Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):173-188. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to analyze the regional differences in dietary protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome.
Methods
Study participants were 1,721 older adults aged 65 and over who participated in 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Using 24-hour recall dietary intake data, protein intake and their food sources were examined. The association between protein intake and metabolic syndrome, obesity, and abdominal obesity were analyzed by multiple logistic regression.
Results
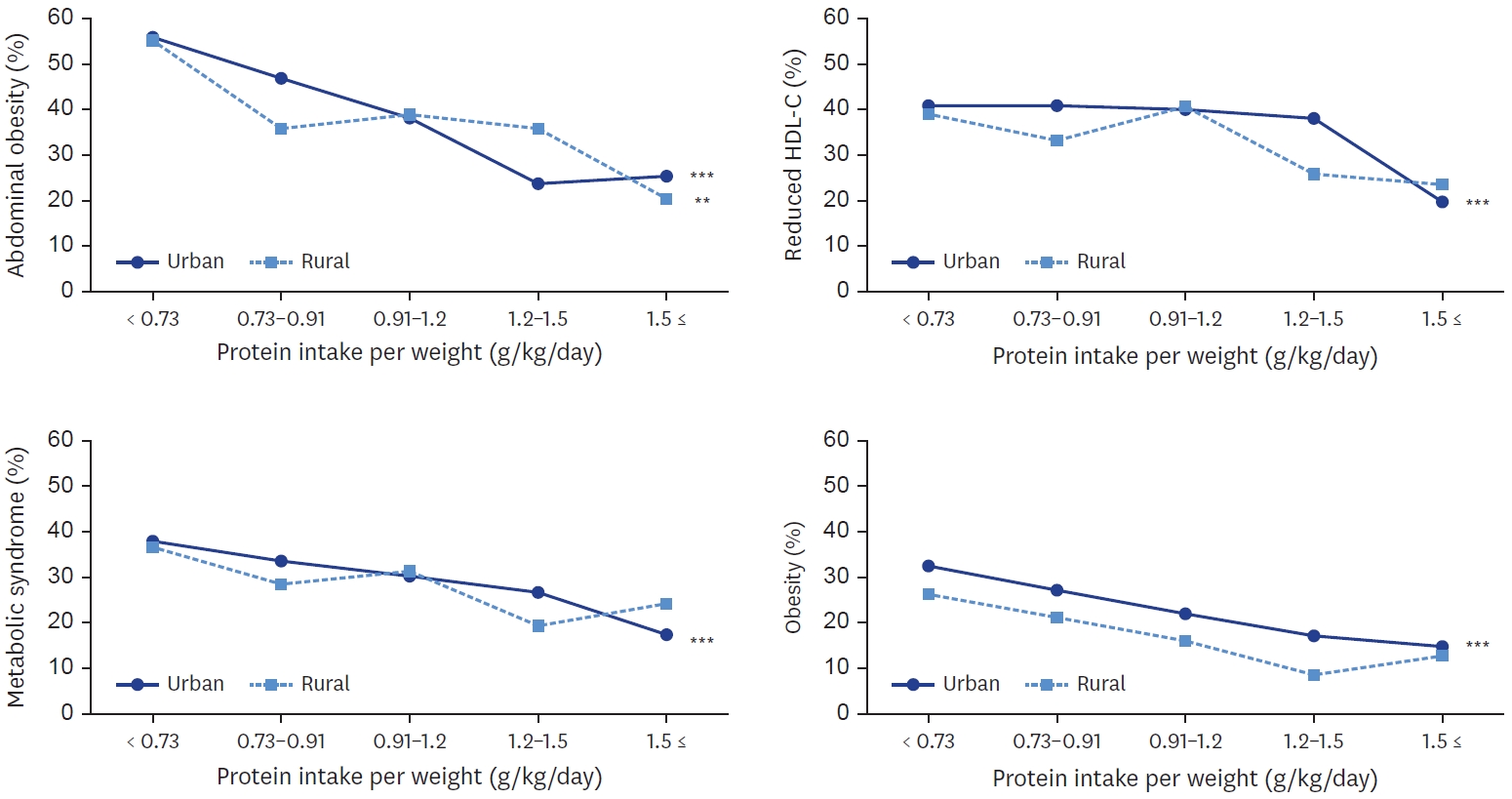
Total protein and animal protein intakes were higher in urban area (60.0 g, 24.4 g, respectively) than in rural area (54.6 g, 19.6 g, respectively). With increase of protein intake level, animal to total protein proportion was increased in both areas. Total protein and plant protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity, abdominal obesity in both areas. Animal protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity in both areas, and with abdominal obesity only in urban area. In urban area, plant protein intake was also negatively associated with the risks of metabolic syndrome, elevated triglyceride, and reduced high density lipoprotein-cholesterol. In urban area, the risk of metabolic syndrome was decreased when their protein intake was more than 0.91 g/kg and was lowest when their protein intake was more than 1.5 g/kg (P for trend < 0.001).
Conclusions
Korean older adults showed inadequate protein intake and those in rural area showed lower animal protein intake than in urban area. The risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome was decreased with the increase of protein intake level. These findings may help develop effective nutrition support strategy for older adults to reduce regional health disparity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
Yea-Chan Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Soyoung Jeon, Yae-Ji Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2026; 50(1): 178. CrossRef - The association between dietary protein intake and metabolic syndrome: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Dorsa Ghazvineh, Ali Hosseinpour, Vahid Basirat, Elnaz Daneshzad
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between total, animal-based, and plant-based protein intake and cognitive decline in older adults
Maud Peperkamp, Margreet R. Olthof, Marjolein Visser, Hanneke A. H. Wijnhoven
European Journal of Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
- 10,059 View
- 107 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Changes in nutritional status of Korean older adults during COVID-19 Pandemic by household income and demographic factors -using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(2019-2020): a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):302-316. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to identify changes in the nutritional status of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic according to household income and demographic characteristics.
Methods
Study participants were 2,408 adults aged 65 and over who participated in the 2019–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). To examine changes in nutrient intake levels resulting from COVID-19, data of 2019 and of 2020 were compared. Study participants were divided into three groups based on household income level to compare these changes. The changes were compared according to household income level, age group, and household type.
Results
Percentages of recommended intakes for energy, protein, and most micronutrients were the lowest for the low-income group of both males and females in 2020. The Mean Adequacy Ratio (MAR) score was the lowest for the low-income group in both years. When comparing nutrient density for 2019 and 2020 by income group, the male low-income group experienced a decrease in nutrient densities of vitamin A, thiamine, calcium, and iron. For the same group, a decreased percentage for energy intake from protein was noted. Fruit intake was lowest in the low-income group for both males and females. Low-income males had the lowest intake levels for meat, fish, eggs, and legumes in both 2019 and 2020 and the lowest milk and milk product intake levels in 2020. Older adults living alone or single older adults with children had lower MAR scores than those living with a spouse. Older adults living alone experienced decreases in energy and thiamine and iron intake levels in 2020 compared to their intake levels in 2019.
Conclusions
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, nutrition intake levels worsened for older adult males in the low-income group and older adults living alone. This finding shows the need for a more systematic nutritional support strategy for the vulnerable older adults population in national disaster situations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
Yong-Seok Kwon, Dasol Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1973. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Comparison of nutrient intake and Korean Healthy Eating Index among the elderly in rural areas pre- and post- COVID-19 pandemic: the 2018–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Sangyeon Kim, Hye-Sook Hong, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(5): 496. CrossRef
- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
- 2,349 View
- 43 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):422-434. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.422
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With an increase in the population of the elderly in Korea, their nutritional status has become a cause for concern. This study was designed to compare the nutritional intake and health status of the Korean elderly according to their body mass index.
Methods
The subjects were 3,274 elderly people aged 65 and above who had participated in the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The subjects were divided into four groups: underweight, normal, overweight, and obese, based on their BMI. The general characteristics, daily energy, and nutrient intakes, nutrient intakes compared to the recommended nutrient intake, percentage of participants whose nutrient intake was lower than the estimated average requirement (EAR), index of nutrient quality, the mean adequacy ratio (MAR), intakes by food group, and health status of the four groups were compared.
Results
Underweight elderly people showed lower energy, lipids, dietary fiber, vitamin C, riboflavin, niacin, phosphorus, sodium, and potassium intake and MAR score (P < 0.001) compared to the normal or obese elderly. The mean protein, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin C, phosphorus, and iron intake of the underweight elderly was lower than the EAR (P < 0.05). Underweight elderly people also had a lower intake of vegetables and fats, oil and sweets food groups than the other groups (P < 0.001). The prevalence of diabetes and dyslipidemia was higher in the obese group, but the percentage of anemia was higher in the underweight group.
Conclusions
Underweight elderly people were vulnerable to undernutrition and were at a higher risk of anemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the Association Between Older Adults’ Body Mass Index and Their Fall Experience, Chronic Diseases, and Exercise Frequency: Evidence from Korea
Daekeun Kwon, Su-Yeon Roh, Jeonga Kwon
Medicina.2025; 61(9): 1622. CrossRef - Effect of physical activity on free fatty acids, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in obese older women
Woo-Hyeon Son, Min-Seong Ha, Tae-Jin Park
Physical Activity and Nutrition.2024; 28(2): 1. CrossRef - Determinants of Length of Stay for Medical Inpatients Using Survival Analysis
Jaekyeong Kim, Haegak Chang, Seiyoung Ryu, Ilyoung Choi, Angela Eunyoung Kwon, Haeyong Ji
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2024; 21(11): 1424. CrossRef - The Relationship of Pork Meat Consumption with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Biomarkers of Health Status in Korean Older Adults
Ah-Jin Jung, Anshul Sharma, Mei Chung, Taylor Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4188. CrossRef
- Exploring the Association Between Older Adults’ Body Mass Index and Their Fall Experience, Chronic Diseases, and Exercise Frequency: Evidence from Korea
- 3,334 View
- 50 Download
- 4 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Children's Food Intake and Nutrition Levels, and Obesity by Maternal Employment: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2015
- Geunyeong Kang, Yoonna Lee, Mihyang UM, Seunghee Kye
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):331-342. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.331
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examines the intake of food and nutrients of children according to the employment and working hours of their mothers.
METHODS
The married women in the source data from the 6th National Health and Nutrition Survey were classified into full-time working mothers, part-time working mothers and housewives according to the working type and the data on their children from 3 to 18 years old were analyzed using SAS 9.4.
RESULTS
The group from 3 to 5 years old was the smallest group with 682 children (20.2%), followed by the group from 6 to 11 years with 1,345 children (39.8%) and the group from 12 to 18 years old with 1,355 children (40.1%). The lowest rates for having no breakfast and dinner were observed in the group with housewives (p<0.05). The calcium and phosphorous intakes were the highest in the group with housewives at 61.9% and 126.8%, respectively, and the lowest in the group with full-time working mothers at 54.7% and 115.3%, respectively (p<0.05). The group with full-time working mothers had the highest rate in the calcium and iron intake less than the dietary reference intake at 74.9% and 30.0%, respectively. It indicated that the group with full-time working mothers did not have sufficient nutrients as compared to the other two groups. Moreover, the group with the part-time working mothers showed the high vitamin A intake ratio of 41.4% (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
This study found evidence of a negative association between mother's employment status and children's diet quality. The employment and economic activity of married women will continuously increase in the future. Therefore, a national nutrition policy is required to provide quality nutrition care for children in the households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,238 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Study of the Coverage of Nutrition Labeling System on the Nutrient Intake of Koreans - using the 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
- Ji Eun Park, Haeng Shin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):116-127. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.116
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to examine the coverage of the current mandatory nutrition labeling system on the nutrient intake of Koreans.
METHODS
KNHANES dietary intake data (2013) of 7,242 subjects were used in the analysis. KNHANES dietary intake data were collected by a 24-hour recall method by trained dietitians. For analysis, all food items consumed by the subjects were classified into two groups (foods with mandatory labeling and other foods). In the next step, all food items were reclassified into four groups according to the food type and nutrition labeling regulations: raw material food, processed food of raw material characteristics, processed foods without mandatory labeling, and processed foods with mandatory labeling. The intake of energy and five nutrients (carbohydrate, protein, fat, saturated fat, and sodium) of subjects from each food group were analyzed to determine the coverage of the mandatory nutrition labeling system among the total nutrient intake of Koreans.
RESULTS
The average intake of foods with mandatory labeling were 384g/day, which was approximately one quarter of the total daily food intake (1,544 g/day). The proportion of energy and five nutrients intake from foods with mandatory labeling was 18.1%~47.4%. The average food intake from the 4 food groups were 745 g/day (48.3%) for the raw food materials, 54 g/day (3.5%) for the processed food of raw material characteristics, 391 g/day (25.3%) for the processed foods without mandatory labeling, and 354 g/day (22.9%) for the processed foods with mandatory labeling.
CONCLUSIONS
Although nutrition labeling is a useful tool for providing nutritional information to consumers, the coverage of current mandatory nutrition labeling system on daily nutrient intake of the Korean population is not high. To encourage informed choices and improve healthy eating habits of the Korean population, the nutrition labeling system should be expanded to include more food items and foodservice menus.
- 1,161 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Study on Energy and Nutrient Intake and Food Preference of the Elderly in Care Facilities
- Jong Sook Kwon, Seung Hee Lee, Kang Min Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(2):200-217. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.2.200
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to assess energy and nutritional intake and investigate the preference for food and cooking methods of the residents in elderly care facilities.
METHODS
Data were collected from 72 residents (10 males and 62 females) aged ≥ 70 years in elderly care facilities using questionnaires, food photographs for estimating dietary intake and records for daily physical activity.
RESULTS
Average age of the study participants was 85.0 years and 41, 36 and 8 had dementia, hypertension and diabetes mellitus, respectively. 15%, 65% and 19% of subjects were physically mobile, enervated, and immobile, respectively. Daily energy intake was 1360.2 kcal in men and 1378.0 kcal in women, which were 68.0% and 86.1% of the estimated energy requirement (EER) of dietary reference intake for Koreans (KDRI) for ≥ 75 year old individuals, respectively. Estimated energy expenditure (EEE) of subjects calculated using formula from KDRI was 1361.9 kcal and EER calculated using estimated daily physical activity (EDPA) was 1232.9 kcal. Energy intake and EEE from KDRI were higher than EER from EDPA. Dietary intake of dietary fiber, calcium, potassium, zinc, vitamin B2, niacin, vitamin C were lower, and protein, phosphorous, iron, sodium, vitamin A, vitamin B1, vitamin B6, vitamin E were higher than the corresponding ones of KDRI. Subjects liked meats, fishes and shellfish, and fruits, while subjects disliked milk, seaweeds and salted fish and salted vegetables. Cooked rice, soybean paste soup, beef, cooked sliced radish strip, and yogurt were favorite foods, with steam being a favorite cooking method. Subjects considered nutrition as the most important factor for improving food service quality.
CONCLUSIONS
Results of this study could be utilized for improving food-service for the residents in elderly care facilities, and provide a basis for setting reference intake of energy and nutrients of the elderly having very low activity levels. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
Seo Young Choi, Hyun joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 286. CrossRef - Snack Provision Practice in Long-Term Care Hospitals and Facilities in Korea
Dayeong Yeo, Hae Jin Kang, Hyejin Ahn, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(2): 108. CrossRef - A Comparison of Status of Nutrition Management in Long-Term Care Facilities With and Without Dietitian
Jin Hee Kwon, Rah Il Hwang, Jaehyeon Ryu
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Classification of Texture-Modified Korean Soups with a Thickener under IDDSI Criteria
Kui-Jeong Choi, Hyun-Jung Lee, Weon-Sun Shin
Journal of the Korean Dysphagia Society.2022; 12(2): 123. CrossRef - Current status of foodservice nutrition management and effects of welfare facility support for the elderly in Cheongju City
Joo-Eun Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(4): 527. CrossRef - Comparison of Food Service Provision by Food Service Operational Types for Residential Facilities
Jin Hee Kwon, Rah Il Hwang, Hyeon Jin Jeong, Hye Min Jang
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(4): 258. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Care Workers at Long-term Care Facilities
Geun-Young Kim, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 13. CrossRef - Dietary quality of lunches in senior leisure service facilities in South Korea: analysis of data from the 2013–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Daeun Choi, Youngmi Lee, Haeryun Park, Kyunghee Song, Jinah Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(2): 266. CrossRef - Evaluation of the dietary quality and nutritional status of elderly people using the Nutrition Quotient for Elderly (NQ-E) in Seoul
Sun-Wook Ham, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 68. CrossRef - Status of health and nutritional intake of the elderly in long-term care facilities: focus on Gwangju Metropolitan City
Gyusang Han, Eunju Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 27. CrossRef - Study on the Nutrient Intake and Dietary Quality of Elderly Residents on Various Meal Types in Long-Term Care Facility
Hee-Sook Lim, Eun Bi Oh, Yoo Kyoung Park, Hae-Yun Chung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(2): 172. CrossRef - Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 502. CrossRef - Nutritional status of Korean elderly with dementia in a long-term care facility in Hongseong
Ji-Yeon Lee, Yeong-Soon Hyun, Hee-Seon Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2019; 13(1): 32. CrossRef - Food and nutrient intake status of Korean elderly by perceived anxiety and depressive condition: data from Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 ~ 2015
Da-Mee Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(1): 58. CrossRef - Analysis of Food Preference, Recognition and Experience of Elderly Foods among Elderly People
Mi Young Kim, Yoo Na Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 971. CrossRef
- A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
- 1,514 View
- 5 Download
- 15 Crossref

- [English]
- The Development and Validation of Eating Behavior Test Form for Infants and Young Children
- Youngshin Han, Su An Kim, Yoonna Lee, Jeongmee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(1):1-10. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to develop and validate Eating Behaviors Test form (EBT) for infants and young children, including eating behaviors of their parents and parental feeding practices.
METHODS
Draft version of EBT form was developed after a pretest on 83 mothers. It was consisted of 42 questions including 3 components; eating behavior of children, eating behavior of parents, and parental feeding practices. Using these questionnaires, the first survey was conducted on 320 infants and children, 1 to 6 year old, for exploratory factor analysis, and the second survey was collected on 731 infants and children for confirmatory factor analysis.
RESULTS
Exploratory factor analysis on 42 questions of EBT form resulted in 3 factor model for children's eating behavior, 3 factor model for parents' eating behavior, and 1 factor model for parental feeding practices. Three factors for children's eating behavior could be explained as follows; factor 1, pickiness (reliability alpha=0.89; explanation of variance=27.79), factor 2, over activity (alpha=0.80, explanation of variance=16.51), and factor 3, irregularity (alpha=0.59, explanation of variance=10.01). Three factors for mother's eating behavior could be explained as follows; factor 1,irregularities (alpha=0.73, explanation of variance=21.73), factor 2, pickiness (alpha=0.65, explanation of variance= 20.16), and factor 3, permissiveness (alpha=0.60, explanation of variance=19.13). Confirmatory factor analysis confirmed an acceptance fit for these models. Internal consistencies for these factors were above 0.6.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results indicated that EBT form is a valid tool to measure comprehensive eating and feeding behaviors for infants and young children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on the factors affecting the omnivorous diet of adolescents and the typology: focusing on inherited and acquired cultural capital
Hyewon Lee, Rando Kim
Journal of Families and Better Life.2024; 42(1): 81. CrossRef - Assessment of Dietary Characteristics and Eating Behavior in Children Using a Dietary Screening Test
Sun-Im Won
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 557. CrossRef - Associations between maternal comprehensive feeding practices and dietary practices in preschool children
Myeongil Cho, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 141. CrossRef - The effect of the mother's modeling and feeding practices on the eating behavior of young children
Hyeonmi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 296. CrossRef - The influence of parental eating behaviors, child-feeding practices, and infants’ temperaments upon infants’ eating behaviors
Goh Woon Lim, Kyoung Min Shin
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2022; 65(9): 466. CrossRef - The status of food allergy and parental burden of preschoolers in Jeju area
Jeong Eun Oh, Eunyoung Kim, Yunkyoung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 664. CrossRef - MAMAS: Supporting Parent--Child Mealtime Interactions Using Automated Tracking and Speech Recognition
Eunkyung Jo, Hyeonseok Bang, Myeonghan Ryu, Eun Jee Sung, Sungmook Leem, Hwajung Hong
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction.2020; 4(CSCW1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of the types of eating behavior affecting the nutrition of preschool children: using the Dietary Behavior Test (DBT) and the Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
Hyeon Mi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 604. CrossRef - The Infant and Child Growth Assistance System Based on a Smartphone
Ki-Won Byun, Joon-Gyu Kang
Journal of the Korea Society of Computer and Information.2016; 21(8): 95. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Program Designed to Reduce Sugar Intake in Preschool Children
Ma-Young Yeom, Youn-Ok Cho
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(3): 179. CrossRef - The Development of Sugar Intake Reduction Test for Young Children
Nam-Hee Kim, Jee-Young Yeon, Mi-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(5): 818. CrossRef
- A study on the factors affecting the omnivorous diet of adolescents and the typology: focusing on inherited and acquired cultural capital
- 1,263 View
- 5 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Dietary Behaviors, Health-Related Lifestyle of Adult Visitors at Public Health Centers in Gyeonggi Urban Area
- Jong Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hyun Chang Seo, Yoonna Lee, Seunggeon Lim, Young Sug Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(6):611-625. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.6.611
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate dietary behaviors and health-related lifestyles of adult visitors at a public health center in Gyeonggi urban area. A survey using questionnaire was conducted with 949 visitors at Seongnam public health centers from June to August, 2012. The data from 905 respondents were analyzed by gender, consisting of 322 males and 583 females, and age group, consisting of 243 low-age group (LA), 312 middle-age group (MA), 350 high-age group (HA), aged 20 to 30 years, 31 to 50 years, and 51 to 69 years, respectively. Average Body Mass Index was 23.0, which increased with age, and education level was high in LA. 59.0 percent of the subjects had various diseases, and the incidence of hypertension was the highest, followed by allergy, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, joint rheumatism. Incidence rates of chronic disease increased with age, which were lower than those from 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Weekly drinking frequency rate and smoking rate decreased with age, and exercise performing rate was high at male and HA, which showed the same tendency as KNHANES. Female and HA showed more healthy dietary behaviors such as restricting salt, sugar, oily foods, foods containing food additives, calorie, caring for balanced diet, and referring to nutrition label. Subjects chose stress as the first factor, followed by diet, exercise, etc., among 13 suggested factors which strongly influence on human's life-span. In general, public health center visitors, especially female and HA, showed better dietary behaviors and health-related lifestyles compared with KNHANES.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 112. CrossRef - Factors associated with the dietary quality and nutrition status using the Nutrition Quotient for adults focusing on workers in the manufacturing industry
Ji Suk Yim, Young Ran Heo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(5): 488. CrossRef
- Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
- 1,137 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of Nutrition Education Program for Hypertension Based on Health Belief Model, Applying Focus Group Interview
- Seoyun Park, Jong Sook Kwon, Cho il Kim, Yoonna Lee, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(5):623-636. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.623
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Health Belief Model is a socio-psychological theory of decision making to individual health-related behaviors. This study was aimed to develop an effective education program for hypertension based on health belief model. The main factors of health belief model were investigated by focus group interview (FGI) with 23 hypertensive or prehypertensive subjects aged over fifty years. 'Perceived susceptibility' to hypertension was family history, neglect of health care, preference for salty food, broth of soup and stew. Lifelong medication, complications, and medical costs were reported as 'perceived severity' of hypertension. 'Perceived benefits' of hypertension management were decrease of medicinal dose, reduction of medical costs, and healthy eating habits of the family, while 'perceived barriers' were lack of palatability of low salt diet, convenience-oriented dietary habits, and limited choice of foods when eating out. Subjects mentioned TV health programs, public health center programs, and advice from doctors and family as 'cues to action' of hypertension management. These qualitative information provided basis for developing a nutrition education program for hypertension which could be implemented in the public health center. Eight week program was composed of understanding hypertension, risk factor management (eating habits, weight), low salt diet (principles, cooking), advanced management for healthy diet in 2 sessions, and summary. Each session was designed to alert the susceptibility and severity, to emphasize the benefits, and to reduce the barriers by providing dietary monitoring, practical advice, and action tips.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Educational Materials for Block Programming-Based Data Structures to Enhance Teacher Competence in Software Classes
Sook-Young Yoon, Hyun-Jong Choi, Seung-Hyun Kim
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(4): 743. CrossRef - Dietary habits and nutrient intake status of university students according to obesity risk based on body mass index and percent body fat
Chae Hong Lee, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 714. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
Ji Suk Yim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Consumption of Weight-control or Health Functional Foods, Dietary Habits, and Weight Perceptions According to the Body Mass Index of Adult Women in the Chungcheong Area
Gayoung Seong, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 81. CrossRef - Comparison of low-salt preference trends and regional variations between patients with major non-communicable diseases and the general population
Eun Young Choi, Young-Kwon Park, Minsu Ock, Masaki Mogi
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(10): e0276655. CrossRef - Comparison of the health and nutritional status of Korean elderly considering the household income level, using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 39. CrossRef - Effects of Gender and Age on Dietary Intake and Body Mass Index in Hypertensive Patients: Analysis of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination
Hyunju Dan, Jiyoung Kim, Oksoo Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4482. CrossRef - A study on the experience of mHealth based on health belief model: Focus group interview
Na Young Park, Jeong Hae Hwang, Yun-Kyoung Choi, Seong-Hi Park, Yeon Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(3): 97. CrossRef - Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
Mijin Jo, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Effect of a public health center-based nutrition education program for hypertension in women older than 50 years of age
Seoyun Park, Jong-Sook Kwon, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(3): 228. CrossRef - Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(4): 332. CrossRef - Status and Need Assessment on Nutrition & Dietary Life Education among Nutrition Teachers in Elementary, Middle and High Schools
Na Gyeong Oh, Su Jin Gwon, Kyung Won Kim, Cheong Min Sohn, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 152. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - Patient and Healthcare Provider Barriers to Hypertension Awareness, Treatment and Follow Up: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Qualitative and Quantitative Studies
Rasha Khatib, Jon-David Schwalm, Salim Yusuf, R. Brian Haynes, Martin McKee, Maheer Khan, Robby Nieuwlaat, Noel Christopher Barengo
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(1): e84238. CrossRef - Development of Nutrition Education Program for Consumers to Reduce Sodium Intake Applying the Social Cognitive Theory: Based on Focus Group Interviews
So-Hyun Ahn, Hye-Kyeong Kim, Kyung Min Kim, Jin-sook Yoon, Jong Sook Kwon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 342. CrossRef - Factors affecting Weight-Control Behavior Intention in Female College Students: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior
Eun Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(2): 195. CrossRef - Comparison of practice of dietary guidelines and health beliefs according to stage of weight loss behavior change among male workers
Su Jeong Song, HongSeok Ahn, Jinmo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(3): 276. CrossRef - A Study on the Health and Nutritional Characteristics according to Household Income and Obesity in Korean Adults Aged over 50 -Based on 2005 KNHANES-
So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son, Hye Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(4): 463. CrossRef - Estimation of Sodium Intake of Adult Female by 24-Hour Urine Analysis, Dietary Records and Dish Frequency Questionnaire (DFQ 55)
Eun-Kyung Shin, Hye-Jin Lee, Jung-Jeung Lee, Moon-Young Ann, Sook-Me Son, Yeon-Kyung Lee
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2010; 43(1): 79. CrossRef - Effects of Weight Control Program on Dietary Habits and Blood Composition in Obese Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Kyung Kim, Mi-Jeong Kim
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2010; 43(3): 273. CrossRef - Diet Quality Index-International Score is Correlated with Weight Loss in Female College Students on a Weight Management Program
Hee Kyung Yun, Hyesook Kim, Namsoo Chang
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2009; 42(5): 453. CrossRef
- Educational Materials for Block Programming-Based Data Structures to Enhance Teacher Competence in Software Classes
- 1,595 View
- 11 Download
- 21 Crossref

- [English]
- Influencing Factors on the Dietary supplements Consumption among Children in Korea
- Jeeyeon Lee, Dohee Kim, Yoonna Lee, Eunmi Koh, Youngsoo Jang, Hyeyoung Lee, Youngae Jang, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):740-750. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.740
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - With a recent increase in dietary supplements (DS) consumption among children in Korea, this study was performed to examine the influencing factors on children's DS consumption. A nationwide survey was conducted employing 3 representative samples of children for summer & fall of 2008 and spring of 2009 by stratified multistage sampling of 120 survey sites per season based on the 2005 census population. Approximately 30 households from each survey site were screened for residing children of 0-19 years and about 1,700 households remained as eligible samples per season. Trained dietitians visited households to perform face-to-face interview to children and/or parents regarding DS consumption including health functional foods (HFF), vitamins/minerals (V/M) supplements and other food supplements during 1 month prior to interview. Out of 5,328 children responded, 18.7% reported DS consumption. Consumption rate was higher in boys (19.9% vs. 17.3% in girls, P < 0.05) and youngsters (22.8% compared to 15.0% in adolescents, P < 0.001). Children from higher income family (P < 0.001), those living in apartments (P < 0.001), those residing in metropolitan area (P < 0.001), and those of mothers with higher education (P < 0.001) were more likely to take DS. Also, mother's employment status and occupation were significantly associated with children's DS consumption. The most popular DS was HFF (72.1%), which was consumed more in children of higher income family. It is revealed that socioeconomic factors affect children's DS consumption significantly. Also it is necessary to estimate children's V/M intake from DS and foods together especially because there are tolerable upper limits set for V/M for safety purposes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef - Use of vitamin and mineral supplements and related variables among university students in Seoul
Jung-Hwa Choi, Youjin Je
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(4): 352. CrossRef - The Status of Dietary Supplements Intake in Korean Preschool Children: Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010-2012
Dong Soo Kang, Kun Song Lee
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2014; 17(3): 178. CrossRef - A Survey on the Usage Patterns of Vitamin and Mineral Supplements as Over-The-Counter Drugs among Korean Adolescents
Ji Hye Han, Hyun Sook Lee, Sun Hyo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(4): 364. CrossRef - Dietary Supplements Use and Related Factors of Preschoolers in 3 Korean Cities
Hye Sil Kim, Hye Young Lee, Mi Kyung Kim
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2013; 16(2): 104. CrossRef
- A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
- 1,343 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Major Sources of Sodium Intake of the Korean Population at Prepared Dish Level: Based on the KNHANES 2008 & 2009
- Miyong Yon, Yoonna Lee, Dohee Kim, Jeeyeon Lee, Eunmi Koh, Eunjeong Nam, Hyehyung Shin, Baeg won Kang, Jong Wook Kim, Seok Heo, Hea young Cho, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(4):473-487. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.4.473
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We attempted to define the sources of sodium intake for the Korean population at prepared dish level to provide a basis for developing sustainable nutrition policies and feasible programs for sodium intake reduction. Dietary intake data from 2008 and 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey was used in the analysis for sodium intake sources. Sodium intake from individual dish consumed by each subject was calculated and used in delineating major sodium sources at dish and dish group level for sub-populations of different sex and age. Also, sodium intake was compared between eaters and non-eaters of some specific dish groups with considerable contribution to total sodium intake. The number of subjects included in the analysis was 18,022 and mean sodium intake was 4,600 mg/capita/day. Major sources of sodium intake at dish group level were in the following order: kimchi (1125 mg, 24.5%), noodles (572 mg, 12.4%), soups (488 mg, 10.6%), stews (399 mg, 8.7%), and cooked rice (284 mg, 6.2%). The magnitude of contribution to total sodium intake by soups and stews was different by age group. Sodium intake difference between eaters and non-eaters was much larger for kimchi group (2,343 mg for male, 1,452 mg for female) than for soups or stews. Interaction between consumption of aforementioned specific dish groups and age was highly significant (p < 0.0005) for both sexes. This study revealed an importance of having not only the control over sodium content of foods/dishes, but also the customized approach for different groups of population to accomplish an appreciable reduction in sodium intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploration of the relationship between gastric cancer and nutritional risk factors: insights from the Korea National Health Insurance Database
You Na Kim, Chi Young Kim
Frontiers in Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating food portion estimation accuracy with multi-angle photographs
In-Young Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 605. CrossRef - Mineral Intake and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Comparative Study Based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys in Korea and the United States
Jiwoo Kim, Inho Kim, Junhui Lee, Kyungwhan Jeon, Juseong Kang, Dongchan Lee, Sera Choi, HyunSoo Kim, Minkook Son
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2593. CrossRef - A traditional Korean fermented food, Gochujang exerts anti-hypertensive effects, regardless of its high salt content by regulating renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in SD rats
Jung Eun Park, Anna Han, Eun-Gyung Mun, Youn-Soo Cha
Heliyon.2024; 10(9): e30451. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and nutrient intake of the elderly with type 2 diabetes according to comorbidity burden: a cross-sectional study
Yejung Choi, Kyong Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 418. CrossRef - Exposure to Extreme Temperatures and Change in Dietary Patterns in Korea
Seungyeon Cho
Atmosphere.2024; 15(12): 1477. CrossRef - Comparison between 24-hour diet recall and 24-hour urine collection for estimating sodium and potassium intakes and their ratio among Korean adults
Taisun Hyun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Young-Ran Heo, Heekyong Ro, Young-Hee Han, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 284. CrossRef - Evaluation of diet quality according to the eating-out patterns of preschoolers and school-aged children in South Korea: based on data from the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-na Ju, Youngmi Lee, Kyunghee Song, Yujin Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(2): 165. CrossRef - Status of serving labeling of home meal replacement-soups and stews, and evaluation of their energy and nutrient content per serving
Mi-Hyun Kim, In-Young Choi, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(5): 560. CrossRef - Trends in sodium intake and major contributing food groups and dishes in Korea: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2017
Yeseung Jeong, Eui Su Kim, Jounghee Lee, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(3): 382. CrossRef - Gastric Cancer and the Daily Intake of the Major Dish Groups Contributing to Sodium Intake: A Case-Control Study in Korea
Jung-Hyun Kwak, Chang-Soo Eun, Dong-Soo Han, Yong-Sung Kim, Kyu-Sang Song, Bo-Youl Choi, Hyun-Ja Kim
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1365. CrossRef - EOSINOPHIL CATIONIC PROTEIN AND IRON STATUS IN PATIENTS INFECTED WITH Enterobius vermicularis
Esraa Wathah, Saleem Khteer Al-Hadraawy
Journal of Experimental Biology and Agricultural Sciences.2021; 9(5): 672. CrossRef - Progress on sodium reduction in South Korea
Hye-Kyung Park, Yoonna Lee, Baeg-Won Kang, Kwang-il Kwon, Jong-Wook Kim, Oh-Sang Kwon, Laura K Cobb, Norman R C Campbell, Drew E Blakeman, Cho-il Kim
BMJ Global Health.2020; 5(5): e002028. CrossRef - Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
Na-Yeong Lee, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Comparison of the sodium content of Korean soup-based dishes prepared at home, restaurants, and schools in Seoul
Yanghee Park, Jihyun Yoon, Sang-Jin Chung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 663. CrossRef - Nineteen-year trends in fermented food consumption and sodium intake from fermented foods for Korean adults from 1998 to 2016
Sang Young Kim, Jeanne H Freeland-Graves, Hyun Ja Kim
Public Health Nutrition.2020; 23(3): 515. CrossRef - Customers' Perceptions of Operational Status of and Needs for Sodium Reduction in the Industry Foodservice in Seoul
Na-Young Yi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 21. CrossRef - Changes in the Quality of Life in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus According to Physician and Patient Behaviors
Young-Joo Kim, In-Kyung Jeong, Sin-Gon Kim, Dong Hyeok Cho, Chong-Hwa Kim, Chul-Sik Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kyu-Chang Won, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Doo-Man Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 91. CrossRef - Periodic Revisions of the International Choices Criteria: Process and Results
Sylvie van den Assum, Rutger Schilpzand, Lauren Lissner, Rokiah Don, Krishnapillai Madhavan Nair, Ngozi Nnam, Ricardo Uauy, Yuexin Yang, Ayla Gulden Pekcan, Annet J. C. Roodenburg
Nutrients.2020; 12(9): 2774. CrossRef - Validity of Estimating Sodium Intake using a Mobile Phone Application of 24-hour Dietary Recall with Meal Photos
Seo-Yoon Kim, Sang-Jin Chung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(4): 317. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life in elderly patients with diabetes mellitus according to age: based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yeji Kang, Kyong Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(2): 129. CrossRef - Food Sources of Sodium in Korean Americans With Type 2 Diabetes: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease
Jisook Ko, Gayle M. Timmerman, Kim B. Kim, Miyong T. Kim
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2019; 30(2): 154. CrossRef - Risk of Metabolic Syndrome among Middle-Aged Koreans from Rural and Urban Areas
Seohyun Lee, Yoonjin Shin, Yangha Kim
Nutrients.2018; 10(7): 859. CrossRef - Risk of Metabolic Syndrome according to Intake of White Rice and Kimchi in Korean Adults: based on the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2013–2015
Jin-Su Kim, So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(6): 525. CrossRef - Effect of a public health center-based nutrition education program for hypertension in women older than 50 years of age
Seoyun Park, Jong-Sook Kwon, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(3): 228. CrossRef - Analysis of Sodium Content and Tastes of Ramyeon Cooked Using Different Recipes
Chang-Hwan Oh, Chung Ha-Yull
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(5): 450. CrossRef - Impacts of High Sodium Intake on Obesity-related Gene Expression
Minjee Lee, Miyoung Park, Juhee Kim, Soyoung Sung, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(5): 364. CrossRef - Low Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Is Prevalent among North Korean Refugees in South Korea
Young-Soo Song, Seong-Woo Choi
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2018; 39(3): 161. CrossRef - Nutritional Evaluation of Convenience Meals in Convenience Stores near the Universities
Go-Na Shin, Yu-Ri Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(5): 375. CrossRef - Stages of Behavioral Change for Reducing Sodium Intake in Korean Consumers: Comparison of Characteristics Based on Social Cognitive Theory
So-hyun Ahn, Jong Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Nutrients.2017; 9(8): 808. CrossRef - Study of the characteristics of dietary behavior and the effects of nutrition education for sodium reduction according to the stages of behavioral change in sodium reduction of male adult subjects in Gwangju·Jeonnam regions
Young Ran Heo, Hyun Young Oh, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 472. CrossRef - Status of Recognition, Effort, and Satisfaction of Customers on Low-Sodium Diet in Industry Foodservice
Sang Jin Yoon, Kun Og Kang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(2): 168. CrossRef - Dietary assessment according to intake of Korean soup and stew in Korean adults: Based on the 2011~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yong-Suk Kwon, Gyusang Han
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(5): 335. CrossRef - Major Dishes Contributing Absolute and Between-Person Sodium Intake Variations in University Students in Gyeonggi-do
Eun-Jung Chung, Ha-Jung Ryu, Eugene Shim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2016; 45(3): 409. CrossRef - Dietary quality differs by consumption of meals prepared at home vs. outside in Korean adults
Kyung Won Lee, Won O. Song, Mi Sook Cho
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(3): 294. CrossRef - Association Between Estimated 24-h Urinary Sodium Excretion and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
Jong Chul Won, Jae Won Hong, Jung Hyun Noh, Dong-Jun Kim
Medicine.2016; 95(15): e3153. CrossRef - Changes in Adherence to Non-Pharmacological Guidelines for Hypertension
Kyong Park, Sukyung Cho, Julie K. Bower, Yan Li
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0161712. CrossRef - Quality and sensory characteristics of commercial kimchi according to sodium contents
Eun-Sun Hwang, Hyo Sung Kim, Soo Hyun Kim, Hyun Joo Ko, Mi Young Lee, Eun-Kyung Yoon
Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology.2016; 48(5): 413. CrossRef - A Comparison of Sources of Sodium and Potassium Intake by Gender, Age and Regions in Koreans: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2010-2012
Yang-hee Park, Sang-Jin Chung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(6): 558. CrossRef - Verification of Utility of Simple Mensuration of Cl-from Urine to Estimate the Amount of Sodium Intake
Sung-Ho Lee, Chae-Joon Lee, Sung-Mi Ju, Hyun-Joo Lee, Wang-Yeon Ra, Soon-Ok Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(1): 27. CrossRef - Major Foods and Nutrient Intake Quality According to Body Image Perception among Korean Women: Based on the 2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
Young Suk Lim, Soo Bin Jeon, Hee Mang Kim, So Yeon Jeong, Jae Young Ahn, Hae Ryun Park
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(2): 154. CrossRef - A Study on the Kimchi Consumption of Korean Adults:Using Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010~2012)
Eun-Kyung Kim, Yoo-Kyung Park, Se-Young Ju, Eun-Ok Choi
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(4): 406. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Parathyroid Hormone, Calcium, and Sodium Bridging Between Osteoporosis and Hypertension in Postmenopausal Korean Women
Jee Soo Park, Soo Beom Choi, Yumie Rhee, Jai Won Chung, Eui-Young Choi, Deok Won Kim
Calcified Tissue International.2015; 96(5): 417. CrossRef - Evaluation of Consumer Nutrition Education Program to Reduce Sodium Intake Based on Social Cognitive Theory
So-Hyun Ahn, Jong Sook Kwon, Kyung Min Kim, Jin-Sook Yoon, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(6): 433. CrossRef - A Study on Sodium-related Dietary Attitude and Behaviors According to Sodium-related Nutrition Knowledge of University Students
Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon, Jong Wook Kim, Jae-Eon Byun, So-Young Bu, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Yun-Jung Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 327. CrossRef - A Study on Eating Out Behavior and Recognition of Salinity in Restaurant Food in Jecheon Area
Soojin Park, Sung Hee Min
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(1): 20. CrossRef - Contents of Sodium and Potassium for Restaurant Dishes in Seoul
Mi-ra Jang, Mi-sun Hong, Bu-chuhl Choi, Sung-hee Han, Kyeong-ah Lee, Li-la Kim, Jib-ho Lee, Jung-hun Kim, Kweon Jung
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2015; 30(2): 189. CrossRef - The Relationship between Daily Sodium Intake and Obesity in Korean Adults
Jung-hoon Kim, Gyeong Eun Lim, Sunyoung Kang, Kayoung Lee, Tae-jin Park, Jinseung Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2015; 15(4): 175. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics of Low-sodium Tomato Jangajii according to Storage Time by Cultivars
Yeon Sook Park, Hae Jeong Gweon, Ki Hyeon Sim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(3): 460. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - Survey on Nutrition Knowledge, Food Behaviors, and Food Frequency of Sodium Intake in Korean University Students
Hee-Ok Pak
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(1): 12. CrossRef - Preparation of Sun-dried Salt Containing GABA by Co-crystallization of Fermentation Broth and Deep Sea Water
Bu-Young Choi, Seok-Cheol Cho
Food Engineering Progress.2015; 19(4): 420. CrossRef - Study on Sodium Reduction: 'Healthy Restaurant for Sodium Reduction'
Soon Myung Hong, Jee Hye Lee, Hye-Kyung Kim, Rina Yu, Jeong Hee Seo, Eun Jeong Huh, Seong Suk Cho, Jeongah Yang
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(3): 174. CrossRef - Salt-related Dietary Behaviors of University Students in Gyeongbuk Area
Kyung-A Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2014; 43(7): 1122. CrossRef - Blood Pressure and Dietary Related Risk Factors Associated with High Sodium Intake Assessed with 24-hour Urine Analysis for Korean Adults
Yeon-Seon Jeong, Hwa-Jae Lim, Sook-Bae Kim, Hee Jun Kim, Sook Mee Son
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 537. CrossRef - Comparison of sodium content of workplace and homemade meals through chemical analysis and salinity measurements
Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(5): 558. CrossRef - Effects of short-term supplementation of erythritol-salt on urinary electrolyte excretion in rats
Myungok Kyung, Ji Ye Lim, Kyungsun Lee, Sangwon Jung, Keunbum Choe, Chang-kun Yang, Yuri Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(2): 99. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Dietary Habit and Nutritional Status by Household Income in Female Adults over the Age of 20 - Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hee-Kyung Jang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 660. CrossRef - A study of the major dish group, food group and meal contributing to sodium and nutrient intake in Jeju elementary and middle school students
Yang-Sook Ko, Hye-Yun Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(1): 51. CrossRef - Analysis of presumed sodium intake of office workers using 24-hour urine analysis and correlation matrix between variables
Hyun-Hee Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2013; 46(1): 26. CrossRef - Trends in the major dish groups and food groups contributing to sodium intake in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1998-2010
Da Young Song, Jong Eun Park, Jae Eun Shim, Jung Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2013; 46(1): 72. CrossRef - Factors Associated with a Low-sodium Diet: The Fourth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Won Joon Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, Sun Min Oh, Dong Phil Choi, Jaelim Cho, Il Suh
Epidemiology and Health.2013; 35: e2013005. CrossRef - Sodium density and obesity; the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2010
Y S Yoon, S W Oh
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2013; 67(2): 141. CrossRef - Sodium Content and Nutrients Supply from Free Lunch Meals Served by Welfare Facilities for the Elderly in Gyeonggi-do
Seoyun Park, So Hyun Ahn, Jin Nam Kim, Hye-Kyeong Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2013; 26(3): 459. CrossRef - Establishment of One Portion Size of Dishes Frequently Consumed by Korean Adults using 2010 KNHANES and Its Comparison with the One Portion Size using 2005 KNHANES - Focusing on Rice, Noodles, Soups, and Stews -
Sook-Bae Kim, Soon-Kyung Kim, Se-Na Kim, Young-Sook Cho, Mi-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2013; 26(4): 745. CrossRef - A Survey on the Salt Content of Kindergarten Lunch Meals and Meal Providers' Dietary Attitude to Sodium Intake in Gyeonggi-do Area
Jin Nam Kim, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(5): 478. CrossRef - Salt content of school meals and comparison of perception related to sodium intake in elementary, middle, and high schools
Sohyun Ahn, Seoyun Park, Jin Nam Kim, Sung Nim Han, Soo Bin Jeong, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2013; 7(1): 59. CrossRef - A Study on the Knowledge, Dietary Behavior related to Sodium, Attitudes towards a Low-Salt Diet of Adults in the Jeonbuk Area
Jeongok Rho, Hyuna Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2013; 22(4): 693. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Habits and Practicability of Guidelines for Reducing Sodium Intake according to the Stage of Change in Housewives
So-Hyun Ahn, Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Jin-Sook Yoon, Baeg-Won Kang, Jong wook Kim, Seok Heo, Hea-Young Cho, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(6): 724. CrossRef - Salt Intake and Diabetes
Jeong Hyun Lim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2012; 13(4): 211. CrossRef
- Exploration of the relationship between gastric cancer and nutritional risk factors: insights from the Korea National Health Insurance Database
- 2,453 View
- 3 Download
- 72 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of the Nutrient Intakes by the Score of Dietary Action Guides for Korean Children among the Elementary School Students in Gwangju City
- Bok Hee Kim, Mi young Sung, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(4):411-425. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.4.411
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to examine differences in nutrient intakes by the compliance with the Dietary Action Guide for Korean Children. The subjects included 343 elementary school students in Gwangju city. Compliance with the Dietary Action Guide for Children showed that 62.4% of subjects had breakfast everyday; 44.3% of subjects ate vegetables/fruits/milk and dairy products daily; 26.8% of subjects ate a variety of lean meats/fish/eggs/bean products daily; 32.9% of subjects enjoyed outdoor activity everyday and ate according to their energy needs; 40.2% of subjects chose healthy and nutritious foods for snack; and 15.5% of subjects avoided food waste. Intakes of most of nutrients including energy were significantly higher (p < 0.05) in those who complied with the Dietary Action Guide well. Also nutrient intakes had the positive correlation with the scores of Dietary Action Guide (p < 0.05). From these results, nutrient intakes of children were significantly influenced by dietary factors suggested in the Dietary Action Guide for Children. In addition, the results also confirmed that good food behaviors were indispensible to maintaining a proper nutritional status. Based on these results, good food behaviors and practice were critical to secure good health and proper nutritional status for children, and that nutrition education should be strengthened in school as well as at home.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
Eunyoung Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 220. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Behavior among Elementary School Students in Seoul Area Using Nutrition Quotient for Children
Ji Ye Lim, Jung Hyun Kim, Sung Hee Min, Myung Hee Lee, Min June Lee
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(1): 84. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Adolescents' Dietary Perceptions and Practices
Taejung Woo, Hye-Jin Lee, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 165. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - Relationships between children's Nutrition Quotient and the practice of the Dietary Guidelines of elementary school students and their mothers
Jae Ran Kim, Hyeon-Sook Lim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(1): 58. CrossRef - Relationships between children's Nutrition Quotient and the practice of the Dietary Guidelines of elementary school students and their mothers
Jae Ran Kim, Hyeon-Sook Lim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(1): 58. CrossRef - Relationships of Dietary Behavioral Factors and Stress Perception Levels in College Students in Gwang-ju City
Bok Hee Kim, Bang Geul Shim, Eun Jeong
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(5): 771. CrossRef - A Survey of Satisfaction with Quality attributes of Meal Services for Low-income Children in Wonju
Hae Sook Oh
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2014; 25(2): 233. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Dietary Habit and Nutritional Status by Household Income in Female Adults over the Age of 20 - Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hee-Kyung Jang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 660. CrossRef - Relationship between adhering to dietary guidelines and the risk of obesity in Korean children
Soo Hyun Yu, YoonJu Song, Mijung Park, Shin Hye Kim, Sangah Shin, Hyojee Joung
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(6): 705. CrossRef - Association between the Number of Unfamiliar Vegetables and Dietary Factors of Elementary School Children
Kyunghee Song, Hongmie Lee
Preventive Nutrition and Food Science.2013; 18(4): 280. CrossRef - The prevalence of obesity and the level of adherence to the Korean Dietary Action Guides in Korean preschool children
Yuni Choi, Yeji You, Kyeong Ah Go, Zuunnast Tserendejid, Hyun Joo You, Jung Eun Lee, Seungmin Lee, Hae-Ryun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2013; 7(3): 207. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Dietary Action Guide for Adolescence among Middle and High School Students in Korea
So-Hyun Park, Hae-Ryun Park, Soo-Bin Jeon, So-Yeon Jeong, Zuunnast Tserendejid, Jung-Sook Seo, Kyung-Hae Lee, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(2): 133. CrossRef - Correlation between Intake of Dietary Fiber and Adherence to the Korean National Dietary Guidelines in Adolescents from Jeonju
Sunmi Park, Woori Na, Misung Kim, Eunsoo Kim, Cheongmin Sohn
Preventive Nutrition and Food Science.2012; 17(4): 254. CrossRef - Association between dental caries experience and performance of the dietary action guides among the special school for students of disability
Hee-Jung Moon, Seol-Ak Kim, Hee-Jung Park
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2012; 12(6): 1193. CrossRef - Development and Effects' Analysis of Nutrition Education Pamphlet for the Lower Grades Elementary Students -Focused on Individual Daily Needed Food Exchange Units-
Min-Jung Son, Young-Sook Cho, Se-Na Kim, Hye-Ji Seo, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(6): 647. CrossRef
- Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
- 1,195 View
- 3 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutritional Environment Influences Hypertension in the Middle-aged Korean Adults: based on 1998 & 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Hae Jeung Lee, Haeng Shin Lee, Yoonna Lee, Young Ai Jang, Jae Jin Moon, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(3):272-283. Published online June 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to delineate the relationship between lifestyle and nutritional risk factors associated with hypertension in representative middle-aged Korean population. Hypertension in this study is defined as hypertensive (SBP> or = 140 mmHg or DBP> or = 90 mmHg) adults without recognition of a disease state before a health exam. With data from the 1998 and 2001 National Health and Nutritional Survey, nutrient intakes of 6,112 adults, 40-64 years of age were calculated using food composition database and matched with health examination records by individual ID. After excluding those with extreme intake values, the number of final subjects included in the analysis was 5,200 (male 2,458, female 2,742). Using logistic regression method, socio-demographic data, lifestyle factors, and nutrient intakes were analyzed. Risky factors for hypertension revealed in this study were age, sex, BMI over 23, waist circumference, alcohol intake of more than 16 g (male) or 8 g (female). Regarding nutrient intakes, the intakes of highest quartile for energy (> or = 2363.0 kcal) and protein (> or = 90.2 g) were significantly associated with higher risk of hypertension after adjusting for age, sex, and other socio-demographic factors (OR = 1.312 (1.046-1.711), OR = 1.488(1.194-1.854), respectively)). Although high intakes of sodium (> or = 6604.0 mg) and phosphorus seemed to be risk factors of hypertension also before energy adjustment (OR = 1.278(1.034-1.581), OR = 1.280(1.024 -1.600), respectively), only high intakes of energy and protein remained significant after adjustment. This study revealed that modifying risky lifestyles and dietary patterns, especially high energy intake, high protein intake, and high alcohol drinking, in middle-aged Korean adults could result in a prevalence decrease and/or prevention of hypertension.
- 286 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Characteristics of Infants' Temperaments and Eating Behaviors, Mothers' Eating Behaviors and Feeding Practices in Poor Eating Infants
- Yoonjung Kim, Young Shin Han, Sang Jin Chung, Yoonna Lee, Sang Il Lee, Haymie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(4):449-458. Published online August 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics of infants' temperaments and eating behaviors, mothers' eating behaviors and feeding practices in poor eating infants. The participants were 80 infants of 12 - 24 months (27 poor eaters and 53 matched normal controls) from a hospital and a public health center. Mothers were questioned about their eating behaviors and feeding practices, and infants' temperaments, eating behaviors, and nutrient intakes by one day food recall. Subjects were divided by mean nutrient adequacy ratio (MAR, < 0.75; poor eater). Intakes of Ca, P, Fe, Zn, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin C, E, folate were below 75% RDA in poor eaters, whereas protein, thiamin, riboflavin, vitamin B6, C, folate exceeded 125% RDA in good eaters. Rhythmicity of infants' temperaments and eating behaviors, restriction of mothers' eating behaviors and feeding practices were significantly lower, whereas activity levels of infants' temperaments were higher than good eaters. In multiple logistic regression model of poor eaters, activity of infants' temperaments (T, OR: 1.19, CI: 1.05 - 1.35) and attention spans of infants' eating behaviors (A, OR: 1.18, CI: 1.03 - 1.35) were significantly positive, whereas rhythmicity of infants' eating behaviors (R, OR: 0.79, CI: 0.67 - 0.94) was significantly negative [E (the logit) = -6.8644 + 0.1712 x T - 0.2337 x R + 0.1641 x A]. Our findings suggest that examination of eating behaviors, feeding practices, and temperaments will help target interventions to improve infants' food intakes, and these variables should be examined at the time of nutrition counseling.
- 316 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Intake Pattern of the Korean Adult Population by Weight Status: 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Yoonna Lee, Haeng Shin Lee, Young Ai Jang, Hae Jeung Lee, Bok Hee Kim, Cho Il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(3):317-326. Published online June 30, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To explore the relationship between weight status and food intake pattern, the Nutrition Survey results of the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed. Dietary intake data of Korean adults aged 20 to 64, years who participated in the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey, was used along with their demographic data. Subjects were classified into 4 groups based on the BMI value of subjects: underweight, normal, overweight and obese. For male adults, obese subjects had significantly higher mean intake of energy, protein, carbohydrates, and fat than normal subjects. In addition, obese male adults consumed more animal foods, especially more meats, than normal subjects. However, females obese subjects did not show higher intake of energy or fat. Although obese male adults showed higher energy intake, calcium and iron intake per 1000 kcal was lower than normal adults. Average calcium intake in females was low; about 70% of RDA regardless of obesity level. In addition, riboflavin and Vitamin A intake was lower in overweight and obese female than in normal females. Percentage of subjects with low fruit and vegetable intake (<400 g per day) was also high in female subjects. These results showed that food and nutrient intake patterns of obese population were different between male and female adults. These dietary intake patterns need to be considered in developing and implementing nutrition policy and intervention programs to prevent and control obesity. Moreover, the National Survey and monitoring system should be developed for continuous and effective investigation on the relationship between obesity and dietary intake.
- 352 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Food and Nutrient Consumption Patterns of the Korean Adult Population by Income Level - 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Bok Hee Kim, Joung Won Lee, Yoonna Lee, Haeng Shin Lee, Young Ai Jang, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(6):952-962. Published online December 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To explore the relationship between economic status and food and nutrient intake patterns, the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey result was analyzed. Dietary intake data of 6,978 Korean adults of 20 years and older who participated in the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey were used along with their demographic data. Economic status of the subjects was classified into the following 4 groups based on the self-reported average monthly income of household with reference to the minimum monthly living expenses (MLE) in 2001: low<100% MLE < or = middle<200% MLE < or = high<300% MLE < or = higher. Individuals in the higher income class had significantly higher mean intake for most of the nutrients including energy, protein, carbohydrate, fat, calcium, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin and vitamin C, and a higher percentage of energy intake from fat. In addition, they consumed more animal foods including meats, eggs, fish/shellfish, milk/dairy products and fats. On the other hand, the mean intakes of individuals in the lower economic class for calcium, vitamin A, and riboflavin were lower than 75% of RDAs. And, there was a predominant difference in contribution of fat to total energy intake among the groups of different economic status. These results showed that household income is an important factor influencing the food and nutrient intake patterns of the Korean adult population. Although individuals at different age classes may respond differently to a change in economic status, developing and implementing nutrition policy and intervention programs for those nutritionally vulnerable groups should consider the economic status as an important factor to customize and differentiate the content of the program.
- 305 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- The Characteristics of Infants' Temperament, Maternal Feeding Behavior and Feeding Practices in Picky Eaters
- Yoon Jung Kim, Sang Jin Chung, Young Shin Han, Yoonna Lee, Sang Il Lee, Ki Won Byun, Haymie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(4):462-470. Published online August 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics of infants' temperaments, maternal feeding behaviors and feeding practices in picky eaters. Participants were 83 infants (aged 12 - 24 months) from "A" hospital (Seoul) and "B" public health center (Kyunggido). Mothers completed questionnaires that assessed their own feeding behavior, feeding practices, infants' temperament and infants' feeding behavior. Picky eaters' demographics were not significantly different from non-picky eaters after adjusting sex and age. The average of thiamin, niacin and vitamin E intakes of picky eaters were below 75% Korean RDA, whereas vitamin A intakes exceed 120% RDA in both groups. Activity level of infants' temperament and disinhibition of maternal feeding behavior in picky eaters were significantly higher than those in non-picky eater. All constructs of infants feeding behavior were significantly associated with certain constructs of infants' temperament, maternal feeding practice and maternal feeding behavior. The pickiness of infants feeding behavior was positively correlated with activity level of infants' temperament, pickiness and disinhibition of maternal feeding behavior and negatively correlated with adaptability of infants' temperament. Findings suggest that maternal feeding behavior and feeding practices as well as infants' temperament should be addressed in nutrition education for picky eaters.
- 275 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Factors Associated with Breakfast Skipping in Elementary School Children in Korea
- Sang Jin Chung, Yoonna Lee, Sunja Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(1):3-11. Published online February 29, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to examine relationships between breakfast skipping and ecological factors related to eating practice. Participants were 537 children (male: 274, female: 263) from two elementary schools in Kyunggido (School A) and Seoul (School B). Analysis included cross-tabulation of demographics, factors related to eating practice and weight status, frequency of breakfast skipping and types of breakfast and the number of foods at breakfast by schools. Logistic regression were conducted to identify the factors associated with breakfast skipping. Children in school B showed higher socioeconomic status by living environment and the type of fathers' job than those in school A. Eighty six percent of children in school B and 75% in school A ate breakfast 5 times and more per week. School and father's occupation differences correlated with the frequency of breakfast, but not mother's employ status was not. After controlling school, type of father's job, mother's employ status, eating breakfast 5 times and more was associated with eating with other family members, feeling hungry before breakfast, normal weight status, eating Korean traditional meal type and number of food eaten at breakfast. The results stress the need for intervention programs aimed at decreased skipping breakfast among elementary school children. While programs need to reach all children skipping breakfast, approaches need to be suitable to in particular those from low socioeconomic backgrounds.
- 454 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Effect of Nutrition Education Program on Body Fat and Blood Lipids of Obese Young Adolescent Girls
- Yoonna Lee, Haymie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 1999;4(1):11-19. Published online March 31, 1999
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of a nutrition education program on 42 obese young adolescent girls. Nutrition education was performed for six months including both group and individual programs, and was focused on improving their eating habits and food composition. The topics discussed once a week included : eating habits, lifestyle management, 5 basic food groups, snack and fast-food, how to eliminate empty calories, fat and hyperlipidemia, food diary, benefits and methods of exercise, vitamin and minerals, evaluation of fad diets, yo-yo effects and so on. The effects of the nutrition education program were evaluated for nutrition education and exercise regimen group (NE+E), nutrition education only group(NE), and control group(C). NE+E group had additional exercise programs 3times each week, while NE group was educated about exercise only by a nutrition education program. In both NE+E and NE groups, there was a significant decrease in bodyfat compared to C group, but NE+E group had a greater change than NE group(5.5% vs 3.1%). In addition, serum triglycerides decreased about 40mg/dl and total cholesterol 20mg/dl in both NE+E and NE groups. But HDL-C level was increased only in NE+E group. The greater changes in body fat and blood lipid levels occurred between the pre- and mid terms fo the education regimen. They kept their changed measurement throughout the 6 months follow-up studies. The results of this study show that this nutrition education program is helpful for obese adolescent girls in decreasing body fat and serum lipid levels. Also, the combination of an exercise regimen with the nutrition education proved to be more effective.
- 361 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Bone Density of the Middle Aged Women Residing in Urban Area and the Related Factors: I. distribution of Bone density According to Age and the Prevalence of Osteoporosis in the Middle Aged Women Residing in Urban Area
- Sook Mee Son, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 1998;3(3):380-388. Published online August 31, 1998
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the distribution of bone density according to age and the prevalence rate of osteoporosis I 613, middle-aged women who visited Saint Bundo Hospital in Pusan from June to December, 1997. Mean bone density of lumbar spine(L2L4), and femoral neck of 50-59 years of age was significantly lower than those of 40-49 years of age(p<0.05). At the 60years of age, mean bone density of two sites were less than those of 50-59 years of age. Mean bone density of lumbar spine tin the group of sixties were 20.7% lower than that of group aged under 40 ; For femoral neck, women in their sixties showed 22.6% lower density compared to the women aged under forty. Bone density of ward's triangle of sixties were the least, which was 34.2% lower than that of group aged under 40. Bone density in lumbar spine, femoral neck, trochanter and ward's triangle correlates strongly with each other(p<0.001). The proportion of osteoporosis was 3.6% in the group of forties, 10.9% in the group of fifties and 33.8% for the group aged over 60, which was assessed by bone density of lumbar spine. Bone density of lumbar spine, femoral neck and ward's triangle were positively correlated with height, weight and BMI(p<0.001~p<0.01), and weight showed highest correlation with the bone density. Forty-four percent of variation in lumbar spine bone density was explained by age and weight.
- 306 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



