Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung Su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):53-63. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
To apply a healthy dietary program with reduced sodium intake, developed using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), focusing on the sodium intake level and eating patterns.
Methods
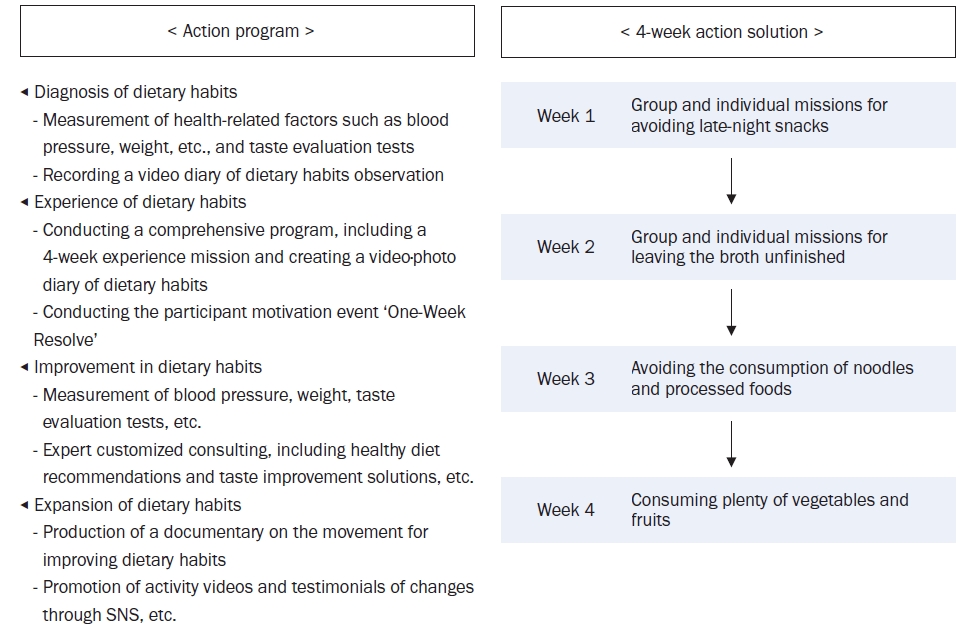
The program was implemented using a living lab model, an open innovation ecosystem for user-centered problem-solving. Analysis of the KNHANES data revealed that older age groups had a low energy intake but a high sodium intake, particularly among those who frequently dined out. The program was designed to improve sodium-reduction literacy and enhance practical competency. Over four weeks, 40 participants tracked their dietary intake and worked with a clinical nutritionist through a process of diagnosis, experience, improvement, and expansion. A self-administered survey was conducted before and after the program to assess effectiveness.
Results
Participants were four teenagers (10%), 26 in their twenties (65%), and 10 aged ≥ 30 years (25%), with eight males (20%) and 32 females (80%). Post-program analysis showed significant improvements in sodium-related nutrition knowledge (P < 0.01), with increased agreement on adopting low-sodium intake practices (e.g., interest in sodium content, choosing lower-sodium foods). Nutrient intake analysis showed a decrease in energy, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (P < 0.001), with sodium intake decreasing from 3,382.37 mg/d to 2,119.05 mg/d (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The community-based, living lab model for the sodium-reduction program effectively improved participant sodium-reduction literacy and practical competency, suggesting that step-by-step, autonomous learning, can reduce sodium intake and promote healthier eating habits.
- 1,342 View
- 47 Download

- [English]
- Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
- Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):382-395. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00010

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study investigated whether outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors differed according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students. Methods: The participants were students recruited from nine universities in Seoul, Korea. An online survey was conducted, and data from 351 participants were analyzed. Participants were classified into pre-action and action stages based on adequate sodium intake. Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, analysis of covariance, and correlation analysis. Results: Participants in the action stage (22.8%) felt fewer disadvantages of eating sodium adequately compared to those in the pre-action stage (77.2%, P < 0.001) and perceived more self-efficacy for healthy eating behaviors (P < 0.001) and controlling sodium intake (P < 0.01). The participants in the action stage also showed more desirable eating behaviors than those in the pre-action stage, including general eating behaviors, behaviors related to sodium intake, and sodium checks (P < 0.001). The physical environment in the action stage was more supportive of adequate sodium intake (P < 0.05). Eating behaviors, self-efficacy, and outcome expectations were significantly correlated with the stages of change; however, some differences were noticed in the correlation of the subscales of variables with the stages of change when examined by sex. Conclusion: We observed differences in factors according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake. For the pre-action stage, nutrition education can be planned to modify negative expectations of eating adequate sodium, foster self-efficacy, and practice general eating behaviors and behaviors to gradually reduce sodium intake. It is also necessary to alter the physical environment to reduce sodium intake. In the action stage, support and reinforcement are needed to continually practice and maintain desirable eating behaviors. Nutrition education for women may be planned using multiple paths, whereas a simple strategy may be useful for men.
- 2,032 View
- 42 Download

- [English]
- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
- Jiwoo Min, Youngmi Lee, Yunhee Chang, Yujin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):304-317. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the importance and performance of sodium reduction practices among childcare center cooks in the Yongin area before and after a 3-month salinometer support program.
Methods
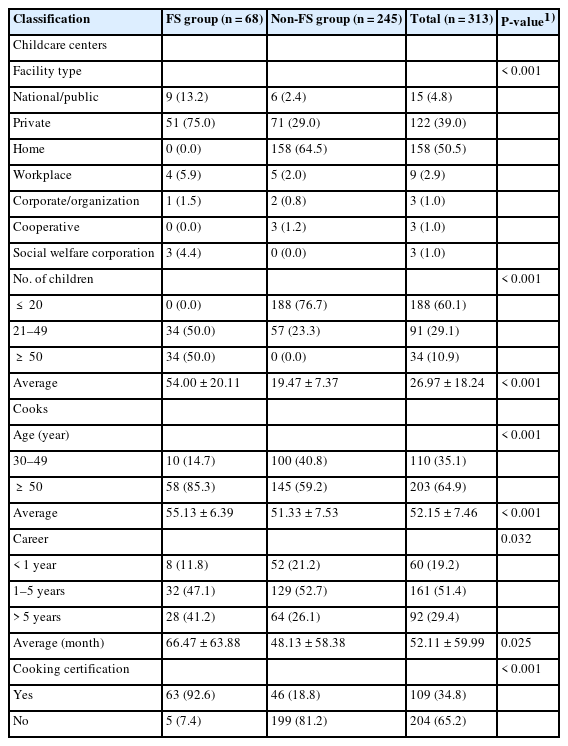
In total, 313 cooks employed in childcare centers in Yongin were surveyed before and after participating in a salinometer support program. The survey included questions on general information, sodium-related dietary habits, and perceived importance and performance levels of sodium reduction approaches in the purchasing, cooking, and serving areas. The centers were divided into childcare centers registered as group-feeding facilities (FS group, n = 68) and those not registered as such (non-FS group, n = 245). The differences between the two groups were analyzed.
Results
The overall importance levels increased significantly after the program in both the FS-group (P < 0.001) and non-FS group (P = 0.005). The overall performance levels also increased significantly in both groups (P < 0.001 for all). Consequently, the significant difference between the importance and performance levels disappeared in both groups after the program. However, unlike the FS group, which showed no significant differences between the importance and performance levels after the program in all three areas, the non-FS group still demonstrated lower performance levels than importance levels in the purchasing (P = 0.011) and serving (P = 0.034) areas after the program.
Conclusions
The use of salinometers significantly enhanced the performance and importance of low-sodium management practices among cooks in childcare centers, especially in the FS group. The continuous monitoring of salinity measurements and tailored education specialized for the FS and non-FS groups are recommended.
- 1,220 View
- 26 Download

- [English]
- Relationship of sodium index with the obesity indicators of university students in Daegu, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Young-Won Jang, Jian Ma, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):189-198. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The sodium index is an index that converts the estimated sodium intake calculated using a verified and reliable sodium estimation formula. This study aimed to determine the relationship between the sodium index and obesity indicators and the potential impact of excessive sodium consumption on obesity.
Methods
Obesity indicators, such as body mass index (BMI), body fat percentage, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), and visceral fat levels, were analyzed in 120 university students (60 men and 60 women). The sodium index was calculated by indexing the estimated sodium intake according to age, sex, BMI, salt-eating habits, and salt-eating behaviors. The relationship between sodium index and obesity indicators was analyzed using multiple logistic regression.
Results
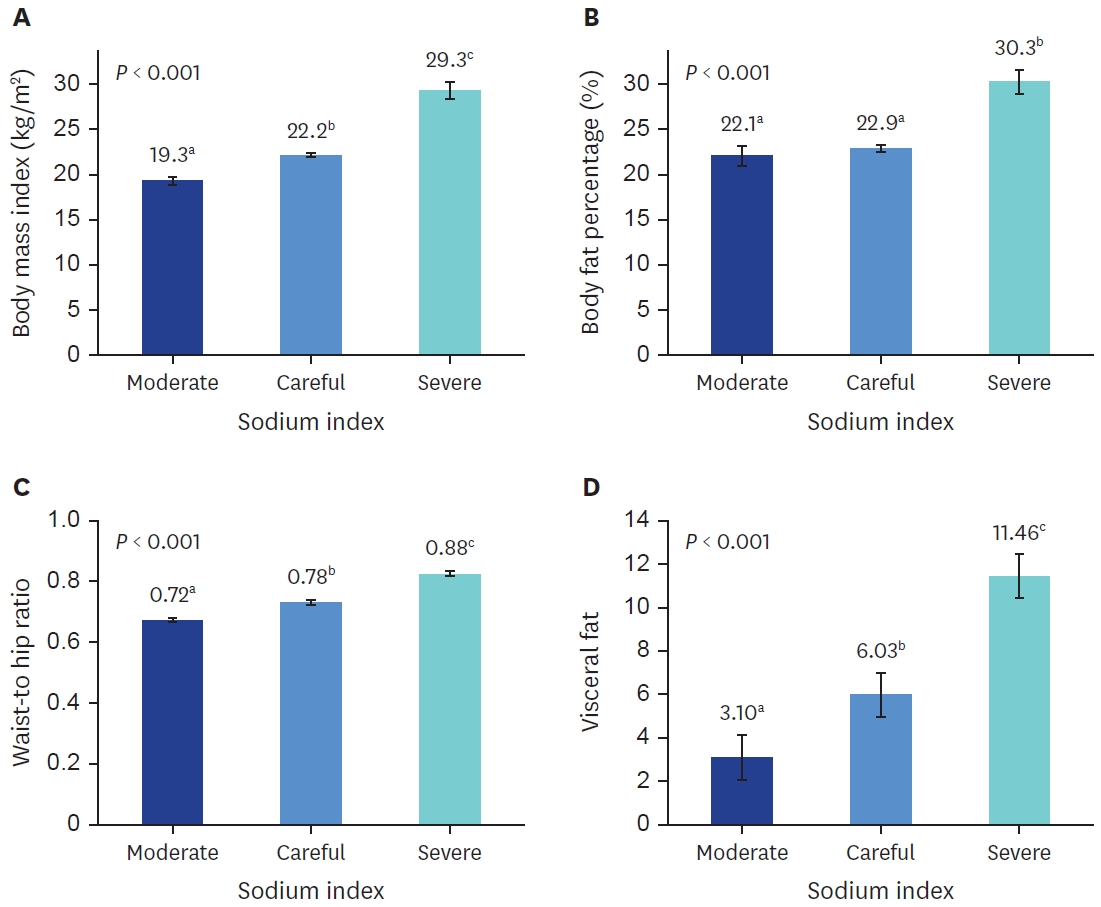
The estimated sodium intake was 3,907.1 mg, with 76.7% of the participants categorized under the “careful” level of sodium index and 10.8% under the “moderate” level. As the sodium index increased, the BMI, body fat percentage, WHR, and visceral fat levels significantly increased. All obesity indicators significantly increased in patients with a “severe” sodium index than in those with a “moderate” sodium index. In addition, a strong positive correlation was identified between obesity indicators and sodium index. When the “severe” sodium index was compared with the “moderate” sodium index, the risk of obesity based on body fat percentage increased by 2.181 times (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.526–3.118), while the risk of obesity based on visceral fat level increased by 4.073 times (95% CI, 2.097–7.911).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest a correlation between excessive sodium intake and obesity. Moreover, the sodium index can be used to determine sodium intake.
- 2,756 View
- 33 Download

- [English]
- The frequency of convenience food consumption and attitude of sodium and sugar reduction among middle and high school students in Seoul: a descriptive study
- Seoyeon Park, Yeonhee Shin, Seoyeon Lee, Heejung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):269-281. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.269
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the frequency of convenience food consumption at convenience stores (CVS) and the CVS usage patterns of middle and high school students as well as to understand students’ attitude toward sodium and sugar reduction.
Methods
We used an online questionnaire for data collection. The questionnaire comprised five distinct categories: general characteristics, CVS usage, frequency of consumption according to convenience food menus at CVS, attitude toward sodium and sugar reduction, and adherence to dietary guidelines.
Results
A total of 75 students from Seoul (14 middle school students and 61 high school students) participated in the study. Most respondents visit CVS 3-5 times a week. CVS are predominantly used during weekdays, mostly during lunch, and dinner. The students mostly checked the caloric content and expiration date as food labeling information. The participants were aware of the need to reduce their sugar and sodium intake. Among frequent CVS convenience food consumers, there was an increased consideration of the need to reduce their sugar and sodium consumption, despite their actual selection of foods with high sugar and sodium content. Additionally, they did not check the sugar and sodium levels indicated in food labeling. Further, the dietary action guide from the Ministry of Health and Welfare were poorly followed by most students.
Conclusions
There is a need for nutrition education specifically addressing the sugar and sodium content of the convenience foods predominantly consumed by students. Additionally, educating students with frequent convenience food consumption to actively check the sugar and sodium information on food labels could help promote healthier food choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 514. CrossRef
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- 1,927 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary sodium and potassium intake of Koreans estimated using 2 different sources of their contents in foods, Food & Nutrient Database and the Korean Total Diet Study : a comparative study
- Jee Yeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Soo Hyun Lee, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):235-244. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Based on the results from the Korean Total Diet Study (KTDS), the sodium (Na) and potassium (K) intake of Koreans were estimated and compared with intake estimates from the Food & Nutrient Database (FNDB), as in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) to verify the validity of these estimates.
Methods
One hundred and thirty-four representative foods (RFs) covering 92.5% of the total food intake of Koreans were selected, and 228 pairs of corresponding ‘RF x representative cooking method’ were derived by reflecting the methods used mainly in terms of frequency and quantity in their cooking. RF samples were collected from three cities with a larger population size in three regions (nine cities) nationwide, and six composite samples were made for each RF, considering its regional and/or seasonal characteristics. One thousand three hundred and sixty-eight ‘RF x representative cooking method’ pair samples were prepared, and the Na and K contents were assessed using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-MS). The Na and K intake of the Korean population was estimated by linking the content with the food intake data from the 7th KNHANES.
Results
The mean Na and K intake of Koreans were 2,807.4 mg and 2,335.0 mg per person per day, respectively. A comparison with the Na and K intake from KNHANES, including only RFs of KTDS, showed comparable results with less than 5% variation. While the contribution and ranking of food items to Na intake were similar between KNHANES and KTDS, there were differences in K intake. This was attributed to the large discrepancies in the K content of rice and coffee between KTDS results and the values in the 9th Revision of the National Food Composition Table used in KNHANES.
Conclusions
The Na and K intake of Koreans estimated based on the KTDS, which performed nutrient analysis on samples prepared to a ‘table-ready’ state using foods of the representative collection, was similar and comparable with that of KNHANES. This supports the validity and usefulness of FNDB-based nutrient intake estimation at the population level. The list of nutrients studied in KTDS is expected to be expanded, allowing for intake estimation of nutrients with currently insufficient or absent information in the FNDBs in use.
- 1,480 View
- 52 Download

- [Korean]
- Comparison of Sodium Reduction Practice and Estimated Sodium Intake by Salty Food Preference on Employees and Customers of Sodium Reduction Restaurant in Daegu, Korea
- Su-Jin Lee, Keon-Yeop Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(1):27-35. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.1.27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purposes of this study were to compare the degree of sodium reduction practice and estimate sodium intake by salty food preference.
Methods
Sodium reduction practices, salty food preferences and estimated sodium intake were surveyed for restaurant owners (n = 80), employees (n = 82) and customers (n = 727) at the restaurants participating in the sodium reduction project in Daegu, Korea. Estimated sodium intake was performed by examining sex, age, body mass index (BMI), salty eating habit and dietary behaviors.
Results
The degree of sodium reduction practice was significantly higher in salinity meter use (P < 0.001), low salt seasonings (P < 0.001) and efforts to make the foods as bland as possible overall (P < 0.001) in the restaurants participating in sodium reduction project than in homes (P < 0.001). The degree of sodium reduction practice appeared lower in the high salty food preference group than in the low-preference group in such items as efforts to make the foods as bland as possible overall (P < 0.05) and washing the salty taste and then cooking (P < 0.05). The high-preference group showed high-salt dietary behavior, including eating all the soup until nothing was left (P < 0.05) more than the low-preference group, but low-salt dietary behavior included checking the sodium content in processed foods (P < 0 .0 5) less than the low-preference group. The high-preference group was higher in the soup and stew intake frequency than the low-preference group (P < 0.05) and much lower in nuts (P < 0.05) and fruits (P < 0.05) intake frequency. The high-preference group had a higher salty eating habit (P < 0.05), salty taste assessment (P < 0.05) and estimated sodium intake (P < 0.05) than the low-preference group.
Conclusions
The present study showed that the salty food preference was strongly associated with lower sodium reduction practice and higher estimated sodium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Amelioration of metabolic disturbances and adipokine dysregulation by mugwort (Artemisia princeps P.) extract in high-fat diet-induced obese rats
Yun-Hye Kim, Chung-Mu Park, Gun-Ae Yoon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(6): 411. CrossRef - Comparison of Serum Adiponectin Levels According to Body Mass Index and Dietary Behaviors of Female University Students in Seoul
Mi Joung Kim, Hyun Young Jun, Hye Bog Rha
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(4): 354. CrossRef - Effects of age on changes of body composition through caloric restriction in overweight and obese women
Jung-Eun Yim, Young-Seol Kim, Ryowon Choue
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(5): 410. CrossRef - Nutrient Intake, the Concentrations of Leptin, Adiponectin, Cotisol & Insulin by the Body Fat Content of Women
Soon Yei Lee, Hyun Sook Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(6): 714. CrossRef - Relationship between Nutrients Intakes, Dietary Quality, and Serum Concentrations of Inflammatory Markers in Metabolic Syndrome Patients
Misung Kim, Juyoung Kim, Wookyung Bae, Sohye Kim, Yesong Lee, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(1): 51. CrossRef - Comparison of Serum Insulin, Leptin, Adiponectin and High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels according to Body Mass Index and their Associations in Adult Women
Mi Young Lee, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(1): 126. CrossRef
- Amelioration of metabolic disturbances and adipokine dysregulation by mugwort (Artemisia princeps P.) extract in high-fat diet-induced obese rats
- 825 View
- 7 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Sodium and Sugar Reduction Practices at Samsam Foodservices and General Foodservices in Daegu
- Sung-young Kwon, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(4):270-279. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.4.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of the sodium and sugar reduction practices of the Samsam foodservice project of Daegu, in comparison with that of general foodservices in Daegu. Methods: A survey was conducted on 80 Samsam foodservice workers and 80 general foodservice workers from Sep. to Oct. 2020. We compared each worker's taste preferences, stage of behavior change and dietary behavior regarding sodium and sugar, and each foodservice's practices regarding sodium and sugar reduction. Results: There was no significant difference between the salty taste and sweet taste preferences between the workers at the Samsam foodservices and those at the general foodservices. The percentage of foodservice workers in action or maintenance stage of behavior change for eating less salty was higher in the Samsam foodservices than in the general foodservices (P < 0.05). In addition, regarding the degree of saltiness and sweetness of meals, the workers at the general foodservices perceived their meals to be saltier (P < 0.001) and sweeter (P < 0.01) than the workers at Samsam foodservices. The workers at Samsam foodservices had fewer salty dietary behaviors compared to the workers at general foodservices (P < 0.01). The sodium reduction practice was significantly higher in the Samsam foodservices than the general foodservices (P < 0.001), especially in “efforts to make the food as bland as possible overall” (P < 0.001), and “serving less soup and stew” (P < 0.001). The sugar reduction practice too was significantly higher in the Samsam foodservices than the general foodservices (P < 0.001). Conclusions: The Samsam foodservices were shown to be better in the practice of sodium and sugar reduction compared to general foodservices. Therefore, it is necessary to provide continuous and practical support and incentives at the national level to expand the sodium and sugar reduction practices in foodservices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of participant and non-participant perceptions on healthy restaurant for sodium reduction: a qualitative study
Jeehee Pyo, Mina Lee, Yunjeong Jang, Minsu Ock
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 503. CrossRef
- Comparison of participant and non-participant perceptions on healthy restaurant for sodium reduction: a qualitative study
- 605 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
- Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):386-395. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate sodium reduction practices in school foodservice in Daegu. Methods The survey included 199 nutrition teachers and dietitians working at elementary, middle and high schools in Daegu. The survey topics included the following: the frequency of salinity measurement, workers in charge of the measurement, average salinity of the soup and stew served, frequency and difficulties of offering low-sodium meals, Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA) of sodium reduction methods in school foodservice and the need for political support in encouraging sodium reduction. Results The mean salinity of the soup and stew was higher in high school foodservice than in elementary and middle school foodservice. Middle and high schools have difficulties in offering low-sodium meals due to concerns of decreasing satisfaction for the meals. The results of the IPA of programs to reduce sodium in school meals showed that most of the items in the cooking and serving stages were in the 2nd quadrant (Keep up the good work), and all purchasing and menu planning stages occupied the 3rd quadrant (Low priority). To reduce sodium in school meals, government support is required in developing low-sodium recipes for school foodservice, encouraging education on sodium reduction for school foodservice officials and developing low-sodium food for institutional foodservice. Conclusions To encourage sodium reduction in school meals, the priority is to make low-sodium recipes available. Also, it is necessary to develop a program that calculates the sodium content in menus and processed foods through National Education Information System and to establish standards for sodium levels in school foodservice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
Jiwoo Min, Youngmi Lee, Yunhee Chang, Yujin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 304. CrossRef - 충북지역 중등학생의 건강식생활 관련 식행동과 영양관리 정책에 대한 인식
은서 고, 영은 이
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 197. CrossRef - Importance-performance analysis of sodium reduction practices by school nutrition teachers and dietitians in the Republic of Korea
Youngmi Lee, Sooyoun Kwon, Meeyoung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(4): 812. CrossRef - Comparison of Sodium Reduction Practice and Estimated Sodium Intake by Salty Food Preference on Employees and Customers of Sodium Reduction Restaurant in Daegu, Korea
Su-Jin Lee, Keon-Yeop Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 27. CrossRef - Comparison of the Sodium and Sugar Reduction Practices at Samsam Foodservices and General Foodservices in Daegu
Sung-young Kwon, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(4): 270. CrossRef
- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
- 672 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Validity of Estimating Sodium Intake using a Mobile Phone Application of 24-hour Dietary Recall with Meal Photos
- Seo-Yoon Kim, Sang-Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):317-328. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
The objective of this study was to verify the validity of a mobile phone application (app) that applies a 24-hour dietary recall with meal photos, as a means of being a more accurate method of estimating dietary sodium intake.
Methods
Of the 203 subjects enrolled, 172 subjects (84 males and 88 females) were selected for the final analysis, excluding those with an intake less than 500 kcal and urine output less than 500 ml. Dietary sodium assessment methods used for comparing with the 24-hour urinary sodium excretion are as follows: 1) face-to-face 24-hour dietary recall, 2) 24-hour dietary recall using the mobile app, 3) face-to-face 24-hour dietary recall considering liquid intakes from soup, stew, water kimchi and noodle, etc (liquid-based dishes), 4) 24-hour dietary recall using the mobile app considering liquid intakes from liquid-based dishes, and 5) food frequency questionnaire. Repeated ANOVA with Bonferroni method was used for comparing the average sodium intake, and Pearson’s correlation was applied to correlate the methods used.
Results
In women, no significant difference was observed in the average sodium intake between all methods. Moreover, analysis in men and total adults revealed no significant difference between the 24-hour urinary sodium secretion, and 24-hour dietary recall using the app and 24-hour dietary recall using the app considering liquid intakes. Sodium intake by food frequency questionnaire was significantly different when compared with the intake determined from 24-hour urinary sodium excretion. Sodium intake from all methods (except food frequency questionnaire) significantly correlated with values obtained from 24-hour urine sodium excretion.
Conclusions
Results of this study validated a mobile phone app using a 24-hour dietary recall with meal photos to better estimate dietary sodium intakes. It is believed that further studies in the future will enable the application as a tool to more accurately determine sodium intake.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Sodium and Fluid Restriction for Patients with Heart Failure
Eloisa Colin-Ramirez, Amitai Segev, Meghan Rozmahel, Justin Ezekowitz
Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine.2024; 26(12): 347. CrossRef - Comparison between 24-hour diet recall and 24-hour urine collection for estimating sodium and potassium intakes and their ratio among Korean adults
Taisun Hyun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Young-Ran Heo, Heekyong Ro, Young-Hee Han, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 284. CrossRef - Validity of Interviewer-Administered 24-h Dietary Recalls in Older Korean Women: A Pilot Study
Seunghee Kim, Clara Y. Park
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1757. CrossRef
- Dietary Sodium and Fluid Restriction for Patients with Heart Failure
- 674 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Analysis of Dietary Calcium and Phosphorus Intakes and Contribution Rates of Major Dish Groups according to Gender, Age, and Region in Korea
- Yeon Kyung Lee, Mi Kyeong Choi, Taisun Hyun, Eun Soon Lyu, Haeryun Park, Hee Kyong Ro, Young Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):32-47. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - OBJECTIVES
Calcium (Ca) is an insufficiently consumed nutrient, whereas phosphorus (P) intake has exceeded the recommended intake level in Korea over the past decade. The purpose of this study was to analyze dietary Ca and P intakes and their contribution rate according to dish groups.
METHODS
A 24-hour dietary recall survey of 640 healthy adults (aged 19–69 years) was undertaken twice in four Korean provinces. Dietary Ca and P intakes and their rates of contribution from 31 major dish groups were analyzed and compared by gender, age group, and region.
RESULTS
The average Ca and P intakes of the subjects were 542.1 ± 222.2 mg/d and 1,068.3 ± 329.0 mg/d, respectively. The intakes of Ca and P as percentages of recommended nutrients intake (RNI%) were 71.7 ± 29.8% and 152.6 ± 47%, respectively, and the percentages under the estimated average requirement were 60.3% for Ca and 3.8% for P. The RNI% of Ca was not significantly different between males and females, but was significantly higher in subjects in the sixties age group than in other age groups and was significantly lower in the Korean capital than in other regions. The RNI% of P did not significantly differ by gender or age groups, but it was significantly higher in the capital than in Gyeong-sang. The five major dish groups contributing to Ca intake (contribution rate) were milks/dairy products 69.2 ± 109.2 mg/d (12.6%), soups 55.6 ± 69.6 mg/d (10.1%), stir-fried foods 53.1 ± 70.7 mg/d (9.7%), stews 43.4 ± 85.4 mg/d (7.9%), and kimchi 38.4 ± 31.8 mg/d (7.0%). The five major dish group contributing to P intake (contribution rate) were cooked rice 160.7 ± 107.1 mg/d (14.9%), stir-fried foods 88.5 ± 89.4 mg/d (8.2%), soups 76.7 ± 85.8 mg/d (7.1%), one-dish meals 63.3 ± 94.4 mg/d (5.9%), and stews 62.6 ± 89.3 mg/d (5.8%). The dish groups contributing to Ca and P intakes differed somewhat by gender, age group, and region.
CONCLUSIONS
Programs to improve the nutritional status of Ca and P intakes should consider the differences in Ca and P contribution rates by dish groups as well as by gender, age group, and region. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Lactarius hatsudake fortification on
physicochemical, microbiological and antioxidant properties of stirred-type
yogurt during cold storage
Hanyu Zhu, Geqing Li, Huijing Liu, Weifeng Sun, Xiaoqian Yao, Rui Wu, Jiajia Hu, Qihui Yang
Food Science of Animal Resources.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Restructured Black Goat Jerky with
Various Types of Ultra-Ground Seaweed Powders
Ui-Bin Baek, Hack-Youn Kim
Food Science of Animal Resources.2024; 44(2): 483. CrossRef - Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Longitudinal Effects of Serum Calcium and Phosphate Levels and Their Ratio on Incident Ischemic Heart Disease among Korean Adults
Dong Hyuk Jung, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Biomolecules.2022; 12(1): 103. CrossRef - Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Bone Mineral Density in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients With Osteoporosis
Oh Chan Kwon, Ji Seon Oh, Min-Chan Park, Yong-Gil Kim
Frontiers in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of Lactarius hatsudake fortification on
physicochemical, microbiological and antioxidant properties of stirred-type
yogurt during cold storage
- 1,160 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Customers' Perceptions of Operational Status of and Needs for Sodium Reduction in the Industry Foodservice in Seoul
- Na Young Yi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):21-31. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to compare customers' perceptions of the need for a low-sodium diet and sodium-reduced operations in the industry foodservice by age. The relationships between health concerns and perceptions of the need for sodium-reduced operations and low-sodium diets in the industry foodservice were analyzed.
METHODS
A survey was conducted among 340 industry foodservice customers aged 20–50 years and residing in Seoul, Korea. This study investigated the respondents' health concerns, their perception of the need for sodium-reduced foodservice operations, their perception of a sodium-reduced diet, and the general details of the foodservices they used. A cross-tabulation analysis and ANOVA were performed to identify differences in measurement items by age, and a simple regression analysis was performed to examine relationships between measurement items.
RESULTS
For the customers' perception of the need for a sodium-reduced foodservice operation, the item “it is necessary to provide separate spices and sauces to reduce sodium intake†achieved the highest score (3.88 points out of a possible 5 points). For the perception of a sodium-reduced diet, the item “I think it is helpful for one's health†obtained the highest score (4.13 points). Respondents' health concerns had a positive effect on increasing the level of perception of the need for sodium-reduced foodservice operations and that of a sodium-reduced diet.
CONCLUSIONS
Foodservice nutritionists could help enhance their customers' perceptions of the needs for sodium-reduced foodservice operations and sodium-reduced diets by frequently providing them with sodium-related health information.
- 664 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
- Na Yeong Lee, Yeon Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):13-20. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the salinity of soups provided at childcare centers by measuring the salinity for three years and providing basic data for sodium reduction.
METHODS
The soup salinity was measured using a Bluetooth salinity meter from January 2015 to December 2017 at 80 childcare foodservice establishments enrolled in the Suseong Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Daegu.
RESULTS
An analysis of the soup salinity each year showed that the salinity decreased significantly from 0.48% in 2015 to 0.41% in 2017, particularly in clear soups and soybean soups compared to other soups (P < 0.05). The salinity and sodium content in seafood soups (0.45% and 179.1 mg/100 g, respectively) were highest, followed by soybean soups (0.44%, 175.2 mg/100 g), with perilla seed soups containing the lowest (0.42%, 167.2 mg/100 g) (P < 0.05). The salinity was significantly higher in institutional foodservice establishments than small foodservice establishments (P < 0.001). The salinity and sodium content were the highest in foodservice establishments with a small number of measurements, and the salinity was the lowest in foodservice establishments with salinity measurements performed an average of 151 times each year (three times a week) or more (P < 0.05). The soup salinity was low in the order of winter, spring, summer, and autumn, and the salinity decreased significantly year by year in all seasons. (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The soup salinity was significantly lower in foodservice establishments where the salinity was measured more than three times a week, indicating that continuous salinity management is effective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
Do Hee Kim, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(4): 421. CrossRef - Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 386. CrossRef
- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
- 937 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Daily Water Consumption and its Contribution to Calcium Intake in Korean Adults
- Eun Sun Park, Yeon Kyung Lee, Mi Hyun Kim, Mi Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):18-23. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
Although water is essential for life and can supply essential minerals, studies that evaluate calcium intake through drinking water are limited. The aim of this study was to assess calcium contents of natural mineral water (NMW) and its possible contribution to calcium intake in healthy adults.
METHODS
This study examined water consumption in 640 Korean adults with selfselected diet, analyzed the calcium content of 10 different brands of bottled NMWs sold in Korea, and assessed the amount of calcium intake from drinking water and its daily contribution to the recommended nutrient intake (RNI) of calcium.
RESULTS
Mean calcium content in 10 bottled NMWs was 20.9 mg/l. Daily water intakes from food composition database and calculated using energy intake based on 0.53 ml/kcal were 957.2 ml and 1109.8 ml for men and 848.3 ml and 951.6 ml for women, respectively, with a significant difference by gender (p < 0.001). Daily drinking water intake was significantly higher among men than women (1203.9 ml vs. 1004.3 ml, respectively, p < 0.001). Daily calcium intakes from foods were 564.0 mg for men and 534.2 mg for women. Daily possible calcium intakes from drinking bottled water were 25.2 mg for men and 21.0 mg for women (p < 0.001). The contribution of daily calcium intake from drinking bottled water to RNI of calcium was 3.3% for men and 2.9% for women without significant difference.
CONCLUSIONS
One half of the daily total water intake was consumed as drinking water, and possible calcium intake through drinking water was about 3% of RNI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing contribution of bottled water in nutrient absorption using the bottled water nutritional quality index (BWNQI) in Iran
Masoomeh Askari, Reza Saeedi, Ramin Nabizadeh, Ahmad Zarei, Maryam Ghani, Marzieh Ehsani, Mahmood Alimohammadi, Mehrnoosh Abtahi
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Variability of urinary creatinine, specific gravity, and osmolality over the course of pregnancy: Implications in exposure assessment among pregnant women
Gowoon Lee, Sunmi Kim, Hyunwoong Park, Jeonghwan Lee, Jung Pyo Lee, Younglim Kho, Gyuyeon Choi, Jiwon Park, Suwalee Worakhunpiset, Hyo-Bang Moon, Kyungho Choi
Environmental Research.2021; 198: 110473. CrossRef
- Assessing contribution of bottled water in nutrient absorption using the bottled water nutritional quality index (BWNQI) in Iran
- 1,561 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Salinity of Representative Korean Foods High in Sodium from Home Meals, Foodservices, and Restaurants
- Lin Jiang, Damin Shin, Yeon Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):333-340. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to analyze the salinity of representative Korean foods high in sodium to generate data for use as a fundamental resource for setting salinity standards in foods.
METHODS
A total of 480 foods from 16 representative Korean foods high in sodium were collected from 10 households, 10 industry foodservice establishments, and 10 Korean restaurants in four regions (Capital area, Chungcheong Province, Gyeongsang Province, and Jeolla Province) and analyzed for salinity.
RESULTS
Among the foods, stir-fried anchovies (4.07~4.45%) showed the highest salinity, followed by pickled onion (1.86~2.62%), cabbage kimchi (1.83~2.2%), braised burdock and lotus root (1.79~2.17%), and sliced radish kimchi (1.78~1.89%) (p < 0.001). The salinity of kimchi from home meals (2.2%) was significantly higher than that of foodservice (1.83%) and restaurant (1.93%) kimchi (p < 0.05). Salinity in each group of food was highest in kimchi (1.83~2.04%), followed by braised dishes (1.54~1.78%), steamed dishes (1.0~1.22%), stir-fried dishes (1.02~1.18%), and soup or stew (0.74~1.02%) (p < 0.001). The salinity of soup and stew from restaurants (1.02%) was significantly higher than that of home meal (0.84%) and foodservice (0.74%) soup and stew.
CONCLUSIONS
Determination of the salinity of representative Korean foods known to be high in sodium by eating place is expected to be useful to establishing guidelines for reduction of salinity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 514. CrossRef - A Literature Review Study on Chronic Changes in Yukgaejang
Soon-Ah Choi, Bokyung Ryu, Lana Chung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 386. CrossRef - Comparison of the portion sizes of Korean adults across eating places: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2012–2016)
Hye-Sook Hong, Seon-Joo Park, Do-Kyung Lee, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 676. CrossRef - Development of standards for reducing the sodium content and salinity of Korean fermented soybean sauces and representative Korean foods high in sodium
Lin Jiang, Eun-Kyung Shin, Jung-Sook Seo, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(2): 185. CrossRef - Current status, perception and practicability of restaurant staffs related to reducing sodium use in Seongnam, Korea
So-Hyun Ahn, Jong Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Yoonna Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 475. CrossRef
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- 1,073 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
- Mijin Jo, Young Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(1):38-47. Published online February 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to analyze the association between sodium excretion and obesity for healthy adults in the Gwangju area.
METHODS
The participants included 80 healthy adults aged 19 to 69 years in Gwangju. The dietary intake and sodium excretion were obtained using the 24-hour recall method and 24 hour urine collection. The participants were classified into two groups according to the amount of urinary sodium excretion: (≤ 141.75 mmol/dL, > 141.75 mmol/dL).
RESULTS
After adjusting for sex, age, smoking history, and income, the high excretion of sodium group was significantly higher for weight, body mass index, body fat mass, percent body fat, visceral fat area (VFA), waist circumference, hip circumference, and WHR. The energy and nutrients intake were significant after adjusting for sex, age, smoking history, and income. The LSE group had a significantly higher fat intake and Na/K intake ratio. The HSE group had significantly higher fiber intake, and K intake. As the amount of urinary sodium excretion increased, the risk of obesity before correction was 3.57 (95% CI: 1.13–11.25) times greater, and the risk of obesity of T3 increased significantly by 3.33 times (95% CI: 1.05–10.59). After correcting for sex and age, the obesity risk of T2 increased significantly by 4.23 times (95% CI: 1.11–16.06), and after correcting for sex, age, smoking history, and income, the obesity risk of T2 increased significantly by 6.81 times (95% CI: 1.44–32.19) the risk of obesity.
CONCLUSIONS
An association exists between sodium excretion and obesity in Korean adults. In this study, the high excretion of sodium group was obese and the risk of obesity was higher than the low excretion of sodium group. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preventive Effects of Whole Grain Cereals on Sarcopenic Obesity in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
Mi-Bo Kim, Sein Lee, Changhee Kim, Jae-Kwan Hwang
Food Engineering Progress.2018; 22(4): 358. CrossRef
- Preventive Effects of Whole Grain Cereals on Sarcopenic Obesity in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
- 791 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of Nutrition Education Contents for Pregnant Women Based on Effective Communication Strategies
- Taeksang Yoo, Young Hee Han, Jung Hyun Kim, Min Jun Lee, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(2):115-126. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.2.115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to develop communication strategies for effective nutrition education targeting pregnant women and to create nutrition education contents.
METHODS
The format and the contents of online resources on nutrition information for pregnant women provided by reliable institutions were analyzed. Possible solutions to overcome barriers of nutrition education as well as communication strategies for effective nutrition education were identified by a brainstorming process. Based on the communication strategies, contents for nutrition education were created. Understandability, level of interest, applicability to daily life, harmony of text and illustration, and overall satisfaction of the contents were evaluated by dietitians and pregnant women.
RESULTS
The four communication strategies were developed; (1) to focus on a few important messages, (2) to provide evidence-based information, (3) to create illustrations or infographics with a minimum amount of text, and (4) to provide tips on how to improve the current diet options. Based on these strategies, the contents were focused on three important nutrients for pregnant women, folate, iron, and calcium. The percentages of the recommended nutrient intakes of the three nutrients on selected menu and its improved version by adding a dish or changing a dish into another dish were calculated and provided. Finally, the contents were delivered as illustrations with a minimum amount of text. Overall, dietitians and pregnant women were satisfied with the contents.
CONCLUSIONS
The contents developed in this study can be used in a pamphlet or a pregnancy diary, or can be shared in social networking services. Further contents on other nutrients and various menu are expected to be developed using these communication strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Education Materials as a Card News Format for Nutrition Management of Pregnant and Lactating Women
Young-Hee Han, Jung Hyun Kim, Min Jun Lee, Taeksang Yoo, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 248. CrossRef
- Development of Education Materials as a Card News Format for Nutrition Management of Pregnant and Lactating Women
- 938 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- A Comparison of Sources of Sodium and Potassium Intake by Gender, Age and Regions in Koreans: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2010-2012
- Yang Hee Park, Sang Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):558-573. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.558
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the main sources of dietary sodium and potassium intake in Koreans by gender, age and regions.
METHODS
We used the data from 2010-2012 KNHANES. A total of 20,387 subjects aged 8 years and older were included. Intakes were compared by gender, age (8-18, 19-49 and >50 years) and geographical regions in Korea. Dishes were classified into 28 dish groups based on cooking methods. Statistical analysis was performed by using the SAS 9.3 and SUDAAN 11.0.1 software.
RESULTS
The mean sodium intake of Koreans was 4866.5 ± 35.9 mg/day, which was 2.4 times higher than the adequate intake (AI) of sodium for Koreans. We found that daily sodium intakes were significantly different by age, gender and regions. Men and aged over 50 years had significantly higher sodium intake than women and other age groups. The mean potassium intake in Koreans was 3002.2 ± 19.4 mg/day and daily potassium intakes were significantly different by age, gender and regions. Women and age 50 years and over had significantly higher potassium intakes than men and other age groups. The average Na/K ratio was 2.89 ± 0.01 and was highest in men and in the age group of 19-49 years. The major sources of dietary sodium were soup and stew, followed by Kimchi, noodles and dumpling, pickled vegetables and seasonings, which represented 63.1 % of total sodium intakes. Soup and stew or Kimchi were the primary sources of dietary sodium intake. The major sources of dietary potassium were cooked rice, followed by soup and stew, Kimchi, fruits and beverages.
CONCLUSIONS
Sodium and potassium intakes and the major sources of those were significantly different by gender, age groups and regions. Therefore, different approaches based on gender, age and regions are needed to decrease sodium intake and increase potassium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 225. CrossRef - Dietary Habits of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer in Korea
Jaehoon Shin, Jiyeon Lee, Yooeun Yoon, Hye Sun Lee, Hyungmi Kim, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2024; 45(3): 149. CrossRef - Role of geographic characteristics in the spatial cluster detection of cancer: Evidence in South Korea, 1999–2013
Insang Song, Eun-Hye Yoo, Inkyung Jung, Jin-Kyoung Oh, Sun-Young Kim
Environmental Research.2023; 236: 116841. CrossRef - Development and application of the sodium index to estimate and assess sodium intake for Korean adults
Yeon-Kyung Lee, Taisun Hyun, Heekyong Ro, Young-Ran Heo, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(3): 366. CrossRef - Trends in sodium intake and major contributing food groups and dishes in Korea: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2017
Yeseung Jeong, Eui Su Kim, Jounghee Lee, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(3): 382. CrossRef - Predictive Analysis of Food Behavior and Related Factors Using Spatial Analysis: Based on Community Health Survey Data 2016
Se-Mi Jeong, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(2): 189. CrossRef - The association of dietary patterns with insulin resistance in Korean adults: based on the 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
I Seul Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 247. CrossRef - Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
Na-Yeong Lee, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - Comparison of the sodium content of Korean soup-based dishes prepared at home, restaurants, and schools in Seoul
Yanghee Park, Jihyun Yoon, Sang-Jin Chung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 663. CrossRef - Designing optimized food intake patterns for Korean adults using linear programming (II): adjustment of the optimized food intake pattern by establishing stepwise intake goals of sodium
Kana Asano, Hongsuk Yang, Youngmi Lee, Meeyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(4): 342. CrossRef - The association between genetic variants of angiopoietin-like 3 and risk of diabetes mellitus is modified by dietary factors in Koreans
Clara Yongjoo Park, Jiyoung Moon, Garam Jo, Juhee Lee, Oh Yoen Kim, Hannah Oh, Hyunjung Lim, Min-Jeong Shin
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of biogenic amines and inorganic elements in Cheonggukjang
Min-Jeong Seo, Chang-Do Lee, Ji-Na Lee, Hee-Jong Yang, Do-Youn Jeong, Gae-Ho Lee
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2019; 26(1): 101. CrossRef - Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
Mijin Jo, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Diet-Related Risk Factors for Incident Hypertension During an 11-Year Follow-Up: The Korean Genome Epidemiology Study
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Nutrients.2018; 10(8): 1077. CrossRef - Study on the prevalence and incidence of urolithiasis in Korea over the last 10 years: An analysis of National Health Insurance Data
Joon Se Jung, Chang Hee Han, Sangrak Bae
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2018; 59(6): 383. CrossRef - Dietary status of young children in Korea based on the data of 2013 ~ 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eun-kyung Kim, Byengchun Song, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 330. CrossRef - Effects of Sodium Intake on the Association between the Salt-Sensitive Gene, Alpha-Adducin 1 (ADD1), and Inflammatory Cytokines in the Prevalence of Children Obesity
Mi-Young Park, Myoung-sook Lee
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2018; 7(2): 98. CrossRef - Dietary intakes of adolescents from food insecure households: analysis of data from the 6th(2013-2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mariam Nakitto, Kana Asano, Injoo Choi, Jihyun Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(6): 507. CrossRef
- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 2,023 View
- 2 Download
- 19 Crossref

- [English]
- Recommended Intake and Dietary Intake of Vitamin A for Koreans by Unit of Retinol Activity Equivalent
- Youngnam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):344-353. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.344
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
New retinol activity equivalent (RAE) was introduced as vitamin A unit in Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) for Koreans 2015. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the adequacy of 2015 reference intake (RI) of vitamin A in RAE unit by the comparison with RI and dietary intake of vitamin A.
METHODS
Analyses on RI of vitamin A were based on the Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) for Koreans (1962~2000) and DRIs for Koreans (2005~2015). Analyses on Koreans dietary intake of vitamin A were based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES) reports (1969-2014). For recalculation of RI and dietary intake of vitamin A in RE to RAE, 2013 Koreans intake of retinol: carotenoids ratio of 13: 87 was applied.
RESULTS
RI of vitamin A was 600~750 RE for Korean adult, and 339~425 RAE when calculated by applying the retinol and carotenoids intake ratio. Vitamin A intakes of Koreans were <100% RI, 267~668 RE from 1969 to 2001. From 2005, vitamin A intake had increased to >700 RE, >100% RI. When vitamin A intake was converted from RE to RAE (2005~2014), 718~864 RE became 405.8~488.1 RAE, decreased to 56.5% level. The recent 2015 RI of vitamin A is 850 RAE, two times of 2005 & 2010 RI of 425 RAE for adult male.
CONCLUSIONS
When nutritional status of vitamin A was assessed for Koreans using the estimated average requirement (EAR) of 2015 (570, 460 RAE for male, female adults, respectively), ratio of deficient people increased significantly when judged based on the previous intake of Koreans, <490 RAE. We needs to examine the 2015 RI (EAR) of vitamin A, find a way to measure the accurate intake of dietary vitamin A, and to increase the dietary intake of this vitamin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in three types of Korean watery kimchi
Hyosun Park, Suna Kim, Jaecheol Kim, KyeongJin Lee, BoKyung Moon
Applied Biological Chemistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans: vitamin A
Yuri Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 201. CrossRef - Dynamics of Serum Retinol and Alpha-Tocopherol Levels According to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Status
Dongsub Jeon, Minkook Son, Juhyun Shim
Nutrients.2021; 13(5): 1720. CrossRef - Representative Nutrients Contents and Nutritional Adequacy Evaluation of Single-Dish Meal for Middle School Students
Gisun Lee, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(2): 93. CrossRef
- Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in three types of Korean watery kimchi
- 1,156 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Thermic Effect of Food, Macronutrient Oxidation Rate and Satiety of Medium-chain Triglyceride
- Hee Ryoung Son, Myung Ju Lee, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):468-478. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.468
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to evaluate the thermic effects, the macronutrient oxidation rates and the satiety of medium-chain triglycerides (MCT).
METHODS
The thermic effects of two meals containing MCT or long-chain triglycerides (LCT) were compared in ten healthy men (mean age 24.4 +/- 2.9 years). Energy content of the meal was 30% of resting metabolic rate of each subject. Metabolic rate and macronutrient oxidation rate were measured before the meals and for 6 hours after the meals by indirect calorimetry. Satiety was estimated by using visual analogue scales (VAS) at 8 times (before the meal and for 6 hours after meal).
RESULTS
Total thermic effect of MCT meal (42.8 kcal, 8.0% of energy intake) was significantly higher than that (26.8 kcal, 5.1% of energy intake) of the LCT meal. Mean postprandial oxygen consumption was also significantly different between the two types of meals (MCT meal: 0.29 +/- 0.35 L/min, LCT meal: 0.28 +/- 0.27 L/min). There were no significant differences in total postprandial carbohydrate and fat oxidation rates between the two meals. However, from 30 to 120 minutes after consumption of meals, the fat oxidation rate of MCT meal was significantly higher than that of the LCT meal. Comparison of satiety values (hunger, fullness and appetite) between the two meals showed that MCT meal maintained satiety for a longer time than the LCT meal.
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed the possibility that long-term substitution of MCT for LCT would produce weight loss if energy intake remained constant.
- 929 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- Associations between 24-hour Urine Sodium Excretion Level and Obesity-related Metabolic Risk Factors
- Hyun Woo Oh, Hyun Jung Kim, Dae Won Jun, Seung Min Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):460-467. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.460
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
Excess sodium intake has been linked to obesity and obesity-related indices. However, the scientific evidence for this association is inadequate. The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between urinary sodium excretion and obesity-related indices among Korean adults.
METHODS
A convenience sample of 120 subjects (60 obese and 60 non-obese subjects) were recruited applying frequency matching for sex and age between two groups. Sodium intake level was assessed through 24-hour urine collection. Obesity-related metabolic risk factors, including fasting blood lipid indices, subcutaneous and visceral fat through computed tomography (CT), insulin resistance indices, blood pressure and liver enzymes were measured in all subjects. These obesity-related metabolic risk factors were compared between obese and non-obese group according to sodium excretion levels (<110 mEq/day, 110~180 mEq/day, >180 mEq/day).
RESULTS
After adjusting for age, gender, health behaviors (smoking, exercise, drinking), and energy intake, several obesity-related metabolic risk factors, including abdominal circumference, body fat percentage, subcutaneous and visceral fat, triglyceride, and systolic blood pressure were found to be significantly deteriorated as the sodium excretion level increases. In addition, multivariate adjusted-odds ratios of abdominal obesity, high blood triglyceride, and high blood pressure were found significantly higher in the highest sodium excretion group compared to the lowest group. The mean number of metabolic syndrome risk factors was also significantly greater in the highest sodium excretion group than in the lowest group.
CONCLUSIONS
The current study findings suggested that high sodium intake can affect obesity and metabolic syndrome risk negatively, implying the necessity of future research on low-sodium diet intervention in relation to obesity and related health problems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of sodium index with the obesity indicators of university students in Daegu, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Young-Won Jang, Jian Ma, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 189. CrossRef - Dietary salt intake and kidney function in rural Senegalese populations: a cross-sectional study
Ndongo Modou, Lot Nehemie Motoula Latou, Toure Maimouna, Amadou Diop Dia, Sidy Mohamed Seck
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiometabolic Risk of Visceral Fat Obesity and Factors Influencing Visceral Fat in Overweight or Obese Middle-Aged Korean Women: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sujin Kim, Nah-Mee Shin, Jiwon Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 320. CrossRef - The association between dietary sodium intake and obesity in adults by sodium intake assessment methods: a review of systematic reviews and re-meta-analysis
Jounghee Lee, Cheongmin Sohn, Oh-Yoen Kim, Young-Min Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Myoungsook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 175. CrossRef - Relationship between urinary sodium-creatinine ratios and insulin resistance in Korean children and adolescents with obesity
So Yoon Han, Nan Hee Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seon Mee Kim
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 31(4): 375. CrossRef - Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
Mijin Jo, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Relationship of sodium consumption with obesity in Korean adults based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2014
Se Young Cheon, Hye Won Wang, Hwa Jung Lee, Kyung Mi Hwang, Hae Seong Yoon, Yoon Jung Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 64. CrossRef - Associations of Obesity and Dyslipidemia with Intake of Sodium, Fat, and Sugar among Koreans: a Qualitative Systematic Review
Yoon Jung Kang, Hye Won Wang, Se Young Cheon, Hwa Jung Lee, Kyung Mi Hwang, Hae Seong Yoon
Clinical Nutrition Research.2016; 5(4): 290. CrossRef
- Relationship of sodium index with the obesity indicators of university students in Daegu, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 865 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Consumer Nutrition Education Program to Reduce Sodium Intake Based on Social Cognitive Theory
- So Hyun Ahn, Jong Sook Kwon, Kyung Min Kim, Jin Sook Yoon, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):433-446. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.433
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to evaluate the consumer education program for reducing sodium intake based on social cognitive theory (SCT) and investigate consumer perceptions of environmental, cognitive and behavioral factors.
METHODS
Consumers (n=4,439) were recruited nationwide in Korea to participate in a nutrition education program for reducing sodium intake which was targeted on senior housewives (SH), parents (P), and office workers (OW). Questions regarding main factors of SCT were asked both before and after the education program.
RESULTS
SH and P recognized external social efforts and information to reduce sodium including nutrition labeling more than OW. The main barriers to practice reducing sodium intake were limited choice of low sodium food and menu, interference with social relationship when dining with others, and limited information, knowledge and skills. SH had lower barriers to practice reducing sodium intake and OW perceived 'preference to soup or stew' and 'preference to Kimchi, salted fish and fermented sauces' as barriers more than other groups at the baseline. Less than 50% of participants knew the relationship between sodium and salt, sodium in nutrition labeling, and recommended sodium intake. In addition, OW had little knowledge for capability to reduce sodium intake and lower self-efficacy to practice compared with SH and P. After education, positive outcome expectations such as lowering blood pressure, prevention of cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis were increased and barriers to practice reducing sodium intake were decreased in all groups (p < 0.05). The knowledge for behavioral capability and self-efficacy to reduce sodium intake were also improved but OW had still lower scores compared with other groups.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggested that nutrition education programs could be an effective tool to impact general population by facilitating awareness and increased capability to reduce sodium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Consumer acceptance of reduced sodium white and multigrain bread: Impact of flavor enhancement and ingredient information on sample liking
Aubrey N. Dunteman, Soo‐Yeun Lee
Journal of Food Science.2023; 88(1): 417. CrossRef - The frequency of convenience food consumption and attitude of sodium and sugar reduction among middle and high school students in Seoul: a descriptive study
Seoyeon Park, Yeonhee Shin, Seoyeon Lee, Heejung Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 269. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a nutrition education program for housewives to reduce sodium intake: application of the social cognitive theory and a transtheoretical model
Sohyun Ahn, Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 174. CrossRef - Customers' Perceptions of Operational Status of and Needs for Sodium Reduction in the Industry Foodservice in Seoul
Na-Young Yi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 21. CrossRef
- Consumer acceptance of reduced sodium white and multigrain bread: Impact of flavor enhancement and ingredient information on sample liking
- 872 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Sodium-related Dietary Attitude and Behaviors According to Sodium-related Nutrition Knowledge of University Students
- Mi Hyun Kim, Jee Young Yeon, Jong Wook Kim, Jae Eon Byun, So Young Bu, Mi Kyeong Choi, Yun Jung Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(5):327-337. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.5.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
Dietary life is closely associated with dietary attitude and diet-related knowledge. Particularly, dietary habit such as sodium intake can be affected by various dietary behaviors such as food choices, dietary attitude toward salty food and a preference for salty taste. The purpose of this study was to assess sodium-related nutrition knowledge and to identify sodium-related attitude and behaviors according to the level of sodium-related knowledge of university students.
METHODS
Anthropometric measurements were provided by 408 students who participated in this study. The study participants answered questionnaires to provide information on general dietary behaviors, sodium-related dietary attitude and other behavioral factors. A total score of nutrition knowledge was used to categorize study participants in to two groups, namely, low level in sodium-related knowledge (LNaK) or high level in sodium-related knowledge (HNaK) and the attitude and the behaviors of students toward sodium intake were compared between these two groups.
RESULTS
The ratio of female students in HNaK group was higher than that in the LNaK group. HNaK group had a higher score in checking nutrition label of processed food than the LNaK group. Total score of sodium-related attitude and behaviors of HNaK group were 34.81 and 32.75, respectively and these scores were significantly higher than that of the LNaK group whose scores were 32.57 and 30.57, respectively. Total energy intake was not different between two groups but the intakes of calcium, vitamin B2 and folate were higher in HNaK group than in the LNaK group. Correlation analysis adjusted for age and gender revealed that total score of sodium-related nutrition knowledge was positively correlated with total score of sodium-related attitude and behaviors.
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, students who had high level of sodium-related nutrition knowledge had desirable attitude and behaviors toward sodium intake and these results can be considered in nutrition education for university students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal nutrition intervention focused on the adjustment of salt and sugar intake can improve pregnancy outcomes
Yuri Seo, Yeon Seon Jeong, Kyung‐A Koo, Jeong In Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park
Food Science & Nutrition.2020; 8(7): 3900. CrossRef - Effect of Protection Motivation Factors on Behavioral Intention to Reduce Sodium Intake among University Students in Gyeongnam and Busan
Soo-Hyun Jang, Eunju Yoon
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(1): 104. CrossRef
- Maternal nutrition intervention focused on the adjustment of salt and sugar intake can improve pregnancy outcomes
- 846 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Sodium Related Recognition, Dietary Attitude and Education Needs of Dietitians Working at Customized Home Visiting Health Service
- Yun Jeong Mo, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):558-567. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.558
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate recognition, dietary attitude and education needs for reducing sodium intakes of dietitian at customized home visiting health service (CHVHS).
METHODS
The subjects were 75 dietitian at CHVHS. We investigated several variables (recognition, dietary attitude, education needs for reducing sodium intakes) and determined sodium intakes level of subjects as 'low', 'middle' and 'high' by Dish Frequency Questionnaire 25 (DFQ 25). Also, we assessed the differences in recognition, dietary attitude, sodium intake level and education needs by dietitian career period (under 3 yrs vs. over 3 yrs) at CHVHS.
RESULTS
In recognition related reducing sodium intake, they showed 'checking a sodium content in nutrition labeling' score 2.5/4.0 and 'perception difference between sodium and salt' score 3.1/4.0. There was no difference in the recognition between under 3yrs' group and over 3yrs' group. In dietary attitude related reducing sodium intake, they showed 'palatability for salty taste' score 0.8/1.0, 'attitude in related soups' 0.7/1.0, 'attitude in related using natural spice' 0.6/1.0. There was a difference in 'attitude in related soups' between under 3yrs' group and over 3yrs' group (0.6 vs. 0.7). In sodium intake level by DFQ 25, they showed 'low group' 41.3%, 'middle group' 41.3% and 'high group' 17.3%. There was no difference in the distribution of sodium intake level by the career. In education needs related reducing sodium intakes, there were 'teaching experience' 93.3%, 'have a difficulty in teaching about reducing sodium intakes' 86.6%, and 'necessity of education for CHVHS dietitians' 100.0%. 'Needed education contents for CHVHS dietitians' were ranked as 'cooking way to reduce sodium intake' 58.7%, 'relation between hypertension and sodium' 17.3%, 'composing way to reduce sodium intake' 17.3%. There was a difference in needed education contents 'relationship between hypertension and sodium' (33.3% vs. 2.6%) and 'The cooking way to reduce sodium intake' (38.9% vs. 76.9%) by the career.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggested that a capacity training program for reducing sodium intake may be needed for dietitians at CHVHS to improve health of the community elderly. For effective training program related reducing sodium intake for dietitians at CHVHS, it may be necessary to consider the career period as dietitians at CHVHS.
- 567 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Blood Pressure and Dietary Related Risk Factors Associated with High Sodium Intake Assessed with 24-hour Urine Analysis for Korean Adults
- Yeon Seon Jeong, Hwa Jae Lim, Sook Bae Kim, Hee Jun Kim, Sook Mee Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):537-549. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.537
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to examine blood pressure and other characteristics of a high sodium intake group assessed with 24-hr urine analysis and the dietary factors related to the risk of high sodium intake among Korean adults.
METHODS
A cross-sectional study was conducted with adults aged 20-59 years. Subjects who completed 24-hr urine collection (N = 205) were divided into 3 groups (tertile) according to the sodium intake estimated with 24-hour urine analysis. We compared the blood pressure, BMI and dietary related factors of the 3 groups (low, medium, high sodium intake group) with General Linear Model (GLM) and Duncan's multiple range test (p < 0.05). The risk factors related to high sodium intake were assessed with odds ratio (p < 0.05).
RESULTS
The sodium intake (mg/day) of the 3 groups were 3359.8 +/- 627.9, 4900.3 +/- 395.1 and 6770.6 +/- 873.9, respectively, corresponding to daily salt intake (g/day) 8.5, 12.4 and 17.2, respectively. High sodium group showed significantly elevated age, BMI and systolic/diastolic blood pressure. Being male gender was associated with significantly increased risk of sodium intake (OR = 1.972; 95%CI: 1.083-3.593). The other factors related to high sodium intake were higher BMI (> or = 25) (OR = 2.619; 95% CI: 1.368-5.015), current alcohol consumption (OR = 1.943; 95%CI: 1.060-3.564), and having salty soybean paste with salt percentage > 14% (OR = 3.99; 95% CI: 1.404-6.841). The dietary attitude related to increased risk of high sodium intake included 'enjoy dried fish and salted mackerel' (p < 0.001) and 'eat all broth of soup, stew or noodle' (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Because high sodium intake was associated with higher blood pressure, nutrition education should focus on alcohol consumption, emphasis on related dietary factors such as using low salt soybean paste, improvements in the habit of eating dried fish and salted mackerel or eating all broth of soup, stew or noodle. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of fermented soybean on metabolic outcomes, anthropometric indices, and body composition: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Fatemeh Maleki Sedgi, Nazanin Mozaffari, Mohammad Reza Pashaei, Fatemeh Hajizadeh-Sharafabad
Food & Function.2025; 16(2): 389. CrossRef - Comparison between 24-hour diet recall and 24-hour urine collection for estimating sodium and potassium intakes and their ratio among Korean adults
Taisun Hyun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Young-Ran Heo, Heekyong Ro, Young-Hee Han, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 284. CrossRef - Development and application of the sodium index to estimate and assess sodium intake for Korean adults
Yeon-Kyung Lee, Taisun Hyun, Heekyong Ro, Young-Ran Heo, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(3): 366. CrossRef - Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
Qi Li, Ji Eun Lee, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(2): 91. CrossRef - Estimation model for habitual 24-hour urinary-sodium excretion using simple questionnaires from normotensive Koreans
Ji-Sook Kong, Yeon-Kyung Lee, Mi Kyung Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Young-Ran Heo, Taisun Hyun, Sun Mee Kim, Eun-Soon Lyu, Se-Young Oh, Hae-Ryun Park, Moo-Yong Rhee, Hee-Kyong Ro, Mi Kyung Song, Tatsuo Shimosawa
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(2): e0192588. CrossRef - Relationship of sodium consumption with obesity in Korean adults based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2014
Se Young Cheon, Hye Won Wang, Hwa Jung Lee, Kyung Mi Hwang, Hae Seong Yoon, Yoon Jung Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 64. CrossRef - Study of the characteristics of dietary behavior and the effects of nutrition education for sodium reduction according to the stages of behavioral change in sodium reduction of male adult subjects in Gwangju·Jeonnam regions
Young Ran Heo, Hyun Young Oh, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 472. CrossRef - Correlation analysis of sodium-related knowledge, dietary behavior, attitudes towards a low-salt diet and meal attitude guidance for elementary school teachers in Jeonbuk area
Hyun Ok Moon, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 180. CrossRef - Verification of Utility of Simple Mensuration of Cl-from Urine to Estimate the Amount of Sodium Intake
Sung-Ho Lee, Chae-Joon Lee, Sung-Mi Ju, Hyun-Joo Lee, Wang-Yeon Ra, Soon-Ok Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(1): 27. CrossRef
- Effect of fermented soybean on metabolic outcomes, anthropometric indices, and body composition: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
- 842 View
- 2 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effects of Low-sodium Diet Education Program on Dietary Habits, Diet Quality and Obesity Index in Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women
- Soo Bin Jeong, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Jin Nam Kim, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):513-526. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.513
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of low sodium diet education program on dietary habits, diet quality, and measures of obesity in overweight or obese middle-aged women.
METHODS
Subjects were 81 individuals aged 45 years or over, who completed an 8-week nutrition education. The subjects were divided into a normal group (N = 30) and an overweight-obese group (N = 51) according to the BMI. The effects were evaluated by anthropometric measurement, biochemical analysis, questionnaire, and diet records before and after the program.
RESULTS
Overweight-obese group showed significant decreases in weight (p < 0.0001), BMI (p < 0.0001), percent of body fat (p = 0.0087), waist circumference (p < 0.0001), systolic (p = 0.0003) and diastolic blood pressure (p = 0.0261). Nutrients intakes were not different between the two groups and only sodium intake was decreased after education. Total score of general dietary habits, dietary behavior related to sodium intake, dietary diversity score (DDS), diet variety score (DVS), and diet quality index-international (DQI-I) were improved in both groups compared to the baseline. Overweight-obese group showed significant improvement in 'having fruits everyday', 'having fish everyday', 'trying to eat many kinds of food', 'eating less broth when eating soup, stew, and noodles', 'eating less kimchi and salt-fermented vegetable', and 'propensity to think that dishes should be pretty seasoned'. In addition, moderation of empty calories food (p = 0.0064) and macronutrient ratio (p = 0.0004) were improved in the overweigh-obese group, but in the normal group, the results did not reach statistical significance.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggested that low sodium diet education program may contribute to obesity management by improving diet quality and dietary habits in middle-aged women.
- 698 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Development of Nutrition Education Program for Consumers to Reduce Sodium Intake Applying the Social Cognitive Theory: Based on Focus Group Interviews
- So Hyun Ahn, Hye Kyeong Kim, Kyung Min Kim, Jin Sook Yoon, Jong Sook Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(4):342-360. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.4.342
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to develop nutrition education program for consumers to reduce sodium intake based on social cognitive theory (SCT).
METHODS
The main factors of SCT related to low sodium diet were investigated by using focus group interview (FGI) with 30 women who participated in consumer organizations.
RESULTS
The main target groups for the education program were housewives (H), parents (P), and the office workers (OW), for which we considered their influences on other people and the surroundings. According to the results of FGI, in carrying out low sodium diet, 'positive outcome expectation' were prevention of chronic disease and healthy dietary habit, and 'negative outcome expectation' were low palatability of foods, difficulty in cooking meals, and limited choice of foods. The contents of the program and education materials were individualized by each group to raise self-efficacy and behavioral capability, which reflected the results of the FGI. The program included 'salt intake and health' to raise positive outcome expectation. For improving the ability to practice low-sodium diet, the program contained the contents that focused on 'cooking' and 'food purchasing' for H, on 'purchasing and selection of low-sodium food with the children' for P, and on 'way of selecting restaurant menu' for OW. Also the program included 'way of choosing the low-sodium foods when eating out' with suggestions on sodium content of the dishes and snacks. Further, 'dietary guidelines to reduce sodium intake' was also suggested to help self-regulation.
CONCLUSIONS
This nutrition education program and education materials could be utilized for the community education and provide the basis for further consumer targeted education program for reducing sodium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
Ji-Won Kang, Su-Jin Lee, Sil-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 224. CrossRef - Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 382. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a nutrition education program for housewives to reduce sodium intake: application of the social cognitive theory and a transtheoretical model
Sohyun Ahn, Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 174. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
Ji Suk Yim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Reach Out Emergency Department: Partnering With an Economically Disadvantaged Community in the Development of a Text-Messaging Intervention to Address High Blood Pressure
Emily Champoux, Rory Price, Joan E. Cowdery, Mackenzie Dinh, William J. Meurer, Narmeen Rehman, Caitlin Schille, Alina Oliver, Devin L. Brown, Jordan Killingsworth, Lesli E. Skolarus
Health Promotion Practice.2020; 21(5): 791. CrossRef - Factors contributing to the reduction of sodium intake by food manufacture and cooking venues according to the national sodium reduction policies
Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park, Jee Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 648. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Awareness of Health Risks and the Risk Reduction Measures Related to Sodium Intake between Female and Male University Students in Busan and Gyeongnam: An Application of Protection Motivation Theory
Soo-Hyun Jang, Eunju Yoon
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(1): 136. CrossRef - School Dietitian Awareness, Practice, and Sodium Reduction Plan in School Meal Service
Eun Kyung Kim, Hae Young Kim
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 222. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Program Designed to Reduce Sugar Intake in Preschool Children
Ma-Young Yeom, Youn-Ok Cho
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(3): 179. CrossRef - Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(4): 332. CrossRef - ‘When operating a cafeteria, sales come before nutrition’ – finding barriers and facilitators to serving reduced-sodium meals in worksite cafeterias
Sohyun Park, Jounghee Lee
Public Health Nutrition.2016; 19(8): 1506. CrossRef - Study on Energy and Nutrient Intake and Food Preference of the Elderly in Care Facilities
Jong-Sook Kwon, Seung Hee Lee, Kang Min Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 200. CrossRef - Evaluation of Consumer Nutrition Education Program to Reduce Sodium Intake Based on Social Cognitive Theory
So-Hyun Ahn, Jong Sook Kwon, Kyung Min Kim, Jin-Sook Yoon, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(6): 433. CrossRef - The Development of a Nutrition Education Program for Low-income Family Children by applying the Social Cognitive Theory and Health Belief Model
Saes-byoul Lee, Yu-Ri Jeong, Hyo-Jin Ahn, Min-Ji Ahn, Su-A Ryu, Nam-E Kang, Se-Young Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(3): 165. CrossRef
- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
- 895 View
- 6 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [English]
- The use Frequency and Amount of Food Sources of Sodium and Knowledge Requirement, and Job Satisfaction of Dietitians and Nutrition Teachers according to the School Types in Busan
- Jee Young Yeon, Soon Kyu Lee, Baeg Won Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(2):198-211. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.2.198
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
To investigate the use frequency and amount of food sources of sodium and knowledge requirement, and job satisfaction with school food services according to the school types in Busan.
METHODS
A total of 98 schools were surveyed and knowledge requirement and job satisfaction were assessed using a questionnaire. In addition, the use frequency and amount of food sources of sodium for 10 school days were examined.
RESULTS
The response rate of the most difficult area among dietitians' tasks was significantly high in 'nutrition education and counseling' for elementary schools and 'hygiene management' for high schools (p < .05). The response rate of the factors to be considered in meal planning was significantly high in 'energy and nutrients requirement' for elementary schools and 'menu/taste preference of students' for middle and high schools (p < .05). The response rate of whether school food services affect health and eating habits of students or not was significant high in 'very helpful' for elementary schools (p < .001). The average sodium contents in the meals of elementary, middle and high schools was 1981.4 mg/meal/person/day, 1867.3 mg/meal/person/day and 1,329.9 mg/meal/person/day, respectively. For foods in highest sodium, Kimchi, Oribulgogi, and Kare rice were ranked 1st, 2nd and 3rd respectively. The main reason for not providing the fruits was 'price' among all groups. The knowledge requirement such as 'nutrition and menu management', 'nutrition education', and 'nutrition counseling' was significantly higher in elementary school compared with middle and high school (p < .001, p < .01, and p < .01 respectively). The dietitians and nutrition teachers of elementary schools have a higher job satisfaction compared with those of middle schools (p < .01). The job satisfaction was positively correlated with knowledge requirement of dietitians and nutrition teachers of elementary and middle schools.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggest that developing dietitians' education program about knowledge requirement contribute to increasing the school food service and job satisfaction in elementary and middle schools. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- School Dietitian Awareness, Practice, and Sodium Reduction Plan in School Meal Service
Eun Kyung Kim, Hae Young Kim
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 222. CrossRef - Status and Need Assessment on Nutrition & Dietary Life Education among Nutrition Teachers in Elementary, Middle and High Schools
Na Gyeong Oh, Su Jin Gwon, Kyung Won Kim, Cheong Min Sohn, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 152. CrossRef
- School Dietitian Awareness, Practice, and Sodium Reduction Plan in School Meal Service
- 804 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Blood Pressure, Sodium Intake and Dietary Behavior Changes by Session Attendance on Salt Reduction Education Program for Pre-hypertensive Adults in a Public Health Center
- Eun Jin Jung, Jong Sook Kwon, So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(6):626-643. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.6.626
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - This study was performed to evaluate the differences in blood pressure, sodium intake and dietary behavior changes according to the extent of session attendance on sodium reduction education program for pre-hypertensive adults in a public health center. Sodium reduction education program consisted of 8 sessions for 8 weeks. Fifty three patients who completed the pre and post nutritional assessments were classified into 2 groups according to the session attendance rate. Nineteen participants who attended the education program 3 times or less (< or = 3) were categorized into the less attendance (LA) group and 34 participants attended 4 times or more (> or = 4) into the more attendance (MA) group. Blood pressure, anthropometric measurements, serum lipid profile, nutrient intakes including sodium, nutrition knowledge and dietary behavior score were assessed before and after the nutrition education program. Mean sodium intakes (p < 0.001), systolic/diastolic blood pressure (p < 0.001), and weight (p < 0.001) were significantly decreased in the MA group after sodium reduction education program. Compared to the MA group, mean sodium intakes, systolic/diastolic blood pressure were not significantly changed after the education program even with significantly increased nutrition knowledge (p < 0.05) and dietary behavior score (p < 0.01) in the LA group. It appears that pre-hypertensive adults need to attend the sodium reduction education program for at least 4 times or more to gain beneficial effects from the intervention. Positive feedback of healthcare team or offering more cooking classes may be needed to raise the attendance rate in the sodium reduction education program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Status of Recognition, Effort, and Satisfaction of Customers on Low-Sodium Diet in Industry Foodservice
Sang Jin Yoon, Kun Og Kang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(2): 168. CrossRef - Study of the characteristics of dietary behavior and the effects of nutrition education for sodium reduction according to the stages of behavioral change in sodium reduction of male adult subjects in Gwangju·Jeonnam regions
Young Ran Heo, Hyun Young Oh, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 472. CrossRef - The Effects of Hypertension Health School Program on Hypertension-related Knowledge, Self-efficacy, Self-care Behavior and Physiological Parameters in Hypertensive Patients
Koung Oh Chang
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(1): 49. CrossRef - Food Safety and Nutrition Education Program for Elderly and Assessment of Program Effectiveness Based on Health Belief Model
Jung-Hwa Choi, Eun-Sil Lee, Yoon-Jin Lee, Hye-Sang Lee, Hye-Ja Chang, Kyung-Eun Lee, Na-Young Yi, Yoon Ahn, Tong-Kyung Kwak
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2016; 45(9): 1366. CrossRef - Dietary Life related to Sodium of Participants in Hypertension and Diabetes Preventive Education at the Public Health Center
Hee-Ok Pak, Chun-Young Sohn, Jung-Hwa Park
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(2): 219. CrossRef - A Study on Eating Out Behavior and Recognition of Salinity in Restaurant Food in Jecheon Area
Soojin Park, Sung Hee Min
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(1): 20. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - The Study on Dietary Behavior and Health Related Behaviors of Self Perceived Sodium Intake Groups
Juhyeon Kim, Hei-Ryeo Yoon, Nam-E Kang
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(6): 511. CrossRef - The Relationship between Dietary Behaviors/health Risk Factors and Preference for Salty Taste among Korean Elderly People Living in Rural Areas
Mee Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(5): 448. CrossRef
- Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
- 748 View
- 1 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- A Survey on the Salt Content of Kindergarten Lunch Meals and Meal Providers' Dietary Attitude to Sodium Intake in Gyeonggi-do Area
- Jin Nam Kim, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(5):478-490. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.5.478
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - Dietary habit of excess sodium consumption is formed mainly by excessive salt intake from the younger age and this may lead to hypertension, stroke, and stomach cancer. This study was performed to estimate the salt content in kindergarten meals and provide basic data on meal providers' dietary attitude to sodium intake for nutrition education. We collected data on161 food items from 16 institutions in Gyeonggi-do and salt content was calculated from salinity and weight of individual food items. The average salt content from lunch meals was 2.2 g, which was about daily adequate intake of sodium for children aged 3 to 5 years old. Greatest contributor to the salt content in a meal was soup and stew (47.8%). The most salty dishes were sauces and kimchi followed by stir-fried food, deep-fried food, braised food, and grilled food. The salt content was higher in soup and stew despite of low salinity, due to the large quantity per serving. The salt contents of soups and kimchi were 40.6% and 14.3%, respectively of the total salt content in dish groups. Staff members and caregivers at home who prepared food for the child showed preference for one-dish rice meal, dried fish and salted mackerel, and broth when eating soup, stew, and noodles. Caregivers showed higher sodium index score and had higher preference for processed food such as Ramen, canned food, and ham compared with staff members (p < 0.05). These results suggested that monitoring salt content of kindergarten meals and nutrition education for those prepare meals for children are needed to lower sodium intake in childhood.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
Jiwoo Min, Youngmi Lee, Yunhee Chang, Yujin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 304. CrossRef - Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 386. CrossRef - Dietary status of young children in Korea based on the data of 2013 ~ 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eun-kyung Kim, Byengchun Song, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 330. CrossRef - Effects of a Practice Program for Low-Salt Meals on Infant Foodservices : Focusing on Infant Foodservices registered in Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Busan Metropolitan City
Chae-Young Jo, Jin-Suk Han
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(1): 66. CrossRef - Comparison of nutrients and food intakes of young children according to lunch places: based on the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(3): 254. CrossRef - Status of Recognition, Effort, and Satisfaction of Customers on Low-Sodium Diet in Industry Foodservice
Sang Jin Yoon, Kun Og Kang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(2): 168. CrossRef - Salinity Monitoring of Soups of The Institutions Enrolled at Center for Children’s Foodservice Management
Hyun Nae Park, Soon Mi Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(6): 507. CrossRef - School Dietitian Awareness, Practice, and Sodium Reduction Plan in School Meal Service
Eun Kyung Kim, Hae Young Kim
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 222. CrossRef - Survey on Actual Situation and Importance of Use of Snacks according to Young Children Mother’s Nutrition Knowledge
Sun-Hyun Kim, Geum-Soon Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(2): 141. CrossRef - Study on the Salt and Sodium Content of Middle School Lunch Meals in Gyeongsangbuk-do Area - Focus on Application of 'SamSam Foodservice' -
So-Young Park, Kyung-A Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2016; 45(5): 757. CrossRef - The awareness level and needs for education on reducing sugar consumption among mothers with preschool children
Younhee Lee, Nami Joo
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(2): 229. CrossRef - Study on Sodium Contents of Kindergarten Lunch Meals in Gyeoungsangbuk-do Area
Dan-Bi Song, Kyung-A Lee
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(5): 648. CrossRef - An Evaluation of the Foodservice Quality and Management of Preschool Foodservice Establishments by IPA - Focusing on Parents of Preschoolers in Metropolitan Area of Korea, China and Japan -
Sanghyun Park, Nami Joo
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(1): 160. CrossRef - Sodium-related Eating Behaviors of Parents and Its Relationship to Eating Behaviors of Their Preschool Children
Ye Seul Kim, Hong Mie Lee, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 11. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - A Study on Eating Out Behavior and Recognition of Salinity in Restaurant Food in Jecheon Area
Soojin Park, Sung Hee Min
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(1): 20. CrossRef - Assessment of Nutritional Status of Children in Community Child Center by Nutrition Quotient(NQ) - Gyeongiu -
Na-Hyung Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(1): 73. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Na Reduction Program for Cook in Child-care Center: Focus on Self-reevaluation and Strengthen Consciousness
Hyewon Shin, Youngmee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(5): 425. CrossRef
- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
- 1,043 View
- 1 Download
- 18 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



