Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):492-503. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
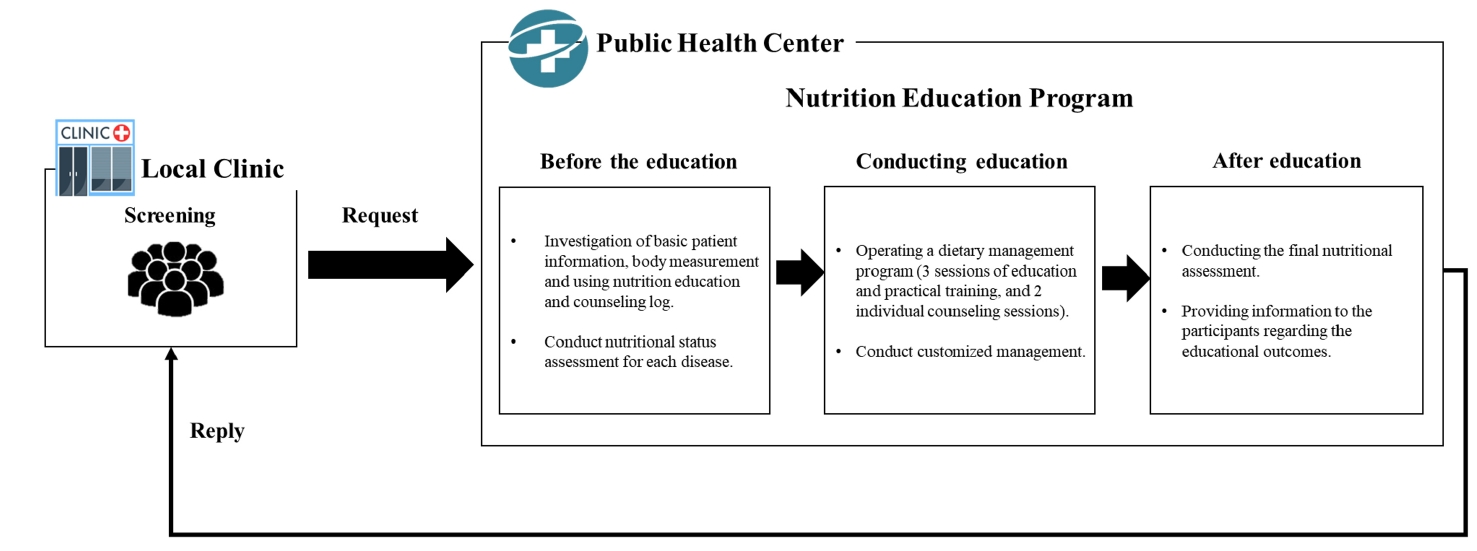
We investigated the impact of an advanced “Nutrition Education Program” on patients with Diabetes mellitus, type 2 from public health centers enrolled in a primary health care-based chronic disease management project. This 12-week dietary management program was developed by the Korea Health Promotion and Development Institute. We assessed if this program improved glycemic control and other health indicators through dietary and nutritional improvements.
Methods
Seventeen patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2 were enrolled in the “Nutrition Education Program.” These patients were referred to public health centers for lifestyle management based on physician assessments at local clinics that were participating in a pilot project on primary health care-based chronic disease management. The participants attended the program comprising face-to-face basic, in-depth, and practical training sessions at the health center during the third, fifth, and seventh weeks, respectively. Anthropometric measurements, body composition analysis, blood biochemical characteristics, nutritional knowledge, and self-efficacy evaluation were performed before and after the program. Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 28.0.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 62 years, and most participants were female (14, 82.4%). No significant changes in patients’ anthropometric measurements or body composition were observed after the training. However, significant reductions were observed in the blood biochemical characteristics, including glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels. Additionally, patients’ nutritional knowledge and self-efficacy scores increased significantly.
Conclusions
The “Nutrition Education Program” helped in improving glycemic control and other health indicators in patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2. Further research is required to objectively confirm the long-term and sustained effects of the program in a controlled study. Trial Registration Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010010
- 2,434 View
- 87 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of health behavior changes among residents in depopulation areas in Korea: a cross-sectional study based on Community Health Survey data from 2010 to 2019
- Miyong Yon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):348-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
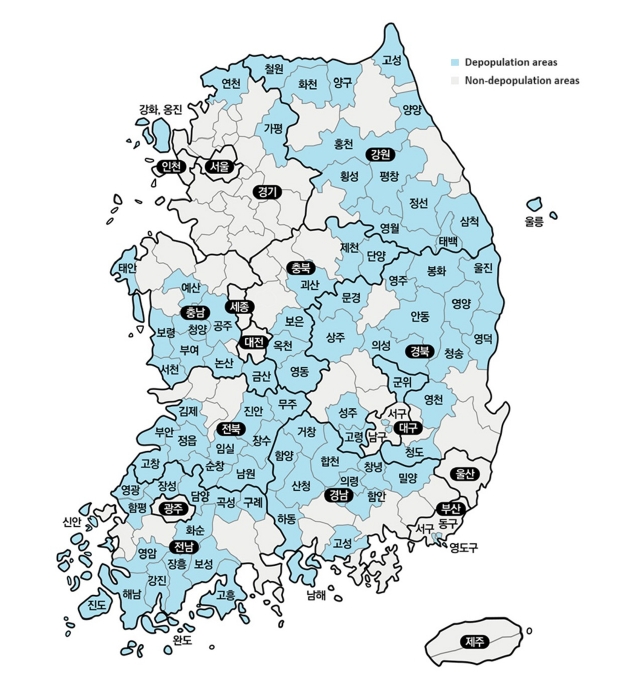
PDF - Objectives
The total population of Korea began to decline in 2019; in particular, the population in rural areas has been rapidly decreasing and is aging. Therefore, the government has designated depopulation areas and is seeking ways to support them. To assess whether health disparities exist between areas with population decline and those without, this study used community health survey data to observe temporal changes in health behaviors between the two types of areas. Methods: The analysis used Community Health Survey data from 2010 to 2019, and regional classification was divided by depopulation areas designated by the Ministry of the Interior and Safety. Trends in health behavior and chronic disease prevalence between depopulation and non-depopulation areas were analyzed. All analyses were conducted using complex sample analysis procedures in SAS 9.4 software. Results: The smoking rate steadily decreased in both depopulation and non-depopulation areas, whereas the high-risk drinking rate increased slightly. The walking practice rate did not improve in depopulation areas compared to non-depopulation areas. Furthermore, nutritional labeling usage rate was consistently lower in depopulation areas than in non-depopulation areas, with the gap being the largest. The prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension showed that the gap between depopulation and non-depopulation areas is continuously increasing. Conclusions: Health behaviors in depopulation areas have not improved, and the prevalence of chronic diseases is increasing rapidly. Therefore, the demand for health care services that support healthy lifestyle practices and chronic disease management in these areas is expected to increase.
- 2,842 View
- 28 Download

- [Korean]
- Effectiveness of NQ-E index-based individual nutrition counseling for community-care elderly: an intervention study on improving nutritional status, complex chronic diseases, and quality of life
- Yoonjeong Choi, Jihyun Lee, Heesook Lim, Yoo Kyoung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):480-494. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.480
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study sought to assess the effectiveness of community-based nutrition counseling on improving nutritional status, managing complex chronic diseases, and enhancing the quality of life for elderly individuals with chronic conditions, particularly in older adults with high levels of food insecurity and multiple chronic illnesses.
Methods
Thirty elderly subjects with diabetes and hypertension who were registered at local Senior Welfare Center received individualized nutrition counseling, based on their Nutrition Quotient for the Elderly (NQ-E) index. Over a 16-week period, they received tailored counseling and underwent various health and nutritional assessments. The final analysis included 28 participants after two dropped out. Data analysis was conducted using the SPSS v28.0.
Results
The subjects were over 70, with multiple chronic diseases including diabetes and hypertension and predominantly female. After 16 weeks, significant improvements were observed in the subjects’ grip strength, and HbA1c levels, as well as in their NQ-E scores, indicating improved dietary balance and diversity. There were no significant improvements in the ‘Moderation’ subdomain of the NQ-E index, suggesting that this aspect requires further attention in nutritional counseling. The subjects' nutritional risk scores (NSI) were also significantly decreased, indicating less nutritional risk. Lastly, as measured by the SF-36K, the subjects’ quality of life showed significant improvement in several domains including physical role performance and social function.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that tailored nutrition counseling, based on the NQ-E index, can improve elderly health, manage chronic diseases, and enhance quality of life. This approach potentially broadens the scope of community nutritionists' roles within an aging society. However, additional research is necessary to evaluate these interventions' long-term effects and sustainability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related Quality of Life in Multimorbid Adults: A Random Forest Cross-sectional Analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moonchang You, Geun-Myun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(3): 349. CrossRef - A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
Kyoung-Min Lee, Woo-jeong Kim, So-young Kim, Young-mi Park, Hwa-young Yoon, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 376. CrossRef - A Basic Study to Establish a Nutrition Education System for Welfare Facilities for the Elderly at Home Using Body Composition Analysis and Nutritional Management Cards
Sun Hee Lee, Seung-Lim Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 471. CrossRef
- Health-related Quality of Life in Multimorbid Adults: A Random Forest Cross-sectional Analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,760 View
- 63 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Changes in dietary habits and chronic diseases before and after COVID-19 by regions using data from the 2018-2020 Korea Community Health Survey and Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods: a cross-sectional study
- Surim Park, Eun-hee Jang, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):124-140. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.124
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the changes in dietary habits, the prevalence of chronic diseases, and mental health problems in the regional areas of the Republic of Korea before and after the COVID-19 pandemic to provide evidence of the status of regional health inequalities.
Methods
This study analyzed Korean adults aged 19 or older who participated in the Korea Community Health Survey (n = 686,708) and Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods (n = 19,109) from 2018 to 2020. The participants were classified according to their residence area (Seoul metropolitan area, Metropolitan cities, Provinces); 2018-2019 were defined as before COVID-19, and 2020 as after COVID-19. The dietary behaviors, chronic diseases, and mental health problems were measured using a self-report questionnaire.
Results
After COVID-19, the eating-out usage rate in the Seoul metropolitan area and Provinces decreased compared to before COVID-19 (P < 0.001), and when responding that they eat out, the frequency of eating out with household members in the Seoul metropolitan area increased (P = 0.024). The deliveries/takeout usage rate in the Provinces decreased after COVID-19 compared to before (P < 0.001). After COVID-19, the prevalence of obesity decreased in all regions (P < 0.001), and the prevalence of hypertension increased significantly in the Provinces (P = 0.015). The prevalence of diabetes mellitus increased continuously before and after COVID-19 in all regions (P < 0.002). High-risk subjective stress levels increased significantly in the Seoul metropolitan area (P < 0.001), and sleep duration significantly increased in all regions (P < 0.001). Major depressive disorder was reduced significantly in Metropolitan cities (P = 0.042) and Provinces (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
After the COVID-19 pandemic, the prevalence of chronic diseases and mental health problems showed regional differences along with changes in dietary habits. It is necessary to reflect the regional differences in dietary habits in future policies resolving regional health inequalities.
- 1,183 View
- 16 Download

- [Korean]
- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
- Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):363-381. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the Korean elderly’s dietary intake status, subjective health-related perception and chronic disease prevalence among age groups. Associations of dietary quality with subjective health-related perception and chronic diseases were also examined.
Methods
Based on data from the 7th National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a total of 3,231 elderly were selected and categorized into 4 age groups of ‘65 ~ 69’, ‘70 ~ 74’, ‘75 ~ 79’ and ‘over 80’. Nutrient intakes, proportions of those with insufficient nutrient intakes, Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI), some subjective health-related perceptions and prevalence of major chronic diseases were compared according to the age groups. Differences in the subjective health-related perceptions and odds ratios of the chronic diseases according to the quartile levels of KHEI within the same age group were analyzed.
Results
With the increase of age, several nutrient intakes (P < 0.001) and KHEI scores significantly decreased (P < 0.01). In women, activity restriction increased (P < 0.05), and EQ-5D score decreased with age (P < 0.001). Prevalence of hypertension (P < 0.0001), hypercholesterolemia (P < 0.05) and anemia (P < 0.01) significantly increased, while hypertriglyceridemia (P < 0.01) significantly decreased only in men. Obesity prevalence decreased, while underweight prevalence increased (P < 0.05). Subjective health status, EQ-5D score and PHQ-9 score significantly improved as KHEI score increased in certain age groups of women (P< 0.05). Odds ratio of hypercholesterolemia significantly increased with the increase of KHEI score in 65 ~ 69-year-old women. However, hypertension and anemia significantly decreased with the increase of KHEI score in 75 ~ 79-year-old women (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
The study findings suggest that nutrition management and policy for the Korean elderly need to apply a segmented age standard that can better reflect their dynamic characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 359. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef - Blood Biochemical Characteristics, Dietary Intake, and Risk Factors Related to Poor HbA1c Control in Elderly Korean Diabetes Patients: Comparison between the 4th(2007-2009) and the 7th(2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 406. CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 422. CrossRef
- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
- 1,598 View
- 21 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
- Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):502-511. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.502
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the health and nutritional status of the elderly according to the number of chronic diseases, using data obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015. Methods: Data from a total of 2,310 individuals, aged 65 years and over, were used for the analysis. The elders were divided into 0 (n=375), 1 (n=673), 2 (n=637) and 3 or more (n=625) groups, by considering the number of chronic diseases. Results: Compared to other groups, the elderly subjects who were living with their spouse had the highest ratio in group 0 (P < 0.05), whereas subjects without economic activities had highest ratio in 3 or more group (P < 0.05). The EQ-5D index of subjects in the 0 group (0.90 ± 0.01) was higher than that in the 3 or more group (0.86 ± 0.01) (P< 0.05). After adjusting for confounding factors, the energy intake of subjects was determined to be lowest in the 3 or more group (P < 0.05). Protein (P < 0.05) and riboflavin (P < 0.05) intakes of the 3 or more group were also lower than other groups. Conclusions: This study indicates that multimorbidity of the elderly is associated with their health and nutritional status. The nutrients intake of the elderly, especially energy, protein and riboflavin, tended to be lowest in the 3 or more group. Further research is required to elucidate the risk factors related to presence of multimorbidity in the elderly. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Duration Is Associated with the Risk of Tooth Loss, Chewing Difficulty, and Undernutrition among Older Korean Women: Results of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2013–2015
Ye Rang Jo, Yoo Kyoung Park, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2023; 15(24): 5024. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,316 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
- Yunhwa Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):112-125. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Diet and incidence of chronic diseases are highly related. This study examined the characteristics of dietary safety awareness and competency for chronic disease prevention among adults.
Methods
Data were collected from 247 adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk areas using a self-administered questionnaire in May and June of 2018. Data were analyzed by frequency analysis, χ 2-test, factor analysis, reliability analysis, t-test, one-way analysis of variances, and correlation.
Results
The results of the factor analysis indicate that dietary safety awareness of health management was classified into chronic disease anxiety and obsession. Awareness of dietary safety management was sub-grouped into difficulty in acquiring knowledge, lack of awareness of over and malnutrition, food safety anxiety, importance of weight management, education requirement for cancer prevention, and knowledge. Dietary safety behavior composed of a balanced diet, unhealthy diet, and healthfunctional pursuit. Dietary safety management competency was comprised of health management, food management, and cooking. The competency scores of dietary safety management factors were significantly different according to sex, age, and education level (P < 0.05). Balanced diet factor was significantly correlated with knowledge, health-functional pursuit, health management, food management, and cooking capacity factors (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
Active education for dietary safety management competency according to age, gender, and education level should provide dietary safety education to reduce anxiety and obsession regarding chronic diseases and sustainable health management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of evaluation items for accessing practice and compliance with dietary guidelines among Korean adults
Min-Ah Kim, Sung-Min Yook, Jieun Oh, Jimin Lim, Hye Ji Seo, Young-Suk Lim, Ji Soo Oh, Hye-Young Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 244. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics of Nutritional Bar with Varying Concentrations of Enteromorpha intenstinalis Powder
KyungHee Kim, JaeSuk Kim
Human Ecology Research.2024; 62(2): 295. CrossRef - Correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency and value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using dietary area: a descriptive study
Yunhwa Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 317. CrossRef - Dietary safety management competency for the sustainable health management of adolescents
Yunhwa Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(3): 406. CrossRef - Cancer survivor's dietary safety management awareness and competency type
Yun Hwa Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(5): 532. CrossRef - Factors associated with the dietary quality and nutrition status using the Nutrition Quotient for adults focusing on workers in the manufacturing industry
Ji Suk Yim, Young Ran Heo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(5): 488. CrossRef
- Development of evaluation items for accessing practice and compliance with dietary guidelines among Korean adults
- 1,037 View
- 7 Download
- 6 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- An Evaluation of Chronic Disease Risk Based on the Percentage of Energy from Carbohydrates and the Frequency of Vegetable Intake in the Korean Elderly: Using the 2007-2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoon Suk Suh, Min Seon Park, Young Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(1):41-52. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Korean elderly people are known to consume diets high in carbohydrates low in vegetables compared to other age groups. This study evaluated the chronic disease risks and nutritional status in this group based on the percentage of energy from carbohydrates and the frequency of vegetable intake.
METHODS
Using the 2007~2009 Korean National Health Nutrition Examination Survey data, except those who were undergoing treatment for chronic disease, final 1,487 subjects aged 65 and older were divided into 4 groups: moderate carbohydrate energy ratio of 55~70% and low frequency of vegetable intake defined as less than 5 times per day (MCLV), moderate carbohydrate ratio and high frequency of vegetable intake more than 5 times (MCHV), high carbohydrate energy ratio above 70% and low frequency of vegetable intake less than 5 times (HCLV), and high carbohydrate ratio and high frequency of vegetable intake more than 5 times (HCHV). All data were analyzed after the application of weighted value, using a general linear model or logistic regression.
RESULTS
More than half of Korean elderly consumed diets with HCLV, and this group showed poor nutritional status and lower frequency of intake of most food items, but with no risk of chronic disease such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, cardiovascular disease or anemia probably due to low intake of energy. On the contrary, MCHV group with a high percentage of energy from fat and protein showed the highest intake of energy and most nutrients, the highest frequency of intake of most of food items and a tendency of high risk of abdominal obesity, being followed by the MCLV group. Meanwhile, HCHV group showed a tendency of high risk of hypertension, followed by HCLV group with low frequency of intake of vegetables compared with the two moderate carbohydrate groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggested that the percentage of energy from carbohydrate and the frequency of vegetable intake affected the nutritional status, but not significantly affected the risk of chronic disease in Korean elderly. Further studies using more detailed category of % energy from carbohydrates and of type and amount of vegetables with consideration of individual energy intake level, excessive or deficient, are needed to confirm the results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef - Energy big data acquisition and application based on service portfolio quality
Pingping Sun, Lingang Gu
Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments.2021; 45: 101134. CrossRef - Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 502. CrossRef - Analyzing the Relative Importance for the Development Plan of the Public Health Care System
You Ho Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(4): 300. CrossRef - The Quality of a Traditional Dietary Pattern in Relation to Metabolic Syndrome in Elderly South Koreans
Chorong Oh, Jaekyung No
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2018; 27(4): 254. CrossRef - Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Estimation of Usual Intake and Assessment of Nutrient Intake for Korean Adolescents: Analysis of the 2010-2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Meeyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
Family and Environment Research.2017; 55(4): 385. CrossRef
- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
- 1,229 View
- 0 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- A Comparison between Asia-Pacific Region Criteria and Entropy Model Criteria about Body Mass Index of Elderly Females Using Morbidity of Chronic Disease
- Gu Beom Jeong, Jin Yong Park, Se Young Kwon, Kyung Ok Park, Pil Sook Park, Mi Yeon Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(5):490-498. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.5.490
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to propose the need of re-establishing the criteria of the body weight classification in the elderly. We compared the Asia-Pacific Region Criteria (APR-C) with Entropy Model Criteria (ENT-C) using Morbidity rate of chronic diseases which correlates significantly with Body Mass Index (BMI).
METHODS
Subjects were 886 elderly female participating in the 2007-2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). We compared APR-C with those of ENT-C using Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) curve and logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS
In the case of the morbidity of hypertension, the results were as follows: Where it was in the T-off point of APR-C, sensitivity was 67.5%, specificity was 43.1%, and Youden's index was 10.6. While in the cut-off point of ENT-C, it was 56.7%, 56.6%, and 13.3 respectively. In the case of the morbidity of diabetes, the results were as follows: In the cut-off point of APR-C, Youden's index was 14.2. While in the cut-off point of ENT-C, it was 17.2 respectively. The Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) of the subjects who had more than 2 diseases among hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia was 0.615 (95% CI: 0.578-0.652). Compared to the normal group, the odds ratio of the hypertension group which will belong to the overweight or obesity was 1.79 (95% CI: 1.30-2.47) in the APR-C, and 2.04 (95% CI: 1.49-2.80) in the ENT-C (p > 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
We conclude that the optimal cut-off point of BMI to distinguish between normal weight and overweight was 24 kg/m2 (ENT-C) rather than 23 kg/m2 (APR-C). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors related to cancer screening behaviors
Boyoung Choi, Tae Rim Um, Kwang-Soo Lee
Epidemiology and Health.2018; 40: e2018011. CrossRef - Nutrition States and Related Factors of Female Elderly according to Residence
Mi-Yeon Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(1): 39. CrossRef
- Factors related to cancer screening behaviors
- 1,046 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationships among Serum Adiponectin, Leptin and Vitamin D Concentrations and the Metabolic Syndrome in Farmers
- Seo Eun Yeon, Hee Ryoung Son, Jung Sook Choi, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(1):12-26. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationships among serum adiponectin, leptin and vitamin D concentrations and the metabolic syndrome in Korean farmers. 105 (26 males, 79 females) farmers (39~78 years, mean age 59.4 +/- 9.6 years) in Gangwon - area were included in this study. Anthropometric measurements and biochemical blood analysis of subjects were carried out. The prevalence of obesity, abdominal obesity, hypertension, diabetes, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia and hyper LDL-cholesterolemia, metabolic syndrome were 51.9%, 65.7%, 49.5%, 15.3%, 17.3%, 13.5%, 11.5% and 40.9%, respectively. Serum adiponectin and leptin levels (8.90 microg/ml and 12.6 ng/ml) of females were significantly higher than those (6.49 microg/ml and 4.88 ng/ml) of males. But there was no significant difference in 25(OH)vitamin D concentration between males (15.4 ng/ml) and females (16.9 ng/ml). In the subjects with metabolic syndrome, the adiponectin levels were significantly lower and leptin levels were significantly higher than those of the subjects without metabolic syndrome. Serum adiponectin level had positive correlations with HDL-cholesterol level (r = 0.325, p < 0.001), but showed negative correlations with triglyceride and fasting blood glucose concentrations, body weight and waist/hip circumference ratio (r = -0.202 ~ -0.317, p < 0.05). Serum leptin and 25(OH)vitamin D concentrations were positively correlated with body fat (kg, %) and BMI, waist and hip circumferences (r = 0.244 ~ 0.682, p < 0.001). The results of this study suggested that adiponectin and leptin levels could be credible indices to predict chronic diseases in farmers. However, further research on vitamin D should be carried out considering another factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Serum Adiponectin Biomarker with Metabolic Syndrome Components in Koreans with Extremely High HDL Cholesterol Levels in General Health Checkup
Hyun Suk Yang, Gun-Hyuk Lee, Donghwan Kim, Kyeong Ryong Lee, Mina Hur
Metabolites.2022; 12(11): 1086. CrossRef - The Measurements of the Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) and the Accuracy of RMR Predictive Equations for Korean Farmers
Hee-Ryoung Son, Seo-Eun Yeon, Jung-Sook Choi, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 568. CrossRef
- Association of Serum Adiponectin Biomarker with Metabolic Syndrome Components in Koreans with Extremely High HDL Cholesterol Levels in General Health Checkup
- 1,211 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on the Prevalence of Chronic Diseases, Health-related Habits and Nutrients Intakes according to the Quality of Life in Korean Adults
- Jee young Chung, Mi Young Lee, Mi Joung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(4):445-459. Published online August 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was done to analyze the chronic diseases prevalence and dietary intake status according to the health related quality of life and to identify its significant properties. This study was conducted based on 2906 subjects ranging from 20~64 years old, out of 9704 total subjects from the 4th Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey in 2008. The average quality of life (QL) score was 0.915, where 983 subjects were below the average (low QL group) and 1923 subjects were above (high QL group). In the high QL group, there was more likely to be young, male, and with higher income and education. For high QL group, the self-related health score was high, and the subjective stress level was low. The prevalence of diabetes was significantly higher in the low QL group and anthropometric and biochemical measures were not shown differences between the two groups but waist circumference was significantly higher in the low QL group. The QL score was significantly negative correlated with the waist circumference and the body mass index. As for the recognition rate of Nutrition Guideline, there were no significant differences but high QL group had higher scores in "Eat a variety of foods", "Avoid too much Sodium", and "Enjoy meals and Eating a breakfast". Carbohydrate intake was significantly lower in the high QL group than in low QL group and the high QL group showed higher intake in legumes, meat and poultry, fruits, daily products and beverages. Overall results suggest that increased diabetes prevalence in people with low quality of life might be affected by the diets based on high carbohydrate, increased waist circumference, and lower rate of practice nutritional guideline.
- 311 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Determinants of Nutrition Service Utilization in Health Centers
- Youngok Kim, Kyunghee Jang, Mi Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(1):91-96. Published online February 28, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to identify the determinants of nutrition service utilization in health centers. Utilization of nutrition services for chronic discase were also investigated. Interview survey using questionnaire was conducted to collect the data required for analysis. The study subjects were 300 residents over 40 years of age, and 15 health workers representing health center service personnel in Kypnggi province. A wilcoxon 2-sample test and Kruskal-Wallis test were used to compare the distribution of health centers by health center characteristics and nutrition services. A chi-square test was used to test the association between service utilization and personal variables of the population. A multiple logistic regression analysis was used to measure the relative importance between the variables on service utilization. The results showed that only 10.0% of the study subjects used nutrition services provided by the health centers. Pilot project implementation and location of health centers, as well as educational level of the residents were significant factors influencing the utilization of the nutrition services provided by the health centers. Among the variables, pilot project implementation was the most important factor that influenced the nutrition service utilization in health centers.
- 325 View
- 2 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



