Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
- Prevalence of coronary artery disease according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years and older: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Areum Song, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):457-470. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To examine the prevalence of coronary artery disease (CAD) according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years.
Methods
Data were derived from 11,025 participants aged ≥ 40 years in the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were assigned to a CAD group (n = 470) or a non-CAD group (n = 10,555). Socio-demographic characteristics (age, sex, residence, income, marital status, education level, and employment status), lifestyle characteristics (smoking, drinking, walking, strength training, sleep duration, stress level, and subjective health perception), energy and nutrient intakes, and comorbidities, including obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, stroke, cancer, depression, renal failure, cataract, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, and osteoporosis were analyzed.
Results
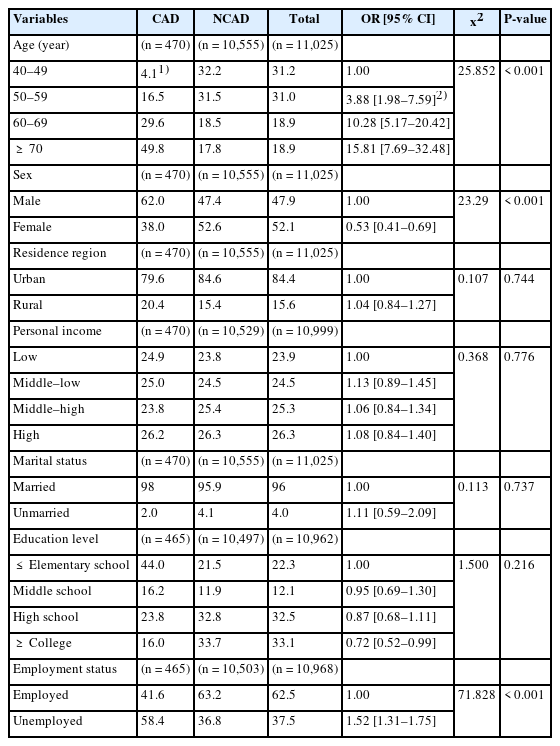
The prevalence of CAD was higher in older participants and in male. Participants with CAD had higher rates of smoking, engaged in less strength training, experienced higher stress, and had poorer perceived health. They had lower intakes of energy, fiber, folate and iron. The prevalence of obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, stroke, depression, renal failure, cataract, asthma, allergic rhinitis, osteoarthritis, or osteoporosis was significantly higher in the CAD group. The likelihood of having CAD was significantly higher among participants with renal failure (odds ratio [OR], 4.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.24–8.08), depression (OR, 2.14; 95% CI, 1.55–2.95), asthma (OR, 2.07; 95% CI 1.48–2.91), and dyslipidemia (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.69–2.44).
Conclusion
In Koreans aged 40 years, CAD was associated with unhealthy lifestyle habits, low nutrient intake, and increased comorbidities such as renal failure, depression, asthma, and dyslipidemia. These findings suggest the need for lifestyle management and intensive chronic disease management to reduce the risk of CAD.
- 94 View
- 10 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- Dietary Habits and Nutritional Status of Young Women according to Breakfast Frequency in Seoul
- Da Mee Kim, Youl Ri Kim, Kyung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):102-115. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Although breakfast is important to nutrition balance, prevention of overeating, and weight control, people in their 20s (males: 55.1%, females: 49.9%) were reported to have the highest rate of skipping breakfast in 2016 Korea Health Statistics. This study aims to examine dietary habits and nutrient intake depending on breakfast frequency among young women in Seoul.
METHODS
The subjects were 655 young women in Seoul from August to October 2016, and the survey was performed by using a questionnaire that included general characteristics, dietary habits, and eating behavior. Body composition was determined by bioelectric impedance analysis. Nutritional status was examined by the 24-hour recall method.
RESULTS
The participants were classified by breakfast intake frequency; ‘≥ 5 times/week (n=160)’, ‘1–4 times/week (n=327)’, and ‘breakfast skipping (n=168)’. The ‘breakfast skipping’ group had lower frequency and regularity of meals. In addition, the ‘breakfast skipping’ group had a higher frequency of eating-out and late-night meals. There was no difference in total calories between the ‘breakfast skipping’ group and other groups, but the ‘breakfast skipping’ group had significantly low carbohydrate and fiber intakes. The participants showed lower intakes of calories, fiber, vitamin A, vitamin C, niacin, folic acid, calcium, potassium, and zinc in comparison with recommended intakes. Especially, the ‘breakfast skipping’ group had significantly lower fiber, vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium, potassium levels compared to the ‘≥ 5 times/week’ group. For Mean Adequacy Ratio (MAR), the ‘breakfast skipping’ group recorded a ratio of 0.60, which was lower than those of other groups. Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ) including fiber, vitamin C, calcium and phosphorus were significantly lower in the breakfast skipper group, compared to the breakfast eater group.
CONCLUSIONS
The ‘breakfast skipping’ group showed low regularity of meals and a high frequency of eating-out and late-night meals. The breakfast regular eater group showed high intake of micronutrients and quality of meals was high in general. Skipping breakfast could lower nutrient intake and quality of meals, which requires attention. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Attributes of multiple concurrent functional gastrointestinal disorders in female university students in South Korea
Hyo Kyung Kim, Hyunjung Kim, Aram Lee
Women & Health.2024; 64(8): 674. CrossRef - Beliefs, self-efficacy, subjective norms, and eating behaviors according to the breakfast frequency among female university students in South Korea
Hye Jin Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1170. CrossRef - Revision of Nutrition Quotient for Korean adults: NQ-2021
Sung-Min Yook, Young-Suk Lim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ki-Nam Kim, Hyo-Jeong Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 278. CrossRef - Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 350. CrossRef - Dietary Life of Chinese International Students according to the Frequency of University Foodservice Use in Korea
Yan Cui, Hye-Jong Yoo, Injoo Choi, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(4): 291. CrossRef - Development of Nutrition Quotient for Korean adults: item selection and validation of factor structure
Jung-Sug Lee, Hye-Young Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 340. CrossRef
- Attributes of multiple concurrent functional gastrointestinal disorders in female university students in South Korea
- 1,818 View
- 18 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
- Mijin Jo, Young Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(1):38-47. Published online February 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to analyze the association between sodium excretion and obesity for healthy adults in the Gwangju area.
METHODS
The participants included 80 healthy adults aged 19 to 69 years in Gwangju. The dietary intake and sodium excretion were obtained using the 24-hour recall method and 24 hour urine collection. The participants were classified into two groups according to the amount of urinary sodium excretion: (≤ 141.75 mmol/dL, > 141.75 mmol/dL).
RESULTS
After adjusting for sex, age, smoking history, and income, the high excretion of sodium group was significantly higher for weight, body mass index, body fat mass, percent body fat, visceral fat area (VFA), waist circumference, hip circumference, and WHR. The energy and nutrients intake were significant after adjusting for sex, age, smoking history, and income. The LSE group had a significantly higher fat intake and Na/K intake ratio. The HSE group had significantly higher fiber intake, and K intake. As the amount of urinary sodium excretion increased, the risk of obesity before correction was 3.57 (95% CI: 1.13–11.25) times greater, and the risk of obesity of T3 increased significantly by 3.33 times (95% CI: 1.05–10.59). After correcting for sex and age, the obesity risk of T2 increased significantly by 4.23 times (95% CI: 1.11–16.06), and after correcting for sex, age, smoking history, and income, the obesity risk of T2 increased significantly by 6.81 times (95% CI: 1.44–32.19) the risk of obesity.
CONCLUSIONS
An association exists between sodium excretion and obesity in Korean adults. In this study, the high excretion of sodium group was obese and the risk of obesity was higher than the low excretion of sodium group. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preventive Effects of Whole Grain Cereals on Sarcopenic Obesity in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
Mi-Bo Kim, Sein Lee, Changhee Kim, Jae-Kwan Hwang
Food Engineering Progress.2018; 22(4): 358. CrossRef
- Preventive Effects of Whole Grain Cereals on Sarcopenic Obesity in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
- 1,103 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Quality of Nutrient Adequacy and Health-related Quality of life of the Rural Elderly
- Mee Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):423-432. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.423
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
In Korea, the percentage of elderly is increasing at an unprecedented rate, and is expected to account for 40% of the population by 2060. This massive demographic change stresses the importance of research on aging as it is necessary to improve the quality of life (QoL) of this population. This study aimed to examine the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of the rural elderly and to clarify its association with the nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR).
METHODS
A cross-sectional study was performed in S-gun, Chonbuk, a critical agricultural area. The elderly people without abnormal physical functioning composed our study population and the data were collected by personal visits to 336 elderly people aged over 65 years (110 males and 226 females). Subjects were interviewed with questionnaires pertaining to general characteristics and EuroQol (EQ-5D). Nutrient intakes were assessed two days by 24-hours recall method. Subjects were defined as high QOL group if EQ-5D index with Nam's model was above the median.
RESULTS
Generally, EQ-5D index was lower in women than in man, and lower in older subjects than in younger subjects. The percentages of people below the median were 42% (low QoL group) and 58% (high QoL group) were found to be the above the median. The high QoL group had higher NAR, especially for vitamin C, vitamin B1, vitamin B2 and folate. All dimensions in the EQ-5D were affected by NAR of some nutrients and especially anxiety/depression dimension was significantly correlated with NAR of 5 nutrients (protein, calcium, iron, vitamin C and vitamin B1) and EQ-5D scores.
CONCLUSIONS
HRQol was significantly reduced in elderly with increasing age and this was more pronounced in women than in man. The NAR of some nutrients were associated with the EQ-5D index, especially anxiety/depression dimension, among rural elderly. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health and dietary characteristics of the men and women in their middle age according to health-related quality of life: using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data in 2019 and 2021
Sarim Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 307. CrossRef - Snack Provision Practice in Long-Term Care Hospitals and Facilities in Korea
Dayeong Yeo, Hae Jin Kang, Hyejin Ahn, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(2): 108. CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Patterns and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Older Adults
Ae-Rim Seo, Tae-Yoon Hwang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3703. CrossRef - Food and nutrient intake status of Korean elderly by perceived anxiety and depressive condition: data from Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 ~ 2015
Da-Mee Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(1): 58. CrossRef
- Health and dietary characteristics of the men and women in their middle age according to health-related quality of life: using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data in 2019 and 2021
- 1,217 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Assessment of Menu Plan Prepared by Middle School Students According to Ordinary Meal Pattern and Single Serving Size
- Jung Ok Kim, Youngnam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(4):333-343. Published online August 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.4.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is important to prepare and execute the menu plan for proper and balanced intake of nutrients in the adolescence. This study investigated the new approach for planning menu by ordinary meal pattern based on cooked foods groups. The amounts of cooked foods in the menu plan assumed to be single serving size. The middle school second graders participated for the study. A total of 313 questionnaires were analyzed using CAN-pro 3.0 and SPSS WIN 12.0 program. The average content of energy in the menu plan was 2,453 kcal, the average ratios of energy contribution by carbohydrate, protein and fat were 54.3%, 17.9%, 27.8%, respectively. A total of 56.9% menu plans (94.9% of male and 8.7% of female students') were below the lowest limit of optimum carbohydrate energy ratio of 55%. A total of 29.1% menu plans (33.1% of male and 23.9% of female students') were exceed the highest limit of optimum fat energy ratio of 30%. The NAR of minerals and vitamins were all 1.0 except for calcium (0.92) and folate (0.88). When INQ of the individual cooked food groups were calculated, kimch was the highest in all minerals and vitamins examined, suggesting that kimch may be the best source for all minerals and vitamins, including calcium and folate with the minimum change in energy content. In conclusion, the menu plan by ordinary meal pattern in this study was low in carbohydrate, high in fat, and contained enough minerals and vitamins except for calcium and folate for middle school students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Status of serving labeling of home meal replacement-soups and stews, and evaluation of their energy and nutrient content per serving
Mi-Hyun Kim, In-Young Choi, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(5): 560. CrossRef - Nutritional Adequacy Analysis of Recommended Menu in Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015
Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(4): 279. CrossRef - Proposition and Application of a Dish-Based Target Pattern for Korean Adolescent Girls
Mi Jin Park, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(2): 87. CrossRef - Validation of Nutrient Intake Estimation based on One Serving Size
Yi-Yeong Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(5): 871. CrossRef - Revision of the Target Pattern based on Single Serving Size of Dishes for Korean Adolescent Meal Plan
Mi Jin Park, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 21. CrossRef - Revision and Application of the Target Pattern in Food Guidance System: Administered to 2nd grade middle school students
Ha Yeon Lee, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(3): 274. CrossRef
- Status of serving labeling of home meal replacement-soups and stews, and evaluation of their energy and nutrient content per serving
- 1,297 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on the Sodium and Potassium Intakes and Urinary Excretion of Adults in Busan
- Hwa Jae Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(6):737-751. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.6.737
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to assess sodium and potassium intakes and urinary excretion of adults in Busan and to evaluate the relationship of urinary sodium/potassium excretion (UNa/UK) to the status of anthropometric, blood pressure, urine analysis, and nutrient intake of subjects. Nutrient intake by 24-h recall, 24-h UNa/UK were measured with 87 adults aged 20-59 yrs (42 men and 45 women). The mean intakes of sodium and potassium were 3915.4 mg and 3093.9 mg, respectively. The mean 24-h UNa/UK was 3457.0/1680.4 mg. UNa showed significant positive correlations with sodium intake (p < 0.001, p < 0.001), sodium/potassium ratio (p < 0.001, p < 0.01), UK (p < 0.001, p < 0.001), and UNa/UK ratio (p < 0.05, p < 0.01) in men and women and with age, BMI, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure in women (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05). The UK showed significant positive correlations sodium intake (p < 0.001, p < 0.001), UNa (p < 0.001, p < 0.001) in men and women and with sodium density in men (p < 0.001) and with age, intakes of protein and potassium in women (p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.05). Mean SBP was lowest in the second quartile and highest in the fourth quartile of UNa. Mean UNa in the second, third, and fourth quartiles were 2821.1 mg, 3621.3 mg, and 5456.4 mg, respectively. Mean SBP in the second, third, and fourth quartiles were 115.8 mmHg, 120.7 mmHg, and 125.9 mmHg, respectively. Based on the results, UNa was related to sodium intake, UK, and SBP. We conclude that nutritional education for the reduction of high sodium intake is needed in the general population to prevent and control adverse blood pressure levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison between 24-hour diet recall and 24-hour urine collection for estimating sodium and potassium intakes and their ratio among Korean adults
Taisun Hyun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Young-Ran Heo, Heekyong Ro, Young-Hee Han, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 284. CrossRef - Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
Mijin Jo, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - A Comparison of Sources of Sodium and Potassium Intake by Gender, Age and Regions in Koreans: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2010-2012
Yang-hee Park, Sang-Jin Chung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(6): 558. CrossRef - Salt Preference and Sodium Intake among Pregnant Women
Mi Jeung Im, Dong Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(4): 297. CrossRef - Processing and Characteristics of Snacks Make from Extrusion Rice Oryza sativa and Dried Shrimp Acetes chinensis
Hae-Soo Je, Kyung-Hun Kang, Hee-Bum Jung, Si-Young Park, Young-Mi Kang, Tae-Jong Seoung, Jae-Dong Lee, Jin-Hyo Park, Jeong-Gyun Kim
Korean Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.2016; 49(3): 293. CrossRef - Contents of Sodium and Potassium for Restaurant Dishes in Seoul
Mi-ra Jang, Mi-sun Hong, Bu-chuhl Choi, Sung-hee Han, Kyeong-ah Lee, Li-la Kim, Jib-ho Lee, Jung-hun Kim, Kweon Jung
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2015; 30(2): 189. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Nutrient Intake Status of Male and Female University Students in Chuncheon Area
Yoon-Sun Kim, Bok-Ran Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(12): 1856. CrossRef - The Risk of Metabolic Syndrome by Dietary Patterns of Middle-aged Adults in Gyeonggi Province
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 527. CrossRef - Benefits of potassium intake on metabolic syndrome: The fourth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV)
Doosup Shin, Hee-Kyung Joh, Kyae Hyung Kim, Sang Min Park
Atherosclerosis.2013; 230(1): 80. CrossRef
- Comparison between 24-hour diet recall and 24-hour urine collection for estimating sodium and potassium intakes and their ratio among Korean adults
- 1,143 View
- 0 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Dietary Mineral Intakes, Urinary Mineral Excretions, and Bone Mineral Density in Korean Postmenopausal Women
- Jee Young Yeon, Chung Ja Sung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(5):569-579. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.5.569
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine the urinary Ca, P, Mg, Zn, Cu, and Mn levels and bone mineral density (BMD) in sixty-two postmenopausal women. The study was conducted through anthropometric checkup, 24-hour recall, 24-hour urine and bone mineral density using DEXA. Average age, height, weight and body fat of the subjects were respectively 65.39 years, 150.19 cm, 58.03 kg and 37.22%. The average spine and femoral neck BMD of subjects were -2.19, -3.13. The mean intakes of Ca, P and Mg were 524.7 mg, 993.10 mg, and 254.6 mg and those of Zn, Cu and Mn were 8.6 mg, 1.5 mg, and 3.5 mg. The average 24-hour urinary excretion of Ca (UCa), P (UP) and Mg (UMg) were 161.07 mg, 673.68 mg, and 99.87 mg. The average 24-hour urinary excretion of Zn (UZn), Cu (UCu) and Mn (UMn) were 366.50 microg, 22.57 microg, and 1.55 microg. Ca intake showed significantly positive correlations with urinary UCa (p < 0.05), UMg (p < 0.01) and spine BMD (p < 0.05). P intake showed significantly positive correlations with UCa (p < 0.05), UMg (p < 0.05) and UZn (p < 0.05). Mg intake showed significantly positive correlations with UZn (p < 0.05) and Mn intake showed significantly positive correlations with UCa (p < 0.05). Multiple regression analysis indicates that Ca intake and UMg is the most important factor to increase spine BMD. On the other hand, UCa is the most important factor to decrease spine BMD. Higher femoral neck BMD was related to UP, while lower femoral neck BMD was related to UCa. In conclusion, Dietary intake of Ca showed positive effect of spine BMD, while excessive P intake showed negative effect on BMD due to increases in UCa, UMg and UZn. Further studies are required to investigate the relationship between bone metabolism and mineral excretion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Magnesium intake and dietary sources among Koreans: findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Jee-Seon Shim, Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(1): 48. CrossRef - Association between dietary intake, body measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study
Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 282. CrossRef - Daily Intake of Magnesium and its Relation to Urinary Excretion in Korean Healthy Adults Consuming Self-Selected Diets
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Connie M. Weaver
Biological Trace Element Research.2017; 176(1): 105. CrossRef - Prevalence of Osteopenia/Osteoporosis and Related Risk Factors of Men Aged 50 Years and Older: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2011 Data
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(2): 106. CrossRef - Analysis of Bone Mineral Density, Biochemical Index and Nutrient Intakes of 30-70 Years Old Women: Based on 2011 KNHANES
Jae Ok Koo, Myung Sook Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 328. CrossRef - The Association between Changes in Food and Nutrient Intakes and Changes in Bone Metabolic Indicators in Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia after a 12-week Intervention of Nutrition Education and Aerobic Exercise
Seo-Jin Kim, Suh-Jung Kang, Yoon Jung Park, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 213. CrossRef - Factors Related to Calceneal Broadband Ultrasound Attenuation, Anthropometric Indexes and Nutrient Intakes among Elementary School Children in Chungnam
Ye-Jung Kim, Yoon Jeong Choi, Hee-Seon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(4): 312. CrossRef - Association of Bone Mineral Density and Blood Pressure, Calcium Intake among Adult Women in Seoul · Kyunggi Area - Based on 2011 KNHANES -
Jae Ok Koo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 269. CrossRef - Dietary factors affecting bone mineral density in Korean rural postmenopausal women
Jeong Sook Choe, Eun Mi Ahn, Sung Ok Kwon, Young Hee Park, Jinyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(5): 470. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Zinc, Copper, Manganese and Selenium Intake in Female University Students
Yun-Jung Bae, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(2): 146. CrossRef
- Magnesium intake and dietary sources among Koreans: findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
- 1,017 View
- 0 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on the Calcium and Sodium Intakes and Urinary Calcium Excretion of Adults in Busan
- Hwa Jae Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(2):215-226. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.2.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to assess calcium and sodium intakes and urinary excretion of adults in Busan and to evaluate the relationship between urinary calcium excretion (UCa) and the status of anthropometric, blood pressure, urine analysis, and nutrient intake of subjects. Nutrient intake by 24 hr recall, 24 hr urinary calcium and sodium excretion (UNa) were measured with 87 adults aged 20-59 yrs (42 men and 45 women). The mean calcium intake was 88.0% for men and 103.0% for women of Recommended Intake. The mean sodium intake was 283.4% for men and 250.5% for women of Adequate Intake (AI). The mean 24hr UCa was 127.4 mg in men and 107.3 mg in women. The mean 24 hr UNa was 3650.6mg in men and 3276.4mg in women. The intake and urinary excretion of calcium and sodium were not significantly different by gender. UCa showed significantly positive correlations with sodium intake and UNa in men (p < 0.001, p < 0.05) and women (p < 0.001, p < 0.001) and with age, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and sodium density in women (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.01). The UCa/creatinine showed significantly positive correlations with age, sodium intake, sodium density, and UNa in women (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.01, p < 0.01). When UCa was stratified into quartile (Q1-Q4), age, SBP, UCa, UNa, sodium intake, and AI percentage of sodium (p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.001, p < 0.001, p < 0.001, p < 0.001) were significantly higher in Q4. The mean intake and AI percentage of sodium in Q4 were 4768.8mg and 329.0. Based on the results, UCa was related to age, SBP, UNa, and sodium intake. Therefore, nutritional education of decreasing sodium intake for decreasing UCa is needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between dietary intake, body measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study
Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 282. CrossRef - Sex- and age group-specific associations between intakes of dairy foods and pulses and bone health in Koreans aged 50 years and older: Based on 2008~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Bi Seo, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(3): 165. CrossRef - Comparison of sodium content of workplace and homemade meals through chemical analysis and salinity measurements
Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(5): 558. CrossRef - Calcium Status and Bone Mineral Density by the Level of Sodium Intake in Young Women
Jin-Sook Yoon, Mi Jung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(2): 125. CrossRef - A Study on Dietary Mineral Intakes, Urinary Mineral Excretions, and Bone Mineral Density in Korean Postmenopausal Women
Jee-Young Yeon, Chung Ja Sung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(5): 569. CrossRef
- Association between dietary intake, body measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study
- 1,170 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of the Dietary Diversity and Nutrient Intakes in Obese Adults
- So Hye Kim, Ju Young Kim, Kyoung A Ryu, Cheong Min Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(5):583-591. Published online October 31, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to assess the diet diversity, food habit and nutrient intake of obese adults who were visiting the health promotion center. This study was accomplished with the 138 obese adults (men = 103, women = 35) aged over 20 years old whose BMI were above 25 kg/m2. Nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR), the number of foods (Dietary Variety Score, DVS), and food group consumed (Dietary Diversity Score, DDS) by using the data from the three days record were analyzed and the food habit and lifestyle were assessed by self reporting questionnaire. The average energy intake of men was 2150.2 kcal which was significantly higher than that of women (p < 0.05). The intake ratio of carbohydrate, protein and fat over total energy was 54.8% : 19.3% : 25.8% in men, 59.5% : 17.8% : 22.6% in women, respectively. Frequency of the breakfast in a week above 4, 2~3 time and under one time was 75.7%, 10.7% and 9.7% in men, 77.1%, 5.7% and 14.3% in women respectively. Frequency of eating between meals in a day under one time was 73.8% in men, 57.1% in women (p < 0.05). The average DDS and DVS was 3.63 +/-0.07 and 14.10 +/-3.45, respectively which was significantly correlated with MAR (r = 0.40 in DDS, r = 0.64 in DVS, p < 0.01). The most frequent style of food pattern was DMGFV = 01101 in 35% of men, and DMGFV = 01111 in 37.1% of women. Our results show that dietary diversity and variety are useful parameters for evaluating nutrient intakes in obese adults. These findings suggest that nutritional education based on obese persons' eating behavior and eating diversity may be required to increase educational efficiency of weight control programs.
- 333 View
- 11 Download

- [English]
- Levels of Serum Antioxidant Minerals and Enzyme Capacities of Korean Male Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
- Eugene Shim, Soo Yeon Kim, Eun Jung Chung, Seung Yun Cho, Yang Cha Lee-Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(4):396-404. Published online August 31, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Increased oxidative stress contributes to the progression of atherosclerosis. We measured serum antioxidant mineral concentrations, capacities of serum antioxidant enzymes and fasting lipid profile in 97 male patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and 21 male controls. Nutrient intake was assessed by the semi-quantitative food frequency method. CAD patients were divided into single-vessel disease (SVD, n = 66) and multi-vessel disease (MVD, n = 31) groups on the coronary angiography. The ratio of serum LDL- to HDL-cholesterol elevated with an increasing number of diseased vessels compared to the control (control < SVD
- 258 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Life and Eating-Out Style Related to Breakfast Frequency of Male Students in Culinary College
- Sookhee Kim, Kyunghee Joung, Byoungsook Chae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(1):13-24. Published online February 28, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was to investigate dietary life and eating-out style related to breakfast frequency of male students in culinary college. This survey was conducted using questionnaires for 110 male students at college in Hongseung. Mean height and body weight of those we investigated was 174 cm and 70.5 kg. The one to two times per week breakfast eating group was 34.55%, which is exceedingly numerous; none per week breakfast eating group was 30%; three to four times per week breakfast eating group was 15.45%; everyday breakfast eating group was only 9.09%. The breakfast frequency was very low, and the not-eating breakfast problem is serious to think of in male college students. Mean weight, body fat and body mass index (BMI) of the everyday breakfast eating group was lower than the other group even it was not significant. The self-boarding house or dormitory living condition group was not eating breakfast was significant. So a correct dietary life and eating habit should be taught further for male college students. The smoking group was a significant low frequency of breakfast eating, as well as the lower frequency of breakfast, or worse recognition of self health condition. Higher frequency of breakfast showed more contentment of self body weight. Cooked rice was significantly the most preferable for breakfast. The lower breakfast frequency tended to eat breads or cereals. The lower frequency of breakfast, self recognition of eating rate as speedier was significant, and tended to have a higher frequency of eating-out because of being annoyed by cooking. The lower breakfast frequency ate out more. Twenty five percent of the everyday breakfast eating group ate out because of a special day, and thirty five percent of the not eating breakfast group did so because of being annoyed by cooking. Their mean dietary evaluation grade was under the normal grade, which means that culinary college male students?dietary lives were poor. The lower frequency of breakfast and lower grade of food life evaluation, indicates the importance of nutritional breakfasts education should be improved for male culinary college students also.
- 344 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Relationship between Time Spent on Lunch and Degree of Obesity,Eating Habits in Culinary College Male Students
- Sookhee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(6):695-706. Published online December 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was to investigate the relationship between time spent on lunch and degree of obesity, eating habits in culinary college male students. This survey was conducted using questionnaires for 106 male students in a Hongseung-located culinary college. Over 16 minutes of time spent on lunch group had significantly lower body weights, obesity degrees and body mass index (BMI) and tended to have lower body fat % than the other groups. It suggests that shorter time spent on lunch is related with lower body weight, obesity degree and BMI. Those who ate the meal prepared by mother had longer time spent on lunch. The shorter times spent on lunch group recognized their body shape was lean, the longer time spent on lunch group recognized the overweight or obesity significantly. The shorter time spent on lunch group tended to eat the cooked rice in the gug and recognized that they were not healthy. Those who had diseases in the past tended to have shorter time spent on lunch. The more they chewed cooked rice and then longer time spent on lunch they had, they recognized their eating speed was not significantly speedy. The shorter time spent on lunch they had, the fewer fruits and salty foods they ate significantly. This study suggests that more chewing time, slower eating speed and longer time spent on eatmg lunch is very related with lowering weight, BMI, body fat % and obesity degrees, so male college students should be educated to have correct eating habits.
- 301 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Risk Factors Associated with Hypertension in Patients
- Sook Mee Son, Gwui Yeop Huh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(5):661-672. Published online October 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to determine the dietary risk factors associated with hypertension. The hypertensive group were composed of 112 hypertensive patients (male 53, female 59) who first visited the hypertension clinic and had been diagnosed as having primary hypertension (SBP > or = 140 mmHg or DBP > or = 90 mmHg). The regular visitors or the subjects on special diets or medical therapies were excluded. The normal group consisted of as subjects (male 41, female 54) matched with age and socioeconomic levels. The subjects having higher intakes (above the 75 percentile) in energy, protein, iron, vitamin A or C showed significantly higher hypertension risk estimated with odds ratio after the covariance factors (age, sex and BMI) were adjusted. More than 2400 mg of sodium (6 g of salt) intake was associated with significantly higher risk of hypertension (odds ratio: 1.773, CI: 1.014 - 3.014 for SBP > or = 140 mmHg; odds ratio: 2.373, CI: 1.359 - 4.215 for DBP > or = 90 mmHg). Hypertensive group showed significantly increased intakes of vegetables and fish and shell fish compared to the normal group. When the vegetable intakes were classified into Kimchi, fresh vegetables and cooked vegetables with seasoning, the hypertensive group was observed as having higher intakes of Kimchi and cooked vegetables with seasoning. The intakes of highest quartile for vegetables (> or = 327 g/day)(odds ratio: 3.164, CI: 1.740 - 5.752), fish and their products (> or = 102 g/day)(odds ratio: 2.756, CI: 1.486 - 5.109), grains(> or = 311 g/day)(odds ratio 2.393, CI: 1.186 - 4.832), meats and their product (> or = 106 g)(odds ratio: 2.210, CI: 1.225 - 3.987) compared to the lower were significantly associated with the higher risk of hypertension estimated with DBP (> or = 90 mmHg) after covariance factors were adjusted. In conclusion, our findings confirm that higher intake of energy or sodium are associated with the increased risk of hypertension. Because increased intake of vegetable or fish was associated with the higher risk of hypertension, in contrast with the finding of western countries, choosing or preparation of vegetables or fish with reduced salt is recommended.
- 328 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Intakes and Serum Lipids and Iron Indices in Obese Children
- Jin Yi Kim, Young Shin Han, Hyun Sook Bae, Hong Seok Ahn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(5):575-586. Published online October 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to compare nutrient intakes, diet quality and serum indices (TG, Total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, RBC, Hb, Hct, Serum iron, ferritin, MCV) of obese and normal weight children. The subjects were 149 children living in the Seoul and Gyeonggi areas. Each subject was assigned to one of such as normal weight group (15th < or = BMI percentile < 85th, n = 82) or obese children (85th < or = BMI percentile, n = 67) according to their percentile of BMI by The Korean Pediatric Society. Data on dietary intakes, body composition and serum indices were obtained. Differences of all the above variables were assessed. Energy, carbohydrate, fat, cholesterol, total fatty acid, SFA, MUFA, PUFA, phosphate, potassium, zinc, vitamin B1 and vitamin B6 intakes of girls in the obese group were higher than those of the normal weight group (p < 0.05). The intake of fiber was as insufficient as below 50% of KDRIs in both groups. Nutrient adequacy ratio of calcium, iron, phosphate, zinc and folate in obese boys were lower than those of normal weight boys (p < 0.05). Energy intakes of grain and milk and dairy food in the obese girl group (905.9 +/- 344.5 kcal, 210.9 +/- 166.4 kcal) were higher than those of normal weight girls (671.2 +/- 360.7 kcal, 184.0 +/- 103.5 kcal) (p < 0.05). HDL-cholesterol level of obese boys (52.7 +/- 6.3 mg/dL) was significantly lower than that of normal weight boys (65.3 +/- 15.6 mg/dL). Serum iron level of obese boys and girls (boys: 79.4 +/- 32.6 mg/dL, girls: 98.3 +/- 16.2 mg/dL) was significantly lower than those of normal weight children (boys: 104.8 +/- 38.6 mg/dL, girls: 106.7 +/- 28.9 mg/dL) (p < 0.05). These results suggest that there should be sensible food selection and more intakes of fruit and vegetable are needed to improve the nutritional status in obese children.
- 252 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Effects of the Life Style and Self-Recognition of Health Conditions on the of Body Fat % in Hotel Culinary College Students
- Sookhee Kim, Kyunghee Joung, Yoonjung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(6):825-834. Published online December 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was to investigate the effects of the body fat % on life styles and self-recognition of health conditions in hotel culinary college students. This survey was conducted using the questionnaires for 144 students (110 males, 34 female) in Hongseung-located college. More exercise time and less frequency of alcoholic beverage they intake, lowered their body fat %. Males did stronger exercise and had lower body fat % than females. The stronger exercise they did, the lower body fat % they had, and were more satisfied with their present weight. Since they had more alcoholic beverage, they smoked more. Less smoking, more abdominal obesity they were. The less satisfaction with their body weights, the higher body fat % they had. The obese less were content with their weights. More recognition of obese shape, higher body fat % they had and abdominal obesity they were. Female had higher body fat % and were more abdominal obesity, did weak action, less smoke and weak exercise than male. Higher body fat % they had, more abdominal obesity they were. The more part time jobs they had, they did not smoke or were not satisfied with their body weights. Female students in culinary arts division had higher body fat % and were dissatisfied with their body weights and did less exercise or subnormal exercises.
- 295 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on Nutritional Intakes in Elderly People in Wando Area
- Bok Kyeong Cha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(6):880-891. Published online December 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate nutrients intakes and nutritional quality of Adults and Elderly People in an island area (Wando). A three-day dietary intakes survey, using a 24 hour recall method was obtained from 187 subjects aged 46 to 84 (mean age 65.3) living in an island area (Wando). Nutient intakes were analyzed using CAN-pro soft program and compared to Korean RDA. The quality of nutrients was assessed by analyzing nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR), mean adequacy ratio (MAR), and index of nutritional quality (INQ). The average daily mean energy intakes were 1869.0 kcal for males and 1943.9 kcal for females, respectively. Daily intakes of protein for males and females were 28.0 and 30.4 g and those of fat were 31.5 and 28.51 g, respectively. Nutrient consumed below 75% of Korean RDA was protein, vitamin A, Ca and Zn in both males and females. Average CPF ratio of males and females were 78.8 : 6.0 : 15.1 and 80.0 : 6.4 : 13.4, respectively. Energy intake ratio from protein was significantly higher in over 60 years males. Carbohydrate dependency decreased with age. Protein dependency increased with age. Nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR) of energy, protein, vitamin A and vitamin E were increased with age in males. The mean adequacy ratio (MAR), an index of overall dietary quality, were not significantly different by age group. Average MAR for males and females was 0.77 and 0.78, respectively. The index of nutritional quality (INQ) showed the tendency to decrease with age. Especially, there were significantly decreases in INQ of all nutrients, except protein, with age. Based on these results, it is evident that people in the island area did not consume enough nutrients. Specially, dietary intake of protein, vitamin A, vitamin E, and Ca were not adequate.
- 283 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Dietary Habits of the Nonagenarian Population in Longevity Belt in Korea
- Mee Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(4):513-524. Published online August 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The dietary habits and eating behaviors of nonagenarian subjects over 90 years old in Korean representative longevity belts of Damyang, Gokseong, Kurye, Sunchang were evaluated. The subjects of the study were 91 elderly people (26 males and 65 females) over 90 years old and their dietary habits, food preferences and meal patterns were collected by individual interview. The percentage of subjects, who answered "very good" or "good" for their health status, was 65.9%. In this study, 55% of subjects were without chronic diseases, and there was no significance difference in gender. Many subjects had performed regular exercise and outdoor activity. The rate of eating together with their family was 79.1%. Most of subjects (91.2%) had a regular mealtime consuming three meals a day, and they had good appetite and pleasure of eating. The higher preference of food group was fruits (95.6%), legumes (94.5%), mushrooms (93.4%) and vegetables (92.3%), but the amount of intakes is higher in vegetables than the others. Eating with family, regular exercise and self-rated good health are improved their nutrient intakes. Most frequently consumed meal pattern was rice plus soup and side dishes. The side dish consumed frequently was Namul (blanch and seasoned vegetables). From this study, the nonagenarian populations in longevity belt in Korea have good dietary habits such as regular mealtime, constant amount of meal and eat with pleasure. They are taking Korean traditional meal pattern, providing enriched antioxidant vegetable foods. Also, it can be concluded that the amount and quality of diet in the long-lived elderly are responsible for the Korean traditional family system.
- 308 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Food Habit and Seasonal Difference of Nutrient Intake of Adult Working Women
- Hwa Jae Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(4):501-512. Published online August 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To assess the food habits and the seasonal differnces of nutrient intakes and diet qualities of adult working women aged 30 - 49y in Busan, dietary survey was conducted in summer and in winter by a questionnaire and two-day food record. Anthropometric assessment was also investigated in two seasons. 91.8% of those skipped breakfast in the main. 44.3% had irregular meals. The mean daily energy intake was 1725.8 kcal with 63.3% of energy intake being supplied by carbohydrates, 14.7% by protein, 22.3% by fat in summer and 1598.4 kcal with 62.1% of energy intake being supplied by carbohydrates, 15.6% by protein, 22.1% by fat in winter. Over 70% of iron intake came from plant origin in two seasons. The mean intakes of energy, calcium, iron and vitamin A in summer and energy, calcium, iron, vitamin A and vitamin B2 in winter were below Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for Koreans. As well as insufficiency in iron, the bioavailability of iron is considered to have been low because most of iron intake came from plant origin in two seasons. For calcium and iron in summer and calcium, iron, vitamin A and vitamin B2 in winter, proportions of subjects with intake levels less than 75% of RDA were over 40% in summer and over 50% in winter, respectively. The nutrient adequacy ratios (NAR) were below 0.75 for calcium and iron in summer and calcium, iron, vitamin A and vitamin B2 in winter. NARs of iron (p < 0.05), vitamin A (p < 0.01) and vitamin B2 (p < 0.001) in winter were significantly lower than those in summer. The mean adequacy ratios (MAR), an index of overall dietary quality were 0.85 in summer and 0.80 in winter. The MAR in winter was significantly lower than that in summer (p < 0.05). The indexes of nutritional quality (INQ) were below 1 for calcium and iron in summer and calcium, iron, vitamin A and vitamin B2 in winter. The intake (p < 0.05) and NAR (p < 0.05) of vitamin B2 showed positive significant correlations with height in winter. In conclusion, nutrient intake and diet quality of adult working women were different between the summer and the winter. So nutritional education programs for summer and winter are needed for adult working women.
- 343 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Investigation of Factors Influencing Career Decision-Making of Students in Foodservice Management and Culinary Arts Programs
- Kyung Eun Lee, Tae Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(3):311-318. Published online June 30, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purposes of the study were to identify important attributes in foodservice management and culinary arts students' career decision-making and to investigate factors determining their preferred employment fields. A questionnaire that consisted of preferred employment fields, importance rating of 19 attributes related to job choices, and demographic information was developed based on a review of literature. A total of 319 students enrolled in food and nutrition, foodservice management, and culinary arts programs of eight 2-year colleges and 4-year universities in Seoul and Kyunggi Province participated in the survey. Data were analyzed using SPSS Win (version 10.0) with descriptive statistics, chisquare analysis, one-way analysis of variance, factor analysis, and discriminant analysis. Attributes of the highest importance scores included fringe benefits, wages and promotion opportunities, working environments, professional development opportunities, and organizational culture. The students who preferred non-commercial foodservice as a career choice depended more on "word-of-mouth from faculty" than those who preferred other fields (F = 3.094, p < .05) and rated importance of "participation in job fairs" higher than those who selected hotel food and beverage (F = 5.048, p < .01). A factor analysis of the 19 attributes resulted in five factors:job/compensation policy, impersonal communication, company image, word-of-mouth, and personal experience. The five factors explained 67% of the total variance. A discriminant analysis revealed that students who perceived "impersonal communication" and "word-of-mouth" more important were likely to prefer non-commercial foodservice as a career choice. The results would be used by university faculty in advising graduating students on career selection and by recruiters in developing effective and attractive recruiting programs.
- 317 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Nutritional Status of the Nonagenarian Population in Longevity Belt in Korea
- Mee Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(3):290-302. Published online June 30, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The nutrients intake and health-related habits of nonagenarian subjects in Korean representative longevity belts of Damyang, Gokseong, Kurye, Sunchang were evaluated for the purpose of providing the information on the desirable food selection and dietary pattern of elderly population. A survey was conducted with 91 subjects (26 males and 65 females) and their food intakes were measured by the combination of one meal weighing and 24-hr recall, and their general background information was collected by visit. The mean age of the subjects was 93.6 +/- 2.2 (male) and 97.6+/- 4.6 (female). The average smoking rate was 20.9%; the rate of regular drinking was 26.4%. The average energy intake was 1,284.9 kcal comprising 77.1% of RDA for elder people over 75. The energy ratio of carbohydrate, protein and fat were 66.5 :18.2 :15.3. The average intake of protein, calcium, iron and zinc were 107.4%, 59.9%, 106.3% and 60% of RDA respectively. The lower intake of vitamins as low as 70% was found except vitamin B6 and niacin. The majority of the subjects consumed rice as staple diet and mostly consumed white plain rice rather than mixed grain rice. The animal and plant food intakes were 88.4 :11.6 in males and those of females were 83.0 :17.0 showing a tendency of plant-based meals. Nutrients that showed NAR over 0.7 were protein, iron, vitamin B6, niacin and phosphate, but those with INQ over 1. Nutrient with INQ below 0.7 was only vitamin E. Even though their nutritional quantity did not appear to be enough, but their nutritional quality was relatively high. The adding dairy products, nuts and fruits for the purpose of proving sufficient vitamin and minerals can achieve the optimal nutritional intake patterns. Further research on RDA of this age population should be followed.
- 331 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Minimal Weight and Body Fat Percentage in Relation to the Onset of Menarche in Korean Females
- Eun Sook Jeong, Jeong A Lee, Hyeon Sook Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(2):196-204. Published online April 30, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Menarche is a main indicator of sexual maturity which relates to a reproductive function. The onset of the menstrual cycle differs individually and is influenced by many variables such as socio-economic situation, race, genetics, climate, altitude, nutritional status, and physical growth. Among them physical growth has been known to be the most influencing factor, particularly when expressed as body fat designated by weight. This study intended to investigate the body composition of girls around the menarche period and to evaluate the minimal levels of weight and fat percentage needed for the onset of menarche. A total of 101 female subjects, aged 11 to 13 years, were recruited from the 5th and 6th grades of an elementary school, in Mokpo, Korea. The subjects were placed into one of two groups Pre-menarche and Post-menarche groups according to their experience with menarche. Thereafter, the subjects in the Post-group were placed into 4 subgroups based on the number of menstruations they experienced: Post-I (1 - 3 times), Post-II (4 - 6 times), Post-III (7 - 9 times), and Post-IV (> 10 times). The average age at the onset of menarche of the subjects in Post groups was 11.2 +/- 0.6 years. There were significant differences in the data of anthropometry and body composition between the Pre and Post groups, although the mean ages of both Pre and Post groups were the same. Weight, waist, hip and thigh girths, fat percentage, and lean body mass of the Post groups were significantly higher than those of the Pre group. Height was not significantly different between the groups. Weight was highly correlated with body fat mass (r = 0.92, p < 0.001), fat percentage (r = 0.85, p < 0.001), and body mass index (r = 0.91, p < 0.001). These results indicate that weight, compared with height, reflects body composition well and influences the onset of the menstrual cycle. It could also be suggested that the minimal weight and fat percentage needed for the onset of menarche in Korean females are 41 kg and 17% to 19%, respectively.
- 365 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrient Intake Quality Over 40 Year-Old People Living in Rural and Suburban Areas
- Ji Eun Lee, Younjhin Ahn, Juyoung Lee, Jung Ho Cha, Chan Park, Kuchan Kimm
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(4):491-500. Published online August 31, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - ABSTRACT To assess the quality of nutrient intake by area of Korean adults, a dietary survey with the 3-day record method was obtained from 324 subjects aged 40 years and older but younger than 70 (52.4 +/- 8.7) living in a rural area (Ansung) and suburban area of a middle-sized city (Ansan). The quality of nutrient intake was assessed by analyzing Nutrient Adequacy Ratio (NAR), Mean Adequacy Ratio (MAR) and Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ). The average daily mean energy intakes were 1,832 kcal for Ansung and 1,842 kcal for Ansan, respectively. Daily intakes of fat for Ansung and Ansan subjects were 40.9 and 40.3 g, and those for protein were 75.1 and 73.1 g, respectively. The overall calorie: protein: fat ratio (CPF) of energy intake was 63 : 17 : 20. Daily mean intakes of protein, fat, calcium, phosphorus, iron, potassium, carotene, sodium, thiamin, and niacin were significantly higher in Ansung residents than in Ansan subjects (p< .05). The average intakes of energy, calcium, vitamin A were lower than Recommend Dietary Allowance (RDA) in both areas. Note, over 30% of the study subjects had less than 75% of RDA of calcium, vitamin A and riboflavin. The MAR was higher in Ansung than Ansan residents (0.86 and 0.85, respectively; p< .05). INQs were over 1 for most nutrients except calcium (0.87), and that of calcium and phosphorus was each significantly higher in Ansung than Ansan subjects. Based on these results, nutrient intake quality of subjects aged 40 to 69 years living in the surveyed rural area is comparable to that of semi-industrialized suburban area in Korea. Dietary deficiency in all of calcium, vitamin A, and riboflavin, however, was a common problem for both rural and suburban residents.
- 347 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- The Relationship between the Diversity of Food Intake and Nutrient Intake among Korean College Students Participating in a Nutrition Education Class via the Internet
- Jeong Hee Lee, Kyung Ja Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(5):689-698. Published online October 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the diversity of food intake and nutrient intake among Korean college students participating in a nutrition education class via the internet. The subjects were 796 college students throughout South Korea (278 males, 518 females). A 3 days dietary recall survey was conducted and results were analyzed using the Computer-aided Nutritional Analysis Program. Dietary variety was assessed by DDS (dietary diversity score), MBS (meal balance score), and DVS (dietary variety score). Dietary quality was assessed by NAR (nutrient adequacy ratio), and MAR (mean adequacy ratio). As the DDS, MBS and DVS increased, the NAR and MAR improved. The subjects with a DDS of above 4 or a MBS of above 10 or a DVS of above 11 met two-thirds of the Korean recommended dietary allowance for most nutrients. The DDS, MBS and DVS correlated positively and significantly with the NAR and MAR. Associations between the NAR and high levels of DVS were more positive than those between the NAR and the DDS. Based on these results, the food intake of these subjects was not adequate. Specially, the dietary intake of calcium and iron were not adequate. Therefore, dietary guidelines should be made considering nutritional characteristics so as to improve the intake from all of the major food groups and provide a variety of foods in their diets.
- 348 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Measuring Service Quality Perception of University Faculty Members & Staffs Towards Faculty Foodservice Based on Lifestyle Segmentation
- Moon Kyung Park, Il Sun Yang, Dong Hoon Kim, Seo Young Shin, Hae Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(4):556-565. Published online August 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Market segmentation helps providers to find better marketing opportunities and allows foodservice managers to develop the right product for each target market. Therefore, this study, taking university faculty and staff as subject, is intended to diagnose the relative value of service quality attribute, on the basis service quality scenario of faculty foodservice; to suggest price for improving customer loyalty in market segments. A questionnaire was developed ar d mailed to 600 Yonsei university faculty and staffs. A total of 385 questionnaires were usable; resulting in a 58.7% of faculty and a 69.7% of staff response rate, respectively. Statistical data analysis was completed using the SAS/Win 6.12 for descriptive Analysis, ANOVA, principal factor analysis, cluster analysis, reliability test and discriminant analysis. The results of the study are as below. Eighteen questions were selected for measuring respondents' lifestyle by AIO method and the seven lifestyle factors derived from factor analysis and aggregated distinct 4 clusters. Service quality attributes of the scenario were determined with 'food quality', 'menu variety', 'atmosphere', 'fast service', and 'clean and sanitation'. 'Food quality', 'menu variety', 'atmosphere', 'fast service', and 'clean and sanitation', in decreasing order, were identified as improving customer loyalty. However, most faculty and staffs were satisfied with the present meal price. The result of this study indicates that the relative value of service quality was differed significantly among the various market segments. 'Food quality', 'menu variety', and 'atmosphere' were determined as major service quality attributes. Thus, customer loyalty could be increased by improving food taste and quality, atmosphere, and service delivery.
- 264 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- An Assessment of Dietary Fiber Intake in Preschool Children in Busan
- Hwa Jae Lim, Jung In Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(2):167-176. Published online April 30, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To assess the dietary fiber intake of preschool children in Busan and to evaluate the relationship between of the intake of dietary fiber and nutrient intake. Nutrient intake using 24 hour recall, and total dietary fiber (TDF) intake based on tables of TDF of common Korean floods developed by the modified Prosky Method, were estimated for 176 preschool children. The mean daily intakes of TDF, and TDF after adjusting energy intake, were 10.20 g and 7.69 g/1,000 kcal, respectively. The mean daily intakes of TDF for children aged 1-3 and 4-6 years were 9.20 g and 11.08 g, respectively. The range of TDF intake was 1.86 to 22.16 g. The major sources of TDF were cereals (31.0%), vegetables (18.9%) and fruits (11.9%). The TDF intake showed positive correlations with nutrient adequacy ratios (NAR) of iron and Vitamin B1, (p<0.05, p<0.05). The TDF intake per 1,000 kcal showed negative correlations with the NARs of protein, calcium, phosphate, iron, Vitamin A, vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, and niacin (p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.05, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001) and with the mean adequacy ratio (MAR, p<0.001). When children were stratified into quartiles (Q1-Q4) on the basis of their fiber intake per 1,000 kcal, their NARs for calcium, phosphate, iron, Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2 and niacin (p<0.05, p<0.05, p<0.001, p<0.05, p<0.05, p<0.001, p<0.001), and their U? (p<0.001) were significantly lower in the children with higher fiber intake per 1,000 kcal (the upper quartile). The NARs fur calcium (0.63), iron (0.60), Vitamin A (0.66), Vitamin B2 (0.74), niacin (0.64), Vitamin C (0.65) and the MAR (0.74) were lower than 0.75 in the children with fiber intakes of more than 9.25 g per 1,000 local (0,), the highest fiber intake per 1,000 kcal. Based on these results, the mean TDF intake of children was higher than the 'age (yr)+5g', the minimum recommended level for American children. Meals with a fiber intake of more than 9.25 g per 1,000 local (Q4) could cause a decreased nutritional status for minerals and vitamins. The result of this study could contribute to the establishment of Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) for dietary fiber for Korean Preschool children.
- 289 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Assessment of Dietary Intake of Preschool Children in Busan : Assessment Based on Food Group Intake
- Hwa Jae Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(1):3-15. Published online February 28, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To assess diet quality by food group intake and to investigate the interrelationship of age, dietary diversity score(DDS), dietary variety score(DVS), dietary frequency score(DFS), food group intake and nutrient intake with food group intake, a dietary survey was conducted with 176 preschool children aged 1 to 6 in Busan using a 24-hr recall method. Food group intake was assessed by food number consumed and intake frequency by six food groups(grain, meat, vegetable, fruit, dairy, sweets group). The mean food numbers consumed and intake frequencies by six feed group were 3.1 and 4.0 in the grain group, 3.6 and 4.0 in the meat group, 3.5 and 4.1 in the vegetable group, 1.0 and 1.1 in the fruit group, 1.3 and 1.5 in the dairy group, 1.4 and 1.4 in the sweets group respectively. As age increased, the intake frequency of the grain group(p<0.05) increased but that of the dairy group(p<0.05) decreased significantly. The DVS and DFS didn't show significant correlations with intake frequency of the dairy group. The grain group intake had significant positive correlations with intakes of the meat, vegetable, and fruit groups. The vegetable group intake had signigicant positive correlations with intakes of the grain and meat groups. The dairy group intake had significant positive correlation with sweets group intake but negative correlations with intakes of the grain and vegetable groups. As the intake frequency of the meat group increased, the NAR(nutrient adequacy ratios) of all nutrients and NAR(mean adequacy ratio) increased significantly. NARs of provein iron, vitamin B1, niacin had the highest correlation with the meat group intake and those of protein, calcium, phosphorous, and vitamin B2 had the highest correlation with the dairy group intake. NARs of vitamin A and vitamin C had the highest correlation with intake of the vegetable and fruit groups respectively. Children with food number consumed and intake frequency of above 6 and 4 in the grain group or above 6 and 6 in the meat group or above 4 and 8 on the v......
- 309 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Zinc Status and Taste Acuity of Old and Young Women
- Jin Sook Yoon, Junghyun Lee, Phil Sook Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2000;5(3):484-492. Published online September 30, 2000
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In an attempt to figure out the relationship between zinc status and taste acuity of old and young women, dietary zinc intake, urinary zinc excretion, and taste acuity were determined for 118 women. Zinc intake was measured by 2-day food records and food frequency method. Urinary zinc excretion was measured from urine samples collected for twenty four hours. Body fat, lean body mass (LBM), and total body water were measured by bio-impedence. Average dietary zinc intake by food record was 4.15+/-1.33mg (=35% if Korean RDA) for the old women and 5.41+/-2.76mg (=25% of RDA) for young women. When zinc intake was measured by a frequency method, the average intakes of the old and young women were 3.5+/-1.7mg 4.5+/-1.9mg, respectively. It appears that dietary zinc intake of young women was significantly higher than that of the old women. Average urinary zinc excretion of the subjects was 0.27+/-0.16mg in the elderly and 0.24+/-0.13mg in young women, which indicated a marginal zinc status. However, zinc status was not significantly different between old and young women. Correlation analysis indicated that zinc intake and urinary zinc excretion were positively related to BMI and LBM in young women. The old women (m=49) showed significantly higher taste detection thresholds than young subjects (n=47) for both sweet and salty tastes. Recognition thresholds for sodium chloride and sucrose were not significantly different between old and young women. The lower the taste thresholds for salty taste, the higher the average dietary zinc intake. However, taste perception concentration was not related to the urinary zinc excretion level.
- 313 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of Dietary Factors of Chronic Disease Using a Neural Network
- Sim Yeol Lee, Hee Young Paik, Song Min Yoo
- Korean J Community Nutr 1999;4(3):421-430. Published online September 30, 1999
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A neural network system was applied in order to analyze the nutritional and other factors influencing chronic diseases. Five different nutrition evaluation methods including SD Score, %RDA, NAR INQ and %RDA-SD Score were utilized to facilitate nutrient data for the system. Observing top three chronic disease prediction ratio, WHR using SD Score was the most frequently quoted factor revealing the highest predication rate as 62.0%. Other high prediction rates using other data processing methods are as follows. Prediction rate with %RDA, NAR, INQ and %RDA-SD Score were 58.5%(diabetes), 53.5%(hyperlipidemia), 51.6%(diabetes), and 58.0%(diabetes)respectively. Higher prediction rate was observed using either NAR or INQ for obesity as 51.7% and 50.9% compared to the previous result using SD Score. After reviewing appearance rate for all chronic disease and for various data processing method used, it was found that iron and vitamin C were the most frequently cited factors resulting in high prediction rate.
- 269 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Balance of Iron and Zinc in Korean Children
- In Seon Choi, Kyung Hwa Lee, Seung Ho Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 1998;3(1):12-20. Published online February 28, 1998
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, the food intake, feces and urine of 14 primary school age boys and girls were collected and intake and excretion of iron and zinc were measured. The boys and girls were 8-12 years old and measurement continued for four weeks during which they maintained their normal living pattern. Each boy's and girl's daily intake and excretion of iron and zinc were measured and apparent digestibility and balance were also calculated. The results are as follows. Mean daily intake of iron was 14.9+/-0.6 mg for the boys and 12.4+/-0.5 mg for the girls. Mean daily intake of zinc was 11.8+/-1.2 mg for the boys and 11.5+/-0.4 mg for the girls. Mean daily fecal loss and apparent digestibility of iron was 6.1+/-0.3 mg and 58.8+/-2.0% for the boys and 6.8+/-0.1 mg and 44.1+/-2.0% for the girls. Mean daily fecal loss and apparent digestibility of zinc was 9.3+/-0.2 mg and 14.4+/-5.1% for the boys and 9.7+/-0.4 mg and 14.3+/-4.3% for the girls. Mean daily urinary loss of iron was 1.1+/-0.1 mg and showed the positive balance of 7.86+/-0.6 mg for the boys and 0.5+/-0.1 mg and showed the positive balance of 5.14+/-0.4 mg for the girls. Mean daily urinary loss of zinc was 0.5+/-0.1 mg and showed the positive balance of 1.03+/-0.6 mg for the girls.
- 442 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Intake/Balanc of Dietary Protein in Korean College Women
- Seung Ho Oh, In Seon Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(4):523-529. Published online October 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to obtain accurate data on the intake, digestibility and nitrogen balance of protein in Korean college women. Subjects were 8 female college students, aged from 21 to 23, and maintained their menu and life patterns regular during a 4-week study. The same amount of diet that the subjects had consumed, and feces and urine were collected and measured to extract their nitrogen content by Kjeldahl method. From this data, apparent digestibility and the body nitrogen balance were estimated by determing daily protein intake and excretion. The daily protein intake was 56.9+/-1.4g and daily fecal protein loss was 6.3+/-0.2g. The apparent digestibility of protein was 89.6+/-0.7%. The daily nitrogen intake measured by Kjeldahl method was 9.43+/-0.2g. The urinary nitrogen excretion was 7.64+/-0.23g and fecal nitrogen excretion was 1.02+/-0.03g. The nitrogen balance indicated a positive balance of 0.45+/-0.18g.
- 338 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Zine Status of Adult Female in the Taegu Region as Assessed by Dietary Intake and Urinary Excretion
- Hyun Mee Oh, Jin Sook Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(1):52-62. Published online February 28, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was intended to examine the zinc status of free-living adult women living in the Taegu region. Zine intake of 102 female subjects was measured by food frequency method for 3 consecutive days. Urinary zine was assessed from urine samples collected fir twenty four hours. Average dietary zinc intake of adult female subjects using food record was 5.9+/-1.8 mg which was 49% of Korean RDA. When zine intake by frequency method was higher than by food record. Average urinary zine intake by frequency method was higher than that by food record. Thus, it appeared that zinc intake by frequency method was higher than that by food record. Average urinary zinc excretion of 102 adult female subjects was 0.28+/-0.16 mg, which belonged to marginal zinc deficiency range. Fifty nine of 102 subjects showed marginal zinc deficiency as assessed by urinary zinc excretion. If we compare the zinc status of adult female subjects by age group, zinc intake in the 50s was significantly higher than any other age groups. However, there were no significant differences in zinc status according to BMI groups and BMI groups. Significant correlations were found between zinc intake and energy, protein, carbohydrate and fat intake. Based on dietary zinc intake and urinary zinc, we concluded that zinc status of adult female living in the Taegu region is marginally deficient.
- 323 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



