Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):103-113. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00255
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors such as medication use, dietary supplementation, dietary habits, and physical activity among Koreans aged 20–60 years.
Methods
Data from a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) living in Seoul and Gyeonggi provinces in Korea were analyzed to assess the relationship between health behaviors and dietary supplements (DSs) related to self-care. Based on self-care levels, the participants were classified into three groups: low (LS, n = 124), medium (MS, n = 78), and high (HS, n = 98).
Results
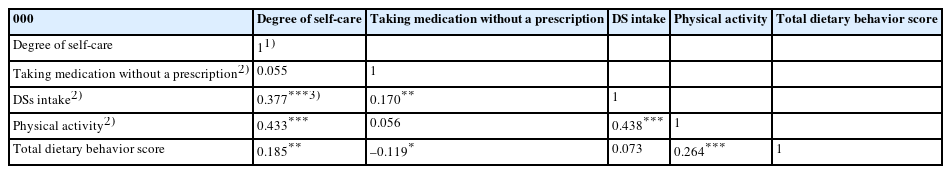
DSs (P < 0.001), physical activity (P < 0.001), recognizing the perceived health benefits of self-care (P < 0.001), self-care when sick (P = 0.039), and the reasons for self-care (P = 0.028) differed among the self-care groups. Daily diet frequency (P = 0.001), breakfast frequency (P = 0.026), regular exercise (P < 0.001), DSs use rate (P < 0.001), DSs use frequency (P = 0.013), and total dietary behavior score (P < 0.001) also differed significantly depending on the degree of self-care. The degree of self-care was significantly and positively correlated with DSs intake (r = 0.377, P < 0.001), physical activity (r = 0.433, P < 0.001), and total dietary behavior score (r = 0.185, P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The results demonstrated that the degree of self-care was related to DSs, physical activity, and total dietary behavior scores in Korean adults. Additionally, self-care capacity should be increased through health-related behaviors based on health education programs.
- 2,275 View
- 55 Download

- [English]
- Arterial stiffness index, physical activity and food and nutrient intake: cross-sectional study in adults aged 40 years and older
- Eun-A Kim, Yun-Mi Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):81-96. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate arterial stiffness index, physical activity, and food and nutrient intake in middle-aged adults over 40 years when the incidence of cardiovascular disease begins to increase.
Methods
This study included 106 subjects (48 males and 58 females) aged between 40 and 64 years. The arterial stiffness index (brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity [baPWV], and ankle-brachial index [ABI]) were measured using a blood pressure pulse wave testing device. Physical activity was assessed using the Korean version of the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire, and food and nutrient intake was calculated using the Food Frequency Questionnaire.
Results
The mean age of the subjects was 54.4 years. Although the ABI of the subjects was within the normal range, they were divided into tertiles to compare physical activity and food and nutrient intake. In males, the time spent on moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) was significantly higher in T3 (600.6 min/week) than in T1 (304.4 min/week). In females, the time spent in sedentary behavior was significantly lower in T3 (294.5 min/week) than in T1 (472.1 min/week). In addition, the frequency of fish consumption was significantly higher in T3 (1.27 frequency/day) than in T1 (0.64 frequency/day) in females. Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) and ω-3 fatty acid intake, adjusted for energy intake, were significantly positively correlated with ABI (r = 0.200 and r = 0.218, respectively).
Conclusions
High MVPA (in males), low sedentary behavior (in females), and PUFA and ω-3 fatty acid intake through fish consumption may be associated with low peripheral artery stiffness. Therefore, arteriosclerosis can be prevented through physical activity and proper dietary therapy.
- 1,310 View
- 38 Download

- [English]
- The Study of Dietary Habits and Health Behaviors according to Physical Activity Type in Korean Adults -Based on the 2016~2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
- Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):122-133. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated the dietary habits and health behaviors of Korean adults according to their physical activity. Methods: Adults aged 19~64 years, who participated in the 2016~2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, were enrolled in this study. The subjects were classified into the physical inactivity group, aerobic physical activity group, strength exercise group, and combined exercise group. Results: Significant differences in skipping breakfast, frequency of eating out, dietary supplements, and alcohol drinking status were observed among physical activity groups (P < 0.001). The combined exercise group had the highest % KDRI of protein, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, calcium, potassium, and iron (P < 0.001). The physical inactivity group had the highest obesity rate (35.1%), and they perceived their body image type to be obese. In the combined exercise group, 47.8% of respondents said they were in good health (P < 0.001). The health-related quality of life score of the physical inactivity group was the lowest, with a score of 0.94. The metabolic syndrome risk rate of the combined exercise group was lower at 0.62 times (95% CI, 0.51-0.75) than the physical inactivity group. Conclusions: The physical activity type was associated with metabolic syndrome. These results can be useful for supporting dietary education and physical activity programs for adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
Soyean Kang, Hae Sagong, Juyoung Lee
Public Health Nursing.2025; 42(3): 1182. CrossRef - The Association between the Type and Level of Physical Activity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults Aged 40 Years and over: Results from the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Namkuk Son
The Korean Journal of Sports Medicine.2024; 42(2): 145. CrossRef - Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
Hyoju Lee, Youjeong Jang, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 261. CrossRef - 고령자의 신체건강 및 식생활 행태가 영양소 섭취량에 미치는 영향
하리 임, 다솔 김, 나미 주
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(6): 518. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef
- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
- 1,452 View
- 15 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and Physical Activity Level Assessed by International Physical Activity Questionnaireshort form (IPAQSF) in the Elderly
- HyunJu Lee, JiYeon Gwak, HaYeon Jun, EunKyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):236-245. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Cardiovascular disease is a major cause of death in the elderly in Korea. Increased arterial stiffness is linked to risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between arterial stiffness and physical activity in the elderly.
Methods
A total of 209 older adults (110 men and 99 women) participated in this study. Arterial stiffness of subjects such as brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) and ankle brachial pressure index (ABI) was measured using a non-invasive vascular screening device (VP-1000 Plus, Omron, Kyoto, Japan). The interviewed Korean version of the international physical activity questionnaire short form (IPAQ-SF) was used to evaluate subject’s physical activity level and classify subjects as active or inactive group based on the time spent doing moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA).
Results
The mean age of total subjects was 75.3 ± 5.6 years. There was no significant difference in sex distribution between the active group (39.7%) and inactive group (60.3%). The baPWV (1,758.1 ± 375.2cm /sec) of the active group was significantly lower than that (1,969.7 ± 372.3 cm/sec) of the inactive group (P < 0.05). There was a significant inverse association between time spent in MVPA and baPWV (r = -0.245, P < 0.01).
Conclusions
This study suggests that physical activity programs for older adults are needed to prevent arteriosclerosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Arterial stiffness index, physical activity and food and nutrient intake: cross-sectional study in adults aged 40 years and older
Eun-A Kim, Yun-Mi Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 81. CrossRef - Influence of Physical Activity Level on Cardiovascular and Autonomic Nerve Function
Shin-Young Park, Jin-Su Kim, Seungho Lee, Ruda Lee, Eui-Young Lee, Moon-Hyon Hwang
Exercise Science.2023; 32(1): 111. CrossRef - Association between physical activity measured using an accelerometer and arterial stiffness based on pulse wave velocity and ankle-brachial index in healthy adults
Hyunju Lee, Kye Wol Park, Ha Yeon Jun, Ji Yeon Gwak, Eun Kyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(4): 506. CrossRef
- Arterial stiffness index, physical activity and food and nutrient intake: cross-sectional study in adults aged 40 years and older
- 1,359 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Comparison of Physical Activity Level, Physical Activity Pattern and Energy Expenditure in Male and Female Elementary School Soccer Players using Accelerometer and Physical Activity Diary
- Hae Sun An, Su Ji Choi, Mo Ran Lee, Jung Sook Lee, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(6):529-542. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.6.529
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to compare the physical activity level (PAL), the physical activity pattern and the energy expenditure in male and female elementary school soccer players using the accelerometer and the physical activity diary.
METHODS
Twenty-five (male 11, female 14) elementary school soccer players (9–12 years) participated in this study. During their daily activities, they wore an accelerometer for seven days (five weekdays and two weekend days) and completed the physical activity diary for three days (two weekdays and one weekend day). PAL was calculated by using the physical activity diary and three equations (Pate Preschool, Freedson Children, and Freedson) were used to calculate the intensity of physical activity and energy expenditure from the counts of accelerometer.
RESULTS
The average of physical activity by day of the week, CPM (Counts Per Minute) and METs (Metabolic Equivalents) were significantly higher in males (723.3 ± 149.2 CPM, 2.07 ± 0.18 METs) compared to females (505.6 ± 119.9 CPM, 1.79 ± 0.20 METs), but there was no significant difference in PAEE (Physical Activity Energy Expenditure) between the two groups (males: 15.5 ± 9.1 kcal/day, females: 11.5 ± 6.0 kcal/day). During weekdays, physical activity intensity was significantly higher in males compared to females at lunch time and training time than at other times. In both genders, the PAL was higher during weekdays (males 1.98, females 1.89) compared to weekend (males 1.62, females 1.61) (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Our study observations suggest the necessity to develop an accelerometer equation for accurately evaluating the physical activity of elementary school athletes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validation of a physical activity classification table in Korean adults and elderly using a doubly labeled water method
Hye-Ji Han, Ha-Yeon Jun, Jonghoon Park, Kazuko Ishikawa-Takata, Eun-Kyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 391. CrossRef - Establishment and future tasks of estimated energy requirement in 2020 dietary reference intakes for Koreans
Eun-Kyung Kim, Oh Yoen Kim, Jonghoon Park, EunMi Kim, Juhyeon Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 573. CrossRef
- Validation of a physical activity classification table in Korean adults and elderly using a doubly labeled water method
- 1,300 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Changes After Breast Cancer Diagnosis: Associations with Physical Activity, Anthropometry, and Health-related Quality of life Among Korean Breast Cancer Survivors
- Sihan Song, Hyun Jo Youn, So Youn Jung, Eunsook Lee, Zisun Kim, Jihyoung Cho, Young Bum Yoo, Hyeong Gon Moon, Dong Young Noh, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):533-544. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.533
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
We aimed to examine levels of physical activity, anthropometric features, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among Korean breast cancer survivors who reported changes in their diet after diagnosis.
METHODS
A total of 380 women who had been diagnosed with stage I to III breast cancer and had breast cancer surgery at least six months before the interview were included. Participants provided information on dietary change after diagnosis, post-diagnostic diet, physical activity, anthropometric measures, and HRQoL through face-to-face interview. We assessed HRQoL levels of breast cancer survivors using a validated Korean version of European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30 (EORTC QLQ-C30) and Breast Cancer Module (BR23). We used the logistic regression and generalized linear models to identify the associations of dietary changes in relation with physical activity, anthropometry, and HRQoL.
RESULTS
The majority of participants (72.6%) reported that they have changed their diet to a healthier diet after diagnosis. Breast cancer survivors who reported to have change to a healthy diet had higher intakes of vegetables and fruits and lower intakes of red and processed meats, and refined grains than those who did not. Also, survivors with a healthy change in their diet were more likely to engage in physical activity (top vs. bottom tertile: odds ratio [OR], 1.85; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 1.02-3.36) and have lower body mass index (BMI) (OR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.82-0.98 for one kg/m² increment in BMI) compared to those who did not. We found that a healthy change in diet was associated with higher scores of physical functioning (p=0.02) and lower scores of constipation (p=0.04) and diarrhea (p=0.006) compared to those who did not.
CONCLUSIONS
Healthy changes in diet after breast cancer diagnosis may be associated with lower levels of BMI, and higher levels of physical activity and HRQoL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Effects of a Smartphone Application to Improve Self-Management in Workers Who Underwent Thyroid Cancer Surgery
Myoyoun Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Cancer Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Behaviors of Middle-Aged Cancer Survivors: A Comparative Study with Matched Non-Cancer Controls Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI–VII (2013–2018) Data
Mi Lee KIM, Ju Ri JEONG, Yu Ri CHOE
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2025; 25(1): 20. CrossRef - Cancer survivor's dietary safety management awareness and competency type
Yun Hwa Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(5): 532. CrossRef - Health-related Quality of Life and Its Related Factors among Cancer Survivors and General Adults: Focusing on Lifestyle Behaviors and Mental Health
Eun A Song, Youngran Kweon, Yoon Young Hwang, Minjeong An
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 385. CrossRef
- Development and Effects of a Smartphone Application to Improve Self-Management in Workers Who Underwent Thyroid Cancer Surgery
- 1,326 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Measurement of Energy Expenditure Through Treadmill-based Walking and Self-selected Hallway Walking of College Students - Using Indirect Calorimeter and Accelerometer
- Ye Jin Kim, Cui Sang Wang, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):520-532. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.520
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to assess energy expenditure and metabolic cost (METs) of walking activities of college students and to compare treadmill based walking with self-selected hallway walking.
METHODS
Thirty subjects (mean age 23.4 ± 1.6 years) completed eight walking activities. Five treadmill walking activities (TW2.4, TW3.2, TW4.0, TW4.8, TW5.6) were followed by three self-selected hallway walking activities, namely, walk as if you were walking and talking with a friend: HWL (leisurely), walk as if you were hurrying across the street at a cross-walk: HWB (brisk) and walk as fast as you can but do not run: HWF (fast) were performed by each subject. Energy expenditure was measured using a portable metabolic system and accelerometers.
RESULTS
Except for HWF (fast) activity, energy expenditures of all other walking activities measured were higher in male than in female subjects. The lowest energy expenditure and METs were observed in TW2.4 (3.65 ± 0.84 kcal/min and 2.88 ± 0.26 METs in male), HWL (leisurely) (2.85 ± 0.70 kcal/min and 3.20 ± 0.57 METs in female), and the highest rates were observed in HWF (fast) (7.72 ± 2.81 kcal/min, 5.84 ± 1.84 METs in male, 6.65 ± 1.57 kcal/min, 7.13 ± 0.68 METs in female). Regarding the comparison of treadmill-based walking activities and self-selected walking, the energy expenditure of HWL (leisurely) was not significantly different from that of TW2.4. In case of male, no significant difference was observed between energy costs of HWB (brisk), HWF (fast) and TW5.6 activities, whereas in female, energy expenditures during HWB (brisk) and HWF (fast) were significantly different from that of TW5.6.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we observed that energy expenditure from self-selected walking activities of college students was comparable with treadmill-based activities at specific speeds. Our results suggested that a practicing leisurely or brisk walking for a minimum of 150 minutes per week by both male and female college students enable them to meet recommendations from the Physical activity guide for Koreans. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Accuracy of Accelerometer for the Prediction of Energy Expenditure and Activity Intensity in Athletic Elementary School Children During Selected Activities
Su-Ji Choi, Hae-Sun An, Mo-Ran Lee, Jung-Sook Lee, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(5): 413. CrossRef - Energy expenditure of physical activity in Korean adults and assessment of accelerometer accuracy by gender
Yeon-jung Choi, Mun-jeong Ju, Jung-hye Park, Jong-hoon Park, Eun-kyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(6): 552. CrossRef
- Accuracy of Accelerometer for the Prediction of Energy Expenditure and Activity Intensity in Athletic Elementary School Children During Selected Activities
- 1,279 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- The Relations between Diabetic Dietary Compliance, Dietary Intake, and Physical Activity and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MS) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Dong Eun Kim, Seung Hee Hong, Ji Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(5):351-361. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.5.351
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relations between diabetic dietary compliance and dietary intake, physical activity and prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MS) in type 2 diabetic patients.
METHODS
Seventy five subjects diagnosed with type 2 diabetes visiting the D hospital in Dongducheon from May 2014 to Dec 2014 were included in this study. The subjects were divided into two groups according to their diabetic dietary compliance score (median 39); low diabetic dietary compliance (LDDC) group (n=44) and high diabetic dietary compliance (HDDC) group (n=31). Survey data collection was carried out by direct interview method. The nutrient intake, food intake and KDDS (Korean's dietary diversity score), DVS (dietary variety score) and GMVDF (grain, meat, vegetable, dairy and fruit) were analyzed using data from the 24-recall method. Metabolic parameters were obtained from the hospital records. Data was analyzed using Chi-square test and general linear model adjusted for sex.
RESULTS
The prevalence of MS was 59.7% in the participating diabetic patients. The prevalence of MS of the HDDC (39.3%) was significantly lower than that of the LDDC (72.7%). The distribution of physical activity showed a significant difference between the groups (p=0.006). The intakes of seeds and nuts of the HDDC were significantly lower than those of the LDDC. Fat and vegetable fat intakes and % fat of energy in the HDDC were significantly lower than those in the LDDC. But, carbohydrate (CHO) and potassium intake and %CHO of energy in the HDDC were significantly higher than those in the LDDC. KDDS and GMVDF showed significant differences between groups (p=0.033; p=0.012).
CONCLUSIONS
Continuous intervention by specialized nutritionists for long-term self-regulation is needed for diabetic patients, and the high compliance to diabetic diet and increasing physical activity may be effective in the prevention of metabolic syndrome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Depression, Patient Activation, and Family Support on Patient Role Behavior of Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Jeong Hyun Park, Jung Suk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 355. CrossRef - The Relationship between Meal Regularity and Oral Health and Metabolic Syndrome of Adults in Single Korean Households
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, On-Ju Ju
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 185. CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef - Healthy Dining Out in Diabetic Patients
Hae-Young Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(4): 264. CrossRef
- Effects of Depression, Patient Activation, and Family Support on Patient Role Behavior of Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- 1,176 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Assessment of Physical Activity Pattern, Activity Coefficient, Basal Metabolic Rate and Daily Energy Expenditure in Female University Students
- Yoonji Park, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(1):45-54. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.1.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the physical activity pattern, activity coefficient, basal metabolic rate and energy expenditure of female university students. One-day activity diaries were collected from 95 female university students in Seoul. Body composition was measured by Inbody 720. Subjects spent 7 hr 8min on sleeping, 6 hr 31min on studying, 2 hr 50min on physiological activity, 2 hr 3min on leisure, 2 hr 2min on walking and jogging, 1 hr 58 min on commuting and 22min on house chores. The activity coefficient of these subjects was 1.58. The comparison of body composition of subjects according to PAL showed that body weight, body fat mass, arm circumference and arm muscle circumference of physically active group were significantly higher than those of the sedentary group. BMR calculated by Harris-Benedict (H-B) formula and DRI formula and BMR measured by Inbody 720 was 1375 kcal, 1306 kcal and 1209 kcal, respectively. Total energy expenditure (TEE) examined by one-day activity diaries and calculated by H-B formula and estimated energy requirement (EER) formula in DRI was 2102.1 kcal, 2184.4 kcal, and 2164.5 kcal, respectively. The Pearson correlation coefficient between TEE examined by one-day activity diaries and H-B TEE was 0.795 (p < 0.001) while that between TEE examined and DRI EER was 0.604 (p < 0.001). Overall data indicated that female university students seemed to be less active. Therefore it is recommended that universities develop good exercise programs for their students. Further studies are needed to generate more meaningful results with a larger sample size and using machine attached to the body, which are able to detect physical activity more accurately.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Measurement of Energy Expenditure Through Treadmill-based Walking and Self-selected Hallway Walking of College Students - Using Indirect Calorimeter and Accelerometer
Ye-Jin Kim, Cui-Sang Wang, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(6): 520. CrossRef - A Study on the Body Composition, Physical Activity Level, Basal Metabolic Rate, and Daily Energy Expenditure of Elderly in Busan
Hwa-Jae Lim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 178. CrossRef
- Measurement of Energy Expenditure Through Treadmill-based Walking and Self-selected Hallway Walking of College Students - Using Indirect Calorimeter and Accelerometer
- 1,685 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Assessment of Energy Intake and Physical Activity Level for Korean Farmers to Establish Estimated Energy Requirements during the Off-Season for Farmers
- Sun Hee Lee, Seo Eun Yeon, Hee Ryoung Son, Jung Sook Choi, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(5):652-663. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.652
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to assess the physical activity level of Korean farmers to establish estimated energy requirements during the off-season. Subjects were 90 healthy males (n = 25) and females (n = 65). Body weight, height and body fat and muscles of subjects were measured. The prevalence of obesity among farmers was 56.7% according to the BMI. The farmers spent about 18 hours 7 minutes (75.5%) in sleeping and resting. The farmers spent about 19 hours 56 minutes (83.1%) out of 24 hours (one day) in "sedentary activities" and spent about 3 hours 56 minutes (16.4%) in "light activities". Physical activity level (PAL, activity coefficient) of female farmers was 1.42 which was not significantly higher than that (1.37) of male farmers. Estimated energy requirements (EER) for farmers who were different in age groups and gender were calculated. For example, the EERs for male and female farmers were 2190 kcal/day and 1712 kcal/day, respectively. The daily energy intakes of male and female farmers were 1803 kcal/day and 1610 kcal/day, respectively. The EER of male farmers was 2190 kcal/day which was significantly higher than that (1803 kcal/day) of the recommended daily energy intake of male farmers. The results of this study suggest that estimated EER of farmers should be modified according to seasonal workload and energy balance of farmers should be evaluated to prevent obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
Ho-Jung Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Yookyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 320. CrossRef - Water intake and oral disease symptoms in adolescents: a cross-sectional study conducted in Korea in 2021
So-Yeong Kim, Sun-A Lim
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2023; 23(5): 343. CrossRef - The Gangwon Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Study: Methods and Initial Baseline Data
Yoon Jeong Cho, Sohyun Park, Sung Soo Kim, Hyo Jin Park, Jang Won Son, Tae Kyung Lee, Sangmo Hong, Jee-Hyun Kang, Seon Mee Kim, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won Jun Kim, Young Eun Seo, Yoosuk An, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Sookyoung Jeon, Kyungho Park, Bong-Soo Kim, Cha
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(4): 303. CrossRef - Establishment and future tasks of estimated energy requirement in 2020 dietary reference intakes for Koreans
Eun-Kyung Kim, Oh Yoen Kim, Jonghoon Park, EunMi Kim, Juhyeon Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 573. CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Habits, Life Stress and Nutrition Knowledge of High School Students in Gyeonggi Area
Kyung Ae Park, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 126. CrossRef - Amounts of physical activity and sedentary behavior patterns in older adults: using an accelerometer and a physical activity diary
Na-Young Go, Didace Ndahimana, Eun-Kyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(1): 36. CrossRef - A Study on the Body Composition, Physical Activity Level, Basal Metabolic Rate, and Daily Energy Expenditure of Elderly in Busan
Hwa-Jae Lim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 178. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Dietary Behavior in Nursing Students
Eun Kyung Byun, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(2): 81. CrossRef - Effects of High-speed Elastic Band Training on Physical Fitness and Muscle Function in Rural Community-dwelling Elderly: a Single-blinded Randomized Controlled Trial
Jun Seok Son, Dongheon Kang, Dong Hyun Yoon, Dae-Young Kim, Hee-jae Kim, Jang Hoe Kim, Byunghun So, Han Sol Song, Su Seung Hwang, Wook Song
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2015; 15(4): 254. CrossRef - The Measurements of the Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) and the Accuracy of RMR Predictive Equations for Korean Farmers
Hee-Ryoung Son, Seo-Eun Yeon, Jung-Sook Choi, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 568. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Dietary Action Guide for Adolescence among Middle and High School Students in Korea
So-Hyun Park, Hae-Ryun Park, Soo-Bin Jeon, So-Yeon Jeong, Zuunnast Tserendejid, Jung-Sook Seo, Kyung-Hae Lee, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(2): 133. CrossRef - Comparison of Life Style, School Achievement and Snaking Behaviors among Underweight and Overweight Adolescents
Hye-Kyung Kim, Jin-Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2011; 44(2): 131. CrossRef
- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
- 1,484 View
- 0 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Assessment of Physical Activity Level of Korean Farmers to Establish Estimated Energy Requirements during Busy Farming Season
- Eun Kyung Kim, Sun Hee Lee, Su Young Ko, Seo Eun Yeon, Jeong Sook Choe
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):751-761. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.751
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to assess the physical activity level of Korean farmers to establish their estimated energy requirements during busy farming season. 113 farmers (mean age 51.9 +/- 7.2 years, male 42, female 71) who own farmland area above 300 pyung participated in measurement of body weight and height and interviewing of one-day activity diaries. There was no significant difference in age, BMI between male and female. Obesity prevalence according to BMI among male and female farmers was 40.5% and 50.7% respectively. The farmers spent about 7 hours in sleeping and spent about 4 hours 35 minutes working on the farm and spent about 15 hours 30 minutes (64.6% of 24 hours) in "very light activities" and spent about 3 hours 31 minutes (14.7%) in "light activities". Physical activity level (PAL, activity coefficient) of male farmers was 2.63 which was significantly higher than that (2.19) of female farmers (p < 0.05). Estimated energy requirements (EER) for farmers who were different in age and gender were suggested. For example, the estimated energy requirements for male and female farmers were 3058 kcal/day and 2279 kcal/day, respectively. The results of this study suggest that estimated energy requirements (EER) of farmers should be differentiated according to seasonal workload and energy balance of farmers should be evaluated to prevent obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Gangwon Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Study: Methods and Initial Baseline Data
Yoon Jeong Cho, Sohyun Park, Sung Soo Kim, Hyo Jin Park, Jang Won Son, Tae Kyung Lee, Sangmo Hong, Jee-Hyun Kang, Seon Mee Kim, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won Jun Kim, Young Eun Seo, Yoosuk An, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Sookyoung Jeon, Kyungho Park, Bong-Soo Kim, Cha
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(4): 303. CrossRef - Development of physical activity classification table for Koreans: using the Compendium of physical activities in the United States
Eun-Kyung Kim, Ha-Yeon Jun, Ji-Yeon Gwak, Justice Otoo Fenyi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(2): 129. CrossRef - Establishment and future tasks of estimated energy requirement in 2020 dietary reference intakes for Koreans
Eun-Kyung Kim, Oh Yoen Kim, Jonghoon Park, EunMi Kim, Juhyeon Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 573. CrossRef - Amounts of physical activity and sedentary behavior patterns in older adults: using an accelerometer and a physical activity diary
Na-Young Go, Didace Ndahimana, Eun-Kyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(1): 36. CrossRef - Comparison of Physical Activity Level, Physical Activity Pattern and Energy Expenditure in Male and Female Elementary School Soccer Players using Accelerometer and Physical Activity Diary
Hae-Sun An, Su-Ji Choi, Mo-Ran Lee, Jung-Sook Lee, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(6): 529. CrossRef - A Study on the Body Composition, Physical Activity Level, Basal Metabolic Rate, and Daily Energy Expenditure of Elderly in Busan
Hwa-Jae Lim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 178. CrossRef - Comparison of total energy expenditure between the farming season and off farming season and accuracy assessment of estimated energy requirement prediction equation of Korean farmers
Eun-Kyung Kim, Seo-Eun Yeon, Sun-Hee Lee, Jeong-Sook Choe
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(1): 71. CrossRef - The Measurements of the Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) and the Accuracy of RMR Predictive Equations for Korean Farmers
Hee-Ryoung Son, Seo-Eun Yeon, Jung-Sook Choi, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 568. CrossRef - Assessment of Physical Activity Pattern, Activity Coefficient, Basal Metabolic Rate and Daily Energy Expenditure in Female University Students
Yoonji Park, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(1): 45. CrossRef - Assessment of Energy Intake and Physical Activity Level for Korean Farmers to Establish Estimated Energy Requirements during the Off-Season for Farmers
Sun-Hee Lee, Seo-Eun Yeon, Hee-Ryoung Son, Jung Sook Choi, Eun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(5): 652. CrossRef
- The Gangwon Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Study: Methods and Initial Baseline Data
- 1,205 View
- 4 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Daily Sleep Duration with Obesity, Macronutrient Intake, and Physical Activity
- Inkyung Baik, Chol Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(3):315-323. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.3.315
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are a few studies that reported the association of sleep duration with calorie intake and energy expenditure. Using cross-sectional data from a population-based prospective study, we evaluated the association of sleep duration with indicators of obesity including body mass index and waist circumference, calorie intake and its proportion of macronutrients, and physical activity. The study subjects were 4,226 male and female adults, who were aged 40 to 69 years and were free of diagnosed cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia at baseline. Robust regression analysis was used to analyze associations. The study found that sleep duration is inversely associated with waist circumference, calorie intake, and percent of calories from fat intake and is positively associated with percent of calories from carbohydrate intake and physical activity. The inverse association between sleep duration and waist circumference was stronger among men than among women. The inverse association between sleep duration and calorie intake was stronger among women than among men and such association was also stronger among obese persons than those with a normal body mass index. The positive association between sleep duration and physical activity was strongly demonstrated regardless of sex or obesity. Physical activity is positively associated with sleep duration independent of potential confounding factors including age, sex, income, occupation, marital status, education, smoking status, waist circumference, calorie and macronutrient intake, and alcohol intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Anti-Stress and Sleep-Inducing Effects of a Zizyphus jujuba Mill.-Hypericum perforatum L. Mixture and Its Bioactive Compounds
June-Seok Lim, Yeon-Seok Seong, Geon Oh, Ji-Hyun Im, Xiaolu Fu, Min-Hye Kim, Jin-Ho Roh, Ok-Hwan Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(6): 489. CrossRef - A comparative study on eating habits and mental health of Korean middle school students according to their bedtime across regions: using data from the 2020–2022 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Sarim Kim, Jiyoung Jeong, Juyeon Kang, Jihye Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(2): 269. CrossRef - Grit in Community‐Dwelling Older Adults with Low Back Pain Is Related to Self‐Physical Training Habits
Tsubasa Kawasaki, Ryosuke Tozawa
PM&R.2020; 12(10): 984. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Dietary Habits according to Sleep Duration in Korean Adults Based on the 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(4): 237. CrossRef - The longitudinal influence of child maltreatment on child obesity in South Korea: The mediating effects of low self-esteem and depressive symptoms
Aely Park, Youngmi Kim
Children and Youth Services Review.2018; 87: 34. CrossRef - Dietary behavior status and its association with study-related factors in middle school students in Gyeonggi area
Myoung Sook Lee, Wha Jin Hyun, Kyung Hee Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 455. CrossRef - Relationship between Bone Mineral Density and Bone Metabolic Biochemical Markers and Diet Quality Index-International(DQI-I) in Postmenopausal Obese Women
Yeonah Jeong, Misung Kim, Saeron Shin, Ahreum Han, Geomsuk Seo, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 284. CrossRef - Difference in Sleep Circadian Rhythm and Sleep Quality between Normal-weight and Obese Group
Hyun Jin Suk, Yeon Kyung Na, Hae Sook Hong
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(4): 309. CrossRef - Experiences of Health Related Lifestyles in High Body Fat but Non-obese Female College Students in Korea
Jeongsoo Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5(1): 68. CrossRef - Predictors of Poor Sleep Quality among Nursing Students
Young Ran Chae, Dong Hee Choi, Su Jeong Yu
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(2): 98. CrossRef - Correlation between Sleep Quality and Snack Intake in Third Year Middle and High School Students in the Gwangju Area
Hyo Bok Kim, Yang Won Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(2): 212. CrossRef - A Study on the Correlation of the accompanying symptoms, Heart Rate Variability and Body Component Analysis in 350 Insomnia Patients
Ji-Won Ha, Bo-Kyung Kim, Jin-Hyeong Jung
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2012; 23(3): 47. CrossRef - Physical activity level, total daily energy expenditure, and estimated energy expenditure in normal weight and overweight or obese children and adolescents
Myung Hee Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(6): 511. CrossRef
- Analysis of Anti-Stress and Sleep-Inducing Effects of a Zizyphus jujuba Mill.-Hypericum perforatum L. Mixture and Its Bioactive Compounds
- 1,258 View
- 0 Download
- 13 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on the Physical Activity, Food Habit and Nutrient Intakes of Adults in Pusan
- Hwa Jae Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(4):460-474. Published online August 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to assess the physical activity, food habit and nutrient intakes by gender and age groups in 193 adults aged 20-59 years (84 men and 109 women) in Pusan. Data for physical activity and dietary survey was assessed by a questionnaire and 24hr recall method. The mean BMIs of men and women were 24.0 and 22.2 respectively and BMI of women in the 20-29 years group (20.9) was significantly lower than that of women in the 30-49 and 50-59 years group (22.7, 23.2) (p < 0.01). 56.0% for men and 44.0% for women exercised regularly. The mean exercise duration per once of men (69.7 minutes) was significantly higher than that of women (52.4minutes) (p < 0.01). The mean exercise duration per day was 36.0 minutes for men and 29.9 minutes for women. 67.9% for men and 78.0% for women often skipped meals and 68.4% for men and 69.4% for women skipped breakfast in the main. The mean energy intake of men was 2067.2 kcal and that of women was 1783.1 kcal comprised of 87.2% and 92.1% of the Estimated Energy Requirements (EER). The mineral intakes of men and women were over Recommended Intake (RI) and Adequate Intake (AI) except calcium and potassium. The mean calcium intake was 88.3% for men and 84.0% for women of RI. The mean potassium intake was 63.3% for men and 59.2% for women of AI. The mean vitamin intakes of men and women were over RI and AI except vitamin C and folic acid. The mean vitamin C intake was 92.5% for men and 85.6% for women of RI. The mean folic acid intake was 76.6% for men and 70.0% for women of RI. The mean energy, protein, sodium and zinc intakes of men were significantly higher than those of women (p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05). The mean vitamin B6, vitamin C and folic acid intakes of men in the 20-29 years group were significantly lower than those of men in the 30-49 and 50-59 years group (p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.05). For energy, proportions of subjects with intake levels less than 90% EER were 64.3% for men and 56.0% for women. For calcium, proportions of subjects with intake levels less than Estimated Average Requirement (EAR) were 52.4% for men and 59.6% for women. For folic acid, proportions of subjects with intake levels less than EAR were 78.6% for men and 83.5% for women. For iron and phosphorus, proportions of women (36.7%, 14.7%)with intake levels less than EAR were significantly higher than those of men (6.0%, 1.2%) (p < 0.01, p < 0.001). For men, age was positively correlated with intakes of potassium, vitamin B6, vitamin C and folic acid (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.01). For men, weight showed significantly negative correlations with intakes of carbohydrate, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, vitamin B6 and folic acid (p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.01) and BMI showed significantly negative correlations with protein, lipid, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, vitamin E and folic acid (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05) For men, exercise duration per once showed significantly positive correlations with intakes of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, niacin, vitamin C and folic acid (p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.01, p < 0.01, p < 0.05). Therefore, nutritional education for adult health management is needed by gender and age groups.
- 347 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Assessment of Physical Activity, Activity Coefficient of Preschool Children and Actual Condition of Daycare Center Outdoor Play
- Jae Hee Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):777-788. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to assess physical activities and activity coefficient of preschool children and was to give some concrete information to activate outdoor play and to probe the suggestions to activate outdoor play. 42 preschool children (17 boys and 25 girls) were included. Body weight and height were measured and one-day activity diaries were collected by interviewing with their parents and kindergarten teachers. To measure physical activity during outdoor play, this study was researched the current conditions and content of outdoor play activity in daycare centers, and teacher's perceptions of that outdoor play. The average age of the subjects was 5.0 years. Average height, weight, body fat and body muscle of subjects were 108.9 cm, 18.9 kg, 17.7% and 26.8%, respectively. The subjects spent about 10 hours 39 minutes sleeping; 4 hours 16 minutes personal hygiene and computer working. They spent 88.2% of 24 hours (one day) in "very light activities" and 11.3% in "light activities". Activity coefficient (1.34) of weekday was significantly higher than that of weekend (1.21). And in this study, it was found that most of daycare centers (87.7%) have outdoor play space, 95.2% of them were garden. The teachers recognized that have a outdoor play frequency everyday (48%), three or four times (46%) in a week but they have three or four times (38%), one or two times (30%) because of various indoor program. Also, they recognized that have a outdoor play expending time 21- 30 minutes (48%), 31-40 minutes (26%) but they have 21-30 minutes (64%). They answered that have frequency and expending time less than their recognition of outdoor play. Most of daycare center teachers perceived outdoor play to be as important as indoor play, and the teachers believed outdoor play supports children's physical, cognitive, social, and language development. The results of this study may be used to utilize as a basic data for estimate physical activity for preschool children and developed that exercise program to increase physical activity of daycare center outdoor play.
- 323 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of Weight Maintenance Behavior among Female University Students
- Seolhyang Baek, Eunjeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(2):150-159. Published online April 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Since the 1980's, despite the conclusion of a number of studies in Western countries focusing upon weight maintenance there has been no similar research in Korea which takes into account the contrasts of culture and eating habits between east and west. In order to identify eating, snacking and exercise behaviors, 24 female university students who have maintained weight for at least a year were enrolled for an 11 day study. Participants were required to sign into the program and complete the questionnaire, answering questions by concerning what they ate and did everyday. After excluding unanswered questions, data over 11 days were exported into the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet, then both ANOVA and Kendall's tau correlation were applied with SPSS. 75% of weight maintainers had normal BMI (18-23.5) in relation to Korean standard, and appeared to eat a main meal smaller than moderate in portion size. Only two days showed that amount of breakfast eaten negatively correlated with lunch (p < 0.05), while no correlations between amounts of lunch and dinner eaten over all study period. Compared with breakfast or lunch, dinner was usually larger in portion size, but some variables such as TV viewing, restaurant meals, number of people at dinner table seemed not correlated with amount of dinner eaten. In addition, the weight-maintainers reported they rarely consumed snacks or sweetened beverages. Unlike their western counterparts, few participants reported that they took part in regular exercise during the day, which may lead us to the conclusion that these young female weight maintainers seem to maintain their weight with eating behaviours such as 'eat small portion', 'avoid snacking' and 'avoid soft drinks' rather than doing regular exercise. The study did not include a control group, and was foreshortened due to technical difficulties so it may be necessary to repeat the study while considering these two points.
- 298 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Weight Control Behavior and Self-esteem between Healthy Weight and Obese Children
- Seolhyang Baek, Junghee Yeo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(5):562-574. Published online October 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The study compared eating and physical activity related behaviors and self-esteem between healthy weight and obese children by presenting 175 primary school students in Busan City and Gyeongsang province with a self-reported questionnaire and Coopersmith's self-esteem inventory. The questionnaire was composed of 25 items, weighted primarily by a Likert scale. The self-esteem inventory presented to the students comprised 25 "Yes" or "No" response questions to different statements. The study found obese children were more likely to think they always had to control their weight (p = 0.000), reportedly measuring their weights significantly more than the healthy weight children. Also the study found that obese children are significantly more likely than healthy weight children to go on a diet, however neither group were successful in losing weight as the duration of the diet in 79.5% of the total sample lasted no longer than one week. In comparison to healthy weight children, obese children reported that they consumed fewer snacks during the day, avoided snacking subsequent to an evening meal and exercised more frequently for as long as physically possible. Interestingly, we found no difference of reported self-esteem between groups, though the obese group were more likely to answer that their parents did not understand them (p = 0.055). Based on these findings, we concluded that the obese children who participated in the study were more aware of their body weights than the healthy weights children. It may be necessary to investigate further the relationship between self-esteem and participants' weights while considering other variables such as personality and body image.
- 366 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Status and Associated Factors in Premenopausal Working Women
- Hwa Jae Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(1):79-90. Published online February 28, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to estimate serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and to evaluate the relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and associated factors. The subjects were 61 premenopausal working women aged 30 - 49 y in Busan. The serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level was measured by radioimmunoassay. Data for physiological characteristics, lifestyle factors, physical activity and nutrient intake were assessed by questionnaire including information about outdoor activity time, daily activity diary and 24 hr recall method. The mean vitamin D intake was 3.12 ug, which corresponded to 62.5% of the Korean RDA. The mean level of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D was 31.0 ng/mL. Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D (<25 nmol/L) was not found in the subjects. The serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level showed positive significant correlations with exercise hours, daily energy expenditure, hours of outdoor activity per weekdays (p< 0.001, p< 0.05, p< 0.05). Exercise hours were found to be the most important determinant of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level. Therefore nutritional education for increasing hours of physical activity including indoor and outdoor exercise, is needed for premenopausal working women to increase vitamin D status.
- 292 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Factors Effecting the Bioavailability of Carotenoid in Elderly Korean Women
- Jae Yeon Lim, Hae jeung Lee, Seon Joo Park, Hay Mie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(6):822-830. Published online December 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Carotenoid-rich foods focus one's attention on the prevention age-related diseases. This study was conducted to investigate the carotenoid status and look into the factors that affect the bioavailability of carotenoid in 121 elderly nonsmoking Korean women. Carotenoids and lipids in plasma, and nutrient intakes including carotenoid were studied. The mean plasma total-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and triacylglycerol concentrations were 220.0 mg/dl, 49.5 mg/dl, 139.2 mg/dl and 157.4 mg/dl, respectively. Significantly positive correlations were found between the plasma lutein + zeaxanthin, lycopene and beta-carotene concentrations and the intake of fruits (r = 0.17, r = 0.20, r = 0.19). However, significantly negative correlations were found between the plasma lutein+zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene concentrations that adjusted for carotenoid intakes and intakes of vegetables (r = - 0.21, r = - 0.19), and between plasma lutein+zeaxanthin, lycopene and beta-carotene concentrations that adjusted for carotenoid intakes and intakes of fruits (r = - 0.21, r = - 0.18, r = - 0.24). After the adjustment for plasma lipids, there was no correlation between the plasma carotenoid concentrations and the carotenoid-rich foods. However, after adjustment for fiber intake, significantly strong positive correlations were found between the plasma carotenoid concentrations and carotenoid-rich foods. The plasma levels of carotenoid biomarkers (plasma carotenoid concentrations adjusted for dietary fiber intakes) decreased with age, and the plasma levels of lycopene biomarkers (plasma lycopene concentrations adjusted for dietary fiber intakes) increased with regular exercise. However alcohol drinking had no impact. These results suggested that age, physical activity, and dietary fiber intake affected the bioavailability of carotenoid. Therefore, when the elderly have carotenoid-rich foods, they should consider ways of increasing the bioavailability of carotenoid through cooking methods and physical activity.
- 307 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Television Watching, Family Social Class, Parental Overweight, and Parental Physical Activity Levels in Relation to Childhood Overweight
- Gun Ae Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(2):177-187. Published online April 30, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was done to determine the factors associated with childhood overweight in 721 sixth grade elementary school students, in Busan. The students' heights, weights, waist circumferences and triceps-skinfold thicknesses were measured using standard techniques. Other data were collected using a questionnaire that included information about physical activity, television watching, and the amount of exorcise taken during leisure times, family history of diseases related to obesity: social data including family income, parents' education and occupations, eating behaviors; parental weights and heights; and parental activity levels. Childhood overweight was defined as a body mass index at or above the 85th percentile for age and sex. The prevalence of overweight revealed no significant difference between sexes, (24.2% in boys and 22.03% in girls). The risk of childhood overweight was significantly greater if either the mother or the father were overweight. The odds ratio for childhood overweight associated with maternal overweight was 5.045 (94% CI : 3.262-7.801), and 2.727 (95% CI : 1.764-4.218) was the case for parental overweight. Children having a history of hear diseases had higher odds ratios than those who did not. The odds ratios for overweight associated with income were not different. However, a higher odds ratio for overweight was observed in children whose fathers had only an elementary or middle school education than those whore fathers had a high school or college education. Children whose fathers' occupations were service workers or shopkeepers (OR : 3.314, 95% C = 1.851-5.934) or had no occupation (OR = 3.756, 95% CI : 1.898-7.430) had a treater risk of overweight than those whose fathers' were professionals or once workers. The risk of overweight increased in children having more irregular meal times and faster eating times, rather than those having an intake pattern of high energy and sugar containing floods. The amount of exercise taken during leisure times, and daily physical activity showed no difference between overweight and non-overweight children. However, television watching time, especially on weekends, was greater in overweight children than in non-overweight children. Television watching time was positively correlated with BMI, triceps-skin(31d thickness, waist circumference and waist/height ratio. Therefore, television watching was found to be a useful predictor of overweight in children. Television watching in children was negatively related to paternal activity levels, and positively related to parental television watching time. In fact, fathers whose children were overweight were physically less active than fathers whose children were non-overweight. Parents appeared to be a strong influence on their children's physical activity levels. In conclusion, a low family social class, defined on the basis of the father's occupation or education, parental overweight, increased television watching, and unhealthy physical activity levels in parents were all considered risk factors for childhood overweight. Among these, television watching time and lack of physical activity were considered to be the most important risk factors that could be easily modified for the prevention of and intervention in, overweight in children.
- 261 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Riboflavin Status between Traditional Farming Women and Commercial Farming Women in Korea
- Hwa Jae Lim, Jin Sook Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(5):701-710. Published online December 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - this study was undertaken to compare the riboflavin status of rural women with different physical activity intensity and to determine factors influencing biochemical fiboflavin status. The study was carried out over three different farming seasons : planting (June), harvest(October) and interim(February) in two rural regions of Korea. One was a traditional farming region, the other a commercial farming region with heavier work intensity. Twenty women in the traditional region and eighteen women in the commercial region were involved. The intensity of physical activity was determined by a daily activity record. Body composition was assessed by bioelectrical impedence. Dietary riboflavin intake was measured by the food frequency method. Riboflavin biochemical status was assessed by erythrocyte glutathione reductase activity coefficient (EGR AC) and ruinary riboflavin excretion. The results from the EGR AC and urinary riboflavin excretion during the period showed the overall riboflavin status of the commercial farming women was significantly worse than that of the traditional farming women(EGR AC p<0.0001, urinary riboflavin excretion p<0.05). The traditional farming group had about 40% with risk of riboflavin deficiency, whereas the commercial farming group had about 70%. Overall mean nutrient intake was not significantly different between the two groups, however, overall mean percent lean body mass representing long term physical activity was significantly higher in the commercial farming group (<0.005). It appears that the biochemical riboflavin status of traditional farming women was significantly influenced by riboflavin intake and crude nitrogen balance while the biochemical riboflavin status of the commercial farming women was significantly influenced by riboflavin intake and percent of lean body mass over the three seasons.
- 326 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



