Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Sex differences in the association between Korean Healthy Eating Index and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korean adults: a prospective cohort study
- Yeeun Park, Minji Kim, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):331-340. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Dietary quality is a modifiable determinant of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, evidence on the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI) and sex-specific differences in its association with T2DM risk remains limited. This study is to examine the longitudinal association between KHEI and incident T2DM in Korean adults, with a focus on potential sex differences.
Methods
We analyzed 56,000 adults (37,684 women and 18,316 men) from the Health Examinee cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Dietary intake was assessed using a validated semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire, and KHEI scores were constructed based on national guidelines. Incident T2DM was defined using physician diagnosis, treatment history, or biochemical criteria. Cox proportional hazards models and restricted cubic spline analyses were applied to evaluate associations, with adjustments for demographic, lifestyle, and clinical covariates.
Results
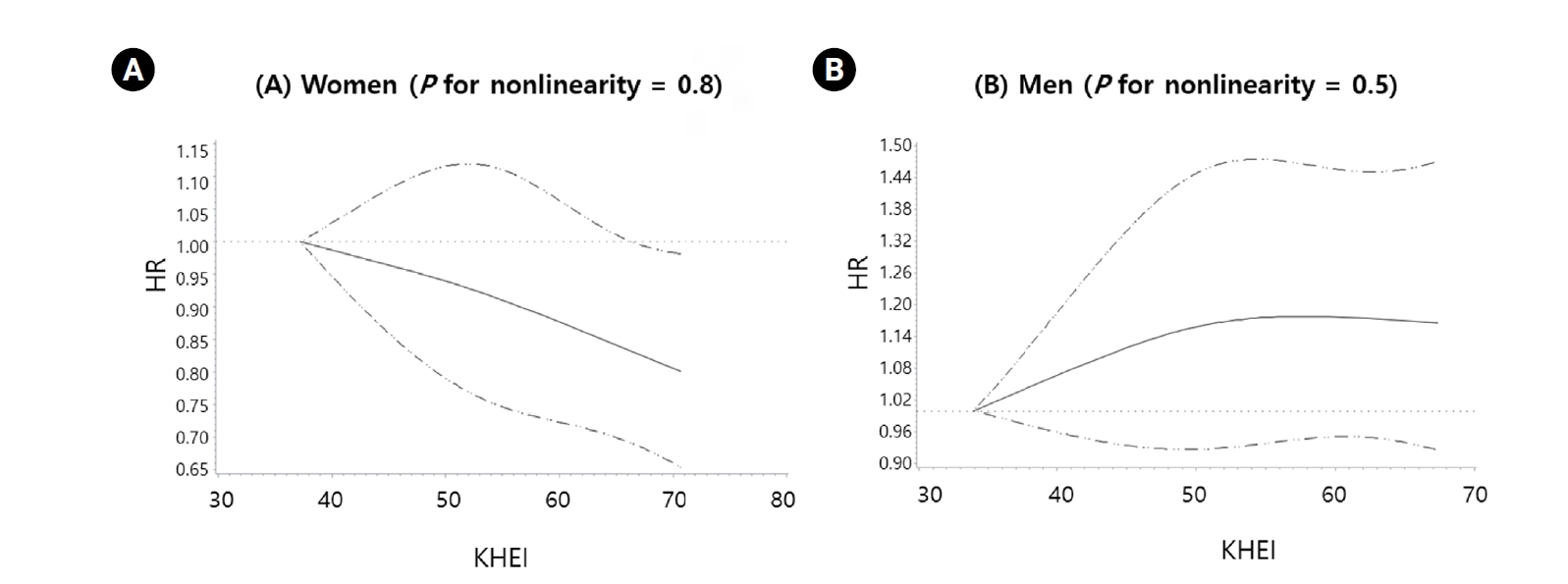
Over a median follow-up of 4.2 years, 2,252 women and 1,776 men developed T2DM. Women in the highest quartile of KHEI had a 18% lower risk of T2DM compared with those in the lowest quartile (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.82, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.71–0.93; P for trend = 0.007). In men, no significant association was observed (HR: 1.11, 95% CI: 0.95–1.29). The interaction by sex was statistically significant (P for interaction < 0.05). Spline analyses indicated a linear inverse association between KHEI and T2DM risk in women, whereas no trend was evident in men.
Conclusion
Higher diet quality, as measured by the KHEI, was associated with a reduced risk of T2DM in women but not in men, suggesting sex-specific effects of dietary patterns on diabetes prevention. These findings highlight the need for tailored nutritional strategies that consider biological and behavioral differences between women and men in Korea.
- 672 View
- 28 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of clinical characteristics and dietary intakes according to phenotypes of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Jin Kim, Ji-Sook Park, Sung-Rae Cho, Daeung Yu, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):127-139. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Clinical nutrition treatment is the central part of diabetes management, such as prevention, treatment, and self-management of diabetes, and personalized clinical nutrition treatment, which enables improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study aimed to contribute to the improvement of appropriate nutrition management in personalized treatment for obese and non-obese diabetes patients.
Methods
T2DM patients were recruited as participants, and 36 final participants were assigned to the lean diabetes mellitus group (LDM; body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and the obese diabetes mellitus group (ODM; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). We assessed the dietary intakes, body composition, dietary habits, the Korean version of obesity-related quality of life, and biochemical indices.
Results
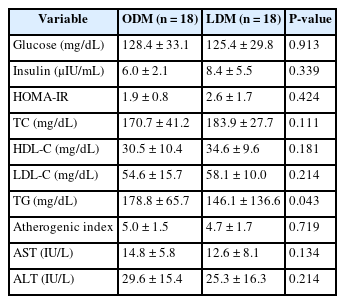
According to the phenotype’s comparison, the ODM group had a high prevalence of T2DM complications and hypertension, had a dietary habit of less than 10 minutes of mealtime duration and preferred fast food intake, and had a low obesity-related quality of life. However, the LDM group had a high choice of Korean dishes at the time of eating out and a high intake of vitamin C, and iodine because of the intake of vegetables and seaweeds.
Conclusion
We observed differences in diet, nutrient intake, and clinical characteristics according to the phenotype of T2DM patients. In particular, obese diabetes patients have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, bad dietary habits, and low obesity-related quality of life. Therefore, personalized nutrition treatment is needed in consideration of the risk of cardiovascular disease and dietary habits for patients in the ODM group, as well as determining the energy requirements of Korean patients with T2DM.
- 2,036 View
- 32 Download

- [English]
- Effects of a multi-component program based on partially hydrolyzed guar gum (Sunfiber®) on glycemic control in South Korea: a single-arm, pre-post comparison pilot clinical trial
- Hyoung Su Park, A-Hyun Jeong, Hyejung Hong, Hana Jang, Hye-Jin Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):40-52. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00276
- Correction in: Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to assess the impact of a multi-component program, including partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG, Sunfiber®) supplementation, on glycemic control, gut health, and nutritional status to support diabetes prevention and management among Korean adults.
Methods
A single-arm trial was conducted with 29 adults (aged 20-55 years) with fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 100 mg/dL. Over a six-week period, participants engaged in a multi-component program that incorporated the supplementation of PHGG (Sunfiber®, 12.5 g/day), weekly nutritional coaching, and the use of continuous glucose monitoring devices. The program’s effectiveness was evaluated by measuring FPG and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels through blood tests conducted before and after the intervention. Improvements in gut health were gauged using the Korean Gut Quotient Measurement Scales, while enhancements in nutritional status were assessed using the Nutrition Quotient (NQ) and surveys that evaluated improvements in gut health and nutritional status.
Results
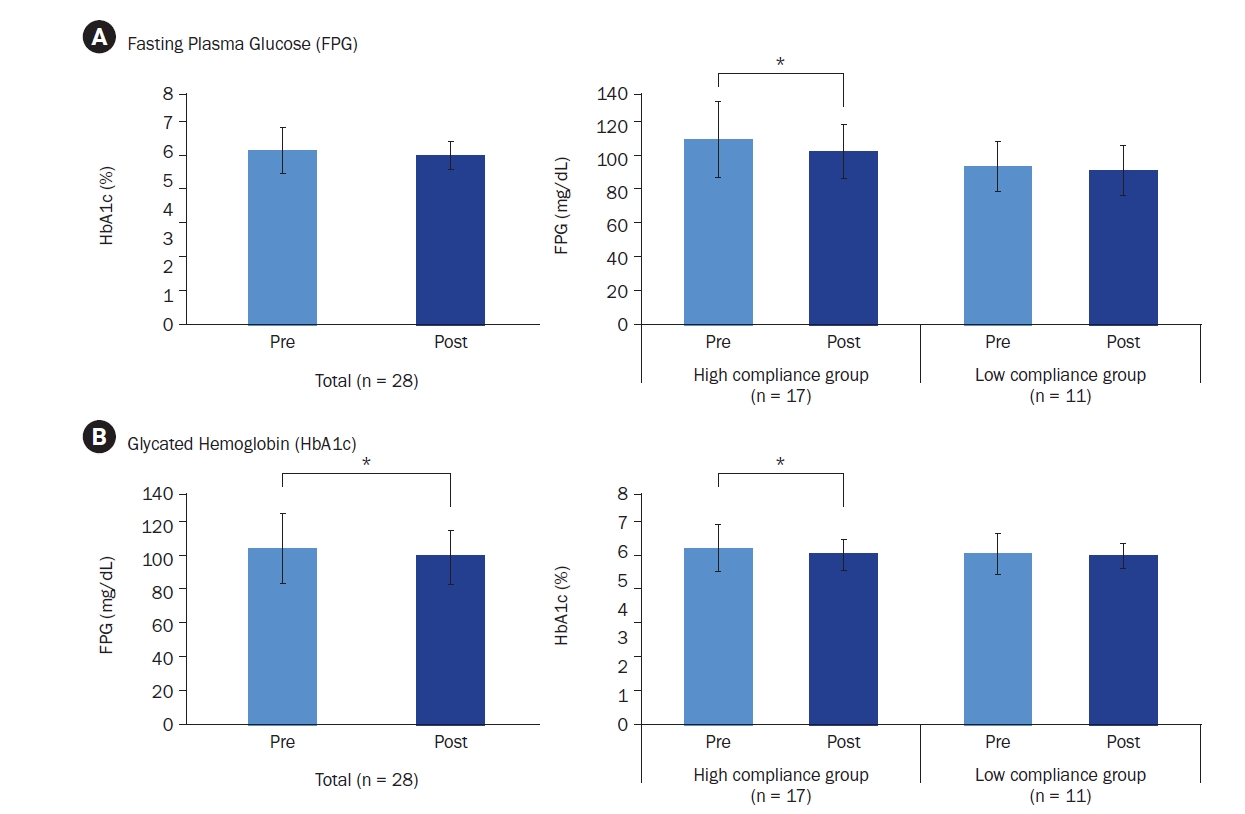
Participants’ average age was 43.89 years, with approximately 80% being male. Most participants (about 75%) were classified as overweight or obese. After six-weeks, 17 participants who adhered closely to the program (meeting certification criteria) exhibited significant reductions in key blood glucose markers. FPG levels decreased from 113.06 ± 23.16 mg/dL to 106.24 ± 16.33 mg/dL (P < 0.05), and HbA1c levels decreased from 6.08% ± 0.81% to 5.87% ± 0.53% (P < 0.05). The NQ evaluation revealed significant increases in comprehensive nutrition scores, and in the balance and practice domain scores for all participants (P < 0.05). Furthermore, in the gut health survey, approximately 82.1% of all participants reported experiencing positive changes.
Conclusion
Among adults with elevated FPG levels, a multi-component intervention program that included PHGG (Sunfiber®) supplementation, structured dietary management, and the use of health-monitoring devices showed significant benefits in improving glycemic control, overall nutritional status, and gut health. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010049. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of dietary and lifestyle habits according to the prediabetic status in young adults
Joungyoon Seo, SeongHee Shin, Yuri Kim, Yoo Kyoung Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 468. CrossRef - Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Combined with a Low-Fat Diet Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites
Zhiqiang Cao, Hongxia Li, Quantao Cai, Li Chen, Liangzhong Liu, Yuhan Tang, Zhe Zhu, Ping Yao
Nutrients.2025; 17(23): 3746. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of dietary and lifestyle habits according to the prediabetic status in young adults
- 7,434 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):528-540. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine health-related characteristics and chronic disease risk in middle-aged Koreans based on their fat energy intake ratio.
Methods
We analyzed data from 7,274 Koreans aged 40–64 years using the 7th (2016–2018) Koreans National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were classified into three groups based on their fat energy intake ratio: insufficient (< 15%), adequate (15%–30%), and excessive (> 30%). We assessed their socio-demographic characteristics; lifestyle characteristics; biochemical characteristics; quantitative and qualitative nutrient intakes, measured using dietary reference intakes for Koreans and index of nutrition quality (INQ); and chronic disease risk.
Results
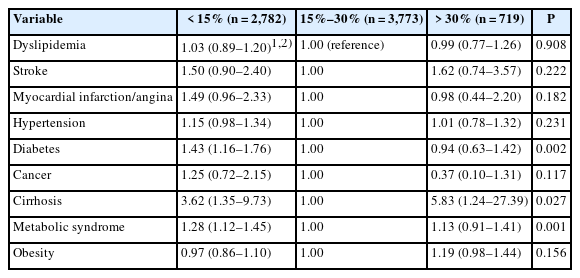
Significant differences were observed between the groups in age, gender, income, education, and residence region. The insufficient group had the highest proportion of older adults, male, lower income, rural residents, and lower education levels. The groups differed significantly in lifestyle characteristics, with the insufficient group having the highest rates of no walking, heavy drinking, smoking, and poor subjective health perception. Biochemical characteristics in the insufficient group exhibited the lowest levels for fasting blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and triglycerides. Significant differences were found in both the quantitative and qualitative intake of nutrients. The insufficient group had the lowest intake of most nutrients except fiber, whereas the excessive group had the lowest fiber intake. Based on the INQ, vitamin A and Ca were the lowest in the insufficient group, and vitamin C and folic acid were the lowest in the excessive group. The risk of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome was highest in the deficient group, and the risk of liver cirrhosis was highest in the excessive group.
Conclusion
Insufficient or excessive fat energy intake ratio negatively affects nutrient intake and chronic disease risk. Fat energy intake of 15%–30% is important for improving nutrient intake and managing chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and liver cirrhosis. We suggest that education and an appropriate social environment are necessary to ensure this fat energy intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
Yu Hyeon Jo, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef
- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
- 1,536 View
- 50 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):492-503. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
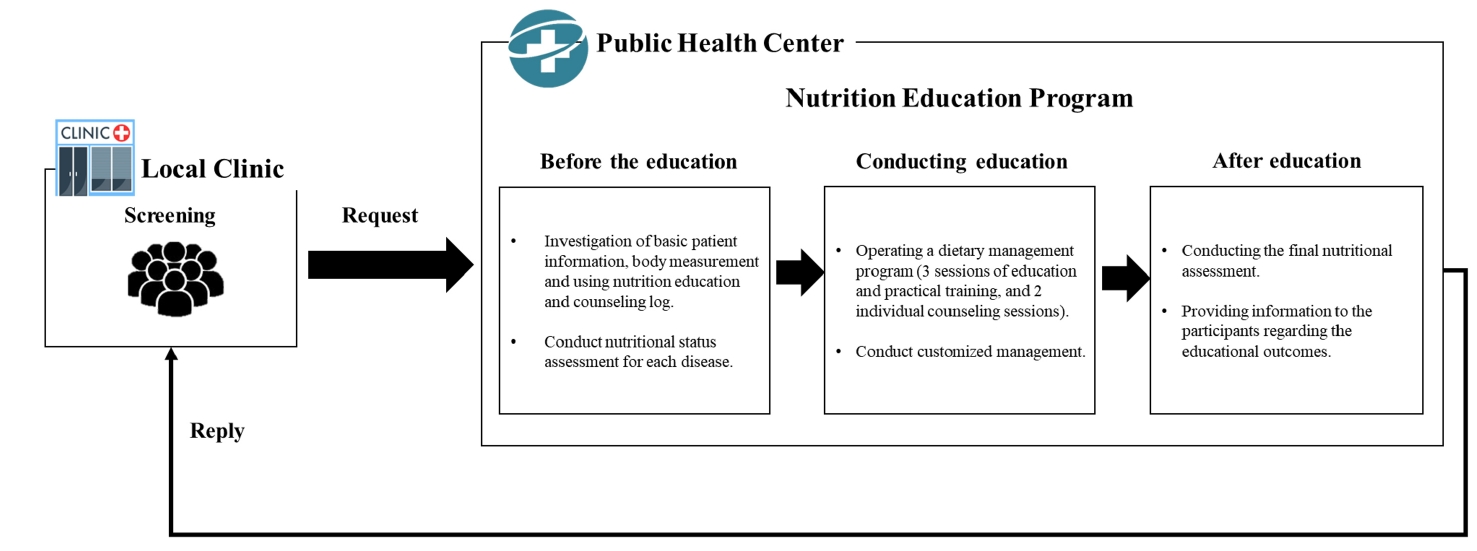
We investigated the impact of an advanced “Nutrition Education Program” on patients with Diabetes mellitus, type 2 from public health centers enrolled in a primary health care-based chronic disease management project. This 12-week dietary management program was developed by the Korea Health Promotion and Development Institute. We assessed if this program improved glycemic control and other health indicators through dietary and nutritional improvements.
Methods
Seventeen patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2 were enrolled in the “Nutrition Education Program.” These patients were referred to public health centers for lifestyle management based on physician assessments at local clinics that were participating in a pilot project on primary health care-based chronic disease management. The participants attended the program comprising face-to-face basic, in-depth, and practical training sessions at the health center during the third, fifth, and seventh weeks, respectively. Anthropometric measurements, body composition analysis, blood biochemical characteristics, nutritional knowledge, and self-efficacy evaluation were performed before and after the program. Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 28.0.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 62 years, and most participants were female (14, 82.4%). No significant changes in patients’ anthropometric measurements or body composition were observed after the training. However, significant reductions were observed in the blood biochemical characteristics, including glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels. Additionally, patients’ nutritional knowledge and self-efficacy scores increased significantly.
Conclusions
The “Nutrition Education Program” helped in improving glycemic control and other health indicators in patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2. Further research is required to objectively confirm the long-term and sustained effects of the program in a controlled study. Trial Registration Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010010
- 2,352 View
- 85 Download

- [English]
- Health-related quality of life and nutrient intake of the elderly with type 2 diabetes according to comorbidity burden: a cross-sectional study
- Yejung Choi, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):418-430. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00014

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to explore the cross-sectional association between health-related quality of life (HRQoL) according to the number of comorbidities in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) using the Euro Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) index. Methods: This study included 3,553 participants aged ≥ 65 years from the 2008–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Dietary data were collected through 24-hour recall interviews by trained researchers, and demographic and lifestyle information via self-administered questionnaires. HRQoL was measured using a modified EQ-5D scale. Multivariable linear regression analyzed the associations between EQ-5D scores, nutrients and comorbidity, controlling for sociodemographic and health variables. Results: Most participants reported ‘no problems’ in the EQ-5D scores, although approximately 17% to 47% of participants reported ‘some problems’ or ‘extreme problems,’ depending on the dimension. As comorbidities increased, significant declines were observed across all dimensions, particularly in mobility, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/ depression. Nutrient intake analysis revealed that participants with three or more comorbidities consumed less carbohydrates, but more fat. Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that among older adults with T2DM, a higher number of comorbidities is associated with decreased HRQoL. Additionally, there are differences in nutrient intake patterns among those with more comorbidities, specifically decreased carbohydrate intake and increased fat intake. These results emphasize the need for comprehensive and tailored management strategies that consider both diabetes and the co-occurring health conditions. By addressing the complex healthcare needs of individuals with multiple comorbidities, it is possible to enhance their HRQoL and overall well-being.
- 2,046 View
- 32 Download

- [English]
- Sex differences in health-related quality of life among older Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
- Hyeonji Jeong, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):336-347. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This cross-sectional study examined sex differences in Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) among seniors with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2008–2020) were analyzed. The EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D), a measure of HRQoL, was used. It comprises five dimensions: mobility, self-care, usual activity, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression, each with three levels.
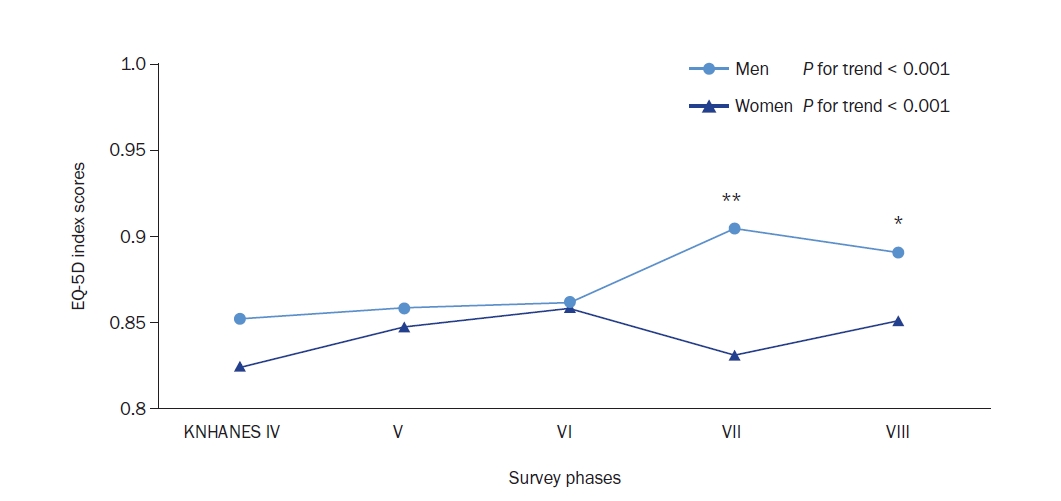
Results
Analysis of 3,826 older adults with T2DM showed a significant increasing trend in the EQ-5D Index from the 4th survey phase onwards (P for trend < 0.001 for both men and women). Men consistently reported higher EQ-5D levels than women across all survey years. Women’s EQ-5D levels remained lower than men’s, maintaining a decade-old disparity (P < 0.05). Men scored significantly higher (P < 0.05) in most EQ-5D domains, except for self-care and anxiety/depression, resulting in a higher total EQ-5D Index (P = 0.001). Increased comorbidities were strongly associated with lower EQ-5D levels in both sexes. Additionally, there was a negative correlation between the EQ-5D Index and refined grain intake for both sexes (P for trend < 0.001), with high-EQ-5D groups consuming fewer refined grains. Women in the high-EQ-5D group consumed more nuts, vegetables, and meat compared to men (P for trend < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our study highlights the sex disparities in HRQoL among older adults with T2DM. The findings suggest the need for tailored treatment guidelines aimed at improving the HRQoL of elderly T2DM patients, with a focus on their sex-specific characteristics. Implementing these tailored guidelines could enhance the HRQoL of older women with T2DM and promote more equitable healthcare outcomes. This underscores the importance of considering sex differences to comprehensively improve the well-being of this population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding Gender Disparities in Quality of Life Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Ethiopia: An Institutional‐Based Study
Enguday Demeke Gebeyaw, Girma Deshimo Lema
Lifestyle Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Understanding Gender Disparities in Quality of Life Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Ethiopia: An Institutional‐Based Study
- 2,524 View
- 40 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Blood Biochemical Characteristics, Dietary Intake, and Risk Factors Related to Poor HbA1c Control in Elderly Korean Diabetes Patients: Comparison between the 4 th (2007-2009) and the 7 th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):406-421. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.406
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the blood biochemical characteristics, comorbidities, dietary intake, and other risk factors leading to poor glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) control in elderly Korean diabetes patients over 65 years of age.
Methods
Data from the 4 th (2007-2009) and the 7 th 2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) were used. Socio-demographic characteristics (age, gender, region, household income, education level, marital status, nutrition education, diabetes duration and diabetes treatment), lifestyle characteristics (drinking, smoking, regular walking, and subjective health perception), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, and waist circumference), blood biochemical characteristics (HbA1c, high- density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, total cholesterol, blood urea nitrogen, and blood creatinine), co-morbidities (obesity, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and anemia), energy and nutrients intake, food group intake, and HbA1c control-related risk factors were compared.
Results
Compared to the 4 th survey, the 7 th survey showed an increase in diabetes prevalence among men, an increase in the prevalence of diabetes in the older patients, and an increase in the duration of diabetes. The energy ratio from carbohydrate consumption in the 7 th survey was lower than in the 4 th .Compared to the 4 th survey, thiamine and riboflavin intake had improved, and the intakes of vitamin A, vitamin C, and niacin had worsened in the 7 th . A comparison of food group intakes showed that there was a decrease in the consumption of whole grains, potatoes, and milk and an increase in the intake of beverages and alcoholic beverages. The risk factors for poor control of HbA1c were the duration of diabetes and co-morbid hypertriglyceridemia in the 4 th survey, whereas subjective health perception, obesity, and hypercholesterolemia as co-morbidities were found to be risk factors in the 7 th in addition to the risk factors highlighted in the 4 th survey.
Conclusions
For the future management of elderly Korean diabetes patients, greater care is indicated for men over 75 years, and those with low levels of education. It is necessary to increase the intake of milk and vegetables, and reduce the intake of beverages and alcoholic beverages. In addition, it is necessary to reduce the incidence of obesity, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertriglyceridemia for proper control of blood sugar. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the Dietary Behavior of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-sectional Study
Sohyun Jin, Youngshin Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 80. CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - Consistency of 1-day and 3-day average dietary intake and the relationship of dietary intake with blood glucose, hbA1c, BMI, and lipids in patients with type 2 diabetes
DaeEun Lee, Haejung Lee, Sangeun Lee, MinJin Lee, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(1): 20. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the Dietary Behavior of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-sectional Study
- 1,941 View
- 41 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Effects of an Intensive Management Program for Diabetic Patients on a Blood Biochemical Profile and Diabetes Knowledge
- Su Jeong Yeo, Bok Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):148-161. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the effects of nutrition education and exercise therapies on the hematological status and diabetes knowledge of diabetic patients. For this purpose, a 12-week intensive management program was provided to diabetic patients participating in an exercise program in S health subcenter in Kwangju city and the effects were analyzed.
METHODS
The subjects were 26 diabetic patients, who provided written informed consent. As a preliminary survey, this study examined the general characteristics, physical status, obesity, blood pressure, hematological status, daily activity level, diabetes knowledge, diet performance, and barriers to diet therapy. After the 12-week intensive management program was completed, a post-test was conducted in the same way as the preliminary test. The data were analyzed with using SPSS 18.0. The data from this study are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. A paired t-test was conducted to compare differences in the means before and after the program. Statistical significance was set to p < 0.05.
RESULTS
The results of the program are presented as follows. The HDL-cholesterol levels changed from 39.8 ± 10.5 mg/dL to 48.3 ± 13.1 mg/dL, showing a significant increase (p < 0.001). The blood sugar 2 hours after a meal changed from 175.2 ± 67.1 mg/dL to 140.5 ± 42.5 mg/dL, showing a significant decrease (p=0.014). The glycosylated hemoglobin levels decreased significantly from 6.7 ± 1.1% to 6.3 ± 1.0% (p=0.010). The total scores of the daily activity levels increased significantly from 3.8 ± 2.4 to 4.8 ± 2.5 (p=0.040). The scores of knowledge on diabetes increased from 11.5 ± 3.6 to 14.0 ± 3.8 (p=0.001). The scores of knowledge on diet therapy changed from 6.7 ± 2.2 to 7.9 ± 1.7, showing a significant increase (p=0.027).
CONCLUSIONS
The 12-week intensive management program intervened by nutrition education and exercise therapies induced positive changes to the HDL-cholesterol, blood sugar 2 hours after a meal, glycosylated hemoglobin, daily activity levels, and knowledge on diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 492. CrossRef - The Associated Factors of Medical Treatment in Diabetic Patients
Sun Ju Choi, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Seong Woo Choi
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 302. CrossRef - Association between diabetes mellitus and anemia among Korean adults according to sex: a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010–2016)
Mihye Kim, Sook-Hyun Lee, Kyoung Sun Park, Eun-Jung Kim, Sujung Yeo, In-Hyuk Ha
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- 1,258 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Needs for Development of IT-based Nutritional Management Program for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Chan Jung Han, Sun Young Lim, Eunsuk Oh, Yoon Hee Choi, Kun Ho Yoon, Jin Hee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(3):207-217. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.3.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to examine self-management status, nutritional knowledge, barrier factors in dietary management and needs of nutritional management program for women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM).
METHODS
A total of 100 women with GDM were recruited from secondary and tertiary hospitals in Seoul. The questionnaire composed of general characteristics, status of self-management, dietary habits, nutrition knowledge, barrier factors in dietary management, needs for nutrition information contents and nutritional management programs. Data were collected by a self-administered questionnaire. All data were statistically analyzed using student's t-test and chi-square test using SAS 9.3.
RESULTS
About 35% of the subjects reported that they practiced medical nutrition and exercise therapy for GDM control. The main sources of nutrition information were ‘internet (50.0%)’ and ‘expert advice (45.0%)’. More than 70% of the subjects experienced nutrition education. The mean score of nutrition knowledge was 7.5 point out of 10, and only about half of the subjects were reported to be correctly aware of some questions such as ‘the cause of ketosis’, ‘the goal of nutrition management for GDM’, ‘the importance of sugar restriction on breakfast’. The major obstructive factors in dietary management were ‘eating more than planned when dining out’, ‘finding the appropriate menu when dining out’. The preferred nutrition information contents in developing management program were ‘nutritional information of food’, ‘recommended food by major nutrients’, ‘the relationship between blood glucose and food’, ‘tips on menu selection at eating out’. The subjects reported that they need management program such as ‘example of menu by calorie prescription’, ‘recommended weight gain guide’, ‘meal recording and dietary assessment’, ‘expert recommendation’, ‘sharing know-how’.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of this study, it is necessary to develop a program that provide personalized information by identifying the individual characteristics of the subjects and expert feedback function through various information and nutrition information contents that can be used in real life. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chronically ailing or failing chronically: a typology of South African diners living with diabetes
Adam Viljoen, Martinette Kruger
International Journal of Spa and Wellness.2024; 7(2): 109. CrossRef - Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Thickness During Pregnancy
Moon Sook Hwang, Eunjeong Song, Jeonghee Ahn, Seungmi Park
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(9): 479. CrossRef - Current Status and Effects of Nutrition Education Programs for Diabetic Patients in Korea
Hae Jin Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(2): 106. CrossRef
- Chronically ailing or failing chronically: a typology of South African diners living with diabetes
- 1,150 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- The Relations between Diabetic Dietary Compliance, Dietary Intake, and Physical Activity and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MS) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Dong Eun Kim, Seung Hee Hong, Ji Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(5):351-361. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.5.351
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relations between diabetic dietary compliance and dietary intake, physical activity and prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MS) in type 2 diabetic patients.
METHODS
Seventy five subjects diagnosed with type 2 diabetes visiting the D hospital in Dongducheon from May 2014 to Dec 2014 were included in this study. The subjects were divided into two groups according to their diabetic dietary compliance score (median 39); low diabetic dietary compliance (LDDC) group (n=44) and high diabetic dietary compliance (HDDC) group (n=31). Survey data collection was carried out by direct interview method. The nutrient intake, food intake and KDDS (Korean's dietary diversity score), DVS (dietary variety score) and GMVDF (grain, meat, vegetable, dairy and fruit) were analyzed using data from the 24-recall method. Metabolic parameters were obtained from the hospital records. Data was analyzed using Chi-square test and general linear model adjusted for sex.
RESULTS
The prevalence of MS was 59.7% in the participating diabetic patients. The prevalence of MS of the HDDC (39.3%) was significantly lower than that of the LDDC (72.7%). The distribution of physical activity showed a significant difference between the groups (p=0.006). The intakes of seeds and nuts of the HDDC were significantly lower than those of the LDDC. Fat and vegetable fat intakes and % fat of energy in the HDDC were significantly lower than those in the LDDC. But, carbohydrate (CHO) and potassium intake and %CHO of energy in the HDDC were significantly higher than those in the LDDC. KDDS and GMVDF showed significant differences between groups (p=0.033; p=0.012).
CONCLUSIONS
Continuous intervention by specialized nutritionists for long-term self-regulation is needed for diabetic patients, and the high compliance to diabetic diet and increasing physical activity may be effective in the prevention of metabolic syndrome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Depression, Patient Activation, and Family Support on Patient Role Behavior of Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Jeong Hyun Park, Jung Suk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 355. CrossRef - The Relationship between Meal Regularity and Oral Health and Metabolic Syndrome of Adults in Single Korean Households
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, On-Ju Ju
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 185. CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef - Healthy Dining Out in Diabetic Patients
Hae-Young Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(4): 264. CrossRef
- Effects of Depression, Patient Activation, and Family Support on Patient Role Behavior of Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- 1,176 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of Web-based u-Health Self-nutrition Management Program for Diabetic Patients
- Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Hee Seon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(4):372-385. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.4.372
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to develop web-based self-nutrition management u-Health program for diabetic patients (DMDMG: Diabetes Mellitus Dietary Management Guide) for achieving systematic self-management of diet.
METHODS
The program consisted of five parts with different contents according to the results of needs assessment. Five major parts were 1) meal management part which contains calorie prescription, meals recording and dietary assessment, 2) prevention of disease part with information of diabetes and assessment of dietary behavior, 3) dietary behavior modification part with an education on dietary behavior modification plan and dietary behavior plan, 4) meal plan containing a training section for meal plan and self constructing part for meal planning by making tables, and 5) information about myself which composed with general and physical information. The system proposed in this study provides nutrients intake results right after input of diet intake, which is possible with simultaneous calculation of input data in the server with 3,495 food and 1,821 meal data base. The nutrients analysis program was evaluated with 26 diabetic patients with two-day 24 hr recall.
RESULTS
The differences of nutrients intakes between DMDMG and CANPRO 3.0 ranged from 13.5-16.5%, which was caused by the differences of databases of the two programs. The characteristics of DMDMG were; 1) it can provide an interactive tailored nutrition management, 2) it is a practical tool of diabetes nutritional management, 3) the program gives motivation for the dietary behavior modification.
CONCLUSIONS
The effectiveness of whole program needs to be conducted, but the program was an innovative tool for self-management of nutrient intakes, diet behaviors, meal management and tailored nutrition education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dyadic Profiles of Health Behaviors Among Korean Baby Boomer Couples
Bon Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jeffrey A. Burr, Joohyun Kim, Gyounghae Han
Journal of Applied Gerontology.2021; 40(10): 1320. CrossRef - Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - The development of a mobile u-Health program and evaluation for self-diet management for diabetic patients
Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Hee-Seon Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(3): 342. CrossRef
- Dyadic Profiles of Health Behaviors Among Korean Baby Boomer Couples
- 1,186 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Lifestyle, Diet, Self-care, and Diabetes Fatalism of Diabetic Patients with and without Diabetic Foot
- Jungha Choi, Juhee Kang, Hongmie Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(3):241-249. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.3.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was to determine diabetes fatalism of diabetic patients with and without diabetic foot and its association with lifestyle, diet, and self-care.
METHODS
The subjects were diabetic patients with (male/female 48/21) and without diabetic foot (male/female 33/26). We administered the questionnaires which were designed to determine diabetes fatalism, lifestyle, diet, and self-care. Diabetes fatalism was determined by Diabetes fatalism scale (DFS), which consisted of total 12 items in three subscales namely, emotional stress, religiou.spiritual coping, and perceived self-efficacy.
RESULTS
The patients with diabetic foot had undesirable diets more frequently (1.37 and 0.91 days/week respectively) and their desirable diets (2.74 and 3.61 days/week respectively) and foot care (4.61 and 5.53 days/week respectively) were less frequent than those without diabetic foot (p < 0.05). An item analysis of the 12 DFS items revealed a Chronbach' alpha of 0.614 and 0.869, respectively in diabetic patients with and without diabetic foot. Perceived self-efficacy related DFS of subjects without diabetic foot was positively associated with smoking (r = 0.350, p < 0.01), undesirable diet (r = 0.295, p < 0.05), and drinking (r = 0.257, p < 0.05), while its negative association with exercise (r = -0.224, p < 0.088) and foot care (r = -0.247, p < 0.059) did not reach to statistical significance.
CONCLUSIONS
This work was the first study reporting the potential usefulness of DFS, especially perceived self-efficacy related subscale as a predictor of lifestyle, diet and self-care on the Korean diabetic patients, at least those without severe diabetic foot to screen those who should be the first target for diabetes education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Glycemic Control by gender in Workers with Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Hee Jang
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(2): 121. CrossRef - Association of selected health behaviors with perceived health, depressive symptom and fatalism among the aged 50-69 living in Seoul
Eun Jin Choi, Min Hye Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2015; 32(2): 53. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Glycemic Control by gender in Workers with Diabetes Mellitus
- 1,207 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitude, and Dietary Behavior among Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
- Na Yeon Noh, So Young Nam, Hee Suk Kang, Ji Eun Lee, Soo Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(2):101-111. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.2.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Type 1 diabetes is on the rise worldwide. Although nutrition education for patients with diabetes has become a routine practice, specifics and impacts of such educations need to be more researched. This study examined the status of nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude, and dietary behavior among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (9-19 year-old) and explored factors influencing dietary behaviors related to diabetes by applying the Theory of Planned Behavior. Face-to-face interviews, using a pre-tested structured questionnaire, were conducted with 32 participants (11 boys and 21 girls) with type 1 diabetes followed by a diabetes clinic in a university hospital. This study found that the level of nutrition knowledge related to diabetes was generally low at 4 points out of a possible 10, however, the dietary attitude related to diabetes was found to be generally good at 26 points out of a possible 30. Participants were motivated to follow medical staff recommendations the most; however, their family was also important. Perceived behavioral control was low especially for eating-out and portion control. The dietary behavior related to blood glucose control showed low at 13 points out of a possible 20. Regression analysis showed that perceived behavioral control (p < 0.001) was significantly related to the dietary behavior related to blood glucose control. This rare study with children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes showed that nutrition education should include a component to improve perceived behavioral control through high-risk situation management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spatial Distribution of Diabetes Prevalence Rates and Its Relationship with the Regional Characteristics
Eun-Kyung Jo, Eun-Won Seo, Kwang-Soo Lee
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(1): 30. CrossRef
- Spatial Distribution of Diabetes Prevalence Rates and Its Relationship with the Regional Characteristics
- 1,191 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutritional Education Practice Program for Cardiocerebrovascular High-risk Group at the Education Information Center
- Hang Me Nam, Seung Hee Woo, Young Ji Cho, Yun Jung Choi, Su Yeon Back, So Yeon Yoon, Jin Young Lee, Jung Jeung Lee, Hye Jin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(5):580-591. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.5.580
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This research was performed to investigate the effects of NEP (Nutritional Education Practice) program developed by KHyDDI (Korea Hypertension Diabetes Daegu Initiative) for hypertension and diabetes patients. The subjects were 116 patients (hypertension 70, diabetes 46) who had completed basic education program at the education information center and four-session program was implemented for them. Nutrient intake was analyzed and compared before and after the program by 24-hr recall method and evaluate weight, waist circumference, body fat, blood pressure and eating habits in terms of nutrition knowledge, eating behavior, salty taste assessment. The improved results after the program were observed in weight, waist circumference, body fat ratio, blood pressure, slightly salty taste in salty taste assessment, nutrition knowledge, eating behavior, sodium, energy, carbohydrate and protein intake ratio to total energy (p < 0.001). Therefore, this program is effective in the improvement of weight, waist circumference and eating behavior, and the continued management would lead to the prevention of cardio-cerebrovascular diseases in the community.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of differential cost sharing of prescription drugs on the use of primary care clinics among patients with hypertension or diabetes
Eunja Park, Daeeun Kim, Sookja Choi
Public Health.2019; 173: 105. CrossRef - Effect of Staged Education Program for Hypertension, Diabetes Patients in a Community (Assessment of Quality of Life Using EQ-5D)
Jung Jeung Lee, Hye Jin Lee, Eun Jin Park
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2014; 39(1): 37. CrossRef - Comparison of the Health Behaviors according to Income and Education Level among Cardio-Cerebrovascular Patients; based on KNHANES data of 2010-2011
Ji-Yeon Choi, Seong-Woo Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(10): 6223. CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education and Personalized Lunch Service Program for Elderly at Senior Welfare Center in Jeonju
Jeong-Sook Bae, Mi-Hyun Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(1): 65. CrossRef - Community-based Nutritional Management for Secondary Prevention of Diabetic Macrovascular Diseases
Hye Jin Lee, Jung Jeung Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(1): 36. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Community Staged Education Program for the Cardiocerebrovascular Disease High-risk Patients
Hye-Jin Lee, Jung-Jeung Lee, Tae-Yoon Hwang, Sin Kam
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2012; 37(3): 167. CrossRef
- The impact of differential cost sharing of prescription drugs on the use of primary care clinics among patients with hypertension or diabetes
- 1,032 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Needs Assessment for Web-based Self-management Program by the Nutrition Knowledge Levels of Diabetic Patients
- Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Jung Eun Youn, Hee Seon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(1):155-168. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.1.155
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to assess needs of self-management nutrition program for diabetic patients. The survey was conducted among 100 diabetic patients, and the mean age of the subjects was 54.2 years old. Thirty three percent of the subjects were diagnosed diabetes less than 2 years ago. The average nutrition knowledge score about diabetes was 10.2 point, and percentages of correct answers were very high in 'foods rich in fiber' (97.0%), 'relevance of exercise and insulin' (97.0%), 'quantity of insulin injection' (91.0%), and 'diabetes menu' (91.0%). The sources of nutrition information were hospitals/healthcare centers (56.1%), TV/radio (19.2%), and internet (13.1%). Sixty nine percent of the subjects have experienced nutrition education on subjects as 'menu planning skills' (22.4%), 'selecting foods' (22.4%), 'relevance of blood glucose and eating foods' (21.5%) by personal counseling (54.4%). The total score of eating behavior was higher after diagnosed diabetes (35.3) than before (30.0) (p < 0.001). The preferred topics in developing diabetes nutrition information websites were 'diabetes mellitus', 'relevance of blood glucose and foods', and 'selecting foods for diabetes'. The subjects wanted the websites developed by 'using mainly illustrations, pictures, tables' (22.8%) and 'using simple design' (19.6%). The preferred contents in developing diabetes self-management nutrition program were 'dietary life diagnosis', 'chronic disease risk diagnosis', 'calorie control by selecting foods and cooking skills', and 'dietary assessment'. In designing the program, the subjects' most wanted designs were 'be handy and simple in using' (29.3%), 'using simple design' (17.9%), and 'using mainly illustrations, pictures, tables' (15.7%).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Needs for Development of IT-based Nutritional Management Program for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Chan-Jung Han, Sun-Young Lim, Eunsuk Oh, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jin-Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 207. CrossRef - The development of a mobile u-Health program and evaluation for self-diet management for diabetic patients
Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Hee-Seon Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(3): 342. CrossRef - Dietary Life related to Sodium of Participants in Hypertension and Diabetes Preventive Education at the Public Health Center
Hee-Ok Pak, Chun-Young Sohn, Jung-Hwa Park
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(2): 219. CrossRef - Development of Web-based u-Health Self-nutrition Management Program for Diabetic Patients
Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Hee-Seon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 372. CrossRef - A Study on Classification of Obesity for Koreans based on the Articles in the Korean Journal of Community Nutrition - Articles Enlisted from 1996 to 2011 -
Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(5): 525. CrossRef
- Needs for Development of IT-based Nutritional Management Program for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- 1,054 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Study on Diet-related Quality of Life in Online Self-help Diabetes Mellitus Patients Who Practice Dietary Regimen
- Han Sul Lee, Jinhee Joo, Ryowon Choue
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(1):136-144. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.1.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Assessment of quality of life (QOL) is a new method to investigate the effectiveness of dietary regimen. Particularly, diet-related QOL is the most appropriate method to estimate social and psychological problems originated from dietary regimen practice. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the diet-related QOL and the correlation between diet-related QOL and health-related QOL, and dietary regimen practice in online diabetes self-help patients who practice the dietary regimen. Sixty one subjects who intended to practice dietary regimen were recruited from online diabetes self-help community, and instructed to fill-up the self report questionnaires. Contents of questionnaire were comprised of general characteristics, clinical characteristics, dietary compliance, and dietary regimen practice. As a result, the mean score of the 'Dietary impact' among the diet-related QOL sub-scales was the lowest suggesting most of the subjects suffer from burden of dietary regimen practice. The "Dietary impact" was correlated with "Taste", "Convenience" and "Cost" (p < 0.05). "Self-care" and "Satisfaction" were positively associated with well-controlled blood glucose and dietary regimen compliance, but negatively associated with "Dietary impact". Diet-related QOL was significantly correlated with the Health-related QOL, particularly the mental and social component (p < 0.05). Diet-related QOL was negatively associated with BMI, and self monitoring blood glucose was negatively correlated with "Self-care" (p < 0.05). In conclusion, Diet-related QOL might be appropriate to evaluate the effects of dietary regimen or nutrition education. The need for dietary education of cognitive-behavioral strategies and problem-solving ability is required.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Topic Modeling Analysis of Diabetes-Related Health Information during the Coronavirus Disease Pandemic
Soyoon Min, Jeongwon Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(13): 1871. CrossRef - The Relations between Diabetic Dietary Compliance, Dietary Intake, and Physical Activity and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MS) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Dong Eun Kim, Seung Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 351. CrossRef - Effects of Diet Modification on Meal Quality and Quality of Life in Korean Diabetic Patients: Data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007-2011)
Yoonsu Cho, Min-Jeong Shin, Hye-Kyung Chung
Clinical Nutrition Research.2014; 3(2): 106. CrossRef - Association of diet-related quality of life with dietary regimen practice, health-related quality of life, and gastrointestinal symptoms in end-stage renal disease patients with hemodialysis
JinJu Lee, Ji-Myung Kim, Yuri Kim
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2013; 46(2): 137. CrossRef
- Topic Modeling Analysis of Diabetes-Related Health Information during the Coronavirus Disease Pandemic
- 1,197 View
- 4 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Development and Effects' Analysis of Nutrition Education Program for Diabetes Mellitus at Community Health Center: Focused on Individual Daily Energy Requirements and Food Exchange Units
- Ji Yoon Oh, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(4):485-497. Published online August 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of the developed nutrition education program focused on individual daily energy requirements and food exchange units using Food Exchange System for diabetes mellitus at a community health center. Developed the nutrition education program, four weeks' nutrition education including provided twice individual meal as diet therapy (2 hour/lesson/week, 4 week), was provided to 20 diabetic elderly (12 male, 8 female, 50-75 yrs): 1st lesson "Introduction: management of diabetes mellitus", 2nd lesson "6 Food groups and sources of 6 food groups", 3rd lesson "Individual daily energy requirements and food exchange units", and 4th lesson "Food choice for diabetes mellitus". For effects' analysis of the developed program, we assessed the changes in anthropometric characteristics; biochemical characteristics and nutrient intakes using 24 hr recall method. Effects of the developed nutrition education program were as follows: weight was significantly decreased, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were significantly decreased, and distribution of subjects in BUN and HbA1c was significantly changed. In protein : fat : carbohydrate (PFC) ratio, it was significantly changed from 15.98 : 16.30 : 66.69 to 17.51 : 18.94 : 64.10. In evaluation of nutrient intakes by Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans (KDRI), protein, fiber, fat, vitamin E, niacin, folic acid, calcium and zinc were shown significantly positive changes in distribution of subjects according to intake level. The index of nutrition quality (INQ), nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean nutrition adequacy ratio (MAR) were significantly increased. In conclusion, the developed 4 weeks' nutrition education program focused on individual daily energy requirements and food exchange units using Food Exchange System for diabetes mellitus at community health center may improve the symptom of diabetes mellitus.
- 260 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrition Education for Diabetes Mellitus Management of Older Adults
- Hyun Joo Kang, Eun Mi Shin, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):734-745. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diabetes mellitus is the prevalent disease among older adults. The purpose of this study was to implement and evaluate the nutrition education program for diabetes mellitus patients aged 60 and over. The one group pretest and posttest design was employed to evaluate the program effectiveness. Nutrition education program for diabetes mellitus patients was carried out at the public healthy center in Guri city. The 38 out of 63 patients completed education program. They received four sessions of group education during four weeks. Nutrition education materials (booklet, leaflet) for older adults were provided to participants. Data about blood glucose, blood pressure, nutrition and diabetes mellitus knowledge, dietary behavior, dietary intake by 24-hour recalls were collected before and after nutrition education to evaluate the program effectiveness. All data were statistically analyzed using SAS package (ver.8.2) and significant difference was evaluated by chi-square-test, paired t-test and Wilcoxon signed rank test. Study results showed that blood pressure and blood glucose were slightly decreased after nutrition education but they did not reach statistical significance. There were positive changes in nutrition knowledge and dietary behavior. The total score of nutrition and diabetes knowledge increased significantly (p < 0.001), and the total score of dietary behavior was improved (p < 0.05) after nutrition education. Dietary intakes of most of nutrients examined were not significantly different between preand post-test. Based on study results, it appears that nutrition education program for the aged diabetes mellitus patients might effectively increase nutrition knowledge, dietary behavior and diet quality. This nutrition education program can be used at the public health centers or senior centers for the management of diabetes mellitus for older adults.
- 355 View
- 14 Download

- [English]
- A Factor Analysis Study on Blood Glucose Control in Diabetics Mellitus Patients(1):Focus on Blood Glucose Control and Lifestyle Factors
- Jungeun Jun, Youngmee Lee, Yu jin Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(2):236-244. Published online April 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dietary therapy is a basic and emphasized treatment for diabetes. Several clinical studies have shown that diet can play a major role in preventing and managing diabetes. The purposes of this study were to evaluate the dietary behavior and to find solutions to barriers of diabetes mellitus patients. From February to July in 2007, questionnaires were distributed to one hundred and ten patients who were diagnosed DM by physicians and excluded first coming out-patients. One hundred and three data were used for statistical analysis using SPSS/Win 12.0. The main results of this study included the following: To measure dietary behaviors and barriers, a five point scale was used with the following labels: 'strongly yes', 'yes', 'fair', 'no', 'strongly no'. Thirteen dietary behaviors related to diabetes were grouped into the following 4 factors using factor analysis; 'taste control factor', 'blood glucose influence factor', 'practice volition factor', and 'exercise factor'. The mean scores of 4 factors were 3.88, 3.48, 3.55, 3.21, respectively. The 'taste control behaviors' score of subjects who had practiced diet therapy (4.00) was higher than those who had not practiced diet therapy (P < 0.05). The 'blood glucose influence behaviors' score of subjects who had nutrition education (3.59) was higher than those who had no nutrition education (P < 0.05) and subjects who had practiced diet therapy showed higher score (3.59) than those who had not practiced diet therapy (P < 0.05). 'Exercise behaviors score' of subjects who were over 60 (3.59) was the lowest (P < 0.05). Subjects who had nutrition education showed higher 'exercise behaviors' scores (3.38) than those who had no nutrition education (P < 0.05). Subjects who had practiced diet therapy showed higher 'practice volition behaviors' scores (3.72) than those who had not practiced diet therapy (P < 0.001). Subjects who were over weight showed the highest 'practice volition behaviors' scores (3.78) concerning BMI (P < 0.05). In conclusion, this study expected that Nutrition educators (Dietitian) applied to patient effective nutrition education and counseling through evaluation of Dietary behaviors and barriers considered management types and ecological factors of diabetes patients. Also diabetic patients were easy to change dietary habits because they formed behaviors through education and counsel and there were positive effects in their blood glucose control through removing barriers related to dietary therapy.
- 260 View
- 2 Download

Randomized Controlled Trial
- [English]
- Nutritional Status of Zinc and Copper in Type 2 Diabetic Patients after Short-term Zinc Supplementation
- Hyun Mee Oh, Jin Sook Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(2):229-235. Published online April 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to determine whether a short-term zinc supplementation could improve the zinc status without adverse changes in copper status among type 2 diabetic patients. Seventy-six diabetic subjects and 72 normal adults participated in this study. Subjects were randomly divided into supplemented and control groups. Forty-four diabetic patients and 34 normal subjects were supplemented with 50 mg zinc gluconate daily for 4 weeks. Dietary intakes of participants were measured for two non-consecutive days by 24-hour recall method. Nutritional status of zinc and copper were also evaluated by biochemical measurement of fasting plasma samples and spot urinary collection. At baseline, diabetic patients showed significantly lower levels of dietary zinc intake and higher urinary zinc excretion than the normal adult group (P < 0.05, P < 0.0001). Plasma level of zinc was not significantly different between diabetic and normal adults at baseline. However, plasma zinc level increased significantly in both diabetic patients and normal adults after zinc supplementation. The changes in plasma copper levels following zinc supplementation were not statistically significant in diabetic subjects as well as in normal adults. These results indicated that four weeks of zinc supplementation did not influence Cu status and that it may contribute to improving the zinc status. Therefore, we suggest that Zn supplementation for a short-term period may improve marginal zinc status of diabetic patients without interfering with their copper status
- 265 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- Dietary Antioxidant Vitamins Intakes and Plasma Antioxidant Levels in Korean Elderly with Diabetes Living in Ulsan
- Mi Joung Kim, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(2):276-287. Published online April 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diabetic mellitus in an older population is associated with increased basal oxidative stress and free radical accentuated by hyperglycemic challenge. Enhanced free radical in diabetic elderly can cause the oxidative damage and such damage can be protected by antioxidant defense system. It is believed that vitamin C, A and E are the most abundant and effective antioxidants in human plasma. The purpose of this study was to determine the antioxidant status in Korean diabetic elderly using the case-control study. The antioxidant status was examined by determining plasma levels of antioxidant vitamins (vitamin C, A, E, beta-carotene), total antioxidant status (TAS) and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) and intakes of vitamin C, A, beta-carotene and retiol. Fasting glucose and HbA1c levels and serum lipid profiles (triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol) were also determined. Diabetic subjects were 122 elderly persons over 60 years old, visiting public health center, and control subjects were 96 healthy elderly persons living in Ulsan, Korea and they were matched by age, gender, smoking and drinking status. The diabetic and control subjects were divided into sub-groups according to the status of using diet therapy and vitamin supplement. The subjects were interviewed to collect data on their general characteristics, disease history, vitamin supplement, diet therapy and health-related habits by questionnaires. Their dietary intakes were obtained by means of semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaires (SQFFQ). Fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c levels were significantly higher in diabetes than in control subjects, and plasma total cholesterol level of diabetes was not significantly different from that of control subjects. However serum HDL cholesterol level of diabetes was significantly lower and serum TG level of diabetes was significantly higher than those of control group. The average vitamin A and beta-carotene intakes of diabetes were significantly higher than those of control subjects. There was no significant difference in plasma vitamin C, beta-carotene, and TBARS levels between two groups, but plasma vitamin A, E and TAS levels were significantly higher in diabetes than those in control group. Plasma vitamin A and TAS levels of diabetic subjects using diet therapy were higher than those of control using diet therapy, and plasma vitamin E, beta-carotene and TAS levels of diabetic subjects using vitamin supplements were significantly higher than those of controls using vitamin supplements. These results suggested that diabetic mellitus could enhance antioxidant defences against reactive oxygen species and interest in healthy eating such as consumption of more antioxidant nutrients.
- 340 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Nutritional Status and Inflammational Markers in DM and nonDM Hemodialysis Patients
- Suan Kim, Cheongmin Sohn, Dong Wan Chae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(5):693-699. Published online October 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Protein-calorie malnutrition is common in maintenance dialysis patients. Indeed, diabetic patients with chronic renal failure are considered to be at increased risk of malnutrition. The aim of this study was to compare the nutritional status and markers of inflammation of hemodialysis patients with and without type 2 diabetes. We compared nutritional parameters and C-reactive protein (CRP) as a marker of inflammation in 30 type 2 diabetic patients and age-matched 30 non-diabetic patients with hemodialysis. Serum albumin was significantly lower in patients with type 2 diabetes (3.45 +/- 0.43 g/dL) than in non-diabetic patients (3.64 +/- 0.36 g/dL) (p < 0.05). In contrast, the concentration of serum CRP was significantly higher in type 2 diabetes (1.42 +/- 1.8 mg/dL) (p < 0.05). There were significant negative-relationships between serum albumin and CRP level in both diabetic (r = -0.553, p < 0.01) and non-diabetic (r = -0.579, p < 0.01) patients. In diabetic patients, serum albumin level was significantly correlated with hemoglobin (r = 0.488, p < 0.01) and hematocrit (r = 0.386, p < 0.01). Diabetic patients as compared to non-diabetic patients showed a significant (p < 0.01) increased serum triglyceride (TG) (153.1 +/- 80.1 mg/dL vs 101.6 +/- 62.4 mg/dL) and decreased serum HDL cholesterol (36.89 +/- 13.48mg/dL vs 47.00 +/- 14.02 mg/dL, P < 0.05). There were significant correlations in the intake of calorie and serum albumin levels in both diabetic (r = 0.438, p < 0.05) and non-diabetic (r = 0.527, p < 0.05) patients. Serum CRP level was negatively correlated with calorie (r = -0.468, p < 0.05), protein (r = -0.520, p < 0.01) and fat intakes (r = -0.403, p < 0.05) in diabetic patients and calorie (r = -0.534, p < 0.05) and protein intakes (r = -0.559, p < 0.05) in non-diabetic patients. The prevalence of protein malnutrition and the risk factors of cardiovascular disease were significantly higher in type 2 diabetic patients than in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients. Thus, we can suggest that the higher comorbidity and mortality rate in diabetic hemodialysis patients are partially explained by malnutrition and inflammation.
- 320 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Relationship between Zinc Status and Obesity of Type 2 Diabetic Women
- Jung Hee Lee, Hee Ja Lee, In Kyu Lee, Jin Sook Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(1):70-78. Published online February 28, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Zinc is known to have important effects on insulin activity and to increase the body fat deposition. The purpose of this study was to investigate the zinc status and obesity in 50 type 2 diabetic women visiting public health center and hospital. The mean age was 57.9 +/- 6.9 years old. The mean of diabetic duration was 8.0 +/- 6.5 years. Body mass index (BMI) of diabetes was 23.2 +/- 2.3 kg/m2. There were no significant differences of mean age, anthropometric indices, and insulin level other than fasting blood sugar (p< 0.001) and insulin resistance (p< 0.001) between diabetes and control group. The obesity ratio of diabetes was 20%, 66% and 84% for BMI, waist circumference and waist/hip ratio (WHR), respectively. Plasma zinc level was not significantly different between diabetes and control group. However, urinary zinc excretion of diabetes was approximately twice of control group (p< 0.001). Urinary zinc loss was fivefold higher in the hyperglycemia (HbA1c > 10%) than in normal blood glucose (p< 0.001). Anthropometric indices were decreased in hyperglycemia. On the other hand, there were the tendency of increased urinary zinc in obese group for waist circumference and percent of body fat. These results suggested that controlled normal blood glucose could improve hyperzincuria and anthropometric changes in type 2 women diabeties.
- 316 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Dietary Intakes and Plasma Lipid Levels in Diabetes and Control Elderly
- Sang Eun Lee, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(1):98-112. Published online February 29, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - ABSTRACT This study was done to investigate and compare the nutritional status and plasma lipids in the diabetes and control elderly. Subjects were 105 persons (male 32, female 73) aged over 65 years and visited public health centers in Ulsan area. The subjects were divided into 2 groups, diabetes and control group. Athropometric measurement, dietary intakes, and plasma biochemical indices were examined. Body Mass Index (BMI), Percentage of Ideal Body Weight (PIBW) and Waist-Hip Ratio (WHR) of diabetes group were higher than those of control group. Overall eating behavior were worse in diabetes group than those of control group. There was no significant difference in smoking and exercise status among groups. The ratio of drinkers was significantly higher in control group. But the amount of alcohol consumed at once was higher in the diabetes group. There was no significant difference in most nutrient intakes between males and females. The intakes of fiber, natrium (Na), vitamin A, and beta-carotene were significantly higher in diabetes group than control groups while that of potassium (K) was lower in diabetes group. Diabetes group had the higher levels in triglyceride, VLDL-cholesterol, Chol/HDL-cholesterol ratio, LDL/HDL-cholesterol ratio, while they had lower HDL-cholesterol level. Overall results might imply that the elderly with diabetes have to be more careful to their meals and health-related behaviors to increase the likelihood of a healthier life.
- 286 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Sociopsychological Factors Influencing the Dietary Compliance of Diabetics by Using Focus Group Interview
- Sun Jung Choe, Hae Ryun Park, Dong Yean Park, Hong Seok Ahn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2000;5(1):23-35. Published online March 31, 2000
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to find the sociopsychological factors influencing the compliance of dietary regimen in diabetes by using focus group interviews. The data were collected from fifty three diabetes patients in eleven focus groups from September 1997 to March, 1998 in Seoul and Suwon Korea. The interviews were tape-recorded and the contents of the interviews were analysed by researchers. The subjects knew the causes, complications, and therapies of diabetes although they were incorrect at times . Patients had a wide range of outcome expectations from very optimistic to pessimistic. They recognized diabetes as a disease which needs life-time care, and they though that good care could provide a normal life. One the other hand they thought diabetes could lead to death through complications, and cause financial problems as well as social isolation. As for self-efficacy they recognized the importance of compliance to diet regimen but they thought the diet therapy was very difficult and were not very willing to follow it. They felt medical professionals, especially doctors, were influential for the therapies. However they frequently felt counselling provided by doctors was insufficient in time and content and led to attitude problems. They felt support from families and others was often insufficient and inadequate. Nutrition education fostering outcome expectation, social support, and self-efficacy is needed to increased compliance. The most influential referents were medical professional including doctors, nurses, dieticians, so their role in diet therapy should by emphasized.
- 340 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Distribution and Prevalence Estimation of Cardiovascular Risk Factors through Community Based Health Examination Survey
- Soon Young Lee, Youngok Kim, Kun Sik Han, Hae Kyung Kim, Ju Won Park, Yeon Kyung Lee, Seung Soo Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 1999;4(4):521-528. Published online December 31, 1999
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cardiovascular disease is very prevalent in Korea, and many risk factors, if properly identified are possibly corrected. However, the study results on prevalence and distribution of risk factors may not be reliable while the risk factors of disease are always issued on health promotion projects conducted recently in a community. The subjects of this study were 854 adults who participated in the health and nutrition survey in a community. They were aged between 20 and 69 and sampled representatively. This study intended to estimate the prevalence and the distribution of risk factors of cardiovascular disease such as hypertention, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity. Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure levels were estimated at 123.9+/-2.2mgHg(men), 117.9+/-1.7mgHg(women), and 80.4+/-1.5mg(men), 74.9+/-1.1mgHg(women), respectively. Glucose level was estimated at 99.1+/-2.3mg/dl in men, and 95.7+/-1.7mg/dl in women. The estimated level of total cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol were 183.4+/-3.8mg/dl(men), 181.7+/-3.1mg/dl(men), and 122.0+/-4.5mg/dl (women), and body mass index was estimated at 24.0+/-0.4kg/m2 in men and 23.9+/-0.4kg/m2 in men and 23.9+/-0.3kg/m2 in women. The prevalence of hypertension was 20.5% for men, and 14.4% for women. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus was estimated to 6.9% for men, and 6.1% for women. The estimated prevalence of hypercholesterolemia was 3.8%(men), 3.9%(women). The rate of obesity was estimated to 28.5%(men), 28.4% (women), respectively. The levels of blood pressure, glucose, and cholesterol were higher in men than in women in almost all the almost ate groups. The prevalence of hypertension for men is about 20%. It was found that the prevalence of diabetes mellitus for males aged between 40 and 59 was rapidly increased. The risk factor with highest prevalence was obesity, and hypertension and diabetes mellitus were the second and third most prevalent.
- 308 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Effects of Taurine and ??-alanine on Blood Glucose and Blood Lipid Concentrations in Insulin-treated Diabetic Rats
- Kyung Ja Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 1999;4(1):103-110. Published online March 31, 1999
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to determine the effects oftaurine supplementation and taurine depletion on blood glucose and blood lipid concentrations in insulin-treated diabetic rats. Four groups of Sprague-Dawley male rats were fed the purified diet for 3 weeks ; nontaurine-supplemented diabetic rats(E0), nontaurine-supplemented diabetic rats with insulin treatment(E0+I), 1% taurine-supplemented diabetic rats with insulin treatment(E1+I) and taurine-depleted diabetic rats with insulin treatment(EA+I). Diabetes was induced by streptozotocin injection(50mg/kg B.W.). Isophane insulin was given subcutaneously into the abdominal wall of the diabetic rats(4 unit/rat/day). E1+I were supplemented with 1% taurine in drinking water. To induce taurine depletion, EA+I were treated with 5% beta-alanine in drinking water. E1+I had significantly higher body weight compared to that fo E0. The food intakes of E1+I and E0+I were significantly decreased compared to that of E0. There was no sigfniciant difference in food intake between E1+I and E0+I. The water intake of rats was significantly different among the groups ; E0>E0+I>E1+I>EA+I. The urine volume of E0 was significantly increased compared to those of insulin-treated goups. The blood glucose concentration of E0 was significantly increased compared to those of insulin-treated groups. In the oral glucose tolerance test(OGTT), E0+I and E1+I had significantly lower blood blucose concentrations compared to E0 after 30 min. Also EA+I had significantly lower bloodglucose concentrtion compared to E0 and E0+I. The plasma total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol concentratons of EA+I were significantly incrased compared to those of other groups. Therefore, it may be suggested that tuarine supplementation is useful for insulin-dependent diabetes in order to prevent diabetic complications suchas cardiac vascular diseases.
- 293 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



