Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Prevalence of coronary artery disease according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years and older: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Areum Song, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):457-470. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To examine the prevalence of coronary artery disease (CAD) according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years.
Methods
Data were derived from 11,025 participants aged ≥ 40 years in the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were assigned to a CAD group (n = 470) or a non-CAD group (n = 10,555). Socio-demographic characteristics (age, sex, residence, income, marital status, education level, and employment status), lifestyle characteristics (smoking, drinking, walking, strength training, sleep duration, stress level, and subjective health perception), energy and nutrient intakes, and comorbidities, including obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, stroke, cancer, depression, renal failure, cataract, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, and osteoporosis were analyzed.
Results
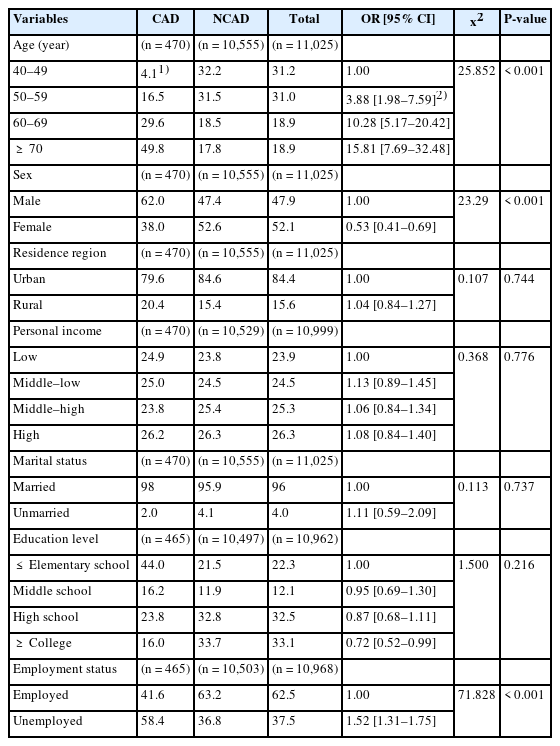
The prevalence of CAD was higher in older participants and in male. Participants with CAD had higher rates of smoking, engaged in less strength training, experienced higher stress, and had poorer perceived health. They had lower intakes of energy, fiber, folate and iron. The prevalence of obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, stroke, depression, renal failure, cataract, asthma, allergic rhinitis, osteoarthritis, or osteoporosis was significantly higher in the CAD group. The likelihood of having CAD was significantly higher among participants with renal failure (odds ratio [OR], 4.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.24–8.08), depression (OR, 2.14; 95% CI, 1.55–2.95), asthma (OR, 2.07; 95% CI 1.48–2.91), and dyslipidemia (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.69–2.44).
Conclusion
In Koreans aged 40 years, CAD was associated with unhealthy lifestyle habits, low nutrient intake, and increased comorbidities such as renal failure, depression, asthma, and dyslipidemia. These findings suggest the need for lifestyle management and intensive chronic disease management to reduce the risk of CAD.
- 534 View
- 39 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):352-363. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The dietary habits of school-aged children play a critical role in their growth and development, and are strongly influenced by the home environment. Household income is closely associated with caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. This directly affects the nutritional status of children. This study aimed to provide evidence to inform policies and educational programs for improving dietary habits in children, and to establish a foundation for tailored support strategies for low-income families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 846 primary caregivers of school-aged children from 17 regions across Korea, recruited through an online survey. Household income, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment were assessed. Nutritional status in children was measured using the Nutrition Quotient for Children (NQ-C). Statistical analyses included descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), correlation analyses, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Caregivers from higher income households demonstrated significantly greater food literacy and social support (P < 0.001). Children from these households showed high balance scores and a large proportion of these children were in the “high” NQ-C grade. The NQ-C score in children was positively correlated with food literacy (r = 0.425), social support (r = 0.471), and the food environment (r = 0.235) (P < 0.001). Multiple regression analysis showed that food literacy (β = 0.256) and social support (β = 0.348) were significant predictors of nutritional status in children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that the nutritional status in children is not only determined solely by household income but is also mediated by caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. These findings highlighted the limitations of providing only economic support. The findings underscore the need for multifaceted interventions such as strengthening parental nutrition education, expanding social support networks, and improving access to healthy foods.
- 822 View
- 42 Download

- [English]
- Self-reported weight change and diet quality in relation to metabolic syndrome among Korean cancer survivors: a cross-sectional study using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019–2021
- Hye Won Kim, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):341-351. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Using data from the 2019‒2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, we examined the association between dietary quality and metabolic syndrome by self-reported weight change among adult Korean cancer survivors.
Methods
We analyzed 340 cancer survivors (≥ 5 years post-diagnosis) by one-year weight change (stable, loss, and gain). Dietary quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI), and metabolic syndrome was defined according to standard criteria. Relative risks (RR) were estimated using a modified Poisson regression.
Results
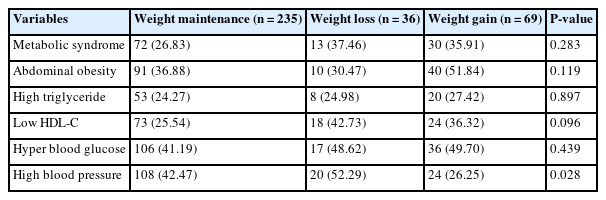
The weight loss group was older than the weight gain group (P < 0.001). Females were more prevalent in the loss and gain than in the maintenance group (P = 0.008). Hypertension prevalence was highest in the loss and lowest in the gain group (P = 0.028); other risk factors were similar. The gain group had the highest body mass index (P = 0.011). KHEI scores were highest in the maintenance (66.59 ± 0.76) and lowest in the gain group (60.42 ± 1.77; P = 0.006), with significantly lower whole grain (P = 0.036) and fruit intake (P = 0.014). Compared with the maintenance group, the gain group demonstrated higher risks of metabolic syndrome (RR: 2.07, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.40–3.06; P < 0.001), abdominal obesity (RR: 1.93, 95% CI: 1.36–2.74; P < 0.001), and impaired fasting glucose (RR: 1.70, 95% CI: 1.23–2.34; P < 0.01). Within the gain group, participants in the lowest KHEI quartile had increased risks of metabolic syndrome (RR: 2.81, 95% CI: 1.06–7.43; P < 0.05) and hypertriglyceridemia (RR: 7.29, 95% CI: 1.54–34.61; P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Accordingly, weight change and dietary quality may critically affect the metabolic health of cancer survivors. Lifestyle management, including weight control and tailored diets, may help prevent metabolic disorders and support long-term health.
- 1,133 View
- 26 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung–Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):150-162. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00038

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To determine the association between night eating habits and oral health in adolescents.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 were analyzed. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed the frequency of night eating per week, dietary habits, oral health characteristics, and factors affecting the presence of symptoms of poor oral health.
Results
Almost thirty-seven percent (36.6%) of Korean adolescents have eaten at night one to two times per week and 23.0% more than three times per week. An increased frequency of night eating was associated with poor dietary habits. Adolescents who consumed more at night were less likely to have breakfast, drink water, and eat fruit, while their consumption of fast food, sweet drinks, and high-caffeine drinks increased (P < 0.001). An increased frequency of night eating was also associated with poor oral health. In a logistic regression analysis, more frequent night eaters were significantly less likely to brush their teeth at least three times per day (odds ratio [OR], 0.78; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75–0.82; P for trend < 0.001), and brush their teeth before going to sleep (OR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.65–0.75; P for trend < 0.001), while they were more likely to experience sealant (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.13–1.26). More frequent night eaters were significantly more likely to have tooth fracture (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.30–1.53; P for trend < 0.001), tooth pain when eating (OR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.50–1.67; P for trend < 0.001), toothache (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.52–1.70), and bad breath (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.43–1.60).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that frequent night eating is linked to symptomatically poor oral health in adolescents. Therefore, oral health education programs related to dietary habits are necessary to reduce the potential of night eating to negatively influence dietary habits and oral health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Bo Young Park, Eun Bi Sim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(4): 370. CrossRef
- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,638 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):528-540. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine health-related characteristics and chronic disease risk in middle-aged Koreans based on their fat energy intake ratio.
Methods
We analyzed data from 7,274 Koreans aged 40–64 years using the 7th (2016–2018) Koreans National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were classified into three groups based on their fat energy intake ratio: insufficient (< 15%), adequate (15%–30%), and excessive (> 30%). We assessed their socio-demographic characteristics; lifestyle characteristics; biochemical characteristics; quantitative and qualitative nutrient intakes, measured using dietary reference intakes for Koreans and index of nutrition quality (INQ); and chronic disease risk.
Results
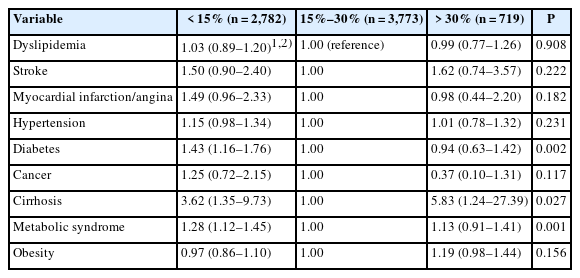
Significant differences were observed between the groups in age, gender, income, education, and residence region. The insufficient group had the highest proportion of older adults, male, lower income, rural residents, and lower education levels. The groups differed significantly in lifestyle characteristics, with the insufficient group having the highest rates of no walking, heavy drinking, smoking, and poor subjective health perception. Biochemical characteristics in the insufficient group exhibited the lowest levels for fasting blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and triglycerides. Significant differences were found in both the quantitative and qualitative intake of nutrients. The insufficient group had the lowest intake of most nutrients except fiber, whereas the excessive group had the lowest fiber intake. Based on the INQ, vitamin A and Ca were the lowest in the insufficient group, and vitamin C and folic acid were the lowest in the excessive group. The risk of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome was highest in the deficient group, and the risk of liver cirrhosis was highest in the excessive group.
Conclusion
Insufficient or excessive fat energy intake ratio negatively affects nutrient intake and chronic disease risk. Fat energy intake of 15%–30% is important for improving nutrient intake and managing chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and liver cirrhosis. We suggest that education and an appropriate social environment are necessary to ensure this fat energy intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
Yu Hyeon Jo, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef
- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
- 1,740 View
- 63 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Exploring the customer perceived value of online grocery shopping: a cross-sectional study of Korean and Chinese consumers using Means-End Chain theory
- Xinyu Jiang, Hyo Bin Im, Min A Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):318-335. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Despite the growing market share of online grocery shopping, there is a need to understand customer perceived value due to the ongoing advancements in information technology. This study explores the connections between attributes, consequences, and values. Additionally, it conducts a cross-country comparison of consumers’ online grocery shopping behaviors to gain a deeper understanding of consumer market segments and any potential variations among them.
Methods
Data was collected through an online questionnaire survey conducted from May 1 to 15, 2024, targeting 400 consumers in Seoul, Korea, and Shanghai, China, who have experience with online grocery shopping. The survey utilized the Means-End Chain theory and association pattern technique hard laddering. Data collation and analysis were conducted using the IBM SPSS Statistics 28.0 program. The LadderUX software was employed to analyze the links between attributes, consequences, and values and create the consumer purchasing process’s implication matrix and hierarchical value map (HVM).
Results
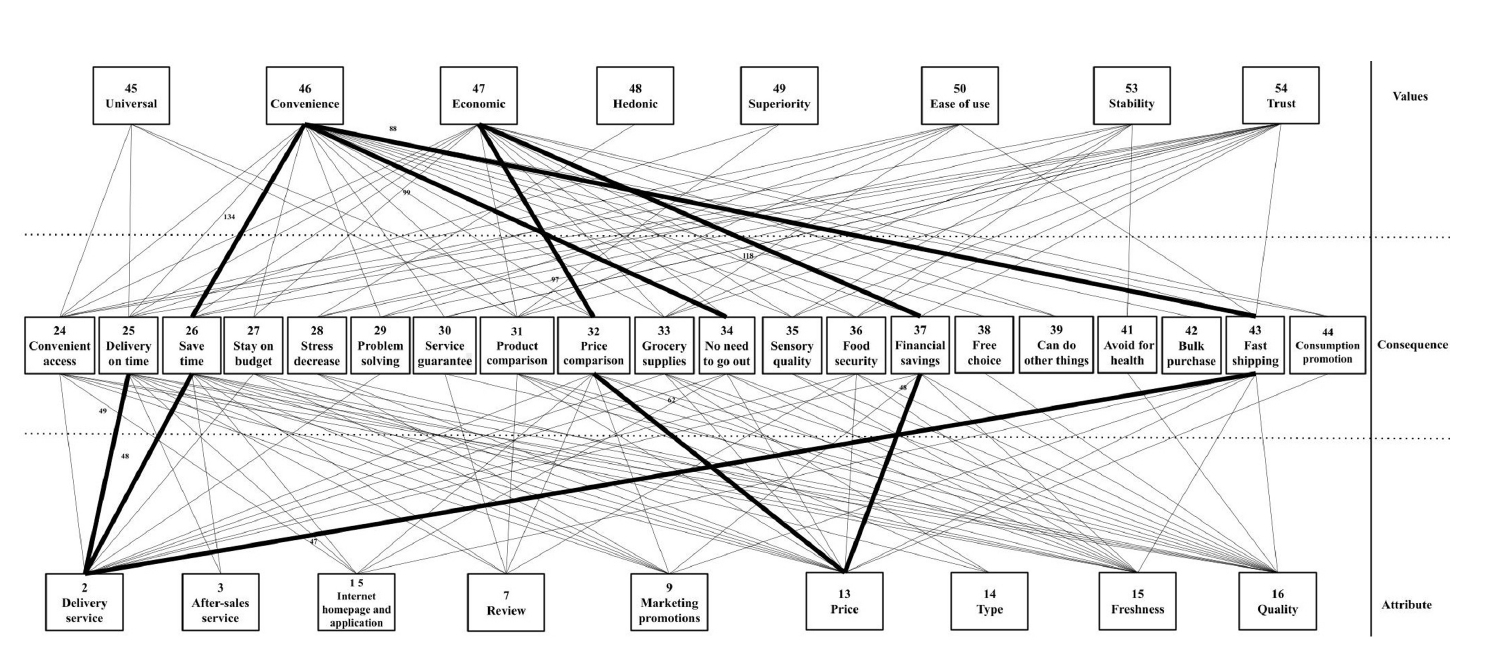
The study identified key attributes that influence online grocery shopping decisions, including delivery service, price, freshness, and quality. Korean consumers demonstrated a higher sensitivity to price (19.0%) and delivery service (17.0%). In contrast, Chinese consumers prioritized delivery service (15.0%) and after-sales service (14.8%). Commonly cited consequences included time saving (12.6% for Koreans, 11.3% for Chinese), whereas prevalent values encompassed convenience (36.8% for Koreans, 19.6% for Chinese) and economic value (26.6% for Koreans, 14.7% for Chinese). The HVM underscored these insights, highlighting diverse consumer preferences and country-specific nuances.
Conclusions
The findings highlight the current state of online food consumption and consumers’ value systems, revealing variations among countries. These findings offer empirical insights that can be used to create customized global marketing strategies that resonate with various consumer preferences and market dynamics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the stage: how performing arts tourism shapes tourist perceptions and destination image
Islam Elbayoumi Salem, Mohammed Ali Bait Ali Sulaiman, Enrico di Bella, Sara Preti, Mohamed Kamal Abdien, Ahmed Magdy
Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights.2026; 9(1): 375. CrossRef
- Beyond the stage: how performing arts tourism shapes tourist perceptions and destination image
- 6,076 View
- 80 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
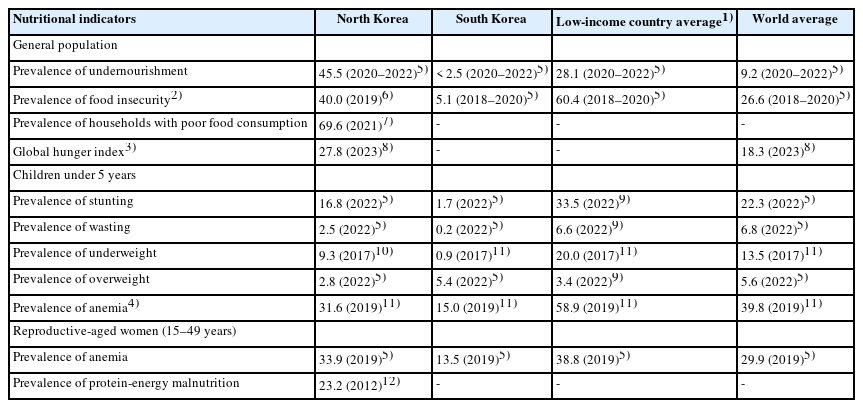
- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
- Youngmin Nam, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):288-303. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
North Koreans have been facing chronic food shortages and malnutrition. This study examined the nutritional status of North Koreans and the perceptions of South Korean adults regarding their nutritional status.
Methods
The nutritional status was examined using nutritional indicators for the general population, children, and reproductive-aged women in North Korea. An online survey was conducted among 1,000 South Korean adults aged 19–69 years to investigate their perceptions regarding the nutritional status of North Koreans.
Results
Although the nutritional status of children in North Korea has consistently improved, significant progress in the general population and reproductive-aged women in the country remains elusive. The prevalence of malnutrition among North Korean children has decreased to a level that is not considered severe based on international standards, although it shows a substantial difference from that among South Korean children. The prevalence of undernourishment and food insecurity in North Korea remains over 40%. South Korean adults perceive the nutritional status of North Koreans as being more severe than it is in reality. Notably, a significant inconsistency exists between the perceived and actual nutritional status of North Korean children, with over 95% of South Korean adults perceiving North Korean children’s malnutrition as being more severe than it actually is. Moreover, South Korean adults in their 20s to 40s tended to perceive the nutritional status of North Koreans as being more severe than those in their 50s to 60s did.
Conclusions
The nutritional status of North Koreans is a matter of concern. The disparity between South Koreans’ perceptions of the nutritional status of North Koreans and the actual status highlights the need for accurate information dissemination to effectively address malnutrition in North Korea. These efforts could be instrumental in enhancing public awareness and fostering social consensus on food aid and nutritional support programs for North Korea.
- 4,032 View
- 74 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung-Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):156-170. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the association between how often Korean adolescents watch Mukbang and Cookbang videos and their dietary habits.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 was analyzed for this study. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed various aspects, including demographics, frequency of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos per week, dietary habits, health behaviors, and mental health factors.
Results
Nearly a third (29.3%) of Korean adolescents watched Mukbang and Cookbang videos one to four times a week, while 13.5% watched them more than five times weekly. Females, those with lower academic achievement, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds were significantly more likely to be frequent viewers (P < 0.001). Increased viewing frequency was associated with poorer dietary habits. Adolescents who watched more frequently were less likely to eat breakfast and consume fruits and milk, while their consumption of fast food, high-caffeine drinks, sugary drinks, and late-night snacks increased (P < 0.001). Higher viewing frequency correlated with increased feelings of stress, depression, and loneliness (P < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis confirmed these associations. More frequent viewers were significantly less likely to eat breakfast (odds ratio (OR), 0.63; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.58–0.68), and more likely to consume fast food (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.69–2.02), high-caffeine drinks (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30–1.56), sugary drinks (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.41–1.67), and late-night snacks (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.25–1.51).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that frequent exposure to Mukbang and Cookbang content is linked to unhealthy dietary habits in adolescents. Educational programs may be necessary to mitigate the potential for these videos to negatively influence dietary choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
Seung Jae Lee, Yeseul Na, Kyung Won Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2652. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef
- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
- 3,860 View
- 105 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Knowledge on complementary foods of mothers with young children and their perception of convenience complementary foods
- Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang, Youngmin Nam
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):16-33. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.16
- Correction in: Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine mothers’ knowledge levels on complementary foods and their perception of convenience complementary foods.
Methods
An online survey was conducted with mothers aged 20–49 years who had purchased convenience complementary foods and had a preschool child aged 4 months or older. The respondents were categorized into 3 groups based on their knowledge scores: low- (0–50 points), mid- (55–65 points), and high- (70–100 points) knowledge groups.
Results
The average score of mothers’ knowledge on complementary foods was 58.8 out of 100 points. Working mothers were found to have lower levels of knowledge compared to mothers who were housewives. Only 1/4 of responding mothers had educational experience on complementary foods. Mothers expressed a desire for information on the types of complementary foods (72.2%) and the intake amounts (60.3%) corresponding to each phase of their child’s development. Multivariate analysis of variance revealed significant differences in health (P = 0.002), variety (P = 0.039), and hygiene (P = 0.041) among the factors taken into consideration when purchasing convenience complementary foods according to the mothers’ knowledge levels. Mothers in the high-knowledge group placed a greater importance on ‘balanced nutrition’ (P = 0.022) and ‘hygienic cooking’ (P = 0.010) compared to mothers in the low-knowledge group. The results of the modified importance-performance analysis, which compared the importance and performance of the factors taken into consideration when purchasing convenience complementary foods, highlighted the need for efforts in ‘health,’ ‘hygiene,’ and ‘price,’ while also indicating an excessive effort in ‘convenience.’
Conclusions
This study suggests expanding relevant education programs to enhance mothers’ knowledge on complementary foods, especially for working mothers. In the industry, marketing strategies for complementary food products could be developed that align with the needs of mothers, focusing on health, hygiene, and price. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Website for the Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity
Miyong Yon, Chan Park, Kwan-Hee Yoo, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(4): 390. CrossRef - Breakfast Skipping and Related Factors in Children in Poverty
Kyung Ja June, Jin-Young Kim, Seungmi Park, Ji Yun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(2): 204. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Website for the Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity
- 3,668 View
- 74 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Factors related to adolescent obesity and changes: a cross-sectional study based on the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Bora Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):363-375. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to identify factors associated with adolescent obesity, as well as any new factors that correlated with a change in the rate of obesity over time.
Methods
The study used 5-yearly data collected by the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey starting from the year 2006 up until 2021 (data from 2nd, 7th, 11th, and 17th surveys were analyzed). Factors such as demographics, dietary factors, health behavioral factors, and mental health factors were studied. All data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27.0, employing chi-square tests and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results
This study included data from a total of 255,200 participants. Factors contributing to obesity varied with time. Over the survey duration of 15 years, low academic achievement, parents with low levels of education, low frequency of fruit consumption, low frequency of fast food intake, long periods of being seated, and high levels of stress were significantly associated with a high rate of obesity. Factors that showed a new correlation with an increase in obesity rates included living with single parents, low frequency of muscle strengthening exercises, and experiencing intense sadness and despair in the past year. Factors that were correlated with a change in obesity rates over time included household economic status, frequency of carbonated beverage consumption, frequency of intense physical activity, and frequency of alcohol consumption. Breakfast intake and smoking were not significantly associated with obesity rates in the 15-year period.
Conclusions
While several factors associated with obesity remained consistent over time, several new factors have emerged in response to social, economic, and environmental changes contributed to a change in obesity rate over time. Therefore, to prevent and manage adolescent obesity, continuous research into the new emergent factors contributing to obesity is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,937 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Problems Encountered in Analyzing the Market Size, Purchase, and Consumption of HMR in the Republic of Korea
- Sung Ok Kwon, Injoo Choi, Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):480-491. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.480
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the problems encountered when analyzing the market size, purchase, and consumption of HMR (home meal replacements) in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
The macro data relevant to the market size and purchase status of HMR were critically summarized. The micro data retrieved from the 2019 & 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) were analyzed to understand the consumption of HMR.
Results
The Korea Agro-Fisheries & Food Trade Corporation and the Ministry of Food and Drug Administration reported the market size of HMR, whereas the Korean Rural Economic Institute and the Rural Development Administration reported the purchase expense and frequencies of HMR. Since the values on the market size and purchase status were calculated or surveyed using different scopes of HMR, there have been reliability issues for the data presented. Additionally, lack of consensus on the use of Korean terms corresponding to HMR was found to be a problem. To examine the consumption of HMR, analysis of the food intake data from KNHANES presented results with very low validity due to the inappropriate survey and coding scheme not reflecting the inclusion of new food types.
Conclusions
Several problematic discrepancies were encountered in the statistics on HMR. The fundamental cause of these problems was the absence of agreement on the scope of HMR and the Korean terms corresponding to it. Considering the increasing importance of HMR in Korean diets, urgent cooperative efforts are required between the government and academia to derive an agreed Korean term and establish the scope of HMR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Human Resource Management in Emergencies: The Case of the Lithuanian Logistics Sector
Kristina Čižiūnienė, Gabrielė Voronavičiūtė, Dragan Marinkovic, Jonas Matijošius
Sustainability.2025; 17(6): 2591. CrossRef - Evaluation of Thermal Resistance in Geobacillus thermodenitrificans subsp. Calidus and Ureibacillus suwonensis Spores Isolated in Korea
Ju-Hee Nam, Du-Yeong Jung, Zi-On Choi, Hyun-Jung Jung, Jung-Beom Kim
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2025; 40(1): 13. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties and Quality Analysis of Miichthys miiuy Products Processed by Drying and Smoking
Yu-Jin Heo, Hayoun Kim, Hae-In Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 629. CrossRef - Survey on consumer perceptions, health benefits and preferences of kindergarten and school foodservices in Korea, including related keywords reported in newspaper: a mixed-methods study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 309. CrossRef - Eating behaviors, home meal replacement consumption, and nutrition quotient: a comparative study of male shift and non-shift workers in Chungcheong, Korea
Yeon Jin Lee, Munkyong Pae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 758. CrossRef - Usage and Quality Satisfaction of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores according to the Eating Behavior of University Students in Southern Gyeonggi Province
Se-In Oh, Ok-Sun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 492. CrossRef
- Sustainable Human Resource Management in Emergencies: The Case of the Lithuanian Logistics Sector
- 5,956 View
- 139 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Trends in Dietary Behavior Changes by Region using 2008 ~ 2019 Community Health Survey Data
- Yun-Hui Jeong, Hye-Young Kim, Hae-Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):132-145. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined trends in the health status and dietary behavior changes by region using the raw data from the 2008 ~ 2019 Community Health Survey.
Methods
This study analyzed the data of 2,738,572 people among the raw data of the Community Health Survey from 2008 to 2019. The regional differences in health status and dietary behavior were examined by classifying the regions into capital and non-capital regions, and the non-capital regions were classified into metropolitan cities and provinces. A chi-square test was conducted on the body mass index (BMI), diagnosis of diabetes and hypertension, frequency of eating breakfast, salty taste in usual diet, recognition of nutrition labeling, reading of nutrition labeling, and utilization of nutrition labeling.
Results
In determining obesity using the BMI, the normal weight by year decreased, and the obesity rate by year was 34.6% in 2019, which increased by 13% compared to 2008. In addition, the diabetes diagnosis rate and hypertension diagnosis rate continued to increase with the year. Both diabetes and hypertension diagnosis rates were higher in the non-capital regions than in the capital region. Eating breakfast five to seven times per week was most common and showed a significant decreasing trend by year (P < 0.001). The percentage of respondents who said they eat slightly bland foods increased from 19.5% in 2008 to 19.9% in 2010 and then to 22.1% in 2013. The percentage then decreased to 19.9% in 2019, but showed an overall increasing trend (P < 0.001). According to the region, the capital region had a higher percentage than the non-capital region. The nutrition labeling's recognition rate and utilization rate increased yearly, whereas the reading rate decreased.
Conclusions
The study results presented the primary data necessary to develop nutrition education programs and establish strategies for local nutrition management projects to improve disease prevention and dietary problems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 274. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Comparison of the levels of energy intake from dish and food groups by gender and age among Korean obese adults: data obtained from the 2013-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Cheongmin Sohn, Woori Na, Chaeryeon Kim, Seunghee Choi, Oh Yoen Kim, Jounghee Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(6): 670. CrossRef
- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
- 1,367 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of Surveys to Determine the Real Prices of Ingredients used in School Foodservice
- Seo-Hyun Lee, Min A Lee, Jae-Yoon Ryoo, Sanghyo Kim, Soo-Youn Kim, Hojin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):188-199. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose was to identify the ingredients that are usually surveyed for assessing real prices and to present the demand for such surveys by nutrition teachers and dietitians for ingredients used by school foodservice.
Methods
A survey was conducted online from December 2019 to January 2020. The survey questionnaire was distributed to 1,158 nutrition teachers and dietitians from elementary, middle, and high schools nationwide, and 439 (37.9% return rate) of the 1,158 were collected and used for data analysis.
Results
The ingredients which were investigated for price realities directly by schools were industrial products in 228 schools (51.8%), fruits in 169 schools (38.4%), and specialty crops in 166 schools (37.7%). Moreover, nutrition teachers and dietitians in elementary, middle, and high schools searched in different ways for the real prices of ingredients. In elementary schools, there was a high demand for price information about grains, vegetables or root and tuber crops, special crops, fruits, eggs, fishes, and organic and locally grown ingredients by the School Foodservice Support Centers. Real price information about meats, industrial products, and pickled processed products were sought from the external specialized institutions. In addition, nutrition teachers and dietitians in middle and high schools wanted to obtain prices of all of the ingredients from the Offices of Education or the District Office of Education.
Conclusions
Schools want to efficiently use the time or money spent on research for the real prices of ingredients through reputable organizations or to co-work with other nutrition teachers and dietitians. The results of this study will be useful in understanding the current status of the surveys carried out to determine the real price information for ingredients used by the school foodservice.
- 932 View
- 16 Download

- [English]
- Development of a Zinc Database to Estimate the Zinc Intake Levels in the Korean Toddlers and Preschool Children
- Su-In Yoon, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):103-110. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to develop a zinc database (DB) to estimate the intake levels of zinc in Korean toddlers and preschool children using the data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Methods: A total of 3,361 food items for the DB representing the usual diet of Korean toddlers and preschool children were selected based on KNHANES (2009~2013) and the food composition table of Rural Development Administration (RDA). The existing values of zinc in foods were collected from the latest food composition tables of RDA (9th revision) and the US Department of Agriculture (legacy release). The zinc contents were filled preferentially with these collected values. The missing values were replaced with the calculated values or imputed values using the existing values of similar food items from the data source. The zinc intake levels of Korean toddlers and preschool children were estimated using KNHANES and zinc DB Results: A total of 1,188 existing values, 412 calculated values, and 1,727 imputed values were included in the zinc DB. The mean intake levels of zinc for 1-2-year-old children and 3-5-year-olds were 5.17 ± 2.94 mg/day and 6.30 ± 2.84 mg/day, respectively.There was no significant difference in the zinc intake levels between boys and girls in each group. Conclusions: This newly developed zinc DB would be helpful to assess the zinc nutritional status and investigate the association between the zinc intakes and related health concerns in Korean toddlers and preschool children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food sources of zinc and nutritional status with usual dietary zinc intake in Korean toddlers and preschool children
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1211. CrossRef
- Food sources of zinc and nutritional status with usual dietary zinc intake in Korean toddlers and preschool children
- 1,601 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Vegetable and Nut Food Groups are Inversely Associated with Hearing Loss- a Cross-sectional Study from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Sunghee Lee, Jae Yeon Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):512-519. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.512
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A cross-sectional study was conducted to investigate the associations between food groups and hearing loss. Methods: Data of 1,312 individuals were used from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013. Hearing loss was determined with a pure tone average (PTA) of greater than 25 dB in either ear. The PTA was measured as the average hearing threshold at speech frequencies of 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 kHz. The dietary intake was examined with a food frequency questionnaire with 112 food items. The food items were classified into 25 food groups. A weighted logistic regression was used to investigate the association. Results: Individuals in the highest tertile of vegetables and nuts food groups were less likely to have hearing loss than those in the lowest tertile [Odds Ratio (OR) = 0.58 (95% Confidence interval (CI) 0.38-0.91), P = 0.019; OR = 0.59 (95% CI 0.39-0.90), P = 0.020, respectively], after adjusting for confounding variables of age, sex, body mass index, drinking, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and physical activity. Conclusions: In this cross-sectional study, we observed that high intake of vegetables and nuts food groups revealed significant inverse associations with hearing loss, after adjusting for confounding variables among 1,312 participants.
- 1,061 View
- 4 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Quality Comparison of the School and Home Lunches Consumed by Chinese School-Age Children and Adolescents:Analysis of the 2011 China Health and Nutrition Survey
- Chengyu Zhang, Suhua Jin, Jihyun Yoon, Meeyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):474-484. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.474
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The number of schools offering school lunches has increased in China. This study examined the dietary quality of the lunches consumed by Chinese school-age children and adolescents, with a focus on comparing school lunches with home lunches. Methods: The first weekday 24-hour dietary recall data of 6~17-year-old students (n=1,084) from the 2011 China Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed. The subjects were divided into the school lunch group and the home lunch group, and the dietary quality of lunches was compared between the two groups among 6~11-year-old students (n=634; 177 in the school lunch group and 457 in the home lunch group) and 12~17-year-old students (n=450; 144 in the school lunch group and 306 in the home lunch group), respectively. Frequently consumed foods, amount of food group intake, food group intake pattern, Dietary Diversity Score (DDS), and Dietary Variety Score (DVS) were examined. Results: The most frequently consumed foods in both lunch groups were rice and pork. An excessive intake of meat and insufficient intake of seafood were noted in both lunch groups. The school lunch group showed a lower level of vegetable consumption than the home lunch group (P=0.017 in 6~11-year-old students, P=0.003 in 12~17-year-old students).Although more students ate meals with a better dietary pattern in the school lunch group than the home lunch group, there were no significant differences in DDS and DVS between the two groups. Conclusions: Overall, the dietary quality of lunches was not superior in the school lunch group compared to the home lunch group. This suggests that much room remain for improving dietary quality of school lunches in China. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- [Retracted] Analysis of the Influence of Rural Family Education Environment on School‐Age Children’s Social Behavior and Patterns
Wenwen Yao, Ying Zhen, Yu Zhang, Zhao Kaifa
Journal of Environmental and Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- [Retracted] Analysis of the Influence of Rural Family Education Environment on School‐Age Children’s Social Behavior and Patterns
- 1,830 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutritional Status of Vitamins and Minerals According to Consumption of Dietary Supplements in Korean Adults and the Elderly: Report Based on 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):329-339. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study was undertaken to evaluate the intake of vitamins and minerals from dietary supplements (DSs) in Korean adults and elderly.
Methods
Data for this study was generated from the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). We analyzed 4,204 individuals aged 19 years and older (2,579 users and 1,625 non-users). The survey included 24-h recall questions on food and DS intakes, as well as questions on DS use over the past year. The nutrient DSs evaluated were calcium, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and vitamin C. Total nutrient intakes were obtained by combining nutrient intakes of foods and DSs consumed by each subject.
Results
Most micronutrient intakes from food (except for thiamin) in adult users, and the four micronutrient intakes (iron, vitamin A, vitamin B2 and vitamin C) in elderly users, were significantly higher than values obtained in non-users. For total intake of nutrients and DSs, both adult and elderly users had a significantly higher intake than non-users. While proportions below Estimated Average Requirements for all micronutrients by adding respective DSs in users were significantly reduced in adults and elderly as compared to non-users, the proportions of above Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for calcium and vitamin A in adults, and vitamin A in elderly, were significantly increased. In the total subjects examined, consumption of DSs was associated with lower odds ratios of undernutrition of micronutrients, and with higher odds ratios of overnutrition of calcium, iron, and vitamin A, as compared to non-users of DSs.
Conclusions
Although DSs consumption by adults and the elderly improves the micronutrient status, it also increases the risk of excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 103. CrossRef - Folate intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey with newly established folate database
Eun-Ji Park, Inhwa Han, Kyoung Hye Yu, Sun Yung Ly
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(4): 418. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimated dietary vitamin D intake and major vitamin D food sources of Koreans: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 451. CrossRef - A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- 2,233 View
- 10 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Life of Chinese International Students according to the Frequency of University Foodservice Use in Korea
- Yan Cui, Hye-Jong Yoo, Injoo Choi, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):291-302. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.291
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study investigated the current use of university foodservice among Chinese international students in Korea, focusing on the relationship between the frequency of university foodservice use and their dietary life.
Methods
An online survey was conducted on 452 Chinese international students from February 6 to 12, 2020. The respondents were classified into “the Low-frequency group” (< one time/week; n=144), “the Mid-frequency group” (one-two times/week; n=133), and “the High-frequency group” (≥three times/week; n=175) according to their frequency of using university foodservice. The dietary life was compared among the three groups. Binominal logistic regression models were constructed to determine the associations between the frequency of university foodservice use and the changes in dietary life.
Results
More than 2/3 (68.1%) of the respondents used the university foodservice at least once per week. Chinese international students who were males and Han Chinese people, lived on campus, had stayed longer in Korea, and had no cooking facilities tended to use the university foodservice more often. The level of satisfaction with the university foodservice was not high (3.52 out of 5-points). Only 20% ate meals three times per day, and only 22% ate breakfast almost every day. The frequencies of overeating and skipping meals increased after studying in Korea. The frequency of university foodservice use, along with the length of residence in Korea, was associated with these negative changes in dietary life. Overeating (OR=2.11) and skipping meals (OR=1.79) were more likely to increase after studying in Korea in the Mid-frequency group than in the High-frequency group.
Conclusions
The frequency of university foodservice use was associated with the dietary life of Chinese international students in Korea. A high frequency (i.e. ≥three times/week) of using university foodservice may positively affect the dietary life of Chinese international students in Korea.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
Qi Li, Ji Eun Lee, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(2): 91. CrossRef
- Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
- 1,275 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- ary Characteristics and Needs for Community Kitchens among Young Adults of Single-person Households in Seoul according to the Cooking Attitude
- Mina Yang, Kana Asano, Nalae Kim, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):204-213. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the dietary characteristics and needs for community kitchens among young adults of single-person households in Seoul according to the cooking attitude.
Methods
During April 2018, an online survey was conducted on young adults of singleperson households in their 20s and 30s residing in Seoul. The respondents were classified into the more positive cooking attitude group (More Positive Group; n=152, mean=4.11) and the less positive cooking attitude group (Less Positive Group; n=190, mean=3.03) based on the mean score (3.51) of the 4-item 5-point Likert scales measuring the cooking attitude. The responses of the two groups were compared.
Results
Approximately 90% of the More Positive Group had the cooking ability to prepare ordinary meals or more advanced cooking skills, whereas only 61% of the Less Positive Group had such skills. Approximately a half of the More Positive Group cooked at home three times a week or more; only 30% of the Less Positive Group did so, and more than 30% of the group seldom cooked. The More Positive Group had higher mean scores in the levels of satisfaction with dietary life and care for food safety and nutrition than the Less Positive Group. Approximately 30% of all the respondents expressed their needs for community kitchens. The most frequently answered reason for such needs was “being able to have a meal with others”.
Conclusions
The young adults of single-person households with a more positive cooking attitude possessed a higher cooking ability, cooked more often, and cared more about food safety and nutrition than those with a less positive cooking attitude. There were moderate needs for community kitchens among young adults of single-person households living in Seoul. Therefore, societal efforts to improve their cooking attitude would be meaningful for improving their quality of dietary life. Cooking lessons or social dining programs based on community kitchens could be an option. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Qualitative Study on Health Problems and Health Behaviors Perceived by College Students Focusing on Students Registered in - Dietary Life and Health- Course for General Education
Young Hye Jeong
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(2): 277. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Associations of cooking practices and healthy eating habits among young Korean adults in their 20s
So-Young Kim, Ji Yu Choi
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2023; 31: 100644. CrossRef
- Qualitative Study on Health Problems and Health Behaviors Perceived by College Students Focusing on Students Registered in - Dietary Life and Health- Course for General Education
- 1,269 View
- 14 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Children's Food Intake and Nutrition Levels, and Obesity by Maternal Employment: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2015
- Geunyeong Kang, Yoonna Lee, Mihyang UM, Seunghee Kye
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):331-342. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.331
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examines the intake of food and nutrients of children according to the employment and working hours of their mothers.
METHODS
The married women in the source data from the 6th National Health and Nutrition Survey were classified into full-time working mothers, part-time working mothers and housewives according to the working type and the data on their children from 3 to 18 years old were analyzed using SAS 9.4.
RESULTS
The group from 3 to 5 years old was the smallest group with 682 children (20.2%), followed by the group from 6 to 11 years with 1,345 children (39.8%) and the group from 12 to 18 years old with 1,355 children (40.1%). The lowest rates for having no breakfast and dinner were observed in the group with housewives (p<0.05). The calcium and phosphorous intakes were the highest in the group with housewives at 61.9% and 126.8%, respectively, and the lowest in the group with full-time working mothers at 54.7% and 115.3%, respectively (p<0.05). The group with full-time working mothers had the highest rate in the calcium and iron intake less than the dietary reference intake at 74.9% and 30.0%, respectively. It indicated that the group with full-time working mothers did not have sufficient nutrients as compared to the other two groups. Moreover, the group with the part-time working mothers showed the high vitamin A intake ratio of 41.4% (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
This study found evidence of a negative association between mother's employment status and children's diet quality. The employment and economic activity of married women will continuously increase in the future. Therefore, a national nutrition policy is required to provide quality nutrition care for children in the households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,393 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of the Nutrition Status and Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence of the Members according to the Number of Household Members based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2014)
- Jin Young Lee, Soo Kyong Choi, Jung Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):232-244. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated the nutritional status and prevalence of metabolic syndrome of the people who participated in the KNHANES according to the number of household members. They were assessed by using information from the 2013~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
A total of 6,088 persons aged 19 years and over participated in 2013~2014 KNHANES, and they were classified into three groups according to the number of household members (single-person, two-person, three-person & over). The dietary behavior, nutritional status, health-related factors and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome of the subjects were investigated with using information from the survey questionnaires of KNHANES. The nutrient intake data of the subjects were obtained by the 24-hour recall method and this was analyzed for evaluating the nutrition adequacy ratio and the index of nutritional quality. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome among the subjects, and according to the study groups, was estimated using the blood and physical measurement data of the subjects.
RESULTS
As for EQ-5D index available for all the health states generated by the EQ-5D descriptive system, the single-person household member was the lowest among all the household types. The index of nutrition quality for protein, crude fiber, calcium, phosphorus, potassium, riboflavin and vitamin C in the single-person household was lower than that of the two-person or the three-person and over households (p<0.001). The mean adequacy ratio of single-person households was significantly decreased compared with that of the other types of households (p<0.001). The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was higher in the single-person households than that in the multiple-person households (p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
These results showed that dietary behaviors, nutrition status and health status might be influenced by the number of household members. The results from this study would be useful for improving Korean people's dietary life and health status by implementing evidence-based, specialized intervention for the members of diverse types of households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Beyond individual integration: Family systems, social support networks and living environment as health determinants among migrants in Germany
Franziska Reinhardt, Imad Maatouk
Journal of Migration and Health.2025; 12: 100368. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - The association of the Korean Healthy Eating Index with chronic conditions in middle-aged single-person households
EunJung Lee, Ji-Myung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 316. CrossRef - Analysis of Agrifood Consumer Competency and Dietary Satisfaction according to Household Type Using the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Meera Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 414. CrossRef - An analysis of customer needs for the operation of unmanned food stores on a university campus
Se-Eun Kim, Min-Seo Park, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(5): 587. CrossRef - Assessment of Nutrient Intake and Dietary Quality of Korean Adults in Metabolic Syndrome Patients According to Taking Medical Care: Based on the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Juhee Lee, Kyungsuk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(4): 321. CrossRef - Relationships of Dietary Factors with Obesity, Hypertension, and Diabetes by Regional Type among Single-Person Households in Korea
Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1218. CrossRef - Living Environment Considerations on Obesity Prevention Behaviors and Self-Efficacy among Chinese Americans
Doreen Liou, Jessica A. Karasik
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(17): 9322. CrossRef - The Relationship between Meal Regularity and Oral Health and Metabolic Syndrome of Adults in Single Korean Households
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, On-Ju Ju
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 185. CrossRef - Association of Household Income Level with Vitamin and Mineral Intake
Haegyu Oh, Juyeon Kim, Yune Huh, Seung Hoon Kim, Sung-In Jang
Nutrients.2021; 14(1): 38. CrossRef - Nutritional status and metabolic syndrome risk according to the dietary pattern of adult single-person household, based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu Been Keum, Qi Ming Yu, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 23. CrossRef - Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Eun-Sun Park, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 476. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 408. CrossRef
- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 2,921 View
- 9 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of Model for 「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€
- Hae Young Lee, Bo Sook Yi, Jina Cha, Sun Ok Ham, Moon Kyung Park, Mi Nam Lee, Hye Young Kim, Haeng Hwa Kang, Jin Wook Kwon, Yun Hui Jeong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):60-76. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.60
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to develop a systematic and standardized「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€that can identify the current status of school meals on the nationwide level.
METHODS
This study was carried out in six steps of the analysis of report/investigation data related to school foodservice in metropolitan and provincial offices of education, analysis of preceding research related to the actual status of school foodservice, field verification of the actual condition of the school foodservice site, development of a draft of「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€, pilot study of a draft of 「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€, and suggestions of a final model of「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€from August to December, 2017. Statistical analysis was performed for frequency analysis and descriptive analysis using the SPSS program ver. 23.
RESULTS
A draft of「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€was developed by analyzing the current status of report/research data on school meals in metropolitan and provincial offices of education, analyzing the preceding research on school meals, and identifying the actual conditions at school foodservice sites. To verify the validity of the school foodservice survey questionnaire, 1,031 schools were sampled from a total of 10,251 schools and the pilot test of ‘2017 School Foodservice Survey’ was conducted. The final model of「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€consisted of 12 survey sections, 29 survey categories, and 433 survey items, and the survey cycle was set for one year and three years for each survey item.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the objective statistical data through「The Survey on School Foodservice Programã€, it is possible to develop the school foodservice policy, which will help establish the reliability of the school meals. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- 1,353 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Analysis of the Difference in Nutrients Intake, Dietary Behaviors and Food Intake Frequency of Single- and Non Single-Person Households: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2014–2016
- Na Yeon Kang, Bok Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):1-17. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to compare the dietary life of single- and non single-person households in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
A nationally representative sample of 20,421 19-64-year-olds who had 24-hour recall data was taken from the 2014-2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Single- and non single-persons were compared for nutrient intake, dietary behaviors, food consumption patterns, nutrition education and confirm nutrition label.
RESULTS
The dietary intakes of dietary fiber and iron were lower in single-person households than in non single-person households. The lower the level of education and income, the lower the nutrient intake of single-person households. In the case of those aged 19 to 29, the breakfast skipping rate was higher in single-person households than in non single-person households. The higher the education level, the higher the breakfast skipping rate and the eating out frequency in the single-person households. In the food intake survey, the frequency of healthy food intake in single-person households was much lower than that of non single-person households. The confirmation rate of nutrition labeling was lower in single-person households than in non single-person households.
CONCLUSIONS
This study shows that single-person households have poorer health-nutritional behaviors than multi-person households. Therefore, a nutrition education program based on the data of this study needs to be developed for health promotion of single-person households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Cooking Fuel Choices on Household Food Security and Healthy Food Consumption in Indonesia
Moh Shadiqur Rahman, Sujarwoto Sujarwoto, Hery Toiba, Tri Wahyu Nugroho, Fahriyah Fahriyah, Mohammad Ilyas Shaleh, Tina Sri Purwanti, Bagus Andrianto
Review of Development Economics.2025; 29(4): 2242. CrossRef - A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 140. CrossRef - Generalized Anxiety Disorder Due to Household Type and Economic Status during COVID-19 Pandemic: Focusing on Gender Differences
Ye Eun Cha, Ju Yeong Hwang, Jin Young Nam
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(1): 89. CrossRef - Association of delivered food consumption with dietary behaviors and obesity among young adults in Jeju
Minjung Ko, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 336. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Diabetes Nutritional Management for Single-Person Households
Min Young Noh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(4): 236. CrossRef - Analysis of intake trends of kimchi, fruits and vegetables (1998–2020) and factors associated with the intake (2016–2020): based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jiwon Jeong, Jungmin Park, Yu Kyung Lee, Sung Wook Hong, Sangah Shin
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 404. CrossRef - The relationship between the prevalence of anemia and dietary intake among adults according to household types based on data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Won Kim, Ji-Myung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 510. CrossRef - Analysis of Agrifood Consumer Competency and Dietary Satisfaction according to Household Type Using the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Meera Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 414. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Associations of cooking practices and healthy eating habits among young Korean adults in their 20s
So-Young Kim, Ji Yu Choi
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2023; 31: 100644. CrossRef - Perception to the dietary guidelines for Koreans among Korean adults based on sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle
Yejin Yoon, Soo Hyun Kim, Hyojee Joung, Seoeun Ahn
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 742. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behaviors between Adults with Hypertension in Single- and Multi-Person Households: Based on the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yongjae Yu, Youn Huh, Sung Sunwoo
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
Ji Suk Yim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Association between eating alone and cardiovascular diseases in elderly women: a cross-sectional study of KNHANES 2016 data
Han-Gyo Choi, Hye-Jin Kim, Seok-Jung Kang
Menopause.2022; 29(1): 82. CrossRef - An analysis of customer needs for the operation of unmanned food stores on a university campus
Se-Eun Kim, Min-Seo Park, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(5): 587. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behaviors and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Single- and Multi-Person Households among Korean Adults
Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Healthcare.2021; 9(9): 1116. CrossRef - Nutritional status and metabolic syndrome risk according to the dietary pattern of adult single-person household, based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu Been Keum, Qi Ming Yu, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 23. CrossRef - Relationship between Eating Behavior and Healthy Eating Competency of Single-Person and Multi-Person Households by Age Group
Seung-Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 337. CrossRef - Current Trends in Nursing Research Across Five Locations: The United States, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, and Hong Kong
Eun‐Ok Im, Reiko Sakashita, Chia‐Chin Lin, Tae‐Hwa Lee, Hsiu‐Min Tsai, Jillian Inouye
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2020; 52(6): 671. CrossRef - Short-term Cudrania tricuspidata fruit vinegar administration attenuates obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice by improving fat accumulation and metabolic parameters
Jun-Hui Choi, Myung-Kon Kim, Soo-Hwan Yeo, Seung Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Healthy Eating Capability of One-person Households-The Effects of Eating Alone, Meal Types, and Dietary Lifestyles
Seonglim Lee, Ilsook Choi, Junghoon Kim
Family and Environment Research.2020; 58(4): 483. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 408. CrossRef - Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Eun-Sun Park, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 476. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Nutrition Status and Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence of the Members according to the Number of Household Members based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2014)
Jin-Young Lee, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 232. CrossRef
- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
- 2,393 View
- 24 Download
- 28 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of Strategies to Improve the National Nutrition Survey System
- Narae Yang, Seungmin Lee, Youngsuk Lim, Haeryun Park, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(5):444-455. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.5.444
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The current survey environment is changing and participation rates in national nutrition surveys are decreasing. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to develop strategies for improving the nutrition survey system in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
To develop an alternative system for conducting the KNHANES nutritional survey, we conducted focus group interviews with stakeholders of the survey, SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis, and expert reviews. In addition, spatial analysis of potential sites for conducting surveys instead of relying on household visits was performed, and the perception of nutritional surveys in the population eligible for KNHANES was evaluated.
RESULTS
Based on the results of the focus group interviews, SWOT analysis, and expert reviews, we propose two options for survey sites: vehicles specifically prepared for nutritional surveys and public facilities such as community service centers or public health centers. Among public facilities, community service centers were found to be more appropriate sites than public health centers because they were considered more accessible. About 90% of respondents would participate in the survey in public facilities and about 74% would in vehicles.
CONCLUSIONS
Conducting national nutrition surveys in specially designed vehicles and public facilities could be a viable alternative to home visits. Next, the validity of these newly proposed nutrition survey methods needs to be compared to the results of the current national nutrition survey.
- 1,067 View
- 4 Download

- [English]
- Study of the Coverage of Nutrition Labeling System on the Nutrient Intake of Koreans - using the 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
- Ji Eun Park, Haeng Shin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):116-127. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.116
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to examine the coverage of the current mandatory nutrition labeling system on the nutrient intake of Koreans.
METHODS
KNHANES dietary intake data (2013) of 7,242 subjects were used in the analysis. KNHANES dietary intake data were collected by a 24-hour recall method by trained dietitians. For analysis, all food items consumed by the subjects were classified into two groups (foods with mandatory labeling and other foods). In the next step, all food items were reclassified into four groups according to the food type and nutrition labeling regulations: raw material food, processed food of raw material characteristics, processed foods without mandatory labeling, and processed foods with mandatory labeling. The intake of energy and five nutrients (carbohydrate, protein, fat, saturated fat, and sodium) of subjects from each food group were analyzed to determine the coverage of the mandatory nutrition labeling system among the total nutrient intake of Koreans.
RESULTS
The average intake of foods with mandatory labeling were 384g/day, which was approximately one quarter of the total daily food intake (1,544 g/day). The proportion of energy and five nutrients intake from foods with mandatory labeling was 18.1%~47.4%. The average food intake from the 4 food groups were 745 g/day (48.3%) for the raw food materials, 54 g/day (3.5%) for the processed food of raw material characteristics, 391 g/day (25.3%) for the processed foods without mandatory labeling, and 354 g/day (22.9%) for the processed foods with mandatory labeling.
CONCLUSIONS
Although nutrition labeling is a useful tool for providing nutritional information to consumers, the coverage of current mandatory nutrition labeling system on daily nutrient intake of the Korean population is not high. To encourage informed choices and improve healthy eating habits of the Korean population, the nutrition labeling system should be expanded to include more food items and foodservice menus.
- 1,304 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Current Status of Parents' Monitoring of and Level of Trust in School Lunch Programs
- Boyoung Hur, Injoo Choi, Meeyoung Kim, Jinwook Kwon, Jiyoung Lee, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(5):401-412. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.5.401
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the current status of parents' monitoring of school lunch programs and to examine the relationship of parents' school lunch monitoring with their level of trust in school lunch programs.
METHODS
During November 2016, a web survey was conducted with 1,283 parents who had participated in monitoring of school lunch programs. A total of 621 parents completed the questionnaires (48.4% response rate) and the responses from 442 parents were analyzed (34.5% analysis rate) for elementary (n=196) and middle/high school parents (n=246), respectively.
RESULTS
Both the elementary and middle/high school parents most wanted to participate in monitoring 1~2 times per month, which was less frequent than their current practice. They showed the highest experience rate in ‘food sanitation’ area in both the prior training and actual practice of school lunch monitoring. They most responded ‘increasing trust in school lunch programs’ as a merit and ‘lack of parents participating in monitoring’ as a problem of school lunch monitoring. The average levels of trust did not differ between elementary and middle/high school parents. Multiple regression analyses showed that elementary school parents' level of satisfaction in the monitored school lunch programs was positively associated with the parents' level of trust in general school lunch programs. Monitoring frequency and parents' age, in addition to level of satisfaction in the monitored school lunch program, were associated with level of trust in general school lunch programs among middle/high school parents.
CONCLUSIONS
There was room for change in parents' school lunch monitoring programs to meet parents' needs better. Well-managed school lunch monitoring programs contributing to parents' satisfaction with school lunch programs could increase parents' level of trust in school lunch programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
민지 손, 은주 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 213. CrossRef - Analysis of the CCP Performance and Barriers of School Foodservice Employees in the Incheon Area
Ji Eun Lee, Jung Hwa Choi
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2020; 31(3): 411. CrossRef - Development of Model for 「The Survey on School Foodservice Program」
Hae-Young Lee, Bo-Sook Yi, Jina Cha, Sun-Ok Ham, Moon-Kyung Park, Mi-Nam Lee, Hye-Young Kim, Haeng-Hwa Kang, Jin-Wook Kwon, Yun-Hui Jeong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 60. CrossRef
- 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
- 1,271 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Associations between Exposure to Unhealthy Food Outlets Within Residential District and Obesity: Using Data from 2013 Census on Establishments and 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoonjung Kim, Sung Nim Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(5):463-476. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.5.463
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Environmental, social and personal factors influence eating patterns. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between unhealthy food outlets within a residential area and obesity using nationally representative Korean survey data and data from the Census on Establishments.
METHODS
Data on the food intakes and socioeconomic variables of a total of 9,978 adults aged ≥ 19 years were obtained from the 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Geographic locations of restaurants were obtained from the 2013 Census on Establishments in Korea. Administrative area was categorized into tertiles of count of unhealthy food outlets based on the distribution of number of unhealthy food outlets among all urban (Dong) and rural (Eup or Myun) administrative districts in Korea. Multilevel logistic regressions model were used to assess the association between the number of unhealthy food outlets and obesity.
RESULTS
People living in the district with the highest count of unhealthy food outlets had higher intakes of fat (45.8 vs. 44.4 g/day), sodium (4,142.6 vs. 3,949.8 mg/day), and vitamin A (753.7 vs. 631.6 µgRE/day) compared to those living in the district with the lowest count of unhealthy food outlets. A higher count of unhealthy food outlets was positively associated with frequent consumption of instant noodles, pizza, hamburgers and sandwiches, sweets and sour pork or pork cutlets, fried chicken, snacks, and cookies. Higher exposure to unhealthy food outlets was associated with increased odds of obesity (1st vs. 3rd tertile; OR 1.689; 95% CI 1.098-2.599).
CONCLUSIONS
A high count of unhealthy food outlets within a residential area is positively associated with the prevalence of obesity in Korea. The results suggest that food environmental factors affects the health outcomes and interventions aiming to restrict the availability of unhealthy food outlets in local neighborhoods may be a useful obesity prevention strategy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity-Related Factors in Adult Women with Early Menarche
Hunha Cho, Jeong-Won Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(4): 557. CrossRef - Associations between adolescent dietary habits, obesity and food environment around schools in Seoul
Hyun-Jae Woo, Hong Lim Lee, Hae-Young Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(5): 55. CrossRef - Relationship between the Intake of Children's Favorite Foods and Policy based on Special Act on Safety Control of Children's Dietary Life
Taejung Woo, Jihye Yoo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 106. CrossRef
- Obesity-Related Factors in Adult Women with Early Menarche
- 1,543 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Status of Maternal Nutrition in South and North Korea
- Soh Yoon Yun, Young Hye Kwon, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(3):265-273. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study compared the nutritional status of child-bearing age women between the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) and the Republic of Korea (South Korea).
METHODS
The data presented in the DPRK Final Report of the National Nutrition Survey 2012 was utilized for the nutritional status and food intake of North Korean women. To produce the South Korean women's data comparable to those of North Korean women, the data from the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed and the data presented in the 2010 Report of the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards were utilized.
RESULTS
The prevalence of maternal anemia (blood hemoglobin < 12.0 g/dL) was over 30% in all the age groups of North Korean women and 8.9%, 14.2%, 16.4% in 20-29, 30-39, 40-49 year old South Korean women, respectively. The prevalence of maternal protein-energy malnutrition (Mid-Upper Arm Circumference < 22.5 cm) was 25.2%, 21.4%, 21.8% in 20-29, 30-39, 40-49 year old North Korean women, respectively and less than 10% in all the age groups of South Korean women. Result of dietary diversity comparison showed that North Korean women consumed less food than South Korean women at all food groups: grains, fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy. Percentage of North Korean women having consumed protein rich foods-meat and fish, eggs or dairy products-were much lower than those of South Korean women.
CONCLUSIONS
The striking disparity of nutritional status between South and North Korean women indicates that nutrition support for North Korean women is essential in the process of preparation for a unified nation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
Youngmin Nam, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 288. CrossRef - The Present and Future Status of Maternal and Child Health From the Perspective of Unification Medicine
Ji Young Kim, Eun Saem Choi, Ki Hoon Ahn
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(3): 132. CrossRef - Timely Initiation of Complementary Feeding and Associated Factors among Mothers of Children Aged 6–24 Months in Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia, 2019
Atsedemariam Andualem, Afework Edmealem, Belachew Tegegne, Lehulu Tilahun, Yitayish Damtie, C. S. Johnston
Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Systematic review of evidence on public health in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea
John J Park, Ah-Young Lim, Hyung-Soon Ahn, Andrew I Kim, Soyoung Choi, David HW Oh, Owen Lee-Park, Sharon Y Kim, Sun Jae Jung, Jesse B Bump, Rifat Atun, Hee Young Shin, Kee B Park
BMJ Global Health.2019; 4(2): e001133. CrossRef - Frequently covered diseases in North Korean internal medicine journal Internal Medicine [Naegwa]—Secondary publication
Shin Ha, Yo Han Lee
Science Editing.2019; 6(2): 99. CrossRef
- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
- 1,825 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Factors Associated with Fruit and Vegetable Consumption of Subjects Having a History of Stroke: Using 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010, 2011)
- Sung Je Kim, Mi Kyung Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(5):468-478. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.5.468
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Intake of fruits and vegetables has protective effects against stroke attack. This study intended to examine the status of consuming fruits and vegetables and to find out which factors may influence the frequency of consumption of fruits and vegetables in individuals with a history of stroke.
METHODS
The data of 208 subjects from 5th (2010, 2011) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES) who reported a stroke diagnosis was used for analysis. To identify major factors influencing the consumption of fruits and vegetables, a classification-tree analysis was carried out.
RESULTS
Among those who reported a stroke diagnosis, the frequencies of consumption of fruits and vegetables were influenced by their age, place of residence (urban or rural), economic status, educational level, occupation, number of family members, frequency of eating out, and having meals (breakfast or lunch) with family members. Two factors from fruits and three factors from vegetables were generated by exploratory factor analyses. Urban residents ate fruits and vegetables more frequently in all factors than rural residents. Eating frequencies of 'seasonal fruits (orange, apple, strawberry, melon, pear and watermelon)', 'easily-accessible fruits (persimmon, tangerine, grape, peach, banana)', and 'Western-style vegetables (cabbage, mushroom, carrot, tomato, spinach)' were influenced by the socioeconomic status. Eating frequencies of 'Korean-style vegetables (bean sprout, radish leaves, pumpkin/squash, sea weed)', 'preserved vegetables (Korean cabbage, radish, laver, cucumber)' were influenced by having breakfast with amily members.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study suggested that by eating more fruits and vegetables, more preventive effects against secondary stroke attack are expected in stroke patients who live in the rural areas and who do not eat breakfast with family members. In addition, more outreach and education programs are needed for them. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Classification tree analysis for an intersectionality-informed identification of population groups with non-daily vegetable intake
Emily Mena, Gabriele Bolte, Christine Holmberg, Philipp Jaehn, Sibille Merz, Alexander Rommel, Anke-Christine Saß, Kathleen Pöge, Sarah Strasser, Gabriele Bolte, Emily Mena
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Functional and nutraceutical properties of pumpkin – a review
Simran Kaur, Anil Panghal, M.K. Garg, Sandeep Mann, Sunil K. Khatkar, Poorva Sharma, Navnidhi Chhikara
Nutrition & Food Science.2019; 50(2): 384. CrossRef - Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Factors affecting vegetable preference in adolescents: stages of change and social cognitive theory
Taejung Woo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(4): 340. CrossRef - Association between Grapes Intake and Diabetic Retinopathy: Inhibitory Effect of Resveratol on Diabetic Retinopathy
Bo Young Lee, Donghyun Jee
Journal of the Korean Ophthalmological Society.2016; 57(2): 276. CrossRef
- Classification tree analysis for an intersectionality-informed identification of population groups with non-daily vegetable intake
- 1,463 View
- 8 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutritional Evaluation and Its Relation to the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome according to the Consumption of Cooked Rice and Cooked Rice with Multi-grains in Korean Adults: Based on 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Soo Hyun Son, Hwa Jung Lee, Kyong Park, Tae Youl Ha, Jung Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(1):77-87. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the nutrient intakes of subjects by quartile of percent energy intake from cooked rice, consumption of cooked rice mixed with multi-grains and to evaluate rice consumption in relation to the risk of metabolic syndrome. The subjects were 5,830 males and females aged between 20~64 years based on 2007-2008 KNHNES data. Levels of percent energy intake from cooked rice were classified into 4 groups (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4 groups: 25% of each) using data of 24-hour recall method from KNHNES. Using medical examination and questionnaire, subjects were classified according to diagnostic criteria of metabolic syndrome. The subjects with higher age, being married, lower education, lower economic level were more likely to take higher percent energy intake from cooked rice. Quartile Q3 of percent energy intake from cooked rice tended to show higher Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ) for fiber, calcium, iron, potassium and vitamin A. INQ of protein, dietary fiber, calcium, thiamin, phosphorus, potassium, riboflavin, niacin and vitamin C by consumption of cooked rice mixed with multi-grains was higher than that by consumption of cooked white rice when adjusted for age. No association with a risk for metabolic syndrome was found for quartile of percent energy intake from cooked rice or cooked rice mixed with multi-grains compared to cooked white rice after adjusting for energy, gender, age, BMI, alcohol, smoking, income and physical activity. In conclusion, consumption of over 54% energy intake from cooked rice or only cooked white rice showed relatively low INQs, but was not associated with a higher risk for metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary patterns and diet quality among adults in their 20s according to rice consumption: a co-occurrence network analysis using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2019–2021
Eun-kyung Kim, Jin-Young Lee, Yong-Seok Kwon, Minji Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(6): 571. CrossRef - Associations of Whole Grain and Refined Grain Consumption With Metabolic Syndrome. A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies
Hongbin Guo, Jun Ding, Jieyu Liang, Yi Zhang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Korean fermented cabbage kimchi consumption with an incidence of metabolic syndrome: 10-year follow-up results of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Suk Hyeon Seo, Jiyoun Hong, Im Huei Son, Young Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 569. CrossRef - Dietary quality differs by consumption of meals prepared at home vs. outside in Korean adults
Kyung Won Lee, Won O. Song, Mi Sook Cho
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(3): 294. CrossRef - Diet Pattern According to Socio-Economic status - Using the Fifth (2010-2012) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Han Na Kim, Hyo Eun Park
The International Journal of Advanced Culture Technology.2016; 4(3): 24. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - The Development of Institutional Food-Service Menu with Temple Food
Sim-Yeol Lee, Jin-A Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 338. CrossRef - Adequate Standard Pot and Number of Plants Per Tree of Raising Seeding Pot on the Foxtail Millet Transplanting Culture in the Southern Province
Yong-Soon Kim, Dong-Kwan Kim, Jin-Gyung Choi, Heung-Gyu Park, Myeong-Seok Kim, Hae-Ryoung Shin, Gyung-Ju Choi, Jong-Tag Yun
The Korean Journal of Crop Science.2015; 60(1): 23. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Intake Status and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome According to White Rice Consumption in Korea: Basted on Data 1st (1998), 4th (2007~2009), 6th (2013) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
Fang-Fang Song, Jin-A Jang, Yang-suk Kim, Hei-ryeo Yoon, Mi-Sook Cho
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(5): 682. CrossRef - The Effect on Behavior of Instant Rice Selected Attributes According to Food Lifestyle
Inja Youn, Sohyeong Myeong, Deokihn Yoon
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(6): 804. CrossRef - The Relationship between Health Behavior and General Health Status: Based on 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Chunhoo Cheon, So-Mi Oh, Soobin Jang, Jeong-Su Park, Sunju Park, Bo-Hyoung Jang, Yong-Cheol Shin, Seong-Gyu Ko
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5(1): 28. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Dietary Habit and Nutritional Status by Household Income in Female Adults over the Age of 20 - Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hee-Kyung Jang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 660. CrossRef - The Risk of Metabolic Syndrome by Dietary Patterns of Middle-aged Adults in Gyeonggi Province
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 527. CrossRef - Cooking Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Cooked Rice According to the Addition of Glutinous and Non-glutinous Sorghum
Koan Sik Woo, Jee Yeon Ko, Jung In Kim, Jae Saeng Lee, Seuk Bo Song, Jae Min Cho, Tae Wook Jung, Ki Young Kim, In Seok Oh
Korean Journal of Crop Science.2013; 58(4): 399. CrossRef - Nutritional Assessment and Perioperative Nutritional Support in Gastric Cancer Patients
Kyung Won Seo, Ki Young Yoon
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2013; 61(4): 186. CrossRef
- Dietary patterns and diet quality among adults in their 20s according to rice consumption: a co-occurrence network analysis using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2019–2021
- 1,559 View
- 4 Download
- 15 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Behaviors Related to Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
- Jinkyung Park, Sanghui Kweon, Yangha Kim, Myoung Jin Jang, Kyungwon Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(5):664-675. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.664
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the cross-sectional associations between dietary factors and the risk of metabolic syndrome (MetS) in 12,755 subjects (males 5,146, females 7,609) aged 19 years or above using data from the 4th (2007-2009) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). The prevalence of MetS in Korean adults was 23.6% (males 26.1%, females 20.9%) with the criteria for modified National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III. While males had a higher prevalence of abdominal obesity, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and high blood pressure than females, the prevalence of low HDL-cholesterol level was higher in females than in males. Among dietary guidelines, the response of 'yes' for asking practice of 'avoiding salty foods', and 'eating moderately and increasing physical activity for healthy weight' were significantly associated with the decreased risk of MetS in both males and in females. Especially, the risk of MetS was significantly lower in the subjects that responded the practice of all items of Korean Dietary Guidelines. Significantly negative associations with MetS were also found in the responding for practice of 'limiting consumption of alcoholic beverages' in males, and taking dietary supplements in females. Skipping breakfast was positively associated with the risk of MetS. In conclusion, dietary behaviors such as having breakfast, practice of dietary guidelines, and food consumption in moderation could modify the prevalence of MetS, and our findings could be useful for establishing guidelines for preventing MetS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - Comparison of health indicators and lifestyle according to atherogenic index of plasma in Korean adults in their 20s and 30s
Bora Hwang, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 168. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Diet Quality between Meal Frequency and Cardiometabolic Risk among Korean Adults: Data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES)
Yoo Mi Cho, Kyoung Suk Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(2): 67. CrossRef - Association of Seaweed Consumption with Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Haeun Park, Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Foods.2022; 11(11): 1635. CrossRef - Effect of Household Type on the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korea: Using Propensity Score Matching
Jisu Park, Ilsu Park
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 1894. CrossRef - Association between breakfast skipping and metabolic outcomes by sex, age, and work status stratification
Jun Heo, Won-Jun Choi, Seunghon Ham, Seong-Kyu Kang, Wanhyung Lee
Nutrition & Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistence of metabolic syndrome and osteopenia associated with social inequalities and unhealthy lifestyle among postmenopausal women in South Korea: the 2008 to 2011 Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (KNHANES)
Hansongyi Lee, Jieun Kim, Hyunjung Lim
Menopause.2020; 27(6): 668. CrossRef - Effects of BeHaS Program on Health Behavior, Physiologic Index and Self-Esteem of the Elderly Living Alone with Metabolic Syndrome Based on Community Based Participatory Research
Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim, Keumok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Lina Lee, Si Wan Choi, Bon Jeong Ku
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 571. CrossRef - A Study on the Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome and Sodium among the Clients of the General Medical Examination Center
Mi-Jung Yun, Young-Mi Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(6): 404. CrossRef - Field Application and Evaluation of Health Status Assessment Tool based on Dietary Patterns for Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(4): 277. CrossRef - Motivation Factors for Stages of Behavioral Change among Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
Rhayun Song, Moonkyoung Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 60. CrossRef - Comparative study on prevalence and components of metabolic syndrome and nutritional status by occupation and gender: Based on the 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga Ram Kim, Hae Ryun Park, Young Mi Lee, Young Suk Lim, Kyung Hee Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 74. CrossRef - Alcohol Consumption and Diabetes Mellitus
Hye-Kyung Chung
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(1): 41. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Inflammatory Index of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean : Data from the Health Examinee Cohort (2012-2014)
Mi-Sung Kim, Cheong-Min Sohn
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(6): 823. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Dietary Fat Energy Ratio in Middle-aged Men - Using the 2012~2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data -
Eun-Sil Her
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 1030. CrossRef - Relationship between metabolic syndrome and metabolic syndrome score and beta cell function by gender in Korean populations with obesity
Hyun Yoon, Dae Keun Jeong, Kyu Su Lee, Han Soo Kim, Ae Eun Moon, Jong Park
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(9): 785. CrossRef - Effect of a Worksite-based Dietary Intervention Program for the Management of Metabolic Syndrome
Hye Jin Kim, Injoo Choi, Won Gyoung Kim, Kana Asano, Jeongmin Hong, Young Min Cho, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 237. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Chronic Disease Risk Based on the Percentage of Energy from Carbohydrates and the Frequency of Vegetable Intake in the Korean Elderly: Using the 2007-2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yoon Suk Suh, Min Seon Park, Young-Jin Chung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 41. CrossRef - Antioxidative activities of various solvent extracts from haw (Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge)
Yishan Duan, Min-A Kim, Jong-Hwan Seong, Hun-Sik Chung, Han-Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2014; 21(2): 246. CrossRef - Antioxidative Activity of Feral Haw (Crataegus pinnatifida BUNGE) Seed Extracts Using Various Solvents
Min-A Kim, Yishan Duan, Jong-Hwan Seong, Hun-Sik Chung, Han-Soo Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2014; 30(1): 33. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Metabolic Syndrome Prevention Program for University Students using Mobile Application.
Han Kyu Kang, Tae Bin Kim, Kyu Hyung Kim, Min Jin Kim, Jin Hyun Kim, Hyun Yong Kim, Kyung Hoon Yeom, Ka Hyun Lee, Eun Young Choi, Kyung Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(3): 205. CrossRef - Relation between Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity Pattern Identification Questionnaire in Middle-aged Health Check-up Examinees
Jeong-Eun Yoo, Young-Hye Cho, Hyun-Gyung Gu, Bo-Young Kim, Young-Ju Yun
Journal of Korean Medicine.2014; 35(1): 124. CrossRef - The study of metabolic risk factors and dietary intake in adolescent children by the status of mothers' metabolic syndrome: Using the data from 2007-2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
SoYeon Kwon, Mijung Park, YoonJu Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(6): 531. CrossRef
- Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
- 2,326 View
- 11 Download
- 23 Crossref

- [English]
- Changes in Food and Nutrient Intakes of College Students between 1999 and 2009
- Han Byul Jang, Hwa Young Lee, Young Hee Han, Jeehye Song, Ki Nam Kim, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(3):324-336. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.3.324
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of the study was to examine the changes of food and nutrient intakes of college students between 1999 and 2009. Dietary survey of 169 college students was conducted by a 24-hour recall method for three days in 2009. Food and nutrient intakes in 2009 were compared with the data from 106 students collected by the same methods in 1999. The intakes of cereals & grain products and vegetables in 2009 were lower than those of 1999, but the intakes of meats, eggs, milk & milk products, and manufactured food were higher. The intake of rice per person decreased greatly from 452.2 g in 1999 to 351.4 g in 2009 in males, and from 306.9 g to 237.2 g in females. While the intakes of protein, fat, thiamin, niacin, vitamin B6, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and cholesterol were significantly higher, the intakes of dietary fiber were significantly lower in 2009 compared to 1999 both in males and females. The nutrients consumed less than the Recommended Intakes were vitamin A, riboflavin, vitamin C, and calcium in males and additionally folate, iron, and zinc in females in both 1999 and 2009. The ratio of carbohydrate, protein and fat as energy was 61 : 15 : 24 and 60 : 14 : 26 in 1999, and 54 : 16 : 30 and 56 : 15 : 29 in 2009 in males and females respectively, showing that carbohydrate intake decreased and fat intake increased greatly. Our data suggest that nutrition education is necessary for college students to help them consume more vegetables and fruits and less fat and cholesterol.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary zinc intake and sources among Koreans: findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Jee-Seon Shim, Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 257. CrossRef - Nutritional Assessment Focusing on Minerals of Ready-to-Cook Foods Sold in Korea
Eun-Sun Park, Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(6): 501. CrossRef - Trends in energy intake among Korean adults, 1998-2015: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sungha Yun, Hyun Ja Kim, Kyungwon Oh
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(2): 147. CrossRef - University Students’ Eating Habit, Perception and Acceptance of Korean Food in Jeollabuk-do Province
Kyung Jin Min, Hwi-Jin Joung, Ye-Ji Lee, Moon Sook Kim, Il Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2017; 33(5): 588. CrossRef - Recognition and Consumption of Meal Alone and Processed Food according to Major of College Students
Byung Bum Choi
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 911. CrossRef - Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(4): 332. CrossRef - A Comparative Analysis of Salt-Related Dietary Patterns According to the Sodium Intake of College Students in Busan
Sang Hee Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(1): 167. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Self-efficacy, Obesity Stress, and Obesity-related Quality of Life According to BMI and Stages of Change in Vegetable Consumption for Nursing Students
Myoung Sook Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 65. CrossRef - The Study of Nutrient Intakes, Blood Lipids and Bone Density According to Obesity Degree Among University Students in Jeonbuk
Hye-Soon Chang
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2014; 23(4): 743. CrossRef - A Study on the Health Status, and Nutrient Intakes according to Body Mass Index (BMI) of College Men in Seoul Area
Kyung Ok Shin, Kyung Soon Choi
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(3): 507. CrossRef - Comparison of dietary habits, perception and consumption frequency of fast foods between youths working part-time at fast food restaurants and other food-related services
Mi Yang Jo, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(3): 206. CrossRef - Salt-related Dietary Behaviors of University Students in Gyeongbuk Area
Kyung-A Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2014; 43(7): 1122. CrossRef - Consumption of health functional food and dietary habits, nutrient intake and dietary quality of college students in Incheon
So Young Kim, Jeong Soon You, Kyung Ja Chang
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2013; 46(2): 166. CrossRef - The study of Perception in Body Somatotype and Dietary Behaviors - The Comparative Study between Korean and Chinese College Students -
Youngmee Lee, Lin Sun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(1): 25. CrossRef - Intake and blood concentrations of folate and their association with health-related behaviors in Korean college students
Han-Byul Jang, Young-Hee Han, Chandrika J Piyathilake, Heon Kim, Taisun Hyun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2013; 7(3): 216. CrossRef - Comparison of the lipids levels, C-reactive protein and adiponectin in adolescent male by fat intake
Sung-Hye Lee, Mi-Young Park, Soon-Kyung Kim, Young-Ki Min
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(4): 303. CrossRef - Beliefs Regarding Vegetable Consumption, Self-Efficacy and Eating Behaviors according to the Stages of Change in Vegetable Consumption among College Students
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the lipids levels, C-reactive protein and adiponectin in adolescent male by fat intake
Sung-Hye Lee, Mi-Young Park, Soon-Kyung Kim, Young-Ki Min
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(4): 303. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Behavior between Commensality and Solo-eating of University Students by BMI
Youngmee Lee, Wookyoun Cho, Yujin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(3): 280. CrossRef - How do the work environment and work safety differ between the dry and wet kitchen foodservice facilities?
Hye-Ja Chang, Jeong-Won Kim, Se-Young Ju, Eun-Sun Go
Nutrition Research and Practice.2012; 6(4): 366. CrossRef - Survey on Consumption of Coffee Beverages and Energy Contribution Ratios of Coffee Beverages and Accompanying Snacks by College Students in Daejeon City and Chungnam Province in Korea
Young-Hee Lim, Sun-Hyo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2012; 27(3): 240. CrossRef
- Dietary zinc intake and sources among Koreans: findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
- 1,345 View
- 1 Download
- 21 Crossref

- [English]
- A Comparison of Cluster and Factor Analysis to Derive Dietary Patterns in Korean Adults Using Data from the 2005 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoon Ju Song, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):722-733. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to explore dietary patterns and compare dietary patterns using cluster and factor analysis in Korean adults. This study analyzed data of 4,182 adult populations who aged 30 and more and had all of socio-demographic, anthropometric, and dietary data from 2005 Korean Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Socio-demographic data was assessed by questionnaire and dietary data from 24-hour recall method was used. For cluster analysis, the percent of energy intake from each food group was used and 4 patterns were identified: "traditional", "bread, fruit & vegetable, milk", "noodle & egg", and "meat, fish, alcohol". The "traditional" pattern group was more likely to be old, less educated, living in a rural area and had higher percentage of energy intake from carbohydrates than other pattern groups. "Meat, fish, alcohol" group was more likely to be male and higher percentage of energy intake from fat. For factor analysis, mean amount of each food group was used and also 4 patterns were identified; "traditional", "modified", "bread, fruit, milk", and "noodle, egg, mushroom". People who showed higher factor score of "traditional" pattern were more likely to be elderly, less educated, and living in a rural area and higher proportion of energy intake from carbohydrates. In conclusion, three dietary patterns defined by cluster and factor analysis separately were similar and all dietary patterns were affected by socio-demographic factors and nutrient profile.
- 379 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Relation of Breakfast Intake to Diet Quality in Korean School-Aged Children: Analysis of the Data from the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Yoon Jae Yeoh, Jihyun Yoon, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(1):1-11. Published online February 28, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aims of this study were to assess the quality of breakfast intake and to examine the relation of breakfast intake to the quality of daily diet in Korean school-aged children. The one day 24-hour recall data from the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed. The sample of this study consisted of 1,600 children aged 7 to 18 years attending elementary, middle, or high schools. By calorie level of breakfast intake, the children were grouped into Breakfast Skippers (0 kcal; n = 268, 17%), Low Calorie Breakfast Eaters (0 kcal < and < 10% of Estimated Energy Requirement (EER); n = 190, 12%), Moderate Calorie Breakfast Eaters (10% < or = and < 25% of EER; n = 861, 54%), or Sufficient Calorie Breakfast Eaters (> or = 25% of EER; n = 281, 17%). General characteristics including weight status and nutritional quality of breakfast and daily diet were compared among the four groups. The average daily calorie intake of Breakfast Skippers, Low, Moderate, and Sufficient Breakfast Eaters were 1,771 kcal, 1,719 kcal, 1,902 kcal, and 2,349 kcal, respectively; they were 86.3%, 85.9%, 98.0%, and 124.9% of EER, respectively. The percentages of students consuming daily diet with protein, vitamin A, B1, B2, niacin, vitamin C, calcium, phosphorus, or iron less than Estimated Average Requirement decreased in the breakfast groups with the higher calorie level of breakfast intake. The Dietary Variety Score of daily diet significantly increased by increasing the calorie level of breakfast intake. The results indicated the quality of daily diet was positively related to the level of calorie intake from breakfast.
- 412 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Factors Associated with Skipping Breakfast in Korean Children: Analysis of Data from the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Yoon Jae Yeoh, Ji hyun Yoon, Jae Eun Shim, Sang Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(1):62-68. Published online February 29, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to identify the factors associated with skipping breakfast of Korean children by analyzing the 24-hour recall intake data from the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey. The sample of this study consisted of 1,600 children aged 7 to 18 years. About 17% of the children skipped breakfast, consuming no food or beverage at all. About 30% of children reporting breakfast skipping in a self-administered survey were shown to have eaten some foods as a result of analysis of the 24-hour recall data. Students having eaten breakfast consumed 21% of Estimated Energy Requirement at breakfast. The multivariate logistic regression analyses showed that age was associated with skipping breakfast both in elementary and middle/high school students; older students were more likely to skip breakfast. Elementary school students from low-income families were more likely to skip breakfast than those from upper-high income families. Intervention programs are needed to prevent children from skipping breakfast by targeting older students. For elementary school students, such programs should be first developed for those from lowincome families.
- 423 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Pattern by Sex and Age with Menu Analysis Using 1998, 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey of Korea
- Jihyun Choi, Hyun Kyung Moon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(6):798-814. Published online December 31, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study is to compare menu patterns by sex and age (3-6, 7-12, 13-19, 20-29, 30-49, 50-64, 65 over years old) between the 1998 and 2001 National Health and Nutrition Surveys of Korea. Frequently consumed menu patterns were investigated using the 24-hour recall data for 19,809 subjects (1998:10,102; 2001:9,707). To analyze patterns, dishes were classified into 29 categories by cooking method (KHIDI 2003). The results are as follows: the most frequent menu patterns were "rice + soup + kimchi" and "rice + stew + kimchi" in both men and women in both 1998 and 2001. Intake frequency of these menu patterns, a traditional Korean menu pattern, was higher with increased age. Intake frequency of "noodles" and "bread" increased in 2001 in both men and women, compared to 1998. And these patterns increased in the younger age groups, especially women in their twenties. Menu patterns of 2001 showed greater variety than those of 1998. Overall, the men's menu patterns showed more side dishes than those of women; intake frequencies of "seasoned vegetables", "stir-fried foods", and "grilled foods" were higher in men than in women. In short, so far the main menu pattern has been "rice-style" in both men and women, and in all age groups in Korea, whereas the Western menu pattern is increasing in younger age groups. The diet of 2001 showed more side dishes than that of the 1998 menu pattern; however, certain groups such as female and males in adolescents and young adults were still a simple menu pattern. Consequently, to make recommended menu patterns and nutrition education programs for Koreans should take into consideration sex and age.
- 384 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption Does Not Prevent the Hypertension among Korean: the 2001 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Young Ok Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(6):707-713. Published online December 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to test whether moderate alcohol consumption has any positive effect on lowering blood pressure among Koreans. Study subjects were Korean adults 20 years or older (n=5,234) who participated in the 2001 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Analysis of variance and analysis of covariance were used to construct univariate and multivariate models relating alcohol consumption to blood pressure for the analysis. After adjustment for possible covariates, drinkers (regardless of drinking level) had significantly higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure, compared with never-drinker for male subjects. Diastolic and systolic blood pressures were also significantly elevated with the drinking frequency and amount of alcohol intake among male subjects. For the female subjects, only diastolic blood pressure was significantly associated with the alcohol consumption at multivariate model, however, low level alcohol consumption did not show any sign of lowing effects on blood pressure. The result implies that moderate alcohol consumption did not have any positive effect on lowering blood pressure among Koreans for either sex.
- 356 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Intake Pattern of the Korean Adult Population by Weight Status: 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Yoonna Lee, Haeng Shin Lee, Young Ai Jang, Hae Jeung Lee, Bok Hee Kim, Cho Il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(3):317-326. Published online June 30, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To explore the relationship between weight status and food intake pattern, the Nutrition Survey results of the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed. Dietary intake data of Korean adults aged 20 to 64, years who participated in the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey, was used along with their demographic data. Subjects were classified into 4 groups based on the BMI value of subjects: underweight, normal, overweight and obese. For male adults, obese subjects had significantly higher mean intake of energy, protein, carbohydrates, and fat than normal subjects. In addition, obese male adults consumed more animal foods, especially more meats, than normal subjects. However, females obese subjects did not show higher intake of energy or fat. Although obese male adults showed higher energy intake, calcium and iron intake per 1000 kcal was lower than normal adults. Average calcium intake in females was low; about 70% of RDA regardless of obesity level. In addition, riboflavin and Vitamin A intake was lower in overweight and obese female than in normal females. Percentage of subjects with low fruit and vegetable intake (<400 g per day) was also high in female subjects. These results showed that food and nutrient intake patterns of obese population were different between male and female adults. These dietary intake patterns need to be considered in developing and implementing nutrition policy and intervention programs to prevent and control obesity. Moreover, the National Survey and monitoring system should be developed for continuous and effective investigation on the relationship between obesity and dietary intake.
- 408 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Food and Nutrient Consumption Patterns of the Korean Adult Population by Income Level - 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Bok Hee Kim, Joung Won Lee, Yoonna Lee, Haeng Shin Lee, Young Ai Jang, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(6):952-962. Published online December 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To explore the relationship between economic status and food and nutrient intake patterns, the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey result was analyzed. Dietary intake data of 6,978 Korean adults of 20 years and older who participated in the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey were used along with their demographic data. Economic status of the subjects was classified into the following 4 groups based on the self-reported average monthly income of household with reference to the minimum monthly living expenses (MLE) in 2001: low<100% MLE < or = middle<200% MLE < or = high<300% MLE < or = higher. Individuals in the higher income class had significantly higher mean intake for most of the nutrients including energy, protein, carbohydrate, fat, calcium, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin and vitamin C, and a higher percentage of energy intake from fat. In addition, they consumed more animal foods including meats, eggs, fish/shellfish, milk/dairy products and fats. On the other hand, the mean intakes of individuals in the lower economic class for calcium, vitamin A, and riboflavin were lower than 75% of RDAs. And, there was a predominant difference in contribution of fat to total energy intake among the groups of different economic status. These results showed that household income is an important factor influencing the food and nutrient intake patterns of the Korean adult population. Although individuals at different age classes may respond differently to a change in economic status, developing and implementing nutrition policy and intervention programs for those nutritionally vulnerable groups should consider the economic status as an important factor to customize and differentiate the content of the program.
- 360 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Differences in Characteristics and Dietary Habits between Volunteers and Selected Subjects in Nutrition Survey
- Wan Soo Kim, Mi Jung Kim, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(4):511-518. Published online August 31, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to compare general characteristics and dietary habits between volunteers for a nutrition survey and non-volunteers using a questionnaire. Volunteers were recruited by advertising on the homepage of a university to assess nutritional status by examining dietary intake for three days and blood analysis. Non-volunteers were selected from some classes not related to nutrition. There were no significant differences in sex, monthly allowances, eating-out cost, drinking and exercise between the two groups, while the proportion of self-boarding was higher in the volunteer group than in the non-volunteer group, and smoking rate of volunteers was approximately 2.4 times lower than that of non-volunteers. Volunteers were less concerned about their diet than non-volunteers. No significant differences in concern about health, considering factors in their diet, self-evaluation of their diet, learning experience about nutrition, and vitamin/mineral supplement use were observed. The frequency and the place of eating-out for dinner were significantly different between the two groups. More proportions of volunteers tended to eat regularly and eat breakfast. Volunteers consumed seaweeds more frequently, and milk, fruits and fast foods less frequently than nonvolunteers. Our results indicate that some characteristics and dietary habits of volunteers are different from those of non-volunteers. However, we could not show that volunteers were more interested in their diet and had desirable dietary habits than non-volunteers. Further research on the characteristics of volunteers who participate in nutrition survey may be helpful to interpret and generalize the survey results.
- 393 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Identification of the Dietary Intake Patterns of Korean Adults according to Their Exercise Levels
- Young Ok Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(6):769-780. Published online December 31, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to identify the differences in dietary consumption patterns according to the exercise level of Korean adults. The study subjects were the 7,370 Koreans aged 20 years and older of the 1998 Korean Health and Nutrition Survey. The dietary assessment was conducted by means of the 24 hour recall method. Data for individual exercise behavior were collected by interviews as part of the National Health Behavior Survey. Following the analysis of variances the Duncan's Multiple Range Test was used to test the differences in food and nutrient intakes among groups with different levels of exercise. Current exercise practices were reported by 22% of the male subjects and 15% of the female subjects. Unlike observations from the American and European studies, a greater amount of meat intake was observed more frequently among high exercises group than among middle and low exercisers in the case of the male subjects. This was reflected in the increasing levels of protein and fat intake in proportion to the exercise levels. However, the food and nutrient intake patterns of female exercisers were quite different from those of the males. The least intake of fatty foods was observed among the high exercisers. Energy intake from fat was the lowest among the high exercisers. These results may imply that the motivation to exercise was quite different between male and female Koreans. This dietary pattern may have a risk of undernution. Summerizing the results, whatever the motivation of the exercise, the Korean exercisers of both sexes had unhealthy dietary pattern. Therefore, nutritional education should be conducted to encourage the eating of a balanced diet along with exercise, among Koreans of both sexes, in order to promote a healthy lifestyle.
- 334 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Food and Nutrient Consumption Patterns of Korean Adults by Socioeconomic Status
- Youngok Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(4):645-656. Published online October 31, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The relationship between socio-economic status and food and nutrient consumption patterns was studied in 7,370 Koreans aged 20 years and older in the 1995 Korean Health and Nutrition Survey. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of rapid economic growth on food and nutrient consumption for Korean adults in the last 30 years. Monthly household income, and individual's educational level and occupation were chosen as variables of socio-economic status for individuals. A one day 24 hour recall method was used for the dietary survey. One way analysis of varience was adopted to test tole association between socio-economic variables and food and nutrient consumption patterns. Individuals who had a high socio-economic status had significantly higher daily intake of most of the nutrients including calcium, vitamin A, vitamin B2 which reached above the recommended dietary allowances(RDA) and a higher percentage energy consumption from fat. In addition, individual who belonged to a low socio-economic status consumed less animal foods, including meat, egg, milk and consumed low proportion of energy from fat. The results suggest that in spite of rapid economic growth during the last 30 years in Korea, individuals who belonged to low socio-economic status categories are still nutritionally vulnerable. Among the socio-economic variables, income and education except occupation were the influential factors on the food and nutrient consumption of Koreans. Therefore, nutrition policy should focus on influencing the dietary patterns of lower social class individuals to improve the health status of the population as a whole.
- 437 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Survey of Alcoholic and Non-alcoholic Beverage Preference in College Students of the Chonnam Area
- Bok Mi Jung, Eun Sil Oh, Sung Mi Choi, Youn Soo Cha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(3):290-296. Published online August 31, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the intake of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages in college students. Five hundred and eighty seven students age 19-30 (432 male and 155 female) responded to the beverage consumption survey. Of the students 19.9% were freshman, 42.2% sophomore, 23% junior, and 15% seniors. Results are summarized as follows : 1) Beer and soju were the most commonly consumed alcoholic beverages by the college students. The amount of beverage normally consumed was 3 cans of beer or 1 bottle of soju. 2) There was no age related change in amount of alcoholic beverage consumed, but preference for liquor rather than beer increased with age. 3) Foods most commonly consumed prior to drinking were cooked rice and milk. 4) Following the drinking of alcoholic beverages the most commonly consumed food or beverage was cold water for both males and females. The next most commonly foods were cooked rice, instant noodles, and cola for males ; and cooked rice, milk, and fruit for females. 5) Cola and pear juice were the preferred non-alcoholic beverages for college students. Also popular among students were date juice for males and orange juice for females. Milk and non-cola carbonated beverages were not commonly consumed. This study provides information for the identification of possible alcoholic beverage related public health risks among college students.
- 512 View
- 16 Download

- [English]
- Content Analysis of the Questionnaires Used in Dietary Surveys
- Ki Nam Kim, Ae Jung Kim, Eun Sook Park, Mee Kyung Woo, Bo Kyung Lee, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2000;5(4):697-708. Published online December 31, 2000
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study is to analyze the contents of the questionnaires used in dietary surveys and to evaluate each item in relation to the item construction strategy. Articles of which the contents were related to food, nutrition, diet, dietary behavior, and related areas. Published from 1997 to 1999 were searched fir and a total of 121 questionnaires were collected and analyzed. The questions in the questionnaires were classified into related areas and sub-areas. Among the keywords in the title of the articles, the term 'nutritional status'(or 'dietary intake status') was most frequently used. The terms such as dietary status, obesity, health, food habit, and dietary behavior were also frequency used. Major topics of the items in the questionnaires varied according to the life cycle of the subjects of the study. The topics most frequently asked in each lift cycle were as follows : overeating, snack, and food preference for preschool- and school-aged children ; anthropometry, weight control, and snack for middle and highschool students : meal skipping, smoking, and drinking for college students : disease, smoking, drinking, and exercise for adults : and smoking, drinking, disease and perceived health for the elderly. Inappropriate questions with complicated language, typographic and grammatic errors, unnecessary words, and negative questions were found. Therefore, care should be taken to construct each question so as to avoid possible misinterpretation. Also, a standardized questionnaire be developed for survey researchers.
- 472 View
- 11 Download

- [English]
- The Nutritional Status of Various Populations Living in Selected Areas for Model Nutritional Work in Korea
- Ae Ja Shin, Seoung Hee Kye, Dong Yeon Kim, Haeng Shin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 1999;4(4):529-538. Published online December 31, 1999
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is very important to collect information on the nutritional status of the Korean population for the development of health promotion programs including nutrition. The purpose of this study was to assess the nutritional status of various population living in selected areas for model nutritional work. Seven hundred eighty households(30 households per each area)from 26 areas participated in this study from November 1 to November 20, 1996. Dietary intake data for two consecutive days were collected at household level by a weighting method. The mean energy intake of the subjects(1,934 kcal) was higher than that resulted from the '95 Korean National Nutrition Survey(1,839 kcal). The proportion of energy derived from cereals was 60.1%. The proportion of total protein intake from animal sources was 49.4%. These results were similar to those found in the '95 Korean National Nutrition Survey. Most nutrients(except iron, thiamin, riboflavin, vitamin C, and crude fiber) were higher than the result of the '95 Korean National Nutrition Survey. However, the average iron intake was about 68% of the result of '95 Korean National Nutrition Survey. This may be due to the adjustment of iron content in rice(3.7mg/100g-->0.5mg/100g) included in nutrient database for calculating nutrient intakes. The mean energy contribution from carbohydrate, protein, and fat were 64.2%, 16.4% and 19.4%, respectively. Significant differences of nutrient intakes were noted among some areas, which may be due to different food intake patterns according to the needs of the particular area. Therefore, the result of this study indicates that there are significant differences in food and nutrient intakes among the areas, suggesting that nutritional improvement programs may need to be developed differently by areas.
- 333 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of Food Consumption Patterns by Income Levels Using Annual Report on the Family Income and Expenditure Survey
- Hae Ryun Park, Hyung Hee Lee, Jeong Soon Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(4):633-646. Published online October 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Korea has not tried any food consumption survey so far except the national nutrition survey, which does not show food consumption patterns of different income stratas. The results of the family income and expenditure survey(FIES) by the national statistical office can be precious sources which show household food consumption patterns due to large, random. Samples, year-round survey period and socioeconomic background data. This study analyzed the FIES data to find out food consumption patterns including nutrient intakes and frequently consumed foods by households among different monthly income levels. Big difference was found in food consumption patterns among the quartile-income groups especially the amount of consumed foods, food expenditure, and nutrient intakes. For every food item, the higher the monthly invomr, yhr motr og goof yhry vondumrf. The monthly food expenditure of higher higher income strata was composed with higher percentage of relatively expensive foods compared to other stratas. Nutrient intake levels of lower income strata were 50-60% of the RDA, which showed the necessicity of food assistance programs for those high risk groups to complement the nutritional difficiency.
- 468 View
- 9 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



