Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):441-456. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to clarify parental perceptions of dietary and nutritional education provided to young children, identify parental support needs, and suggest directions for improvement.
Methods
A mixed-method sequential explanatory design was followed. Quantitative data were collected through an online survey conducted nationwide that included 200 parents of children aged three to six years in South Korea. Qualitative data were subsequently obtained through focus group interviews with fifteen parents to explore their contextual insights and experiences.
Results
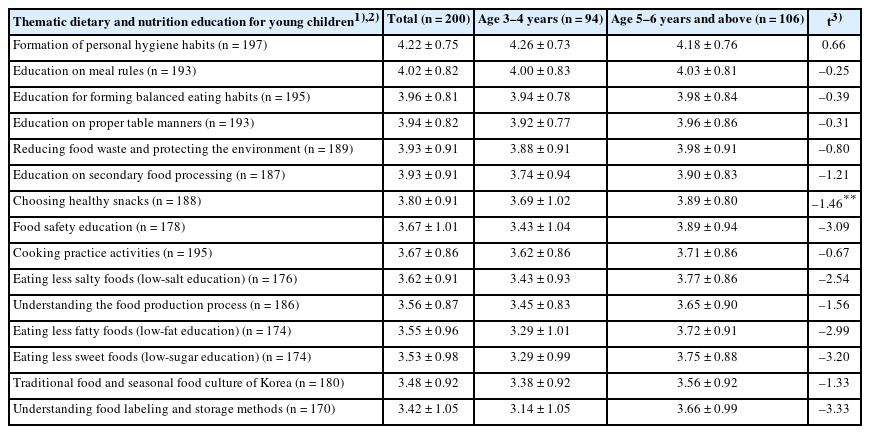
Needs ratings prioritized expanding activity-based/experiential education (3.65 ± 0.88), followed by strengthening home-school communication and connectivity (3.59 ± 0.84), diversifying topics and content (3.55 ± 0.88), and increasing instructional time (3.39 ± 0.94). Integrated with the focus group interview findings, multilevel barriers were revealed—individual level: strong preferences of children for sweet/processed foods; interpersonal level: strong parental modeling and peer effects counterbalancing limited teacher expertise/time; organizational level: insufficient effective event-based experiential activities, and resource gaps across institutions; community/policy level: infrequent external support, uneven access to local resources, lack of standardized guidance, and limited opportunities for parental participation. Parents favored short, interactive digital content and expressed concerns about overexposure. These convergent findings indicate needs to 1) formalize and extend experiential programs within the regular curriculum, 2) provide standardized guidelines and home resource kits, and 3) institutionalize parental involvement.
Conclusion
These findings reveal that dietary and nutritional education for young children should move beyond fragmented, event-based programs toward an integrated three-tiered model incorporating (1) a structured, experiential curriculum, (2) home-linked educational packages, and (3) safe and interactive digital content. Establishing standardized guidelines, enhancing educational infrastructure, and institutionalizing parental participation are essential for sustainable improvement of early childhood dietary education.
- 481 View
- 38 Download

Educational Material
- [Korean]
- Development and evaluation of play-based food and nutrition education materials for early childhood through sensory experiences: a pre-post observational study
- Hyunjoo Ryou, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):471-483. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00276

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop play-based nutrition education (PBNE) materials for young children and to evaluate their applicability and effectiveness.
Methods
An online survey of 1,253 primary caregivers of preschool children was conducted, and the findings were used to develop age-specific utilization guides, slides, activity sheets, activity cards, posters, educational videos, and parent newsletters. Selected materials were implemented in child-care centers through the Children’s Foodservice Management Centers between October and November 2023. The effectiveness of the PBNE program was assessed by examining changes in mushroom consumption as well as food awareness and preferences, before and after the intervention.
Results
A total of eight media formats and 320 educational contents were developed, and mushrooms were as the pilot theme among the 12 possible food items. Following the intervention, children’s positive awareness of mushrooms increased, and > 96% of participants attempted to consume them. Teachers in child-care centers rated the appropriateness and applicability of the content, its contribution to behavioral improvement, and their overall satisfaction at > 4.9 out of 5 points.
Conclusion
This study developed experiential, PBNE materials aligned with the national standard child- and play-centered curriculum. The materials were effective in enhancing food awareness and promoting attempts at consumption. Future efforts should focus on developing additional experiential teaching tools that incorporate teacher feedback and on strengthening home-linked programs to support healthy seasonal food intake and positive dietary experiences in young children.
- 444 View
- 17 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
- Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):431-440. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00234

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this qualitative study was to explore and understand the behaviors and challenges of self-nutrition management from the perspective of elderly.
Methods
In May 2025, ten elderly aged 65–83 years with prior experience using digital devices were recruited through purposeful sampling. Data were collected via focus group interviews using a semi-structured questionnaire until saturation was reached, and all interviews were recorded, transcribed, and analyzed using traditional content analysis methods. The collected interview data were extracted focusing on phrases or sentences relevant to the research purpose, and various concepts derived through memo writing and the constant comparison were categorized based on common meanings. Subsequently, the categorized statements were deeply interpreted and reclassified into subcategories for final analysis.
Results
Under the overarching theme of development directions for a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly, three main categories and 13 subcategories were derived. The three main categories include: (1) processes of acceptance and utilization of digital technologies; (2) potential for applying digital self-nutrition management; and (3) strategies for implementing digital-based nutrition education.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that elderly face barriers to utilizing digital tools for self-nutrition management not only due to physical or technical limitations, but also because of the confusion arising from limited nutrition knowledge and information overload. To overcome the barriers that may arise during the digital-based education process for elderly, strategies (educational topics, delivery strategies, and operational strategies) were derived to vitalize a digital self-nutrition management education program. These results highlight the necessity of developing tailored digital nutrition education programs that reflect the characteristics of elderly, which may enhance their practical applicability and provide foundational evidence for establishing a digital–nutrition integrated care model within the senior customized care service.
- 543 View
- 50 Download

- [Korean]
- A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Kyoung-Min Lee, Woo-jeong Kim, So-young Kim, Young-mi Park, Hwa-young Yoon, Min-Sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):376-388. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
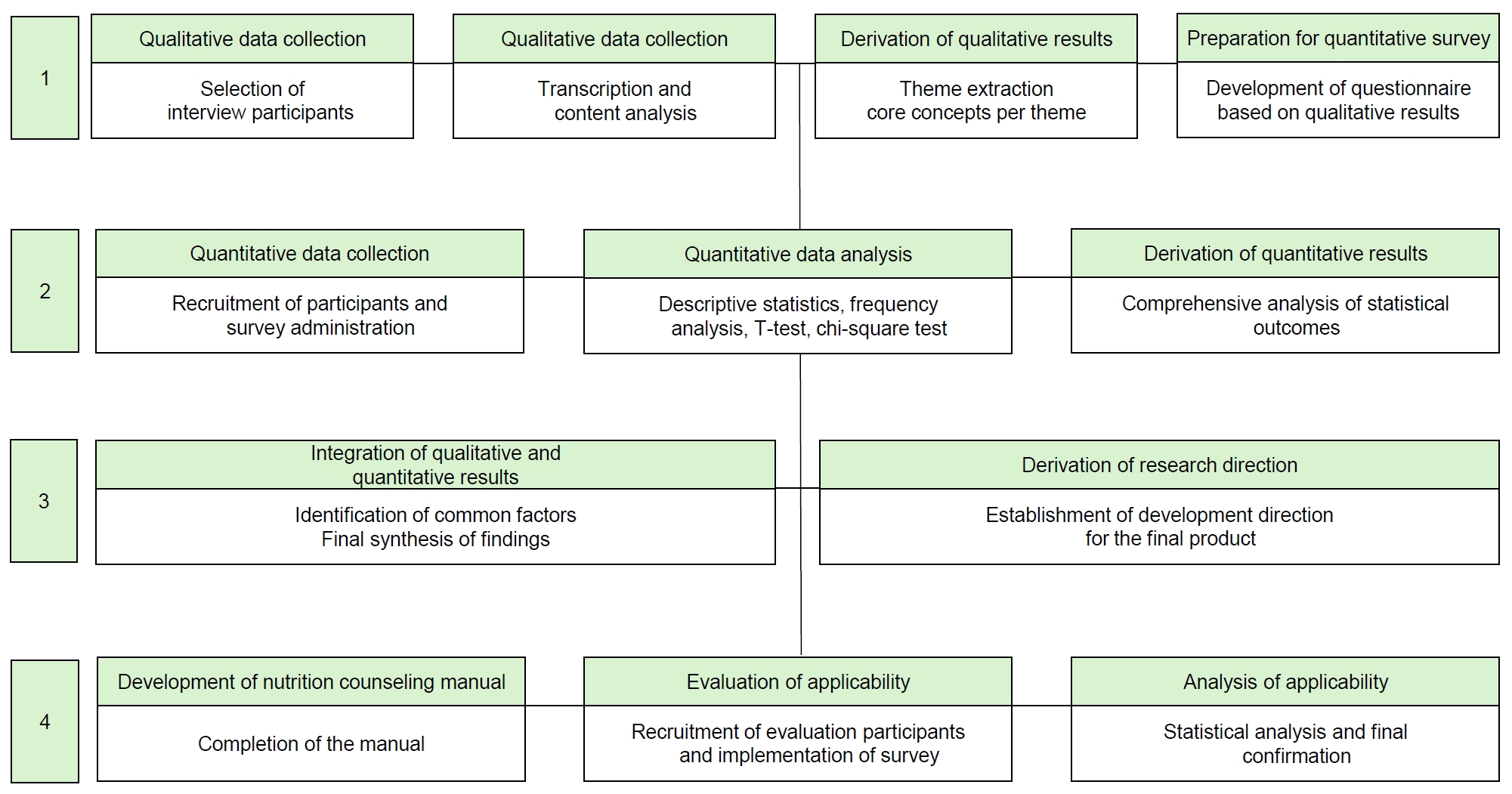
Individuals with disabilities require targeted interventions to ameliorate disability-related conditions and improve overall health status. Nutritional challenges and counseling needs vary according to the type of disability, necessitating comprehensive assessments of dietary habits, physical activity, and food intake. Compared to traditional education, nutrition counseling offers a more sustainable and environmentally adaptable approach that effectively addresses individualized nutritional issues. Therefore, this study aimed to develop and evaluate a practical nutrition counseling manual and meal guidelines for people with disabilities in Korea, addressing their diverse dietary needs and improving nutritional care in social welfare facilities.
Methods
A four-stage integrated research design was employed. Stage 1 involved qualitative research through in-depth interviews with 11 facility staff. In Stage 2, a nationwide survey (n = 249) was conducted based on the results of the interviews. Stage 3 integrated both qualitative and quantitative findings. Stage 4 focused on developing and evaluating a nutrition counseling manual and five types of meal guidelines through feedback from 26 nutritionists at 24 Korean Centers for Social Welfare Foodservice Management.
Results
Six major nutrition counseling topics were identified: healthy eating, managing salt and sugar intake, dysphagia diet, appropriate intake, and hygiene. The manual and guidelines demonstrated high field usability, with average satisfaction scores of 3.98 and 3.99, respectively.
Conclusion
The integrated study resulted in the development of a specialized nutrition counseling manual and handbook for individuals with disabilities in Korean social welfare facilities. The materials were revised and improved based on practical evaluations by dietitians, enhancing their field applicability. These tools are expected to contribute to better dietary management and health promotion among facility residents. The developed materials reflect the real-world needs of people with disabilities and offer practical tools for effective nutrition counseling and dietary management in institutional settings.
- 533 View
- 25 Download

Research Note
- [English]
- Pilot evaluation of a cooking-based nutrition education program to promote vegetable intake among children in Seoul, South Korea: a single-group pre–post study
- Sil-Ah Kim, Su-Jin Lee, Min-Ah Kim, Ji-Eun Oh, Sohyun Park, Hyun-Joo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):249-260. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00220

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Food neophobia in children is often associated with limited exposure and familiarity to some foods. Cooking-based nutrition education (CBNE), which promotes acceptance through direct experience, may support the development of healthy eating habits. This study aimed to develop and implement a standardized CBNE program for school-aged children in Seoul, South Korea, and to evaluate its effectiveness by assessing changes in raw vegetable intake. Raw vegetable intake is an early indicator of the effectiveness of nutrition education on diverse topics in promoting healthy eating habits.
Methods
A single-group pre–post study was conducted with 37 children aged 6–11 years who participated in a 2-day CBNE program in October 2023. The participants completed pre- and post-education questionnaires and raw vegetable intake assessments. Four low-preference vegetables (bell pepper, carrot, cucumber, and tomato) were selected and served raw (25 g each) before and after the program. Intake changes were analyzed using paired t-tests, and Pearson’s correlation and hierarchical regression analyses were performed to identify predictors.
Results
Total raw vegetable intake significantly increased post-education (P = 0.008), particularly for carrots (P = 0.023). By subgroup, raw vegetable intake significantly increased in girls, upper-grade students, and those who consumed four or more vegetable side dishes per meal. Hierarchical regression analysis revealed that while vegetable preference was initially significant, vegetable-related experiences (β = 0.395, P = 0.026) and diversity of vegetable side dishes per meal (β = 0.403, P = 0.032) were stronger predictors in the final model (adj R2 = 0.333).
Conclusion
The CBNE program may enhance vegetable intake in children. Although preference remained the strongest individual factor, vegetable experience and the diversity of vegetable side dishes per meal had a greater combined effect. These findings underscore the importance of repeated and diverse exposure, not only by supporting previous studies that link such exposure to increased intake but also by suggesting that environmental support may be essential for sustaining healthy eating habits.
- 2,071 View
- 61 Download

Research Article
- [English]
- Safety education status and needs priorities of Korean military food service personnel using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model: a cross-sectional study
- Jeongeun Park, Eunsil Her
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):261-273. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00185

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Since the enactment of the Serious Accidents Punishment Act in Korea in 2021, the importance of safety management in food service facilities has increased. This study was conducted to examine the status of safety education and to identify educational needs for safety accident prevention among army food service personnel.
Methods
This study included 157 food service personnel from Army units located in Gyeongsangnam-do. Participants were divided into two groups based on the daily number of meals served. Demographic characteristics, the status of safety education, and priority for safety accident prevention education were evaluated.
Results
A total of 97.5% of participants received safety education, with 60.8% attending at least monthly. “Lecture” (63.4%) was the most commonly used educational method. The preferred educational methods were “Lecture” (23.5%) and “Counselling” (23.5%), showing significant group differences (P < 0.001). A total of 79.6% of participants reported applying the educational content in their performance. The mean importance score for safety accident prevention (4.78) was higher than the performance score (4.44), with significant differences between the two groups observed in the importance scores (P < 0.05). “Slip & burn” had the highest importance score, while “Electric shock and fire” had the highest performance score. The educational needs analysis revealed that the highest priority item for the < 100 meals group was “When moving heavy items, an assistive device or assistance from colleagues should be utilized”, while for the ≥ 100 meals group, it was “When using a vegetable cutter or grinder, use an exclusive stick.”
Conclusion
This study can serve as a foundational database for developing customized safety education programs tailored to Korean army food service personnel.
- 2,650 View
- 24 Download

Review
- [Korean]
- Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
- Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):175-182. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00094
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
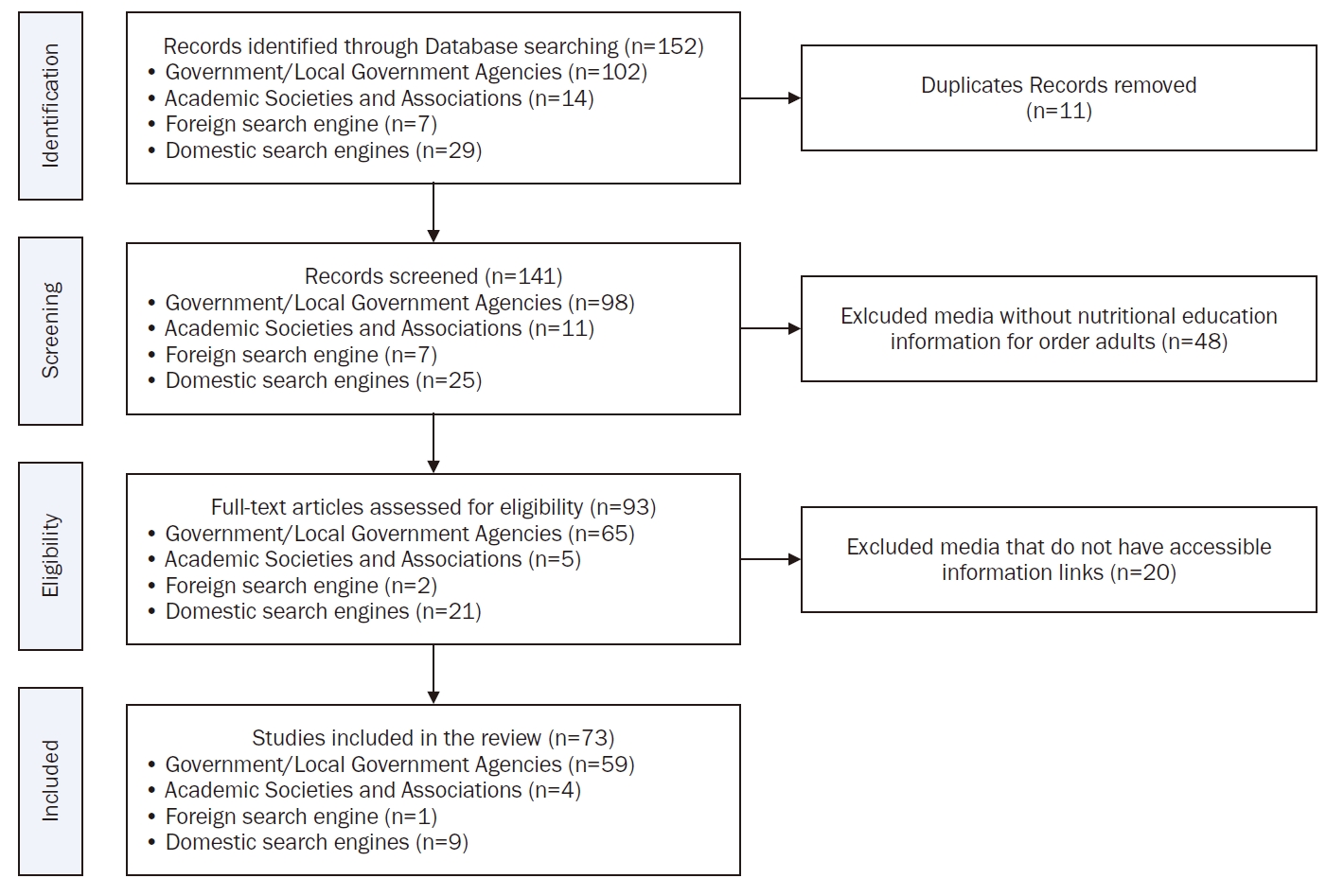
This study analyzes the status of nutrition education media among Korean older adults based on the transtheoretical model (TTM) and their food literacy to propose effective strategies for the development and utilization of educational media.
Methods
A literature review was conducted using The Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) protocol. The literature search was performed using government and local government agency websites, as well as those of affiliated institutions, health and nutrition-related academic societies, and academic search engines. A total of 144 studies were identified, and after a cross-evaluation by two reviewers based on the literature selection criteria, 73 studies were included in the final analysis.
Results
Among the types of nutrition education media, card news had the highest proportion, followed by video media. The development and distribution of nutrition education media for older adults were primarily carried out by government and local government agencies, as well as related affiliated institutions, accounting for 80.8% (n = 59) of the total. When nutrition education topics in the media were categorized according to the stages of behavior change in the TTM, the largest proportion, 64.6% (n = 61), was applicable to the precontemplation and contemplation stages. When categorized by food literacy domains, all topics fell under the categories of nutrition and safety.
Conclusion
Nutrition education media for older adults were found to be primarily focused on knowledge acquisition and information delivery, making them mostly applicable to the precontemplation and contemplation stages of behavior change. The concept of food literacy addressed in the different types of media was limited to the domains of nutrition and safety, with no content covering the cultural and relational domains or the social and ecological domains. For tailored nutrition education, it is necessary to develop diverse educational materials that comprehensively reflect each stage of the TTM and all aspects of food literacy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 431. CrossRef
- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
- 1,919 View
- 93 Download
- 1 Crossref

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Development and applicability evaluation of a nutrition education program for residents and users of disability social welfare facilities in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Jin-kyung Kim, Kyoung-min Lee, Min-sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):64-74. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
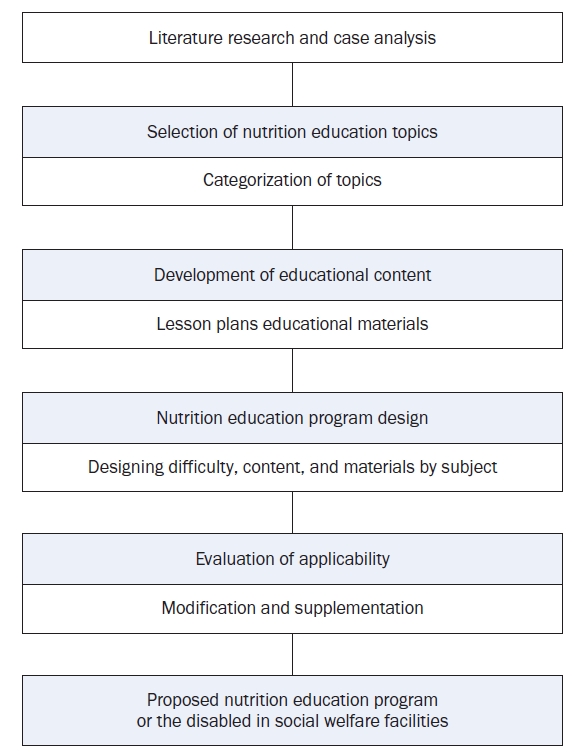
This study aimed to develop a nutrition education program based on social cognitive theory to promote the health of individuals using facilities for people with disabilities. It also sought to evaluate the applicability of the educational materials through assessments by counselors at the Social Welfare Food Service Management Support Center.
Methods
A group of six experts developed the program based on a needs assessment of nutrition education in facilities for individuals with disabilities. Applicability was evaluated through an online survey of 26 counselors from Social Welfare Food Service Management Support Centers nationwide in July 2023, and the results were analyzed.
Results
The nutrition education program includes a basic course on personal hygiene, dining etiquette, picky eating prevention, and obesity management. The advanced course covers dietary management for chronic diseases, such as meal planning for hypertension, diabetes management, and dietary principles for dysphagia. Additionally, lecture PPTs, individual activity sheets, and experiential teaching aids were developed. Applicability evaluations showed high scores, with the teaching-learning plan and PPT averaging 4.15 and the experiential teaching aids scoring 4.17, all above 4.0.
Conclusion
This study developed a nutrition education program for individuals with disabilities and assessed its applicability and usability. Implementing this program in disability welfare institutions could enhance health promotion and improve the quality of life for individuals with disabilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research trends in dietary behaviors and nutrition education among individuals with developmental disabilities in Korea: a scoping review (2015–2025)
Nakyung Kwak, Wonyeong Park, Yu-Ri Kim, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2026; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
Su-Jin Lee, Ji-Won Kang, Sil Ah Kim, Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Hyunjoo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 498. CrossRef
- Research trends in dietary behaviors and nutrition education among individuals with developmental disabilities in Korea: a scoping review (2015–2025)
- 2,887 View
- 82 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Development and application of a dietary program to reduce sugar intake using a living lab approach in Korea: an intervention study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, Seul Ki Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):504-513. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop and apply a dietary program to reduce sugar intake among community residents using a Living Lab approach.
Methods
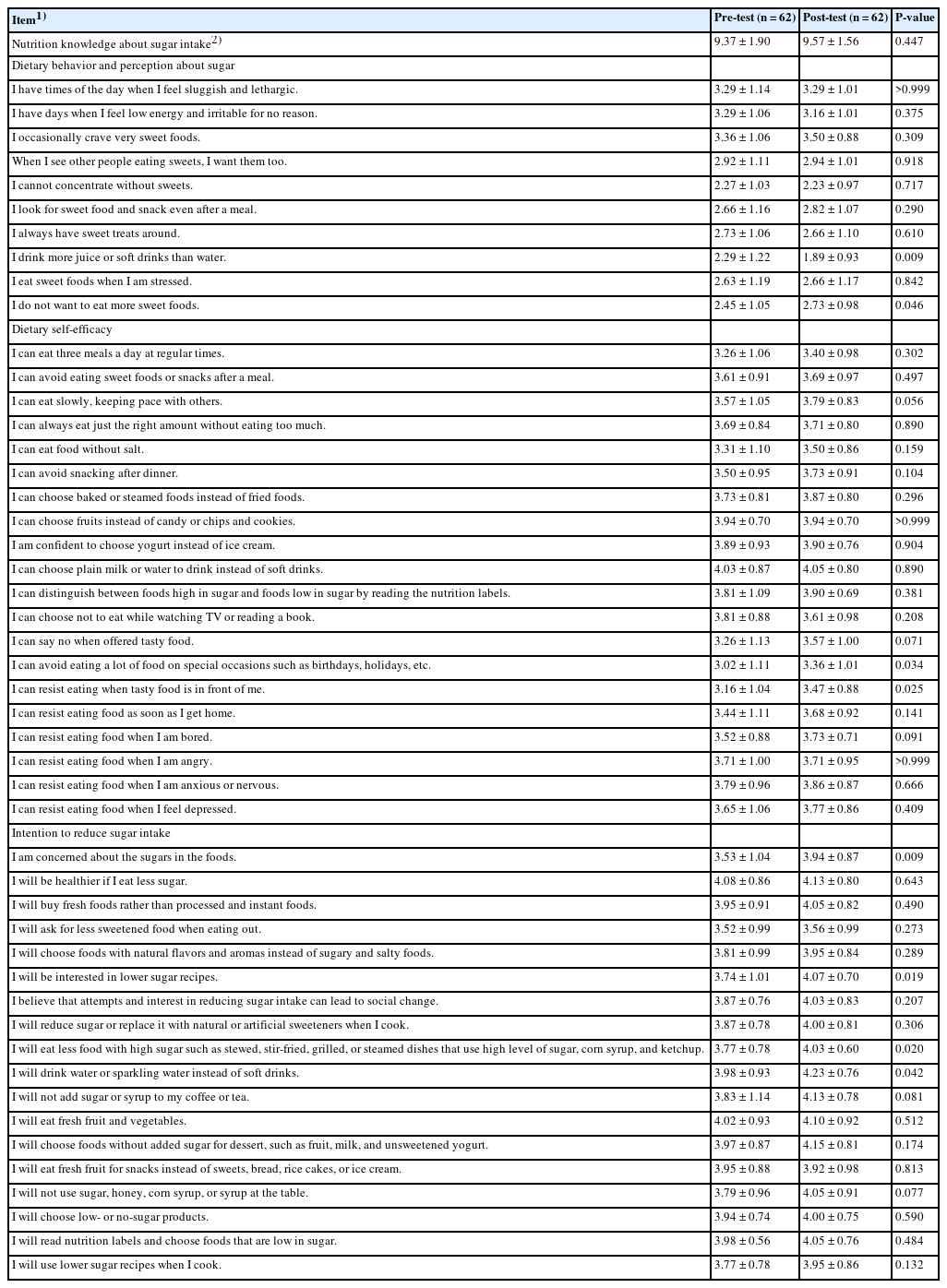
We developed and applied a community-based dietary program to reduce sugar intake. Participants were recruited from community organizations, including a children’s food service management center, elementary to high schools, a university, a family center, a community health center, and an elderly welfare center. The dietary program was conducted in two phases; start and next levels. The start level included a pre-assessment of dietary behaviors and participation in educational platforms, whereas the next level included activities using educational platforms, tailored mission and feedback, and pre- and post-surveys. Extension educators at each community organization implemented the dietary program following organization-specific guidelines. Changes in participants’ nutrition knowledge, dietary behaviors and perceptions, self-efficacy, intention to reduce sugar intake, and participants’ program satisfaction were analyzed using paired t-tests.
Results
In total, 1,238 and 339 individuals participated in the start and next level, respectively. Participants reported significantly lower scores on dietary behavior items regarding drinking more juice or soft drinks after program participation (P = 0.009) and craving sweet foods (P = 0.046). They reported a higher intention to take interest in sugar content in food (P = 0.009) and lower-sugar recipes (P = 0.019), eat less food with high sugar content (P = 0.020), and drink water or sparkling water instead of soft drinks (P = 0.042). Nutrition knowledge did not significantly change after program participation. Program satisfaction significantly increased from the start level to the next level (P<0.050).
Conclusion
This study showed the potential of using a Living Lab approach to implement community-wide dietary interventions. Further research is required to evaluate the effectiveness of the Living Lab approach in various community settings.
- 1,901 View
- 63 Download

- [Korean]
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):492-503. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
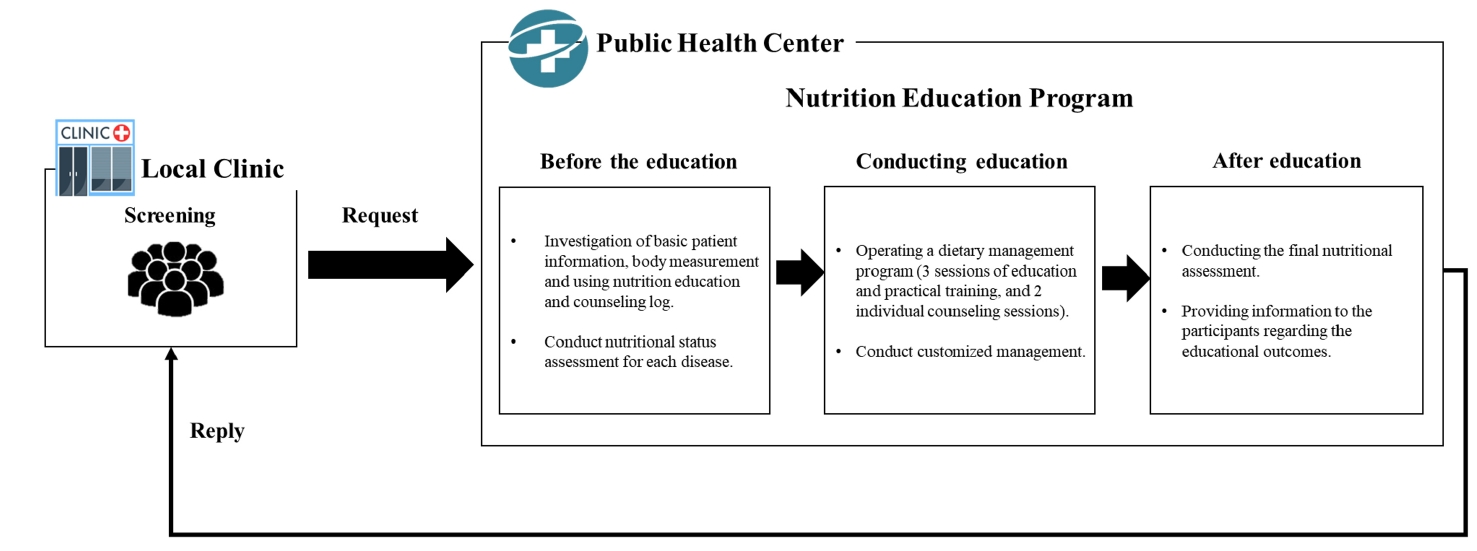
We investigated the impact of an advanced “Nutrition Education Program” on patients with Diabetes mellitus, type 2 from public health centers enrolled in a primary health care-based chronic disease management project. This 12-week dietary management program was developed by the Korea Health Promotion and Development Institute. We assessed if this program improved glycemic control and other health indicators through dietary and nutritional improvements.
Methods
Seventeen patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2 were enrolled in the “Nutrition Education Program.” These patients were referred to public health centers for lifestyle management based on physician assessments at local clinics that were participating in a pilot project on primary health care-based chronic disease management. The participants attended the program comprising face-to-face basic, in-depth, and practical training sessions at the health center during the third, fifth, and seventh weeks, respectively. Anthropometric measurements, body composition analysis, blood biochemical characteristics, nutritional knowledge, and self-efficacy evaluation were performed before and after the program. Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 28.0.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 62 years, and most participants were female (14, 82.4%). No significant changes in patients’ anthropometric measurements or body composition were observed after the training. However, significant reductions were observed in the blood biochemical characteristics, including glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels. Additionally, patients’ nutritional knowledge and self-efficacy scores increased significantly.
Conclusions
The “Nutrition Education Program” helped in improving glycemic control and other health indicators in patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2. Further research is required to objectively confirm the long-term and sustained effects of the program in a controlled study. Trial Registration Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010010
- 2,647 View
- 92 Download

- [Korean]
- An educational needs analysis of sustainable dietary education for nutrition teachers: an application of the IPA, Borich needs assessment and The locus for focus model
- Eunseo Yang, Borham Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):372-381. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00008

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the importance and performance levels of sustainable dietary education across the health, environment, and society domains as perceived by nutrition teachers and evaluate the needs and priorities for sustainable dietary education.
Methods
An online survey was conducted for 151 nutrition teachers in Jeollanam-do. The survey included 20 questions across the health, environment, and society domains. The data were analyzed using a paired-sample t-test, the importance-performance analysis (IPA), the Borich needs assessment model, and the locus for focus model.
Results
Overall, the average importance levels of the 20 items of sustainable dietary education were significantly higher than their average performance levels (4.44 vs. 3.68). The examination of each educational domain revealed that although the importance of education in the health domain was recognized and actively practiced by the nutrition teachers, the performance was comparatively lower in the environment and society domains. The Borich needs assessment and the locus for focus model identified education on biodiversity conservation, plant-based protein, and the use of local food as the top-priority group in the environment domain along with fair and ethical food, food security, regional food culture, food policy and trade, and family dining culture as the second-priority group in the society domain.
Conclusions
The results of this study underscore the need to support the nutrition teachers’ perception and practice of sustainable dietary education in the environment and society domains. We believe that the educational needs and priorities proposed in this study will be considered in the future development and modification of sustainable dietary education programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Jounghee Lee, Juhyun Lee, Wookyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 75. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef - Analysis of students’ need for artificial intelligence content in the 「Digital education」 subject
SungAe Kim, Ji Won You
The Journal of Korean Association of Computer Education.2025; 28(7): 71. CrossRef - Safety education status and needs priorities of Korean military food service personnel using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model: a cross-sectional study
Jeongeun Park, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 261. CrossRef
- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 2,803 View
- 79 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middle-aged Korean adults: an intervention study
- Minji Kang, Young-Hee Park, Subeen Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Hyun Wook Baik, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):265-277. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
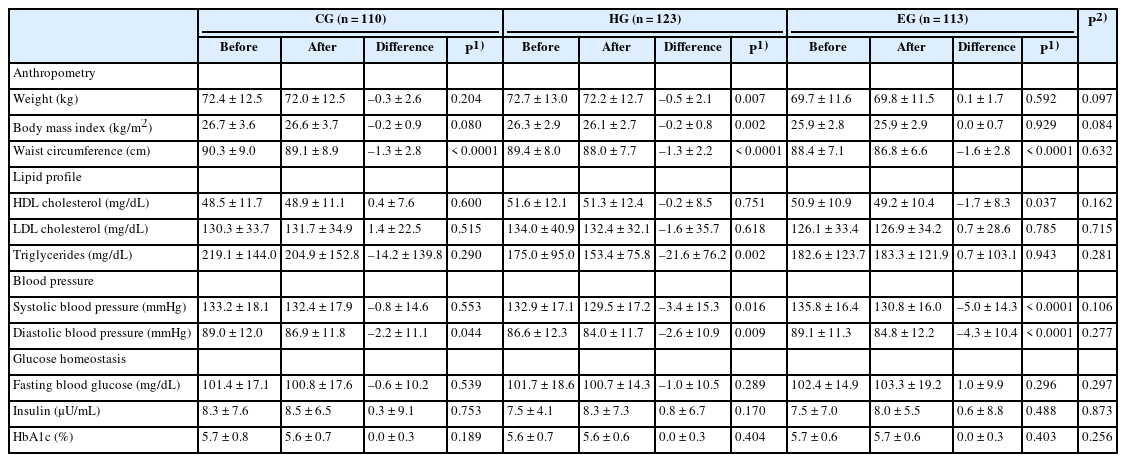
A total of 411 Korean adults 30–59 years of age were allocated randomly into three groups: the nutrition education group for promoting Han-sik consumption (HG), the nutrition education group for eating balanced diet (EG), and the control group (CG). The HG and EG received four face-to-face nutrition education sessions over 16 weeks to improve nutritional problems based on the individual’ usual diet. Effectiveness of the program was evaluated with the differences of self-reported dietary behaviors, dietary intakes, anthropometric measurements and biochemical indices between the baseline and the end of the nutrition education program. The changes within groups were analyzed using paired t-test and McNemar test and effectiveness among three groups was analyzed by repeated analysis of variance.
Results
After the nutrition education, the percentages of participants who achieved the recommended food group consumption in the Korean Food Guidance Systems significantly increased in HG (P = 0.022). Body weight (P = 0.007), body mass index (P = 0.002), and triglycerides (P = 0.002) significantly decreased in HG. Waist circumference and diastolic blood pressure decreased in all three groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
This study found that tailored nutrition education program for middle aged Korean adults showed beneficial effects on improving dietary behaviors and metabolic syndrome risk factors. Further studies are needed to assess the long-term effects of the nutrition education programs on metabolic syndrome risks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multicomponent intervention increases nutrition knowledge scores in rural China
Zhifan He, Ming Feng, Lu Li, Jing Li, Xiaohui Li
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Multicomponent intervention increases nutrition knowledge scores in rural China
- 4,585 View
- 88 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):97-113. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Since the enactment of the School Nutrition Act in 1981, school lunch programs in South Korea have grown quantitatively and qualitatively with a current student participation rate of 99.8%. Nonetheless, educational materials are needed to reduce misunderstanding and ignorance about school lunch programs. This study aimed to develop 3 educational videos that help students of various ages (kindergarteners/lower-grade elementary, upper-grade elementary, and secondary school, respectively), understand the school lunch program.
Methods
A scenario was created, was made, and the opinions on the scenario from experts in foodservice sectors were collected. A survey was conducted to students and parents to determine topics they wanted to know about school foodservice. The final videos were produced using this information and the expert opinions. The data were analyzed using SPSS 27.0 for Mac (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA); a P-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Three videos on school foodservice were developed for various age levels of students: kindergarten/lower-grade elementary, upper-grade elementary, and secondary school. Additionally, English subtitles were included for the multicultural student population. These videos, each lasting about 7 minutes, cover topics such as nutrition, hygiene, and the cultural significance of the school lunch program. The survey results showed that parents and students wanted to know the following topics about the school lunch program: “nutritionally balanced diet” (11.9%), “purchasing safe food ingredients” (10.9%), and “healthy eating habits” (9.9%).
Conclusions
The developed videos will serve as valuable educational resources on school foodservice, foster a deeper understanding of the school lunch program in parents and students, and potentially address their inquiries regarding production processes, nutrition, hygiene, cultural heritage, and health.
- 3,603 View
- 39 Download

- [English]
- Exploring factors of nutrition teachers’ intentions for sustainable dietary education in South Korea: an application of the theory of planned behavior
- Eunseo Yang, Borham Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):114-128. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the perception of nutrition teachers and the factors influencing their intention toward sustainable dietary education utilizing the theory of planned behavior (TPB).
Methods
The self-administered online survey was completed by nutrition teachers in Jeollanam-do, South Korea. A total of 151 valid questionnaires were analyzed. Factor analysis and multiple regressions were employed to test the research model.
Results
The study findings demonstrated that all TPB variables significantly influenced the sustainable dietary educational intention, with the degree of influence ranking as follows: external perceived behavioral control (β = 0.417), attitude (β = 0.240), internal perceived behavioral control (β = 0.207), and subjective norms (β = 0.181). For external perceived behavioral control, nutrition teachers and elementary schools exhibited higher levels compared to dietitians and middle/high schools, respectively. The participants in sustainable dietary education training programs exhibited a higher level of internal perceived behavioral control compared to those who did not participate. The highest perception levels were reported for attitude (4.26), followed by subjective norms (4.02), internal perceived behavioral control (3.67), and external perceived behavioral control (3.20).
Conclusions
This study affirmed that the TPB variables elucidated the sustainable dietary educational intentions of nutrition teachers. The significant impacts of external and internal perceived behavioral control, attitude, and subjective norms on educational intentions were confirmed. Consequently, proactive support from schools and governments is essential to enhance the facilitating factors and mitigate the barriers toward sustainable dietary education in schools. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
Ji-Won Kang, Su-Jin Lee, Sil-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 224. CrossRef - An educational needs analysis of sustainable dietary education for nutrition teachers: an application of the IPA, Borich needs assessment and The locus for focus model
Eunseo Yang, Borham Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 372. CrossRef
- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
- 1,831 View
- 39 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrition education programs necessary for social welfare facilities for persons with disabilities: a cross-sectional study
- Jinkyung Kim, Min-Sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):1-15. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the need for nutrition education aimed at improving the health of residents and users of social welfare facilities for persons with disability and aimed to provide basic information for developing a nutrition education program that meets the needs of the field.
Methods
Altogether, 249 employees working in social welfare facilities for people with disabilities were included in the study. Data on the health status of residents/users, meal management, nutritional education, nutritional education needs, and awareness of nutritional education were obtained through online surveys. A descriptive analysis was conducted to analyze the demographic characteristics, needs, and perceptions of the respondents, and independent t-tests and χ2 tests were performed to analyze and compare the differences between residential and daycare facilities.
Results
The majority of residents/users of social welfare facilities for persons with disabilities have developmental disabilities. When educating residents with residents/users of social welfare facilities, ‘personal hygiene’ was the most necessary topic, followed by ‘obesity management’ education. Regarding the methods of providing education, face-to-face lectures demonstrated a high demand. They responded that when nutrition education experts provide nutrition education to people with disabilities, they must understand ‘the physical characteristics of persons with disabilities’ and have the ability to determine appropriate nutrition for such people. The most appropriate nutrition program training would be twice a year, lasting 30 min to 1 h per training session.
Conclusions
It will present a direction for operating a nutrition education program for persons with disabilities that meets their needs of social welfare facilities and ultimately contribute to the establishment and activation of nutrition education tailored to welfare facilities for such individuals in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and applicability evaluation of a nutrition education program for residents and users of disability social welfare facilities in Korea: a mixed-methods study
Jin-kyung Kim, Kyoung-min Lee, Min-sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 64. CrossRef
- Development and applicability evaluation of a nutrition education program for residents and users of disability social welfare facilities in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- 2,756 View
- 44 Download
- 1 Crossref

Educational Materialses
- [Korean]
- Systematization of food and nutrition education content based on national kindergarten curriculum: a qualitative formative study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Eunyoung Baik
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):509-522. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.509
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study is intended to develop a curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aimed at preschool children, reflecting government policy and meeting the demands of preschool settings.
Methods
Existing educational materials were analyzed, and key elements of the 2019 Revised Nuri Curriculum (“Nuri Curriculum”) and Guidelines for Nutrition and Food Education in Kindergartens, Elementary, Middle, and High Schools (“Guidelines”) were examined as foundational information for developing the curriculum for food and nutrition education.
Results
Basing ourselves on the five domains of the Nuri Curriculum, “Physical Activity and Health,” “Communication,” “Social Relationships,” “Art Experience,” and “Natural Science Inquiry,” we integrated three areas from the Guidelines, namely “Dietary Habits and Health,” “Dietary Habits and Safety,” and “Dietary Habits and Culture,” to structure the curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education. Three specific domains, “Nutrition and Health,” “Food and Culture,” and “Safe Dietary Practices,” were tailored for preschool children, each comprising core concepts, content elements, and educational materials. In the “Nutrition and Health” domain, core concepts such as “nutrition” were addressed through content elements such as “balanced eating” and “vegetables and fruit,” while “health” included elements such as “eating regularly” and “nutrients for disease prevention,” each with two educational content components. The “Food and Culture” domain focused on “food” with content on “local foods (vegetable-garden experience)” and “food culture” with content on “our dining table (rice and side dishes),” “our agricultural products,” “global cuisine (multiculture),” and “considerate dietary practices,” each with four educational content components. The “Safe Dietary Practices” domain included core concepts such as “hygiene” with content on “hand-washing habits” and “food poisoning management,” and “safety” with content on “food labeling.”
Conclusions
The systematized curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aligns with the Nuri Curriculum and is interconnected with the Guidelines. This curriculum can be used as foundational material for developing educational resources tailored to the characteristics of preschoolers, contributing to effective implementation in early childhood education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 441. CrossRef
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- 1,216 View
- 53 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
- Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):495-508. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.495
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop a campus-based intervention program to enhance food literacy (FL) among university students.
Methods
In the initial phase, we conducted a literature review of FL intervention studies and held in-depth interviews with university students to identify facilitators and barriers to improving and practicing FL. Expert counseling sessions were conducted with nutrition education, marketing, and service design professionals. The results of this phase led to the creation of an initial curriculum draft. In the second phase, a follow-up survey was conducted with young adults to assess the acceptability of the developed curriculum. After the follow-up survey, additional meetings were conducted with the aforementioned experts, and the curriculum was further refined based on their input.
Results
An 11-week FL intervention program was devised using constructs from the Social Cognitive Theory. The weekly curriculum consisted of 90-min theory-based and 90-min hands-on experience sessions. Three primary aspects of FL were covered: nutrition and food safety, cultural and relational dimensions, and socio-ecological aspects. Program highlights included cooking sessions for crafting traditional Korean desserts, lectures on animal welfare, insights into zero-waste practices, and communal eating experiences. Based on the study team’s previous research, the program also addressed mindful eating, helping participants understand the relationship with their eating habits, and providing strategies to manage negative emotions without resorting to food. Yoga sessions and local farm visits were incorporated into the curriculum to promote holistic well-being.
Conclusions
This study elucidated the comprehensive process of creating a campus-based curriculum to enhance FL among university students, a group particularly susceptible to problematic eating behaviors and low FL levels. The developed program can serve as a blueprint for adaptation to other campuses seeking to bolster students’ FL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of nutrition class with cooking lab on college students’ eating behaviors and well-being in the United States: a mixed-methods study
Borham Yoon, Kyungyul Jun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 305. CrossRef - The Dragon Fruit Advantage: Exploring University Students’ Experiences and Perceptions of a Targeted Nutrition Education Module
Adelfa Silor, Faith Stephanny C. Silor
Seminars in Medical Writing and Education.2025; 4: 924. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of a food literacy pilot program for university students: using a mixed-methods research approach
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(6): 885. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef
- Effects of nutrition class with cooking lab on college students’ eating behaviors and well-being in the United States: a mixed-methods study
- 2,687 View
- 79 Download
- 4 Crossref

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
- Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):38-47. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between the experience of disease management education and the use of nutrition labels according to the sociodemographic characteristics and health behaviors of people diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes living in the community.
Methods
Among the participants from the Community Health Survey (2018), 74,283 individuals diagnosed with hypertension or diabetes were included in the study population. According to gender, this study evaluated nutrition label use by the experience of disease management education, individual sociodemographic characteristics, and health behavior. Finally, using multiple logistic regression analysis, the association between disease management education and nutrition labels was calculated using the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results
Males (24.5%) experienced more disease management education than females (22.6%). In addition, younger age, higher education level, and higher equalized personal income experienced more disease management education (P < 0.001). The educational experience rate was higher in the male subjects who did not smoke or were involved in high-risk alcohol consumption (P < 0.001). In addition, the rate of disease management education experience was significantly higher for both men and women who exercised by walking (P < 0.001). The use of nutrition labels was higher in females (9.9%) than males (5.8%), and both males and females were significantly higher in young age, high education, high income, and professional and office positions (P < 0.001). The utilization rate of nutrition labels was high in non-smoking male subjects and high-risk-drinking female subjects. In addition, the utilization rate of nutrition labels was significantly higher in males and females who exercised by walking and those who experienced disease management education (P < 0.001). After adjusting for individual sociodemographic characteristics, health behavior, and disease management education, the use of nutrition labels was high among females (OR 3.19, 95% CI 2.85-3.58), high income (Q4; OR 1.62, 95% CI 1.41-1.87, Q5; OR 1.58, 95% CI 1.37-1.84) and highly educated (high school; OR 2.87, 95% CI 2.62-3.14, above college; OR 5.60, 95% CI 5.02-6.23) while it was low in the elderly (OR 0.43, 95% CI 0.40-0.47), and economically inactive (OR 0.86, 95% CI 0.76-0.96). The use of nutrition labels was high in non-smokers (OR 1.29, 95% CI 1.13-1.48), non-high-risk drinkers (OR 1.22, 95% CI 1.08-1.38), and subjects who exercised walking (OR 1.44, 95% CI 1.34-1.54). There was no difference in the utilization rate of nutrition labels according to obesity, and the utilization rate of nutrition labels was significantly higher in subjects who had experienced disease education (OR 1.34, 95% CI 1.24-1.44).
Conclusions
Education on the use of nutrition labels, which contributes to food selection for healthy eating, might be a tool for dietary management. Moreover, the utilization rate can be a good indicator for predicting the proportion of the population practicing the guide for disease management. Improving the utilization rate of nutrition labels through disease management education can be a useful intervention for people with chronic diseases who need healthy eating habits for disease management and preventing complications, particularly those diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Nutrition Label Utilization and Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: Using the Data of the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2021)
Ae-Seul Lee, Seong Woo Choi, So Yeon Ryu
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(3): 249. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Status and Life Satisfaction According to Food Security in Single-Person Households of Elderly Population
Dong Hoon Jung, Jae Won Han, Wonha Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(1): 42. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Dietary Behavior of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-sectional Study
Sohyun Jin, Youngshin Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 80. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Participation in Hypertension Management Education Among Diagnosed Hypertensive Patients in Busan: Utilizing the 2021 Community Health Survey
Hye Jung Jun, Kyoung Mi Kim
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 424. CrossRef - An association between socioeconomic status and preventive screening for diabetic eye and kidney complications among individuals with type 2 diabetes
Changwoo Shon, Jongnam Hwang
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(5): 27. CrossRef
- Association between Nutrition Label Utilization and Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: Using the Data of the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2021)
- 3,706 View
- 66 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Nutrition teacher’s perception and current status of nutrition education for free learning semester program: a preliminary study
- Mi Joo Park, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):24-37. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the current status of nutrition education via a free learning semester program (NE). The understanding of the program, the potential difficulties, and future initiatives for NE improvement were also investigated.
Methods
A total number of 161 nutrition teachers from Gwangju and Jeonnam filled in a questionnaire and participated in this survey, which was performed from July to August 2019.
Results
Our results showed that 8.1% of the nutrition teachers had taught nutrition education in free learning semester programs. The most frequently implemented model was subject selection, followed by club activities. Most of the nutrition teachers comprehended the purpose of NE. The attitude of nutrition teachers to NE differed by the understanding of its purpose. Positive attitude was evident due to a better understanding of the purpose by nutrition teachers. Nutrition teachers reported the most common difficulties of NE were the lack of preparation due to the heavy workload and the lack of a standard running program. The most effective method of NE was the activity classes. The experience of practicing NE influenced the choice of contents for each operating model. Nutrition teachers that were experienced in NE conducted via free learning semester programs preferred the selected topics model, but those without experience chose the career search model.
Conclusions
Although some obstacles exist, nutrition teachers had a positive attitude and perceived well the importance of NE. Therefore, the awareness for the significance of NE of nutrition teachers needs to be improved. For better NE practice, it is necessary to reduce/ manage the workload of general food service. Furthermore, the development of standard running and promotion programs, and teacher training programs should be ensured. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef
- An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
- 1,693 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of the STEAM Education Program on Food Groups for Kindergarteners
- Jinkyeong Ahn, Seyoen Kim, Donghyuk Kim, Jounghee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):361-372. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to explore the effectiveness of the STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) education program on the use of specific food groups in improving nutrition-related knowledge and attitude, dietary behavior, creative problem solving, and STEAM attitude.
Methods
We selected two classes at a kindergarten in Jeollabuk-do, South Korea. A total of 44 kindergarteners from the two classrooms participated in this study. The experimental group and the control group were formed with 22 students each. The experimental group attended 11 STEAM classes on the use of the grain, fruit, and milk food groups. First, we performed the paired t-test to examine changes from pre-to-post classes for both groups. Then, we used ANCOVA to compare post-test scores between the experimental and control groups with the adjustment of pre-test scores.
Results
The results demonstrate that the STEAM education program on the use of the food groups significantly improved (1) nutrition-related knowledge and attitude, and dietary behavior (P < 0.001), (2) creative problem solving (P < 0.001), and (3) STEAM attitude (P < 0.001) in the intervention group when compared with the control group.
Conclusions
The STEAM education program on the use of food groups is effective in enhancing nutrition knowledge and attitude, dietary behavior, creative problem solving, and STEAM attitudes among kindergarten students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and evaluation of play-based food and nutrition education materials for early childhood through sensory experiences: a pre-post observational study
Hyunjoo Ryou, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 471. CrossRef
- Development and evaluation of play-based food and nutrition education materials for early childhood through sensory experiences: a pre-post observational study
- 1,642 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Program Evaluation using the RE-AIM Framework: A Systematic Review and Application to a Pilot Health Promotion Program for Children
- Ji-Eun Lee, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim, Jae-Heon Kang, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(4):296-308. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.4.296
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop evaluation criteria for the elementary-school-based health promotion program using the RE-AIM framework and to examine their feasibility.
Methods
Previous evaluation studies on health interventions for elementary-school students using the RE-AIM framework were reviewed systematically to identify appropriate evaluation criteria. A diet and physical activity intervention based on the transtheoretical model was implemented in a pilot study using the “Happy Me” application. The feasibility of using the RE-AIM framework to evaluate it was examined.
Results
The review yielded the following evaluation criteria: “reach,” the ratio of participants out of the total target population; “efficacy/effectiveness,” the difference in outcomes between the intervention and control groups, or between a pre- and post-test; “adoption,” the rate of use of the program and participation in the next stage of the program; “implementation,” the progress on the program components; “maintenance,” the participants’ and teachers’ intention to continue using the program. The pilot study reached 76.6% of the targeted population. The intake of sugar-sweetened beverages decreased (P < 0.0001), and the duration of walking increased (P < 0.0001). Other indicators could not be evaluated; therefore, potential indicators were suggested.
Conclusions
This study produced feasible evaluation criteria for elementary-school-based health promotion using the RE-AIM framework. Nevertheless, the feasibility needs to be validated with a broader range of studies and long-term interventions.
- 2,077 View
- 36 Download

- [Korean]
- Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
- Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):167-176. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to identify the awareness and practice of reducing sugar in school meals and the status of nutrition education regarding sugar reduction.
Methods
An online survey was conducted on 101 nutrition teachers (dietitians) working at elementary, middle, and high schools in Daegu.
Results
School nutrition teachers in Daegu recognized the need for efforts to reduce the sugar intake in the Korean diet, and it was found that elementary nutrition teachers were more aware of the implementation of the sugar reduction policy at the national level than middle and high school nutrition teachers (P = 0.002). Among the policies to reduce sugar intake at the national level, there was a high need for the promotion of self-control and limiting the sales of food with high sugar content in schools and their vicinity. The degree of practice for reducing sugar in school meals was found to be higher in the preparation, purchase, and cooking stage compared to the serving stage (P < 0.05). There was a high need for changing the preferences of the subjects for a sweet taste as a means of reducing the sugar in school meals. Thirty-six percent of nutrition teachers conducted sugar reduction education, and sending out school newsletters was the highest type of nutrition education at 80.6%.
Conclusions
To effectively promote reduced sugar intake in school meals, it is necessary to change the preference of the subjects for sweetness and to conduct continuous education that can improve the awareness of people for reducing their sugar intake. For this, it is necessary to set aside time for nutrition education and to prepare an institutional framework for providing this education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Learning to care in the food system: Education for Sustainable Development resources, food education and the farming of animals for food
Verity Jones, Christopher Bear
Environmental Education Research.2026; 32(1): 169. CrossRef - Analytic Hierarchy Process approach to estimate weights of menu management in the school foodservice
Hyo Bin Im, Seo Ha Lee, Hojin Lee, Lana Chung, Min A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 349. CrossRef - Sugar Intake and Perception of Sugar Reduction among University Students in Gwangju
Yeon-Ok Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1170. CrossRef - Analysis of the Perception and Need for Education about Genetically Modified Foods among Elementary, Middle and High School Parents:Focus on the Jeonnam Region
Da-Hye Choi, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(1): 67. CrossRef - Comparison of the Sodium and Sugar Reduction Practices at Samsam Foodservices and General Foodservices in Daegu
Sung-young Kwon, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(4): 270. CrossRef
- Learning to care in the food system: Education for Sustainable Development resources, food education and the farming of animals for food
- 1,181 View
- 17 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Development and Evaluation of Booklets and Video Clips to Prevent Children from Developing Picky Eating
- Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):451-463. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.451
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to develop and evaluate booklets and video clips to prevent children from picky eating.
Methods
Based on a survey conducted on food preferences of preschool children aged 2 to 5 years, 14 kinds of less preferred vegetables were selected. Accordingly, educational videos, activity books, and teaching-learning guides were produced for preschool children using the 'food bridge' theory, and the educational materials were named “Friendly vegetables”. Educational materials were distributed to childcare institutions, and their effectiveness was investigated for preschool children who were instructed on these materials once every 30 days from March to November, 2019. The children were examined for changes in their knowledge of names, colors, taste/texture, methods of cultivation, and preferences for vegetables before and after the instructional course.
Results
The awareness of vegetables increased significantly in younger children and the picky eating group. When the assessment was carried out in terms of vegetable knowledge, it was observed that the younger the age or the pickier the in eating food, the more effective the education is compared to the counter part. The preference for vegetables also increased after the instruction compared to the pre-instruction period, but significant changes were seen only in the 2~3 year age group for boys and girls. Also, only the picky group of girls showed changes in preference. The children's average interest in the education materials was 3.85 points out of 5 points.
Conclusions
Through this study, we have developed educational materials for standalone use in childcare facilities and confirmed that they have a significant effect on improving awareness and preferences related to vegetables. In summary, the younger the age or the pickier the child in eating food, the more effective the education. It is believed that additional education on mealtime guidance is needed which can alter the eating behavior of preschool children and improve their diet. It is proposed to widen the scope of use of the materials by collecting diverse opinions from child care teachers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pilot evaluation of a cooking-based nutrition education program to promote vegetable intake among children in Seoul, South Korea: a single-group pre–post study
Sil-Ah Kim, Su-Jin Lee, Min-Ah Kim, Ji-Eun Oh, Sohyun Park, Hyun-Joo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 249. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of play-based food and nutrition education materials for early childhood through sensory experiences: a pre-post observational study
Hyunjoo Ryou, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 471. CrossRef
- Pilot evaluation of a cooking-based nutrition education program to promote vegetable intake among children in Seoul, South Korea: a single-group pre–post study
- 975 View
- 19 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Qualitative Study of Compliance with Nutritional Management in Colorectal Cancer Patient Undergoing Chemotherapy
- Heejung Park, Hyonson Kil, Wookyoun Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):303-316. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.303
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
The nutritional status of cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy is closely related to the compliance of nutrition education. However, as chemotherapy is conducted repeatedly, compliance with nutrition management is lowered, leading to malnutrition. Malnutrition is related directly to the quality of life after surgery in cancer patients. Therefore, this study examined the factors related to compliance with nutrition management during chemotherapy.
Methods
In this study, five subjects with colorectal cancer undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy were interviewed in-depth using the Giorgi study method. The contents of the nutrition education visits and in-depth interviews were transcribed in the language of the subject after recording, and the appropriateness of the data was improved by reflecting the subject’s actions and facial expressions.
Results
After conducting the in-depth interviews for each subject, the experience of the subject’s diet and adjuvant chemotherapy was drawn into two domains, six elements, and 26 sub-elements. In the cognitive domain, the patients experienced physical and psychological changes, and the need for nutrition management was recognized by analyzing the dietary causes of the diseases. In the domain of practice, a knowing-doing gap was formed, unlike the patient’s will. Factors that inhibited compliance with nutritional management included digestive problems, sensory changes, loss of appetite, and social interaction stress.
Conclusions
Dietary management is very important for patients receiving periodic anticancer therapy, and step-by-step training and personal monitoring based on the chemotherapy order is necessary to maintain the patient’s will and social and environmental support.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Continuous Nutrition Care on Nutritional Status and Dietary Habits of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Surgery
Jina Son, Ha I Kang, Eun young Jung, Hae won Ryu, Kyung-Ha Lee
Clinical Nutrition Research.2023; 12(2): 99. CrossRef
- Effects of Continuous Nutrition Care on Nutritional Status and Dietary Habits of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Surgery
- 1,372 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Development and Application of an Education Program for Healthy Dietary Life for Elementary School Aftercare Class Children
- Jung Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, In Young Park, Young Sim Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):497-511. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.497
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to develop a school-centered healthy eating environment for children in elementary care classrooms and prevent incorrect eating habits and obesity through the development and application of standardized healthy eating habit-forming educational materials.
METHODS
Ten schools in eight districts of Gyeonggi-do and 400 students from 19 care classes were selected. Based on the developed educational materials, the program was applied to students once in two weeks. ‘Notices for Parents’ forms were also sent to the students' home to educate their parents. Pre and post-surveys were conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the education. The pre-education, education, and aftercare were conducted from September 28 to September 31, 2016, from October 3 to November 30, 2016, and from December 5 to December 9, 2016, respectively.
RESULTS
The healthy eating program for elementary care classes was designed to develop a school-centered healthy eating environment and provide standardized educational material for healthy eating habits. Twelve educational topics were developed: 〈Eat Evenly〉, 〈Eat Breakfast〉, 〈Eat vegetables and Fruits〉, 〈Clean Body, Strong Body〉, 〈Healthy and Tasty Snacks〉, 〈Keep Healthy Weight〉, 〈Food that enters our body〉, 〈What is safe food?〉, 〈Food selection and Storage〉, 〈Our land, Our grain〉, 〈Enjoy Traditional Food〉, and 〈Food manners〉. Moreover, the materials were produced in four forms: for students, for after school caring teachers, for external specialists, and for parents. The effectiveness evaluation was conducted to confirm the application of the program. The average eating habits score was 3.3 ± 0.6, with no significant difference between before and after application. The score of overall satisfaction of the education was 3.9 ± 0.9. The most satisfying content was ‘Did you get to know how to eat evenly?’. Significant increases were observed in two contents for parents regarding their children's knowledge changes after the education: ‘Five nutrients needed for growing children’ and ‘Knowing sugar foods and sugar-containing foods’. On the other hand, their educational satisfaction was 3.6 ± 0.6, which was lower than the children's satisfaction. This might be because their education was conducted only through the ‘Notices for Parents’ form.
CONCLUSIONS
In the long term, the healthy eating habit-formation education for lower elementary school children is expected to be beneficial. To prevent obesity and establish healthy eating habits of children, it is important to develop healthy eating education programs centered on elementary school aftercare classes, including the development of educational materials and an application system through connection with the home and community. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
Jiyoung Park, Sein Hwang, Seolhyang Baek, Gill A. Ten Hoor
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2389. CrossRef
- An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
- 1,535 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effect of Dietary Education Experience (Home, School, and Mass Media) on Food Consumer Information literacy
- Ji Eun Kim, Kyoung Sook Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(5):363-373. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the effects of dietary education experience (home, school, and mass media) on food consumer information literacy.
METHODS
The study subjects were 454 adult consumers who answered a structured questionnaire. The questionnaires addressed the subjects' demographics, dietary education experience (home, school, and mass media), and food consumer information literacy. The data were analyzed through frequency analysis, mean, standard deviation, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson's correlation, and multiple regression analysis using SPSS Win 24.0.
RESULTS
First, the scores of mass media education experience were 3.41 ± 0.64, which was the highest, and 3.15 ± 0.74 for school education experience, which was the lowest. Second, the level of sub-literacies (task definition, information seeking strategy, location and access, use of information, synthesis, and evaluation) showed scores of 3.20 ± 0.72 ~ 3.47 ± 0.68, which were slightly higher than the median. The synthesis literacy was the highest, as opposed to the information seeking strategy literacy, which was the lowest. The location and access and synthesis literacy were higher in women. Third, a significant positive(+) relationship was observed between all sub-literacies and each of three dietary education experiences (home, school and mass media). According to multiple regression analysis, the major variables influencing the sub-literacies of food consumer information literacy were home education, mass media, and school education in that order.
CONCLUSIONS
The dietary education experience was the highest through mass media. The factor that showed the highest food consumer information literacy was synthesis. The factors influencing the food consumer information literacy were dietary education experience through home, school, and mass media. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - Agrifood consumer competency index and food consumption behaviors based on the 2019 Consumption Behaviors Survey for Food
Eun-kyung Kim, Yong-seok Kwon, Da Eun Lee, Hee Jin Jang, Young Hee Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(2): 199. CrossRef - Healthy Eating Capability of One-person Households-The Effects of Eating Alone, Meal Types, and Dietary Lifestyles
Seonglim Lee, Ilsook Choi, Junghoon Kim
Family and Environment Research.2020; 58(4): 483. CrossRef
- Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
- 1,405 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on the Development of the Goals and Contents System of Healthy Dietary Education Program for After-School Care in Lower Grade in Elementary School
- Jung Hyun Kim, Myoung Hee Lee, Okjin Park, Kyung Sook Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):24-37. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study purpose is to develop a content system for a healthy dietary education program for after-school care in lower grade in elementary school.
METHODS
The contents of healthy dietary education in the 2015 revised curriculum and textbooks and the major education programs related to dietary life that are currently used in elementary school education were analyzed. Focus group interviews were held with field experts related to lower grade in elementary care class. Accordingly, the structuring of the education area and the detailed education contents were systematized.
RESULTS
From the analysis results, the contents of curriculum, textbook, and administrative department were classified as hygiene safety, health, and culture. The goal of the educational content system was divided into three areas: nutritional dietary life, food hygiene and health, and food culture. The subjects consisted of dietary balance, healthy body weight, digestion and absorption, food hygiene, Korean agricultural products, traditional food, and table manners. The curriculum was composed of 12 content elements.
CONCLUSIONS
In order to ensure that after-school care students can grow into healthy, growth-oriented and creative talents, the role of the caring guide is important, and associated guidelines are needed in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of an Education Program for Healthy Dietary Life for Elementary School Aftercare Class Children
Jung-Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, In-Young Park, Young Sim Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 497. CrossRef
- Development and Application of an Education Program for Healthy Dietary Life for Elementary School Aftercare Class Children
- 1,351 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Program on Obesity Index and Behavioral Modification in Moderate Obese Women
- Myung Hee Chang, Su Jin Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):318-332. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the behavioral modification of obese adults who underwent nutritional and physical activity education. Twenty obese females, aged 20–60 years old, with BMIs (Body Mass Index) >30 or body fat (%) >40 were subjected to this study.
METHODS
The physical activity education program consisted of doing exercise in a gymnasium together or home exercise. Dietary attitudes and dietary intakes were assessed using weight control, physical activity, and eating habits. The nutrition-exercise educational period was 12 weeks.
RESULTS
After the study period, there was significant improvement in physical activity and eating habits score. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the dietary intakes of fiber, iron, potassium, vitamin A, vitamin B6, and niacin. Blood pressure, blood glucose, and total cholesterol levels showed a tendency to decrease, but there was no significant difference. BMI, fat mass, abdominal circumference, and visceral fat levels were significantly reduced while muscle mass significantly increased.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that behavioral modification by nutrition and physical activity education with feedback has positive effects on dietary intake and anthropometric biomarkers in obese adults. Therefore, lifestyle interventions of this kind could be recommended as a method for obesity management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of tele-nutrition education on weight loss, energy intake, and fat adequacy among obese adults in Banyumas, Central Java, Indonesia
Teguh Jati Prasetyo, Izzati Nur Khoiriani, Sifa Aulia Wicaksari, Gumintang Ratna Ramadhan, A. Khomsan, E. Palupi, S.P. Loh, N. Mohd Esa
BIO Web of Conferences.2025; 153: 02013. CrossRef - Influence of Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention (LSI) Program on Health, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Middle-Aged Women
Su-Jin Jung, Seung-Ok Lee, Min-Jun Choi, Jun Heo, Soo-Wan Chae, Baik-Hwan Cho
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2022; 12(3): 127. CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef
- Effect of tele-nutrition education on weight loss, energy intake, and fat adequacy among obese adults in Banyumas, Central Java, Indonesia
- 1,689 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Effect of Nutrition Education on the Eating Habits and Quality of Life of Gastric Cancer Outpatients Undergoing Gastrectomy
- YoonHee Jung, Joomin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):162-173. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the effects of nutrition education on the nutritional status, including eating habits and quality of life in gastric cancer patients undergoing a gastrectomy.
METHODS
Thirty one out-gastric resection patients at C University Hospital in Gwangju, Korea were enrolled in this study. The patients received an individualized nutritional counseling session, and the effects were assessed before and after a 3-month nutrition education intervention. Nutrition education for gastric cancer outpatients included the dietary guidelines (e.g., food intake), the level of nutrient intake, and nutrition support.
RESULTS
The patients had significantly improved serum albumin and hematocrit levels after nutrition education. Of the dietary habits, the meal time and amount of food compared to the first education were increased significantly. Of the changes in the food intake frequency, fish and meat, and vegetables and fruits intake were increased, but not at a statistically significant level. The score of eating habits related to the gastrectomy was improved significantly after nutrition education from 31.7 to 34.5. The composite scores for the quality of life were also improved significantly after the nutrition education program.
CONCLUSIONS
The nutrition education for gastric cancer outpatients may be crucial and efficient for improving their lifestyle. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Irisin Levels in Cancer Anorexia Cachexia Syndrome and the Relationship between Nutrition Education and Quality of Life
Diler Us Altay, Duygu Mataracı Değirmenci, Salih Can Çelik, Abdullah Üner, Tevfik Noyan, Çağrı Akalın
Cumhuriyet Science Journal.2024; 45(4): 636. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Irisin Levels in Cancer Anorexia Cachexia Syndrome and the Relationship between Nutrition Education and Quality of Life
- 1,639 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of an Intensive Management Program for Diabetic Patients on a Blood Biochemical Profile and Diabetes Knowledge
- Su Jeong Yeo, Bok Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):148-161. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the effects of nutrition education and exercise therapies on the hematological status and diabetes knowledge of diabetic patients. For this purpose, a 12-week intensive management program was provided to diabetic patients participating in an exercise program in S health subcenter in Kwangju city and the effects were analyzed.
METHODS
The subjects were 26 diabetic patients, who provided written informed consent. As a preliminary survey, this study examined the general characteristics, physical status, obesity, blood pressure, hematological status, daily activity level, diabetes knowledge, diet performance, and barriers to diet therapy. After the 12-week intensive management program was completed, a post-test was conducted in the same way as the preliminary test. The data were analyzed with using SPSS 18.0. The data from this study are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. A paired t-test was conducted to compare differences in the means before and after the program. Statistical significance was set to p < 0.05.
RESULTS
The results of the program are presented as follows. The HDL-cholesterol levels changed from 39.8 ± 10.5 mg/dL to 48.3 ± 13.1 mg/dL, showing a significant increase (p < 0.001). The blood sugar 2 hours after a meal changed from 175.2 ± 67.1 mg/dL to 140.5 ± 42.5 mg/dL, showing a significant decrease (p=0.014). The glycosylated hemoglobin levels decreased significantly from 6.7 ± 1.1% to 6.3 ± 1.0% (p=0.010). The total scores of the daily activity levels increased significantly from 3.8 ± 2.4 to 4.8 ± 2.5 (p=0.040). The scores of knowledge on diabetes increased from 11.5 ± 3.6 to 14.0 ± 3.8 (p=0.001). The scores of knowledge on diet therapy changed from 6.7 ± 2.2 to 7.9 ± 1.7, showing a significant increase (p=0.027).
CONCLUSIONS
The 12-week intensive management program intervened by nutrition education and exercise therapies induced positive changes to the HDL-cholesterol, blood sugar 2 hours after a meal, glycosylated hemoglobin, daily activity levels, and knowledge on diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 492. CrossRef - The Associated Factors of Medical Treatment in Diabetic Patients
Sun Ju Choi, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Seong Woo Choi
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 302. CrossRef - Association between diabetes mellitus and anemia among Korean adults according to sex: a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010–2016)
Mihye Kim, Sook-Hyun Lee, Kyoung Sun Park, Eun-Jung Kim, Sujung Yeo, In-Hyuk Ha
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- 1,476 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education Using Dietary Guidebook in Higher Grade Elementary Students of Jeonbuk Area
- Mi Ran Park, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(1):13-27. Published online February 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to examine the effects of nutrition education with a dietary guidebook for children on dietary attitude, nutrition knowledge and nutrient intakes.
METHODS
The subjects were 54 higher grade elementary students (27 educated vs. 27 non-educated). The educated group was provided individual and/or group lessons (40 min/lesson/week, 4 week) using a dietary guidebook of Children developed by The Korean Society of Community Nutrition (KSCN) & Korean Food and Drug Administration (KFDA). The contents were Balanced Diet, Smart Food Choices, Cooking a Healthy Snack and Building a Healthy Body. We examined the differences in nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes and dietary intake between the educated group and non-educated group.
RESULTS
After education, the educated group improved dietary attitude, nutrition knowledge and qualitative nutrient intakes compared to the non-educated group. Specifically, among dietary attitudes, ‘taking a meal with salty and spicy food’ increased, while among nutrition knowledge, ‘functions of protein’, ‘functions of fat’, ‘foods with carbohydrates’, ‘foods with fat’, ‘foods with vitamins’, and ‘foods with minerals’ were increased. Nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) scores for vitamin C, iron, and zinc were increased.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutrition education using a dietary guidebook for children developed by the KSCN & KFDA had positive effects on nutrition knowledge and qualitative nutrient intakes. These findings suggest that nutrition education focused on personalized daily energy and nutrient requirements may improve dietary attitude and quantitative nutrient intakes of children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 167. CrossRef - Development of Educational Board Game for Dietary Education; ‘Food-Bicycle’
Jung Hoon Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2018; 27(5): 411. CrossRef
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- 1,492 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Educational Intervention about Breastfeeding on University Students' Knowledge and Attitudes toward Breastfeeding: Focusing on Gender Differences
- Jo Yoon Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(1):1-12. Published online February 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to examine the impact of a targeted, practical education intervention on university students' knowledge and attitudes toward breastfeeding.
METHODS
A university curricular intervention was designed for students to increase their knowledge and positive attitude toward breastfeeding issues. The participants attended a breastfeeding education lectures two hours of weekly for fifteen weeks in university; 61 students (female, n=31 and male, n=30) participated. The pre- and post-measurements included future breastfeeding intention, knowledge, attitude and perceived control beliefs scores based on the results of a questionnaire.
RESULTS
The statistical analysis results revealed a significant difference in the pretest and posttest scores (0.57 to 5.10 points, p < 0.001) in regard to the students' breastfeeding knowledge. For female students, significant differences were observed in the future breastfeeding intention (p < 0.05), knowledge (p < 0.001), and attitudes towards breastfeeding (p < 0.05) between the pretest and posttest scores. For male students, there were no significant differences in the future breastfeeding intention, attitudes towards breastfeeding, and perceived control beliefs scores after the breastfeeding education lecture.
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that the implementation of practical breastfeeding educational interventions helped improve university students' knowledge and attitudes toward breastfeeding. In summary, despite the limitations, it is necessary to pay more attention to improving students' knowledge and attitudes towards breastfeeding through university curricula.
- 1,137 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- Qualitative Study on Improvement of Operating System and Tailored Nutrition Education Program for Marriage Immigrants to Korea: Program Providers' Perspective
- Mee Young Joe, Ji Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):323-335. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.323
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study is to analyze the current status of nutrition education programs for multicultural families and to provide policy suggestions for improvement.
METHODS
In-depth interviews of a total of 21 multicultural experts were conducted; 15 people were interviewed individually, while 6 people were interviewed in groups of three.
RESULTS
In-depth interviews revealed various problems related to the operation of nutrition education programs. The causes of problems were analyzed and categorized as four factors: systemic, practical, environmental and cultural. As for the systematic factors, insufficient linkage between related organizations and duplicate performance of several projects were identified as concerns Establishment of a control tower and strengthening the linkage among the related organizations may be needed to address this concern. With regard to practical factors, the study identified that language barriers, and lack of nutritional education media and tools translated into multicultural languages were limiting factors. These limitations the development of nutrition education materials that aretranslated into multiple languages, implementation of education programs that are different from the Korean education, and by providing interpreters. As for the environmental factors, low educational level and poor nutritional knowledge of multicultural women made it difficult for them to understand the contents of the education. Demonstration, practical training and urgent education on pregnancy and childbirth nutrition were identified as needs to address these concerns. Withregard to cultural factors, food culture conflict with Korean families, and difficulties in home practices were detected as concerns. Participants in the study suggested that getting education with family and facilitation of weekend and nighttime programs health of this community.
CONCLUSIONS
Further studies are needed to adopt more effective and efficient nutrition intervention to promote the healthy eating of the married immigrant women based on the study results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
Sil-Ah Kim, Min-Ah Kim, Seung-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 614. CrossRef - Study on the Dietary Behavior of Adolescents in Multicultural Families Using the Nutrition Quotient and Their Changes in the Nutrition Knowledge and the Dietary Attitudes after Nutrition Education
Yoo-Jin Jung, Sung Hee Min, Min June Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(3): 208. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Education Experience (Home, School, and Mass Media) on Food Consumer Information literacy
Ji Eun Kim, Kyoung Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 363. CrossRef
- Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
- 1,447 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Survey on Foodservice Satisfaction and Dietary Education needs for Improvement of School Foodservice in Middle School Students in Seoul
- Kyung Hee Shin, Youngmee Lee, Wookyoun Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(2):127-135. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.2.127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to examine the satisfaction of school cafeterias among the surveyed group at two middle schools located in Seoul.
METHODS
574 out of 600 middle school students in Seoul (95.7%) completed the study.
RESULTS
Satisfaction rate of school meals was significantly higher among girls (73.2%) compared to boys (45.1%). The reasons for satisfaction factors of school meals were with the taste of school meals (55.1%), menu (19.3%), nutrition (14.2%), and food hygiene safety (7.0%). Students who had a double-income family, well-educated mother and higher happiness in their life reported a higher satisfaction with school meals. Both boys and girls who consumed milk frequently showed significantly higher satisfaction with school meals. Factors that were related to satisfaction of school meals were food temperature, the amount of food (especially among boys). Variety in the menu and food distribution speed were less related to the satisfaction of meals. In the case of girls, waiting time, food distribution speed were more important to them while the kindness of school staff was a less important factor. Improvements that were needed to increase the satisfaction for the school lunch meals, from the most important to least important were as follows: variety of meals (36.6%), food distribution speed·waiting time (24.6%), taste of food (15.7%), amount of food (7.7%), hygienic management (5.1%), food quality (4.7%), kindness (3.0%), temperature of the food (2.8%). Students preferred to broadcast on campus and cooking practice for the dietary education.
CONCLUSIONS
To improve school meal satisfaction, it is necessary for food distribution facilities to make improvements with regard to variety of meals and reduced waiting time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and evaluation of an intervention to improve food and nutrition literacy among Iranian Kurdish primary school children: An application of intervention mapping approach
Mohammad Ahmadpour, Nasrin Omidvar, Elham Shakibazadeh, Azam Doustmohammadian, Abbas Rahimiforoushani
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility Study on Application of Revised Nutritional Standards for School Lunches: Consumer Satisfaction Survey
Meeyoung Kim, Youngmin Nam
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(5): 367. CrossRef - Improving Perception and Satisfaction on Middle and High School Foodservice: The Role of Student Participation Program in Serving School Meals
Jeong-Eun Park, Kyung-Suk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 243. CrossRef
- Development and evaluation of an intervention to improve food and nutrition literacy among Iranian Kurdish primary school children: An application of intervention mapping approach
- 1,930 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of Nutrition Education Contents for Pregnant Women Based on Effective Communication Strategies
- Taeksang Yoo, Young Hee Han, Jung Hyun Kim, Min Jun Lee, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(2):115-126. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.2.115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to develop communication strategies for effective nutrition education targeting pregnant women and to create nutrition education contents.
METHODS
The format and the contents of online resources on nutrition information for pregnant women provided by reliable institutions were analyzed. Possible solutions to overcome barriers of nutrition education as well as communication strategies for effective nutrition education were identified by a brainstorming process. Based on the communication strategies, contents for nutrition education were created. Understandability, level of interest, applicability to daily life, harmony of text and illustration, and overall satisfaction of the contents were evaluated by dietitians and pregnant women.
RESULTS
The four communication strategies were developed; (1) to focus on a few important messages, (2) to provide evidence-based information, (3) to create illustrations or infographics with a minimum amount of text, and (4) to provide tips on how to improve the current diet options. Based on these strategies, the contents were focused on three important nutrients for pregnant women, folate, iron, and calcium. The percentages of the recommended nutrient intakes of the three nutrients on selected menu and its improved version by adding a dish or changing a dish into another dish were calculated and provided. Finally, the contents were delivered as illustrations with a minimum amount of text. Overall, dietitians and pregnant women were satisfied with the contents.
CONCLUSIONS
The contents developed in this study can be used in a pamphlet or a pregnancy diary, or can be shared in social networking services. Further contents on other nutrients and various menu are expected to be developed using these communication strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Education Materials as a Card News Format for Nutrition Management of Pregnant and Lactating Women
Young-Hee Han, Jung Hyun Kim, Min Jun Lee, Taeksang Yoo, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 248. CrossRef
- Development of Education Materials as a Card News Format for Nutrition Management of Pregnant and Lactating Women
- 1,655 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- The Development of ‘Good Dietary Life Guide’ Textbooks for Elementary School Students
- Eun Young Sang, Jeong Weon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(1):74-83. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.1.74
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to develop dietary education textbooks for elementary school students by focusing on the three core values of environment, health and gratitude from the National Food Education Plan.
METHODS
The contents of textbooks and teacher's guidebooks were developed with brainstorming of the authors as well as consultation with experts and by considering not only the three core values of environment, health, and gratitude, but also the performance indicators of the 2nd National Food Education Plan and the key competencies and creative convergence approach of the 2015 revised national curriculum.
RESULTS
A total of 12 different dietary education textbooks named ‘Good Dietary Life Guide’ and the teachers' guidebooks from the first to the sixth grade of elementary school were developed. The textbooks were fundamentally developed connecting the three core values, the outcome indices of the 2nd National Food Education Plan and the key competences of the 2015 revised national curriculum. Various educational activities such as thinking, debate, writing, cooperative learning, experience, practice were included to promote students' participation. These books could be utilized in every field of dietary education targeting elementary students such as creative experiential activity, convergent classes (integrated subjects, Practical arts, Social studies, Science, Moral education and Korean), after school classes, rural experience, general agricultural education, after-school child care services and community child care centers.
CONCLUSIONS
The continuous and repetitive use of the textbooks from the first to the sixth grade would contribute to the improvement of food habits and the personalities of elementary school students, and consequently make the students grow up as healthy citizens. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Educational Board Game for Dietary Education; ‘Food-Bicycle’
Jung Hoon Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2018; 27(5): 411. CrossRef
- Development of Educational Board Game for Dietary Education; ‘Food-Bicycle’
- 1,251 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Mother's Parenting Style at Meal Time and Their Preschooler's Dietary Behavior
- Soyeon Park, Youngmee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(1):13-21. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to evaluate the nutrition quotient (NQ) by mother's parenting style which may influence the NQ in preschool children.
METHODS
Subjects were 310 mothers and their 4-6 year old children. The questionnaire composed of demographic characteristics, mother's parenting style at meal time and eating behavior as measured by NQ questions. The NQ questions consisted of 19 food behavior checklist items and all items were grouped into 5 factors: balance, diversity, moderation, regularity, and practice. Mother's parenting style was classified by using words for nutrition education at meal time. All data were statistically analyzed by SPSS program (Ver. 23) and the statistical differences in variables were evaluated by Student's t-test, χ²-test, One-way ANOVA.
RESULTS
We observed that in children whose mothers use the parenting style at meal time of ‘explanation’ and ‘compliment & cheer up’ had high dietary regularity, diversity, practice. The children of mothers who use the parenting style at meal time of ‘persuasion’ and ‘reward’ were found to have a lower degree of balance, diversity, and practice. Especially, children of ‘reward’ style mothers had lower moderation of dietary life. On the other hand, among the parenting style at meal time of ‘comparison & demand’, ‘treating’ and ‘faire’, there was no significant difference in the NQ factor by each group. NQ grade was higher among those who used more explanation (p < 0.001) and persuasion (p < 0.01) and with use of less persuasion (p < 0.01) and reward (p < 0.01). The positive association observed between the frequency of dietary education of mothers and higher NQ grade indicated the degree of dietary practices of those children. On the other hand, the children of mothers who rarely practice the dietary education at home had lower NQ grade (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
In order to promote children's proper dietary behaviors, it is important to provide nutrition education to children as well as provide guidance on parenting style at meal time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Designing Interactive Edutech Content to Improve Young Children’s Eating Habits: Focusing on AR Glasses and IoT Chopsticks
Juhyeon Jeon, Dhahye Shin, Yujin Joung, Yoon-Ju Cho
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(10): 2905. CrossRef - Association between Picky Eating Behavior, Growth, and Dietary Practices in Preschool Children
Jisun Kim, Sukyoung Kang, Seunghee Kye
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Study on Recognition and Consumption Behavior of Quality-Certified Children's Preferred Foods of Nursery Directors and Parents in Jecheon Area
Sung Hee Min
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2017; 33(3): 353. CrossRef
- Designing Interactive Edutech Content to Improve Young Children’s Eating Habits: Focusing on AR Glasses and IoT Chopsticks
- 1,294 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Application and the Effect of Nutrition Education Program Based on the Social Cognitive Theory Among Middle School Girls
- Jihea Kim, Taejung Woo, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):497-508. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.497
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of nutrition education using materials based on social cognitive theory. Education topics focused on improving health-related and dietary self-awareness and behavior capability in adolescents.
METHODS
Participants were recruited from a middle school for girls; 67 students (educated group, n=34 and control group, n=33) participated. The education group received 12 lessons in club activity class. Self-administered surveys were conducted for each group before and after the nutrition education program. The questionnaires consisted of variables such as self-efficacy, outcome expectation, outcome expectancy, knowledge, and dietary practices based on the social cognitive theory. Education satisfaction was evaluated using a five-point Likert scale for two sections: a) teaching and learning and b) education results. The data were analyzed using a t-test and Chi Square-test (significance level: p < 0.05).
RESULTS
In the education group, post-education, there were significant differences in self-efficacy (p < 0.05), knowledge (p < 0.01), and dietary practices (p < 0.05), whereas outcome expectation and expectancy did not show any significant differences. None of the variables showed any significant differences in the control group. Educational satisfaction scores were 4.38 ± 0.12 (teaching and learning) and 4.14 ± 0.15 (education results).
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that improving adolescent's awareness and behavior capability has a positive effect on their dietary practices. Moreover, this study suggested that a theory-based determinant should be considered to improve dietary behavior among adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultivating health: the role of interventionist actions in promoting vegetable consumption among children
Letícia Malherbi Byczkovski, João Lucas Mota Nogueira da Costa, Daiana Novello
Caderno Pedagógico.2025; 22(12): e20716. CrossRef - Survey on consumer perceptions, health benefits and preferences of kindergarten and school foodservices in Korea, including related keywords reported in newspaper: a mixed-methods study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 309. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 167. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Education Experience (Home, School, and Mass Media) on Food Consumer Information literacy
Ji Eun Kim, Kyoung Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 363. CrossRef - Factors affecting preference of vegetable in elementary school students: based on social cognitive theory
Su Hyeon Cha, Ho Kyung Ryu
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(3): 285. CrossRef
- Cultivating health: the role of interventionist actions in promoting vegetable consumption among children
- 1,642 View
- 19 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Status and Need Assessment on Nutrition & Dietary Life Education among Nutrition Teachers in Elementary, Middle and High Schools
- Na Gyeong Oh, Su Jin Gwon, Kyung Won Kim, Cheong Min Sohn, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(2):152-164. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.2.152
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the status and need for nutrition and dietary life education among nutrition teachers at schools. These characteristics were analyzed if they were different between elementary schools and middle-high schools.
METHODS
Subjects were 151 nutrition teachers from 70 elementary schools, 41 middle schools and 40 high schools in 17 cities nationwide selected by two-stage stratified cluster sampling process. Survey questionnaires included the items on general characteristics, status and need assessment for nutrition and dietary life education. Chi-square test or t-test was used for data analysis by school groups.
RESULTS
Nutrition education was implemented at 65.7% of elementary schools and 51.9% of middle-high schools. Nutrition education was mainly performed in 'discretionary activities·extracurricular activities' at elementary school and through 'newsletters, school homepage, foodservice bulletin board' at middle-high school (p<0.001). The most needed topic for nutrition education in nutrition teachers was 'healthy dietary habits and table manners' and this was not significantly different by school groups. Responses on adequate frequency (p<0.01), methods used for nutrition education (p<001), materials for nutrition education (p<0.001), information sources for nutrition education (p<0.001) were significantly different by school groups. Major tasks for activating nutrition education included 'securing the time for implementing nutrition education by reducing work loads' and 'developing standardized nutrition education materials' in schools.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutrition education at schools might be activated by improving working conditions of nutrition teachers and developing the practical programs that reflect the needs of nutrition teachers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 16. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef - Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef - Nutrition teacher’s perception and current status of nutrition education for free learning semester program: a preliminary study
Mi Joo Park, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 24. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Need for Obesity Prevention Education Programs through Analysis of Factors Affecting Student Obesity Factors in Seoul during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Seoung Hi Kim, Seonyeong Baek, Min Jeong Choi, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 214. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 167. CrossRef - Analysis of the consumer perception and related education effect on the reduction of sugar for elementary school students in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do
Ki Nam Kim, Jung Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hae Kyung Chung, Hae Rang Chung, Moon-Jeong Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(3): 303. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Quality and Nutritional Status according to the Use of Nutrition Labeling and Nutrition Claims among University Students in Chungbuk Area: Based on Nutrition Quotient
Yun-Jung Bae, Seo Young Park, Hye-Rin Bak
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 179. CrossRef - What Are the Barriers at Home and School to Healthy Eating?: Overweight/Obese Child and Parent Perspectives
Hee Soon KIM, Jiyoung PARK, Yumi MA, Mihae IM
Journal of Nursing Research.2019; 27(5): e48. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Education Experience (Home, School, and Mass Media) on Food Consumer Information literacy
Ji Eun Kim, Kyoung Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 363. CrossRef - Status and Needs Assessment on Nutrition Management and Meal Service for Elementary · Middle · High School Athletes among Athlete's Parents
Jung Hyun Hwang, Ji Yeon Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 47. CrossRef - Status and needs of nutrition education for children's sugars intake reduction in elementary school
Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 433. CrossRef - Current status of dietary education in elementary, middle and high school in Gyeonggi province: Comparison according to school level and placement of nutrition teacher
Youngmi Lee, Soo Youn Kwon, Ji Hea Kim, Ok Sun Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(6): 645. CrossRef - Evaluation of educational school meal programs in Gyeonggi province, South Korea
Youngmi Lee, Oksun Kim, Uiok Lee, Sooyoun Kwon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 111. CrossRef - Needs Assessment for Dietary Education Program Focused on the Increase of HAN-SIK (Korean Food) Consumption in Children and Adolescents Living in Jeonbuk and Gyunggi Areas
Sang-Eun Lee, Yangsuk Kim, Eun Mi Ahn, Young Hwang, Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2016; 27(S): 609. CrossRef
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- 1,658 View
- 10 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- Developing Food Safety Education Program for Employees at School Foodservice Implementing HACCP
- Hye Yeon Lee, Hyun Joo Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):84-92. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.84
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to develop a food safety education program for school foodservice employees and evaluate its effectiveness.
METHODS
Food safety education programs were made into two levels; one for new employees in school foodservice and another for employees in charge of Critical Control Point (CCP) monitoring. The programs were for 40-minute-long lecture using PowerPoint. The effectiveness of these programs were assessed based on eleven evaluation items by school foodservice dieticians (n=30) and the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) specialist (n=13). All statistical analyses are conducted by SPSS package program (ver 20.0).
RESULTS
According to the results of evaluating the food safety education program by dietitian and HACCP specialist, the overall satisfaction score was 4.14, evaluated by 5 point scale. There were no significant difference in results of evaluation between dieticians and HACCP specialists. The score of 'it is helpful to work' and 'pictures, images and charts are pertinent to study' were higher than others while the score of 'education contents is pleasant and interesting' and 'screen is pleasant and interesting' were the lowest among all evaluation items.
CONCLUSIONS
To increase the school foodservice quality, employees should be offered regular food safety education and training through effective education media including prerequisite program and HACCP manual for school foodservice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
해림 조, 서진 김, 중범 김, 수연 김
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2025; 41(3): 151. CrossRef - Analysis of the implementation of legislation mandatory requirements in organizing meals in schools of the Sverdlovsk region
Tatiana Mazhaeva, Valentina Kozubskaya, Elena Potapkina
Food Industry.2025; 10(2): 67. CrossRef - A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
Seo Young Choi, Hyun joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 286. CrossRef - Assessment of Effectiveness of Inspections and Preventive Measures
in Organizing School Meals
Valentina I. Kozubskaya, Tatyana V. Mazhaeva, Elena P. Potapkina, Vladimir B. Gurvich
ЗДОРОВЬЕ НАСЕЛЕНИЯ И СРЕДА ОБИТАНИЯ - ЗНиСО / PUBLIC HEALTH AND LIFE ENVIRONMENT.2025; : 57. CrossRef - Perception on HACCP System of School Foodservices Dietitians in Chungbuk
Ji Hyeoun Im, Miao Miao Li, Young Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2019; 35(1): 57. CrossRef - Perception of Use of Environment-friendly Agricultural Products during School Foodservice of Mothers of Elementary School Students in Gyeonggi
Young-Un An, Myung-Hee Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 234. CrossRef
- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
- 1,571 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education Providing School Lunch by Personalized Daily Needed Food Exchange Units for Adolescent Athletes in Jeonbuk Province
- Kang Mo Ko, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):25-36. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of nutrition education providing school lunch by personalized daily needed food exchange units using Food Exchange System for adolescent athletes.
METHODS
The subjects were 60 sports high school students (educated group, 30 vs. non-educated group 30). Nutrition education was provided for 4 weeks (40 min/lesson/week). In addition, personalized school lunch was served for 4 weeks, nutrition education period. The personalized lunch were provided Food Exchange Units according to personalized daily needed energy. The lessons were '5 Major nutrients, functions and foods', 'My daily needed energy and food exchange units by Food Exchange System', 'My meal plan by food exchange units according to my daily needed energy' and 'Smart choice of healthy snacks and eating outs'. After nutrition education, we examined the differences in anthropometric characteristics, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and dietary intake between the educated and the non-educated group.
RESULTS
We observed improvements in lean body mass in the educated group. With regard to nutrition knowledge, there were improvements in 'Functions of vitamins', 'Functions of minerals', 'Foods of fat', 'Foods of vitamin', and 'Foods of mineral' in the educated group. In relation to dietary attitude, there were improvements in 'Taking a meal with family and friend', 'Taking a meal at ease', 'Taking a meal with kimchi and vegetables', 'Taking a meal with three kinds of side dishes', 'Priority of choosing snacks' and 'Type of snacks' in the educated group. With regard to dietary intakes according to Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans, there were improvements in intakes levels of fiber, vitamin A, vitamin C, folate, calcium, iron and zinc. The index of nutrition quality, as indicated by nutrition adequacy ratio also improved in the educated group.
CONCLUSIONS
These results showed that a nutrition education program providing education lessons and personalized school lunch by food exchange units according to daily needed energy showed positive changes in nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and dietary intake of adolescent athletes. Nutrition education program providing personalized school lunch by Food Exchange Units may improve dietary behaviors and dietary intakes of adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition Quotient and Dietary Self-efficacy according to the Transtheoretical Model in Adolescent Athletes
Nahan Kim, Kwang-Seok Hong, In-Kyung Jung
Exercise Science.2022; 31(4): 499. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to the Frequency of Milk Consumption in Korean Adolescents: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ji Hyun Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 485. CrossRef - Status and Needs Assessment on Nutrition Management and Meal Service for Elementary · Middle · High School Athletes among Athlete's Parents
Jung Hyun Hwang, Ji Yeon Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 47. CrossRef - Evaluation of educational school meal programs in Gyeonggi province, South Korea
Youngmi Lee, Oksun Kim, Uiok Lee, Sooyoun Kwon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 111. CrossRef
- Nutrition Quotient and Dietary Self-efficacy according to the Transtheoretical Model in Adolescent Athletes
- 1,585 View
- 10 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of an Education Program on Sanitation Status at Centers for Children's Food Service Management: Focusing on Jung-gu and Dong-gu regions of Daejeon Metropolitan City
- Yu Jin Seo, Min Sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):447-459. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.447
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to assess the improvement of teachers' sanitation performance and food distribution environment at Centers for children's food service management after a sanitation education program.
METHODS
The subjects were 119 teachers working at child care centers registered in the Daejeon Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Dongu and Jung-gu, Daejeon. The sanitation education was provided three times from March to August in 2014, and the survey questionnaires were distributed before and after the education. The sanitation status of food service environment of the centers was examined by ATP(adenosine-5'- triphosphate) bioluminescence.
RESULTS
After the sanitation education, the teachers showed higher levels of sanitation knowledge. Also, sanitation performance and recognition level of the importance of it significantly improved after the education program. The mean variation scores of importance and performance after the education were 0.14 and 0.23. According to the Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA) results of 26 sanitation attributes about the food service environment, the selection attributes with relatively low performance and importance were mostly distributed in the children's and distributer's personal hygiene management area. However, all attributes except using a personal water bottle and cup were moved to high performance and importance level. Also, the ATP examination results showed that the sanitation status of the food service environment was improved after the education program.
CONCLUSIONS
The sanitation education program was effective in improving the recognition of the importance of sanitation and its performance with regard to food service management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
해림 조, 서진 김, 중범 김, 수연 김
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2025; 41(3): 151. CrossRef - Relationship with the Perception of Foodservice, Nutritional Knowledge, and Foodservice Guidance of Day-Care Center Teachers in Gangwon Area
Seung-Lim Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(3): 203. CrossRef - Relationship between the Nutrition Quotient, Sustainable Diets, and Meal Guidance of Day-Care Center Teachers according to the Type of Day-Care Center : Focus on the Gangwon Area
Seung-Lim Lee, Ji-Hye Kim, Hye-Ji Oh, Myeong-Jong Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 262. CrossRef - A Study of Food Safety Knowledge for Sustainable Foodservice Management of Childcare Centers in South Korea Using Importance–Performance Analysis
Jeong-Sil Choi, Se-Young Ju
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(15): 9668. CrossRef - Evaluation of Food Safety Management Status of Children’s Foodservice Facilities Using Sanitary Check Scores and ATP Bioluminescence Assay in Gyoengbuk Area
Kyung-A Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(2): 196. CrossRef - Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
Na-Yeong Lee, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - Research trends in obesity & obesogenic environments in Korea
Myoungsook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2019; 13(6): 461. CrossRef - Effects of Periodic Visiting Education Support on the Sanitation Management of Foodservice Facilities for Children in the Local Small City: A Focus on the Yecheon-gun Area
Hye-Jin Pak, Chan-Ick Cheigh
Food Engineering Progress.2019; 23(3): 200. CrossRef - Analysis of Sanitary Safety Management Improvement for Children’s Food service in Chilgok-gun Area
Suk-Hyeon Park, Hyeon-A Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(5): 345. CrossRef - The Effect of Personality Type and Job Performance on Emotional Exhaustion and Job Satisfaction - Staff of the Center for Children's foodservice management -
Kyung-Min Lee, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(6): 496. CrossRef - A study on the optimal variable transformation method to identify the correlation between ATP and APC
Hye-Kyung Moon, Jae-Kyoung Shin, Yang Sook Kim
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(6): 1465. CrossRef - A Comparison of Hygiene and Safety Management Execution depending on the Characteristics of Children's Food Service Facilities
Jin-Young Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(4): 573. CrossRef
- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
- 1,435 View
- 4 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Consumer Nutrition Education Program to Reduce Sodium Intake Based on Social Cognitive Theory
- So Hyun Ahn, Jong Sook Kwon, Kyung Min Kim, Jin Sook Yoon, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):433-446. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.433
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to evaluate the consumer education program for reducing sodium intake based on social cognitive theory (SCT) and investigate consumer perceptions of environmental, cognitive and behavioral factors.
METHODS
Consumers (n=4,439) were recruited nationwide in Korea to participate in a nutrition education program for reducing sodium intake which was targeted on senior housewives (SH), parents (P), and office workers (OW). Questions regarding main factors of SCT were asked both before and after the education program.
RESULTS
SH and P recognized external social efforts and information to reduce sodium including nutrition labeling more than OW. The main barriers to practice reducing sodium intake were limited choice of low sodium food and menu, interference with social relationship when dining with others, and limited information, knowledge and skills. SH had lower barriers to practice reducing sodium intake and OW perceived 'preference to soup or stew' and 'preference to Kimchi, salted fish and fermented sauces' as barriers more than other groups at the baseline. Less than 50% of participants knew the relationship between sodium and salt, sodium in nutrition labeling, and recommended sodium intake. In addition, OW had little knowledge for capability to reduce sodium intake and lower self-efficacy to practice compared with SH and P. After education, positive outcome expectations such as lowering blood pressure, prevention of cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis were increased and barriers to practice reducing sodium intake were decreased in all groups (p < 0.05). The knowledge for behavioral capability and self-efficacy to reduce sodium intake were also improved but OW had still lower scores compared with other groups.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggested that nutrition education programs could be an effective tool to impact general population by facilitating awareness and increased capability to reduce sodium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Consumer acceptance of reduced sodium white and multigrain bread: Impact of flavor enhancement and ingredient information on sample liking
Aubrey N. Dunteman, Soo‐Yeun Lee
Journal of Food Science.2023; 88(1): 417. CrossRef - The frequency of convenience food consumption and attitude of sodium and sugar reduction among middle and high school students in Seoul: a descriptive study
Seoyeon Park, Yeonhee Shin, Seoyeon Lee, Heejung Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 269. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a nutrition education program for housewives to reduce sodium intake: application of the social cognitive theory and a transtheoretical model
Sohyun Ahn, Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 174. CrossRef - Customers' Perceptions of Operational Status of and Needs for Sodium Reduction in the Industry Foodservice in Seoul
Na-Young Yi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 21. CrossRef
- Consumer acceptance of reduced sodium white and multigrain bread: Impact of flavor enhancement and ingredient information on sample liking
- 1,566 View
- 18 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- The Influence of Self-resilience on Dietary Management in Middle School Students
- Yunhwa Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):399-410. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.399
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study aims to identify self-resilience factors that drive right dietary and food safety practices in middle school students.
METHODS
Data was collected from 438 middle school students in Daegu using a self-administered questionnaire in December, 2013. The questionnaire consisted of 81 items with the following categories: general information, self-resilience, right dietary and food safety practices. Statistical analyses to determine frequency, average, ANOVA, factor analysis, reliability analysis, and regression analysis were performed using SPSS 21.
RESULTS
The results of factor analysis indicated that self-resilience was classified into challenge, adaptability, patience and achievement needs, and right dietary practices were sub-grouped into family meals, experience of dietary life, eco-friendly, balanced food, economy and bad food control, and food safety practices consisted of management of bacteria, hand washing and eating off a plate, safety food and food purchasing. The score of right dietary and food safety practices showed significant differences by sex, grade, and school achievement (p < 0.05). The economy factor of right dietary practices was significantly affected by the management of bacteria (p < 0.001), hand washing and eating off a plate (p < 0.001), safety food (p < 0.01), food purchasing of food safety practices (p < 0.05). The challenge factor of self-resilience significantly affected family meals, experience of dietary life, balanced food, economy, bad food control, management of bacteria, hand washing and eating off a plate, and safety food (p < 0.05). The adaptability factor of self-resilience was associated with factors such as eco-friendly, balanced food, economy, bad food control, management of bacteria, hand washing and eating off a plate, and food purchasing (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that dietary education programs for middle school students could incorporate food safety practices, and self-resilience such as challenge, adaptability, patience and achievement needs to be effective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the connection between ego-resiliency and health behaviors: a cross-sectional study of Polish health sciences students
Małgorzata Dębska-Janus, Paweł Dębski, Agnieszka Nawrocka, Jacek Polechoński, Wojciech Madejczyk, Karina Badura-Brzoza
BMC Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring the connection between ego-resiliency and health behaviors: a cross-sectional study of Polish health sciences students
- 1,484 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- The Development of a Nutrition Education Program for Low-income Family Children by applying the Social Cognitive Theory and Health Belief Model
- Saes Byoul Lee, Yu Ri Jeong, Hyo Jin Ahn, Min Ji Ahn, Su A Ryu, Nam E Kang, Se Young Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(3):165-177. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.3.165
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - OBJECTIVES
Based on individual and environmental characteristics of low-income children, we developed a nutrition education program for school-aged children from low-income families according to effective use in social welfare centers.
METHODS
We conducted in-depth group interviews to assess program needs in 28 participants, 10 low-income school-aged children and 9 of their care givers, 9 social workers and 9 care-givers. Theoretical backgrounds of our program were heath belief model and social cognitive theory considering motivation, action and environment characteristics.
RESULTS
Based on the findings of this qualitative study, we developed major program themes and contents. Five selected key themes were 'balanced diet', 'processed food', 'food hygiene and safety', 'Korean healthy traditional diet', and 'family cooking' to induce changes in dietary behaviors. Main findings of in-depth group interviews included 'child's active participation', 'simple and easy to understand messages', and 'environmental constraints' such as a lack of child care at home, limited budget of social welfare centers, and less qualified educators for nutrition and health. Each lesson was constructed as a 1-hour program particularly emphasizing activity-based programs, including cooking and teamwork exercises. Program contents in each session consisted of activities that could induce outcome and value expectations, self-efficacy, perceived benefits, and barriers and cues to actions regarding diet behavior.
CONCLUSIONS
We developed a nutrition education programthat is rarely available for low-income children in Korea, considering theoretical bases. Further studies are needed to validate our program. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Multidisciplinary Health Promotion Program Among Children in Community Childcare Center
Yerin Kim, Gyeong Seob Shin, Jungwon Park, Minji Kang, Kumhee Son, Yoon Myung Kim, Kyung Hee Park, Hyunjung Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(1): 8. CrossRef - Developing educational programs to increase awareness of food additives among elementary school students
Soo Rin Ahn, Jae Wook Shin, Jung-Sug Lee, Hyo-Jeong Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(4): 451. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
Ji Suk Yim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Need for Obesity Prevention Education Programs through Analysis of Factors Affecting Student Obesity Factors in Seoul during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Seoung Hi Kim, Seonyeong Baek, Min Jeong Choi, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 214. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Program Designed to Reduce Sugar Intake in Preschool Children
Ma-Young Yeom, Youn-Ok Cho
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(3): 179. CrossRef - Status of Dietary Life Related Knowledge, Self-Efficacy, Food Preference and Dietary Behavior of Preschoolers in Kyunggi Area
A Reum Lee, Ye Lee Yu, Hye Jin Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 274. CrossRef - Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(4): 332. CrossRef
- Effects of Multidisciplinary Health Promotion Program Among Children in Community Childcare Center
- 1,504 View
- 12 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effects of Low-sodium Diet Education Program on Dietary Habits, Diet Quality and Obesity Index in Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women
- Soo Bin Jeong, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Jin Nam Kim, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):513-526. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.513
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of low sodium diet education program on dietary habits, diet quality, and measures of obesity in overweight or obese middle-aged women.
METHODS
Subjects were 81 individuals aged 45 years or over, who completed an 8-week nutrition education. The subjects were divided into a normal group (N = 30) and an overweight-obese group (N = 51) according to the BMI. The effects were evaluated by anthropometric measurement, biochemical analysis, questionnaire, and diet records before and after the program.
RESULTS
Overweight-obese group showed significant decreases in weight (p < 0.0001), BMI (p < 0.0001), percent of body fat (p = 0.0087), waist circumference (p < 0.0001), systolic (p = 0.0003) and diastolic blood pressure (p = 0.0261). Nutrients intakes were not different between the two groups and only sodium intake was decreased after education. Total score of general dietary habits, dietary behavior related to sodium intake, dietary diversity score (DDS), diet variety score (DVS), and diet quality index-international (DQI-I) were improved in both groups compared to the baseline. Overweight-obese group showed significant improvement in 'having fruits everyday', 'having fish everyday', 'trying to eat many kinds of food', 'eating less broth when eating soup, stew, and noodles', 'eating less kimchi and salt-fermented vegetable', and 'propensity to think that dishes should be pretty seasoned'. In addition, moderation of empty calories food (p = 0.0064) and macronutrient ratio (p = 0.0004) were improved in the overweigh-obese group, but in the normal group, the results did not reach statistical significance.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggested that low sodium diet education program may contribute to obesity management by improving diet quality and dietary habits in middle-aged women.
- 1,129 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- A Study of Hospital-based Home-Visit Nutrition Education Needs of Patients at Discharge
- Su Mi Ahn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(4):386-400. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.4.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to provide a basic data of nutrition services in home health care by analyzing hospital-based home-visit nutrition education needs of patients at discharge.
METHODS
Data was collected from September 11 to October 12, 2012 by administering questionnaires to 289 chronic disease patients to be discharged from a university hospital in Pusan. The home-visit nutrition education instruments used for collecting data were developed by the researcher.
RESULTS
Regarding the demands of home-visit nutrition education, 62.3% of subjects were willing to use home-visit nutrition education and 37.7% weren't. The main reason for using the home-visit nutrition education was "the effective nutrient management in consultation with an individual's doctor", 38.9% and 31.2% of patients who did not wish to use the service gave the reason for their decision as, "Just by managing the nutritional requirements of a family's diet and, the patient will be able to fully recover", respectively. As for the demand, classified with the areas of home-visit nutrition education, the demand for the area of basic nutrition (3.75/5.00) was the highest followed by, the area of educational nutrition (3.74/5.00), therapeutic nutrition (3.67/5.00), and dietary nutrition (3.55/5.00). The demand for the area of educational nutrition was high "Considering the state of dietary management, such as disease status and drugs", 73.7%. As for the relation between the characteristics of the study subjects and analysis of demand home-visit nutrition education, the characteristic of subjects, that is, "regular home-visit nutrition education", "practice of diet therapy after discharge" had a significant difference statistically (p < 0.01). As for the relation between the needs for fundamental home-visit nutrition education and the demand of home-visit nutrition education, basic nutrition, educational nutrition, therapeutic nutrition, and dietary nutrition had a significant difference statistically (p < 0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
Hospital-based home-visit nutrition education need the access of home nutrition support team.
- 1,129 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Development of Nutrition Education Program for Consumers to Reduce Sodium Intake Applying the Social Cognitive Theory: Based on Focus Group Interviews
- So Hyun Ahn, Hye Kyeong Kim, Kyung Min Kim, Jin Sook Yoon, Jong Sook Kwon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(4):342-360. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.4.342
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to develop nutrition education program for consumers to reduce sodium intake based on social cognitive theory (SCT).
METHODS
The main factors of SCT related to low sodium diet were investigated by using focus group interview (FGI) with 30 women who participated in consumer organizations.
RESULTS
The main target groups for the education program were housewives (H), parents (P), and the office workers (OW), for which we considered their influences on other people and the surroundings. According to the results of FGI, in carrying out low sodium diet, 'positive outcome expectation' were prevention of chronic disease and healthy dietary habit, and 'negative outcome expectation' were low palatability of foods, difficulty in cooking meals, and limited choice of foods. The contents of the program and education materials were individualized by each group to raise self-efficacy and behavioral capability, which reflected the results of the FGI. The program included 'salt intake and health' to raise positive outcome expectation. For improving the ability to practice low-sodium diet, the program contained the contents that focused on 'cooking' and 'food purchasing' for H, on 'purchasing and selection of low-sodium food with the children' for P, and on 'way of selecting restaurant menu' for OW. Also the program included 'way of choosing the low-sodium foods when eating out' with suggestions on sodium content of the dishes and snacks. Further, 'dietary guidelines to reduce sodium intake' was also suggested to help self-regulation.
CONCLUSIONS
This nutrition education program and education materials could be utilized for the community education and provide the basis for further consumer targeted education program for reducing sodium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
Ji-Won Kang, Su-Jin Lee, Sil-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 224. CrossRef - Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 382. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a nutrition education program for housewives to reduce sodium intake: application of the social cognitive theory and a transtheoretical model
Sohyun Ahn, Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 174. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
Ji Suk Yim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Reach Out Emergency Department: Partnering With an Economically Disadvantaged Community in the Development of a Text-Messaging Intervention to Address High Blood Pressure
Emily Champoux, Rory Price, Joan E. Cowdery, Mackenzie Dinh, William J. Meurer, Narmeen Rehman, Caitlin Schille, Alina Oliver, Devin L. Brown, Jordan Killingsworth, Lesli E. Skolarus
Health Promotion Practice.2020; 21(5): 791. CrossRef - Factors contributing to the reduction of sodium intake by food manufacture and cooking venues according to the national sodium reduction policies
Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park, Jee Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 648. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Awareness of Health Risks and the Risk Reduction Measures Related to Sodium Intake between Female and Male University Students in Busan and Gyeongnam: An Application of Protection Motivation Theory
Soo-Hyun Jang, Eunju Yoon
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(1): 136. CrossRef - School Dietitian Awareness, Practice, and Sodium Reduction Plan in School Meal Service
Eun Kyung Kim, Hae Young Kim
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 222. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Program Designed to Reduce Sugar Intake in Preschool Children
Ma-Young Yeom, Youn-Ok Cho
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(3): 179. CrossRef - Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(4): 332. CrossRef - ‘When operating a cafeteria, sales come before nutrition’ – finding barriers and facilitators to serving reduced-sodium meals in worksite cafeterias
Sohyun Park, Jounghee Lee
Public Health Nutrition.2016; 19(8): 1506. CrossRef - Study on Energy and Nutrient Intake and Food Preference of the Elderly in Care Facilities
Jong-Sook Kwon, Seung Hee Lee, Kang Min Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 200. CrossRef - Evaluation of Consumer Nutrition Education Program to Reduce Sodium Intake Based on Social Cognitive Theory
So-Hyun Ahn, Jong Sook Kwon, Kyung Min Kim, Jin-Sook Yoon, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(6): 433. CrossRef - The Development of a Nutrition Education Program for Low-income Family Children by applying the Social Cognitive Theory and Health Belief Model
Saes-byoul Lee, Yu-Ri Jeong, Hyo-Jin Ahn, Min-Ji Ahn, Su-A Ryu, Nam-E Kang, Se-Young Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(3): 165. CrossRef
- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
- 1,490 View
- 7 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [English]
- Blood Pressure, Sodium Intake and Dietary Behavior Changes by Session Attendance on Salt Reduction Education Program for Pre-hypertensive Adults in a Public Health Center
- Eun Jin Jung, Jong Sook Kwon, So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(6):626-643. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.6.626
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to evaluate the differences in blood pressure, sodium intake and dietary behavior changes according to the extent of session attendance on sodium reduction education program for pre-hypertensive adults in a public health center. Sodium reduction education program consisted of 8 sessions for 8 weeks. Fifty three patients who completed the pre and post nutritional assessments were classified into 2 groups according to the session attendance rate. Nineteen participants who attended the education program 3 times or less (< or = 3) were categorized into the less attendance (LA) group and 34 participants attended 4 times or more (> or = 4) into the more attendance (MA) group. Blood pressure, anthropometric measurements, serum lipid profile, nutrient intakes including sodium, nutrition knowledge and dietary behavior score were assessed before and after the nutrition education program. Mean sodium intakes (p < 0.001), systolic/diastolic blood pressure (p < 0.001), and weight (p < 0.001) were significantly decreased in the MA group after sodium reduction education program. Compared to the MA group, mean sodium intakes, systolic/diastolic blood pressure were not significantly changed after the education program even with significantly increased nutrition knowledge (p < 0.05) and dietary behavior score (p < 0.01) in the LA group. It appears that pre-hypertensive adults need to attend the sodium reduction education program for at least 4 times or more to gain beneficial effects from the intervention. Positive feedback of healthcare team or offering more cooking classes may be needed to raise the attendance rate in the sodium reduction education program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Status of Recognition, Effort, and Satisfaction of Customers on Low-Sodium Diet in Industry Foodservice
Sang Jin Yoon, Kun Og Kang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(2): 168. CrossRef - Study of the characteristics of dietary behavior and the effects of nutrition education for sodium reduction according to the stages of behavioral change in sodium reduction of male adult subjects in Gwangju·Jeonnam regions
Young Ran Heo, Hyun Young Oh, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 472. CrossRef - The Effects of Hypertension Health School Program on Hypertension-related Knowledge, Self-efficacy, Self-care Behavior and Physiological Parameters in Hypertensive Patients
Koung Oh Chang
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(1): 49. CrossRef - Food Safety and Nutrition Education Program for Elderly and Assessment of Program Effectiveness Based on Health Belief Model
Jung-Hwa Choi, Eun-Sil Lee, Yoon-Jin Lee, Hye-Sang Lee, Hye-Ja Chang, Kyung-Eun Lee, Na-Young Yi, Yoon Ahn, Tong-Kyung Kwak
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2016; 45(9): 1366. CrossRef - Dietary Life related to Sodium of Participants in Hypertension and Diabetes Preventive Education at the Public Health Center
Hee-Ok Pak, Chun-Young Sohn, Jung-Hwa Park
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(2): 219. CrossRef - A Study on Eating Out Behavior and Recognition of Salinity in Restaurant Food in Jecheon Area
Soojin Park, Sung Hee Min
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(1): 20. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - The Study on Dietary Behavior and Health Related Behaviors of Self Perceived Sodium Intake Groups
Juhyeon Kim, Hei-Ryeo Yoon, Nam-E Kang
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(6): 511. CrossRef - The Relationship between Dietary Behaviors/health Risk Factors and Preference for Salty Taste among Korean Elderly People Living in Rural Areas
Mee Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(5): 448. CrossRef
- Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
- 1,313 View
- 2 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education for Chinese College Students in Korea: Focused on Personalized Daily Energy Requirement and Food Exchange Units
- Jia Li Guo, Soon Kyung Kim, Jeong Weon Kim, Mi Hyun Kim, Se Na Kim, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(6):565-576. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.6.565
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of nutrition education on nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and dietary intake of Chinese college students in Korea. The subjects were 64 Chinese college students in Korea (educated group, 32 students vs. non-educated group, 32 students). Educated group was lessoned as group and/or individual. Nutrition education program consisted of four lessons (40min / lesson), '6 major nutrients & function (group lesson)', '6 food group and sources (group lesson)', 'personalized daily needed energy and food exchange units using Food Exchange System (individual lesson)', and 'smart choice of snacks and eating-out foods (group lesson)'. We examined the differences between educated group and non-educated group in nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes and nutrients intake. After education, there were positive improvements on nutrition knowledge: 'function and foods of 6 nutrients', on dietary attitudes: 'type of breakfast' in educated group. In the evaluation of nutrient intakes according to Dietary Reference Intakes for Korean (KDRI), there were positive improvements on intake levels of riboflavin, fiber, vitamin B6, vitamin C, folate, Ca and K in the educated group. In the index of nutrition quality (INQ), nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean nutrition adequacy ratio (MAR) were significantly increased in the educated group. In conclusion, it is possible to improve nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and dietary intake of Chinese college students in Korea through the nutrition education focused on personalized daily needed energy and food exchange units.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Nutrition Education Based on the PRECEDE‐PROCEED Model on Improving the Nutritional Status and Growth Status of 7–12‐Year‐Old Malnourished Children in Kermanshah
Fatemeh Maleki, Shaghayegh Sharifi Soltani, Shahab Rezaeian, Mahmood Ghasemi, Mehnoosh Samadi
Food Science & Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of nutritional education based on the precede-proceed model on improving the growth indicators, knowledge, attitude, and food intake of malnourished children: study protocol for a randomized clinical trial
Fatemeh Maleki, Amir Bagheri, Shahab Rezaeian, Fatemeh Rajati, Mahmoud Ghasemi, Mehnoosh Samadi
Trials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education at a Community Health Center on Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women in Jeonbuk Area-Focused on Personalized Daily Energy Requirement and Food Exchange Units
Se-Yeon Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(4): 307. CrossRef - Comparisons of Health Related Lifestyle and Dietary Behaviors according to Gender, Ethnicity and Residence Type of University Students in Yanbian, China
Kyung Hee Hong, Unju Hwa Oh
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(4): 486. CrossRef - A Study on Weight Control Behaviour, Eating Habits and Health-related Life Habits According to Obesity Degree of University Students in Jeonbuk
Hye-Soon Chang
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(1): 73. CrossRef - Acculturation and changes in dietary behavior and anthropometric measures among Chinese international students in South Korea
Jounghee Lee, Ran-Ran Gao, Jung-Hee Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(3): 304. CrossRef - Survey on Health-related Factors, Nutrition Knowledge and Food Habits of College Students in Wonju Area
Seung Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(2): 96. CrossRef - A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
Zhe Sun, Wookyoun Cho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 441. CrossRef
- The Impact of Nutrition Education Based on the PRECEDE‐PROCEED Model on Improving the Nutritional Status and Growth Status of 7–12‐Year‐Old Malnourished Children in Kermanshah
- 1,517 View
- 1 Download
- 8 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



