external specialized institutions. In addition, nutrition teachers and dietitians in middle and high schools wanted to obtain prices of all of the ingredients from the Offices of Education or the District Office of Education.
Conclusions
Schools want to efficiently use the time or money spent on research for the real prices of ingredients through reputable organizations or to co-work with other nutrition teachers and dietitians. The results of this study will be useful in understanding the current status of the surveys carried out to determine the real price information for ingredients used by the school foodservice.
- 617 View
- 14 Download

- [Korean]
- Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
- Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):167-176. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to identify the awareness and practice of reducing sugar in school meals and the status of nutrition education regarding sugar reduction.
Methods
An online survey was conducted on 101 nutrition teachers (dietitians) working at elementary, middle, and high schools in Daegu.
Results
School nutrition teachers in Daegu recognized the need for efforts to reduce the sugar intake in the Korean diet, and it was found that elementary nutrition teachers were more aware of the implementation of the sugar reduction policy at the national level than middle and high school nutrition teachers (P = 0.002). Among the policies to reduce sugar intake at the national level, there was a high need for the promotion of self-control and limiting the sales of food with high sugar content in schools and their vicinity. The degree of practice for reducing sugar in school meals was found to be higher in the preparation, purchase, and cooking stage compared to the serving stage (P < 0.05). There was a high need for changing the preferences of the subjects for a sweet taste as a means of reducing the sugar in school meals. Thirty-six percent of nutrition teachers conducted sugar reduction education, and sending out school newsletters was the highest type of nutrition education at 80.6%.
Conclusions
To effectively promote reduced sugar intake in school meals, it is necessary to change the preference of the subjects for sweetness and to conduct continuous education that can improve the awareness of people for reducing their sugar intake. For this, it is necessary to set aside time for nutrition education and to prepare an institutional framework for providing this education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Learning to care in the food system: Education for Sustainable Development resources, food education and the farming of animals for food
Verity Jones, Christopher Bear
Environmental Education Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Analytic Hierarchy Process approach to estimate weights of menu management in the school foodservice
Hyo Bin Im, Seo Ha Lee, Hojin Lee, Lana Chung, Min A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 349. CrossRef - Sugar Intake and Perception of Sugar Reduction among University Students in Gwangju
Yeon-Ok Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1170. CrossRef - Analysis of the Perception and Need for Education about Genetically Modified Foods among Elementary, Middle and High School Parents:Focus on the Jeonnam Region
Da-Hye Choi, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(1): 67. CrossRef - Comparison of the Sodium and Sugar Reduction Practices at Samsam Foodservices and General Foodservices in Daegu
Sung-young Kwon, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(4): 270. CrossRef
- Learning to care in the food system: Education for Sustainable Development resources, food education and the farming of animals for food
- 663 View
- 14 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
- Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):386-395. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate sodium reduction practices in school foodservice in Daegu. Methods The survey included 199 nutrition teachers and dietitians working at elementary, middle and high schools in Daegu. The survey topics included the following: the frequency of salinity measurement, workers in charge of the measurement, average salinity of the soup and stew served, frequency and difficulties of offering low-sodium meals, Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA) of sodium reduction methods in school foodservice and the need for political support in encouraging sodium reduction. Results The mean salinity of the soup and stew was higher in high school foodservice than in elementary and middle school foodservice. Middle and high schools have difficulties in offering low-sodium meals due to concerns of decreasing satisfaction for the meals. The results of the IPA of programs to reduce sodium in school meals showed that most of the items in the cooking and serving stages were in the 2nd quadrant (Keep up the good work), and all purchasing and menu planning stages occupied the 3rd quadrant (Low priority). To reduce sodium in school meals, government support is required in developing low-sodium recipes for school foodservice, encouraging education on sodium reduction for school foodservice officials and developing low-sodium food for institutional foodservice. Conclusions To encourage sodium reduction in school meals, the priority is to make low-sodium recipes available. Also, it is necessary to develop a program that calculates the sodium content in menus and processed foods through National Education Information System and to establish standards for sodium levels in school foodservice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
Jiwoo Min, Youngmi Lee, Yunhee Chang, Yujin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 304. CrossRef - 충북지역 중등학생의 건강식생활 관련 식행동과 영양관리 정책에 대한 인식
은서 고, 영은 이
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 197. CrossRef - Importance-performance analysis of sodium reduction practices by school nutrition teachers and dietitians in the Republic of Korea
Youngmi Lee, Sooyoun Kwon, Meeyoung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(4): 812. CrossRef - Comparison of Sodium Reduction Practice and Estimated Sodium Intake by Salty Food Preference on Employees and Customers of Sodium Reduction Restaurant in Daegu, Korea
Su-Jin Lee, Keon-Yeop Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 27. CrossRef - Comparison of the Sodium and Sugar Reduction Practices at Samsam Foodservices and General Foodservices in Daegu
Sung-young Kwon, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(4): 270. CrossRef
- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
- 543 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Recognition of Environmentally-friendly Agricultural Products for School Foodservice of Nutrition Teachers and Parents in 2018 at Seongnam in Gyeonggi province
- Jisoo Kwon, Wookyoun Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):290-299. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the nutrition teachers' and parents' recognition of environmentally-friendly agricultural products (EAPs) used in school foodservice.
METHODS
A questionnaire survey was given to 128 school foodservice nutrition teachers in Seongnam and 189 parents from Oct. 16 to Oct. 31, 2018 at Seongnam in Gyeonggi province. The survey included information on the recognition, satisfaction, and improvement of EAPs, and the results of the two groups were compared.
RESULTS
A comparison of the recognition of EAPs showed that nutrition teachers knew more about the EAPs and local government support in school foodservice than the parents. On the other hand, the parents were more aware than the nutrition teachers in that children have a higher affinity for EAPs than for general agricultural products in the school foodservice. A comparison of the level of satisfaction with the EAPs by nutrition teachers and parents revealed the nutrition teachers to be significantly more satisfied than parents in terms of the color, taste and nutrition of EAPs. Among the items that should be provided with EAPs, more than 50% of each group of nutrition teachers and parents answered that vegetables must be provided first. Some 70.9% of nutrition teachers and 84.5% of parents were aware of the certification standards of EAPs. The nutrition teachers had showed a slightly higher score than the parents in the certification system (3.51 vs. 3.25). In terms of improving the EAPs, 36.2% of nutrition teachers answered a reasonable price preferentially, whereas 56.4% of parents answered maintaining quality. In the expected effects of using EAPs, 57.9% of nutrition teachers answered an improvement of parents' satisfaction on the school foodservice. On the other hand, 38.0% of parents answered an improvement of children' satisfaction on school foodservice.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutrition teachers and parents need to be educated on the certification systems that would enhance the trust in EAPs.
- 505 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Development of Model for 「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€
- Hae Young Lee, Bo Sook Yi, Jina Cha, Sun Ok Ham, Moon Kyung Park, Mi Nam Lee, Hye Young Kim, Haeng Hwa Kang, Jin Wook Kwon, Yun Hui Jeong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):60-76. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.60
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to develop a systematic and standardized「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€that can identify the current status of school meals on the nationwide level.
METHODS
This study was carried out in six steps of the analysis of report/investigation data related to school foodservice in metropolitan and provincial offices of education, analysis of preceding research related to the actual status of school foodservice, field verification of the actual condition of the school foodservice site, development of a draft of「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€, pilot study of a draft of 「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€, and suggestions of a final model of「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€from August to December, 2017. Statistical analysis was performed for frequency analysis and descriptive analysis using the SPSS program ver. 23.
RESULTS
A draft of「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€was developed by analyzing the current status of report/research data on school meals in metropolitan and provincial offices of education, analyzing the preceding research on school meals, and identifying the actual conditions at school foodservice sites. To verify the validity of the school foodservice survey questionnaire, 1,031 schools were sampled from a total of 10,251 schools and the pilot test of ‘2017 School Foodservice Survey’ was conducted. The final model of「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€consisted of 12 survey sections, 29 survey categories, and 433 survey items, and the survey cycle was set for one year and three years for each survey item.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the objective statistical data through「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€, it is possible to develop the school foodservice policy, which will help establish the reliability of the school meals. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- 665 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Improving Perception and Satisfaction on Middle and High School Foodservice: The Role of Student Participation Program in Serving School Meals
- Jeong Eun Park, Kyung Suk Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):243-256. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.243
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
We evaluated the extent to which implementation of student participation programs in serving school meals impacts student perception and satisfaction with school foodservice in middle and high school settings.
METHODS
Students' perception of management and satisfaction with quality attributes of school foodservice were assessed by questionnaire methods and compared by the program implementation status of student participation in serving school meals. Correlation and multiple regression analyses were performed to identify factors affecting perception and satisfaction.
RESULTS
The overall mean score for perception regarding the management of school foodservice was low (3.53 out of 10 points) and middle school students showed a higher mean score than high school students (4.10 vs. 2.94 points). In both middle and high schools, student perception was significantly higher in schools implementing the program. The average score for student satisfaction with the quality of school foodservice was 3.50 out of 5 points. Similarly, we observed a significantly higher satisfaction among middle versus high school students (3.93 vs. 3.04 points) and in schools implementing the program versus those that were not. Overall, student participation in serving school meals resulted in increases in satisfaction with school foodservice of 0.269 and 0.466 points among middle and high school students, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Implementation of student participation in serving school meals could be used as a strategy to improve perception and satisfaction of students with their school foodservice. Establishment of guidelines of student serving participation programs encompassing different perspectives from students, dietitians and school faculties are warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef - Causal relationship among quality factors, emotional responses, and satisfaction of school food service in Henan province, China
Miaomiao Li, Young Eun Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 356. CrossRef - Feasibility Study on Application of Revised Nutritional Standards for School Lunches: Consumer Satisfaction Survey
Meeyoung Kim, Youngmin Nam
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(5): 367. CrossRef
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- 651 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Perception of Use of Environment-friendly Agricultural Products during School Foodservice of Mothers of Elementary School Students in Gyeonggi
- Young Un An, Myung Hee Kim, Mi Kyeong Choi, Mi Hyun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):234-242. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study was to investigate the perception of mothers of elementary school students regarding environment-friendly agricultural products in school foodservice.
METHODS
A total of 282 mothers whose children were receiving environment-friendly agricultural products during elementary school foodservice in Gyeonggi participated in this questionnaire survey. The survey was conducted to investigate respondents perception and satisfaction with environment-friendly agricultural products in their children's school meals from May 29 to June 9, 2017.
RESULTS
About 79% of the subjects were satisfied with school foodservice. The most important aspects of school foodservice were nutrition (35.8%) and sanitation (34.8%). Over 80% of the subjects were aware of environment-friendly agricultural products and about 54% of the subjects checked for a certification mark when purchasing environment-friendly agricultural products. Additionally, 72.3% of the subjects knew that environment-friendly agricultural products were used at school. The advantages of using environment-friendly agricultural products in school foodservice were safety (75.5%) and high food quality (16.3%). About 66% of the mothers knew the school was receiving support from the city or education office for using environment-friendly agricultural products. Additionally, 74.5% of the mothers responded that they are willing to pay for use of environment-friendly agricultural products when subsidies were not supported.
CONCLUSIONS
The positive perception and high support for use of environment-friendly agricultural products in school foodservice among elementary students' mothers can be used as basic data for expansion of the use of environment-friendly agricultural products in school foodservice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shifting social perceptions of dietitians in Korea after the legislation of nutrition teachers: a keyword network analysis of unstructured data
Yunkyoung Oh, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 214. CrossRef - Recognition of Environmentally-friendly Agricultural Products for School Foodservice of Nutrition Teachers and Parents in 2018 at Seongnam in Gyeonggi province
Jisoo Kwon, Wookyoun Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(4): 290. CrossRef - When Agricultural Waste Transforms into an Environmentally Friendly Material: The Case of Green Concrete as Alternative to Natural Resources Depletion
Cătălina Mihaela Grădinaru, Adrian Alexandru Şerbănoiu, Danut Traian Babor, Gabriel Constantin Sârbu, Ioan Valentin Petrescu-Mag, Andrei Cristian Grădinaru
Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Ethics.2019; 32(1): 77. CrossRef - A Study on Satisfaction of School Food Service Using Environment-friendly Agricultural Products
Byeol Han, Ho Kim, Sung-Bum Yang
Korean Journal of Organic Agricultue.2018; 26(4): 559. CrossRef - Willingness-to-Pay on Increase of Usage for Environmental-friendly Agricultural Product in School Food Service
Sung-Bum Yang
Korean Journal of Organic Agricultue.2018; 26(4): 609. CrossRef
- Shifting social perceptions of dietitians in Korea after the legislation of nutrition teachers: a keyword network analysis of unstructured data
- 945 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Developing Food Safety Education Program for Employees at School Foodservice Implementing HACCP
- Hye Yeon Lee, Hyun Joo Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):84-92. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.84
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to develop a food safety education program for school foodservice employees and evaluate its effectiveness.
METHODS
Food safety education programs were made into two levels; one for new employees in school foodservice and another for employees in charge of Critical Control Point (CCP) monitoring. The programs were for 40-minute-long lecture using PowerPoint. The effectiveness of these programs were assessed based on eleven evaluation items by school foodservice dieticians (n=30) and the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) specialist (n=13). All statistical analyses are conducted by SPSS package program (ver 20.0).
RESULTS
According to the results of evaluating the food safety education program by dietitian and HACCP specialist, the overall satisfaction score was 4.14, evaluated by 5 point scale. There were no significant difference in results of evaluation between dieticians and HACCP specialists. The score of 'it is helpful to work' and 'pictures, images and charts are pertinent to study' were higher than others while the score of 'education contents is pleasant and interesting' and 'screen is pleasant and interesting' were the lowest among all evaluation items.
CONCLUSIONS
To increase the school foodservice quality, employees should be offered regular food safety education and training through effective education media including prerequisite program and HACCP manual for school foodservice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
해림 조, 서진 김, 중범 김, 수연 김
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2025; 41(3): 151. CrossRef - Perception on HACCP System of School Foodservices Dietitians in Chungbuk
Ji Hyeoun Im, Miao Miao Li, Young Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2019; 35(1): 57. CrossRef - Perception of Use of Environment-friendly Agricultural Products during School Foodservice of Mothers of Elementary School Students in Gyeonggi
Young-Un An, Myung-Hee Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 234. CrossRef
- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
- 667 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Job Perception and the Need for Job Improvement among School Nutrition Teachers in Seoul
- Seoung Hee Kim, Kyung Eun Lee, Jin Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):12-24. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
The objectives of the study were to investigate the school nutrition teachers' perception on their job and to find out recommendations needed for its improvement in order to provide a quality foodservice and nutrition education at schools.
METHODS
A total of 219 school nutrition teachers in Seoul were surveyed using self-administered questionnaires.
RESULTS
The perceived importance of the 16 job duties was rated 3.8 based on a 5-point scale (1: very unimportant - 5: very important). The importance of six duties including nutrition management, production management, nutrition education, and food safety management were rated over 4 point but that of record-keeping for documents, official reporting, and service management was rated the lowest. Importance-Performance Analysis showed that nutrition management, receiving/storage management, production management, menu management, food safety management, and equipment/facilities management should be emphasized to maintain the current performance of duties. The performance of the nutrition education and counseling needed to be improved since the importance scores were greater than average but the performance scores were lower than the average. Official reporting and miscellaneous jobs were rated the highest for simplification need. More than half of the respondents agreed that equipment/facilities management, miscellaneous jobs, service staff supervision, and service line supervision could be allocated to other school departments.
CONCLUSIONS
School nutrition teachers should invest more time and resources on their core job duties such as nutrition management, production management, food safety management, and nutrition education for providing quality foodservice and nutrition education. To reflect the environmental changes of school foodservice, a reasonable staffing index of school nutrition teachers needs to be developed. In addition, hiring an assistant or implementing school nutrition teacher internship programs can be useful to reduce workloads of the nutrition teachers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Importance, performance frequency, and predicted future importance of dietitians’ jobs by practicing dietitians in Korea: a survey study
Cheongmin Sohn, Sooyoun Kwon, Won Gyoung Kim, Kyung-Eun Lee, Sun-Young Lee, Seungmin Lee
Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions.2024; 21: 1. CrossRef
- Importance, performance frequency, and predicted future importance of dietitians’ jobs by practicing dietitians in Korea: a survey study
- 657 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- The use Frequency and Amount of Food Sources of Sodium and Knowledge Requirement, and Job Satisfaction of Dietitians and Nutrition Teachers according to the School Types in Busan
- Jee Young Yeon, Soon Kyu Lee, Baeg Won Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(2):198-211. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.2.198
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
To investigate the use frequency and amount of food sources of sodium and knowledge requirement, and job satisfaction with school food services according to the school types in Busan.
METHODS
A total of 98 schools were surveyed and knowledge requirement and job satisfaction were assessed using a questionnaire. In addition, the use frequency and amount of food sources of sodium for 10 school days were examined.
RESULTS
The response rate of the most difficult area among dietitians' tasks was significantly high in 'nutrition education and counseling' for elementary schools and 'hygiene management' for high schools (p < .05). The response rate of the factors to be considered in meal planning was significantly high in 'energy and nutrients requirement' for elementary schools and 'menu/taste preference of students' for middle and high schools (p < .05). The response rate of whether school food services affect health and eating habits of students or not was significant high in 'very helpful' for elementary schools (p < .001). The average sodium contents in the meals of elementary, middle and high schools was 1981.4 mg/meal/person/day, 1867.3 mg/meal/person/day and 1,329.9 mg/meal/person/day, respectively. For foods in highest sodium, Kimchi, Oribulgogi, and Kare rice were ranked 1st, 2nd and 3rd respectively. The main reason for not providing the fruits was 'price' among all groups. The knowledge requirement such as 'nutrition and menu management', 'nutrition education', and 'nutrition counseling' was significantly higher in elementary school compared with middle and high school (p < .001, p < .01, and p < .01 respectively). The dietitians and nutrition teachers of elementary schools have a higher job satisfaction compared with those of middle schools (p < .01). The job satisfaction was positively correlated with knowledge requirement of dietitians and nutrition teachers of elementary and middle schools.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggest that developing dietitians' education program about knowledge requirement contribute to increasing the school food service and job satisfaction in elementary and middle schools. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- School Dietitian Awareness, Practice, and Sodium Reduction Plan in School Meal Service
Eun Kyung Kim, Hae Young Kim
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 222. CrossRef - Status and Need Assessment on Nutrition & Dietary Life Education among Nutrition Teachers in Elementary, Middle and High Schools
Na Gyeong Oh, Su Jin Gwon, Kyung Won Kim, Cheong Min Sohn, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 152. CrossRef
- School Dietitian Awareness, Practice, and Sodium Reduction Plan in School Meal Service
- 640 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of the Quality Attribute and Satisfaction on School Foodservice in 2010
- Il Sun Yang, Bo Sook Yi, Moon Kyung Park, Seung Hee Baek, Yoo Sun Chung, Jin Yi Jeong, Yoon Ji Kim, Hye Young Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(5):491-504. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.5.491
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - The purposes of this study were to analyze the quality attributes, quality factors and customer satisfaction in school foodservice and to provide suggestions for improving school foodservice environments. The survey was distributed to different respondents (5,771 students, 2,045 parents, and 1,981 faculty members) at different types of schools (elementary school, middle school, and high school) on September 2010 in 16 cities and provinces. The data were analyzed using SPSS for descriptive analysis, one-way ANOVA, t-test and multiple linear regression analysis. First, all foodservice quality attributes were significant different by respondents and the faculty had higher scores than parents and students. A comparison of scores by respondents and distribution place demonstrated that classroom of student and parents had a higher score for quality attributes. The overall satisfaction with school foodservice was significant different by respondents and higher for classroom than for dining hall for student and parents. In comparison of annual data, there was decreased overall satisfaction and quality attributes in student and parents. Second, in the regression results, which showed the effects of the foodservice quality attributes on overall satisfaction by respondents and distribution place, improvements of 'food taste', 'pleasant foodservice environment', and 'kindness of employee' would increase satisfaction in most of the respondents. Third, the overall satisfaction with school foodservice was higher for nutrition teachers than dietitians for students and faculty. Therefore, the operators will need to make different efforts based on each customer needs to improve the overall satisfaction on school foodservice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acceptability of School Menus: A Systematic Review of Assessment Methods
Síntia Almeida Santana, Sueny Andrade Batista, Dayanne da Costa Maynard, Verônica Cortez Ginani, Renata Puppin Zandonadi, Raquel Braz Assunção Botelho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 2242. CrossRef - School Foodservice Employees’ Perception on Food Waste Generation and Needs to Improve Foodservice for Plate Waste Reduction in Gyeonggi Province
Kyung-Eun Lee, Jiyeon Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(5): 408. CrossRef - Development of Model for 「The Survey on School Foodservice Program」
Hae-Young Lee, Bo-Sook Yi, Jina Cha, Sun-Ok Ham, Moon-Kyung Park, Mi-Nam Lee, Hye-Young Kim, Haeng-Hwa Kang, Jin-Wook Kwon, Yun-Hui Jeong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 60. CrossRef - Perception of Use of Environment-friendly Agricultural Products during School Foodservice of Mothers of Elementary School Students in Gyeonggi
Young-Un An, Myung-Hee Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 234. CrossRef - Effects of students' satisfaction with school meal programs on school happiness in South Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Oksun Kim, Youngmi Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(4): 342. CrossRef - Improving Perception and Satisfaction on Middle and High School Foodservice: The Role of Student Participation Program in Serving School Meals
Jeong-Eun Park, Kyung-Suk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 243. CrossRef - Exploratory study on effect of eco-friendly program in high school foodservice on adolescents' dietary behavior and satisfaction with foodservice
Seyoung Ju, Deokhee Song, Hyeja Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 494. CrossRef - Analysis of Perception and Satisfaction of Military Foodservice that are Provided According to the Ranks of the Soldiers
Jun-Hee Kim, Se-Jeong Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 53. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Satisfaction of School Foodservice by High School Type in Chungnam Area
Myung-Hee Kim, Su-Mi Lim, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 213. CrossRef - Evaluation of Foodservice Hygiene in Middle School Students by Meal Service Area in Busan
Yeo Kyeong Kim, Hee Sun Choi, Eun Soon Lyu
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(1): 145. CrossRef - Students’ Satisfaction of School Lunch According to the Dietary Habit and Educational Experience of Nutrition and Food
Sung Hee Park, Young Chan Choe
Family and Environment Research.2015; 53(4): 425. CrossRef - Use and Assessment of Home-Delivered Meal Service for Children from Low-Income Families
Jeong-A Moon, Chang-Hee Yoo, Kyung-Eun Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(6): 935. CrossRef - A Study on the Foodservice Quality Factors and Satisfaction of Community Children Center
Seong Hee Ko, Kyung-Yeoun Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(5): 914. CrossRef - Perception and Satisfaction of Free Foodservice in Male Middle School Students in Chungnam
Yu-Rin Kim, Eun-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 87. CrossRef
- Acceptability of School Menus: A Systematic Review of Assessment Methods
- 703 View
- 1 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [English]
- Recognition of Elementary School Students for The Country-of-Origin Labeling at School Foodservice in Seoul
- So Yeon Kim, Sanghyun Park, Nami Joo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(4):507-512. Published online August 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to offer basic data that give effective ways to inform the country-of-origin labeling, where the ingredients they are serving are from, at school foodservice and to reconsider the importance of the labeling origin based on the survey by the elementary school students. 96.0% of the elementary school students agreed to the regulation about the country-of-origin labeling and the older students were influenced more by media and also supported the labeling. About the tendency of ingesting food from the country the students didn't like, 69% of them disagreed to eat. In the ways to label the country-of-origin labeling at school foodservice, elementary school students recognized easily the indication of origin designed by menu items, letter type. 76% of elementary school students checked the country-of-origin labeling posted at restaurants. When the students eat out, 68% of them were unwilling to have the food using the ingredients from the country they don't like. The country-of-origin for main ingredients such as beef, pork, chicken and other meat products, rice, kimchi had high importance scores. We found that the students think about the country-of-origin for main ingredients is important. Consequently, education and public relations of the country-of-origin labeling for elementary school students would be required.
- 211 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Factors Influencing Job Satisfaction of Dietitians(Nutrition Teachers) of School Foodservice in Daejeon/Chungnam Province
- Wang Mi Shin, Jang Il Han, Seong Ai Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):798-806. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to investigate how to improve job satisfaction for dietitians and nutrition teachers by identifying influencing factors in Daejeon and Chungnam Province, South Korea. A survey was conducted among school foodservice dietitians and nutrition teachers from selected primary, middle and high school in the area. This survey consisted of general characteristics, status of their job, job satisfaction, work satisfaction and work performance. In this study we found current state of general characteristics and status of their job according to frequency analysis and the level of work satisfaction, work performance and job satisfaction using descriptive statistics. The t-test, ANOVA and Duncan-test were also conducted in order to searching for tendency of job satisfaction according to the general characteristics and the status of their job. Pearson's correlation was carried out in order to find correlation with job satisfaction. Also, factors, which influenced job satisfaction according to regression analysis, were drawn. We describe the difference of job satisfaction between irregular dietitians and nutrition teachers as well. Besides we discussed the improvement of dietitians' (nutrition teachers') work environment to raise their job satisfaction through this study.
- 175 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Factors Related to Sanitary Management Performance Based on HACCP System in School Foodservice: Seoul, Gyeonggi, Kangwon and Choongchung Areas in Korea
- Gyoung Mi Kim, Sim Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):817-830. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to analysis the sanitary management performance based on HACCP system for school foodservice. This study was carried out from September 2008 until December 2008 and is targeted towards schools' dietitians that work at schools with school foodservice. The regional distribution of this research is as follows; 377 schools in Seoul, 648 schools in Gyeonggido, 160 schools in Kangwondo, 438 schools in Choongchungdo equaling 1,623 schools in total. When school foodservices were put through sanitation management achievement level analysis applied by the HACCP system, results displayed that management of temperature (3.96 points), time (4.08 points), and cross-contamination (4.07 points) were all below the average achievement level. HACCP system's achievement level based on the TQM showed that areas for strategy development, leadership, information and analysis had low achievement levels. Achievement levels for CCP are quality check, delivery/distribution process, sterilization/cleansing of food's contact surface. As a result of multiple regression analysis of the factors that influenced sanitation management achievement level of school foodservice HACCP system; sanitary job standard showed 35.6% and CCP achievement levels showed 26.8% explanatory rate. In particular, Kangwondo's number of foodservice provided to per cook was small. Also, the better the processing management was assessed, the higher the sanitary job standard achievement level became resulting to a explanatory rate of 39.5%. Elementary schools showed a higher explanatory rate of 37.0% than middle and high schools. CCP achievement levels in middle and high schools with self-operated foodservice had a 28.0% variable explanatory rate, which was the highest. The better the drainage system, leadership and assessments turned out to be, the higher the CCP achievement levels became. In summary, to revitalize HACCP system that is based on the TQM, it is considered that proper database of HACCP system for school foodservice's sanitation management be constructed and more emphasis should be put on strategy development to improve customers' satisfactory level. In addition, improvements in achievement levels of time, temperature, and cross-contamination for sanitary job standard and CCP achievement level are essential.
- 169 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Possibility Analysis of a Rice Based Bread by Analyzing Customers' Needs of Menus for School Foodservice
- So Jung Lee, Min A Lee, Il Sun Yang, Hae Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(5):545-555. Published online October 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - School foodservice customers are likely to be tired of repeated cycle menus and their satisfaction for meals offered in school is inclined to be low. The menu variety is an important factor in increasing customer satisfaction. The purpose of this study was to investigate customer perspectives for applying rice based bread menus in order to add menu variety and promote using rice processed products in school foodservice. The questionnaire was distributed to 760 parent samples in elementary schools and 520 student samples in middle/high schools and a total of 665 and 387 usable data were collected, respectively. Food habits such as preference for cooking method, menu preference, food allergy and nutritional perspectives for menu and customer perception for rice based bread like quality, reliability, price, and purchasing convenience were investigated using 7 Likert scale. Also expected menu types applying rice based bread and offering frequency of rice bread menu were examined. Preference level for bread-based meals were moderate and students' preferences were slightly higher than parents. Menu types applying rice bread expected by middle/high school students were western food (49.4%), spaghetti (28.4%), set menu (13.7%), noodle (17.6%), Korean food (11.1%), Chinese food (10.9%) and porridge (4.5%). The most occupied rate was once in a week for expected offering frequency. Most respondents perceived that rice bread was more nutritive and qualitative than the wheat based one.
- 185 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of the School Foodservice Facilities & Sanitary Education (Seoul, Gyeonggi, Kangwon and Choongchung Areas in Korea)
- Gyoung Mi Kim, Sim Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(5):576-589. Published online October 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to analyze the status of school foodservice facilities, utilities and equipment & sanitary education in provinces, This study was carried out from September 2008 until December 2008 and is targeted towards schools' dietitians that work at schools with school foodservice. 1,623 schools participated in this research and Kangwondo, Choongchungdo including the metropolitan area with frequent occurrence of food bone disease were the targets of this research. The regional distribution of this research is as follows; 377 schools in Seoul, 648 schools in Gyeonggido, 160 schools in Kangwondo, 438 schools in Choongchungdo equaling 1,623 schools in total. And out of the total 1,623 schools, 815 (50.2%) were elementary schools and 808 (48.8%) were middle and high schools (p<0.001). Most of the elementary schools, excluding 4 schools, were self-operated. In the case with middle and high schools, 81.5% (513 schools) were selfoperated and 18.4% (295 schools) were contracted. When dealing with the sanitation management of school foodservice in Kangwondo and Seoul, elementary schools were less equipped with equipment and facilities than middle and high schools which proved that they were in need of improvements (p<0.01). Schools with self-operated foodservice, in particular, were in need of preparation zone improvements. 52.3%~88.0% of stainless equipment such as utensils, spoons/chopsticks, subsidiary food tray, and food trays were sterilized by dryers. Work tables, vegetable slicers, and mincers were chemically sterilized and plastic materials were sterilized by ultraviolet rays. Data from newspapers, Internet and TV are collected beforehand and then an annual hygiene educations plan for employees are put together. Hygiene education for employees are carried out monthly through oral method.
- 166 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on Differences of Sanitation Education and Sanitation Knowledge Between Dietitians in School Foodservice And Managers in Commercial Foodservice
- Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon A Jung, Hyun Joo Bae, Nami Joo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(3):306-315. Published online June 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to compare the status of sanitation education and sanitation knowledge in school foodservice with commercial foodservice. The survey sample was institutional foodservice directors (n = 88) in A office of education and commercial foodservice directors (n = 81) in B foodservice industry. The questionnaire requested information about demographic information, situation of sanitation education, contents of sanitation education practice, importance of sanitation education, and sanitation knowledge. Data were analyzed using frequencies, means, chi-square test, and t-test. Over half (52.1%) of the respondents were institutional foodservice directors, 47.9% of the respondents were commercial foodservice directors. The majority of institutional foodservice directors were 25-29 years of age (38.6%), over 10 years of working experience (63.6%) and commercial foodservice directors were 25-29 years of age (53.1%), 5-10 years of working experience (35.0%). 66.3% of the respondents were educated food safety once a month, but 8.6% of commercial foodservices were never educated. The majority of the respondents used printing materials (73.3%) or lecture (74.8%). The importance level of institutional foodservice directors about sanitation education was significantly higher than commercial foodservice directors. The average score of institutional foodservice directors'sanitation knowledge was 87.05/100.00. The commercial foodservice directors'sanitation knowledge 67.74 was significantly lower than institutional foodservice directors (p< 0.05). Therefore, there should be a systematic education program designed for commercial foodservice directors.
- 167 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Requirements and Self-evaluation of Knowledge and Skills Necessary for Effective Nutrition Teachers Perceived by School Foodservice Deititians
- Na Young Yi, Kyung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(2):190-205. Published online April 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purposes of the study were to identify knowledge and skill levels required for effective nutrition teachers and to compare perceived need and dietitians' self-evaluation of the knowledge and skills. A total of 60 knowledge statements and 70 skill statements associated with 11 job functional areas were specified through a literature review and expert panel reviews. A total of 457 dietitians working at school foodservices in Seoul and Gyeonggi province were surveyed using a self-administrated questionnaire and 148 responses were returned. Excluding responses with significant missing data, 142 responses were used for data analysis. In terms of knowledge, 'sanitation, food safety and employee safety (4.60)' category received the highest perceived need score, followed by 'nutrition education (4.56)' and 'nutrition counseling (4.45).' The knowledge category that received the highest self-evaluation was 'nutrition and menu management (3.66)' while the category that received the lowest self-evaluation was 'teaching practices (2.83).' In terms of skills, the highest perceived need was associated with 'nutrition education (4.49)', followed by 'sanitation, food safety and employee safety (4.46)' and 'nutrition counseling (4.39).' The dietitians rated their skills related to 'sanitation, food safety and employee safety (3.67)' the highest but their skills related to 'teaching practices (2.84)' the lowest. The dietitians' self-evaluated knowledge and skill scores were significantly lower than their perceived need of the knowledge and skills in all job functional areas (P < 0.001). A quadratic analysis based on the requirement and self-evaluation of the knowledge and skills revealed that priorities of the education programs targeting school nutrition teachers or students preparing to be a nutrition teacher should be placed on improving knowledge and skills related to nutrition education, nutrition counseling, teaching practices, sanitation and employee safety, and nutrition and menu management. Educational programs for nutrition teachers should be designed to decrease the gaps between the need and self-evaluation of the knowledge and skills for effective nutrition teachers. The findings of the study can be used to develop education materials for nutrition teachers. The knowledge and skills identified in the study should be updated and revised regularly to reflect changes in regulations and current practices in school foodservice programs.
- 205 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Perception for Management of School Foodservice Using of Environmentally Friendly Agricultural Products of Elementary School Children's Mothers in Gunsan
- Hye Soon Chang, Mi Jung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(6):867-878. Published online December 31, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to compare the degree of understanding about school foodservice management and environmentally friendly agricultural products between urban and rural elementary school children's mothers. The subjects were 280 elementary school children's mothers who lived in Gunsan city and the nearby countryside. The results are summarized as follows. The mothers in urban schools were higher on the degree of participation (p < 0.01) and interest (p < 0.01), but were lower on the degree of satisfaction (p < 0.001) for school foodservice than rural ones. The best improvement of school foodservice management was improving food tastes and qualities of the foodstuffs in urban schools and sanitation at the service area in the rural schools (p < 0.001). The school foodservice program contributed to cure the unbalanced diets and developing of bodies and minds; there was no difference of urban and rural schools. But eating habits in rural schools were more improved than urban schools (p < 0.001). The primary reason for using environmentally friendly agricultural products was to improve their health and in securing safe foods, there was no difference of urban and rural schools, but generating the farmer's income from the products in rural schools was higher than urban schools (p < 0.001). There are conflicting views between urban and rural schools for the additional costs brought by using the environmentally friendly agricultural products (p < 0.001). The order of preference on using environmentally friendly agricultural products was rice and various grains, vegetables, fruits, livestock, seasoning, etc. In conclusion, our central and local governments should change their roles in financially positive ways and reflect the issues in making the policy effective. Responsible administrators of school food suppliers run the system more faithfully with the above government support.
- 159 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Sanitation Management Status and Barriers to HACCP System Implementation of School Foodservice Institutions in Seoul Metropolitan Area
- Gyoung Mi Kim, Sim Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(3):405-417. Published online June 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of the study was to investigate the sanitation management status and implementation barriers of the HACCP system. A survey was conducted based on 760 schools through e-mail after having gone through phone interviews to dieticians in Seoul, Gyeonggi and Incheon areas from December 2006 to March 2007. The following statistics were drawn out from the 459 surveys out of the 760, thus giving a response rate of 60.4% (N = 459). The statistical data analysis was completed using the SPSS program. 92.6% of the respondents operated sanitary education once a month and 67.1% used internet as their sanitary educational source. 50.5% of the pre-preparation rooms were not divided and 78.0% of kitchen floors were always kept wet. Only 15.7% of the respondents used heat and cold insulators and 73.2% of drinking water was natural or purified water. 60.3% of food trays were electronically sterilized and 70.2% of spoons and chopsticks were sterilized by boiling water. The main cause of food-borne diseases was the lack of facilities and equipment (33.1%). Also, the deficiency of facilities and equipment (4.07 points) acted as an implementation barrier of the HACCP system. Compared to Gyeonggi or Incheon area results, Seoul's facilities and equipment (p < 0.001) and implementing barriers of the HACCP system (p < 0.001) results came out relatively high. After the analysis of the implementation barriers of the HACCP system, 91.7% of school principals said it was difficult to apply the HACCP system due to lack of financial support. In consideration to the school foodservice support, solutions for the facilities of school foodservice and a systematic sanitary education of the HACCP system must be made for the employees and everyone else who are related.
- 207 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of Menu Patterns of Noodle Meals in the School Foodservices in Busan and Gyeongnam Province
- Seok Young Kim, Seon Hwa Choi, Ye Sung Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(1):106-113. Published online February 28, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to classify noodle meals into a few groups according to their menu patterns and cooking methods from the 318 noodles and Ttokgook menus of 360 elementary school foodservices around Busan and Gyeongnam province. Noodle meals with high frequency were also analyzed by season and region to give information for menu planning and to improve elementary school foodservices. The menus were collected from the internet (http://www.kdclub.com) and the home pages of elementary schools between December 2004 and September 2005. Taking all kinds of noodle meals together, the serving frequencies were significantly different among regions, but were not different from season to season. Three different menu patterns were revealed from the collected noodle menus. The most frequently served menu pattern was "main dish + starchy food & dessert + fruit & beverage + kimchi" Gooksu, Ttokgook, Udong, and Kalgooksu meals were served with this menu pattern. The menu pattern of Jajangmeon meal was "main dish + side-dish + starchy food & dessert + fruit & beverage + (kimchi)" . For the Bibimmeon and the spaghetti meals "main dish + soup + starchy food & dessert + fruit & beverage + kimchi" was used. Ttigim, Danmugy, Saengchae, and chicken were frequently selected as side dishes in the overall noodle menus. More side dishes of a wide variety were served in Ttokgook meal, whereas Danmugy was the most preferred food item as a side dish with Jajangmeon and Udong meals. Corndog, Mandu, Ttok, Matang, and doughnut were preferred food items as a "starchy food & dessert" with most kinds of noodle meals, except spaghetti with which only garlic-bread was served. The fruit and beverage items were not different with the majority of noodle meals. These results suggest that cost, food habits, compatible flavor combinations, and food preference of children rather than nutritional considerations contributed to the selection of food items for the components of noodle meals in the school foodservices.
- 204 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Relationship between Levels of Dietitians' Management Activities and Job Satisfaction in Elementary School Foodservice Operations
- Yun Jeong Choo, Jung Hee Lee, Jihyun Yoon, Si Hyun Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(4):546-554. Published online August 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship between the levels of foodservice management activities and job satisfaction of the dietitians in elementary schools. Out of 130 questionnaires distributed to elementary school dietitians in In-cheon, 127 were returned and analyzed (98% response rate). The questionnaire included two multipleitem scales for measuring foodservice management activities and job satisfaction, respectively. All the items in the scales were coded 1 to 5 for 'certainly no', 'no', 'neutral', 'yes', and 'certainly yes' and grouped by using factor analyses. Most of the responding dietitians were working for schools in urban areas and have independently managed on-site kitchens. The 19 items on food service management activities were grouped into 6 factors and the mean scores of the levels of Personnel Hygiene Management, Education & Training, Sanitation & Safety Management, Menu Quality Management, Service Management, and Environment Management were 4.76, 4.26, 4.24, 4.05, 3.61 and 3.39, respectively. The 23 items on job satisfaction were grouped into 4 factors and the mean scores of the satisfaction levels of Systematic Environment, Job Duty, Job Condition, and Physical Environment were 3.38, 2.83, 2.53, and 2.08, respectively. Overall, the levels of food service management activities and job satisfaction were positively associated with a correlation coefficient of 0.254 (p < 0.01). In particular, satisfaction levels on job duty itself and systematic environment were positively associated with the levels of overall management activities. The results suggest that improving dietitians' job satisfaction could increase the levels of management activities of school foodservice dietitians, resulting in quality improvement of school food service.
- 156 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Sanitary Management of School Foodservice Operations in Daejeon and Chungnam
- Sang Hyun Park, Young Hee Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(2):234-242. Published online April 30, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to the evaluate sanitary management status of school foodservice in Deajeon and Chungnam and to suggest basic data for sanitary improvement. A questionnaire was used in this study as a survey method. The subjects consist of 529 dietitians that are employed in the school (primary.middle.high school) foodservice. These results may be summarized as follows : 71.0% of surveyed school foodservices managed separately place for contamination and uncontamination. 91.5% didn't maintain adequate temperature at kitchen. A holding rate of hygiene utensils is lower in Chungnam than Daejeon. The dietitian group aged 30 - 34 showed significantly higher scores than other groups in personal hygiene of employees. The dietitian group graduated from a college showed significantly lower scores than other groups in purchasing & receiving, preparation, storage, food remains & waste, kitchen utensils and equipments and personal hygiene. It was significant to serving, personal hygiene and facilities & structure by Daejeon and Chungnam. In serving, Daejeon showed significantly lower scores than Chungnam. In personal hygiene, facilities and structure, Chungnam showed significantly lower scores than Daejeon. The foodservice group (started < 1990) showed significantly lower scores than other groups (started > or = 1990) in preparation.
- 161 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Development of a Computer-Assisted Program for Elementary School Foodservice(II): Based on Foodservice Management
- Kyung Hea Lee, Eun Sil Her
- Korean J Community Nutr 2000;5(2):217-224. Published online July 31, 2000
- 156 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Development of a Computer-Assisted Program for Elementary School Foodservice(I)-Based on Foodservice Management
- Eun Sil Her, Kyung Hea Lee, Kyung Hwa Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2000;5(2):208-216. Published online July 31, 2000
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study is a part of a software program which was developed for efficient foodservice management of elementary school foodservice. The foodservice management system consists of general information, manu planning, inventory management, and printing of results. Advantages of software programs developed in this study, compared with previous elementary school foodservice programs are as follows. 1) This program can be used to foodservice and nutrition management at the same time. 2) The screen is designed as a homepage for convenience. 3) This program is useful in cycle menu planning. 4) Seasonal menu could be reflected in menu. 5) This program has the results printing function. 6) Data can be revisable. 7) This program can be used to middle and high school.
- 184 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Effect of Job Characteristics and Work Values on Organizational Commitment and Job Satisfaction of the School Foodservice Dietitians
- Eun Kyung Sin, Min Ji Lee, Yeon Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 1999;4(3):441-453. Published online September 30, 1999
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study aims to investigate the effects of job characteristics and work on both organizational commitment and job satisfaction of the school foodservice dietitian for the purpose of providing information for quality improvement in productivity of school foodservice. The subjects were 401 school foodservice dietitians in Taegu and the Kyungpook area. The survey questionnaires consisted of five parts including demographic characteristics, job characteristics(JCI), work values, organizational commitment(OCQ) and job satisfaction(JDI). More than half of the subjects(65.3%) were between the age of 26 to 30 years. Seventy-one percent of the participants had bachelor's degrees and monthly wages of 83.2% ranged from 700,000 to 1,200,000 won. The education of thedietitians was found to have a significant relatinship with job satisfaction in all fields. Job characteristics such as feedback, job characcteristics such as job autonomy, feedback and friendship were positively correlated with job satisfaction. The group of dietitians with high work value scores for work as a central life interest had significantly high scores in organizational commitment(p<0.01) and overall job satisfaction(p<0.05). Job satisfaction such as work-itself, pay, supervision, promotion and co-workers were positively correlated with organizational commitment. According to the Lisrel program, organizational commitment was affected by educational level(-0.23). Job satisfaction was also affected by educational level(-0.18), autonomy(0.24), friendship(0.12), feedback(0.08), individualism(-0.07) and organizational commitment(0.44) directly. In conclusion, school foodservice dietitians may increase the level of their commitment to organization and job satisfaction by increasing autonomy, feedback adn friendship of job characteristics and work values.
- 176 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Analysis on Production Processes between Conventional and Commissary School Foodservice Systems in Kyunggi-do
- Il Sun Yang, Jin Mee Lee, Bo Sook yi, Kyung Soo Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(2):206-217. Published online May 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to analyze and compare production management practices and labor productivity between conventional and commissary school foodservices and 46 dietitians of commissary school foodservices in Kyunggi-do. The response rates were 89.7% and 91.3%, respectively. The number of meals served was ranged from less than 100 to over 1,900 in conventional school foodservices and from 200 to 1,600 in commissary foodservices. Thirty three conventional foodservices(42.3%) produced less than 300 meals per day. Numbers of satellite school per central kitchen were ranged from 1 to 5 schools ; fifty percent of commissary foodservices have contained 3 satellite schools. Meals for satellite schools were transported between 11:00 a.m.and 12:00 a.m ; transportation time was from 10 to 90 minutes. Waiting time before service in satellite schools was between 10 minutes and 80 minutes. Part time employees supported by parents were hired in 37.3% of conventional and 50% of commissary school foodservices. Voluntary workers were supplied for 64.9% of conventional and 52.4% of commissary school foodservices. Labor productivity was calculated from work schedule. Labor productivity(labor minutes per meal)was lowest in foodservices with 101-4-- meals(8.48 min)was lower than that of foodservices with above 401 meals ; no significant differences were found among 401-700(6.02 min), 701-1,100(4.01 min), 1,101-1,500(3.41 min), and 1,501-1,900(3.15 min)meals in conventional foodservices. Labor minutes per meal of foodservices which served less than 400 meals(6.90 min) per day was significantly lower than those of foodservices which served 401-1,900 meal(3.41-4.92 min) in commissary foodservices(p<0.05)
- 186 View
- 3 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



