Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Eating habits and dietary supplement utilization according to food-related lifestyle among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):253-264. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
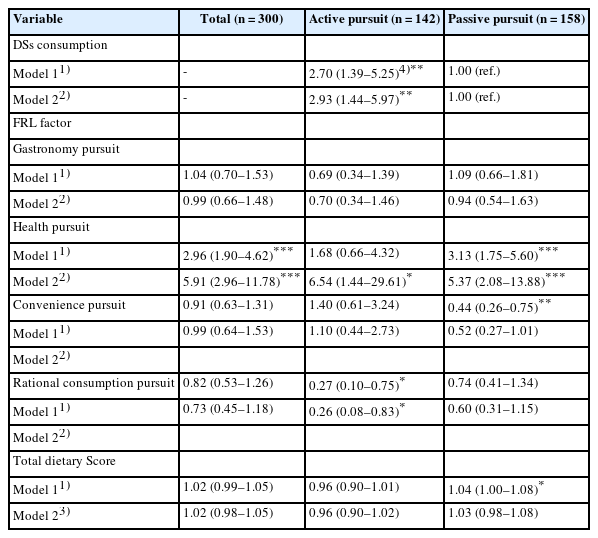
This study investigated the association between eating habits and the utilization of dietary supplements (DSs) according to food-related lifestyle (FRL) among Korean adults. Methods: This study included a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) in their 20s to 60s living in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province. We identified two groups by factor and cluster analysis: an ‘active pursuit’ group and a ‘passive pursuit’ group. Differences in eating habits and DS utilization between the two groups were analyzed by chi-square test and t-test. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the effect of variables on DS consumption according to FRL. Results: There were significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, alcohol drinking frequency, total dietary score, change in DS consumption after coronavirus disease 2019, and current DS consumption (P < 0.05). The proportion who perceived many health benefits of DSs was higher in the ‘active pursuit’ group than in the ‘passive pursuit’ group (P = 0.003). The most commonly consumed type of DSs was multivitamins & minerals for the ‘active pursuit’ group, and omega-3 fatty acids for the ‘passive pursuit’ group. The ‘an active pursuit’ group consumed DSs 2.93 times more (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.44–5.97) compared to the ‘passive pursuit’ group, after adjusting for confounders. In the ‘active pursuit’ group, the health pursuit (odds ratio [OR] = 6.54, 95% CI: 1.44– 29.61) and rational consumption pursuit factors (OR = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.08–0.83) were associated with DS consumption, whereas only the health pursuit factor had a significant association (OR = 5.37, 95% CI: 2.08–13.88) within the ‘passive pursuit’ group. However, total dietary score and DSs consumption did not show a relationship. Conclusions: By understanding the consumption characteristics of DSs according to FRL, this can serve as basic data necessary for promoting health through the utilization of DSs and healthy behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
Hongryul Ahn, Seungwon Kim, Jinmyung Jung, Chan Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(4): 618. CrossRef - Demographic and behavioral correlation of red ginseng consumption in Korea
DeYu Tian, KeunOh Choi, Yong-ung Kim, YoungJoo Lee
Integrative Medicine Research.2025; : 101287. CrossRef
- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
- 5,238 View
- 95 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middle-aged Korean adults: an intervention study
- Minji Kang, Young-Hee Park, Subeen Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Hyun Wook Baik, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):265-277. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 411 Korean adults 30–59 years of age were allocated randomly into three groups: the nutrition education group for promoting Han-sik consumption (HG), the nutrition education group for eating balanced diet (EG), and the control group (CG). The HG and EG received four face-to-face nutrition education sessions over 16 weeks to improve nutritional problems based on the individual’ usual diet. Effectiveness of the program was evaluated with the differences of self-reported dietary behaviors, dietary intakes, anthropometric measurements and biochemical indices between the baseline and the end of the nutrition education program. The changes within groups were analyzed using paired t-test and McNemar test and effectiveness among three groups was analyzed by repeated analysis of variance.
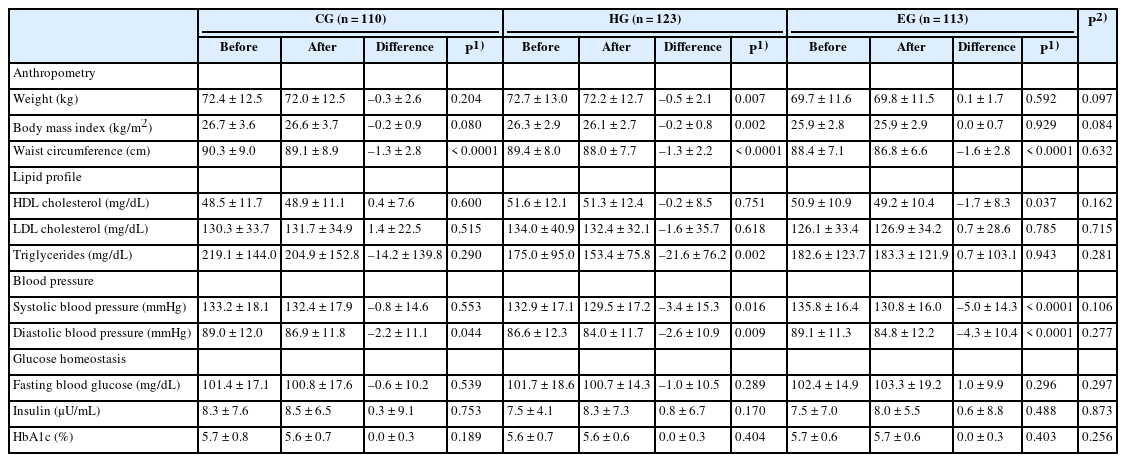
Results
After the nutrition education, the percentages of participants who achieved the recommended food group consumption in the Korean Food Guidance Systems significantly increased in HG (P = 0.022). Body weight (P = 0.007), body mass index (P = 0.002), and triglycerides (P = 0.002) significantly decreased in HG. Waist circumference and diastolic blood pressure decreased in all three groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
This study found that tailored nutrition education program for middle aged Korean adults showed beneficial effects on improving dietary behaviors and metabolic syndrome risk factors. Further studies are needed to assess the long-term effects of the nutrition education programs on metabolic syndrome risks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multicomponent intervention increases nutrition knowledge scores in rural China
Zhifan He, Ming Feng, Lu Li, Jing Li, Xiaohui Li
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Multicomponent intervention increases nutrition knowledge scores in rural China
- 4,513 View
- 88 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):173-188. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to analyze the regional differences in dietary protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome.
Methods
Study participants were 1,721 older adults aged 65 and over who participated in 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Using 24-hour recall dietary intake data, protein intake and their food sources were examined. The association between protein intake and metabolic syndrome, obesity, and abdominal obesity were analyzed by multiple logistic regression.
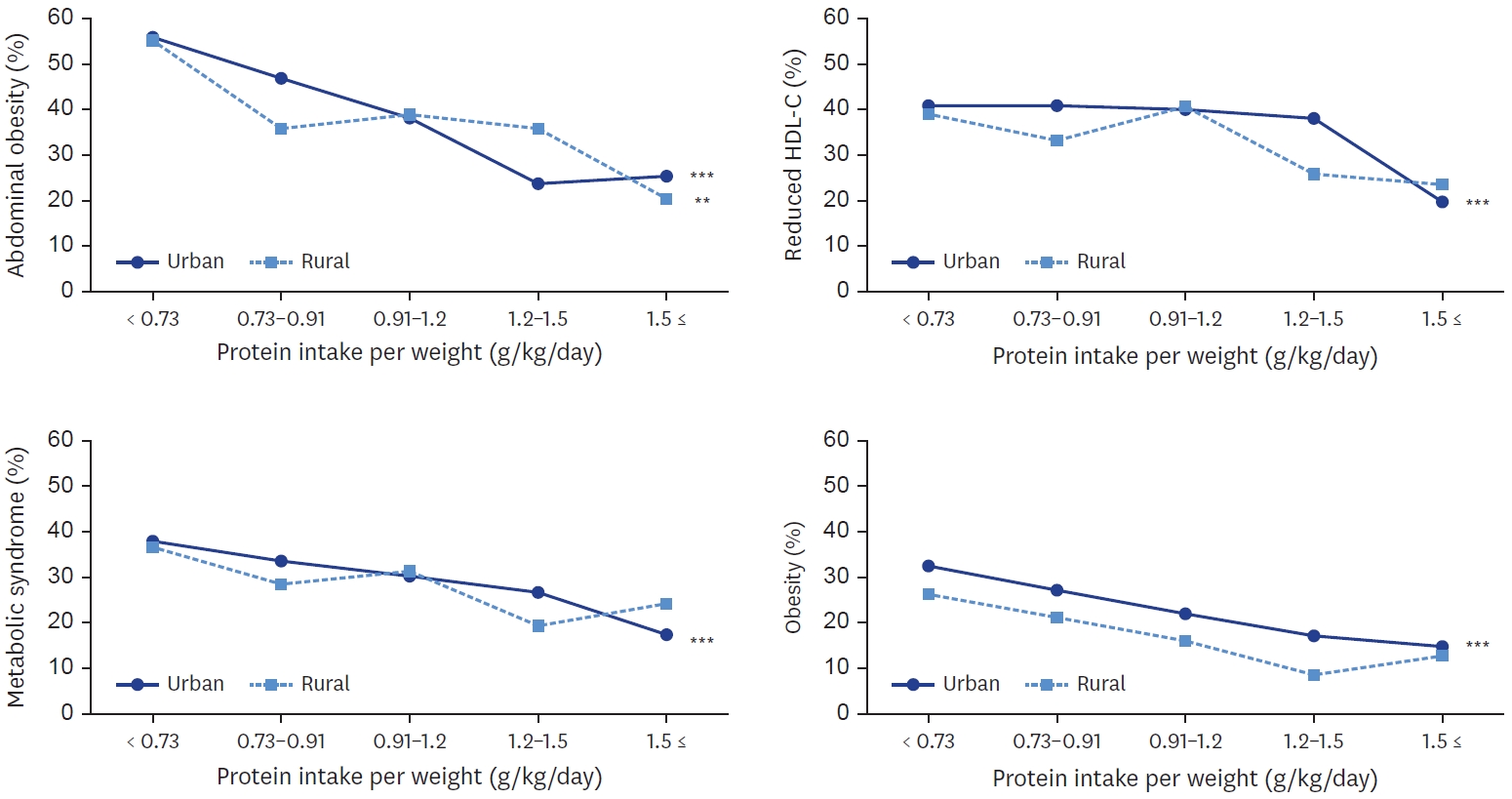
Results
Total protein and animal protein intakes were higher in urban area (60.0 g, 24.4 g, respectively) than in rural area (54.6 g, 19.6 g, respectively). With increase of protein intake level, animal to total protein proportion was increased in both areas. Total protein and plant protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity, abdominal obesity in both areas. Animal protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity in both areas, and with abdominal obesity only in urban area. In urban area, plant protein intake was also negatively associated with the risks of metabolic syndrome, elevated triglyceride, and reduced high density lipoprotein-cholesterol. In urban area, the risk of metabolic syndrome was decreased when their protein intake was more than 0.91 g/kg and was lowest when their protein intake was more than 1.5 g/kg (P for trend < 0.001).
Conclusions
Korean older adults showed inadequate protein intake and those in rural area showed lower animal protein intake than in urban area. The risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome was decreased with the increase of protein intake level. These findings may help develop effective nutrition support strategy for older adults to reduce regional health disparity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
Yea-Chan Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Soyoung Jeon, Yae-Ji Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2026; 50(1): 178. CrossRef - The association between dietary protein intake and metabolic syndrome: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Dorsa Ghazvineh, Ali Hosseinpour, Vahid Basirat, Elnaz Daneshzad
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between total, animal-based, and plant-based protein intake and cognitive decline in older adults
Maud Peperkamp, Margreet R. Olthof, Marjolein Visser, Hanneke A. H. Wijnhoven
European Journal of Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
- 10,647 View
- 112 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Comparative study on the health and dietary habits of Korean male and female adults before and after the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: utilizing data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
- Chaemin Kim, Eunjung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):65-80. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to compare changes in physical factors, health behaviors, eating habits, and nutritional intake among Korean male and female adults over a period of three years (2019–2021) before and after the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods
This study utilized raw data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021). The participants in this study included 6,235 individuals in 2019, 5,865 individuals in 2020, and 5,635 individuals in 2021. Individuals whose daily energy intake was less than 500 kcal or exceeded 5,000 kcal were excluded from the study.
Results
In comparison to 2019, overweight/obesity rates, weight, waist circumference, weekend sleep hours, and resistance exercise days/week increased in both male and female during the COVID-19 pandemic. Regarding eating habits, the proportions of people skipping breakfast, not eating out, consuming health supplements, and recognizing nutritional labels increased in 2020 and 2021, whereas the rate of skipping dinner decreased. Total energy intake has continued to decrease for the two years since 2019. A comparison of nutrient intake per 1,000 kcal before and after the outbreak of COVID-19 revealed that intake of nutrients, including protein, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, riboflavin, and niacin increased, while folic acid intake decreased. In male, calcium, phosphorus, riboflavin, and niacin intakes increased, whereas iron, vitamin C, and folic acid intakes decreased. In female, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, and riboflavin intake increased significantly, while protein and niacin intake decreased significantly.
Conclusions
After COVID-19, the obesity rate, breakfast skipping rate, health supplement intake, and nutritional label use increased, while the frequency of eating out, dinner skipping rate, and total energy intake decreased. These environmental changes and social factors highlight the need for nutritional education and management to ensure proper nutritional intake and reduce obesity rates in the post-COVID-19 era. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Status of Use of Protein Supplement Products according to the Health Concerns of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
Cho-In Oh, Bok-Mi Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 9. CrossRef - A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 140. CrossRef - How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
Yong-Seok Kwon, Dasol Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1973. CrossRef - Intake of energy and macronutrients according to household income among elementary, middle, and high school students before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study
Chae-Eun Jeong, Heejin Lee, Jung Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 234. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef
- Status of Use of Protein Supplement Products according to the Health Concerns of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
- 5,883 View
- 90 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Changes in nutritional status of Korean older adults during COVID-19 Pandemic by household income and demographic factors -using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(2019-2020): a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):302-316. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to identify changes in the nutritional status of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic according to household income and demographic characteristics.
Methods
Study participants were 2,408 adults aged 65 and over who participated in the 2019–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). To examine changes in nutrient intake levels resulting from COVID-19, data of 2019 and of 2020 were compared. Study participants were divided into three groups based on household income level to compare these changes. The changes were compared according to household income level, age group, and household type.
Results
Percentages of recommended intakes for energy, protein, and most micronutrients were the lowest for the low-income group of both males and females in 2020. The Mean Adequacy Ratio (MAR) score was the lowest for the low-income group in both years. When comparing nutrient density for 2019 and 2020 by income group, the male low-income group experienced a decrease in nutrient densities of vitamin A, thiamine, calcium, and iron. For the same group, a decreased percentage for energy intake from protein was noted. Fruit intake was lowest in the low-income group for both males and females. Low-income males had the lowest intake levels for meat, fish, eggs, and legumes in both 2019 and 2020 and the lowest milk and milk product intake levels in 2020. Older adults living alone or single older adults with children had lower MAR scores than those living with a spouse. Older adults living alone experienced decreases in energy and thiamine and iron intake levels in 2020 compared to their intake levels in 2019.
Conclusions
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, nutrition intake levels worsened for older adult males in the low-income group and older adults living alone. This finding shows the need for a more systematic nutritional support strategy for the vulnerable older adults population in national disaster situations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
Yong-Seok Kwon, Dasol Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1973. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Comparison of nutrient intake and Korean Healthy Eating Index among the elderly in rural areas pre- and post- COVID-19 pandemic: the 2018–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Sangyeon Kim, Hye-Sook Hong, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(5): 496. CrossRef
- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
- 2,518 View
- 45 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Status of Iodine Intake and Comparison of Characteristics according to Iodine-sourced Food Intake Patterns of Chinese Adults: A Study Encompassing Three Regions with Different Iodine Nutritional Statuses
- Danying Zhang, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):503-514. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.503
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examines the status of iodine intake and compares the characteristics (region and thyroid disease prevalence) according to the iodine-sourced food intake pattern in Chinese adults.
Methods
An online survey was conducted by enrolling 437 Chinese adults aged 18-65 years, living in three regions with different iodine nutritional statuses: Sichuan, Chongqing, and Guangdong.
Results
The prevalence of thyroid diseases in Sichuan, Chongqing, and Guangdong were 12.5%, 8.5%, and 2.8%, respectively. Conversely, the proportion of people who received thyroid disease-related examinations was a mere 37.5%. Among the subjects who underwent thyroid examination, the prevalence of thyroid disease in the three regions was 32.2%, 21.8%, and 8.0%, respectively. No differences were obtained in the total iodine intake by region, but the type of iodine source foods differed. Regardless of the region, the highest iodine content was obtained from seaweed. However, the iodine content from iodized salt and other foods differed significantly by region. Factor analysis revealed three food intake patterns according to the iodine food source. The study further determined regional differences and differences in the prevalence of thyroid disease according to food intake patterns.
Conclusions
High salt intake can also increase iodine intake, which is thought to have an effect on the occurrence of iodine-excess thyroid disease. Hence, efforts focused on improving salty eating habits need to be implemented.
- 1,243 View
- 10 Download

- [Korean]
- Trends in Dietary Protein Intake and Its Adequacy among Korean Adults: Data from the 2010 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
- Hyunji Ham, Kyungho Ha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(1):47-60. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.1.47
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate dietary protein intake and its adequacy among Korean adults during recent 10 years.
Methods
Based on the 2010 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) data, a total of 51,296 adults aged 19 years old or more who participated in a one-day 24-hr dietary recall were included. Dietary protein intake was estimated as percentages of total energy (% of energy) and grams per body weight (g/kg/ day) and compared with the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans to evaluate the adequacy of protein intake. In addition, proportions of people whose protein intakes were less than the estimated average requirement (EAR) and above the upper limit of the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) (> 20% of energy) were calculated according to sociodemographic characteristics.
Results
Protein intake was increased from 14.7% of energy in 2010 to 15.6% of energy in 2019 among Korean adults. However, there was no increase in protein intake relative to the recommended nutrient intake (% RNI) during the recent 10 years. Protein intake relative to the RNI was decreased from 130.2% in 2010 to 121.1% in 2019 (P for trend < 0.0001) among total participants, and a significant decreasing trend was observed in all age groups except for over 65 years old. However, protein intake relative to the RNI was lowest in the elderly (98.6%). Proportions of low protein intake (< EAR) and high protein intake (> AMDR) increased in the past 10 years (P for trend < 0.0001 for all), and these were associated with socioeconomic statuses, such as education and household income levels.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that protein adequacy in Korean adults has not been improved over the past decade compared with recommended levels. Nutritional education and intervention programs should consider different intake levels according to sociodemographic characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combined associations of protein intake and resistance exercise with handgrip strength in postmenopausal women
Jin Kyung Baek, Hae Rim Kim, Eun Jin Lee, Yun Soo Chung, Seok Kyo Seo
Maturitas.2026; 205: 108808. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment and Trends Among Preschoolers in South Korea: Data from KNHANES 2012–2021
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Jin-Young Lee, Yangsuk Kim, Sohye Kim
Nutrients.2026; 18(2): 240. CrossRef - Status of Use of Protein Supplement Products according to the Health Concerns of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
Cho-In Oh, Bok-Mi Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 9. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment of Older Korean Adults by Level of Plant Protein Intake
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Jeong-Hun Song, Yangsuk Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1976. CrossRef - Trends in dietary amino acid intake and food sources among Korean adults: data from the 2010-2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sumin Kim, Hyunji Ham, Kyungho Ha
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 773. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef - High-Protein Products in 2013 and 2023: Shifts in Diverse Aspects Over the Last Ten Years
Hye Ran Lee, Ihyeon Cho, Hyejin Yi, Hee Jung Park
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 173. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
Hyoju Lee, Youjeong Jang, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 261. CrossRef - Association between Processed Meat Protein Consumption and Incident Osteoporosis in Adults Aged 50 Years and Older: A Prospective Cohort Study Based on Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study Data (2005–2020)
Dohee Lee, Soo Hyoung Lee, Ki Hyun Park, Kunhee Han, Eunjin Jeong
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2024; 45(5): 268. CrossRef - The Relationship of Pork Meat Consumption with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Biomarkers of Health Status in Korean Older Adults
Ah-Jin Jung, Anshul Sharma, Mei Chung, Taylor Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4188. CrossRef - Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - Relationship between protein intake and grip strength in qualitative and quantitative aspects among the elderly in Korea: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi‑Hyun Kim, Mi‑Kyeong Choi, Yun‑Jung Bae
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current status of nutrient intake in Korea: focused on macronutrients
Seung-Won Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(12): 801. CrossRef
- Combined associations of protein intake and resistance exercise with handgrip strength in postmenopausal women
- 7,732 View
- 200 Download
- 15 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Away-from-Home Eating and Dietary Patterns of Ugandan Adults: a Web-based- Survey
- Anthony Kityo, Pil-Sook Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(1):1-11. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Away-from-home (AFH) eating has been associated with poor diet quality and health outcomes like obesity in developed countries. AFH eating is also emerging in lowincome countries, but its influence on overall diet quality is under-researched. We examined the prevalence of AFH eating and its influence on the dietary patterns of Ugandan adults.
Methods
This cross-sectional study employed a web-based survey to interview Ugandan adults aged 18 ~ 65 years. A qualitative food frequency questionnaire was used to assess the food group intake, which was then converted into daily intake frequencies. Principal component analysis was used to derive dietary patterns. The participants were then classified based on the tertiles (T) of dietary pattern scores.
Results
About 75% of the 375 participants reported eating AFH. The young men, food insecure, and urban dwellers were more likely to eat AFH 5 times/week. Three dietary patterns emerged; the animal-based, beverage pattern; the high fat, sweet pattern; and the traditional, plant-based pattern. Participants who frequently ate AFH were 2.85 times and 5.64 times more likely to be in the second and third tertiles, respectively, of the animalbased, beverage pattern compared to the rare eaters (OR = 2.85, 95% CI: 1.35-6.06 for T2 vs T1; and OR = 5.64, 95% CI: 2.50-12.73 for T3 vs T1). The odds of being in the second tertile of the high fat, sweet pattern was significantly higher for frequent AFH eaters compared to the rare eaters (OR = 2.61, 95% CI:1.23-5.52).
Conclusions
The prevalence of AFH eating was high. Frequent AFH eating was common among the young, male, food insecure, and urban dwellers, and was associated with unhealthy dietary patterns. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Difficulties in eating out of home while diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease: A qualitative interview study from China
Tingting Yin, Ran Ye, Qiuqin Wang, Lulu Wang, Wenjing Xu, Wenjing Tu, Guihua Xu, Yogesh Kumar Jain
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(12): e0288908. CrossRef
- Difficulties in eating out of home while diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease: A qualitative interview study from China
- 1,654 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between Eating Alone Patterns and Mental Health Conditions by Region among Korean Adults
- Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):441-454. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the association between the frequency and pattern of eating alone and the mental health status according to region in Korean adults.
Methods
The data of 10,040 Korean adults aged ≥ 19 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2017 and 2019 were used. Participants were divided into 4 groups based on their frequency of eating alone: none (all meals together), 1, 2, and 3 meals/day alone. The regions were divided into urban and rural areas. Mental health status was assessed by stress recognition, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation. Multivariable logistic regressions were conducted to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) on the association of the frequency and pattern of eating alone with poor mental health after controlling for covariates.
Results
Among Korean adults, 74.1% ate more than one meal a day alone. Individuals having 3 meals a day alone tended to be less educated, single, single person households, or living in urban areas (all P < 0.05). In rural areas, those having 3 meals/ day alone had higher odds of stress recognition (AOR: 1.55, 95% CI: 1.02-2.35) than those having all meals together. In urban areas, individuals eating alone 3 times/day had higher odds of stress recognition (AOR: 1.60, 95% CI: 1.31-1.96), depressive symptoms (AOR: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.23-2.12), and suicidal ideation (AOR: 2.14, 95% CI: 1.42-3.22) compared to those having all meals together. Urban residents having dinner alone had higher odds of depressive symptoms (AOR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.05-1.58) and suicidal ideation (AOR: 1.66, 95% CI: 1.19-2.33) than those having dinner with others.
Conclusions
Our findings showed that the frequency and patterns of eating alone were differentially associated with increased odds of poor mental health according to region of residence. Nutrition education is needed for those frequently eating alone, particularly those living in urban areas, to highlight the advantages of eating together and to ensure that they have balanced and healthy meals even if they eat alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Social Activity Restrictions on Depression in Young Single-Person Households: The Moderating Effect of Eating Alone
Jiwon Kim, Youngye Park
Journal of Social Science.2025; 36(3): 27. CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - How Does the Frequency of Eating-Alone among Older People in Korea Affect Their Health and Dietary Behavior?
Yongseok Kwon, Kyung Hee Hong, Yoo-Kyung Park, Sohye Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2085. CrossRef - Impact assessment of a primary care physician counseling program for youth population
Yun-Su Kim, Shin-Ae Kim
Medicine.2022; 101(46): e31916. CrossRef
- The Impact of Social Activity Restrictions on Depression in Young Single-Person Households: The Moderating Effect of Eating Alone
- 2,438 View
- 40 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutritional Status of Vitamins and Minerals According to Consumption of Dietary Supplements in Korean Adults and the Elderly: Report Based on 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):329-339. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study was undertaken to evaluate the intake of vitamins and minerals from dietary supplements (DSs) in Korean adults and elderly.
Methods
Data for this study was generated from the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). We analyzed 4,204 individuals aged 19 years and older (2,579 users and 1,625 non-users). The survey included 24-h recall questions on food and DS intakes, as well as questions on DS use over the past year. The nutrient DSs evaluated were calcium, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and vitamin C. Total nutrient intakes were obtained by combining nutrient intakes of foods and DSs consumed by each subject.
Results
Most micronutrient intakes from food (except for thiamin) in adult users, and the four micronutrient intakes (iron, vitamin A, vitamin B2 and vitamin C) in elderly users, were significantly higher than values obtained in non-users. For total intake of nutrients and DSs, both adult and elderly users had a significantly higher intake than non-users. While proportions below Estimated Average Requirements for all micronutrients by adding respective DSs in users were significantly reduced in adults and elderly as compared to non-users, the proportions of above Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for calcium and vitamin A in adults, and vitamin A in elderly, were significantly increased. In the total subjects examined, consumption of DSs was associated with lower odds ratios of undernutrition of micronutrients, and with higher odds ratios of overnutrition of calcium, iron, and vitamin A, as compared to non-users of DSs.
Conclusions
Although DSs consumption by adults and the elderly improves the micronutrient status, it also increases the risk of excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 103. CrossRef - Folate intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey with newly established folate database
Eun-Ji Park, Inhwa Han, Kyoung Hye Yu, Sun Yung Ly
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(4): 418. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimated dietary vitamin D intake and major vitamin D food sources of Koreans: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 451. CrossRef - A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- 2,243 View
- 10 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Qualitative Study on the Perception of Community Food-accessibility Environment among Urban Older Adults
- Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):137-149. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study explored the community food environmental factors affecting food purchasing using a qualitative research methodology for the elderly as well as the various food environments under their socioeconomic diversity.
Methods
For the qualitative data collection, this study interviewed 20 elderly people aged 65 years or more, who participated in a public health program or lunch services operated by the senior welfare center in Seoul. Five dimensions, such as availability, physical accessibility, affordability, acceptability, and accommodation suggested in previous studies, were used to identify the community food environmental factors.
Results
The elderly participants showed overall similarities to the concepts derived from existing studies on the five dimensions of food accessibility environment. In addition, other important food accessibility environmental factors that were not present in previous studies, such as acceptability for a product of domestic origin, delivery service to home, and small-packaged food sales, were derived. On the other hand, the concept of some subjects differed depending on the household income and specifically for the physical accessibility concept. This showed that the close distance factor from a grocery store at home might not apply to older adults in low-income households in Korea.
Conclusions
This study found that five dimensions of the food environment suggested by previous studies could also be applied to vulnerable older adults in Korea. On the other hand, the socioeconomic characteristics of individuals and households would affect the perspectives of their local food environments differently. The findings of this study could help in the development of tools for evaluating the community food environment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 16. CrossRef - Spatial inequalities and driving factors in food accessibility: Integrating online and offline grocery services in South Korea
Hyebin Kim, Minkyu Kim, Sugie Lee
Applied Geography.2025; 185: 103777. CrossRef - Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 352. CrossRef - Spatial Disparity of Neighborhood Food Environment by Socioeconomic Status: Application of Urban Network Analysis
Taekyung Seong, Sugie Lee
Land.2024; 13(6): 865. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Perceived Community Food Accessibility Measurement Questionnaire for Korean Older Adults
Jisoo Hong, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(19): 4301. CrossRef - A relationship between food environment and food insecurity in households with immigrant women residing in the Seoul metropolitan area
Sung-Min Yook, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 264. CrossRef - Regional Difference in the Effect of Food Accessibility and Affordability on Vegetable and Fruit Acquisition and Healthy Eating Behaviors for Older Adults
Dong Eun Lee, Kirang Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 14973. CrossRef - Analysis of Accessibility Changes to Neighborhood Food Environment and Food Desert Phenomenon in Seoul, Korea : Focused on the High-density Areas of Low-income Older Adults
Taekyung Seong, Sugie Lee
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2021; 56(1): 137. CrossRef - Effects of Perceived Food Store Environment on Malnutrition and Frailty among the Food-Insecure Elderly in a Metropolitan City
Yu-Mi Kim, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2021; 13(7): 2392. CrossRef - Analyzing Socio-Economic and Geographical Factors that Affect the Health of the Elderly
Zacharias Dermatis, Athina Lazakidou, Athanasios Anastasiou, Panagiotis Liargovas
Journal of the Knowledge Economy.2021; 12(4): 1925. CrossRef - Analysis of Awareness, Knowledge, and Behavior about Food Hygiene·Safety Among the elderly
Mi Sook Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 200. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- 1,719 View
- 19 Download
- 12 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Evaluation of Total Fat and Fatty Acids Intakes in the Korean Adult Population using Data from the 2016–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):223-231. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.223
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated dietary intakes of total fat and fatty acids among the Korean adult population.
METHODS
This cross-sectional study used the 2016–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data. A total of 10,772 subjects aged ≥19 y for which dietary data were available were selected. Data pertaining to energy and nutrient intakes were obtained by a 24-h recall method. Total fat and fatty acids intakes were evaluated based on the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDR) of 2015 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans by sex and age groups. All statistical analyses accounted for the complex sampling design effect and sampling weights.
RESULTS
The mean intakes of energy and total fat were 1,952 kcal (95% CI: 1928–1977) and 46.1 g (45.2–47.1), respectively, and about 21% of the energy was obtained from fat in this study population (21.7% in men and 20.2% in women). The mean percentages of energy from saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids were 6.4%, 6.7%, and 5.2%, respectively. About 18% of adults exceeded the AMDR for fat (30% of energy), whereas 37.6% exceeded the AMDR for saturated fatty acids (7% of energy). The proportions of subjects who consumed more than the AMDR for fat and saturated fatty acids decreased across age groups in both sexes. Among young adults (19–29 y), about 63% of the subjects obtained ≥7% of their energy from saturated fatty acids. About 61% of older adults obtained less than 15% of their energy from total fat.
CONCLUSIONS
Increased intake of fat energy was prominent in saturated fatty acids. Our findings suggest current information on total fat and fatty acids intakes in Korean adults and can be used to provide dietary guidelines for the improvement of public health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary patterns derived by reduced rank regression are associated with lipid disorders among Korean adults: a cross-sectional analysis
Hyun Ah Kim, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2016–2021 KNHANES data
Enkhgerel Erdenetsetseg, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 144. CrossRef - Nutrition and food intake status among adults in Jeju according to sociodemographic characteristics and obesity
Hyunji Ham, Hanbin Ko, Sumin Kim, Youjeong Jang, Jong-Seok Byun, Yoonsuk Jekal, Insuk Chai, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(6): 667. CrossRef - Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Content of Snacks for Smart Snack Choices
Chae Young Yoon, Eunju Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(4): 264. CrossRef - Trends in dietary intake and food sources of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids among Korean adults between 2007 and 2018
Jae Eun Shim, Youngmi Lee, SuJin Song
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023069. CrossRef - Diabetes and Dietary Fats
Jae Won Cho
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 154. CrossRef - Association of Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Its Food Sources With Hypercholesterolemia in Middle-Aged Korean Men and Women
In Young Jeong, Jae Eun Shim, SuJin Song
CardioMetabolic Syndrome Journal.2022; 2(2): 142. CrossRef - Increasing trends in dietary total fat and fatty acid intake among Korean children: using the 2007–2017 national data
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(2): 260. CrossRef - Substitution of Carbohydrates for Fats and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes among Korean Middle-Aged Adults: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Hye-Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(3): 654. CrossRef - Food behaviors accounting for the recent trends in dietary fatty acid profiles among Korean adults
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(3): 405. CrossRef - Current status of nutrient intake in Korea: focused on macronutrients
Seung-Won Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(12): 801. CrossRef - Regional Differences in Dietary Total Fat and Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Their Associations with Metabolic Diseases among Korean Adults: Using the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 495. CrossRef - The number of teeth is associated with diet quality in Korean adult population
Hye-Sun Shin
Archives of Oral Biology.2020; 118: 104882. CrossRef - Trends in Dietary Intake of Total Fat and Fatty Acids Among Korean Adolescents from 2007 to 2017
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrients.2019; 11(12): 3073. CrossRef
- Dietary patterns derived by reduced rank regression are associated with lipid disorders among Korean adults: a cross-sectional analysis
- 1,887 View
- 10 Download
- 15 Crossref

- [English]
- Milk Intake Patterns with Lactose and Milk Fat in Korean Male Adults
- Jung Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, Sung Hee Min, Myung Hee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):488-495. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.488
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the milk intake patterns with lactose and milk fat in Korean male adults using the following variables: milk intake level, awareness of lactose, and milk fat, health problems, and necessity of milk intake. In addition, the factors affecting milk intake were analyzed by multiple regression analysis.
METHODS
The subjects were 532 males aged 20 years or older among the nationwide milk purchasing group. The subjects were 223 (41.9%) in the 20–29 year age group, 188 (35.3%) in the 30–49 year age group and 121(22.7%) in the over 50 year age group. The survey was conducted using ANOVA and multiple comparative analysis to examine the differences in age and multiple regression analysis was performed to investigate the factors affecting the intake of milk.
RESULTS
The intake of milk in the subjects was 538.14 ± 494.23 ml per week. There were statistically significant differences in the subjects' age according to processed milk, low fat, nonfat milk, cheese, and ice cream. The perception of milk and lactose and milk fat was recognized as a good food for skeletal health when milk was consumed. Among the milk nutrients, lactose was highly recognized at the age of 20–29, and milk fat was recognized in those over 50 years. In addition to lactose and milk fat, calcium was the most highly recognized among the milk nutrients. Health problems associated with milk were skeletal health, obesity, and lactose intolerance. The perception of lactose intolerance was related to lactose intolerance and fatness, and the dietary behavior was unaffected.
CONCLUSIONS
This study examined the milk intake patterns of adult Korean males. Many variables were found to be related to the intake of milk. In this study, the milk intake was high when there was no problem with the perception and dietary behaviors of milk nutrition (lactose and milk fat). This study focused on lactose and milk fat, which are major nutrients in milk, and it is a new perspective study among milk-related research. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of milk and dairy product consumption with the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular disease incidence in middle-aged and older Korean adults: a 16-year follow-up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Yeseung Jeong, Kyung Won Lee, Hyekyeong Kim, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1225. CrossRef
- Association of milk and dairy product consumption with the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular disease incidence in middle-aged and older Korean adults: a 16-year follow-up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
- 1,910 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Program on Obesity Index and Behavioral Modification in Moderate Obese Women
- Myung Hee Chang, Su Jin Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):318-332. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the behavioral modification of obese adults who underwent nutritional and physical activity education. Twenty obese females, aged 20–60 years old, with BMIs (Body Mass Index) >30 or body fat (%) >40 were subjected to this study.
METHODS
The physical activity education program consisted of doing exercise in a gymnasium together or home exercise. Dietary attitudes and dietary intakes were assessed using weight control, physical activity, and eating habits. The nutrition-exercise educational period was 12 weeks.
RESULTS
After the study period, there was significant improvement in physical activity and eating habits score. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the dietary intakes of fiber, iron, potassium, vitamin A, vitamin B6, and niacin. Blood pressure, blood glucose, and total cholesterol levels showed a tendency to decrease, but there was no significant difference. BMI, fat mass, abdominal circumference, and visceral fat levels were significantly reduced while muscle mass significantly increased.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that behavioral modification by nutrition and physical activity education with feedback has positive effects on dietary intake and anthropometric biomarkers in obese adults. Therefore, lifestyle interventions of this kind could be recommended as a method for obesity management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of tele-nutrition education on weight loss, energy intake, and fat adequacy among obese adults in Banyumas, Central Java, Indonesia
Teguh Jati Prasetyo, Izzati Nur Khoiriani, Sifa Aulia Wicaksari, Gumintang Ratna Ramadhan, A. Khomsan, E. Palupi, S.P. Loh, N. Mohd Esa
BIO Web of Conferences.2025; 153: 02013. CrossRef - Influence of Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention (LSI) Program on Health, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Middle-Aged Women
Su-Jin Jung, Seung-Ok Lee, Min-Jun Choi, Jun Heo, Soo-Wan Chae, Baik-Hwan Cho
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2022; 12(3): 127. CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef
- Effect of tele-nutrition education on weight loss, energy intake, and fat adequacy among obese adults in Banyumas, Central Java, Indonesia
- 1,637 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Relation between Beverage Consumption Pattern and Metabolic Syndrome among Healthy Korean Adults
- Eun Ju Dennis, Minji Kang, Sung Nim Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(5):441-455. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.5.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study is to describe beverage patterns among healthy Korean adults and investigate their association with prevalence and components of metabolic syndrome.
METHODS
Subjects consisted of 6,927 Korean adults, aged 19-64 years in the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES, 2013-2015). Beverages were regrouped into twelve groups based on food codes and beverage intake (g/day) was assessed by 24-hour recall. Factor analysis was used to obtain beverage patterns. Waist circumference and body mass index (BMI) were used as anthropometric data; fasting blood glucose, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein (HDL), and blood pressure were used as biochemical indicators. The odds ratio (OR) for prevalence of metabolic syndrome and components of metabolic syndrome was assessed using logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS
Three beverage patterns were identified using factor analysis: 1) carbonated soft drinks 2) coffee (without added sugar or powdered creamer), and 3) alcoholic beverages. Subjects with high scores for the carbonated soft drink and coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer patterns were younger and subjects with high scores for the alcoholic beverage pattern were older. There were significant differences in gender distribution in all three beverage patterns, with men more likely to have high scores for carbonated soft drink and alcoholic beverage patterns. On the other hand, women were more likely to have higher scores for coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer pattern. Within each pattern, there were significant differences in sociodemographic and lifestyle characteristics such as education, household income, frequency of eating out, and smoking status according to the quartile of pattern scores. Alcoholic beverages and carbonated soft drinks patterns were associated with an increased levels of metabolic syndrome components, but coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer was not associated with any of metabolic syndrome components in healthy Korean adults after adjusting for age, sex, education, BMI, weight management, household income, smoking status, frequency of eating out, and energy intake.
CONCLUSIONS
Alcoholic beverages and carbonated soft drinks patterns are associated with increased levels of metabolic syndrome components while coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer pattern is not associated with any of metabolic syndrome components in healthy Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional and Health Status According to the Frequency of Carbonated Beverage Consumption among Adults in Their 20s : Based on the 2019-2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
You-Sin Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(3): 159. CrossRef - Calcium- and Sodium-Rich Food Intake among Koreans with and without Metabolic Syndrome: Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Byeonggeun Choi, Jiyoon Kim, Yeonjin Kim, Jiae Shin, Sang-Ah Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(15): 2439. CrossRef - Effects of Calamansi Soju and Other Alcoholic Beverages on Resin Restorations
Moon-Jin Jeong, Kyungwon Heo, Myoung-Hwa Lee, Myeong-Ju Jeong, Do-Seon Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(4): 251. CrossRef - Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 350. CrossRef - Association between Dietary Habits, Shift Work, and the Metabolic Syndrome: The Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Heeja Jung, Hyunju Dan, Yanghee Pang, Bohye Kim, Hyunseon Jeong, Jung Eun Lee, Oksoo Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7697. CrossRef - Exploring parenting variables associated with sweetness preferences and sweets intake of children
Taejung Woo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2019; 13(2): 169. CrossRef - Influence of beverage type and ingestion time on tooth corrosion
Jae-Deok Cheon, Eun-Ah Cho, Hyun-Bae Park, Yu-Jin Choi, Han-Ju Kim, Jung-Soo Lee, Eun-Jeong Bae
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2018; 45(3): 169. CrossRef
- Nutritional and Health Status According to the Frequency of Carbonated Beverage Consumption among Adults in Their 20s : Based on the 2019-2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
- 1,846 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- The Relationships among Quality of Life and Stress, Health-related Habits and Food Intake in Korean Healthy Adults Based on 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Su Bin Lee, Hyun Jin Choi, Mi Joung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):411-422. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.411
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study investigated the socioeconomic factors that affect quality of life (QL) in healthy adults and to study the relationship between QL and health-related habits and food intake.
METHODS
Subjects consisted of 1,154 healthy adults without any known disease, aged 19 to 65 years from the 2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data. We used SPSS statistical program version 20.0 for data analysis.
RESULTS
The average age and QL score of the study population were 36.7 years and 0.99 points, respectively. Males had a significantly higher QL score than the females (p < 0.001), and employed subjects and those employed in permanent positions had significantly higher scores as compared respectively with unemployed subjects and those employed in temporary positions (p < 0.001, p < 0.05). The group that responded "almost every day" to the "frequency of binge drinking" and "frequency of disruption of daily life due to drinking" had significantly lower QL scores as compared to other groups (p < 0.05). Further, the scores were significantly higher for individuals who practiced "intense physical activities" and "walking" (p < 0.001). The groups that responded that they were "very stressed" showed significantly lower QL scores in comparison to the other groups (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in QL scores according to anthropometric or biochemical indices. When subjects were divided into two groups based on average QL scores, the frequency of intake of "barbecued beef" was significantly higher while the frequency of intake of "fried eggs or rolled omelet," and "soy milk" was significantly lower in the high QL group.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on these findings, it is evident that in healthy adults without any known underlying illnesses, psychological factors such as economic activity, occupational environment, and stress are considered to have a greater impact on their QL than are nutrient intake, blood biochemical indices, and anthropometric status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
Ho-Jung Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Yookyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 320. CrossRef - DOES HEALTH LITERACY AND LIFE SATISFACTION PROMOTE HEALTHY EATING AMONG MARRIED WOMEN IN TURKEY?
Mahmut Kılıç, Nurgül Nehir Yılmaz
Eskişehir Türk Dünyası Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi Halk Sağlığı Dergisi.2024; 9(3): 323. CrossRef - The Connection between Hand Washing and Brushing Teeth
Ra-Ae Bak, Sun-Jung Shin, Hee-Jung Park, Jin-Young Jung, Hwa-Young Lee, Nam-Hee Kim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2023; 23(2): 132. CrossRef
- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
- 1,332 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Socio-demographic Characteristics, Nutrient Intakes and Mental Health Status of Older Korean Adults depending on Household Food Security: Based on the 2008-2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoon Jung Yang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(1):30-40. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to investigate the associations of food security with socio-demographic characteristics, nutrient intakes and mental health status among older Korean adults.
METHODS
This study was conducted using data from the 2008-2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Subjects were 4,451 adults aged 65~98 years. Food security was measured using a self-reported question on food sufficiency of subjects' household. Based on the answers, study subjects were classified into secure, mildly insecure, moderately insecure, and severely insecure groups. Dietary intake was estimated by 24-hour dietary recall. Nutrient intake was assessed by dietary reference intakes (DRI). As for mental health status, the data on mental stress, depression, and suicide ideation were used.
RESULTS
Rate of food insecurity in older adults was 14.3%. Old age, being female, low education, low income level, living alone, and discomfort in daily living were more related to food insecurity. Means of nutrient intakes were significantly different according to food security status. Intakes of calcium, potassium, and vitamin B2 were lower than recommended intakes in all groups. Consumption amounts of soy and soybean products, vegetables, mushrooms, fruits, vegetable oils, meats, eggs, seafood, and dairy products were lower in food insecure groups. Mental stress, depression, and suicide ideation were higher in food insecure groups independent of the gender and income level.
CONCLUSIONS
These present findings suggested that food security is related to mental health as well as nutrition status in older Korean adults. A national system that include food and psychosocial support programs for the elderly should be considered in order to improve the overall health of older Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food insecurity and its associated characteristics of the elderly in Seoul: analysis of the data from the Seoul Food Survey 2023
Hyunjeong Park, Youngmin Nam, Linxi Huang, Youngmi Lee, Jihyun Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 117. CrossRef - Prediction model for identifying a high-risk group for food insecurity among elderly South Koreans
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A study on the relationship between food insecurity and periodontitis in Korean adults: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII) from 2016-2018
Soo-Jin Kang, Jung-Eun Park, Jong-Hwa Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2023; 47(3): 106. CrossRef - The global burden of suicidal behavior among people experiencing food insecurity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mark Mohan Kaggwa, Rita Akatussasira, Firoj Al-Mamun, Sébastien Prat, Mohammed A. Mamun, Isabelle Combey, Felix Bongomin, Sheila Harms, Gary Chaimowitz, Mark D. Griffiths, Andrew T. Olagunju
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 342: 91. CrossRef - 광주광역시 서구지역 경로식당 이용 노인의 식품안정성에 따른 식생활 실태연구
지수 백, 영란 허
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(5): 402. CrossRef - Socioeconomic status, food security, and chewing discomfort of Korean elders: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye-Sun Shin, Ae-Jung Im, Hee-Jung Lim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(1): 94. CrossRef - Food insecurity and associated depression among older adults in India: evidence from a population-based study
Muhammad T, KM Sulaiman, Drishti Drishti, Shobhit Srivastava
BMJ Open.2022; 12(4): e052718. CrossRef - Association of food insecurity with physical frailty among older adults: study based on LASI, 2017-18
T. Muhammad, Priya Saravanakumar, Abhishek Sharma, Shobhit Srivastava, C.V. Irshad
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2022; 103: 104762. CrossRef - Effects of Perceived Food Store Environment on Malnutrition and Frailty among the Food-Insecure Elderly in a Metropolitan City
Yu-Mi Kim, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2021; 13(7): 2392. CrossRef - Comparison of the health and nutritional status of Korean elderly considering the household income level, using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 39. CrossRef - Is It What They Eat or How Much They Eat That Matters More in Adults with Food Insecurity in a Wealthy-Country Context?
Min Gyeong Kang, Sung-Min Yook, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrients.2021; 13(3): 851. CrossRef - Health and nutrition intake status of the Korean elderly according to their food security level: data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII), 2016–2018
Ahreum Maeng, Jeehyun Lee, Eunju Yoon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(2): 179. CrossRef - Factors associated with bicycle helmet use: A multilevel analysis
Jang-Rak Kim, Euy-Hoon Suh
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2020; 37(3): 39. CrossRef - The effects of a personalized nutrition intervention program on food security, health and nutritional status of low-income older adults in Seoul city
Yeyeon Lee, Narae Yang, Minjeong Shin, Kyung-Eun Lee, Chang Hee Yoo, Kirang Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(4): 416. CrossRef - Gênero, segurança alimentar e nutricional e vulnerabilidade: o Programa das Mulheres Mil em foco
Jussara Maysa Campos, Rita de Cássia Coelho de Almeida Akutsu, Izabel Cristina Rodrigues Silva, Karin Savio Oliveira, Renata Monteiro
Ciência & Saúde Coletiva.2020; 25(4): 1529. CrossRef - Interpersonal and Community Factors Related to Food Sufficiency and Variety: Analysis of Data from the 2017 Community Health Survey
Jiyoun Hong, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 416. CrossRef - The Association between Food Insecurity and Diet Quality Varies by Race/Ethnicity: An Analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2014 Results
Cindy W. Leung, June M. Tester
Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.2019; 119(10): 1676. CrossRef - Dietary and health characteristics of the young-old and the old-old by food security status: analysis of data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ajung Bae, Jihyun Yoon, Soh-Yoon Yun, Kana Asano
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(1): 104. CrossRef - Dietary and health characteristics of the young-old and the old-old by food security status: analysis of data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ajung Bae, Jihyun Yoon, Soh-Yoon Yun, Kana Asano
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(1): 104. CrossRef - Spatial Disparity in Food Environment and Household Economic Resources Related to Food Insecurity in Rural Korean Households with Older Adults
Jae Eun Shim, Seo-jin Kim, Kirang Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrients.2018; 10(10): 1514. CrossRef - Dietary intakes of adolescents from food insecure households: analysis of data from the 6th(2013-2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mariam Nakitto, Kana Asano, Injoo Choi, Jihyun Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(6): 507. CrossRef - Health and nutritional status of Korean adults according to age and household food security: Using the data from 2010~2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Geun Ah Park, Sung Hee Kim, Seok Joong Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(6): 603. CrossRef - Association of food insecurity and depression in Korean adults
Kowoon Lee, Hye-Sook Yoo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 62. CrossRef - A study on nutritional intakes in middle income adults based on data from the 5thKorean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ji-Myung Kim, Hye Sook Kim, Ki Nam Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(4): 364. CrossRef - Food Insecurity and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 Data
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(4): 308. CrossRef
- Food insecurity and its associated characteristics of the elderly in Seoul: analysis of the data from the Seoul Food Survey 2023
- 1,585 View
- 2 Download
- 25 Crossref

- [English]
- The Risk of Metabolic Syndrome by Dietary Patterns of Middle-aged Adults in Gyeonggi Province
- You Sin Lee, Moo Yong Lee, Sim Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):527-536. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.527
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to assess how nutrient intakes are related to risk factors for metabolic syndrome according to dietary patterns in the middle-aged adults.
METHODS
The subjects (n = 187; 47 men, 140 women) consisted of middle-aged adults over 30 years old in Ilsan area. The metabolic syndrome was diagnosed according to the data collected from each subject, including anthropometric measurements and blood analyses. The dietary patterns were derived from the average of two-day dietary intake data.
RESULTS
Factor analysis identified three major dietary patterns which were "Meats and alcohol", "Mixed grains, vegetables and fruits", and "Rice, Kimchi and fish & shellfish". The daily intakes of energy, protein, and sodium increased across quartiles of "Meats and alcohol" pattern scores (p < 0.05), whereas the intakes of carbohydrates, potassium, calcium, and fiber increased across quartiles of "Mixed grains, vegetables and fruits" pattern scores (p < 0.001). The "Meats and alcohol" pattern scores were positively correlated with protein and sodium intakes but inversely correlated with carbohydrates, fiber and potassium intakes which were adjusted for age, sex and energy (p < 0.05). The highest quartile pattern score of "Meats and alcohol" pattern had elevated odds ratio of abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome (p < 0.05). The risk of hypertriglyceridemia decreased in the highest quartile of "Mixed grains, vegetables and fruits" pattern (OR 0.35, 95% CI 0.12-1.00).
CONCLUSIONS
Our results suggested that reducing the consumption of meat and alcohol along with increasing fruits, vegetables and mixed grains would be helpful for preventing the metabolic syndrome and chronic diseases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between the Korean Healthy Diet Score and Metabolic Syndrome: Effectiveness and Optimal Cutoff of the Korean Healthy Diet Score
Soo-Hyun Kim, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(19): 3395. CrossRef - The Relationship between Meal Regularity and Oral Health and Metabolic Syndrome of Adults in Single Korean Households
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, On-Ju Ju
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 185. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Dietary Fat Energy Ratio in Middle-aged Men - Using the 2012~2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data -
Eun-Sil Her
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 1030. CrossRef - Reduction of Plasma Triglycerides and Cholesterol in High Fat Diet-Induced Hyper-Lipidemic Mice by n-3 Fatty Acid from Bokbunja (Rubus coreanus Miquel) Seed Oil
Hyelin Jeon, Su-Jin Oh, Hyun Soo Nam, Yoon Seok Song, Kyung-Chul Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(7): 961. CrossRef
- Association between the Korean Healthy Diet Score and Metabolic Syndrome: Effectiveness and Optimal Cutoff of the Korean Healthy Diet Score
- 1,152 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Investigation on Influencing Environmental Factors on Health Status of Korean Septuagenarians Dwelling in Longevity Region in Jeonla Province
- Chung Shil Kwak, Miyong Yon, Mee Sook Lee, Se In Oh, Sang Chul Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(2):142-162. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.2.142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the critical environmental factors on healthy-aging of Korean people, we investigated the significant factors influencing health status of septuagenarians living in rural area of Jeonla province, known to be one of the representative longevity regions in Korea.
METHODS
We divided subjects into healthy group (36M/25F) or poor-health group (26M/73F) based on self-reported health status, body mass index, a number of prescription, and blood test data. General characteristics, physical measurements, lifestyle, dietary behavior and nutrient intake, physical health and mental health data were statistically compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
Average age was not different between healthy group and poor-health group in men and women, respectively. In men, significantly favorable factors to health were observed to be higher education, regular exercise, higher grip strength and walking function, body mass index (> or = 18.5 kg/m2), moderate frequency of drinking and eating-out, non-smoking, normal red blood cell (RBC) count, higher serum dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEAS) level, good digestive function and appetite, normal hearing function, regular meals, adequate vegetable and fruit intake, diverse food intake, adequate energy and nutrients (protein, vitamin B1, B6, C and E, folate, niacin, P, Zn and K) intake, higher mini-nutrient status assessment (MNA) score and low level of depression. On the other hand, in women, those were literacy, living arrangement, moderate frequency of drinking, healthy teeth, higher grip strength and walking function, bone mineral density, normal RBC and white blood cell (WBC) count, higher DHEAS concentration, higher MNA score, normal cognition and memory function, having snack and adequate fruit intake.
CONCLUSIONS
These results could be useful to plan effective strategies to increase health-life expectancy of Korean old people living in rural areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Validation of the Yonsei Lifestyle Profile-Satisfaction (YLP-S) Using the Rasch Measurement Model
Kang-Hyun Park, Ickpyo Hong, Ji-Hyuk Park
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative analysis of dietary behavior and nutrient intake of elderly in urban and rural areas for development of “Village Lunch Table” program: Based on 2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Youngmi Lee, Yourim Choi, Hae Ryun Park, Kyung Hee Song, Kyung Eun Lee, Chang Hee Yoo, Young Suk Lim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 171. CrossRef - A Study on the Body Composition, Physical Activity Level, Basal Metabolic Rate, and Daily Energy Expenditure of Elderly in Busan
Hwa-Jae Lim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 178. CrossRef - The Comparative Analysis of Health Risk Factor according to HbA1c Level of Elderly Women Dwelling in Jeonla Province - Blood Health Status, Food Habit and Nutrient Intake -
Se In Oh, Chung Shil Kwak, Mee Sook Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(3): 392. CrossRef - Changes in the Nutrition Status of Elderly Females in Health Promotion Programs of Health Centers in Chungbuk Province
Myoung-Sook Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(2): 225. CrossRef - A Study on the Blood Health Status and Nutrient Intake in Elderly Women Dwelling in Longevity Region in Jeonla Province according to Family Arrangement
Se In Oh, Chung Shil Kwak, Miyong Yon, Mee Sook Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(5): 940. CrossRef
- Development and Validation of the Yonsei Lifestyle Profile-Satisfaction (YLP-S) Using the Rasch Measurement Model
- 1,215 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Associations between Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and Consumption Frequencies of Vitamin D Rich Foods in Korean Adults and Older Adults
- Areum Yu, Jihye Kim, Oran Kwon, Se Young Oh, Junghyun Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(2):122-132. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.2.122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the vitamin D status and to determine the association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] concentrations and consumption frequencies of vitamin D rich foods in Korean adults and older adults.
METHODS
Subjects were 10,374 adults and 2,792 older adults participating in the 2008-2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Consumption frequencies of vitamin D rich foods were estimated by using a qualitative food frequency questionnaire (FFQ). Eleven food items such as beef, egg, mackerel, tuna, yellow corvina, pollack, anchovy, mushroom, milk, yogurt, and ice cream were selected as vitamin D rich foods based on previous research.
RESULTS
The proportions of deficiency (< 12 ng/mL), inadequacy (12-20 ng/mL) and sufficiency (> or = 20 ng/mL) of serum 25(OH)D concentrations from June to November and December to May in adults were 8.8%, 42.3%, 48.8%, and 28.2%, 52.8%, 19.1%, respectively. The proportions of deficiency, inadequacy and sufficiency of serum 25 (OH)D concentrations from June to November and December to May in older adults were 10.1%, 32.4%, 57.5%, and 24.1%, 45.4%, 30.5%, respectively. The mean serum 25(OH)D concentrations in adults were positively related to the consumption frequencies of mackerel, anchovy, all fish, milk and milk.dairy products. The mean serum 25(OH)D concentrations in older adults were positively related to the consumption frequencies of yellow corvina and negatively related to the consumption frequencies of ice cream.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results suggest that Korean adults were more deficient in serum 25(OH)D concentrations than older adults. The consumption of vitamin D rich foods may affect vitamin D status in Korean adults. Further studies are required to confirm these findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
Hongryul Ahn, Seungwon Kim, Jinmyung Jung, Chan Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(4): 618. CrossRef - Estimated dietary vitamin D intake and major vitamin D food sources of Koreans: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 451. CrossRef - Impacts of serum vitamin D levels on sleep and daytime sleepiness according to working conditions
Hyuk Joo Lee, Hayun Choi, In-Young Yoon
Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.2020; 16(7): 1045. CrossRef - Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and cognitive function in Korean older adults living in rural area
Ye Som Shin, Bo Youl Choi, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 465. CrossRef - Vitamin D intake, serum 25OHD, and bone mineral density of Korean adults: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES, 2011)
Mi-Yeon Kim, Mi-Ja Kim, Sun Yung Ly
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(6): 437. CrossRef - Relationship of vitamin D status and obesity index in Korean women
Ji-Young Park, Young-Ran Heo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(1): 28. CrossRef - The relationship between Physical Growth and Major Sources of Serum Vitamin D among Hospitalized Children of Changwon City
Haeyoung Kang, Eunsil Her, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(3): 197. CrossRef
- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
- 2,001 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- An Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Nutrition Counseling for Adults with Risk Factors for Dyslipidemia
- Tae Young Nam, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(1):27-40. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.1.27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dyslipidemia is a component of the metabolic syndrome and a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Nutrition counseling is important to improve dyslipidemia. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of nutrition counseling in adults with risk factors for dyslipidemia diagnosed by the national health screening program. The nutrition counseling for adults with risk factors for dyslipidemia was carried out at a public health center in Gyeonggi-do. Thirty four patients out of forty five participants in the program completed the nutrition counseling program. The nutrition counseling was provided 3 times during a 12-week period. Individualized nutrition counseling to improve dietary habits was conducted after examining participants' dietary intake through questionnaires about dietary habits and whether they practice dietary guidelines. Data about serum lipid profiles, body composition, nutrition knowledge, the practice of dietary guidelines, and dietary behavior were collected before and after nutrition counseling to evaluate the effectiveness of nutrition counseling. All data were statistically analyzed by SPSS program (Korea ver.18.0) and significant difference was evaluated by paired t-test and chi(2)-test. Body weight, body fat and WHR were significantly decreased after nutrition counseling. Total-cholesterol, TG, and LDL-cholesterol were significantly decreased but HDL-cholesterol did not show significant changes. Both scores of nutrition knowledge and the practice of dietary guidelines improved significantly (p < 0.001). This study shows that nutrition counseling helps to encourage healthy eating practices and to improve serum lipid profiles of adults with risk factors for dyslipidemia. Overall, results indicated that nutrition counseling resulted in positive changes to lower the reliance on medications. Therefore, nutrition counseling should be considered for the initial treatment of dyslipidemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Facilitators and barriers to achieving dietary and physical activity goals: focus group interviews with city bus drivers and counseling dietitians
Yongmin Jo, Suhyeun Cho, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(5): 376. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behaviors and Nutritional Status related to Dyslipidemia in Korean Middle-Aged Adults - From the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 2007~2010 -
Myung-Gon Shin, Ki-Hong Yoon, Mi-Young Song
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(5): 724. CrossRef - Development of Job Standards for Clinical Nutrition Therapy for Dyslipidemia Patients
Min-Jae Kang, Jung-Sook Seo, Eun-Mi Kim, Mi-Sun Park, Mi-Hye Woo, Dal-Lae Ju, Gyung-Ah Wie, Song-Mi Lee, Jin-A Cha, Cheong-Min Sohn
Clinical Nutrition Research.2015; 4(2): 76. CrossRef - Short-term Effects of a Lifestyle Intervention Program on Eating Behaviors, Physical Activity and Cardiovascular Risks in Korean Adults
Jiyeon Park, Hyekyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(4): 37. CrossRef
- Facilitators and barriers to achieving dietary and physical activity goals: focus group interviews with city bus drivers and counseling dietitians
- 1,306 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Blood Pressure, Sodium Intake and Dietary Behavior Changes by Session Attendance on Salt Reduction Education Program for Pre-hypertensive Adults in a Public Health Center
- Eun Jin Jung, Jong Sook Kwon, So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(6):626-643. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.6.626
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to evaluate the differences in blood pressure, sodium intake and dietary behavior changes according to the extent of session attendance on sodium reduction education program for pre-hypertensive adults in a public health center. Sodium reduction education program consisted of 8 sessions for 8 weeks. Fifty three patients who completed the pre and post nutritional assessments were classified into 2 groups according to the session attendance rate. Nineteen participants who attended the education program 3 times or less (< or = 3) were categorized into the less attendance (LA) group and 34 participants attended 4 times or more (> or = 4) into the more attendance (MA) group. Blood pressure, anthropometric measurements, serum lipid profile, nutrient intakes including sodium, nutrition knowledge and dietary behavior score were assessed before and after the nutrition education program. Mean sodium intakes (p < 0.001), systolic/diastolic blood pressure (p < 0.001), and weight (p < 0.001) were significantly decreased in the MA group after sodium reduction education program. Compared to the MA group, mean sodium intakes, systolic/diastolic blood pressure were not significantly changed after the education program even with significantly increased nutrition knowledge (p < 0.05) and dietary behavior score (p < 0.01) in the LA group. It appears that pre-hypertensive adults need to attend the sodium reduction education program for at least 4 times or more to gain beneficial effects from the intervention. Positive feedback of healthcare team or offering more cooking classes may be needed to raise the attendance rate in the sodium reduction education program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Status of Recognition, Effort, and Satisfaction of Customers on Low-Sodium Diet in Industry Foodservice
Sang Jin Yoon, Kun Og Kang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(2): 168. CrossRef - Study of the characteristics of dietary behavior and the effects of nutrition education for sodium reduction according to the stages of behavioral change in sodium reduction of male adult subjects in Gwangju·Jeonnam regions
Young Ran Heo, Hyun Young Oh, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 472. CrossRef - The Effects of Hypertension Health School Program on Hypertension-related Knowledge, Self-efficacy, Self-care Behavior and Physiological Parameters in Hypertensive Patients
Koung Oh Chang
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(1): 49. CrossRef - Food Safety and Nutrition Education Program for Elderly and Assessment of Program Effectiveness Based on Health Belief Model
Jung-Hwa Choi, Eun-Sil Lee, Yoon-Jin Lee, Hye-Sang Lee, Hye-Ja Chang, Kyung-Eun Lee, Na-Young Yi, Yoon Ahn, Tong-Kyung Kwak
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2016; 45(9): 1366. CrossRef - Dietary Life related to Sodium of Participants in Hypertension and Diabetes Preventive Education at the Public Health Center
Hee-Ok Pak, Chun-Young Sohn, Jung-Hwa Park
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(2): 219. CrossRef - A Study on Eating Out Behavior and Recognition of Salinity in Restaurant Food in Jecheon Area
Soojin Park, Sung Hee Min
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(1): 20. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - The Study on Dietary Behavior and Health Related Behaviors of Self Perceived Sodium Intake Groups
Juhyeon Kim, Hei-Ryeo Yoon, Nam-E Kang
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(6): 511. CrossRef - The Relationship between Dietary Behaviors/health Risk Factors and Preference for Salty Taste among Korean Elderly People Living in Rural Areas
Mee Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(5): 448. CrossRef
- Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
- 1,270 View
- 2 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- Status and Relationships among Lifestyle, Food Habits, and Stress Scores of Adults in Chungnam
- Yeon Ja Seo, Mi Hyun Kim, Myung Hee Kim, Mi Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(5):579-588. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.579
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the association among demographic characteristics, lifestyle, food habits, and stress status of 437 males and females aged over 25 years in Chungnam. Overall, the stress status of the subjects was high showing an average of 103 points out of 156 points based on the something scale. Results of the study revealed that marital status, exercise status, and health status had significant relationships with food habits and stress scores. The subjects who were married, had a higher frequency of exercise, and were healthier, had a significantly higher food habit score but a significantly lower stress score compared with their counterparts. Also, food habit scores had a significantly negative relationship with stress scores. Thus, this research showed possible links among healthy food habits, desirable lifestyle, and low stress status. In other words, people who experience a high level of stress may be more likely to have unhealthy food habits, resulting in a poor healthy conditions. These results show that appropriate food habits and adequate dietary management are deemed necessary for people with a high degree of stress. Further in-depth studies are needed to clarify a direct relationship between stress and food habits and to determine the proper diet that may help relieve stress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between sweet food intake and stress among college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi areas
Jun-Gyeong Kim, Jounghee Lee, Kyunghee Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(4): 373. CrossRef - Association between stress and dietary habits, emotional eating behavior and insomnia of middle-aged men and women in Seoul and Gyeonggi
Onjeong Choi, Jiwon Kim, Yujin Lee, Youngmi Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(2): 225. CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Habits, Life Stress and Nutrition Knowledge of High School Students in Gyeonggi Area
Kyung Ae Park, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 126. CrossRef - Eating Habits of the University Students affected by Stress Levels in the Areas of Seoul and Gangwon Province
Jeongsill Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(5): 782. CrossRef - The Relationship between Stress, Social Support and Healthy Diet Score among Chinese University Students in Korea
Sunghee Lee, Zhen Feng, Youngmee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(4): 273. CrossRef - Antioxidative Activity of Feral Haw (Crataegus pinnatifida BUNGE) Seed Extracts Using Various Solvents
Min-A Kim, Yishan Duan, Jong-Hwan Seong, Hun-Sik Chung, Han-Soo Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2014; 30(1): 33. CrossRef - A comparative study on dietary behavior, nutritional knowledge and life stress between Korean and Chinese female high school students
Sohwan Son, Yoona Ro, Hwajin Hyun, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(2): 205. CrossRef - Antioxidative activities of various solvent extracts from haw (Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge)
Yishan Duan, Min-A Kim, Jong-Hwan Seong, Hun-Sik Chung, Han-Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2014; 21(2): 246. CrossRef - A comparative study on dietary behavior, nutritional knowledge and life stress between Korean and Chinese female high school students
Sohwan Son, Yoona Ro, Hwajin Hyun, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(2): 205. CrossRef
- Relationship between sweet food intake and stress among college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi areas
- 1,262 View
- 3 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrient Intake, Lifestyle Factors and Prevalent Hypertension in Korean Adults: Results from 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Sle Koo, Youngok Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Jin Sook Yoon, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(3):329-340. Published online June 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.3.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hypertension is a well-known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Previous studies have shown that changes in diet and lifestyle factors can prevent the development of hypertension, but the combined effects of these modifiable factors on hypertension are not well established. The objective of this study is to investigate associations of diet and lifestyle factors, evaluated both individually and in combination, with prevalent hypertension among Korean adults. We analyzed data obtained from the 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey, a nationwide cross-sectional study using a stratified, multistage probability sampling design. The associations of 12 nutrient intakes and lifestyle factors with risk of hypertension were explored using restricted cubic spline regression and logistic regression models among 6,351 adults. Total energy and several nutrients and minerals, including, calcium, vitamin A, vitamin C, and sodium, showed non-linear relationships with the risk of prevalent hypertension. In multivariate logistic regression models, dietary score, obesity and alcohol intake were independently associated with the risk of prevalent hypertension, but smoking and physical activity were not. Overall, participants whose dietary habits and lifestyle factors were all in the low-risk group had 68% lower prevalence of hypertension (OR: 0.32, 95 CI: 0.14-0.74) compared to those who were at least one in the high-risk group of any dietary or lifestyle factors. The result suggests that combined optimal lifestyle habits are strongly associated with lower prevalence of hypertension among Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genetic Variations in Thiamin Transferase SLC35F3 and the Risk of Hypertension in Koreans
Ja-young Seo, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2021; 10(2): 140. CrossRef - Association of Soybean Food Intake and Cardiometabolic Syndrome in Korean Women: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007 to 2011)
Sook-Hyun Jun, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Yookyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 143. CrossRef - How Much Intake of Sodium Is Good for Frailty? : The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study (KFACS)
S. Kim, M. Kim, J. Min, J. Yoo, M. Kim, J. Kang, Chang Won Won
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2019; 23(6): 503. CrossRef - Nutritional Status of Hypertensive Men in Gyeongnam Area
Hae-Jin Park, Ye-Ji Choi, Sung-Hee Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(4): 297. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Prevalence of Osteoarthritis and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V), 2010~2012
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 99. CrossRef - Excessive Sodium Intake and Related Factors According to Energy Intakes Among Korean Elderly: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Young-Jin Tak, Jeong-Gyu Lee, Yun-Jin Kim, Sangyeoup Lee, Dong-Wook Jung, Yu-Hyeon Yi, Young-Hye Cho, Eun-Jung Choi, Seung-Hun Lee, Hye-Lim Hwang, A-Ra Cho
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2014; 18(4): 185. CrossRef - The relationship of dietary sodium, potassium, fruits, and vegetables intake with blood pressure among Korean adults aged 40 and older
Mi Kyung Kim, Kirang Kim, Min-Ho Shin, Dong Hoon Shin, Young-Hoon Lee, Byung-Yeol Chun, Bo Youl Choi
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(4): 453. CrossRef - An Analysis of Food Consumption Patterns of the Elderly from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES Ⅴ-1)
Eun Mi Kim, Mi-Kyung Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(5): 818. CrossRef - Prevalence of Hypertension and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Data from the 4th Korean National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007~2009
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2013; 19(1): 14. CrossRef - Association of Bone Mineral Density and Blood Pressure, Calcium Intake among Adult Women in Seoul · Kyunggi Area - Based on 2011 KNHANES -
Jae Ok Koo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 269. CrossRef
- Genetic Variations in Thiamin Transferase SLC35F3 and the Risk of Hypertension in Koreans
- 1,338 View
- 1 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrition Education for Hypertension Patients Aged 50 Years and Over
- Eun Hye Moon, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(1):62-74. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.1.62
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to implement and evaluate a nutrition education program for hypertensive patients aged between 50 and over. Nutrition education consisted of four sessions and, 35 out of 51 patients completed all education sessions at the public health center. To assess program effectiveness (effectively), data about blood pressure, blood cholesterol, anthropometry, nutrition knowledge, eating behavior and dietary intake were collected before and after nutrition education. Data were analyzed using SAS package (ver. 9.2) and significant difference was evaluated by paired t-test, x2-test and Wilcoxon signed rank test. Blood cholesterol was significantly reduced from 200.7 mg/dL to 188.7 mg/dL after nutrition education, although there were not significant changes in blood pressure or blood triglyceride level. Weight (p < 0.05), % body fat (p < 0.001), BMI (p < 0.05) were significantly reduced, especially in women, after nutrition education. Nutrition knowledge was increased significantly (p < 0.05), and some eating behaviors such as 'having fruits & vegetables for snack' and 'having brown rice, barley rice than white rice' were improved after nutrition education (p < 0.05). Sodium intake was reduced from 3,888.9 mg/day to 3,157.4 mg/day after nutrition education (p < 0.05). Except protein and iron intakes, the nutrient intake of hypertensive patients was much below the recommended level for Koreans. Dietary intakes of most of nutrients were not significantly different between pre-test and post-test. It appeared that nutrition education for the aged hypertensive patients was effective in reducing the percentage of % body fat and BMI, increasing the nutrition knowledge and some dietary behaviors. This nutrition education can be implemented at public health centers or senior centers for hypertensive patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pengaruh Pemberian Edukasi Terhadap Pengetahuan Hipertensi Peserta Prolanis Perempuan Di Puskesmas Brambang, Kabupaten Jombang
Finda Istiqomah, Ali Iqbal Tawakal, Chika Dewi Haliman, Dominikus Raditya Atmaka
Media Gizi Kesmas.2022; 11(1): 159. CrossRef - Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Effects of nutrition education on cardio-metabolic outcomes: A randomised clinical trial
Hildemar Dos Santos, W Lawrence Beeson, Gina Segovia-Siapco, Brenda Koranda, Tony Jehi
Health Education Journal.2020; 79(4): 458. CrossRef - Effect of a public health center-based nutrition education program for hypertension in women older than 50 years of age
Seoyun Park, Jong-Sook Kwon, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(3): 228. CrossRef - The Effect of Health Coaching Programs on Self-Efficacy, Health Behaviors, and Quality of Life in Hypertensive People Living in Poverty
Sun Ok Eom, Insook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 380. CrossRef - General Characteristics, Self-Efficacy, and Diet Control of Hypertension Patients at a Diabetes Admission Control Center in the Jeollanma-do Area
Su Jeong Yeo, In Woo Shin, Bok Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(4): 731. CrossRef - Dietary Life related to Sodium of Participants in Hypertension and Diabetes Preventive Education at the Public Health Center
Hee-Ok Pak, Chun-Young Sohn, Jung-Hwa Park
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(2): 219. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Sodium Related Recognition, Dietary Attitude and Education Needs of Dietitians Working at Customized Home Visiting Health Service
Yun-Jeong Mo, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 558. CrossRef - The Effect of the Telemedicine Service System Application for the Patients with Hypertension at Community Health Practitioner Posts in Gangwon Province
Myung Soon Kwon, Ghee-Young Noh, Jounghwa Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(2): 55. CrossRef - The Effects of Low-sodium Diet Education Program on Dietary Habits, Diet Quality and Obesity Index in Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women
Soo Bin Jeong, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Jin Nam Kim, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 513. CrossRef - Development of Nutrition Education Program for Consumers to Reduce Sodium Intake Applying the Social Cognitive Theory: Based on Focus Group Interviews
So-Hyun Ahn, Hye-Kyeong Kim, Kyung Min Kim, Jin-sook Yoon, Jong Sook Kwon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 342. CrossRef - Effects of nutrition education on nutrition-related knowledge, dietary habits, and nutrient intakes of alcoholic patients
An Na Kim, Hyeon-Sook Lim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(4): 277. CrossRef - Effects of Dietary Education on Low-sodium Diet Adaptation
Hae Young Kim, Juhyeon Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(2): 212. CrossRef - An Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Nutrition Counseling for Adults with Risk Factors for Dyslipidemia
Tae Young Nam, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(1): 27. CrossRef - Blood Pressure, Sodium Intake and Dietary Behavior Changes by Session Attendance on Salt Reduction Education Program for Pre-hypertensive Adults in a Public Health Center
Eun-Jin Jung, Jong-Sook Kwon, So-Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(6): 626. CrossRef - Effects of a Comprehensive Lifestyle Improvement Program for Middle-aged Women with Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease-related Risk Factors
Mi-Kyoung Park, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(2): 111. CrossRef - The Effect of Sodium Reduction Education Program of a Public Health Center on the Blood Pressure, Blood Biochemical Profile and Sodium Intake of Hypertensive Adults
Eun Jin Jung, Sook Mee Son, Jong-Sook Kwon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(6): 752. CrossRef - Development of Nutrition Education Program for Hypertension Based on Health Belief Model, Applying Focus Group Interview
Seoyun Park, Jong-Sook Kwon, Cho-il Kim, Yoonna Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(5): 623. CrossRef - Effects of Nutritional Education Practice Program for Cardiocerebrovascular High-risk Group at the Education Information Center
Hang Me Nam, Seung Hee Woo, Young Ji Cho, Yun Jung Choi, Su Yeon Back, So Yeon Yoon, Jin Young Lee, Jung-Jeung Lee, Hye Jin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(5): 580. CrossRef
- Pengaruh Pemberian Edukasi Terhadap Pengetahuan Hipertensi Peserta Prolanis Perempuan Di Puskesmas Brambang, Kabupaten Jombang
- 1,441 View
- 5 Download
- 20 Crossref

- [English]
- Clients' Handling and Consumption of Home-delivered Meals at Home and Their Perceptions on Home-Delivered Meal Services for Older Adults
- Jung Yeon Park, Kyung Eun Lee, Na Young Yi, Tong Kyung Kwak
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(3):379-392. Published online June 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purposes of this study were to investigate recipients' handling and consumption of home-delivered meals at home and to assess their perceptions on home-delivered meal services for older adults. A total of 312 elderly people who received home-delivered foodservice were surveyed using an individual interview technique. A statistical data analysis was completed using SPSS (ver. 14.0). It was found that 90.2% (n = 166) of the lunch box recipients received services for six days per week, and 76.6% (n = 95) of the side-dish recipients got services once per week. More than half of the clients reported that they cooked meals by themselves on days when meals were not delivered. The two hundred thirty-two (75.3%) ate their meals as soon as they were delivered. It was found that 66.8% of the lunch box recipients and 7.3% of the side-dish recipients left delivered meals on the counter (at room temperatures) before eating. Only 11.4% of the lunch box recipients and 48.4% of the side-dish recipients kept delivered meals in the refrigerator before eating. Less than half of the lunch box recipients consumed all foods they were served at once. The reasons the recipients did not eat their all meals delivered at once were "saving for next meals" and "big portion size". Of those clients who left delivered meals, 19% of the lunch box recipients and 9.7% of the side-dish recipients ate leftovers without reheating. An average score of quality of delivered meal services was 3.5 out of 5 points. The results suggest that the clients of the home-delivered meal service should be provided information on proper handling and consumption practices with delivered meals at home. The findings of the study will be used to develop nutrition and food safety management guidelines for senior foodservice.
- 340 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- A Survey on the Breakfast Skipping Rate of Korean Adults Relative to Their Lifestyle and Breakfast Skipping Reasons and Dietary Behavior of Breakfast Skippers
- Sunju Yun, Hye Ryeon Jeong, Mi Hyun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(2):191-205. Published online April 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the rates and reasons for breakfast skipping according to gender, age, and lifestyle related factors in Korean adults. The survey was conducted using questionnaires and the subjects included 1148 male and female adults aged 19-64. The rate of breakfast skipping (frequency of eating breakfast under 4 times/week) was 41.20% of the total subjects. The breakfast skipping rate of the male subjects was significantly higher than that of the female subjects (p < 0.001). As age and household income decreased, the breakfast skipping rate increased. Residents in small cities more frequently skipped breakfast than those in larger cities. The main reason for breakfast skipping was "lack of time for the preparation and consumption of food" and this reason was especially higher for office workers and younger adults among the participants. In addition, the proportion of habitual breakfast skippers increased with age. Among the answers regarding the person who prepares breakfast in their households, the highest proportion was for "family members" in the males and "myself" for the females. Of breakfast skippers, 77.63% answered that they consumed breakfast substitutes such as breads, dairy and fruits/vegetables. To summarize the results, the gender, age and lifestyle factors of adults were significantly related to the rates and reasons for breakfast skipping. Therefore, to reduce breakfast skipping in Korean adults, a differentiated nutritional education approach relative to gender, age, and lifestyle is needed along with the development of balanced breakfast substitutes.
- 683 View
- 16 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrition Education for Diabetes Mellitus Management of Older Adults
- Hyun Joo Kang, Eun Mi Shin, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):734-745. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diabetes mellitus is the prevalent disease among older adults. The purpose of this study was to implement and evaluate the nutrition education program for diabetes mellitus patients aged 60 and over. The one group pretest and posttest design was employed to evaluate the program effectiveness. Nutrition education program for diabetes mellitus patients was carried out at the public healthy center in Guri city. The 38 out of 63 patients completed education program. They received four sessions of group education during four weeks. Nutrition education materials (booklet, leaflet) for older adults were provided to participants. Data about blood glucose, blood pressure, nutrition and diabetes mellitus knowledge, dietary behavior, dietary intake by 24-hour recalls were collected before and after nutrition education to evaluate the program effectiveness. All data were statistically analyzed using SAS package (ver.8.2) and significant difference was evaluated by chi-square-test, paired t-test and Wilcoxon signed rank test. Study results showed that blood pressure and blood glucose were slightly decreased after nutrition education but they did not reach statistical significance. There were positive changes in nutrition knowledge and dietary behavior. The total score of nutrition and diabetes knowledge increased significantly (p < 0.001), and the total score of dietary behavior was improved (p < 0.05) after nutrition education. Dietary intakes of most of nutrients examined were not significantly different between preand post-test. Based on study results, it appears that nutrition education program for the aged diabetes mellitus patients might effectively increase nutrition knowledge, dietary behavior and diet quality. This nutrition education program can be used at the public health centers or senior centers for the management of diabetes mellitus for older adults.
- 410 View
- 14 Download

- [English]
- Effects of Frequent Eating-out and Breakfast Skipping on Body Mass Index and Nutrients Intake of Working Male Adults: Analysis of 2001 Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey Data
- Joung Won Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):789-797. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to investigate the effects of frequent eating-out and breakfast skipping of working men on body mass index and nutrients intake status, working male adults aged 20 or over were selected (n = 1883) from the data of 2001 Korea national health and nutrition survey. The subjects were divided into 4 groups according to the eating-out frequency(high: once or more daily, low: less than once daily) and breakfast eating or not. Four groups were high eating-out with breakfast eating (n = 609), high eating-out with breakfast skipping (n = 192), low eating-out with breakfast eating (n = 877), and low eatingout with breakfast skipping (n = 205). High eating-out group showed higher body mass index (BMI) than low eating-out group, but the difference of BMI was disappeared when adjusted with age, residence region and family income. However high eating-out group in case of breakfast eating, compared with the low eating-out, showed higher intakes or densities of energy, fat, fat-energy% and higher ratio of energy-fat overintake, and also showed higher mean nutritional adequacy ratio and lower ratio of nutrients intake deficiency. Calcium, iron, vitamin A and C intakes were not affected by eating-out frequency, but were lowered by breakfast skipping. Breakfast skipping also decreased intake frequency of unprocessed cereals and increased those of ramyon and carbonated and alcoholic beverages. From the results frequent eating-out with breakfast eating caused increased intakes of energy and fat, but did not cause BMI increase. Breakfast skipping, but not eating-out, had negative influences on mineral and vitamin intakes. Accordingly good eating-out as well as breakfast eating should be exceedingly emphasized at nutrition education for the working males.
- 357 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- A Study on Blood Lipids and Blood Pressure of Adult Men and Women According to Vegetable Intake
- Mi Kyeong Choi, Yun Jung Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(6):761-772. Published online December 31, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It has been suggested that vegetables protect the cardiovascular system in part by attenuating blood pressure. The purpose of the present research was to examine blood lipids according to vegetable intakes. Anthropometric measurements, blood pressures, nutrient intakes using the 24-hour recall method, and serum lipids of < 50th percentile vegetable intake group (< 50th percentile VIG; men = 66, women = 111) and > or = 50th percentile vegetable intake group (> or = 50th percentile VIG; men = 83, women = 94) were estimated. The average age, height, and BMI were 54.7 years, 158.2 cm, 62.2 kg, and 24.9 kg/m2 for < 50th percentile VIG and 53.7 years, 159.6 cm, 63.0 kg, and 24.7 kg/m2 for > or =50th percentile VIG, respectively. The daily food intake of the > or = 50th percentile VIG was significantly higher than that of the < 50th percentile VIG (p < 0.001). Also, daily intakes of cereals (p < 0.001), legumes (p < 0.05), nuts (p < 0.05), vegetables (p < 0.001), and fruits (p < 0.05) of the > or = 50th percentile VIG were significantly higher than those of the < 50th percentile VIG. The daily energy intakes of > or = 50th percentile VIG and< 50th percentile VIG were 1342.7 kcal and 1782.0 kcal (p < 0.001), and most nutrient intakes of the > or = 50th percentile VIG was significantly higher than that of the < 50th percentile VIG. Serum cholesterol of the > or = 50th percentile VIG were significantly lower than that of the < 50th percentile VIG (p < 0.01). Also, vegetable intake showed significantly negative correlations with total cholesterol (p < 0.05) and LDL-cholesterol (p < 0.05). Based on these results, it should be emphasized that increase of vegetable intake improves the blood lipid profile.
- 359 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Nutritional Environment Influences Hypertension in the Middle-aged Korean Adults: based on 1998 & 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Hae Jeung Lee, Haeng Shin Lee, Yoonna Lee, Young Ai Jang, Jae Jin Moon, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(3):272-283. Published online June 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to delineate the relationship between lifestyle and nutritional risk factors associated with hypertension in representative middle-aged Korean population. Hypertension in this study is defined as hypertensive (SBP> or = 140 mmHg or DBP> or = 90 mmHg) adults without recognition of a disease state before a health exam. With data from the 1998 and 2001 National Health and Nutritional Survey, nutrient intakes of 6,112 adults, 40-64 years of age were calculated using food composition database and matched with health examination records by individual ID. After excluding those with extreme intake values, the number of final subjects included in the analysis was 5,200 (male 2,458, female 2,742). Using logistic regression method, socio-demographic data, lifestyle factors, and nutrient intakes were analyzed. Risky factors for hypertension revealed in this study were age, sex, BMI over 23, waist circumference, alcohol intake of more than 16 g (male) or 8 g (female). Regarding nutrient intakes, the intakes of highest quartile for energy (> or = 2363.0 kcal) and protein (> or = 90.2 g) were significantly associated with higher risk of hypertension after adjusting for age, sex, and other socio-demographic factors (OR = 1.312 (1.046-1.711), OR = 1.488(1.194-1.854), respectively)). Although high intakes of sodium (> or = 6604.0 mg) and phosphorus seemed to be risk factors of hypertension also before energy adjustment (OR = 1.278(1.034-1.581), OR = 1.280(1.024 -1.600), respectively), only high intakes of energy and protein remained significant after adjustment. This study revealed that modifying risky lifestyles and dietary patterns, especially high energy intake, high protein intake, and high alcohol drinking, in middle-aged Korean adults could result in a prevalence decrease and/or prevention of hypertension.
- 336 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Development of Nutrition Education Materials for Healthy Aging
- Yun Ahn, Kyung A Kim, Hyunjoo Kang, Kyungwon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(6):740-749. Published online December 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to develop nutrition education materials for older adults, 'nutritional management for healthy aging'. A booklet and four leaflets were developed based on lesson plans. Topics of the lesson plans included eating habit assessment, Korean food guide pyramid, meal planning, eating sensibly and weight management. The titles of the leaflets were 'Eating right for healthy aging', 'Eat calcium-rich foods', 'Enjoy fruits & vegetables' and 'Weight management'. Illustrations and icons appropriate to the texts were designed using Illustrator 9.0 and Photoshop 6.0. Booklet (letter size, 5 chapters, 44 pages) and leaflets (B4 size, 6 sections) focused on modifying undesirable eating habits, providing practical tips for desirable behaviors, and behavioral modification such as recording in a food diary, goal setting and increasing self-efficacy. The drafts were pilot-tested by interviews with older adults(n=10), and minor changes were made. The characteristics of revised materials are as follows; i) materials focused on providing desirable eating behaviors for healthy aging, ii) messages were simple and specific, iii) large fonts(13 pt) were used and materials included interesting pictures and illustrations, iv) materials provided tips for balanced diets and recipes for older adults, v) materials included sections for participation of learners including assessment of nutritional risk factors and obesity, meal planning and games. The revised materials are self-explanatory and can be used by older adults and in nutrition education for older adults.
- 355 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Perception of Foodservice Quality Attributes of Older Adults: Compared by Lifestyle and Dining Frequency in Continuing Care Retirement Communities
- Sunhee Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(2):261-270. Published online April 30, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to identify the differences of older adults' perceptions of foodservice quality attributes of current offerings in Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRCs) in terms of their lifestyles (length of residency, special diet, housing option, travel frequency, dine out frequency), dining frequency, and demographics in the dining room of CCRCs. The survey was administered to residents in three CCRCs. Data was analyzed for 140 surveys using t-test, ANOVA, and factor analysis. This study found female older adults perceived the following attributes were more important than male ones: presentation of food, color and garnish, texture of vegetables, taste and flavor of food, and respectful attitude of serving staff. Older adults who have a special diet perceived the seasoning and bite sized pieces were more important than those who have a general diet. Also, there were significant differences between frequent visitors and occasional visitors in the dining room of CCRCs. By knowing the differences by residents' demographics and residential characteristics, the foodservice manager can establish strategies to increase the dining frequency of residents in the dining rooms of CCRCs.
- 343 View
- 0 Download

Clinical Trial
- [English]
- A Study on Relation among Habitual Isoflavone Intake, Blood Pressure, and Serum Lipid Parameters in Korean Men and Women over 20 Years Old
- Mi Kyeong Choi, Mi Hyun Kim, Chung Ja Sung, Won Young Lee, Jung Duck Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(4):493-500. Published online August 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There is some evidence that soy isoflavone has beneficial effects on the concentration of blood lipids. In this study, we investigated habitual isoflavone intake levels and the relation among dietary isoflavone intake, blood pressure, and blood lipids of adult men (n = 149) and women (n = 205). Anthropometric measurements including blood pressure, dietary intake assessment using 24-hour recall method, and biochemical assessment using blood were conducted. The average age, height, weight, and BMI were 54.7 years, 168.5 cm, 67.3 kg, and 24.5 kg/m2 for men and 53.9 years, 153.8 cm, 59.2 kg, and 25.0 kg/m2 for women, respectively. The mean daily intakes of total food and energy were 1219.1 g and 1740.9 kcal for men and 1071.3 g and 1432.6 kcal for women, respectively. The mean daily isoflavones (daidzein + genistein) intake of men and women were 20.0 mg and 14.2 mg, respectively. Blood pressure of the subjects was 128.3/75.5 mmHg for men and 124.1/73.7 mmHg for women. Serum lipids of men and women were 180.2 and 184.9 mg/dL for total cholesterol, 160.8 and 137.6 mg/dL for triglyceride, 41.5 and 44.7 mg/dL for HDL-cholesterol, 106.6 and 112.7 mg/dL for LDL-cholesterol, and 3.5 and 3.3 for atherogenic index, respectively. Serum triglyceride and atherogenic index of men were significantly higher than those of women. In men, isoflavone intake and the level of total serum cholesterol were negatively (p < 0.05) correlated, after adjusted age. In women, there were significant correlations between isoflavone intake and blood pressure (systolic and diastolic), after adjusted age (p < 0.05). Based on these results, we concluded that higher isoflavone intake seemed to be related to a better lipid profile in men and lower blood pressure in women. But more epidemiological studies and controlled clinical trials would help to confirm the optimal amount required for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease.
- 358 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- Food Habits and Health Food Consumption Patterns of Adults in the Ulsan Area
- Soo Yoen You, Hye Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(6):889-900. Published online December 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to obtain information regarding eating habits, including health related behavior and health food consumption patterns. The subjects of this study were 149 men and 152 women residing in the Ulsan area. We obtained results by means of a questionnaire and an interview, and these were analyzed using the SPSS package program. The results of this study are summarized as follows : The average age of the men was 47.6 +/- 7.3 years and of the women was 47.3 +/- 7.6 years old. The average height and weight of the men were 169.4 +/- 5.5 cm and 67.7 +/- 8.2 kg, respectively. Those of the women were 157.6 +/- 5.0 cm and 58.2 +/- 7.5 kg, respectively. The BMI values of all the subjects ranged from 20.0 to 25.0, all within the normal levels. In the case of dietary patterns, 24.3% of the total population always skipped a meal. In particular, 15.9% of the total population skipped breakfast. No time to eat, no appetite, having no taste, and having poor health were themain reasons for skipping meals. With regard tohealth care, there was a significant difference between the men and the women with respect to smoking and drinking (p < 0.001). Of the total population, 40.5% hardly exercised (less than once a week), 26.2% exercised occasionally, 13.6% frequently exercised, and 19.6% exercised almost every day. A total of 60.7% responded that they were not interested in their health. The mean eating habit score of the subjects was 65.6 +/- 9.9. The women had a higher eating habit score than the men (64.0 +/- 9.6 for the men and 67.2 +/- 9.9 for the women). Except for one group above 60 years, the older group had a higher eating habit score than the younger one. The group having a higher income and a more specialized career had a higher eating habit score than the one having a lower income and a less specialized career. There was also a marital difference. The group of single subjects showed a lower eating habit score than the married group. The group having a higher eating habit score drank, smoked and went out for meals less, and exercised more than the group having lower scores. They also were more concerned about their health. In the older group, there were more diabetic and hypertensive individuals. The subjects who had a higher BMI index were more likely to be patients with hypertension, especially in the men's group. Those who had a higher BMI index and hypertension simultaneously took a variety of medicines and foods for promoting health. Those who worried a lot about their health and had health problems tended to take special foods for their health. Patients usually took tonics. Special foods for health included Chinese medicines, tonic foods, vitamin or mineral supplements and manufactured health food supplements. Preferences for them depended on the sex and age of the subject. In the case of tonic foods, the men liked them more than the women. Foods other than tonic foods were favorites with the women. This study may provide basic information on the eating habits and health related behaviors of middle-aged people. However, further studies are needed to improve the eating habits and to change the nutritional attitudes, so that people can make better choices of health foods.
- 458 View
- 8 Download

- [English]
- Food and Nutrient Consumption Patterns of Korean Adults Based on their Levels of Self Reported Stress
- Young Ok Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(3):340-348. Published online June 30, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Differences in food and nutrient intake among Korean adults based on different stress levels were investigated using information obtained from 7,370 adults who participated in the 1998 Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey. The twenty-four hour recall method was used for this dietary survey. Data pertaining to indivisual stress levels were collected by means of interviews as part of the National Health Behavior Survey. Following the analysis of variance, Duncan's Multiple Range Test was used to test the differences in food and nutrient intake among groups with different levels of stress. Eighty-three percent of the study subjects were reported to have a certain level of stress. Unlike the observations made in European and American studies, there were no significant differences observed in food and nutrient intake based on the stress levels among Korean adults of either sexes. These results may imply that even though stress was clustered with other health related behavior, the association between food intake and stress among Koreans was very weak.
- 351 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Effect of Kimchi Intake on Free Radical Production and the Inhibition of Oxidation in Young Adults and the Elderly People
- Jong Hyen Kim, Jae Du Ryu, Yeong Ok Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(2):257-265. Published online April 30, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to investigate the effect of kimchi intake on free radical and oxidative substance production in young adults and the elderly. Daily kimchi intake by people in their twenties (n = 93, 20 to 29 years old) and over sixty-five (n = 143, over 65 years old) in M city were surveyed and blood was drawn to analyze the free radicals in their plasma. The average amount of kimchi intake by the subjects was 115.8 +/- 91.7 g. The amount of kimchi intake of those in their twenties (106.1 +/- 80.6 g) was significantly lower than that of those over sixty-five (125.5 +/- 102.9 g, p<0.05). Concentrations of total free radicals and OH radicals were 27 and 33% greater respectively, in those over sixty-five than in those in their twenties, indicating that more free radicals were produced by the older group. The concentration of GSH was not signiacantly different in the two groups, but that of GSSG in the over sixty-five age group was 53% greater than in the twenties group, which resulted in a 35% reduction in GSH/GSSG in the elderly group. TBARS concentration in the over sixty-five group was 26% greater than that of the twenties group. In order to see the effect of kimchi intake on free radical production, subjects in same age group were divided into two sub groups-the mean over and the mean under groups-according to the average amount of kimchi intake, which was 115.8 g. The total free radicals, the OH radicals, the GSH, the GSSG, and the GSH/GSSG in the twenties group were not significantly different in the two kimchi intake groups. However, those in the over sixty-five group were significantly different. The concentration of total free radicals and OH radicals of the mean over group were 21 and 26% lower respectively, than those of the mean ova. group (p<0.05). The GSH and GSH/GSSG of the mean ova. groups were higher by 8 and 12%, respectively. The correlation coefficient between the kimchi intake and the total free radicals was -0.1862 (p<0.05) and that for GSH/GSSG was 0.1861 (p<0.05). In conclusion, the production of free radicals and oxidative substances increased with age, and kimchi seemed to retard this phenomena.
- 384 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Consumption Pattern of Health Food by Adults in Taejon
- Nan Sook Koo, Ji Yeun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2000;5(3):452-460. Published online September 30, 2000
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Aspects of health food intake were investigated by conducting a questionnaire survey with over 480 of adults in Taejon and the data were analyzed by chi2-test, t-test and ANOVA, using an SAS program. Eighty two percent of the subjects had taken some kind of health food. The health foods they took frequently were, for example, health drinks, green tea, ginseng products, dietary fiber drinks, honey, general tea, vitamin B, vitamin C, and tonic medicines. The main reason for taking health foods was recovery from fatigue and the frequency of taking health foods was one time per day. Most of the subjects took health foods without knowledge of their components or effects. When they health foods with a perceived knowledge of their components and effects, they responded that the health foods were very helpful for them. Twenty percent of subjects experienced side effects, such as diarrhea, stomachache, headache, nettle rash, and stomach cramps. Information on health foods was obtained mainly from friends or family. The user group showed higher intention to continue health food intake than non users(p<0.001). Health foods were taken without any knowledge about them. Health food intake was significantly correlated with consideration of disease, suffering or disease, medical examination, and self-perceived health status, but not with food habits and health food knowledge. As for the results from the adults consumption pattern of health food, an education program should be developed to choose proper health foods according to the consumers dietary life and health conditions. Also a proper guide line should be established to be chosen the authorized health foods.
- 295 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



