Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
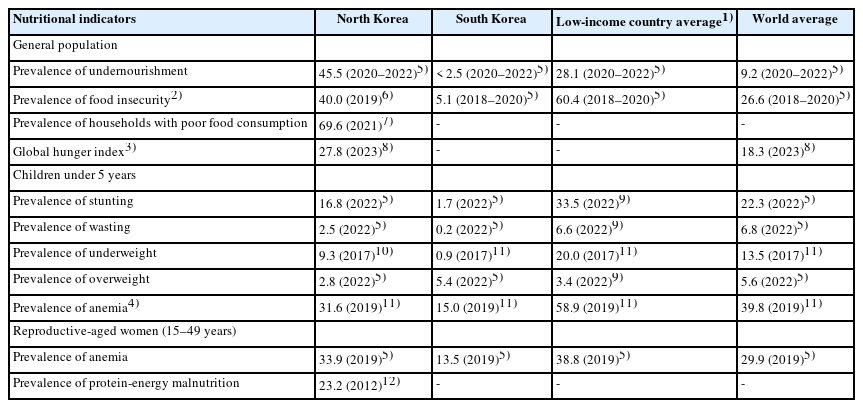
- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
- Youngmin Nam, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):288-303. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
North Koreans have been facing chronic food shortages and malnutrition. This study examined the nutritional status of North Koreans and the perceptions of South Korean adults regarding their nutritional status.
Methods
The nutritional status was examined using nutritional indicators for the general population, children, and reproductive-aged women in North Korea. An online survey was conducted among 1,000 South Korean adults aged 19–69 years to investigate their perceptions regarding the nutritional status of North Koreans.
Results
Although the nutritional status of children in North Korea has consistently improved, significant progress in the general population and reproductive-aged women in the country remains elusive. The prevalence of malnutrition among North Korean children has decreased to a level that is not considered severe based on international standards, although it shows a substantial difference from that among South Korean children. The prevalence of undernourishment and food insecurity in North Korea remains over 40%. South Korean adults perceive the nutritional status of North Koreans as being more severe than it is in reality. Notably, a significant inconsistency exists between the perceived and actual nutritional status of North Korean children, with over 95% of South Korean adults perceiving North Korean children’s malnutrition as being more severe than it actually is. Moreover, South Korean adults in their 20s to 40s tended to perceive the nutritional status of North Koreans as being more severe than those in their 50s to 60s did.
Conclusions
The nutritional status of North Koreans is a matter of concern. The disparity between South Koreans’ perceptions of the nutritional status of North Koreans and the actual status highlights the need for accurate information dissemination to effectively address malnutrition in North Korea. These efforts could be instrumental in enhancing public awareness and fostering social consensus on food aid and nutritional support programs for North Korea.
- 3,866 View
- 72 Download

Erratum
- [English]
- Erratum: Knowledge on complementary foods of mothers with young children and their perception of convenience complementary foods
- Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang, Youngmin Nam
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):171-171. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.171
- Corrects: Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):16
- 628 View
- 19 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Knowledge on complementary foods of mothers with young children and their perception of convenience complementary foods
- Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang, Youngmin Nam
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):16-33. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.16
- Correction in: Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine mothers’ knowledge levels on complementary foods and their perception of convenience complementary foods.
Methods
An online survey was conducted with mothers aged 20–49 years who had purchased convenience complementary foods and had a preschool child aged 4 months or older. The respondents were categorized into 3 groups based on their knowledge scores: low- (0–50 points), mid- (55–65 points), and high- (70–100 points) knowledge groups.
Results
The average score of mothers’ knowledge on complementary foods was 58.8 out of 100 points. Working mothers were found to have lower levels of knowledge compared to mothers who were housewives. Only 1/4 of responding mothers had educational experience on complementary foods. Mothers expressed a desire for information on the types of complementary foods (72.2%) and the intake amounts (60.3%) corresponding to each phase of their child’s development. Multivariate analysis of variance revealed significant differences in health (P = 0.002), variety (P = 0.039), and hygiene (P = 0.041) among the factors taken into consideration when purchasing convenience complementary foods according to the mothers’ knowledge levels. Mothers in the high-knowledge group placed a greater importance on ‘balanced nutrition’ (P = 0.022) and ‘hygienic cooking’ (P = 0.010) compared to mothers in the low-knowledge group. The results of the modified importance-performance analysis, which compared the importance and performance of the factors taken into consideration when purchasing convenience complementary foods, highlighted the need for efforts in ‘health,’ ‘hygiene,’ and ‘price,’ while also indicating an excessive effort in ‘convenience.’
Conclusions
This study suggests expanding relevant education programs to enhance mothers’ knowledge on complementary foods, especially for working mothers. In the industry, marketing strategies for complementary food products could be developed that align with the needs of mothers, focusing on health, hygiene, and price. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Website for the Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity
Miyong Yon, Chan Park, Kwan-Hee Yoo, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(4): 390. CrossRef - Breakfast Skipping and Related Factors in Children in Poverty
Kyung Ja June, Jin-Young Kim, Seungmi Park, Ji Yun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(2): 204. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Website for the Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity
- 3,499 View
- 72 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Problems Encountered in Analyzing the Market Size, Purchase, and Consumption of HMR in the Republic of Korea
- Sung Ok Kwon, Injoo Choi, Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):480-491. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.480
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the problems encountered when analyzing the market size, purchase, and consumption of HMR (home meal replacements) in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
The macro data relevant to the market size and purchase status of HMR were critically summarized. The micro data retrieved from the 2019 & 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) were analyzed to understand the consumption of HMR.
Results
The Korea Agro-Fisheries & Food Trade Corporation and the Ministry of Food and Drug Administration reported the market size of HMR, whereas the Korean Rural Economic Institute and the Rural Development Administration reported the purchase expense and frequencies of HMR. Since the values on the market size and purchase status were calculated or surveyed using different scopes of HMR, there have been reliability issues for the data presented. Additionally, lack of consensus on the use of Korean terms corresponding to HMR was found to be a problem. To examine the consumption of HMR, analysis of the food intake data from KNHANES presented results with very low validity due to the inappropriate survey and coding scheme not reflecting the inclusion of new food types.
Conclusions
Several problematic discrepancies were encountered in the statistics on HMR. The fundamental cause of these problems was the absence of agreement on the scope of HMR and the Korean terms corresponding to it. Considering the increasing importance of HMR in Korean diets, urgent cooperative efforts are required between the government and academia to derive an agreed Korean term and establish the scope of HMR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Human Resource Management in Emergencies: The Case of the Lithuanian Logistics Sector
Kristina Čižiūnienė, Gabrielė Voronavičiūtė, Dragan Marinkovic, Jonas Matijošius
Sustainability.2025; 17(6): 2591. CrossRef - Evaluation of Thermal Resistance in Geobacillus thermodenitrificans subsp. Calidus and Ureibacillus suwonensis Spores Isolated in Korea
Ju-Hee Nam, Du-Yeong Jung, Zi-On Choi, Hyun-Jung Jung, Jung-Beom Kim
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2025; 40(1): 13. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties and Quality Analysis of Miichthys miiuy Products Processed by Drying and Smoking
Yu-Jin Heo, Hayoun Kim, Hae-In Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 629. CrossRef - Survey on consumer perceptions, health benefits and preferences of kindergarten and school foodservices in Korea, including related keywords reported in newspaper: a mixed-methods study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 309. CrossRef - Eating behaviors, home meal replacement consumption, and nutrition quotient: a comparative study of male shift and non-shift workers in Chungcheong, Korea
Yeon Jin Lee, Munkyong Pae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 758. CrossRef - Usage and Quality Satisfaction of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores according to the Eating Behavior of University Students in Southern Gyeonggi Province
Se-In Oh, Ok-Sun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 492. CrossRef
- Sustainable Human Resource Management in Emergencies: The Case of the Lithuanian Logistics Sector
- 5,680 View
- 129 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Quality Comparison of the School and Home Lunches Consumed by Chinese School-Age Children and Adolescents:Analysis of the 2011 China Health and Nutrition Survey
- Chengyu Zhang, Suhua Jin, Jihyun Yoon, Meeyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):474-484. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.474
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The number of schools offering school lunches has increased in China. This study examined the dietary quality of the lunches consumed by Chinese school-age children and adolescents, with a focus on comparing school lunches with home lunches. Methods: The first weekday 24-hour dietary recall data of 6~17-year-old students (n=1,084) from the 2011 China Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed. The subjects were divided into the school lunch group and the home lunch group, and the dietary quality of lunches was compared between the two groups among 6~11-year-old students (n=634; 177 in the school lunch group and 457 in the home lunch group) and 12~17-year-old students (n=450; 144 in the school lunch group and 306 in the home lunch group), respectively. Frequently consumed foods, amount of food group intake, food group intake pattern, Dietary Diversity Score (DDS), and Dietary Variety Score (DVS) were examined. Results: The most frequently consumed foods in both lunch groups were rice and pork. An excessive intake of meat and insufficient intake of seafood were noted in both lunch groups. The school lunch group showed a lower level of vegetable consumption than the home lunch group (P=0.017 in 6~11-year-old students, P=0.003 in 12~17-year-old students).Although more students ate meals with a better dietary pattern in the school lunch group than the home lunch group, there were no significant differences in DDS and DVS between the two groups. Conclusions: Overall, the dietary quality of lunches was not superior in the school lunch group compared to the home lunch group. This suggests that much room remain for improving dietary quality of school lunches in China. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- [Retracted] Analysis of the Influence of Rural Family Education Environment on School‐Age Children’s Social Behavior and Patterns
Wenwen Yao, Ying Zhen, Yu Zhang, Zhao Kaifa
Journal of Environmental and Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- [Retracted] Analysis of the Influence of Rural Family Education Environment on School‐Age Children’s Social Behavior and Patterns
- 1,582 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Life of Chinese International Students according to the Frequency of University Foodservice Use in Korea
- Yan Cui, Hye-Jong Yoo, Injoo Choi, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):291-302. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.291
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study investigated the current use of university foodservice among Chinese international students in Korea, focusing on the relationship between the frequency of university foodservice use and their dietary life.
Methods
An online survey was conducted on 452 Chinese international students from February 6 to 12, 2020. The respondents were classified into “the Low-frequency group” (< one time/week; n=144), “the Mid-frequency group” (one-two times/week; n=133), and “the High-frequency group” (≥three times/week; n=175) according to their frequency of using university foodservice. The dietary life was compared among the three groups. Binominal logistic regression models were constructed to determine the associations between the frequency of university foodservice use and the changes in dietary life.
Results
More than 2/3 (68.1%) of the respondents used the university foodservice at least once per week. Chinese international students who were males and Han Chinese people, lived on campus, had stayed longer in Korea, and had no cooking facilities tended to use the university foodservice more often. The level of satisfaction with the university foodservice was not high (3.52 out of 5-points). Only 20% ate meals three times per day, and only 22% ate breakfast almost every day. The frequencies of overeating and skipping meals increased after studying in Korea. The frequency of university foodservice use, along with the length of residence in Korea, was associated with these negative changes in dietary life. Overeating (OR=2.11) and skipping meals (OR=1.79) were more likely to increase after studying in Korea in the Mid-frequency group than in the High-frequency group.
Conclusions
The frequency of university foodservice use was associated with the dietary life of Chinese international students in Korea. A high frequency (i.e. ≥three times/week) of using university foodservice may positively affect the dietary life of Chinese international students in Korea.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
Qi Li, Ji Eun Lee, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(2): 91. CrossRef
- Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
- 1,130 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- ary Characteristics and Needs for Community Kitchens among Young Adults of Single-person Households in Seoul according to the Cooking Attitude
- Mina Yang, Kana Asano, Nalae Kim, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):204-213. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the dietary characteristics and needs for community kitchens among young adults of single-person households in Seoul according to the cooking attitude.
Methods
During April 2018, an online survey was conducted on young adults of singleperson households in their 20s and 30s residing in Seoul. The respondents were classified into the more positive cooking attitude group (More Positive Group; n=152, mean=4.11) and the less positive cooking attitude group (Less Positive Group; n=190, mean=3.03) based on the mean score (3.51) of the 4-item 5-point Likert scales measuring the cooking attitude. The responses of the two groups were compared.
Results
Approximately 90% of the More Positive Group had the cooking ability to prepare ordinary meals or more advanced cooking skills, whereas only 61% of the Less Positive Group had such skills. Approximately a half of the More Positive Group cooked at home three times a week or more; only 30% of the Less Positive Group did so, and more than 30% of the group seldom cooked. The More Positive Group had higher mean scores in the levels of satisfaction with dietary life and care for food safety and nutrition than the Less Positive Group. Approximately 30% of all the respondents expressed their needs for community kitchens. The most frequently answered reason for such needs was “being able to have a meal with others”.
Conclusions
The young adults of single-person households with a more positive cooking attitude possessed a higher cooking ability, cooked more often, and cared more about food safety and nutrition than those with a less positive cooking attitude. There were moderate needs for community kitchens among young adults of single-person households living in Seoul. Therefore, societal efforts to improve their cooking attitude would be meaningful for improving their quality of dietary life. Cooking lessons or social dining programs based on community kitchens could be an option. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Qualitative Study on Health Problems and Health Behaviors Perceived by College Students Focusing on Students Registered in - Dietary Life and Health- Course for General Education
Young Hye Jeong
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(2): 277. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Associations of cooking practices and healthy eating habits among young Korean adults in their 20s
So-Young Kim, Ji Yu Choi
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2023; 31: 100644. CrossRef
- Qualitative Study on Health Problems and Health Behaviors Perceived by College Students Focusing on Students Registered in - Dietary Life and Health- Course for General Education
- 1,152 View
- 12 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Current Status of Parents' Monitoring of and Level of Trust in School Lunch Programs
- Boyoung Hur, Injoo Choi, Meeyoung Kim, Jinwook Kwon, Jiyoung Lee, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(5):401-412. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.5.401
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the current status of parents' monitoring of school lunch programs and to examine the relationship of parents' school lunch monitoring with their level of trust in school lunch programs.
METHODS
During November 2016, a web survey was conducted with 1,283 parents who had participated in monitoring of school lunch programs. A total of 621 parents completed the questionnaires (48.4% response rate) and the responses from 442 parents were analyzed (34.5% analysis rate) for elementary (n=196) and middle/high school parents (n=246), respectively.
RESULTS
Both the elementary and middle/high school parents most wanted to participate in monitoring 1~2 times per month, which was less frequent than their current practice. They showed the highest experience rate in ‘food sanitation’ area in both the prior training and actual practice of school lunch monitoring. They most responded ‘increasing trust in school lunch programs’ as a merit and ‘lack of parents participating in monitoring’ as a problem of school lunch monitoring. The average levels of trust did not differ between elementary and middle/high school parents. Multiple regression analyses showed that elementary school parents' level of satisfaction in the monitored school lunch programs was positively associated with the parents' level of trust in general school lunch programs. Monitoring frequency and parents' age, in addition to level of satisfaction in the monitored school lunch program, were associated with level of trust in general school lunch programs among middle/high school parents.
CONCLUSIONS
There was room for change in parents' school lunch monitoring programs to meet parents' needs better. Well-managed school lunch monitoring programs contributing to parents' satisfaction with school lunch programs could increase parents' level of trust in school lunch programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
민지 손, 은주 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 213. CrossRef - Analysis of the CCP Performance and Barriers of School Foodservice Employees in the Incheon Area
Ji Eun Lee, Jung Hwa Choi
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2020; 31(3): 411. CrossRef - Development of Model for 「The Survey on School Foodservice Program」
Hae-Young Lee, Bo-Sook Yi, Jina Cha, Sun-Ok Ham, Moon-Kyung Park, Mi-Nam Lee, Hye-Young Kim, Haeng-Hwa Kang, Jin-Wook Kwon, Yun-Hui Jeong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 60. CrossRef
- 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
- 1,109 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Status of Maternal Nutrition in South and North Korea
- Soh Yoon Yun, Young Hye Kwon, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(3):265-273. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study compared the nutritional status of child-bearing age women between the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) and the Republic of Korea (South Korea).
METHODS
The data presented in the DPRK Final Report of the National Nutrition Survey 2012 was utilized for the nutritional status and food intake of North Korean women. To produce the South Korean women's data comparable to those of North Korean women, the data from the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed and the data presented in the 2010 Report of the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards were utilized.
RESULTS
The prevalence of maternal anemia (blood hemoglobin < 12.0 g/dL) was over 30% in all the age groups of North Korean women and 8.9%, 14.2%, 16.4% in 20-29, 30-39, 40-49 year old South Korean women, respectively. The prevalence of maternal protein-energy malnutrition (Mid-Upper Arm Circumference < 22.5 cm) was 25.2%, 21.4%, 21.8% in 20-29, 30-39, 40-49 year old North Korean women, respectively and less than 10% in all the age groups of South Korean women. Result of dietary diversity comparison showed that North Korean women consumed less food than South Korean women at all food groups: grains, fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy. Percentage of North Korean women having consumed protein rich foods-meat and fish, eggs or dairy products-were much lower than those of South Korean women.
CONCLUSIONS
The striking disparity of nutritional status between South and North Korean women indicates that nutrition support for North Korean women is essential in the process of preparation for a unified nation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
Youngmin Nam, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 288. CrossRef - The Present and Future Status of Maternal and Child Health From the Perspective of Unification Medicine
Ji Young Kim, Eun Saem Choi, Ki Hoon Ahn
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(3): 132. CrossRef - Timely Initiation of Complementary Feeding and Associated Factors among Mothers of Children Aged 6–24 Months in Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia, 2019
Atsedemariam Andualem, Afework Edmealem, Belachew Tegegne, Lehulu Tilahun, Yitayish Damtie, C. S. Johnston
Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Systematic review of evidence on public health in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea
John J Park, Ah-Young Lim, Hyung-Soon Ahn, Andrew I Kim, Soyoung Choi, David HW Oh, Owen Lee-Park, Sharon Y Kim, Sun Jae Jung, Jesse B Bump, Rifat Atun, Hee Young Shin, Kee B Park
BMJ Global Health.2019; 4(2): e001133. CrossRef - Frequently covered diseases in North Korean internal medicine journal Internal Medicine [Naegwa]—Secondary publication
Shin Ha, Yo Han Lee
Science Editing.2019; 6(2): 99. CrossRef
- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
- 1,619 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Effect of a Worksite-based Dietary Intervention Program for the Management of Metabolic Syndrome
- Hye Jin Kim, Injoo Choi, Won Gyoung Kim, Kana Asano, Jeongmin Hong, Young Min Cho, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(3):237-246. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.237
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
To investigate the effect of a worksite-based dietary intervention program for the management of metabolic syndrome (MS) among male employees.
METHODS
A dietary intervention program combining individual and environmental approach was implemented targeting white-collar employees at a worksite located in Seoul for 10 weeks. Out of 104 employees having agreed to participate in the program, those having three or more out of five components of MS and having two components, including a waist circumference component were classified into "the high risk group" (n=41) and received group nutrition education and individual nutrition counseling three times each. The rest of the study subjects were considered as "the low risk group" (n=63). The food environment at the worksite, where both the high and low risk groups were exposed, was changed to promote healthy eating. Physical data including MS components were collected and a questionnaire on dietary behaviors was administered before and after the intervention. The data from the high risk group (n=17) and the low risk group (n=20), excluding the subjects ineligible for or failed to complete the study (n=67), were analyzed. The difference before and after intervention was tested for significance by Wilcoxon signed-rank tests.
RESULTS
Weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, blood pressure, HDL-cholesterol, and HbA1c and the healthy dietary practice score improved significantly after intervention in the high risk group. The median number of MS components decreased significantly from 3.0 to 1.0 in the high risk group. In the low risk group, only HbA1c significantly decreased. Conclusions: The 10-week worksite-based dietary intervention program combining individual and environmental approach was found to be effective for managing MS of male employees.
CONCLUSIONS
The 10-week worksite-based dietary intervention program combining individual and environmental approach was found to be effective for managing MS of male employees. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A cohort study of the effects of social support on cerebral cardiovascular disease in subjects with metabolic syndrome
Sung-Kyung Kim, Yong Whi Jeong, Dae Ryong Kang, Jang Young Kim, Hunju Lee, Sang-baek Koh, Yoshihiro Fukumoto
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(7): e0305637. CrossRef - Salutogenesis intervention improves cardio‐cerebrovascular health in at‐risk office workers: A quasi‐experimental study
Ji Hyun Moon, Hosihn Ryu
Public Health Nursing.2024; 41(4): 690. CrossRef - Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 466. CrossRef - Facilitators and barriers to achieving dietary and physical activity goals: focus group interviews with city bus drivers and counseling dietitians
Yongmin Jo, Suhyeun Cho, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(5): 376. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a mobile health intervention on weight loss and dietary behavior changes among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young-Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(2): 141. CrossRef - Predictors of Health Promotion Behaviors Among Working Adults at Risk for Metabolic Syndrome
Sungwon Park, Min Kyeong Jang, Chang Gi Park, Oi Saeng Hong
Nursing Research.2022; 71(4): 275. CrossRef - Inverse association of improved adherence to dietary guidelines with metabolic syndrome: the Seoul Metabolic Syndrome Management program
Dongwoo Ham, YoungYun Cho, Mi-Suk Park, Yun-Sug Park, Sun-Young Kim, Hye-Min Seol, Yoo Mi Park, Sunok Woo, Hyojee Joung, Do-Sun Lim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(6): 621. CrossRef - The Effect of Community-based Health Intervention Program to Improve Metabolic Disease in Jeju Island
Woo Jin Kim, Sang Hoon Kim, Shin Young Park
The Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2018; 50(3): 297. CrossRef
- A cohort study of the effects of social support on cerebral cardiovascular disease in subjects with metabolic syndrome
- 1,182 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Recommendation of Serving Size of the Meal Service of Community Child Centers in Korea
- Sang Eun Lee, Jae Eun Shim, Sooyoun Kwon, Yoonjae Yeoh, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(4):361-371. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.4.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to set easily applicable portion sizes by sex and age for children at the Community Child Centers (CCC) in Korea.
METHODS
Considering the age and gender specific energy level at Target Patterns for children aged 6-18 years, which were suggested as a part of the 2010 Korean Food Guidance System (KFGS), we set three meal sizes. We reclassified the recommended daily servings of Grains, Meat.fish.eggs.beans and Vegetables group at Target Patterns into three meal sizes, and then calculated the recommended serving per meal. Each proposed amount of food per meal was calculated based on serving size of foods commonly eaten at KFGS, which was then allocated to five meal components; rice, soup, stew, protein and vegetable side-dishes and Kimchi. Each proposed amount of food per meal was applied to 173 menus' recipes from CANpro 3.0 as main ingredient's amounts. We cooked the 173 menus at the medium size and measured their weights after cooking.
RESULTS
Each recommended serving per meal was 0.75, 0.9 and 1.2 for Grains; 1.2, 1.6 and 2.4 for Meat.fish.eggs.beans; 2, 2.4 and 2.8 for Vegetables by meal sizes. Among five meal components, the ratio of small and large to medium size was 1/5 less and 1/3 more for rice and 1/3 less and 1/3 more for soup.stew, protein side-dish and Kimchi, respectively. We suggested the same amount for a vegetable side-dish to encourage vegetable intake. Proper portion sizes per meal of medium were rice 190 g, soup.stew 210 g (solid ingredients 60 g), protein side-dish 100 g (meat.eggs.beans) and 70 g (fish), vegetable side-dish 80g and Kimchi 30 g.
CONCLUSIONS
Proper portion size per meal suggested in this study may be useful at the CCC where dietitians are not available and the approach could be applicable to the other types of meal services. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Multidisciplinary Health Promotion Program Among Children in Community Childcare Center
Yerin Kim, Gyeong Seob Shin, Jungwon Park, Minji Kang, Kumhee Son, Yoon Myung Kim, Kyung Hee Park, Hyunjung Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(1): 8. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Behavior and Nutritional Status of Children at Community Child Center in Busan Area Using Nutrition Quotient
Kyung-A Lee, Ha-Yeon Park, Eun-Soon Lyu
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(4): 424. CrossRef - Investigation of the Management of Foodservice Facilities inCommunity Child Centers in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Area
Suk-Hyeon Park, Hyeon-A Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(4): 459. CrossRef - Intakes and Satisfaction of Home-delivered Meal Box for Children from Low-income Families in Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea
Gyusang Han, Sooyoun Kwon
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(5): 716. CrossRef - Assessment of Foodservice and Cooking Program for Children Attending Community Child Centers in Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Yoonjae Yeoh
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(3): 223. CrossRef - tatus of Meal Serving and Nutritional Quality of Foods Served for Children at Community Child Centers in Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Yoonjae Yeoh
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 352. CrossRef
- Effects of Multidisciplinary Health Promotion Program Among Children in Community Childcare Center
- 1,912 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Chinese Female Marriage Immigrants' Dietary Life after Immigration to Korea : Comparison between Han-Chinese and Korean-Chinese
- Kana Asano, Jihyun Yoon, Si Hyun Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(4):317-327. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.4.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate Chinese female marriage immigrants' dietary life after immigration to Korea, focusing on comparison between Han-Chinese (traditional Chinese) and Korean-Chinese (Chinese of Korean descent).
METHODS
An in-person survey was conducted with women married to Korean men, having one child or more aged 1-6 years old, and having resided in Korea for at least one year before the survey. The data were collected from the 309 respondents comprising 151 Han-Chinese and 158 Korean-Chinese in the summer of 2013.
RESULTS
Overall, there was no significant difference in dietary practice, dietary acculturation, dietary behavior, dietary habits, and food intake between the Han-Chinese and the Korean-Chinese respondents. Over 50% of the respondents ate Korean food every day. The overall level of dietary acculturation was about 3.5 out of 5 points. The average score of healthy dietary behavior was a little bit higher than 3 out of 5 points. Approximately 3/4 of the respondents showed increasing frequency of eating out. The respondents reporting increase food diversity were over 70%. Decreased frequency of skipping meal was about 60% of the respondents. Over 50% of the respondents showed increasing consumption of Kimchi, vegetables, fruit, and meat.
CONCLUSIONS
Dietary life of Korean-Chinese female marriage immigrants was similar to that of Han-Chinese female marriage immigrants after immigration to Korea. The results from this study suggest that not only Han-Chinese but also Korean-Chinese should be targeted in various diet-related acculturation support programs as important multicultural populations in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary acculturation and changes of Central Asian immigrant workers in South Korea by health perception
EunJung Lee, Juyeon Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 305. CrossRef - Flavor principle as an implicit frame: Its effect on the acceptance of instant noodles in a cross-cultural context
Meng Li, Seo-Jin Chung
Food Quality and Preference.2021; 93: 104293. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire for marriage migrant women in multicultural families
Jung-Hyun Kim, Oh Yoen Kim, Min June Lee, Eunju Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 76. CrossRef - Consumption of Han-sik and its Association with Socioeconomic Status among Filipino Immigrant Women: the Filipino Women's Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL)
Nayeon Kim, Minji Kang, Grace Abris, Sherlyn Mae P. Provido, Hyojee Joung, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Jung Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(6): 475. CrossRef - Analysis of Korean Dietary Life Adaptation of Married Female Immigrants
Jeong-Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 103. CrossRef - Study on the change and acculturation of dietary pattern of Southeast Asian workers living in South Korea
Eun Jung Lee, Kyung-Ran Lee, Seung-Joo Lee
Appetite.2017; 117: 203. CrossRef - Development of a Korean Food Culture Education Textbook for Married Female Immigrants
Jeong-Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(5): 415. CrossRef - Dietary behaviors of female marriage immigrants residing in Gwangju, Korea
Eun Ju Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(3): 179. CrossRef - Female Marriage Immigrants’ Information Awareness, Perception and Familiarity on Korean Food Culture by Personal Characteristics and Food Neophobia Degree
Hee-sun Jeong, Ji-young Yoon
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 233. CrossRef - Food intake and nutritional status of female marriage immigrants residing in Gwangju, Korea
Eun Ju Yang, Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(5): 358. CrossRef - Acculturation and changes in dietary behavior and anthropometric measures among Chinese international students in South Korea
Jounghee Lee, Ran-Ran Gao, Jung-Hee Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(3): 304. CrossRef - Factors related to Korean Dietary Adaptation in Chinese Female Marriage Immigrants living in the Seoul Metropolitan Area
Kana Asano, Jihyun Yoon, Si-Hyun Ryu
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 234. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Food Preference of Elementary School Children between Multi-cultural Families and Ordinary Families in Gyeongnam Province
Joo Hee Lee, Seon Ok Jeong, Changim Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(6): 973. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Dietary and Weight Control Behavior of Female College Students in Korea and China
Li Song, Na Young An, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(4): 761. CrossRef - Comparative Study on Dietary Life of Southeast Asian Workers Living in South Korea
Eun Jung Lee, Kyung-Ran Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(4): 422. CrossRef - Korean Food Acculturation Phenomena of Married Immigrant Women and Their Children’s Eating Habits
Jisun Lee, Solji Lee, Bokyung Ryu, Lana Chung
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(5): 545. CrossRef - Japanese Female Marriage Immigrants' Dietary Life and Health-related Characteristics by Level of Dietary Adaptation after Immigration to Korea
kana Asano, Jihyun Yoon, Si-Hyun Ryu
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(5): 765. CrossRef
- Dietary acculturation and changes of Central Asian immigrant workers in South Korea by health perception
- 1,355 View
- 1 Download
- 17 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Traditional Aspects of School Lunch Menus in Korea by Analyzing Dish Group Composition
- Youngmi Lee, Meeyoung Kim, Hae Kyung Chung, Haeng Ran Kim, Jae Eun Shim, Hyeyeong Cho, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(4):386-401. Published online August 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.4.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to analyze traditional aspects of school lunch menus in Korea. We conducted a content analysis of menu-related contents included in guidelines for school lunch programs provided by 16 city and provincial education offices. In addition, the data of 10,495 menus for the third week of December 2010 and March, July, October 2011 from 557 elementary, middle, and high school were analyzed by school grade, area, and province. The results showed that there were no specific and detailed guidelines for menu planning in terms of traditional food culture in most of the guidelines for school lunch programs. However, the basic traditional menu composition was maintained in school lunch menus. The percentage of menus including rice and Kimchi was 97% and 95%, respectively, and that including Korean soup was about 72%. However, the frequency of serving Namul, Korean seasoned vegetable dish, accounted for only about 52% of the menus. The percentage of the menus following the traditional food group pattern including such five food groups as rice, Korean soup, Kimchi, Namul, and optional Korean side dish was only about 35%. The percentage of the menus following the traditional food group pattern excluding Namul from the five food groups accounted for about 30%. The traditional food group score, calculated by allocating 1 point to each of the five food groups was 4.06 out of 5 points on average. Elementary schools and schools in rural area and in Jeolla-do province served traditional menus more frequently. In conclusion, school lunch programs need to consider establishing traditional foods-based standards and relevant guidelines for school lunch, particularly for high schools and schools in urban areas and in some provinces.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the Frequently Served Menus and Trends in Nationwide School Lunch Meals: 2021∼2023 Data from the School Meal Menu Information on the NEIS Open Educational Information Portal
Seo Ha Lee, Insun Kang, Bo Kyung Kwon, Hyo Bin Im, Min A Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(10): 1084. CrossRef - Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 514. CrossRef - Food and dish group diversity on menus of daycare centers provided by Center for Children’s Foodservice Management in Korea: a descriptive study
Youn-Rok Kang, Kyeong-Sook Lim, Hyung-Sook Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 449. CrossRef - Comparison of the sodium content of Korean soup-based dishes prepared at home, restaurants, and schools in Seoul
Yanghee Park, Jihyun Yoon, Sang-Jin Chung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 663. CrossRef - Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Analysis of Korean Traditional Dietary (Hansik) Consumption Patterns Focusing on Households’ Characteristics
Yeyoung Lee, Yuna Kim, Sung-Eun Yoo, Kwansoo Kim, Donghwan An
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(6): 453. CrossRef - Public recognition of traditional vegetables at the municipal level: Implications for transgenerational knowledge transmission
Yuta Uchiyama, Hikaru Matsuoka, Ryo Kohsaka
Journal of Ethnic Foods.2017; 4(2): 94. CrossRef - An iodine database establishment and iodine intake in Korean adults: Based on the 1998~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu Mi Ko, Yong Seok Kwon, Yoo Kyoung Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(6): 624. CrossRef - Needs Assessment for Dietary Education Program Focused on the Increase of HAN-SIK (Korean Food) Consumption in Children and Adolescents Living in Jeonbuk and Gyunggi Areas
Sang-Eun Lee, Yangsuk Kim, Eun Mi Ahn, Young Hwang, Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2016; 27(S): 609. CrossRef - Assessment on Dietary Diversity According to Korean Dietary Pattern Score of Korean Adolescents and Children: Using 2007~2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
Yong-Suk Kwon, Yangsuk Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2015; 31(5): 660. CrossRef - The Development of Institutional Food-Service Menu with Temple Food
Sim-Yeol Lee, Jin-A Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 338. CrossRef
- Analysis of the Frequently Served Menus and Trends in Nationwide School Lunch Meals: 2021∼2023 Data from the School Meal Menu Information on the NEIS Open Educational Information Portal
- 2,178 View
- 2 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- Teachers' Participation and Mealtime Instruction in the Food Service at the Kwanak-gu Child-care Centers: Comparison between Child-care Teachers Caring Different Age Groups, Children Younger than Three Years and Those Three Years or Older
- Yoonjae Yeoh, Sooyoun Kwon, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(2):112-124. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.2.112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate how child-care teachers participate, practice mealtime instruction, and perceive difficulties in food service, focusing on comparison between the teachers caring two different age groups: children younger than three years (Younger Group) and those three years or older (Older Group). Questionnaires were distributed to 151 child-care centers in Kwanak-gu, Seoul, Korea during December, 2011. Only the data from 25 child-care centers, where two respective teachers in charge of Younger Group and Older Group completed the questionnaires, were analyzed. The results showed that there was no difference in terms of child-care teachers' participation in food service practice between the two groups, except for serving method; 'Pre-plated' serving was used significantly more often in Younger Group, whereas 'Line-up' serving was used in Older Group. Approximately, three quarters of the child-care centers had policies or guidelines on mealtime instruction. During mealtime, child-care teachers tended to use frequently verbal instructions such as "sit up straight when you eat" about eating manner, "don't be picky with your food" about eating habit, and "wash your hands before eating" about eating procedure in both the groups. There was no statistically significant difference regarding child-care teachers' perceived difficulties in food service between the two groups. These results indicated that child-care teachers' participation and mealtime instruction in food service did not differ between the two age groups, although children's development of digestion and eating skill differed by age. Therefore, training should be provided to child-care teachers about food service practices and mealtime instruction appropriate to children's age.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the Importance-Performance Related service management and feeding practices of teachers at mealtime in childcare centers
Yoonjae Yeoh, Sooyoun Kwon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(3): 289. CrossRef - Effects of an Education Program on Sanitation Status at Centers for Children's Food Service Management: Focusing on Jung-gu and Dong-gu regions of Daejeon Metropolitan City
Yu-Jin Seo, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(6): 447. CrossRef
- Analysis of the Importance-Performance Related service management and feeding practices of teachers at mealtime in childcare centers
- 1,063 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Effect of Sustainability Management at Coffee Houses on Customers' Store Image and Behavioral Intention
- Joongwon Shin, Soyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(4):494-503. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.4.494
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of sustainability management (SM) at coffee houses on customers' store image and behavioral intention. In addition, customers' willingness to pay a premium for sustainable coffee houses was studied. During October 2011, a web survey was conducted via an on-line research company with customers aged 20 to 39 visiting one of the top five coffee houses in Korea at least once a month. A total of 300 targeted customers responded and all the data were analyzed. An exploratory factor analysis derived two dimensions of SM: SM in Social and Environmental Perspective and SM in Economic Perspective. The result of structural equation modeling indicated that SM in Economic Perspective at coffee houses had a significant positive effect on customers' behavioral intention with mediating effect by store image, but SM in Social and Environmental Perspective did not have such effect. Approximately one-third (31%) of the respondents were willing to pay a premium for a sustainable coffee house in a scenario. approximately 84% of the respondents unwilling to pay a premium for the sustainable coffee house chose the cost-related reasons including "Coffee price at the coffee house that they most often visit is already expensive (62.3%)" for such unwillingness. The results of this study showed that SM of coffee houses, especially that in Economic Perspective, could contribute to store image, and therefore increase customers' favorable behavioral intention, although the additional cost resulted from such SM practices might not be easily accommodated by customers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effects of Social Connectedness on the Relationship between Sustainability Management and Brand Loyalty at Coffee Specialty Shops
Na-Young Yi
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(5): 533. CrossRef - Dietitians' Self-Evaluation and Barriers to Sustainable Practices for School Foodservice Management : Focused on Daejeon and Chungnam Area
Na-Young Yi
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2017; 33(3): 342. CrossRef - The influences of sustainability management at institutional foodservice on store image and behavioral intention
Jiyoon Ahn, Sunhee Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(2): 199. CrossRef - Relationship of TBL Component in Corporate Sustainable Management of Fashion Company with Company Evaluation and Brand Image
Dongkyu Na, Jeongwon Lee, Youngjoo Na
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2014; 16(2): 293. CrossRef - Health-related Factors and Nutritional Status in Shift-workers at Coffee Shops - Focused on Single Women in Twenties in Seoul -
Seung-Lim Lee, Soo-Jin Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(5): 467. CrossRef
- Mediating Effects of Social Connectedness on the Relationship between Sustainability Management and Brand Loyalty at Coffee Specialty Shops
- 1,468 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- School Dietitians' Satisfaction with and Needs for School Meal Service Support Centers
- Hyeyeong Cho, Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(2):194-204. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.2.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate school dietitians' satisfaction with and needs for School Meal Service Support Centers. A web-based on-line survey was conducted with 1,102 nutrition teachers or school dietitians using four School Meal Service Support Centers during the summer of 2011. The data from 578 respondents (52.5%), consisting of 165 (44.4%), 334 (53.4%), 41 (67.2%), and 38 (86.4%) dietitians using Seoul, Gyeonggi, Suncheon and Gyeongju centers, respectively, were analyzed. The main reason for using the centers was subsidies from local governments. The dietitians using the metropolitan centers, which were Seoul and Gyeonggi centers, tended to buy agricultural products through the centers only, and those using local centers, which were Suncehon and Gyeongju centers, bought those products from the private suppliers as well as from the centers. The dietitians' overall level of satisfaction with the centers was not high showing 3.3 out of 5 points; it was significantly associated with the operating system and services of the centers such as system efficiency, delivery accuracy, communication, and information provision rather than the agricultural products provided by the centers. The dietitians preferred joint operation of the centers by local governments and producers' groups. They wanted School Meal Service Support Centers to be evaluated every year. It was suggested that efforts should be made to improve the operation system and service of School Meal Service Support Centers for improving dietitians' satisfaction with the centers. In addition, an evaluation system for School Meal Service Support Centers should be implemented soon based on school dietitians' needs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Surveys to Determine the Real Prices of Ingredients used in School Foodservice
Seo-Hyun Lee, Min A Lee, Jae-Yoon Ryoo, Sanghyo Kim, Soo-Youn Kim, Hojin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 188. CrossRef - Recognition of Environmentally-friendly Agricultural Products for School Foodservice of Nutrition Teachers and Parents in 2018 at Seongnam in Gyeonggi province
Jisoo Kwon, Wookyoun Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(4): 290. CrossRef - An Analysis of Importance-Performance on School Meal Support and Local Food Supply Policy
Choong-Seop An, Won-Tae Kim, Ho Kim
Korean Journal of Organic Agricultue.2018; 26(4): 585. CrossRef - Analysis of Nutrition Teachers' Awareness of Necessity for an Operating School Meal Support Center in Chungnam
Jonghwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(6): 506. CrossRef - A Study on the Satisfaction for Food Service with School Food Service Center of Elementary and Middle School Parents in Chungnam
Sung-Bum Yang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(3): 404. CrossRef - Status of Purchasing Food Materials and Satisfaction with Service Quality of Group-buying Companies in Foodservice at Child-care Centers
Yoonjae Yeoh
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(1): 193. CrossRef
- Analysis of Surveys to Determine the Real Prices of Ingredients used in School Foodservice
- 1,070 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- The Current Status of Foodservice Management in the Restaurants Participating in the Government-funded Children's Model Program in Korea during Summer Vacation
- Jinyoung Kim, Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Haelim Choi, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(2):182-193. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.2.182
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the current status of food service management in the restaurants participating in the government-funded children's meal program during summer vacation. A mail survey was conducted with individuals who worked in the restaurants participating in the government-funded children's meal program in Seoul during the summer vacation in 2010. A total of 600 questionnaires were distributed to 274 Chinese, 235 Bunsik and 91 Korean restaurants, which were selected using proportionate stratified sampling by regions and types of operations. A total of 138 usable questionnaires (23.0%) were returned and analyzed. The results showed that over half (57.2%) of the restaurants did not employ any certified cooks. Most of the restaurants (97.8%) provided side dishes; among them, only 42% planned menus for side dishes in advance and only a half changed side dish menus periodically. The suggested reasonable reimbursement rate per meal for children using restaurants differed by types of restaurants; the percentage of restaurants having responded 5,000 won or higher was the highest in Chinese restaurants. This study revealed that food service in the restaurants participating in the government-funded children's meal program was not properly managed during summer vacation, especially in terms of menu and food production. This study also showed that the suggested reasonable reimbursement rate of meals for children using restaurants differed by types of restaurants, implying that adjusting the reimbursement rate according to types of restaurants should be considered in the government-funded children's meal program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparison study of hygiene status in meals for poorly-fed children through microbiological analysis
Ok-Kyeong Yu, Hyun-Suk Kim, Moon-Sun Byun, Mina Kim, Youn-Soo Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(3): 214. CrossRef - A Survey of Satisfaction with Quality attributes of Meal Services for Low-income Children in Wonju
Hae Sook Oh
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2014; 25(2): 233. CrossRef
- A comparison study of hygiene status in meals for poorly-fed children through microbiological analysis
- 1,413 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Assessment of the Support Program of Foodservice Management for Community Child Centers in Jeollanam-do, Korea
- Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Soyoung Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(1):91-100. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.1.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the foodservice management support program focusing on menu management in community child centers. The support program provided reference menus, staff training, and field consulting to 10 community child centers in the Jeollanam-do province for one month, August in 2010. One month menus were developed, based on children's preference for menu items, foodservice personnel's preference for food materials, and availability of local specialty foods, and offered as reference menus. In addition, staff training and field consulting focusing on menu management were conducted before and during the pilot period, respectively. To evaluate the support program, menus, foodservice personnel's knowledge level and perceived performance in foodservice management, and children's level of satisfaction for foodservice were analyzed before and after the support program. As a result of analysis of 222 and 210 menus of before and after the support program, respectively, the number of dishes per meal increased from five to six on average, and the proportion of meals including five food groups, which were grain, meat, vegetable, fruit, and milk and dairy product, rose from 2% to 24%. Foodservice personnel's knowledge level regarding foodservice management increased significantly (p = 0.007), however, their perceived performance in foodservice management did not show any significant changes. Children were more satisfied with 'food' (p = 0.001), 'sanitation' (p = 0.001), and 'environment' (p < 0.008) of foodservice in community child centers after the support program. In conclusion, the foodservice management support program focusing on menu management in this study was effective for improving menu quality of and children's satisfaction with foodservice in community child centers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of the Management of Foodservice Facilities inCommunity Child Centers in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Area
Suk-Hyeon Park, Hyeon-A Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(4): 459. CrossRef - Food Service Status at Community Child Care Centers in Busan
Jeong-Sook Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(1): 50. CrossRef
- Investigation of the Management of Foodservice Facilities inCommunity Child Centers in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Area
- 1,089 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Change of Children's Meal Structure in Terms of Temporal and Spatial Dimensions : Analysis of the Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys of 1998 and 2009
- Youngmi Lee, Jae Eun Shim, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(1):109-118. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.1.109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to characterize changes in the meal structure of Korean children in terms of temporal and spatial dimensions. The data of 1,891 and 1,627 school-aged children and adolescents extracted respectively from the 1998 and 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys were analyzed by gender, age group, and residential area. From 1998 to 2009, the total eating events increased from 4.3 to 4.6 (p = 0.001); the average number of meal intake decreased from 2.8 to 2.7 (p < 0.001) while that of snack intake increased from 1.5 to 1.9 (p < 0.001). The prevalence of "3 meals a day" pattern tended to decrease while that of "2 meals a day" pattern increased over the years. Especially, the "2 meals a day" pattern with "lunch + dinner" increased from 13% in 1998 to 20% in 2009. The percentage of eating breakfast or dinner at home decreased over the years. These results indicate that over the last decade, "destructuration" occurred in Korean children's meal structure in terms of temporal and spatial dimensions. Especially, such alteration was more distinctive in male than female and in the high school-aged group than the elementary or middle school-aged groups. Overall, the difference of meal structure between genders and residential areas became smaller while the difference among age groups became larger over the years.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescent According to the Meal Frequency: The 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yonghoon Ji, Junhee Park, Jun-Hyun Yoo
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2022; 12(3): 158. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Quality and Nutritional Status according to the Use of Nutrition Labeling and Nutrition Claims among University Students in Chungbuk Area: Based on Nutrition Quotient
Yun-Jung Bae, Seo Young Park, Hye-Rin Bak
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 179. CrossRef - Korean Adolescents’ Energy Intake of Selected Foods by Eating Place from 1998 to 2012 During Implementation of Two National School Nutrition Policies
Seul Ki Choi, Edward A. Frongillo, Christine E. Blake, James F. Thrasher
Journal of Hunger & Environmental Nutrition.2018; 13(1): 116. CrossRef - Associations between Exposure to Unhealthy Food Outlets Within Residential District and Obesity: Using Data from 2013 Census on Establishments and 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yoonjung Kim, Sung Nim Han
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(5): 463. CrossRef - Nutrient intakes and frequently consumed foods among Korean adults according to the intake frequency of Baechu (Chinese cabbage) kimchi: Based on the 2012~2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ae-Wha Ha, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(2): 125. CrossRef - Recognition and Usage of Nutrition Labeling for Processed Foods and Restaurant Meals according to the Effort Level of Healthy Dietary Behavior in 5th Grade Elementary School Girls
Jin-Ah Moon, Jung-Eun Kong, Gui-Im Moon, Baeg-Won Kang, Jee-Young Yeon
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(5): 849. CrossRef - Bite Force and Lip Closing Force Measurement in Preschool Children
Nayoung Cho, Hyeongun Kim, Jaegon Kim, Byeongju Baik, Yeonmi Yang
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2015; 42(3): 233. CrossRef - Assessment on Dietary Diversity According to Korean Dietary Pattern Score of Korean Adolescents and Children: Using 2007~2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
Yong-Suk Kwon, Yangsuk Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2015; 31(5): 660. CrossRef - Perception on Nutrition Labeling of the Processed Food among Elementary School Students and Parents in Daegu Area
Jung Mi Kim, Mi Hee Lee, Nan Hee Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(6): 1107. CrossRef - Evaluation of items for the food behavior checklist and nutrition quotient score on children in rural areas of Gyeongbuk
Jung-Sun Yoo, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(5): 427. CrossRef - Development of 'Children's Food Avatar' Application for Dietary Education
Joo-Han Cho, Sook-Bae Kim, Soon-Kyung Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Gap-Soo Kim, Se-Na Kim, So-Young Kim, Jeong-Weon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(4): 299. CrossRef - Current Status and Strategic Plan of Nutrition Education Comparing Nutrition Teachers with Dietitians in Schools, Gyeonggi Area
Young-sun Hong, Joung-hee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 233. CrossRef
- Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescent According to the Meal Frequency: The 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,191 View
- 2 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Government-Funded Meal Support Program for Low-Income Children through Convenience Stores : Current Status and Nutritional Quality of Available Meal Items in Seoul
- Haelim Choi, Sooyoun Kwon, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(2):253-264. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.2.253
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objectives of this study were to investigate the current status of the Korean government-funded meal support program for low-income children through convenience stores and to evaluate the nutritional quality of the meal items available under the program. The POS data of three convenient stores where children had used their electronic meal cards most often in Seoul during January 2010 and the kinds and amounts of ingredients of the meals items available to the children were obtained from the headquarter of the convenient stores. A total of 5,081 transactions by 693 children included in the POS data was analyzed. In addition, nutritional contents of meal items, which were meal boxes (11 kinds), kimbab (13 kinds), rice balls (27 kinds), inari sushi (1 kind), and sandwiches (26 kinds), were analyzed with Can Pro 3.0. The results showed that children had purchased flavored-milk products most often. Children tended to purchase meal items together with drinks (60.9% of transactions), but some purchased drinks (27.6%) or meal items only (11.5%). Except for meal boxes, none of the meal items satisfied 1/3 of Estimated Energy Requirements of the 9-11 year-old boys per day. The average energy contents of different kinds of meal boxes, kimbabs, rice balls, and sandwiches were 619, 357, 200, and 380 kcal, respectively, and the energy content of a package of Inari sushi was 457 kcal. Vitamin C amount was found to be deficient in all the meal items, compared to 1/3 of Recommended Intake of the 9-11 year-old boys per day. The results of this study could be useful to develop nutritionally appropriate meal items for the convenient stores participating in the government-funded meal support program for children from low-income families.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Intake Status and Satisfaction of Home-delivered Meal Boxes for Children from Low-income Families in Seongnam-city, Gyeonggi-do
SooYoun Kwon, OkSun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(2): 149. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study on the Dietary Experience with the Children’s Meal Card : Focused on College Students Living in Busan
Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(2): 205. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Quality of Convenience Store Meal Boxes according to Store Company and Meal Price
Changgyu Cho, Youngmin Nam, Hye-Jong Yoo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 105. CrossRef - Analysis of the Dietary Life of Adolescents by Household Types in Korea using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(2): 285. CrossRef - Analysis of the Affiliate-stores Distribution and Users of an Electronic-card for Children’s Meal Service in Busan
Soo Jin Lee, Ji Yoon Lee, Jung Eun Kang, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(1): 29. CrossRef - Study on Middle and High School Students' Use of Convenience Foods at Convenience Stores in Incheon
Seul-Ki Lee, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 137. CrossRef - A Survey of Satisfaction with Quality attributes of Meal Services for Low-income Children in Wonju
Hae Sook Oh
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2014; 25(2): 233. CrossRef - A comparison study of hygiene status in meals for poorly-fed children through microbiological analysis
Ok-Kyeong Yu, Hyun-Suk Kim, Moon-Sun Byun, Mina Kim, Youn-Soo Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(3): 214. CrossRef - The Current Status of Foodservice Management in the Restaurants Participating in the Government-funded Children's Model Program in Korea during Summer Vacation
Jinyoung Kim, Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Haelim Choi, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(2): 182. CrossRef
- Analysis of Intake Status and Satisfaction of Home-delivered Meal Boxes for Children from Low-income Families in Seongnam-city, Gyeonggi-do
- 1,459 View
- 1 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Factors Related to Eating Breakfast of Middle and High School Students in Seoul
- Yangsuk Kim, Jihyun Yoon, Haengran Kim, Sungok Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(5):582-592. Published online October 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine the factors related to eating breakfast for middle and high school students in Seoul using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Out of 2,280 questionnaires distributed to 22 schools, 2,060 were returned (90.4% response rate) and 1,899 were analyzed (83.3% analysis rate). Gender, self-perceived household income level and mother's working status were examined as demographic factors. "Attitude", "Subjective norm", "Perceived difficulty in access to breakfast", "Perceived time restriction" and "Self restriction to breakfast" were extracted as psychosocial factors as the results of factor analysis and reliability test using 17 items. In case of middle school students, boys were more likely to skip breakfast than girls. The students perceiving their household income level "low or middle low" were more likely to skip breakfast than those who perceived their household income level "high or middle high". The students whose mother had a job tended to skip breakfast than those whose mother had no job. In case of high school students, the students perceiving their household income level "low or middle low" tended to skip breakfast than those perceiving their household income level "high or middle high". The results of analysis of variance, all the psychosocial factors examined in this study-"Attitude", "Subjective norm", "Perceived difficulty in access to breakfast", "Perceived time restriction" and "Self restriction to breakfast"- were related to the frequencies of eating breakfast during weekdays in both the middle and high school students.
- 332 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Use of Likert Scale in Community Nutrition Research: Analysis of the Articles Published in Korean Journal of Community Nutrition
- Si Hyun Ryu, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(5):600-607. Published online October 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to examine if Likert scales had been properly utilized in community nutrition research. A total of 527 research articles published in the 32 issues of Korean Journal of Community Nutrition from the volume 5, issue 1 in 2000 to the volume 10, issue 2 in 2005 were screened and 55 articles were found to have utilized one or more Likert scales for the studies. Therefore, 109 Likert scales used in the 55 studies were reviewed regarding the name, statement and response items, reliability and validity check, and analysis method. The scales were mostly referred as Likert scales (60%) or Likert-type scales (27%). Some scales were found to be referred as Likert scales although they were Likert-type scales when judged based on the information given in the respective articles. However some scales couldn't be judged for the rightness of the names because the information given for the scales in the articles was not enough. About 23% of the scales consisted of items less than 6 or more than 30, and therefore found to be inappropriate. The percentage of the scales listing all the statement items in the articles was only 25%. Most of the scales (85%) included 5 response items, and the rest included 4 (7%), 7 (6%), or 3 (2%). The percentages of the scales including appropriate center and end items were only 2% and 22%, respectively. Less than half of the scales (41%) were found to have been checked for reliability and only one scale was reported to have been checked for validity. In some scales (6%), the responses were scored improperly for analysis. The responses to the scales were frequently found to have been analyzed by parametric statistics such as mean, ANOVA, t-test, and Pearson's correlation, which might be a problem depending on the size and distribution of study samples. In conclusion, there is much room for improvement in the use of Likert scales in community nutrition research.
- 321 View
- 4 Download

- [English]
- Appropriate Size and Dish Combination of Nutritional-Balanced Lunch Boxes Delivered to Children Under the Government-Funded Meal Service Program in Korea
- Kana Asano, Jihyun Yoon, Borham Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(5):565-575. Published online October 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to propose the appropriate sizes and dish combination for nutritional-balanced lunch boxes delivered to children under the government-funded meal service program in Korea. The study was based on the 3 : 1 : 2 Meal Box Magic, a nutrition education method developed in Japan. A total of 290 lunch menus, comprising of 10 day menus from 29 organizations having delivered lunch boxes to children during summer vacation of 2008, were analyzed and used as the base data for lunch box combination. Dishes of the menus were classified into 6 groups: Rice group, Protein side dish group (including meat, fish, egg, and bean dishes), Vegetable side dish group, Kimchi group (including kimchi and jangajji), Soup, stew group, and the other group. Nutrient analysis was conducted for 100 ml of these dishes by CAN Pro 3.0 utilizing volume and weight conversion data used for analysis of the Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and those from the Nutrient Composition of Food for Consumers. All the possible combinations of 5 dishes, comprising of 3 dishes from Rice group, Protein side dish group, and Kimchi group, respectively, and 2 dishes from Vegetable side dish group, were made using the frequently served dishes from the respective dish group. Nutrient analysis of each combination was conducted based on the assumption that a lunch box was 600 ml and filled up to 80% by dishes using the volume ratio of 3 : 1 : 1.5 : 0.5 for Rice group : Protein side dish group : Vegetable side dish group : Kimchi group. The mean and standard deviation of energy and nutrients of all combinations calculated by weighting the serving frequency of each dish selected for the combinations were 621 +/- 81 kcal for Energy, 22.1 +/- 5.0 g for Protein, 120 +/- 45 mg for Calcium, 4.1 +/- 1.1 mg for Iron, 201 +/- 130microgram RE for Vitamin A, 0.34 +/- 0.10 mg for Thiamin, 0.27 +/- 0.10 mg for Riboflavin, and 24.3 +/- 9.6 mg for Vitamin C. The energy percentages from Carbohydrate, Protein and Fat were 66%, 14% and 20%. The analysis results met the nutrition standard of lunch boxes for male elementary students in grades 4 through 6 under the government-funded meal service program regarding calories, nutrients except calcium and riboflavin, and macronutrient distribution ranges. Accordingly appropriate box sizes were suggested for different age and sex groups to meet the respective nutrition standards. In addition, milk or dairy products were suggested to accompany lunch boxes to supplement calcium and riboflavin intake. The method of selecting box sizes and making dish combination suggested in this study could be useful for the organizations preparing lunch boxes under the government-funded children's meal service program where nutrition professionals are not available.
- 373 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Effect of School Breakfast Service on Attitudes Toward Breakfast and School Breakfast of Male Middle School Stu
- Gajin Yi, Jihyun Yoon, Yun Jeong Choo, Sang Jin Chung, Young Hye Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(3):277-285. Published online June 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to analyze the effect of male middle school students'eating school breakfast on their attitudes toward breakfast and school breakfast. In addition, the effect of school breakfast on breakfast-related eating behaviors and academic achievement was investigated. The study subjects were selected from a male middle school located in Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea. Breakfast was provided at the school for 7 weeks during the 2nd semester of the year 2006. Two sophomore classes were selected for the experimental study. All the students from one class (n = 34; School Breakfast Eaters) have eaten school breakfast while none of the students from the other class (n = 33; School Breakfast Non-eaters) have done so. About two weeks after the school breakfast service was terminated, questionnaires were distributed to the two classes and the responses were analyzed. The results showed that School Breakfast Eaters had more positive attitudes toward breakfast and school breakfast than School Breakfast Non-eaters. In addition, School Breakfast Eaters perceived the positive effect of eating breakfast on their school life more highly than School Breakfast Non-eaters. However there was no significant difference between the two groups in their breakfast eating behaviors in terms of breakfast skipping when the breakfast service was not available. No significant difference was found between the two groups with regards to math score variation before and after school breakfast service. In conclusion, school breakfast for 7 weeks had positive effects on male middle school students'attitudes toward breakfast and school breakfast, although the effect was not confirmed in their breakfast-related eating behaviors after the school breakfast service was terminated.
- 342 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Current Status of Meal Box Service Management for Children from Low-income Families During Summer Vacation
- Borham Yoon, Jihyun Yoon, Jae Eun Shim, Sooyoun Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(2):206-215. Published online April 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the current status of foodservice management in organizations delivering meal boxes for low-income children during summer vacation. A survey was conducted with persons in charge of meal box production and service of these organizations via mail. Out of 114 questionnaires distributed nationwide, 100 were analyzed (87.8% analysis rate). Over half (53%) of the organizations delivered meal boxes consisting of rice and side dishes while the rest delivered side dishes only. About 81% of the organizations received KRW 3,000 per meal from their local governments and the rest received KRW 3,500. Only 28% of organizations had employed a dietitian. Over one-third (38%) of the respondents were unaware of the official nutritional standard of the foodservice program for low-income children during vacation. Most of the organizations (94%) had menu planned in advance. The average percentage of food cost was 84.1%. Over 40% of the organizations did not keep food samples for sanitation test (43%) and did not take any measures for keeping food temperature during delivery (45%). The organizations delivering rice and side dishes were more likely to be located in cities rather than rural areas and received higher reimbursement rate. The organizations receiving reimbursement of KRW 3,500 or hiring a dietitian were more likely to use standardized recipes, keep food samples for sanitation test, or take measures for keeping food temperature during delivery compared to the counterparts. Respondents reported that increasing reimbursement rate was the most necessary for improving the quality of meal box. This study results showed that the meal box delivery service for low-income children was not properly managed during the vacation, with regards to menu planning and food production. It is recommended that reimbursement rate for meal boxes should be adjusted depending on meal box types and local conditions.
- 360 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Relation of Breakfast Intake to Diet Quality in Korean School-Aged Children: Analysis of the Data from the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Yoon Jae Yeoh, Jihyun Yoon, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(1):1-11. Published online February 28, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aims of this study were to assess the quality of breakfast intake and to examine the relation of breakfast intake to the quality of daily diet in Korean school-aged children. The one day 24-hour recall data from the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed. The sample of this study consisted of 1,600 children aged 7 to 18 years attending elementary, middle, or high schools. By calorie level of breakfast intake, the children were grouped into Breakfast Skippers (0 kcal; n = 268, 17%), Low Calorie Breakfast Eaters (0 kcal < and < 10% of Estimated Energy Requirement (EER); n = 190, 12%), Moderate Calorie Breakfast Eaters (10% < or = and < 25% of EER; n = 861, 54%), or Sufficient Calorie Breakfast Eaters (> or = 25% of EER; n = 281, 17%). General characteristics including weight status and nutritional quality of breakfast and daily diet were compared among the four groups. The average daily calorie intake of Breakfast Skippers, Low, Moderate, and Sufficient Breakfast Eaters were 1,771 kcal, 1,719 kcal, 1,902 kcal, and 2,349 kcal, respectively; they were 86.3%, 85.9%, 98.0%, and 124.9% of EER, respectively. The percentages of students consuming daily diet with protein, vitamin A, B1, B2, niacin, vitamin C, calcium, phosphorus, or iron less than Estimated Average Requirement decreased in the breakfast groups with the higher calorie level of breakfast intake. The Dietary Variety Score of daily diet significantly increased by increasing the calorie level of breakfast intake. The results indicated the quality of daily diet was positively related to the level of calorie intake from breakfast.
- 364 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Status of Children's Breakfast Skipping and Their Mothers' Needs for Breakfast Service at Child Care Centers
- Kiwon Lee, Jihyun Yoon, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(5):682-692. Published online October 31, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the status of children's breakfast skipping and their mothers' needs for breakfast service at child care centers. A survey was conducted with mothers of children aged 3 to 5 years and attending child care centers in Gwanak-gu, Seoul. Out of 960 questionnaires distributed to the caregivers at 32 child care centers, 633 were returned (66% response rate), and 449 were analyzed (47% analysis rate) after excluding data from the respondents not meeting the selection criteria for this study: mothers of children aged 3 to 5 years. Over 2/3 (69%) of children ate breakfast every weekday (Breakfast Eaters) and almost 1/3 (31%) of children skipped breakfast one time or more often on weekdays (Breakfast Skippers). The collected data were compared between Breakfast Eaters and Breakfast Skippers. The average Good Dietary Practice Score of Breakfast Skippers was significantly lower than that of Breakfast Eaters, implying poorer dietary habits. A higher percentage of mothers of Breakfast Skippers (62%) responded that breakfast service was 'necessary' or 'very necessary' at child care centers than those of Breakfast Eaters (27%). A multiple logistic regression analysis was conducted to determine factors affecting mothers' needs for breakfast service at child care centers. The result showed that the children's ages, mothers' occupational status, household monthly income, frequencies of eating breakfast on weekdays and satisfaction level with morning snack provided at child care centers affected mothers' needs for breakfast service at child care centers. In particular, mothers who had a full-time job (OR = 2.06) than housewives, mothers whose children did not eat breakfast at al (OR = 3.54), ate 1~2 times (OR = 5.50) or ate 3~4 times (OR = 3.80) on weekdays than those whose children ate breakfast every weekday were more likely to have needs for breakfast service at child care centers than housewives. In conclusion, Breakfast Skippers tended to have poorer dietary habits than Breakfast Eaters and Full-time working mothers had higher needs for breakfast service at child care centers. This study results suggest that child care centers consider serving breakfast to children as the number of working mothers increases.
- 309 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Factors Affecting Intention to Participate in School Breakfast Programs of Middle and High School Students in Seoul
- Yangsuk Kim, Jihyun Yoon, Haengran Kim, Sungok Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(4):489-500. Published online August 31, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine factors affecting intention to participate in school breakfast programs of middle and high school students in Seoul using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Out of 2,280 questionnaires distributed to the middle and high school students, 2,060 were returned (90.4% response rate) and 1,799 were analyzed (78.9% analysis rate). To determine factors affecting intention to participate in school breakfast programs, logistic regression analyses were conducted for middle and high school students, respectively. For logistic regression, data of 1,217 out of 1,799 students (637 middle and 580 high school students) were used after excluding 582 students which had an answer 'Not sure' to the question about intention to participate in school breakfast programs. In case of middle school students, male than female students (OR = 1.504), the students who skipped all breakfast (OR = 1.851), who ate breakfast 1~2 times (OR = 3.474) or 3~4 times (OR = 1.950) than those who ate breakfast everyday during weekdays of the previous week were more likely to participate in school breakfast programs. In case of high school students, male than female (OR = 1.967), the students who skipped all breakfast (OR = 4.187), the students who ate breakfast 1~2 times (OR = 3.024) or 3~4 times (OR = 2.095) than those who ate breakfast everyday during weekdays of the previous week were more likely to participate in school breakfast programs. In addition, both possibility of middle and high school students' participation in school breakfast programs increased as the satisfaction with school lunch service (OR = 1.704, 1.653) increased. Middle school students who perceived their household income level 'low or middle low' (OR = 1.999) than those who perceived their household income level 'middle' and the students who had more positive 'attitude' (OR = 1.311) toward eating breakfast were more likely to participate in school breakfast programs. However, high school students who had higher 'perceived difficulty in access to breakfast' (OR = 1.370) were more likely to participate in school breakfast programs. The results of this study could be useful data to plan and develop school breakfast programs in Korea.
- 397 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Status of Early Childhood and Maternal Nutrition in South Korea and North Korea
- Jae Eun Shim, Jihyun Yoon, Seong Yeon Jeong, Mina Park, Yeon Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(2):123-132. Published online April 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to compare the nutritional status of children aged 5 or under and women aged 20 to 34 years between the Republic of Korea (South Korea) and the Democratic Peoples' Republic of Korea (DPRK: North Korea). For the source of nutritional status of North Koreans, the DPRK 2004 Nutrition Assessment-Report of Survey Results was used. As the comparable data of South Koreans, the anthropometric data for children and women were obtained from the reports of the Korean Pediatric Society and the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards, respectively. The blood hemoglobin data of South Korean women were obtained from the data file of the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey and analyzed. In regard to the North Korea, the prevalence of underweight (weight for age Z-score <-2.0) in children under 12 months was about 10~15%, and thereafter progressively increased until 30 to 35 months reaching 30%. In South Korea, the prevalence of underweight was less than 3% in most age groups both in boys and girls. In North Korea, the prevalence of stunting (height for age Z-score <-2.0) reached 20% in children under 12 months and increased with age over the level of 50% in children aged 54 to 59 months. In South Korea, the prevalence of stunting was less than 3% in children under 12 months and was less than 10% throughout the age groups. Maternal protein-energy malnutrition and anemia were assessed for the women aged 20 to 34 years using mid-upper arm circumference (< 22.5 cm) and blood hemoglobin level (< 12 g/DL), respectively. The prevalence of protein-energy malnutrition was 39.6%, 30.7%, 31.7% in North Korea and 12.5%, 5.0%, 1.5% in South Korea for the women in 20~24, 25~29, 30~34 years, respectively. The prevalence of anemia in the North Korean women was about 34~36% while that in the South Korean women was 15~18%. In conclusion, the disparity of nutritional status in early childhood and maternity between South Korea and North Korea is so huge that active and well-planned nutrition support policy and programs for women and children in North Korea is imperative to prepare for the future unified nation.
- 359 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- Satisfaction of Elementary Students Eating School Lunch; Association with Level of Involvement in School Lunch Service
- Jihyun Yoon, Yun Jeong Choo, Sang Jin Chung, Si Hyun Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(5):668-676. Published online October 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine the relationship between the students' levels of involvement in school lunch service and their satisfaction levels with the service. A survey was conducted with 5th and 6th grade elementary students eating school lunches. Out of 1,680 questionnaires distributed to the students from 14 schools, 1,254 complete questionnaires (74.6%) were analyzed. The questionnaire included two 5-point multi-item scales for measuring levels of involvement in and satisfaction with school lunch service, respectively. A factor analysis grouped 20 items measuring school lunch satisfaction into three factors: 'food satisfaction', 'nutrition & sanitation satisfaction', and 'service & environment satisfaction'. As a result of multiple regression analyses controlling the influence of such variables as students' grades, gender, school location, years and places of eating school lunches, students' levels of involvement in school lunch service was proven to be positively associated with levels of school lunch satisfaction overall, as well as satisfaction levels in regard to 'food', 'nutrition & sanitation', and 'service & environment', respectively. It was suggested that efforts such as nutrition education to increase students' levels of involvement in school lunches could be a useful strategy to improve students' satisfaction with school lunch service.
- 348 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Relationship between Levels of Dietitians' Management Activities and Job Satisfaction in Elementary School Foodservice Operations
- Yun Jeong Choo, Jung Hee Lee, Jihyun Yoon, Si Hyun Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(4):546-554. Published online August 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship between the levels of foodservice management activities and job satisfaction of the dietitians in elementary schools. Out of 130 questionnaires distributed to elementary school dietitians in In-cheon, 127 were returned and analyzed (98% response rate). The questionnaire included two multipleitem scales for measuring foodservice management activities and job satisfaction, respectively. All the items in the scales were coded 1 to 5 for 'certainly no', 'no', 'neutral', 'yes', and 'certainly yes' and grouped by using factor analyses. Most of the responding dietitians were working for schools in urban areas and have independently managed on-site kitchens. The 19 items on food service management activities were grouped into 6 factors and the mean scores of the levels of Personnel Hygiene Management, Education & Training, Sanitation & Safety Management, Menu Quality Management, Service Management, and Environment Management were 4.76, 4.26, 4.24, 4.05, 3.61 and 3.39, respectively. The 23 items on job satisfaction were grouped into 4 factors and the mean scores of the satisfaction levels of Systematic Environment, Job Duty, Job Condition, and Physical Environment were 3.38, 2.83, 2.53, and 2.08, respectively. Overall, the levels of food service management activities and job satisfaction were positively associated with a correlation coefficient of 0.254 (p < 0.01). In particular, satisfaction levels on job duty itself and systematic environment were positively associated with the levels of overall management activities. The results suggest that improving dietitians' job satisfaction could increase the levels of management activities of school foodservice dietitians, resulting in quality improvement of school food service.
- 277 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



