- [Korean]
-
Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
-
Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):175-182. Published online June 30, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00094
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material
- Objectives
This study analyzes the status of nutrition education media among Korean older adults based on the transtheoretical model (TTM) and their food literacy to propose effective strategies for the development and utilization of educational media.
Methods
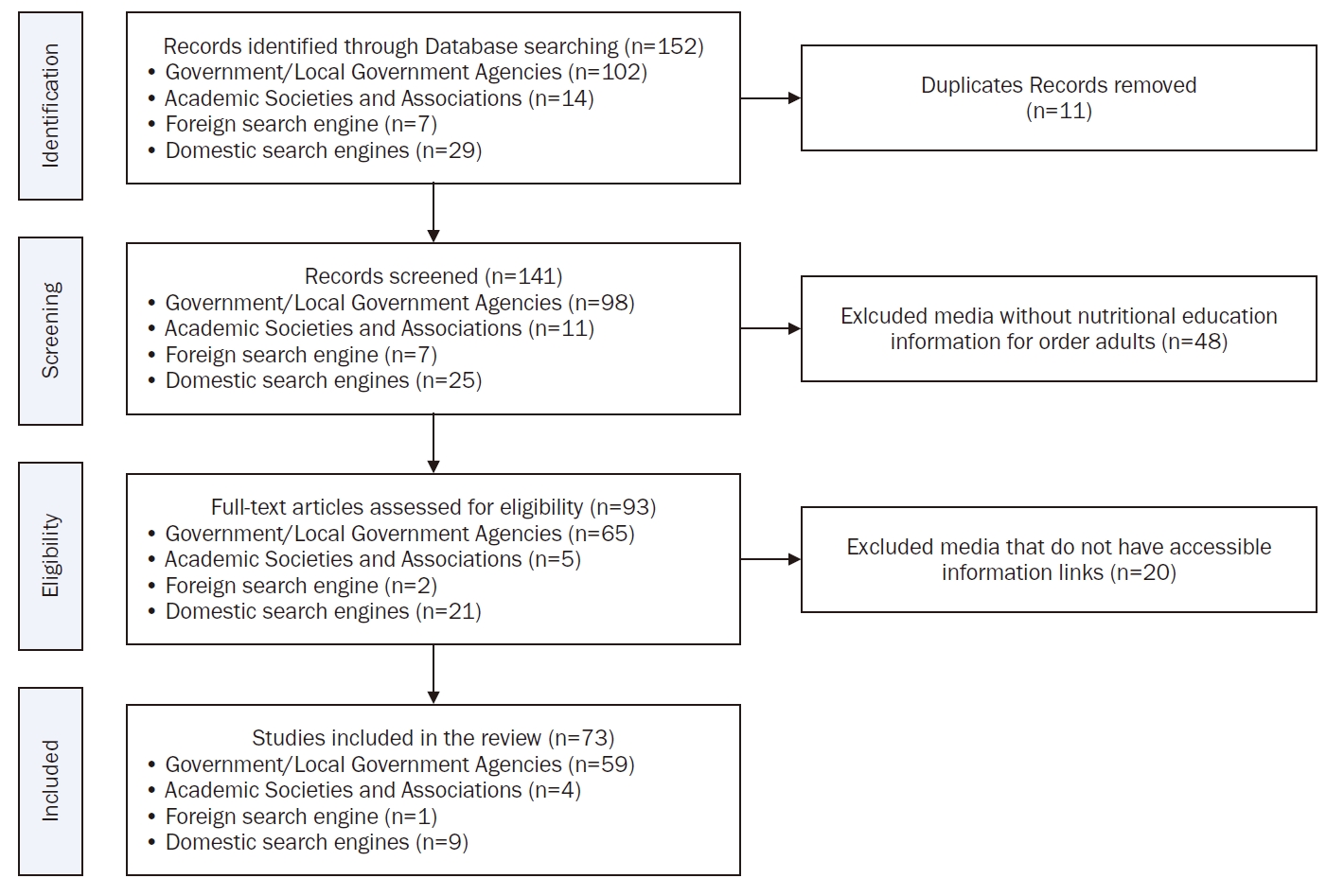
A literature review was conducted using The Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) protocol. The literature search was performed using government and local government agency websites, as well as those of affiliated institutions, health and nutrition-related academic societies, and academic search engines. A total of 144 studies were identified, and after a cross-evaluation by two reviewers based on the literature selection criteria, 73 studies were included in the final analysis.
Results
Among the types of nutrition education media, card news had the highest proportion, followed by video media. The development and distribution of nutrition education media for older adults were primarily carried out by government and local government agencies, as well as related affiliated institutions, accounting for 80.8% (n = 59) of the total. When nutrition education topics in the media were categorized according to the stages of behavior change in the TTM, the largest proportion, 64.6% (n = 61), was applicable to the precontemplation and contemplation stages. When categorized by food literacy domains, all topics fell under the categories of nutrition and safety.
Conclusion
Nutrition education media for older adults were found to be primarily focused on knowledge acquisition and information delivery, making them mostly applicable to the precontemplation and contemplation stages of behavior change. The concept of food literacy addressed in the different types of media was limited to the domains of nutrition and safety, with no content covering the cultural and relational domains or the social and ecological domains. For tailored nutrition education, it is necessary to develop diverse educational materials that comprehensively reflect each stage of the TTM and all aspects of food literacy.
- [Korean]
-
Program Evaluation using the RE-AIM Framework: A Systematic Review and Application to a Pilot Health Promotion Program for Children
-
Ji-Eun Lee, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim, Jae-Heon Kang, Ji-Yun Hwang
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(4):296-308. Published online August 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.4.296
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
This study aimed to develop evaluation criteria for the elementary-school-based health promotion program using the RE-AIM framework and to examine their feasibility.
Methods
Previous evaluation studies on health interventions for elementary-school students using the RE-AIM framework were reviewed systematically to identify appropriate evaluation criteria. A diet and physical activity intervention based on the transtheoretical model was implemented in a pilot study using the “Happy Me” application. The feasibility of using the RE-AIM framework to evaluate it was examined.
Results
The review yielded the following evaluation criteria: “reach,” the ratio of participants out of the total target population; “efficacy/effectiveness,” the difference in outcomes between the intervention and control groups, or between a pre- and post-test; “adoption,” the rate of use of the program and participation in the next stage of the program; “implementation,” the progress on the program components; “maintenance,” the participants’ and teachers’ intention to continue using the program. The pilot study reached 76.6% of the targeted population. The intake of sugar-sweetened beverages decreased (P < 0.0001), and the duration of walking increased (P < 0.0001). Other indicators could not be evaluated; therefore, potential indicators were suggested.
Conclusions
This study produced feasible evaluation criteria for elementary-school-based health promotion using the RE-AIM framework. Nevertheless, the feasibility needs to be validated with a broader range of studies and long-term interventions.
- [Korean]
-
Using Service Design Tools in Community Nutrition Research: A Case Study in Developing Dietary Guidelines for Young Adults
-
Eunbin Jo, Jae Eun Shim, Hyun Joo Ryou, Kirang Kim, Su Jin Song, Hyun Ja Kim, Jeong Sun Ahn, Kwang-il Kwon, Hye Young Lee, Sohyun Park
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):177-191. Published online June 30, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.177
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
Recent epidemiological data reported that young adults in their 20 ~ 30s are a vulnerable population with unhealthy dietary practices and a few signs of deteriorated health indicators. However, there are no dietary guidelines that are specifically developed for the young adult population. This study introduces some data collection tools that are mostly used in the service design field, and demonstrates how these tools can be used in nutrition research for developing dietary guidelines for specific target groups.
Methods
To understand the context of food choices among young people, 39 people were enrolled to complete a probes booklet. Thematic analysis and word cloud were performed to capture the main themes from the probes and a persona was developed based on the findings.
Results
Data from the probes enabled us to grasp the various contextual meanings of eating practices among young people. Most participants understand what a healthy diet is and often have a willingness to practice it. However, there were very few participants who were following the practices. We created four types of persona for developing dietary guidelines: healthy eating, emotional eating, convenient eating, and trendy eating.
Conclusions
Probes and persona were used in order to understand the lives of young adults and develop targeted messages. We hope that this introduction will be helpful to researchers who are looking for new ways of understanding their target population in the field of community nutrition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 495. CrossRef
-
1,718
View
-
29
Download
-
1
Crossref
- [Korean]
-
Basic Concepts and Detailed Dimensions of Food Security and Related Indicators for Policy Development and Evaluation
-
Sohyun Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):429-440. Published online December 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.429
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
Standardized guidelines and reference points for a food security policy are necessary to guarantee that basic social safety nets work properly. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the basic concepts and detailed dimensions of food security, including the potential relevant indicators, and sought to establish standardized well-being baselines.
Methods
A literature review and 14 expert roundtable discussions were carried out to analyze and extract the key concepts of food security. After determining these concepts and detailed dimensions of food security, a conceptual framework was modeled. Then, indicators for each local government that could be monitored and evaluated for each sub-area were suggested.
Results
The concept of food security was defined as follows: Individuals should be provided with sufficient, safe, and quality food, which should be accessible to the community and available for use to achieve health and well-being. In addition, food security should be ensured sustainably in a changing environment. Four dimensions were suggested while conceptualizing food security. First, sufficient food, which means sufficient food supply in quantity, quality, and safety. Second, equitable food which includes creating environments in which high-quality and safe food can be purchased at an appropriate price and can be provided regardless of the socioeconomic gap. Third, healthy food which should be provided to promote people’s health and happiness through the eco-friendly consumption of food.
Fourth, sustainable food, which can be supplied in a sustainable manner and as part of an eco-friendly food system that considers the conservation of natural environments.
Conclusions
The basic concepts and detailed areas of food security including the potential indicators proposed in this study, may be useful for developing and implementing various policies and programs to support food and nutrition security in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Achieving National Food Security in Sub‐Saharan African Countries: The Role of Foreign Agricultural Aid
Mehmet Balcilar, Godwin Olasehinde‐Williams, Berkan Tokar
Food and Energy Security.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction model for identifying a high-risk group for food insecurity among elderly South Koreans
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,302
View
-
23
Download
-
2
Crossref
- [English]
-
Defining Food Literacy and Its Application to Nutrition Interventions: A scoping Review
-
Hye lim Yoo, Eun bin Jo, Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):77-92. Published online April 30, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.77
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
Food literacy (FL) can be an important concept that embodies the nutritional capabilities of individuals. The purpose of this study was to introduce the definition and core elements of FL from previous literature, to summarize measurement tools and intervention programs with FL, and to suggest the direction of future research and programs to integrate the concept of FL.
Methods: The literature review was conducted through PubMed and Google Scholar databases by combining the search term ‘food literacy’ with ‘definition’, ‘measurement’, ‘questionnaire’, ‘intervention’, and ‘program’. Among the 94 papers primarily reviewed 31 manuscripts that suited the purpose of the study were used for analyses.
Results: There is no consensus on the definition of FL that encompasses the multidimensional aspects of the concept. The definitions of FL were slightly different depending on the authors, and the interpretation of the core elements also varied. Based on the review, we propose a framework of FL that is in line with the current discussion among international researchers. This focuses on the core elements adapted from health literacy, namely functional, interactive, and critical FL. Specifically, we suggest some detailed elements for interactive and critical FL, which were often the subject of divergent views among researchers in previous literature. We found that most of the tools in the reviewed literature provided information on validity and reliability and were developed for a specific target population. Also, most of the tools were focused on functional FL. Similarly, most of the interventions targeted functional FL.
Conclusions: This study reviewed the definition and core elements of FL, available measurement tools, and intervention programs using validated tools. We propose the development of tools with sound reliability and validity that encompass the three core elements of FL for different age groups. This will help to understand whether improving food literacy can translate into better nutritional intake and health status among individuals and communities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A qualitative study of facilitators and barriers to healthy eating among older adults in China based on nutritional literacy and the capability opportunity motivation behaviour model
Qian Li, Qian Wang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 175. CrossRef - How food literacy levels shape healthy eating intentions: a cross-sectional study of adults in Shandong Province, China, using the theory of planned behavior
Baicai Xu, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 566. CrossRef - The Concept and Application of the Healing Industry: A Scoping Review
Ji Seong Yi, Sung Yee Yoon, Jae Soo Kim
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2025; 28(4): 537. CrossRef - Development of an evaluation tool for dietary guideline adherence in the elderly
Young-Suk Lim, Ji Soo Oh, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - The development, psychometric properties and refinement of a food literacy scale for specific and general application
Hennie Fisher, Marietjie Potgieter
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2024; 35: 100862. CrossRef - Status of Food Literacy and Association with the Nutrition Quotient among Korean Adults
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Human Ecology Research.2024; 62(3): 399. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of a food literacy pilot program for university students: using a mixed-methods research approach
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(6): 885. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Who has a high level of food literacy, and who does not?: a qualitative study of college students in South Korea
Hyelim Yoo, Eunbin Jo, Hyeongyeong Lee, Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1155. CrossRef - Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 495. CrossRef - Food literacy and its relationship with food intake: a comparison between adults and older adults using 2021 Seoul Food Survey data
Seulgi Lee, Sohyun Park, Kirang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023062. CrossRef - Nutrition and Food Literacy in the MENA Region: A Review to Inform Nutrition Research and Policy Makers
Hala Mohsen, Yonna Sacre, Lara Hanna-Wakim, Maha Hoteit
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 10190. CrossRef - Development of a Food Literacy Assessment Tool for Healthy, Joyful, and Sustainable Diet in South Korea
Hyelim Yoo, Eunbin Jo, Hyeongyeong Lee, Sohyun Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(7): 1507. CrossRef - Effects of University Students’ Perceived Food Literacy on Ecological Eating Behavior towards Sustainability
Yoojin Lee, Taehee Kim, Hyosun Jung
Sustainability.2022; 14(9): 5242. CrossRef - The Relationships between Food Literacy, Health Promotion Literacy and Healthy Eating Habits among Young Adults in South Korea
Yoojin Lee, Taehee Kim, Hyosun Jung
Foods.2022; 11(16): 2467. CrossRef
-
2,572
View
-
87
Download
-
16
Crossref
- [English]
-
Current Barriers of Obesity Management of Children Using Community Child Care Centers and Potential Possibility of Utilizing Mobile Phones: A Qualitative Study for Children and Caregivers
-
Bo Young Lee, Mi-Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwan
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):189-203. Published online June 30, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.189
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
This study was performed to identify the current barriers of obesity management for children using Community Child Care Centers and their caregivers (parents and teachers working in the Centers). Further, this study explored the possibility of utilizing a mobile phone application for tailored obesity prevention and management programs to overcome the current difficulties associated with children's obesity management.
Methods
The qualitative data were collected through in-depth interviews with 20 obese and overweight children or children who wanted to participate in this study using Community Child Care Centers, 12 teachers working at the Centers, and a focus group interview with five parents of children using the Centers. Data were analyzed with a thematic approach categorizing themes and sub-themes based on the transcripts.
Results
The current barriers of obesity management of obese and overweight children using Community Child Care Centers were lack of self-directed motivation regarding obesity management (chronic obesity-induced lifestyles and reduced self-confidence due to stigma) and lack of support from households and Community Child Care Centers (latchkey child, inconsistency in dietary guidance between the Center and household, repetitive pressure to eat, and absence of regular nutrition education). Mobile phone applications may have potential to overcome the current barriers by providing handy and interesting obesity management based on visual media (real-time tracking of lifestyles using behavior records and social support using gamification), environmental support (supplementation of parental care and network-based education between the Community Child Care Center and household), and individualized intervention (encouragement of tailored and gradual changes in eating habits and tailored goal setting). It is predicted that the real-time mobile phone program will provide information for improving nutritional knowledge and behavioral skills as well as lead to sustainable children’s coping strategies regarding obesity management. In addition, it is expected that environmental factors may be improved by network-based education between the Community Child Care Centers and households using the characteristics of mobile phones, which are free from space and time constraints.
Conclusions
The tailored education program for children using Community Child Care Centers based on mobile phones may prevent and reduce childhood obesity by overcoming the current barriers of obesity management for children, providing environmental and individualized support to promote healthy lifestyles and quality of life in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
Jiyoung Park, Sein Hwang, Seolhyang Baek, Gill A. Ten Hoor
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2389. CrossRef
-
961
View
-
6
Download
-
1
Crossref
- [English]
-
Qualitative Study on the Perception of Community Food-accessibility Environment among Urban Older Adults
-
Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):137-149. Published online April 30, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.137
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
This study explored the community food environmental factors affecting food purchasing using a qualitative research methodology for the elderly as well as the various food environments under their socioeconomic diversity.
Methods
For the qualitative data collection, this study interviewed 20 elderly people aged 65 years or more, who participated in a public health program or lunch services operated by the senior welfare center in Seoul. Five dimensions, such as availability, physical accessibility, affordability, acceptability, and accommodation suggested in previous studies, were used to identify the community food environmental factors.
Results
The elderly participants showed overall similarities to the concepts derived from existing studies on the five dimensions of food accessibility environment. In addition, other important food accessibility environmental factors that were not present in previous studies, such as acceptability for a product of domestic origin, delivery service to home, and small-packaged food sales, were derived. On the other hand, the concept of some subjects differed depending on the household income and specifically for the physical accessibility concept. This showed that the close distance factor from a grocery store at home might not apply to older adults in low-income households in Korea.
Conclusions
This study found that five dimensions of the food environment suggested by previous studies could also be applied to vulnerable older adults in Korea. On the other hand, the socioeconomic characteristics of individuals and households would affect the perspectives of their local food environments differently. The findings of this study could help in the development of tools for evaluating the community food environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 16. CrossRef - Spatial inequalities and driving factors in food accessibility: Integrating online and offline grocery services in South Korea
Hyebin Kim, Minkyu Kim, Sugie Lee
Applied Geography.2025; 185: 103777. CrossRef - Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 352. CrossRef - Spatial Disparity of Neighborhood Food Environment by Socioeconomic Status: Application of Urban Network Analysis
Taekyung Seong, Sugie Lee
Land.2024; 13(6): 865. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Perceived Community Food Accessibility Measurement Questionnaire for Korean Older Adults
Jisoo Hong, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(19): 4301. CrossRef - A relationship between food environment and food insecurity in households with immigrant women residing in the Seoul metropolitan area
Sung-Min Yook, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 264. CrossRef - Regional Difference in the Effect of Food Accessibility and Affordability on Vegetable and Fruit Acquisition and Healthy Eating Behaviors for Older Adults
Dong Eun Lee, Kirang Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 14973. CrossRef - Analysis of Accessibility Changes to Neighborhood Food Environment and Food Desert Phenomenon in Seoul, Korea : Focused on the High-density Areas of Low-income Older Adults
Taekyung Seong, Sugie Lee
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2021; 56(1): 137. CrossRef - Effects of Perceived Food Store Environment on Malnutrition and Frailty among the Food-Insecure Elderly in a Metropolitan City
Yu-Mi Kim, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2021; 13(7): 2392. CrossRef - Analyzing Socio-Economic and Geographical Factors that Affect the Health of the Elderly
Zacharias Dermatis, Athina Lazakidou, Athanasios Anastasiou, Panagiotis Liargovas
Journal of the Knowledge Economy.2021; 12(4): 1925. CrossRef - Analysis of Awareness, Knowledge, and Behavior about Food Hygiene·Safety Among the elderly
Mi Sook Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 200. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef
-
1,367
View
-
18
Download
-
12
Crossref
- [English]
-
Effect of Geographic Area on Dietary Quality across Different Age Groups in Korea
-
Hyun Ja Kim, Kirang Kim
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):453-464. Published online December 31, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.453
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to examine whether dietary quality varies among different age groups and geographic areas, and whether the difference between geographic areas varies across several age groups in Korea.
METHODS
The subjects were 14,170 subjects who participated in the 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The dietary quality was assessed using the Korean Health Eating Index (KHEI). Age groups were categorized into six groupings, and areas were categorized into urban and rural according to their administrative districts. The effect of area on the KHEI score was analyzed by multiple linear regression analysis.
RESULTS
The KHEI was the lowest in the 20-30s group (57.7 ± 0.4 score for 20s and 61.2 ± 0.3 score for 30s) and increased with age (p<0.001), showing the highest score in the 60s (67.9 ± 0.3 score), and then decreased again in the 70s and older (64.6 ± 0.3 score). As a result of comparing the KHEI score by area, the urban areas had higher KHEI scores than did the rural areas (63.5 ± 0.2 score for urban area and 62.2 ± 0.4 score for rural area, p=0.002). The difference between areas was dependent on the age group, showing a significant difference for subjects who were aged from 50s and older (p=0.002 for 50s, p<0.001 for 60s and p<0.001 for 70s and older). After adjusting for confounding factors, the effect of area on the KHEI score was only shown for those subjects in the over 60 years old group (p=0.035 for 60s and p<0.001 for 70s and older).
CONCLUSIONS
The dietary quality differed according to the age group and geographic area. The dietary quality was lower for younger people than that for older people, and in rural areas compared to that in urban areas, and especially for older adults. The area factor was a very important factor for the dietary quality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Dietary habits of Koreans aged 95 years and older residing in rural and metropolitan areas
Jieun Mun, Sein Kim, Suyoung Kim, Seunghee Kim, Sang Chul Park, Jae-Young Han, Kwangsung Park, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 66. CrossRef - Prediction model for identifying a high-risk group for food insecurity among elderly South Koreans
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual- and neighborhood-level factors influencing diet quality: a multilevel analysis using Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data, 2010-2019
Dahyun Park, Min-Jeong Shin, S V Subramanian, Clara Yongjoo Park, Rockli Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2025; 47: e2025043. CrossRef - Risk of all-cause mortality is associated with multiple health-related lifestyle behaviors and does not differ between urban and rural areas in Korea
Seunghee Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(4): 554. CrossRef - Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 173. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Perceived Community Food Accessibility Measurement Questionnaire for Korean Older Adults
Jisoo Hong, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(19): 4301. CrossRef - Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Regional Difference in the Effect of Food Accessibility and Affordability on Vegetable and Fruit Acquisition and Healthy Eating Behaviors for Older Adults
Dong Eun Lee, Kirang Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 14973. CrossRef - Regional Differences in Dietary Total Fat and Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Their Associations with Metabolic Diseases among Korean Adults: Using the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 495. CrossRef - Basic Concepts and Detailed Dimensions of Food Security and Related Indicators for Policy Development and Evaluation
Sohyun Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 429. CrossRef
-
1,156
View
-
6
Download
-
10
Crossref
- [English]
-
A Qualitative Study on the Potential Utilization of a Mobile Phone for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children : Parents Perspective
-
Bo Young Lee, Mi Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji Yun Hwang
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(2):117-126. Published online April 30, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.2.117
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the current difficulties surrounding children's obesity management and evaluate the application of a mobile phone as a tool to overcome such difficulties of obesity management from the perspective of main caregivers of elementary school students.
METHODS
The qualitative data were collected through 3 focus group interviews including 6 full-time housewives, 7 mothers with overweight children, and 4 working mothers. Data were analyzed using a thematic approach.
RESULTS
The limitations of current children's obesity management included difficulty in diet management and exercise as well as challenges of setting goals and lack of support at the household and school levels. Mobile technology may be useful to overcome the current problems by providing real-time knowledge on diet management and physical activity, online compensation scheme according to goal setting, and interactive environmental supports at both household and school levels for promoting overall health.
CONCLUSIONS
The mobile-based multiple support program may assist in overcoming the current limitations of child obesity management by providing tailored information and by creating a more supportive environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Current Barriers of Obesity Management of Children Using Community Child Care Centers and Potential Possibility of Utilizing Mobile Phones: A Qualitative Study for Children and Caregivers
Bo Young Lee, Mi-Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 189. CrossRef - Consumers’ Impulse Buying Behavior on Instagram: Examining the Influence of Flow Experiences and Hedonic Browsing on Impulse Buying
Forough Shahpasandi, Azim Zarei, Mohsen Shafiei Nikabadi
Journal of Internet Commerce.2020; 19(4): 437. CrossRef
-
1,111
View
-
2
Download
-
2
Crossref
- [English]
-
Development of Strategies to Improve the National Nutrition Survey System
-
Narae Yang, Seungmin Lee, Youngsuk Lim, Haeryun Park, Kirang Kim
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(5):444-455. Published online October 31, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.5.444
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- OBJECTIVES
The current survey environment is changing and participation rates in national nutrition surveys are decreasing. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to develop strategies for improving the nutrition survey system in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
To develop an alternative system for conducting the KNHANES nutritional survey, we conducted focus group interviews with stakeholders of the survey, SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis, and expert reviews. In addition, spatial analysis of potential sites for conducting surveys instead of relying on household visits was performed, and the perception of nutritional surveys in the population eligible for KNHANES was evaluated.
RESULTS
Based on the results of the focus group interviews, SWOT analysis, and expert reviews, we propose two options for survey sites: vehicles specifically prepared for nutritional surveys and public facilities such as community service centers or public health centers. Among public facilities, community service centers were found to be more appropriate sites than public health centers because they were considered more accessible. About 90% of respondents would participate in the survey in public facilities and about 74% would in vehicles.
CONCLUSIONS
Conducting national nutrition surveys in specially designed vehicles and public facilities could be a viable alternative to home visits. Next, the validity of these newly proposed nutrition survey methods needs to be compared to the results of the current national nutrition survey.
- [English]
-
Current Status and Suggested Future Directions of Nutrition Intervention using Healthy School Tuck Shops: the Teenage Perspective
-
Suhyun Oh, Kirang Kim, Ji Yun Hwang
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):226-233. Published online June 30, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.226
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the current status and to suggest future directions for health management of teenagers who use healthy school tuck shops to improve teenagers' eating habits while reducing and preventing obesity.
METHODS
A total of 29 students (16 middle school students and 13 high school students) took part in the interview for this study, and the interview was conducted for each school's focus group by using qualitative research methodology.
RESULTS
The current status of using healthy school tuck shops and suggested future directions were divided into two categories. Personal barriers such as discrepancies between personal perceptions and behaviors and lack of food choice suitable to individual tastes can be solved by rebuilding the operating system to provide intuitive promotion of behavior and customized products through improvements in existing products and new product development. A lack of consistent management from low utilization convenience and difficulty in maintaining a constant purchase price can be handled by establishing a solution to restricted physical access for products, as well as seeking profit by improving distribution costs via continuous cooperation between the school and community.
CONCLUSIONS
Continuous funding and a system that reflects the needs and preferences of healthy school tuck shop users should be applied for sustainable operation of healthy school tuck shops to improve teenagers' eating habits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
Eun-Jin Choi, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 102. CrossRef
-
1,002
View
-
5
Download
-
1
Crossref
- [English]
-
Leveraging Multimodal Supports using Mobile Phones for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children: Program Providers' Perspective from a Qualitative Study
-
Mi Young Park, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim, Ji Yun Hwang
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(3):238-247. Published online June 30, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.3.238
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate providers' perspectives on current challenges in implementing a program for prevention and management of childhood obesity and adoption of mobile phone as a potential solution of leveraging multimodal delivery and support in a school setting.
METHODS
The qualitative data were collected through face-to-face in-depth interviews with 23 elementary-school teachers, 6 pediatricians, and 6 dieticians from community health centers and analyzed using a qualitative research methodology.
RESULTS
Current challenges and potential solutions of obesity-prevention and -management program for obesity program for elementary school children were deduced as two themes each. Lack of tailored intervention due to limited recipient motivation, lack of individualized behavioral intervention, and different environmental conditions can be solvable by mobile technology-based personalized intervention which brings about interactive recipient participation, customized behavioral intervention, and ubiquitous accessibility. Lack of sustainable management due to stigmatization, limited interactions between program providers and inconsistent administrative support can be handled by multimodal support based on school setting using mobile platform providing education of health promoting behaviors toward larger scale and interactive networking between program participants, and minimizing administrative burden.
CONCLUSIONS
Adoption of mobile-based health management program may overcome current limitations of child obesity program such as lack of tailored intervention and sustainable management via personalized intervention and multimodal supports although some concerns such as increased screen time need to be carefully considered in a further study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Qualitative Study on the Potential Utilization of a Mobile Phone for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children : Parents Perspective
Bo Young Lee, Mi-Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 117. CrossRef
-
978
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
- [English]
-
A Qualitative Study on Attitude, Acceptability, and Adaptation for Home-delivered Meal Services in the Korean Elderly from the Perspective of Life Context
-
Ji Yun Hwang, Bokyoung Kim, Kirang Kim
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(5):459-467. Published online October 31, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.5.459
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to suggest the strategies for improvement of home-delivered meal services for the elderly, to identify reasons for recipients to get started with the services and to evaluate the attitude, acceptability and adaptation of recipients to the services from the perspective of life context.
METHODS
The data was collected through face-to-face in-depth interviews with eighteen low-income elderly recipients of home-delivered meals and analyzed using a qualitative research method.
RESULTS
The results were deduced as four themes which comprised of long-term vulnerable socioeconomic contexts resulted in entry to the services, conflicting acceptability to the services, passive adaptation to taking the services, and positive practices to cope with supplement free meals or other services. The service participation was initiated because of a combination of prolonged, vulnerable socioeconomic contexts, including poverty and unexpected life events such as diseases, disability, living alone, aging and unemployment. With regard to taking the services, conflicting acceptability was observed: positive aspects including saving living cost and good quality of meals, and negative aspects including lack of a tailored service and feeling of stigma. Although the recipients needed an individualized service, they did not express their needs and demands for the services and they accepted the unavailability as an accustomed, prolonged vulnerable socioeconomic context. With regard to lack of tailored services, either self-solution such as modification of eating patterns or community-based network and services were used.
CONCLUSIONS
We suggest that a system to concretely identify recipients' attitude, acceptability and adaptation for home-delivered meal services should be developed in the establishment of a tailored nutrition support system for the low-income elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Food Insecurity and Stress Among Rural Residents in South Carolina: The Moderating Influences of Household Characteristics, Neighborhood Social Environment and Food Environment
Caitlin Koob, Ye Luo, Catherine Mobley, Samuel Baxter, Sarah Griffin, Cassius Hossfeld, Leslie Hossfeld
Journal of Community Health.2023; 48(3): 367. CrossRef - Virtual Grocery Store: Fostering Healthy Nutrition among Seniors
Tara Crowell, Anthony Dissen, Elizabeth G. Calamidas, Elizabeth Finnerty, Laura Engelmann
Journal of Nutrition in Gerontology and Geriatrics.2021; 40(4): 290. CrossRef - Interpersonal and Community Factors Related to Food Sufficiency and Variety: Analysis of Data from the 2017 Community Health Survey
Jiyoun Hong, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 416. CrossRef - Experiences of Healthcare and Daily Life Support Services in Community-dwelling Elders Living Alone: A Thematic Analysis using Focus Group Interviewing
Yeon-Hwan Park, Kyung-Choon Lim, Be Long Cho, Hana Ko, Yu Mi Yi, Eun-Young Noh, So-Im Ryu, Sun Ju Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2019; 21(3): 200. CrossRef - Food Insecurity and Geriatric Hospitalization
Rachel S. Bergmans, Briana Mezuk, Kara Zivin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(13): 2294. CrossRef - Participation in the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program and maternal depressive symptoms: Moderation by program perception
Rachel S. Bergmans, Lawrence M. Berger, Mari Palta, Stephanie A. Robert, Deborah B. Ehrenthal, Kristen Malecki
Social Science & Medicine.2018; 197: 1. CrossRef
-
1,263
View
-
2
Download
-
6
Crossref
- [English]
-
Validation of Food Security Measures for the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
-
Kirang Kim, Seo Ah Hong, Sung Ok Kwon, Bo Youl Choi, Ga Young Kim, Se Young Oh
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):771-781. Published online December 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.771
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The objective of this study was to assess the reliability and validity of food security measures, which was developed based on the US household food security survey module (US HFSSM) with content validity in the Korean population. The reliability and validity were assessed by internal consistency, construct validity and criterion-related validity. The study included 446 households. Among those, 46.2% were households with children. The proportion of food insecure households was 33.3%. Among those, 35.4% and 64.6% households were food insecure with hunger and without hunger, respectively. The Cronbach's alpha coefficients were 0.84 and the infit value by the Rasch model analysis ranged from 0.68 to 1.43. The scale item response curves by food insecurity severity explained well the nature and characteristics of food security, indicating the highest proportion of "yes" for the items on diet quality, followed by those with diet quantity. The result of criterion-related validity showed that food insecurity status was significantly related in a dose-response manner with the household income level, food expenditure, subjective health state, subjects' educational level. Household food security status was also related to dietary diversity regarding protein foods, fruits and fruit juice, and milk and dairy product. These findings suggest that the food security instrument is reliable and valid and would be used to assess food security status in the Korean population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The mediating role of food insecurity in the relationship between income poverty and depressive symptoms and suicidal ideation: A nationwide study of Korean adults
Seong-Uk Baek, Jin-Ha Yoon
Social Science & Medicine.2025; 373: 117972. CrossRef - The food insecurity–obesity paradox: a comparison of three obesity measures and sociodemographic disparities in Korean adults
Sukyoung Jung, Sohyun Park
Obesity.2025; 33(7): 1395. CrossRef - Association Between Food Insecurity and Poor Cardiovascular Health Assessed by the Life’s Essential 8 Metric: A Population-Based Study of Korean Adults
Seong-Uk Baek, Jin-Ha Yoon
Nutrients.2025; 17(13): 2148. CrossRef - Relationship between food insecurity and obesity-related comorbidities
Hee Joon Choi, Jae-Min Park, Youn Huh, Wonsock Kim, Jung Hwan Kim, Young Sik Kim, Seo Young Kang
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2025; : 104435. CrossRef - Changes in food sufficiency among Korean adults in urban and rural areas during the COVID-19 pandemic: an analysis of the 7th and 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sarang Jeong, Jin-Young Jeong, Sohyun Park
Epidemiology and Health.2024; 46: e2024045. CrossRef - Association of food insecurity with the use of tobacco products and urine cotinine-measured smoking intensity: evidence from a population-based study in South Korea, 2019–2021
Seong-Uk Baek, Yu-Min Lee, Jong-Uk Won, Jin-Ha Yoon
Tobacco Control.2024; : tc-2024-058754. CrossRef - Hazardous alcohol use is associated with food insecurity in adults living alone: Findings from a nationwide study in Korea
Seong-Uk Baek, Yu-Min Lee, Jin-Ha Yoon, Jong-Uk Won
Social Science & Medicine.2024; 362: 117468. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity and Its Relation to Food Insecurity in Korean Adults with Obesity
Jimin Lee, Wonsock Kim, Jae-Min Park, Youn Huh, Jung Hwan Kim, Young Sik Kim, Seo Young Kang
Nutrients.2024; 16(22): 3833. CrossRef - How does young adults’ dietary and health-related quality of life vary by food security and household income?
Eun-kyung Kim, Yong-Seok Kwon, Sena Kim, Jin-Young Lee, Young Hee Park
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Food Insecurity with Dietary Inflammatory Potential and Risk of Low Muscle Strength
Su Min Kim, Yoon Jung Park, Hyesook Kim, Oran Kwon, Kwang Suk Ko, Yuri Kim, Yangha Kim, Hyesook Park, Seungyoun Jung
Nutrients.2023; 15(5): 1120. CrossRef - Food insecurity and unmet healthcare needs in South Korea
Hwi Choe, Tae-Young Pak
International Journal for Equity in Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Food Insecurity Is Associated with Dietary Consumption during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019–2020
Jeong-Hwa Choi
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 772. CrossRef - A relationship between food environment and food insecurity in households with immigrant women residing in the Seoul metropolitan area
Sung-Min Yook, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 264. CrossRef - The Health and Nutritional Status of Children (10–18 years) Belonging to Food Insecure Households: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2012–2019)
Sowon Jung, Jieun Shin, Myoungsook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(17): 6695. CrossRef - Relationships of food security with skeletal muscle mass and handgrip strength by sex
Kayoung Lee
Nutrition.2022; 102: 111746. CrossRef - The Gangwon Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Study: Methods and Initial Baseline Data
Yoon Jeong Cho, Sohyun Park, Sung Soo Kim, Hyo Jin Park, Jang Won Son, Tae Kyung Lee, Sangmo Hong, Jee-Hyun Kang, Seon Mee Kim, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won Jun Kim, Young Eun Seo, Yoosuk An, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Sookyoung Jeon, Kyungho Park, Bong-Soo Kim, Cha
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(4): 303. CrossRef - Food Security Moderates the Relationships of Muscle Mass with Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance
Kayoung Lee
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2022; 29(1): 23. CrossRef - Association Between the Use of Tobacco Products and Food Insecurity Among South Korean Adults
Seo Young Kang, Hong-Jun Cho
International Journal of Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Socioeconomic status, food security, and chewing discomfort of Korean elders: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye-Sun Shin, Ae-Jung Im, Hee-Jung Lim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(1): 94. CrossRef - Food Security Status is not Associated with Increased Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
Jung Woo Lee, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Yookyung Kim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(4): 192. CrossRef - Association Between Food Security and 10-Year Cardiovascular Disease Risk Differs by Gender and Weight Status
Kayoung Lee
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Household Food Insecurity: Comparison between Families with and without Members with Disabilities
Jong Eun Park, So Young Kim, Se Hee Kim, Eun Ju Jeoung, Jong Hyock Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(17): 6149. CrossRef - Combined effects of disease management and food insecurity on physical and mental health in Korean adults
Hyun Ja Kim, Kirang Kim
Public Health Nutrition.2020; 23(1): 112. CrossRef - Objective and perceived food environment and household economic resources related to food insecurity in older adults living alone in rural areas
Jae Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwang, Kirang Kim
BMC Geriatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatial Disparity in Food Environment and Household Economic Resources Related to Food Insecurity in Rural Korean Households with Older Adults
Jae Eun Shim, Seo-jin Kim, Kirang Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrients.2018; 10(10): 1514. CrossRef - Health and nutritional status of Korean adults according to age and household food security: Using the data from 2010~2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Geun Ah Park, Sung Hee Kim, Seok Joong Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(6): 603. CrossRef - The Influence of Community Characteristics on Food Insecurity Korean Adults
Jun Park, Gilwon Kang, Yangju Tak, Sounghoon Chang, Kunsei Lee, Hyeongsu Kim
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(3): 226. CrossRef - Association of food insecurity and depression in Korean adults
Kowoon Lee, Hye-Sook Yoo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 62. CrossRef - Household Food Insecurity Is Associated with Adverse Mental Health Indicators and Lower Quality of Life among Koreans: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2012–2013
Hye-Kyung Chung, Oh Kim, So Kwak, Yoonsu Cho, Kyong Lee, Min-Jeong Shin
Nutrients.2016; 8(12): 819. CrossRef - Household food insufficiency is associated with dietary intake in Korean adults
Sang Eun Lee, Yoon Ju Song, Young Kim, Jeongsook Choe, Hee-Young Paik
Public Health Nutrition.2016; 19(6): 1112. CrossRef - Household food insecurity and dietary intake in Korea: results from the 2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun Ja Kim, Kyungwon Oh
Public Health Nutrition.2015; 18(18): 3317. CrossRef - Nutritional and health consequences are associated with food insecurity among Korean elderly: Based on the fifth (2010) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-1)
Seungjae Lee, Kyung Won Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Mi Sook Cho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(6): 519. CrossRef - Food Insecurity and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 Data
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(4): 308. CrossRef - Flavonoid intake according to food security in Korean adults: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2012
Shinyoung Jun, Eunju Hong, Hyojee Joung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(6): 507. CrossRef - A Study on the Living Conditions of Rural Women and the Determinants of Their Life Satisfaction
Jeong In Bae, Ung Im Park, Hye Sang Lee, Geun Mee Ahn, Woon Seon Jeong
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2013; 24(4): 485. CrossRef
-
1,478
View
-
12
Download
-
35
Crossref
- [English]
-
The Effect of Parental Socioeconomic Status on the Nutrient Intake of Urban and Rural Adolescents
-
Mikyung Kim, Moran Ki, Kumnyu Bang, Kirang Kim, Boyoul Choi, Youngjun Kwon, Sangsun Lee, Chan Kim, Yunju Kang
-
Korean J Community Nutr 1998;3(4):542-555. Published online October 31, 1998
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- This study was conducted to assess the nutrient intake patterns among urban and rural adolescents and to investigate the effects due to parent's socioeconomic status and other factors, such as mother's job, family type and regular exercise on that pattern. 2,455 middle and high school students living in Seoul and Yangpong, Kyounffi-Do participated in a self-administered questionnaire that was used to collect data. The one-day dietary intake was surveyed through a 24-hour recall method. The factors significantly different between urban and rural adolescents according to monthly income, parent's education level, mother's job, family type and exercise. Income, the parents' education level and regular exercise were associated with the patterns of nutrient intakes as a percent of the RDA. So, when adjusted for parental income, the father's and mother's education level and regular exercise, there were no signifcant differences within the patterns of nutritional intake between urban and rural adolescents. The results provided the information regarding the determinants of nutrient status among adolescents and were expected to be helpful for planning school health promotion programs.
|