Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- [English]
- Dietary factors and nutritional guidelines for sarcopenia in older adults: a narrative review
- Sumin Heo, Soo Jin Yang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):389-396. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00360
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Sarcopenia is a condition characterized by the loss of muscle mass and function and is often accompanied by aging and chronic diseases such as diabetes and obesity. It increases the risk of falls, frailty, disability, hospitalization, and mortality in older adults. Its global prevalence is estimated as approximately 10%–27% in adults aged > 60 years. This review analyzes evidence from research findings and recommendations to provide a comprehensive overview of dietary factors and nutritional strategies for preventing and managing sarcopenia in older adults.
Methods
Literatures were searched to integrate findings from observational studies, clinical trials, systematic reviews, and meta-analysis on dietary factors and nutritional guidelines for the prevention and management of sarcopenia. Particularly, points were emphasized on protein intake, micronutrient adequacy, dietary patterns, and combined lifestyle interventions relevant to older populations.
Results
Sarcopenia develops through multifactorial mechanisms such as dysfunction in muscle protein synthesis, chronic inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging-related hormonal decline. Nutritional factors, particularly protein intake, play a central role in its development and management. Adequate protein intake is typically 1.0–1.2 g/kg/day for healthy older adults and more than 1.2 g/kg/day for individuals with sarcopenia or frailty. High-quality protein intake, sufficient leucine intake, and amino acids or β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate supplementation may help to counteract dysfunction in muscle protein synthesis. The adequacy of vitamin D supports musculoskeletal health. Dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean and Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension diets have been consistently associated with better muscle mass, strength, and function. Strong evidence has demonstrated synergistic benefits when optimized nutrition is combined with resistance exercise.
Conclusion
The comprehensive management of sarcopenia in older adults requires an integrated strategy that prioritizes adequate protein and energy intake, vitamin D adequacy, healthy dietary patterns, and regular resistance exercise.
- 245 View
- 14 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):441-456. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to clarify parental perceptions of dietary and nutritional education provided to young children, identify parental support needs, and suggest directions for improvement.
Methods
A mixed-method sequential explanatory design was followed. Quantitative data were collected through an online survey conducted nationwide that included 200 parents of children aged three to six years in South Korea. Qualitative data were subsequently obtained through focus group interviews with fifteen parents to explore their contextual insights and experiences.
Results
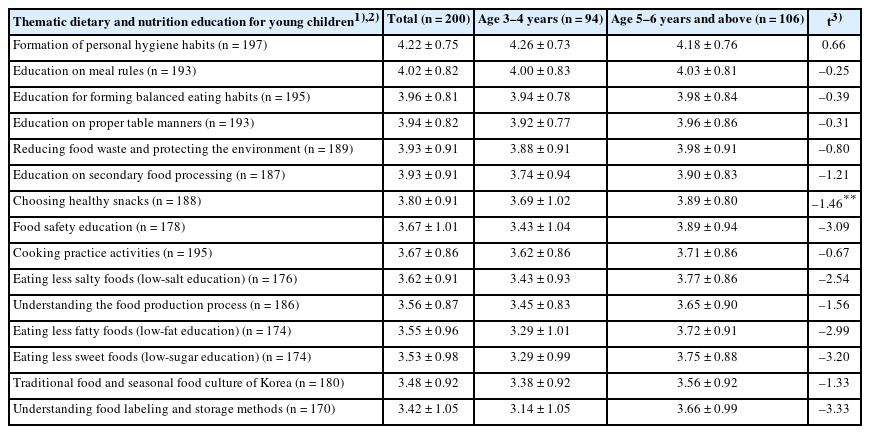
Needs ratings prioritized expanding activity-based/experiential education (3.65 ± 0.88), followed by strengthening home-school communication and connectivity (3.59 ± 0.84), diversifying topics and content (3.55 ± 0.88), and increasing instructional time (3.39 ± 0.94). Integrated with the focus group interview findings, multilevel barriers were revealed—individual level: strong preferences of children for sweet/processed foods; interpersonal level: strong parental modeling and peer effects counterbalancing limited teacher expertise/time; organizational level: insufficient effective event-based experiential activities, and resource gaps across institutions; community/policy level: infrequent external support, uneven access to local resources, lack of standardized guidance, and limited opportunities for parental participation. Parents favored short, interactive digital content and expressed concerns about overexposure. These convergent findings indicate needs to 1) formalize and extend experiential programs within the regular curriculum, 2) provide standardized guidelines and home resource kits, and 3) institutionalize parental involvement.
Conclusion
These findings reveal that dietary and nutritional education for young children should move beyond fragmented, event-based programs toward an integrated three-tiered model incorporating (1) a structured, experiential curriculum, (2) home-linked educational packages, and (3) safe and interactive digital content. Establishing standardized guidelines, enhancing educational infrastructure, and institutionalizing parental participation are essential for sustainable improvement of early childhood dietary education.
- 116 View
- 7 Download

- [English]
- Ultra-processed food intake and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):410-418. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the intake of ultra-processed foods (UPF) and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents.
Methods
This study used 24-hour dietary recall data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2023). In total, 1,720 adolescents aged 12–18 years were included in this study and categorized into quartiles based on the percentage of energy intake from the UPF. Nutritional status, contributing subgroups of UPF intake, and healthy dietary practices were examined using Health Plan 2030 indicators across quartiles of UPF intake.
Results
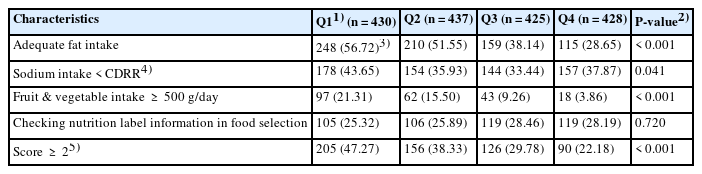
The nutrient intake of protein, vitamins (A, B1, B2, niacin), and minerals (iron, potassium) was the lowest in the fourth quartile of UPF intake compared with the first quartile (P for trend < 0.001), whereas calcium intake increased across quartiles, from 47.68% in the first quartile to 58.51% in the fourth quartile (P for trend < 0.001). The main contributing subgroups to UPF intake differed across quartiles of UPF intake, and the highest contributing subgroups were ‘instant noodles and dumplings,’ ‘desserts, cakes, and ice cream,’ and ‘sauces and seasonings.’ Healthy dietary practices were the lowest in the fourth quartile (22.18%, P < 0.001), and the proportions of appropriate fat and fruit/vegetable intake were significantly lower in the higher quartiles of UPF intake (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that a lower UPF intake was associated with better nutritional status and healthy dietary practices in Korean adolescents. These findings provide fundamental evidence for promoting healthier food choices and balanced dietary practices.
- 162 View
- 9 Download

- [Korean]
- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
- Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):431-440. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00234

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this qualitative study was to explore and understand the behaviors and challenges of self-nutrition management from the perspective of elderly.
Methods
In May 2025, ten elderly aged 65–83 years with prior experience using digital devices were recruited through purposeful sampling. Data were collected via focus group interviews using a semi-structured questionnaire until saturation was reached, and all interviews were recorded, transcribed, and analyzed using traditional content analysis methods. The collected interview data were extracted focusing on phrases or sentences relevant to the research purpose, and various concepts derived through memo writing and the constant comparison were categorized based on common meanings. Subsequently, the categorized statements were deeply interpreted and reclassified into subcategories for final analysis.
Results
Under the overarching theme of development directions for a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly, three main categories and 13 subcategories were derived. The three main categories include: (1) processes of acceptance and utilization of digital technologies; (2) potential for applying digital self-nutrition management; and (3) strategies for implementing digital-based nutrition education.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that elderly face barriers to utilizing digital tools for self-nutrition management not only due to physical or technical limitations, but also because of the confusion arising from limited nutrition knowledge and information overload. To overcome the barriers that may arise during the digital-based education process for elderly, strategies (educational topics, delivery strategies, and operational strategies) were derived to vitalize a digital self-nutrition management education program. These results highlight the necessity of developing tailored digital nutrition education programs that reflect the characteristics of elderly, which may enhance their practical applicability and provide foundational evidence for establishing a digital–nutrition integrated care model within the senior customized care service.
- 131 View
- 15 Download

Review
- [English]
- Evaluation and standardized dietary strategies for dysphagia in older adults: a narrative review
- Jean Kyung Paik
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):323-330. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00290

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This review aimed to elucidate the characteristics of dysphagia and age-related swallowing changes (presbyphagia) in older adults and to comprehensively examine assessment tools and standardized meal management strategies applicable in community settings to propose effective meal management strategies for healthy longevity.
Methods
Domestic and international literatures were analyzed regarding the definition and causes of dysphagia, physiological and structural characteristics and clinical impacts of presbyphagia, assessment and diagnostic tools (K-EAT-10 and K-DRACE), and the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI).
Results
Dysphagia compromises safe swallowing and nutritional intake in older adults, leading to serious complications, such as aspiration pneumonia, dehydration, malnutrition, sarcopenia, and reduced quality of life. The K-EAT-10 and K-DRACE proved effective for rapid screening of dysphagia risk in community-dwelling older adults. Moreover, texture-modified meals and viscosity adjustments based on the IDDSI standards are useful for reducing the risk of aspiration and improving nutrient intake. Meals can be classified as liquidized, minced, chopped, or regular, allowing for individualized management.
Conclusion
Presbyphagia is a multidimensional problem, and the integrated use of assessment tools and standardized meals is crucial. Community-based dysphagia management programs and collaboration among dietitians and healthcare professionals are needed to improve the nutritional status and quality of life of older adults.
- 1,452 View
- 42 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):352-363. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The dietary habits of school-aged children play a critical role in their growth and development, and are strongly influenced by the home environment. Household income is closely associated with caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. This directly affects the nutritional status of children. This study aimed to provide evidence to inform policies and educational programs for improving dietary habits in children, and to establish a foundation for tailored support strategies for low-income families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 846 primary caregivers of school-aged children from 17 regions across Korea, recruited through an online survey. Household income, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment were assessed. Nutritional status in children was measured using the Nutrition Quotient for Children (NQ-C). Statistical analyses included descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), correlation analyses, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Caregivers from higher income households demonstrated significantly greater food literacy and social support (P < 0.001). Children from these households showed high balance scores and a large proportion of these children were in the “high” NQ-C grade. The NQ-C score in children was positively correlated with food literacy (r = 0.425), social support (r = 0.471), and the food environment (r = 0.235) (P < 0.001). Multiple regression analysis showed that food literacy (β = 0.256) and social support (β = 0.348) were significant predictors of nutritional status in children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that the nutritional status in children is not only determined solely by household income but is also mediated by caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. These findings highlighted the limitations of providing only economic support. The findings underscore the need for multifaceted interventions such as strengthening parental nutrition education, expanding social support networks, and improving access to healthy foods.
- 682 View
- 37 Download

- [Korean]
- Survey on consumer perceptions, health benefits and preferences of kindergarten and school foodservices in Korea, including related keywords reported in newspaper: a mixed-methods study
- Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Hyeja Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):309-320. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00199

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With the rapid development of social culture, the perception of kindergarten and school foodservice, as well as opinions on its health benefits, has changed significantly. However, research on this topic remains scarce. We conducted a survey in South Korea on consumers’ perceptions, healthiness, and preferences regarding kindergarten and school foodservice.
Methods
With the nationwide cooperation of 17 city and provincial education offices, online and offline surveys were conducted targeting the parents of kindergarten and lower-grade elementary school children, as well as upper-grade elementary, middle, and high school students. In addition, keywords in newspaper reports were analyzed using the Big Kinds platform. A total of 532 valid questionnaires were collected, and statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 27.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
The average age of the parents and students was 40 and 12.5 years, respectively, with 36.4% of the students attending schools in the Seoul and Gyeonggi areas. The main keywords reported in newspaper articles, as analyzed using the Big Kinds platform, were “eco-friendly agricultural products,” “food ingredients,” “safety,” and “marine products.” The perception of kindergarten and school foodservice was very positive, especially regarding the attributes of safe ingredient use (4.44), menu variety (4.29), cafeteria cleanliness (4.31), cleanliness of plates, spoons, and utensils (4.24), thorough hygiene management (4.2), nutritional excellence (4.24), and support for proper eating habits (4.18). The healthiness of school foodservice was highly rated, although there is still room for improvement in terms of “not serving fried foods more than twice a week”. In terms of preference for school meals, the most preferred items were meat side dishes, followed by chicken, noodles, fried food, beverages, and bread. In contrast, soybean paste soup, vegetables, and mixed-grain rice received relatively low preference.
Conclusion
The results described above may be used to develop educational programs or policies that inform students and parents about the goals of school foodservice and help address common misunderstandings.
- 2,262 View
- 34 Download

- [English]
- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
- Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):274-285. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00157

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Although diet quality is known to be associated with environment and individuals’ characteristics, these have not been studied together. We determined the association of diet quality with regional factors stratified by individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics.
Methods
This study used nationally representative survey data on regional factors (2010–2020) and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data on individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics (2013–2018). Community-dwelling Koreans aged ≥ 20 were included (n = 26,853). Regions were categorized into metropolitan cities or provinces and subsequently according to regional factors (level of educational attainment, income per capita, food security status, physical activity facilities, time to the nearest large retailer, and internet use of the region). Individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics included age, education status, income, and number of household members. Diet quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI).
Results
In the entire population, education status of metropolitan cities was positively associated with the KHEI. Shorter time to retailers and higher internet use were positively associated with the KHEI in metropolitan residents with higher income levels but negatively associated with the KHEI in those with lower income status. Among provincial residents with a low education status or income, regional physical activity facilities were positively associated with the KHEI.
Conclusion
The association between diet quality and regional factors varied depending on the resident’s sociodemographic characteristics. Both regional and individual sociodemographic factors must be considered to address gaps in nutritional equity.
- 1,540 View
- 25 Download

- [English]
- The impact of flash continuous glucose monitoring and nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy and weight management in university students in Korea: a pre-post intervention study
- Soojin Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):183-196. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00073
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of a 4-week multicomponent intervention combining flash continuous glucose monitoring (flash-CGM), group nutrition education, and personalized nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy (DSE) and weight management in healthy university students.
Methods
A total of 27 university students participated in a pre-post intervention study. The intervention included a single 4-hour group-based nutrition education session, flash-CGM usage (FreeStyle Libre; Abbott Diabetes Care), and weekly one-on-one nutrition coaching. Participants wore the CGM device for 28 days (replaced after 14 days), and were guided in using the FoodLens app (DoingLab) for dietary tracking and a mobile app-linked digital scale for weight monitoring. Outcomes measured before and after the intervention included DSE, body mass index (BMI), nutrition quotient (NQ) and glycemic indicators. Statistical analyses included Wilcoxon signed-rank and Mann-Whitney U-tests with significance set at P < 0.05.
Results
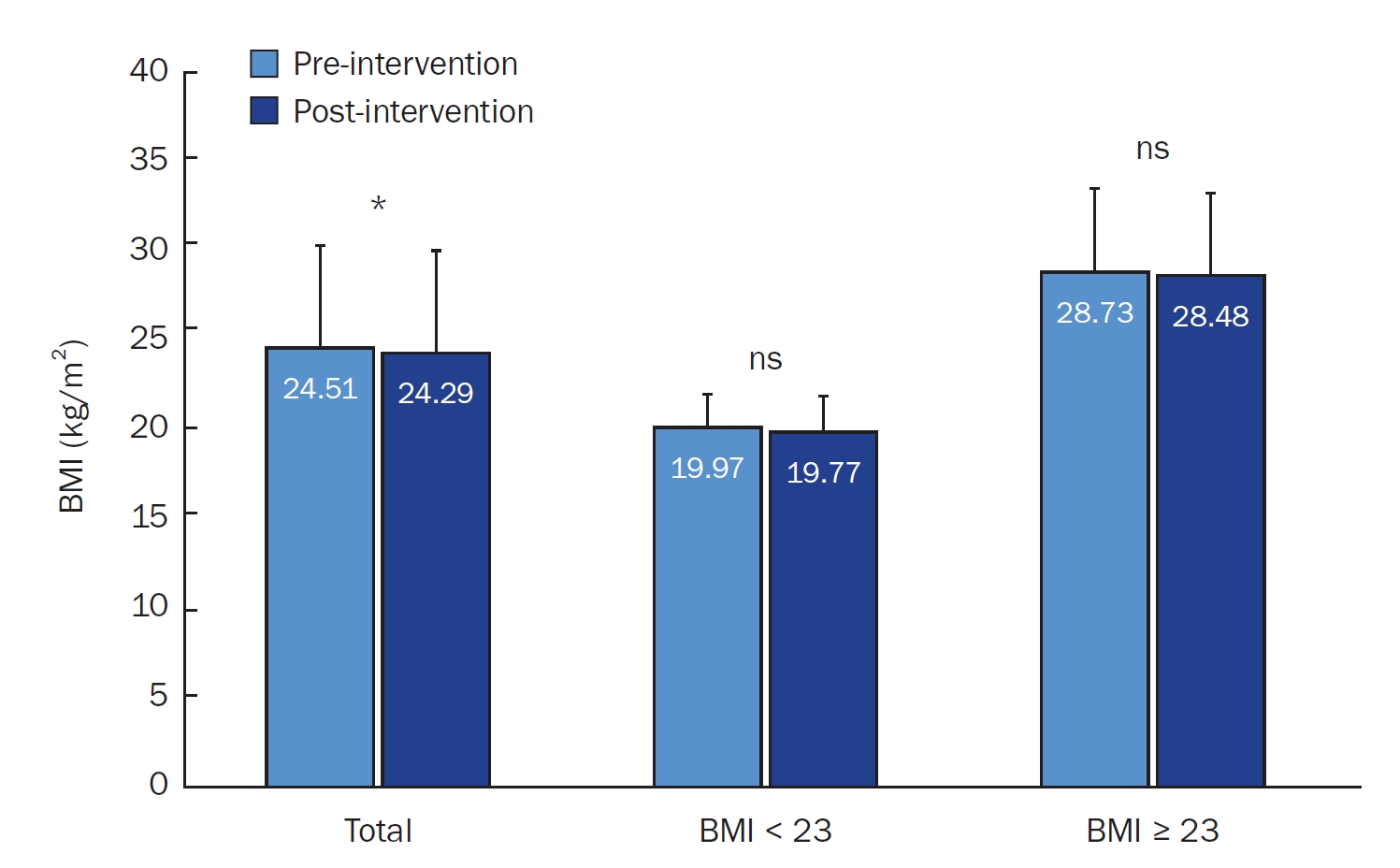
There was a significant increase in DSE (P < 0.05), particularly in managing eating behavior under stress and fatigue. A modest but significant decrease in BMI was observed in the overall group (P < 0.05), though changes were not significant in the BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2 subgroup. Glycemic indicators showed minimal changes. The overall NQ score improved slightly, with significant increases in fruit intake (P < 0.01) and nutrition label checks (P < 0.05). High satisfaction levels (4.52 ± 0.65 on a 5‑point scale) were reported for device usability and coaching services.
Conclusion
The multicomponent intervention improved DSE, NQ scores, and supported modest weight reduction among university students. The combined effect of CGM, nutrition education, and coaching appears promising; however, further studies are needed to isolate the effects of each component and evaluate long-term outcomes. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010255.
- 1,891 View
- 33 Download

- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
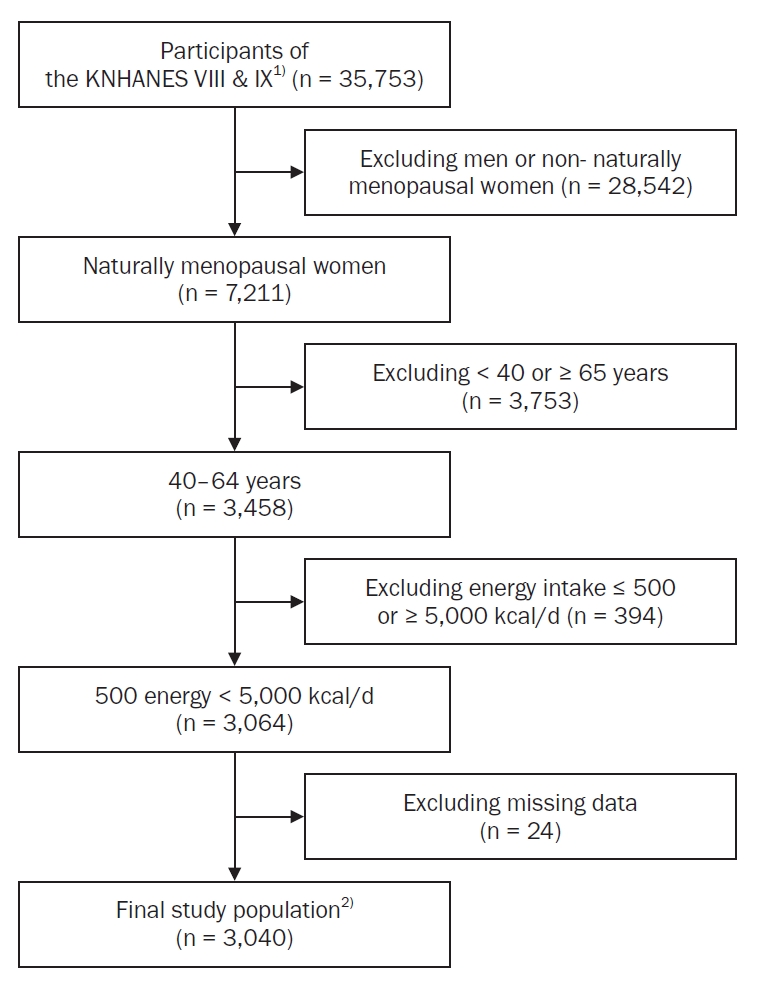
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 3,790 View
- 44 Download

- [English]
- Healthy eating intentions among adults in China: a cross-sectional study of northern and southern regions and city tiers based on the theory of planned behavior
- Yi Jiang, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):114-126. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The theory of planned behavior (TPB) has been widely employed to predict healthy eating intentions. Regional differences may affect dietary habits, health status, and personality traits, whereas variations in urbanization influence accessibility to fresh and healthy food, thereby impacting TPB components. This study aimed to explore whether regional differences between northern and southern China including city-tier development are associated with healthy eating intentions among Chinese adults.
Methods
The study included data from 2,114 Chinese adults aged 19–64 years collected between 2019 and 2023. Participants were categorized by geographic region (north or south) and city-tier status (first-tier or other).
Results
Compared to individuals from northern first-tier cities, those from southern regions exhibited stronger attitudes, perceived behavioral control (PBC), and intention to eat healthily. Participants from other cities in the north had more positive attitudes, subjective norms, PBC, and intentions to participate in healthy eating. Furthermore, residents of southern cities revealed weaker subjective norms than those of cities in the north. The adjusted odds ratio (OR) for compliance with intention to engage in healthy eating was higher among participants from other cities in both the north and south compared to those from northern first-tier cities (northern other cities: OR = 2.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.49–3.97, P < 0.001; southern other cities: OR = 1.95, 95% CI: 1.08–3.51, P = 0.027). No significant differences existed among the subjects from first-tier cities according to their geographic regions. These trends remained consistent even after including the interaction term between geographic regions and city-tier classification.
Conclusion
These findings underscore the complexity of regional variations influencing dietary intentions and indicate that tailored health promotion strategies should incorporate regional characteristics. Future research should explore underlying factors, including regional cultural influences, to better inform policies and interventions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
Md. Asaduzzaman Babu
Food and Humanity.2025; 5: 100779. CrossRef
- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
- 1,656 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Maternal home meal replacement use and attitudes, and young children’s preferences by usage frequency in meals for young children: a cross-sectional study
- Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):163-172. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00066
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With the increase in women’s workforce participation and changing family eating habits, home meal replacements (HMRs) have become more prevalent. However, research on how mothers incorporate HMR into meals of young children remains limited. This study examined mothers’ attitudes toward and use of HMR, as well as their association with young children’s HMR preferences.
Methods
A survey was conducted between June 1 and July 3, 2020, involving 337 mothers of 5-year-old children in Sejong, South Korea. The questionnaire assessed mothers’ perceptions of HMR, consumption patterns, and their children’s preferences for HMR.
Results
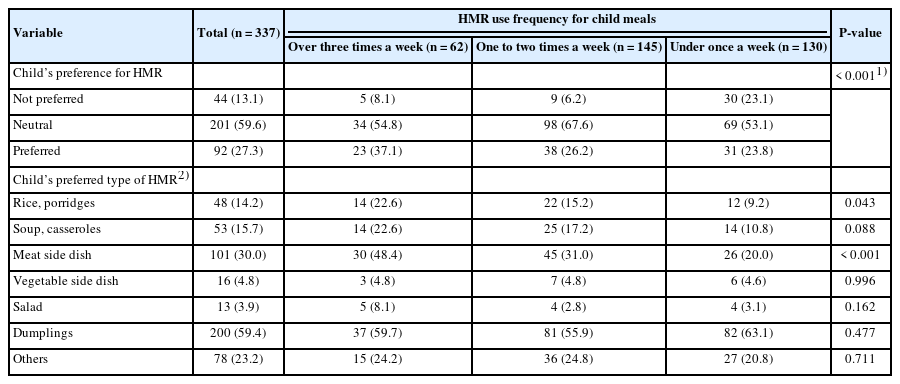
The average age of participating mothers was 38.3 years, with 93.2% living in nuclear families. Full-time homemakers constituted 40.1% of the respondents and showed lower HMR usage among them. HMR was primarily consumed as late-night snacks, side dishes, and dinners, with large discount stores (81.6%) being the primary purchase location. The high HMR consumption group exhibited more positive attitudes toward HMR (P < 0.001). HMR types varied in consumption frequency. Among ready-to-eat foods, kimbap (38.3%) was the most common, followed by meat side dishes (11.3%) and salads (11.0%). Among the heat-and-eat items, dumplings were the most frequently consumed. Simple cooking kits for Korean street food were used by 56.5% of mothers in the high-frequency HMR group, compared to 38.6% and 29.2% in the lower consumption groups (P < 0.01). Children’s preference for HMR was significantly associated with maternal HMR consumption frequency (P < 0.001). The most preferred items among children were rice porridge (P < 0.05) and meat side dishes (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Higher maternal HMR consumption was associated with increased acceptance by children. Mothers who frequently used HMR exhibited more positive attitudes toward its palatability, convenience, nutritional value, and variety. While HMR offers diverse and tasty meal options, overreliance on processed foods warrants caution. Importantly, high HMR consumption during early childhood may influence long-term dietary behaviors, including a continued preference for HMRs.
- 1,310 View
- 34 Download

- [Korean]
- A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
- Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):140-149. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to examine regional differences in dietary behavior and satisfaction between urban and rural residents in Korea, identifying key factors associated with dietary satisfaction in each group to deepen understanding of these variations.
Methods
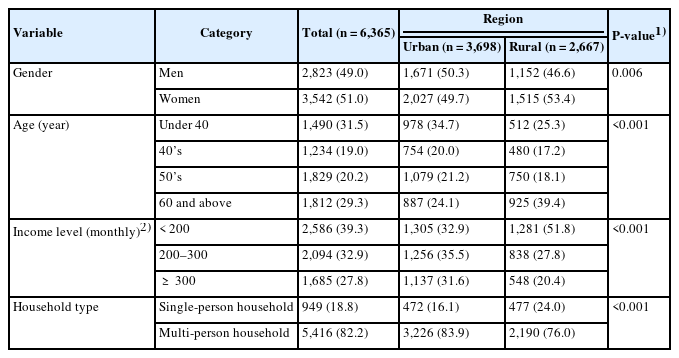
The data were obtained from the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food 2022 by the Korea Rural Economic Institute. The analysis involved 6,365 adult participants, using the complex survey χ2-test and complex survey t-tests to compare dietary behavior across regions and complex survey regression analysis to explore factors related to dietary satisfaction. Data were analyzed with R 4.3.1 (for macOS; Posit PBC).
Results
Urban and rural areas differed in consumer characteristics such as gender, age, income, and household type, as well as in food consumption behaviors and in dietary competencies associated with purchasing and intake. Specifically, dining out and processed food consumption were more prevalent in urban areas, whereas home-cooked meals were more frequent in rural areas. Overall, dietary competencies were higher among urban residents. However, there was no significant difference in dietary satisfaction between the two regions. This finding suggests that satisfaction is based on subjective evaluations, with consumers in each region forming satisfaction in ways that align with their environment and lifestyle. Accordingly, the factors contributing to dietary satisfaction differed by region. In urban areas, information utilization competency and maintaining a balanced diet played a significant role in dietary satisfaction, whereas in rural areas, regular mealtimes were more influential. Urban consumers reported higher dietary satisfaction when meals provided a sense of appropriate convenience, whereas rural consumers showed greater satisfaction when meals were shared with family at home.
Conclusion
The findings indicate regional differences in food consumption behaviors and dietary competencies, as well as variations in how consumers achieve dietary satisfaction. These insights provide a foundation for developing dietary policies and programs aimed at improving dietary satisfaction.
- 1,450 View
- 50 Download

- [English]
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):103-113. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00255
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors such as medication use, dietary supplementation, dietary habits, and physical activity among Koreans aged 20–60 years.
Methods
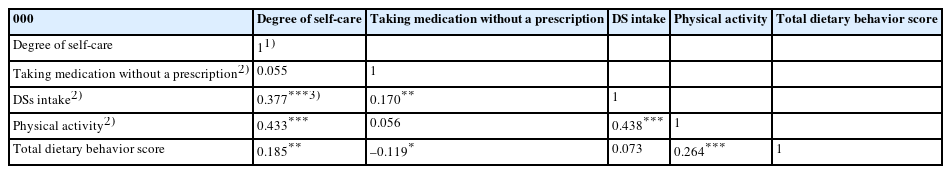
Data from a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) living in Seoul and Gyeonggi provinces in Korea were analyzed to assess the relationship between health behaviors and dietary supplements (DSs) related to self-care. Based on self-care levels, the participants were classified into three groups: low (LS, n = 124), medium (MS, n = 78), and high (HS, n = 98).
Results
DSs (P < 0.001), physical activity (P < 0.001), recognizing the perceived health benefits of self-care (P < 0.001), self-care when sick (P = 0.039), and the reasons for self-care (P = 0.028) differed among the self-care groups. Daily diet frequency (P = 0.001), breakfast frequency (P = 0.026), regular exercise (P < 0.001), DSs use rate (P < 0.001), DSs use frequency (P = 0.013), and total dietary behavior score (P < 0.001) also differed significantly depending on the degree of self-care. The degree of self-care was significantly and positively correlated with DSs intake (r = 0.377, P < 0.001), physical activity (r = 0.433, P < 0.001), and total dietary behavior score (r = 0.185, P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The results demonstrated that the degree of self-care was related to DSs, physical activity, and total dietary behavior scores in Korean adults. Additionally, self-care capacity should be increased through health-related behaviors based on health education programs.
- 2,276 View
- 55 Download

- [Korean]
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung Su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):53-63. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To apply a healthy dietary program with reduced sodium intake, developed using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), focusing on the sodium intake level and eating patterns.
Methods
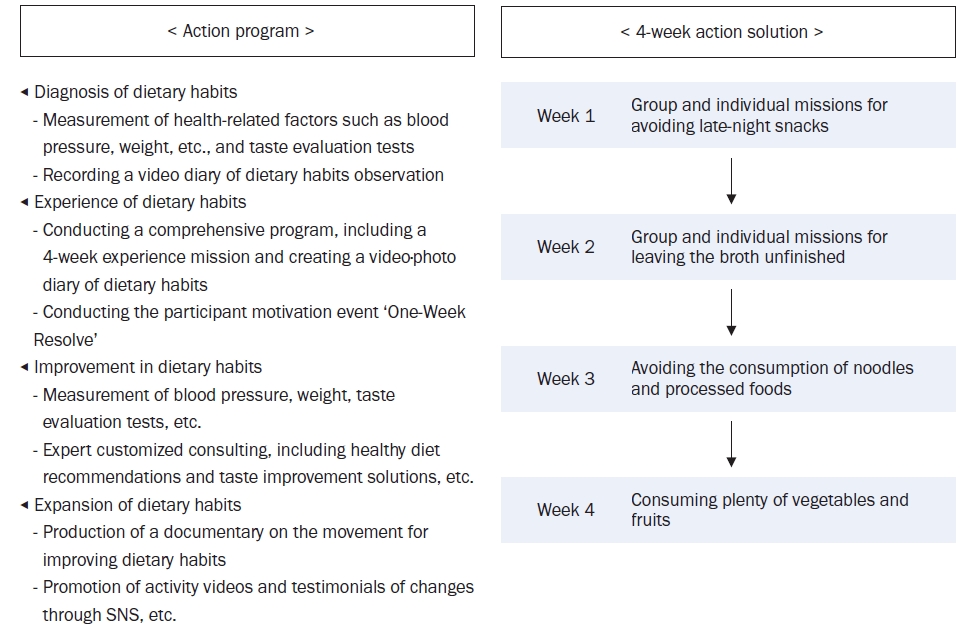
The program was implemented using a living lab model, an open innovation ecosystem for user-centered problem-solving. Analysis of the KNHANES data revealed that older age groups had a low energy intake but a high sodium intake, particularly among those who frequently dined out. The program was designed to improve sodium-reduction literacy and enhance practical competency. Over four weeks, 40 participants tracked their dietary intake and worked with a clinical nutritionist through a process of diagnosis, experience, improvement, and expansion. A self-administered survey was conducted before and after the program to assess effectiveness.
Results
Participants were four teenagers (10%), 26 in their twenties (65%), and 10 aged ≥ 30 years (25%), with eight males (20%) and 32 females (80%). Post-program analysis showed significant improvements in sodium-related nutrition knowledge (P < 0.01), with increased agreement on adopting low-sodium intake practices (e.g., interest in sodium content, choosing lower-sodium foods). Nutrient intake analysis showed a decrease in energy, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (P < 0.001), with sodium intake decreasing from 3,382.37 mg/d to 2,119.05 mg/d (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The community-based, living lab model for the sodium-reduction program effectively improved participant sodium-reduction literacy and practical competency, suggesting that step-by-step, autonomous learning, can reduce sodium intake and promote healthier eating habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
Wonyeong Park, Hae Jin Park, Suah Moon, Jieun Oh
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(6): 917. CrossRef
- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
- 1,818 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Jounghee Lee, Juhyun Lee, Wookyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):75-88. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to identify and analyze how different South Korean lifestyles impact attitudes towards pork consumption.
Methods
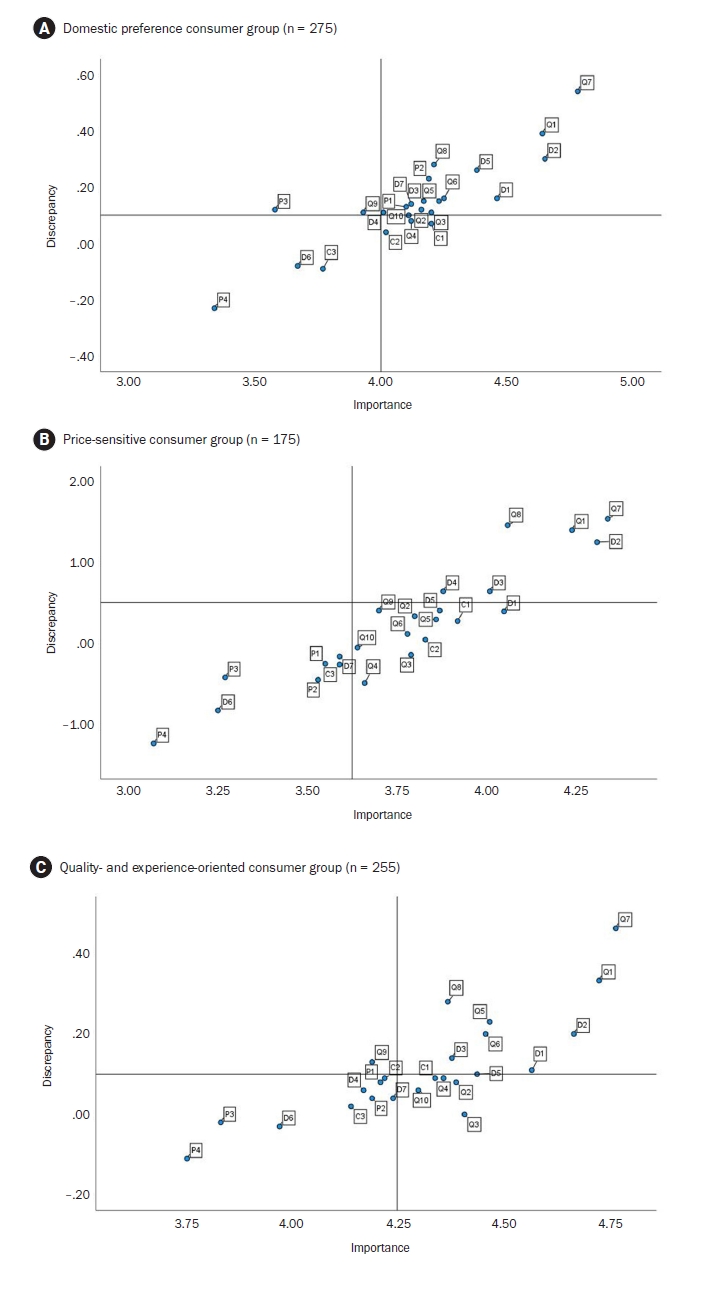
We implemented a cross-sectional survey targeting 705 adult consumers in South Korea using hierarchical and K-means cluster analyses. Respondents were classified into three relevant lifestyles: (1) domestic preference, (2) price-sensitive, and (3) quality-experience-oriented. The importance-performance analysis was employed to evaluate discrepancies between how they rated pork consumption using factors of “importance” and “satisfaction”. We employed Borich’s needs assessment and the Locus for Focus model to prioritize management areas.
Results
The research findings highlight that unpleasant odor/smell (Q7) and hygiene (Q1) were common key areas for management across all consumer groups, emphasizing their importance in enhancing pork consumption satisfaction. Among the groups, the domestic preference group showed high importance-performance discrepancies in attributes like expiry date (D2), suggesting a need for strengthened trust in domestic pork distribution and information transparency. The price-sensitive group prioritized economic factors, with fat thickness (Q8) identified as an essential management area. The quality-experience-oriented group emphasized sensory qualities such as juiciness (Q6) and meat color (Q5), with off-flavors (Q7) displaying the largest discrepancy. These results show the significant role of sensory attributes in consumer satisfaction.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the multidimensional nature of pork consumption behavior, emphasizing the need for tailored strategies across consumer groups. Managing hygiene (Q1) and reducing off-flavors (Q7) are critical for all segments, while group-specific strategies include managing sensory quality for the quality-experience-oriented group, providing product information (D2) to increase trust for the domestic preference group, and emphasizing value for money for the price-sensitive group.
- 1,894 View
- 42 Download

- [English]
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):16-26. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00311

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated the nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P) and analyzed the impact of key factors, such as caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment, on the eating habits of preschool children in Korea. This study also sought to provide foundational data for developing tailored nutrition education programs by identifying the nutrition education needs of caregivers.
Methods
This study was conducted among caregivers of preschool children (aged 0–6 years) using an online self-administered survey conducted from August 22 to August 28, 2023. A total of 1,116 survey responses were analyzed. This study assessed children’s NQ-P score, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and nutritional education needs. Data were analyzed using SPSS 29.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
The average NQ-P score for preschool children was 52, showing a tendency for the balance score to decrease and the moderation score to increase with age. Children from rural and low-income areas exhibited significantly lower NQ-P scores. Caregivers’ food literacy was higher in urban and higher-income groups. Multiple regression analysis revealed that social support, food literacy, income, and food environment significantly affected children's NQ-P scores. The effectiveness of nutrition education varied based on the income level, with nutrition education on healthy eating being the most preferred topic for preschool children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that caregivers’ food literacy and social support significantly affected preschool children’s nutritional status. This suggests a need for tailored nutritional education and dietary support policies, particularly for low-income and rural populations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 352. CrossRef
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- 3,105 View
- 60 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of a multi-component program based on partially hydrolyzed guar gum (Sunfiber®) on glycemic control in South Korea: a single-arm, pre-post comparison pilot clinical trial
- Hyoung Su Park, A-Hyun Jeong, Hyejung Hong, Hana Jang, Hye-Jin Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):40-52. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00276
- Correction in: Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to assess the impact of a multi-component program, including partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG, Sunfiber®) supplementation, on glycemic control, gut health, and nutritional status to support diabetes prevention and management among Korean adults.
Methods
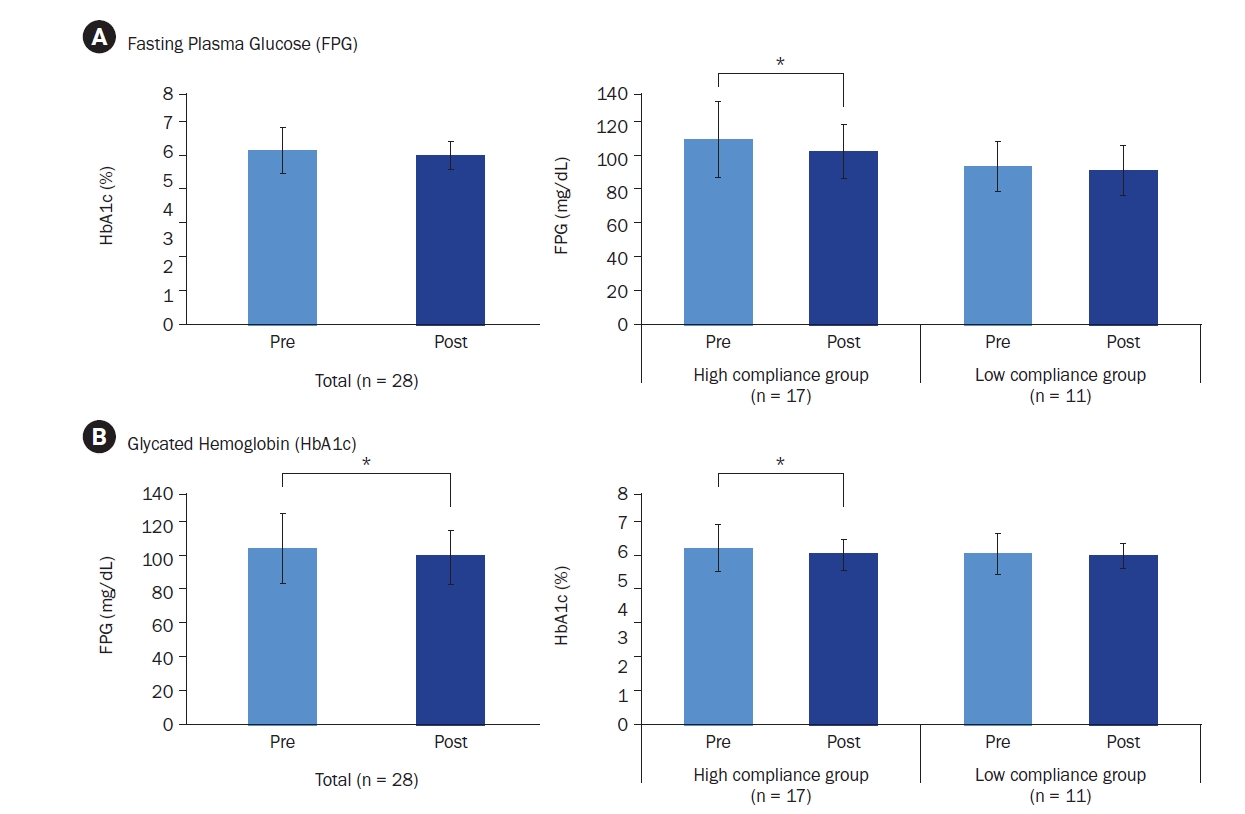
A single-arm trial was conducted with 29 adults (aged 20-55 years) with fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 100 mg/dL. Over a six-week period, participants engaged in a multi-component program that incorporated the supplementation of PHGG (Sunfiber®, 12.5 g/day), weekly nutritional coaching, and the use of continuous glucose monitoring devices. The program’s effectiveness was evaluated by measuring FPG and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels through blood tests conducted before and after the intervention. Improvements in gut health were gauged using the Korean Gut Quotient Measurement Scales, while enhancements in nutritional status were assessed using the Nutrition Quotient (NQ) and surveys that evaluated improvements in gut health and nutritional status.
Results
Participants’ average age was 43.89 years, with approximately 80% being male. Most participants (about 75%) were classified as overweight or obese. After six-weeks, 17 participants who adhered closely to the program (meeting certification criteria) exhibited significant reductions in key blood glucose markers. FPG levels decreased from 113.06 ± 23.16 mg/dL to 106.24 ± 16.33 mg/dL (P < 0.05), and HbA1c levels decreased from 6.08% ± 0.81% to 5.87% ± 0.53% (P < 0.05). The NQ evaluation revealed significant increases in comprehensive nutrition scores, and in the balance and practice domain scores for all participants (P < 0.05). Furthermore, in the gut health survey, approximately 82.1% of all participants reported experiencing positive changes.
Conclusion
Among adults with elevated FPG levels, a multi-component intervention program that included PHGG (Sunfiber®) supplementation, structured dietary management, and the use of health-monitoring devices showed significant benefits in improving glycemic control, overall nutritional status, and gut health. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010049. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of dietary and lifestyle habits according to the prediabetic status in young adults
Joungyoon Seo, SeongHee Shin, Yuri Kim, Yoo Kyoung Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 468. CrossRef - Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Combined with a Low-Fat Diet Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites
Zhiqiang Cao, Hongxia Li, Quantao Cai, Li Chen, Liangzhong Liu, Yuhan Tang, Zhe Zhu, Ping Yao
Nutrients.2025; 17(23): 3746. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of dietary and lifestyle habits according to the prediabetic status in young adults
- 7,434 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):514-527. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study aimed to use big data from elementary, middle, and high school lunches to determine the primary food groups and menu items that contribute to lunch meals through text-mining and investigate the variations in food groups and menu composition patterns across different grade levels.
Methods
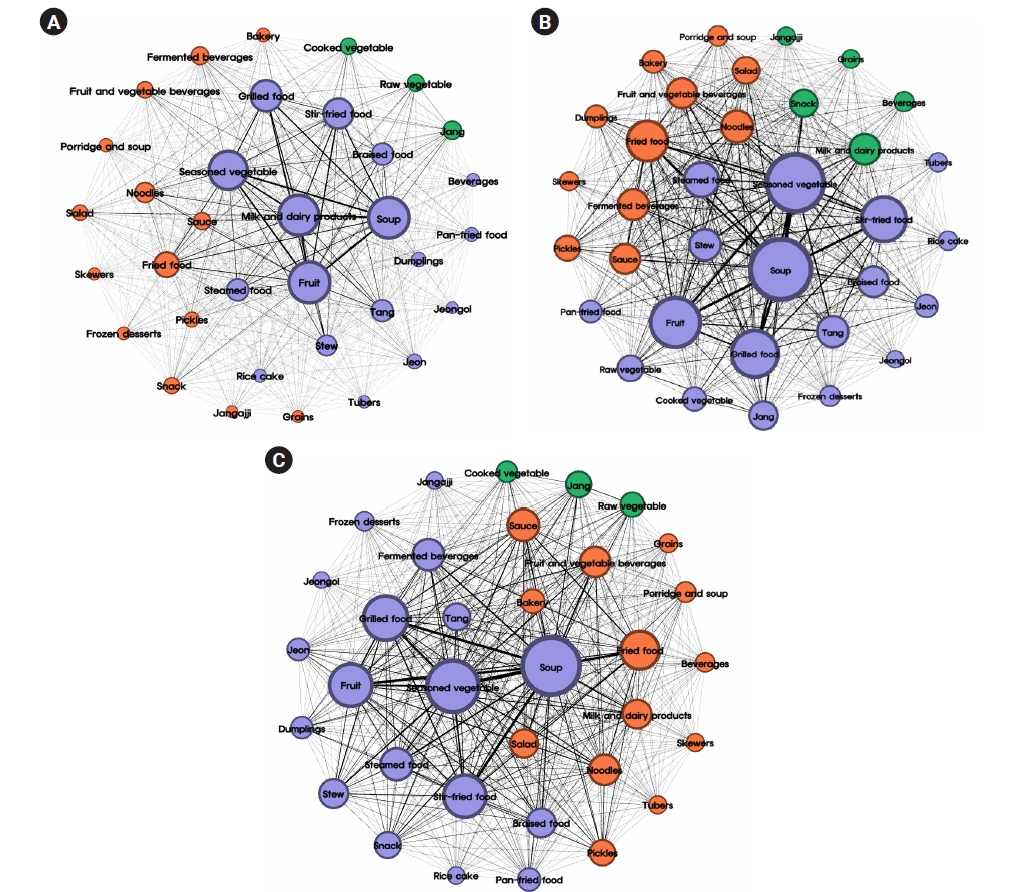
Between 2021 and 2023, a total of 7,892,456 lunch menus from 17 cities and provinces in South Korea were analyzed using big data from the National Education Information System (NEIS) system. After undergoing text preprocessing for text-mining, the collected menus were classified into 34 food groups based on primary ingredients and cooking methods, excluding the types of rice and kimchi. Subsequently, analyses of term frequency, term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF), centrality, and co-occurrence networks were performed on the food group and menu data.
Results
According to the TF-IDF, the most frequent food group across all grade levels was soup and seasoned vegetables, whereas milk was the most frequently provided menu. As the grade level increased, the frequency of grilled and fried food increased. In elementary schools, fruits exhibited the highest centrality, whereas soup had the highest centrality in middle and high schools. Co-occurrence frequency revealed that the soup-fruit combination was the most common in elementary schools, whereas soup and seasoned vegetables were most frequently paired in middle and high schools. The co-occurrence network of food groups and menus further indicated that menus regularly provided as standard meals and those frequently offered as special meals formed distinct communities.
Conclusion
This study investigated the food groups and menu provision patterns in school meals through text-mining techniques applied to large-scale school lunch. The findings may contribute in enhancing the quality of nutritional management, school foodservice, and menu composition of school meal programs.
- 1,969 View
- 51 Download

Research Note
- [English]
- A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
- Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):455-466. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00248
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A campus-based intervention to enhance food literacy (FL) and establish exercise habits among college students was developed and the program’s effectiveness was evaluated.
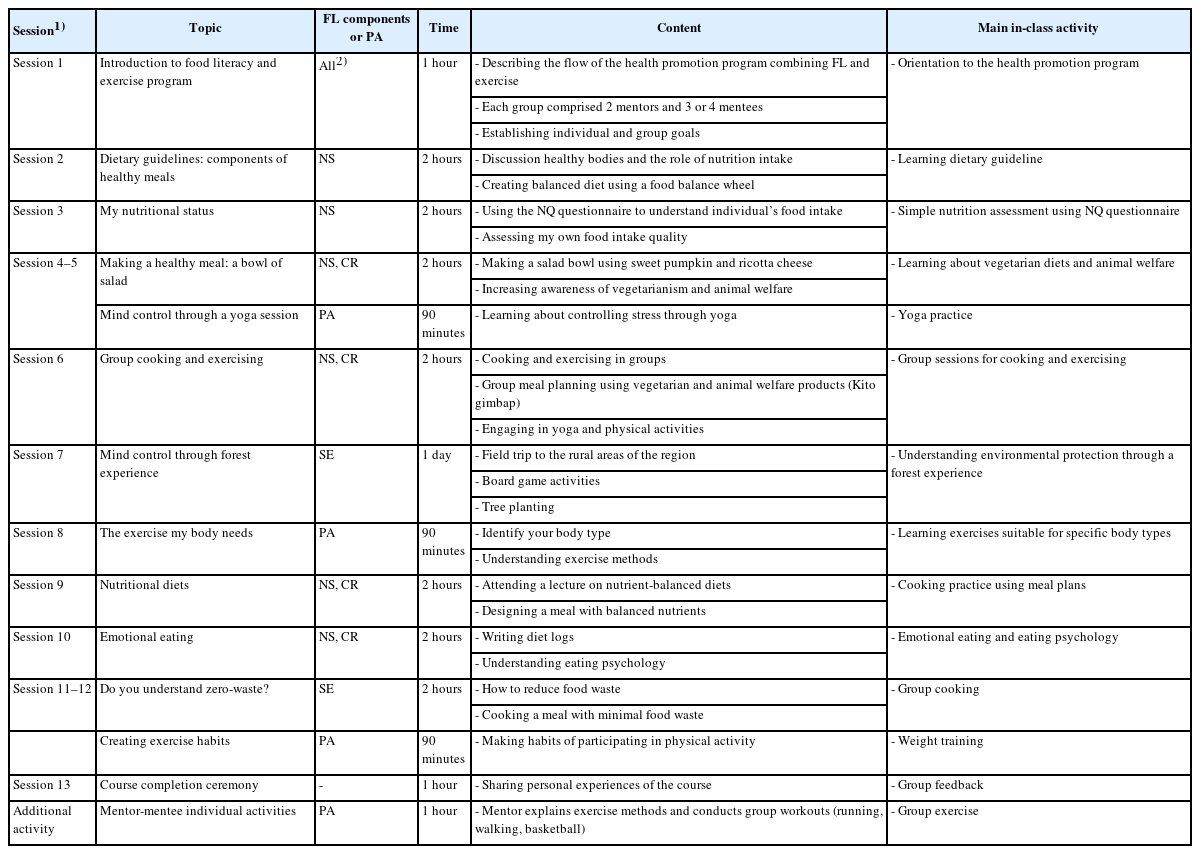
Methods
The 13-session program was developed based on the transtheoretical model and social cognitive theory. Junior and senior students majoring in food and nutrition and physical education were asked to participate as mentors, with freshmen and sophomores from varied majors as mentees. The program encompassed food, nutrition, and exercise lessons including cooking sessions. Data were collected via pre- and post-program surveys using a questionnaire consisting of items on FL and nutrition behaviors and physical fitness measurements.
Results
Among 39 participants (35.9% male, 64.1% female), the overall FL score increased significantly from 64.1 to 70.6 post-program (P = 0.001). Significant increases were observed in the nutrition and safety (P < 0.001), cultural and relational (P = 0.023), and socio-ecological (P = 0.001) domains, as well as knowledge (P = 0.001), self-efficacy (P = 0.013), attitude (P < 0.001), and behavior (P = 0.005) items in three domains of FL. Additionally, meal duration increased significantly (P = 0.007) and sit-up performance among female showed a meaningful change (P = 0.046). Changes in dietary behaviors significantly progressed (P = 0.015) while that in exercise habits approached a marginal significance (P = 0.053) after the intervention.
Conclusion
The results reveal positive changes in FL and some modifications in eating habits, although the program had limited effects on physical activity and fitness measurements. These findings suggest that strategic approaches to foster exercise behavior changes in college students are required. This pilot program can serve as foundational data for improving and expanding multicomponent health promotion programs for this population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Dragon Fruit Advantage: Exploring University Students’ Experiences and Perceptions of a Targeted Nutrition Education Module
Adelfa Silor, Faith Stephanny C. Silor
Seminars in Medical Writing and Education.2025; 4: 924. CrossRef
- The Dragon Fruit Advantage: Exploring University Students’ Experiences and Perceptions of a Targeted Nutrition Education Module
- 2,334 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

Research Articles
- [English]
- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
- Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):359-371. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00013

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate and compare factors associated with malnutrition according to the presence or absence of dementia in community-dwelling elderly people.
Methods
Needs assessment data from 311 long-term care insurance (LTCI) recipients (dementia group 203; non-dementia group 108) that participated in the second pilot program of the integrated care model in community care settings under the Korean LTCI system were used. Descriptive statistical analysis, independent t-test, and analysis of variance were conducted on the sociodemographic characteristics, health and functional status, and nutritional status of the dementia and non-dementia groups. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify factors associated with malnutrition in the dementia and non-dementia groups.
Results
Malnutrition occurred in 33.5% and 26.9% of participants in the dementia and non-dementia groups, respectively. In the dementia group, living with family rather than living alone (odds ratio [OR]: 3.81; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.50–9.66; P = 0.031), increase in Korean Activities of Daily Living (K-ADL) score (OR: 1.35; 95% CI: 1.17–1.55; P < 0.001), and increase in the Neuropsychiatric Inventory-Questionnaire score (OR: 1.02; 95% CI: 1.01–1.03; P = 0.005) were associated with a higher risk of malnutrition. In the non-dementia group, the risk of malnutrition increased as the K-ADL score increased (OR: 1.20; 95% CI: 1.04–1.39; P = 0.011) and in the depressed group (OR: 2.84; 95% CI: 1.04–7.74; P = 0.042).
Conclusions
The study results confirmed the necessity of nutritional management for community-dwelling LTCI recipients. When developing a nutritional management program, considering the differences in factors related to malnutrition between the dementia and non-dementia groups is important. This study proposes policies for improving the LTCI system in terms of nutritional management and the utilization of community resources.
- 2,078 View
- 68 Download

- [English]
- Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
- Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):382-395. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00010

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated whether outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors differed according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students. Methods: The participants were students recruited from nine universities in Seoul, Korea. An online survey was conducted, and data from 351 participants were analyzed. Participants were classified into pre-action and action stages based on adequate sodium intake. Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, analysis of covariance, and correlation analysis. Results: Participants in the action stage (22.8%) felt fewer disadvantages of eating sodium adequately compared to those in the pre-action stage (77.2%, P < 0.001) and perceived more self-efficacy for healthy eating behaviors (P < 0.001) and controlling sodium intake (P < 0.01). The participants in the action stage also showed more desirable eating behaviors than those in the pre-action stage, including general eating behaviors, behaviors related to sodium intake, and sodium checks (P < 0.001). The physical environment in the action stage was more supportive of adequate sodium intake (P < 0.05). Eating behaviors, self-efficacy, and outcome expectations were significantly correlated with the stages of change; however, some differences were noticed in the correlation of the subscales of variables with the stages of change when examined by sex. Conclusion: We observed differences in factors according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake. For the pre-action stage, nutrition education can be planned to modify negative expectations of eating adequate sodium, foster self-efficacy, and practice general eating behaviors and behaviors to gradually reduce sodium intake. It is also necessary to alter the physical environment to reduce sodium intake. In the action stage, support and reinforcement are needed to continually practice and maintain desirable eating behaviors. Nutrition education for women may be planned using multiple paths, whereas a simple strategy may be useful for men.
- 2,544 View
- 44 Download

- [Korean]
- An educational needs analysis of sustainable dietary education for nutrition teachers: an application of the IPA, Borich needs assessment and The locus for focus model
- Eunseo Yang, Borham Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):372-381. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00008

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the importance and performance levels of sustainable dietary education across the health, environment, and society domains as perceived by nutrition teachers and evaluate the needs and priorities for sustainable dietary education.
Methods
An online survey was conducted for 151 nutrition teachers in Jeollanam-do. The survey included 20 questions across the health, environment, and society domains. The data were analyzed using a paired-sample t-test, the importance-performance analysis (IPA), the Borich needs assessment model, and the locus for focus model.
Results
Overall, the average importance levels of the 20 items of sustainable dietary education were significantly higher than their average performance levels (4.44 vs. 3.68). The examination of each educational domain revealed that although the importance of education in the health domain was recognized and actively practiced by the nutrition teachers, the performance was comparatively lower in the environment and society domains. The Borich needs assessment and the locus for focus model identified education on biodiversity conservation, plant-based protein, and the use of local food as the top-priority group in the environment domain along with fair and ethical food, food security, regional food culture, food policy and trade, and family dining culture as the second-priority group in the society domain.
Conclusions
The results of this study underscore the need to support the nutrition teachers’ perception and practice of sustainable dietary education in the environment and society domains. We believe that the educational needs and priorities proposed in this study will be considered in the future development and modification of sustainable dietary education programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Jounghee Lee, Juhyun Lee, Wookyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 75. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef - Analysis of students’ need for artificial intelligence content in the 「Digital education」 subject
SungAe Kim, Ji Won You
The Journal of Korean Association of Computer Education.2025; 28(7): 71. CrossRef - Safety education status and needs priorities of Korean military food service personnel using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model: a cross-sectional study
Jeongeun Park, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 261. CrossRef
- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 2,491 View
- 75 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Eating habits and dietary supplement utilization according to food-related lifestyle among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):253-264. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
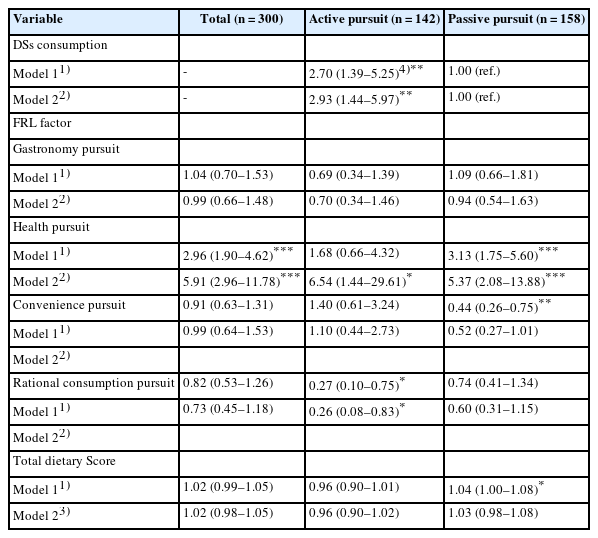
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the association between eating habits and the utilization of dietary supplements (DSs) according to food-related lifestyle (FRL) among Korean adults. Methods: This study included a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) in their 20s to 60s living in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province. We identified two groups by factor and cluster analysis: an ‘active pursuit’ group and a ‘passive pursuit’ group. Differences in eating habits and DS utilization between the two groups were analyzed by chi-square test and t-test. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the effect of variables on DS consumption according to FRL. Results: There were significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, alcohol drinking frequency, total dietary score, change in DS consumption after coronavirus disease 2019, and current DS consumption (P < 0.05). The proportion who perceived many health benefits of DSs was higher in the ‘active pursuit’ group than in the ‘passive pursuit’ group (P = 0.003). The most commonly consumed type of DSs was multivitamins & minerals for the ‘active pursuit’ group, and omega-3 fatty acids for the ‘passive pursuit’ group. The ‘an active pursuit’ group consumed DSs 2.93 times more (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.44–5.97) compared to the ‘passive pursuit’ group, after adjusting for confounders. In the ‘active pursuit’ group, the health pursuit (odds ratio [OR] = 6.54, 95% CI: 1.44– 29.61) and rational consumption pursuit factors (OR = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.08–0.83) were associated with DS consumption, whereas only the health pursuit factor had a significant association (OR = 5.37, 95% CI: 2.08–13.88) within the ‘passive pursuit’ group. However, total dietary score and DSs consumption did not show a relationship. Conclusions: By understanding the consumption characteristics of DSs according to FRL, this can serve as basic data necessary for promoting health through the utilization of DSs and healthy behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
Hongryul Ahn, Seungwon Kim, Jinmyung Jung, Chan Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(4): 618. CrossRef
- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
- 4,975 View
- 94 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Exploring the customer perceived value of online grocery shopping: a cross-sectional study of Korean and Chinese consumers using Means-End Chain theory
- Xinyu Jiang, Hyo Bin Im, Min A Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):318-335. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Despite the growing market share of online grocery shopping, there is a need to understand customer perceived value due to the ongoing advancements in information technology. This study explores the connections between attributes, consequences, and values. Additionally, it conducts a cross-country comparison of consumers’ online grocery shopping behaviors to gain a deeper understanding of consumer market segments and any potential variations among them.
Methods
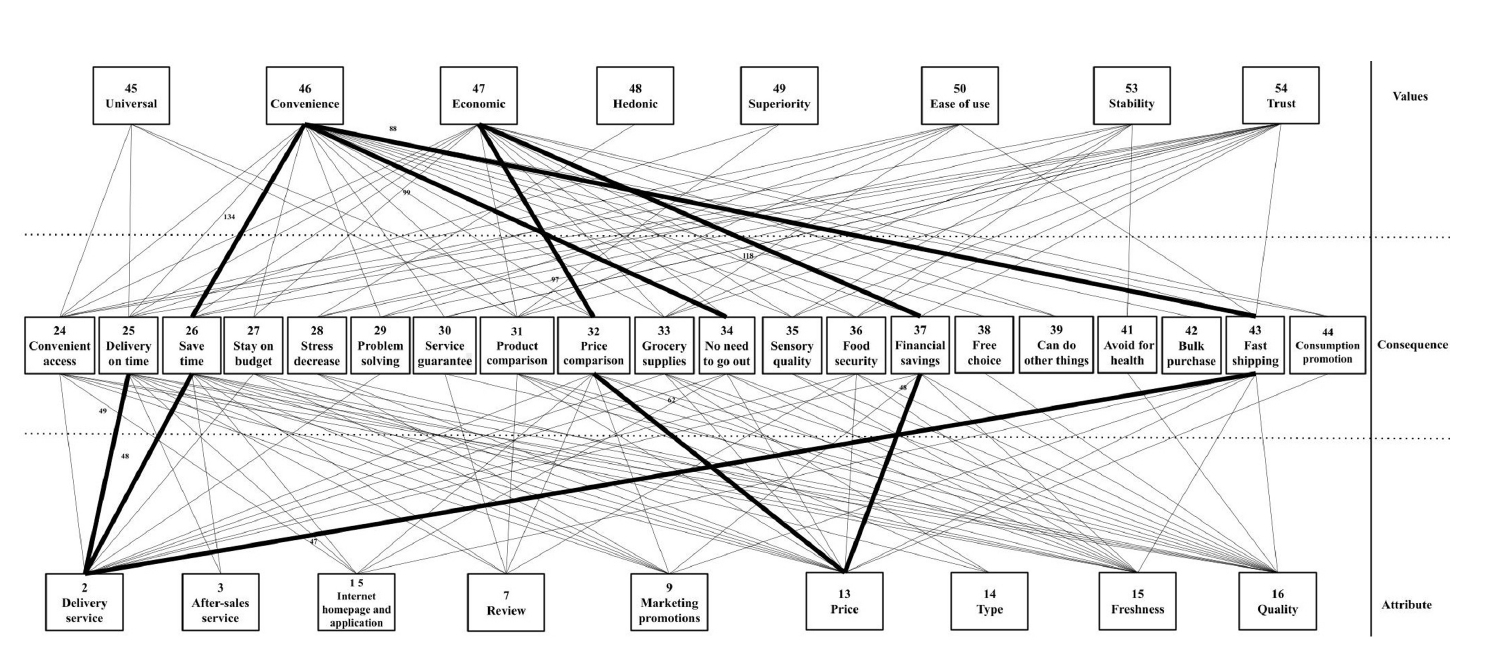
Data was collected through an online questionnaire survey conducted from May 1 to 15, 2024, targeting 400 consumers in Seoul, Korea, and Shanghai, China, who have experience with online grocery shopping. The survey utilized the Means-End Chain theory and association pattern technique hard laddering. Data collation and analysis were conducted using the IBM SPSS Statistics 28.0 program. The LadderUX software was employed to analyze the links between attributes, consequences, and values and create the consumer purchasing process’s implication matrix and hierarchical value map (HVM).
Results
The study identified key attributes that influence online grocery shopping decisions, including delivery service, price, freshness, and quality. Korean consumers demonstrated a higher sensitivity to price (19.0%) and delivery service (17.0%). In contrast, Chinese consumers prioritized delivery service (15.0%) and after-sales service (14.8%). Commonly cited consequences included time saving (12.6% for Koreans, 11.3% for Chinese), whereas prevalent values encompassed convenience (36.8% for Koreans, 19.6% for Chinese) and economic value (26.6% for Koreans, 14.7% for Chinese). The HVM underscored these insights, highlighting diverse consumer preferences and country-specific nuances.
Conclusions
The findings highlight the current state of online food consumption and consumers’ value systems, revealing variations among countries. These findings offer empirical insights that can be used to create customized global marketing strategies that resonate with various consumer preferences and market dynamics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the stage: how performing arts tourism shapes tourist perceptions and destination image
Islam Elbayoumi Salem, Mohammed Ali Bait Ali Sulaiman, Enrico di Bella, Sara Preti, Mohamed Kamal Abdien, Ahmed Magdy
Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights.2025; : 1. CrossRef
- Beyond the stage: how performing arts tourism shapes tourist perceptions and destination image
- 5,711 View
- 75 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Intake of energy and macronutrients according to household income among elementary, middle, and high school students before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study
- Chae-Eun Jeong, Heejin Lee, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):234-252. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.234
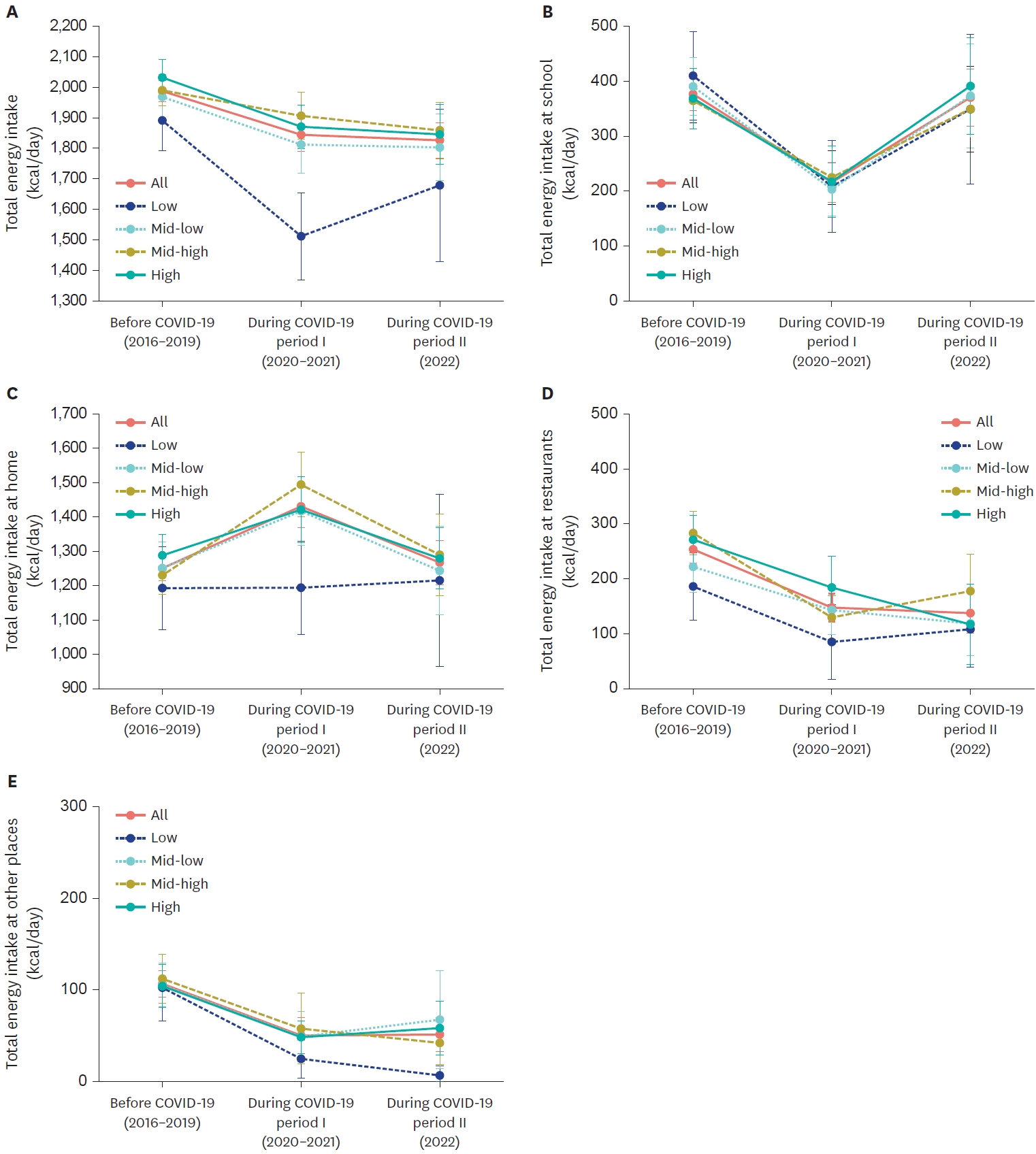
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the intake of energy and macronutrients among elementary, middle, and high school students according to household income before the COVID-19 pandemic (2016–2019), during the social distancing period (2020–2021), and after the social distancing measures were lifted (2022).
Methods
We included 5,217 students aged 5–18 from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) conducted between 2016 and 2022. Dietary intake was assessed using one-day 24-hour dietary recalls. We estimated the least squares means (LS-means) of intake according to household income for each period using a weighted linear regression model, adjusted for age and sex. Differences in LS-means between the periods were analyzed using the t-test.
Results
During the social distancing period, the LS-means of energy intake among students decreased significantly by 143.2 kcal/day compared to pre-pandemic levels (P < 0.001). Students from low-income households experienced a more pronounced decrease in energy intake (−379.1 kcal/day, P < 0.001) and macronutrient intake compared to those from other income groups. Energy intake at school significantly declined for all income groups during the social distancing period compared to before the pandemic. No significant changes in home energy intake were observed among low-income students, whereas there was an increase for students from higher-income groups. Before the pandemic, 8.5% of students from low-income households reported insufficient food due to economic difficulties; this figure rose to 21.3% during the pandemic.
Conclusions
During the pandemic, students from low-income families experienced significantly lower intake of energy and macronutrients compared to pre-pandemic levels. The most substantial reductions were noted among low-income students, largely due to the lack of compensation for decreased school-based intake with increased intake at home. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
Yong-Seok Kwon, Dasol Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1973. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment of Older Korean Adults by Level of Plant Protein Intake
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Jeong-Hun Song, Yangsuk Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1976. CrossRef - Analysis of Risk Factor Changes for Myopia in Korean Adolescents Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic
Seeun Lee, So Ra Kim, Mijung Park
Medicina.2025; 61(10): 1798. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef
- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
- 2,838 View
- 106 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Serum branch chain amino acids and aromatic amino acids ratio and metabolic risks in Koreans with normal-weight or obesity: a cross-sectional study
- Ji-Sook Park, Kainat Ahmed, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.212
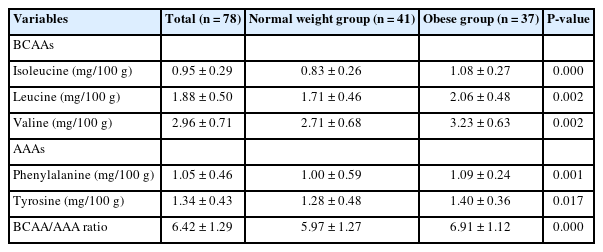
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Metabolic disease is strongly associated with future insulin resistance, and its prevalence is increasing worldwide. Thus, identifying early biomarkers of metabolic-related disease based on serum profiling is useful to control future metabolic disease. Our study aimed to assess the association of serum branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and aromatic amino acids (AAAs) ratio and metabolic disease according to body mass index (BMI) status among Korean adults.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 78 adults aged 20–59 years in Korea. We compared serum amino acid (AA) levels between adults with normal-weight and adults with obesity and investigated biomarkers of metabolic disease. We examined serum AA levels, blood profile, and body composition. We also evaluated the association between serum AAs and metabolic-related disease.
Results
The height, weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-hip-ratio, body fat mass, body fat percent, skeletal muscle mass, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure were higher in the group with obesity compared to normal weight group. The group with obesity showed significantly higher levels of BCAA, AAA, and BCAA and AAA ratio. Further, BCAA and AAA ratio were significantly positively correlated with triglyceride, body weight, and skeletal muscle mass. The evaluation of metabolic disease risks revealed an association between the ratios of BCAAs and AAAs, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome.
Conclusions
Our study is showed the associations between BCAA and AAA ratio, obesity, and obesity-related diseases using various analytical approaches. The elevated BCAA and AAA ratio could be early biomarkers for predicting future metabolic diseases in Korean population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
Apostolos Gkantzos, Stavros Kalogiannis, Olga Deda
Journal of Proteome Research.2025; 24(5): 2208. CrossRef - Current Data on the Role of Amino Acids in the Management of Obesity in Children and Adolescents
Diana Zamosteanu, Nina Filip, Laura Mihaela Trandafir, Elena Ţarcă, Mihaela Pertea, Gabriela Bordeianu, Jana Bernic, Anne Marie Heredea, Elena Cojocaru
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(15): 7129. CrossRef
- The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
- 2,173 View
- 24 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Factors influencing consumers’ continuance intention in online grocery shopping: a cross-sectional study using application behavior reasoning theory
- Binglin Liu, Min A Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):199-211. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.199
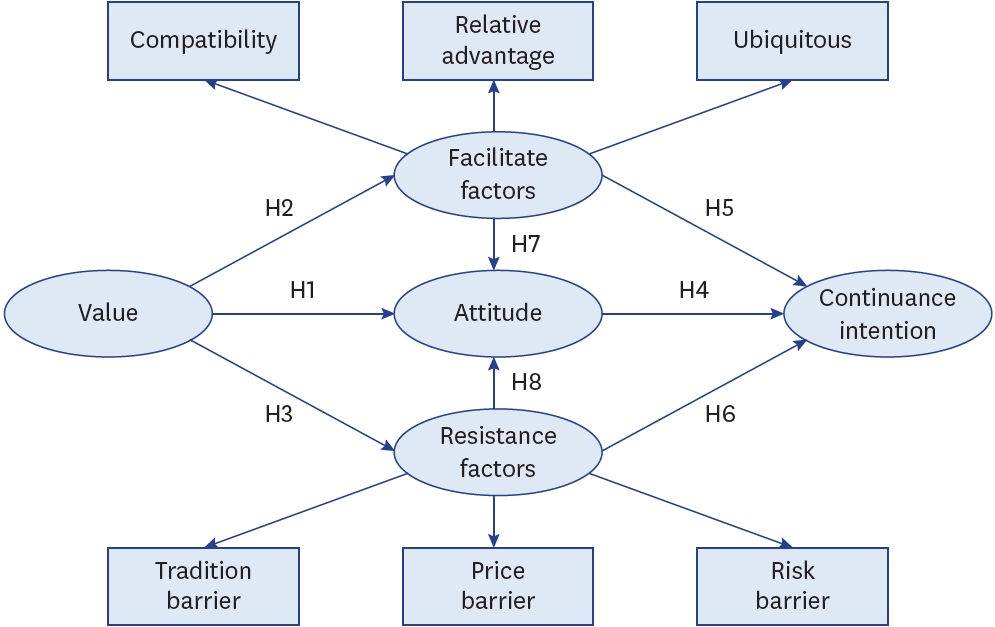
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Online grocery shopping has gained traction with the digital transformation of retail. This study constructs a behavioral model combining values, attitudes, and reasons for behavior—specifically, facilitators and resistance—to provide a more novel discussion and further understand the relative influences of the various factors affecting continuance intention in online grocery shopping.
Methods
Data were collected through an online questionnaire from consumers who had engaged in online grocery shopping during the past month in Seoul, Korea. All collected data were analyzed using descriptive analysis, and model validation was performed using partial least squares structural equation modeling.
Results
Continuance intention is primarily driven by facilitative factors (compatibility, relative advantage, and ubiquity). Attitude can also positively influence continuance intention. Although resistance factors (price, tradition, and risk) do not significantly affect continuance intention, they negatively affect attitude. Values significantly influence consumers’ reasoning processes but not their attitude.
Conclusions
These findings explain the key influences on consumers’ online grocery shopping behavior in Seoul and provide additional discussion and literature on consumer behavior and market management. To expand the online grocery market, consumers should be made aware of the potential benefits of the online channel; the barriers they encounter should be reduced. This will help sustain online grocery shopping behavior. Furthermore, its positive impact on attitude will further strengthen consumers’ continuance intention. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Modelling the mass adoption potentials of fashion-augmented reality among the young consumers: evidence from an emerging economy
Mohima Akther, Mohammad Nurul Hassan Reza, Abdullah Al Mamun, Norzalita Abd Aziz, Marvello Yang
Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal.2025; 29(3): 459. CrossRef
- Modelling the mass adoption potentials of fashion-augmented reality among the young consumers: evidence from an emerging economy
- 7,371 View
- 86 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):173-188. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.173
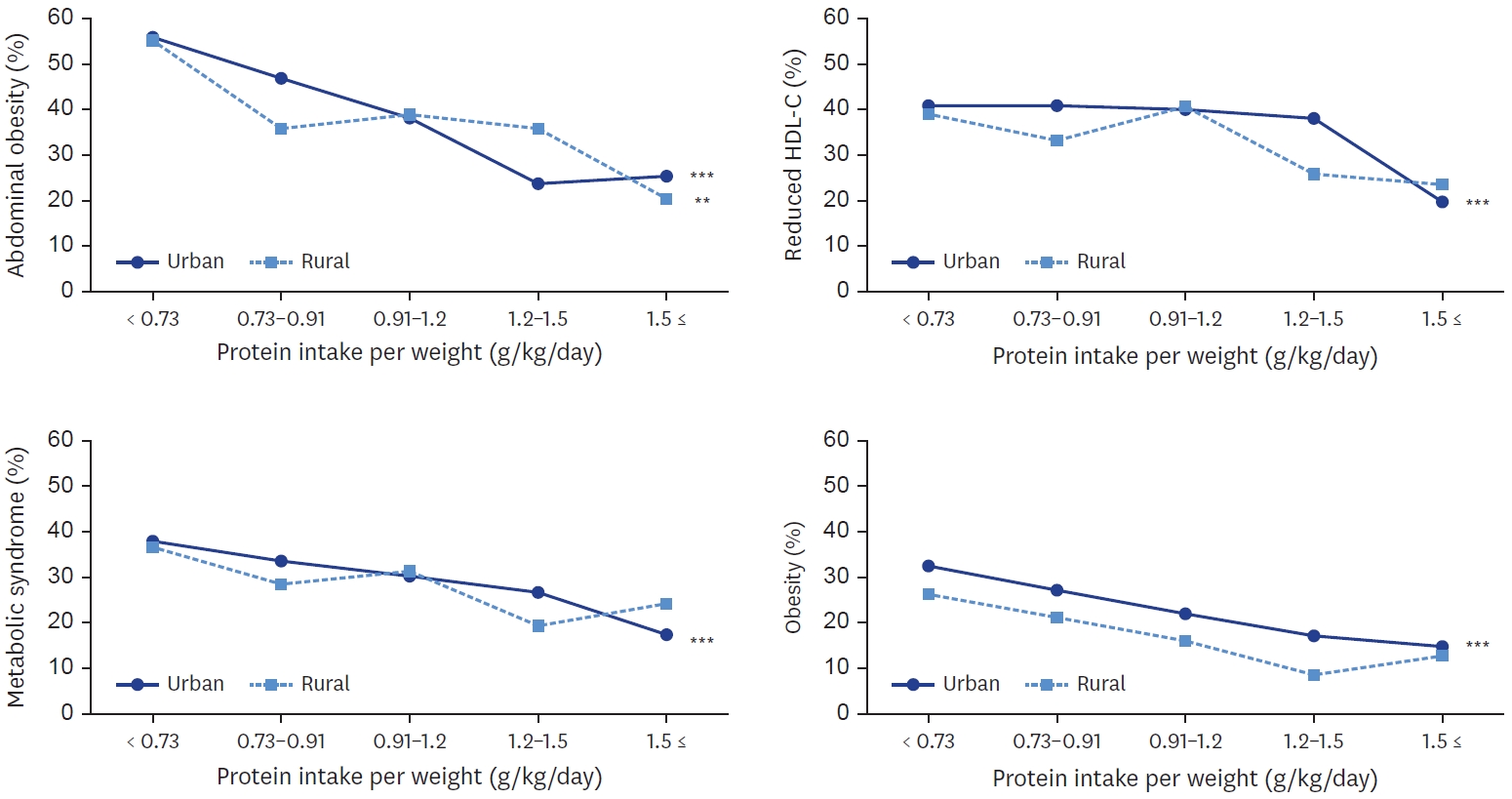
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to analyze the regional differences in dietary protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome.
Methods
Study participants were 1,721 older adults aged 65 and over who participated in 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Using 24-hour recall dietary intake data, protein intake and their food sources were examined. The association between protein intake and metabolic syndrome, obesity, and abdominal obesity were analyzed by multiple logistic regression.
Results
Total protein and animal protein intakes were higher in urban area (60.0 g, 24.4 g, respectively) than in rural area (54.6 g, 19.6 g, respectively). With increase of protein intake level, animal to total protein proportion was increased in both areas. Total protein and plant protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity, abdominal obesity in both areas. Animal protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity in both areas, and with abdominal obesity only in urban area. In urban area, plant protein intake was also negatively associated with the risks of metabolic syndrome, elevated triglyceride, and reduced high density lipoprotein-cholesterol. In urban area, the risk of metabolic syndrome was decreased when their protein intake was more than 0.91 g/kg and was lowest when their protein intake was more than 1.5 g/kg (P for trend < 0.001).
Conclusions
Korean older adults showed inadequate protein intake and those in rural area showed lower animal protein intake than in urban area. The risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome was decreased with the increase of protein intake level. These findings may help develop effective nutrition support strategy for older adults to reduce regional health disparity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
Yea-Chan Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Soyoung Jeon, Yae-Ji Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2026; 50(1): 178. CrossRef - The association between dietary protein intake and metabolic syndrome: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Dorsa Ghazvineh, Ali Hosseinpour, Vahid Basirat, Elnaz Daneshzad
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between total, animal-based, and plant-based protein intake and cognitive decline in older adults
Maud Peperkamp, Margreet R. Olthof, Marjolein Visser, Hanneke A. H. Wijnhoven
European Journal of Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
- 10,061 View
- 107 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):97-113. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Since the enactment of the School Nutrition Act in 1981, school lunch programs in South Korea have grown quantitatively and qualitatively with a current student participation rate of 99.8%. Nonetheless, educational materials are needed to reduce misunderstanding and ignorance about school lunch programs. This study aimed to develop 3 educational videos that help students of various ages (kindergarteners/lower-grade elementary, upper-grade elementary, and secondary school, respectively), understand the school lunch program.
Methods
A scenario was created, was made, and the opinions on the scenario from experts in foodservice sectors were collected. A survey was conducted to students and parents to determine topics they wanted to know about school foodservice. The final videos were produced using this information and the expert opinions. The data were analyzed using SPSS 27.0 for Mac (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA); a P-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Three videos on school foodservice were developed for various age levels of students: kindergarten/lower-grade elementary, upper-grade elementary, and secondary school. Additionally, English subtitles were included for the multicultural student population. These videos, each lasting about 7 minutes, cover topics such as nutrition, hygiene, and the cultural significance of the school lunch program. The survey results showed that parents and students wanted to know the following topics about the school lunch program: “nutritionally balanced diet” (11.9%), “purchasing safe food ingredients” (10.9%), and “healthy eating habits” (9.9%).
Conclusions
The developed videos will serve as valuable educational resources on school foodservice, foster a deeper understanding of the school lunch program in parents and students, and potentially address their inquiries regarding production processes, nutrition, hygiene, cultural heritage, and health.
- 3,377 View
- 37 Download

- [English]
- Arterial stiffness index, physical activity and food and nutrient intake: cross-sectional study in adults aged 40 years and older
- Eun-A Kim, Yun-Mi Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):81-96. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate arterial stiffness index, physical activity, and food and nutrient intake in middle-aged adults over 40 years when the incidence of cardiovascular disease begins to increase.
Methods
This study included 106 subjects (48 males and 58 females) aged between 40 and 64 years. The arterial stiffness index (brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity [baPWV], and ankle-brachial index [ABI]) were measured using a blood pressure pulse wave testing device. Physical activity was assessed using the Korean version of the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire, and food and nutrient intake was calculated using the Food Frequency Questionnaire.
Results
The mean age of the subjects was 54.4 years. Although the ABI of the subjects was within the normal range, they were divided into tertiles to compare physical activity and food and nutrient intake. In males, the time spent on moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) was significantly higher in T3 (600.6 min/week) than in T1 (304.4 min/week). In females, the time spent in sedentary behavior was significantly lower in T3 (294.5 min/week) than in T1 (472.1 min/week). In addition, the frequency of fish consumption was significantly higher in T3 (1.27 frequency/day) than in T1 (0.64 frequency/day) in females. Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) and ω-3 fatty acid intake, adjusted for energy intake, were significantly positively correlated with ABI (r = 0.200 and r = 0.218, respectively).
Conclusions
High MVPA (in males), low sedentary behavior (in females), and PUFA and ω-3 fatty acid intake through fish consumption may be associated with low peripheral artery stiffness. Therefore, arteriosclerosis can be prevented through physical activity and proper dietary therapy.
- 1,310 View
- 38 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung-Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):156-170. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the association between how often Korean adolescents watch Mukbang and Cookbang videos and their dietary habits.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 was analyzed for this study. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed various aspects, including demographics, frequency of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos per week, dietary habits, health behaviors, and mental health factors.
Results
Nearly a third (29.3%) of Korean adolescents watched Mukbang and Cookbang videos one to four times a week, while 13.5% watched them more than five times weekly. Females, those with lower academic achievement, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds were significantly more likely to be frequent viewers (P < 0.001). Increased viewing frequency was associated with poorer dietary habits. Adolescents who watched more frequently were less likely to eat breakfast and consume fruits and milk, while their consumption of fast food, high-caffeine drinks, sugary drinks, and late-night snacks increased (P < 0.001). Higher viewing frequency correlated with increased feelings of stress, depression, and loneliness (P < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis confirmed these associations. More frequent viewers were significantly less likely to eat breakfast (odds ratio (OR), 0.63; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.58–0.68), and more likely to consume fast food (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.69–2.02), high-caffeine drinks (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30–1.56), sugary drinks (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.41–1.67), and late-night snacks (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.25–1.51).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that frequent exposure to Mukbang and Cookbang content is linked to unhealthy dietary habits in adolescents. Educational programs may be necessary to mitigate the potential for these videos to negatively influence dietary choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
Seung Jae Lee, Yeseul Na, Kyung Won Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2652. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef
- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
- 3,629 View
- 103 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2016–2021 KNHANES data
- Enkhgerel Erdenetsetseg, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):144-155. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.144
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids in Korean adolescents.
Methods
This study was comprised of 3,932 adolescents (9–18 years) who participated in the 2016–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids, including alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and linoleic acid (LA) were evaluated using data obtained from one-day 24-hour dietary recall. The proportions of adolescents consuming ALA, EPA + DHA, and LA above or below the adequate intake (AI) of the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans were calculated. All statistical analyses accounted for the complex sampling design effect and appropriate sample weights.
Results
The mean intakes of ALA, EPA, DHA, and LA among Korean adolescents were 1.29 g/day, 69.6 mg/day, 166.0 mg/day, and 11.1 g/day, respectively. Boys had higher intakes of all essential fatty acids compared to girls. By age group, adolescents aged 15–18 years showed lower intakes of EPA and DHA compared to adolescents in younger age groups. The 9–11-year-old adolescents had lower intakes of ALA and LA than older adolescents. The proportions of adolescents who consumed more than AI were 35.7% for ALA, 30.4% for EPA + DHA, and 41.5% for LA. Adherence to the AI for ALA did not differ by sex or age group, although boys showed a lower adherence to the AI for EPA + DHA than girls. Major food sources for ALA and LA were plant-based oils, mayonnaise, pork, and eggs. Mackerel was the most significant contributor to EPA and DHA intake (EPA, 22.6%; DHA, 22.2%), followed by laver, squid, and anchovy.
Conclusions
The proportion of Korean adolescents who consumed EPA + DHA more than AI was low. Our findings highlight that nutrition education emphasizing an intake of essential fatty acids from healthy food sources is needed among Korean adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Harnessing dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids through gut microbiota to enhance ferroptosis in breast cancer therapy
Yara Adel Haroun, Abdulrahman Abdulla Alzyoud, Mohammad Taha Alizadeh, Nashwa Ahmed Mohamed, Riyad Bendardaf, Sameh S.M. Soliman
Nutrition Research.2025; 141: 10. CrossRef
- Harnessing dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids through gut microbiota to enhance ferroptosis in breast cancer therapy
- 3,832 View
- 58 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Impact of postoperative dietary types on nutrition and treatment prognosis in hospitalized patients undergoing oral and maxillofacial surgery: a comparative study
- Sung Bin Youn, Se-Hui Ahn, Dong-Ho Cho, Hoon Myoung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):129-143. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
The objective of this study is to compare a nutritionally balanced soft blend diet (SBD) with a soft fluid diet (SFD) on the health of inpatients who have undergone oral and maxillofacial (OMF) surgery, ultimately aiming to enhance care outcomes, improve health-related quality of life (QOL), and increase satisfaction with the hospital.
Methods
Thirty-two patients were randomized into two groups: sixteen received SFD and sixteen received SBD. Anthropometric, laboratory evaluations were conducted upon admission and discharge. Patients filled out questionnaires on demographics, diet satisfaction, food intake amount, and health-related QOL on the day of discharge, assessed using the EuroQoL 5 Dimensions 3 Level and EuroQoL Visual Analogue Scale (EQ-VAS) instruments. Data were analyzed with descriptive statistics, χ2 tests for group differences, and paired nonparametric t-tests for within-group comparisons. The Mann-Whitney U test evaluated inter-group differences in preoperative weight and body mass index (BMI), postoperative changes, meal satisfaction, intake, health-related QOL, and self-assessed health status. P-values were set at a significance level of 0.05.
Results
The SBD group had higher dietary intake (63.2% vs. 51.0%) and greater diet satisfaction (80.6 vs. 48.1, P < 0.0001) compared to SFD group. Health-related QOL, measured by EQ-VAS, was better in SBD group (70.3 vs. 58.8, P < 0.05). Postoperative weight and BMI decreased in SFD group but increased in SBD group (P < 0.01). Changes in laboratory results showed more stability in the SBD group. No postoperative infections were reported in SBD group, whereas SFD group had a 31.25% complication rate.
Conclusions
While SFD is often recommended after OMF surgery to protect oral wound healing process, our study reveals that SBD not only enhances physical and psychological outcomes but also, somewhat unexpectedly, supports wound healing and reduces complications. Essentially, SBD promotes physical recovery and enhances health-related QOL than SFD by supporting both somatic and mental healing aspects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Effect of Therapeutic Nutrition on Serum Albumin Levels and Nutritional Indices in Patients Undergoing Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for Maxillofacial Fractures – A Prospective Clinical Trial
B. R. Rajanikanth, Amruta T. Achar, Kavitha Prasad, Hema Arvind
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2025; 24(1): 110. CrossRef - Nutritional management for breast cancer patients
Minjeong Kim, Minkyoung Lee, Jisun Sa
The Ewha Medical Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Holistic Approach to Postendodontic Pain Management: A Narrative Review
Hmoud A. Algarni
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 5): S4262. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Effect of Therapeutic Nutrition on Serum Albumin Levels and Nutritional Indices in Patients Undergoing Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for Maxillofacial Fractures – A Prospective Clinical Trial
- 4,187 View
- 108 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
- Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):51-64. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between ultra-processed food (UPF) consumption and chronic diseases in elderly Koreans.
Methods
Data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were analyzed. Dietary intake and UPF consumption were assessed using the NOVA food classification based on 24-hour recall data from 3,790 participants (aged 65+ years). Participants were divided into 4 groups based on the quartile of energy intake from UPFs. Regions were classified as urban or rural. Multivariable logistic regression was employed to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) after controlling for potential confounders.
Results
Among the participants, 71.3% resided in urban and 28.7% in rural areas. Compared to the urban elderly, rural participants tended to be older, have lower education and income levels, be more likely to live in single-person households, and have a higher smoking rate (P < 0.05). Urban elderly consumed more UPFs daily (146.1 g) compared to rural residents (126.6 g; P < 0.05). “Sugar-sweetened beverages” were the most consumed category in both regions. “Sweetened milk and its products” and “traditional sauces” were prominent in urban areas, while rural elderly consumed more “traditional sauces” and “distilled alcoholic beverages.” Rural areas also had a higher carbohydrate-to-calorie ratio than urban areas. Compared to the lowest quartile of UPF intake, the highest quartile was significantly associated with impaired fasting glucose only in rural areas (AOR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.00–2.19; P for trend = 0.0014). No significant associations were observed for diabetes in either urban or rural areas.
Conclusions
This study suggests that high intake of UPFs is associated with increased odds of impaired fasting glucose in rural elderly. Further research is needed to elucidate the specific negative health effects of UPFs in different populations, and targeted efforts should promote healthy diets in both urban and rural areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
Nazlıcan Erdoğan Gövez, Eda Köksal
Current Nutrition Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study of the Chemosensory Properties of Commercial Processed Foods Using Electronic Sensors
Hyeonjin Park, Younglan Ban, Sojeong Yoon, Hyangyeon Jeong, Seong Jun Hong, Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 805. CrossRef - Analysis of Flavor and Taste Patterns of Various Processed Animal Foods: Using the Electronic Tongue and Nose
Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Younglan Ban, Hyeonjin Park, Sojeong Yoon, Na Eun Yang, Seong Jun Hong, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(12): 1267. CrossRef
- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
- 2,223 View
- 72 Download
- 3 Crossref

Educational Materialses
- [Korean]
- Systematization of food and nutrition education content based on national kindergarten curriculum: a qualitative formative study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Eunyoung Baik
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):509-522. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.509
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study is intended to develop a curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aimed at preschool children, reflecting government policy and meeting the demands of preschool settings.
Methods
Existing educational materials were analyzed, and key elements of the 2019 Revised Nuri Curriculum (“Nuri Curriculum”) and Guidelines for Nutrition and Food Education in Kindergartens, Elementary, Middle, and High Schools (“Guidelines”) were examined as foundational information for developing the curriculum for food and nutrition education.
Results
Basing ourselves on the five domains of the Nuri Curriculum, “Physical Activity and Health,” “Communication,” “Social Relationships,” “Art Experience,” and “Natural Science Inquiry,” we integrated three areas from the Guidelines, namely “Dietary Habits and Health,” “Dietary Habits and Safety,” and “Dietary Habits and Culture,” to structure the curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education. Three specific domains, “Nutrition and Health,” “Food and Culture,” and “Safe Dietary Practices,” were tailored for preschool children, each comprising core concepts, content elements, and educational materials. In the “Nutrition and Health” domain, core concepts such as “nutrition” were addressed through content elements such as “balanced eating” and “vegetables and fruit,” while “health” included elements such as “eating regularly” and “nutrients for disease prevention,” each with two educational content components. The “Food and Culture” domain focused on “food” with content on “local foods (vegetable-garden experience)” and “food culture” with content on “our dining table (rice and side dishes),” “our agricultural products,” “global cuisine (multiculture),” and “considerate dietary practices,” each with four educational content components. The “Safe Dietary Practices” domain included core concepts such as “hygiene” with content on “hand-washing habits” and “food poisoning management,” and “safety” with content on “food labeling.”
Conclusions
The systematized curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aligns with the Nuri Curriculum and is interconnected with the Guidelines. This curriculum can be used as foundational material for developing educational resources tailored to the characteristics of preschoolers, contributing to effective implementation in early childhood education.
- 1,102 View
- 50 Download

- [English]
- Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
- Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):495-508. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.495
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop a campus-based intervention program to enhance food literacy (FL) among university students.
Methods
In the initial phase, we conducted a literature review of FL intervention studies and held in-depth interviews with university students to identify facilitators and barriers to improving and practicing FL. Expert counseling sessions were conducted with nutrition education, marketing, and service design professionals. The results of this phase led to the creation of an initial curriculum draft. In the second phase, a follow-up survey was conducted with young adults to assess the acceptability of the developed curriculum. After the follow-up survey, additional meetings were conducted with the aforementioned experts, and the curriculum was further refined based on their input.
Results
An 11-week FL intervention program was devised using constructs from the Social Cognitive Theory. The weekly curriculum consisted of 90-min theory-based and 90-min hands-on experience sessions. Three primary aspects of FL were covered: nutrition and food safety, cultural and relational dimensions, and socio-ecological aspects. Program highlights included cooking sessions for crafting traditional Korean desserts, lectures on animal welfare, insights into zero-waste practices, and communal eating experiences. Based on the study team’s previous research, the program also addressed mindful eating, helping participants understand the relationship with their eating habits, and providing strategies to manage negative emotions without resorting to food. Yoga sessions and local farm visits were incorporated into the curriculum to promote holistic well-being.
Conclusions
This study elucidated the comprehensive process of creating a campus-based curriculum to enhance FL among university students, a group particularly susceptible to problematic eating behaviors and low FL levels. The developed program can serve as a blueprint for adaptation to other campuses seeking to bolster students’ FL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of nutrition class with cooking lab on college students’ eating behaviors and well-being in the United States: a mixed-methods study
Borham Yoon, Kyungyul Jun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 305. CrossRef - The Dragon Fruit Advantage: Exploring University Students’ Experiences and Perceptions of a Targeted Nutrition Education Module
Adelfa Silor, Faith Stephanny C. Silor
Seminars in Medical Writing and Education.2025; 4: 924. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of a food literacy pilot program for university students: using a mixed-methods research approach
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(6): 885. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef
- Effects of nutrition class with cooking lab on college students’ eating behaviors and well-being in the United States: a mixed-methods study
- 2,418 View
- 68 Download
- 4 Crossref

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Effectiveness of NQ-E index-based individual nutrition counseling for community-care elderly: an intervention study on improving nutritional status, complex chronic diseases, and quality of life
- Yoonjeong Choi, Jihyun Lee, Heesook Lim, Yoo Kyoung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):480-494. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.480
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study sought to assess the effectiveness of community-based nutrition counseling on improving nutritional status, managing complex chronic diseases, and enhancing the quality of life for elderly individuals with chronic conditions, particularly in older adults with high levels of food insecurity and multiple chronic illnesses.
Methods
Thirty elderly subjects with diabetes and hypertension who were registered at local Senior Welfare Center received individualized nutrition counseling, based on their Nutrition Quotient for the Elderly (NQ-E) index. Over a 16-week period, they received tailored counseling and underwent various health and nutritional assessments. The final analysis included 28 participants after two dropped out. Data analysis was conducted using the SPSS v28.0.
Results
The subjects were over 70, with multiple chronic diseases including diabetes and hypertension and predominantly female. After 16 weeks, significant improvements were observed in the subjects’ grip strength, and HbA1c levels, as well as in their NQ-E scores, indicating improved dietary balance and diversity. There were no significant improvements in the ‘Moderation’ subdomain of the NQ-E index, suggesting that this aspect requires further attention in nutritional counseling. The subjects' nutritional risk scores (NSI) were also significantly decreased, indicating less nutritional risk. Lastly, as measured by the SF-36K, the subjects’ quality of life showed significant improvement in several domains including physical role performance and social function.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that tailored nutrition counseling, based on the NQ-E index, can improve elderly health, manage chronic diseases, and enhance quality of life. This approach potentially broadens the scope of community nutritionists' roles within an aging society. However, additional research is necessary to evaluate these interventions' long-term effects and sustainability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related Quality of Life in Multimorbid Adults: A Random Forest Cross-sectional Analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moonchang You, Geun-Myun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(3): 349. CrossRef - A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
Kyoung-Min Lee, Woo-jeong Kim, So-young Kim, Young-mi Park, Hwa-young Yoon, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 376. CrossRef - A Basic Study to Establish a Nutrition Education System for Welfare Facilities for the Elderly at Home Using Body Composition Analysis and Nutritional Management Cards
Sun Hee Lee, Seung-Lim Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 471. CrossRef
- Health-related Quality of Life in Multimorbid Adults: A Random Forest Cross-sectional Analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,706 View
- 62 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
- Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):466-479. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.466
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A mobile health intervention program was provided for employees with overweight and obesity for 12 weeks, and a process evaluation was completed at the end of the program. We investigated participant engagement based on app usage data, and whether engagement was associated with the degree of satisfaction with the program.
Methods
The program involved the use of a dietary coaching app and a wearable device for monitoring physical activity and body composition. A total of 235 employees participated in the program. App usage data were collected from a mobile platform, and a questionnaire survey on process evaluation and needs assessment was conducted during the post-test.
Results
The engagement level of the participants decreased over time. Participants in their 40s, high school graduates or lower education, and manufacturing workers showed higher engagement than other age groups, college graduates, and office workers, respectively. The overall satisfaction score was 3.6 out of 5. When participants were categorized into three groups according to their engagement level, the upper group was more satisfied than the lower group. A total of 71.5% of participants answered that they wanted to rejoin or recommend the program, and 71.9% answered that the program was helpful in improving their dietary habits. The most helpful components in the program were diet records and a 1:1 chat with the dietary coach from the dietary coaching app. The barriers to improving dietary habits included company dinners, special occasions, lack of time, and eating out. The workplace dietary management programs were recognized as necessary with a need score of 3.9 out of 5.
Conclusions
Participants were generally satisfied with the mobile health intervention program, particularly highly engaged participants. Feedback from a dietary coach was an important factor in increasing satisfaction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 53. CrossRef
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- 1,300 View
- 64 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Food and dish group diversity on menus of daycare centers provided by Center for Children’s Foodservice Management in Korea: a descriptive study
- Youn-Rok Kang, Kyeong-Sook Lim, Hyung-Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):449-465. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.449
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze menu patterns and food group diversity in daycare centers managed by the Center for Children's Foodservice Management in South Korea.
Methods
Data from 18 Center for Children's Foodservice Management centers across various provinces (excluding Jeju Island) were analyzed. We examined 8,796 meals served in February, May, August, and December 2021, focusing on seasonal lunch and snack menus for children aged 3-5. Foods were categorized into 19 groups for lunch and 21 for snacks. The frequency of food groups and dietary patterns were assessed using the Dietary Diversity Score. Analyses were conducted using Excel 2016 and IBM SPSS Statistics version 28.
Results
Most lunch menus (89%) included five menu items, with a ratio of grain, meat, and vegetables at 88%. Snack menus typically had one item (57%), with significantly more items in the afternoon compared to the morning (P < 0.001). Regarding snack patterns, 75.2% of morning snacks and 61.1% of afternoon snacks contained only one solid food and drink (P < 0.001). Fruit and milk (22.4%) was the most prevalent pattern in morning snacks, while grain and milk (31%) dominated afternoon snacks (P < 0.001). Only 48% of daycare center menus (all snacks and lunch) included all five food groups (grain, meat, vegetables, fruit, and milk). Notably, only 83% included milk and 57% included fruit.
Conclusions
These findings highlight the need to improve food variety and diversity in the Center for Children’s Foodservice Management-managed daycare center menus. Developing more detailed guidelines for menu structure and food composition is crucial to ensure children receive balanced and diverse nutrition. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 225. CrossRef
- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,360 View
- 33 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A comparison of serum lipid concentration by drinking habits based on the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII) : a cross-sectional study
- Chang–Yun Park, Hyung-Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):404-413. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.404
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study compared serum lipid concentration according to drinking habits.
Methods
We analyzed data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII). The study included 8,525 adults (3,651 males and 4,874 females), aged 30 – 59 years.
Results
There were differences in age, gender, education level, smoking status, physical activity, and waist circumference between drinkers and abstainers. The serum low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) level of the drinkers was lower than those of the abstainers (P < 0.05). The serum triglyceride (TG) and high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) concentrations were highest in the group that consumed alcohol ‘more than twice a week’ relative to the other groups (P < 0.001). The LDL-C and atherogenic index (AI) levels were lowest in the ‘more than twice a week’ drinking group compared to the other groups (P < 0.001). The serum TG and HDL-C concentrations were the highest in the ‘7 glasses/time’ group (P < 0.001). The serum LDL-C concentration was the lowest in the ‘7 glasses/time’ group (P < 0.001). Notably, the higher the frequency of binge drinking (7 glasses or more), the higher the concentration of TG (P < 0.001). The serum HDL-C concentration was significantly higher in the ‘no binge’ and ‘more than once a week’ groups compared to the other groups (P < 0.001). The serum LDL-C concentration and AI score were the lowest in the ‘more than once a week’ group (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
As the quantity and frequency of drinking increased, the serum TC concentration increased. Moreover, an increase in the serum HDL-C concentration led to a decrease in AI. The factors exacerbating cardiovascular disease increased simultaneously due to drinking. Our results suggest that for individuals with hypertriglyceridemia and patients with low HDL-cholesterolemia, separate guidelines based on the quantity and frequency of alcohol consumption are warranted.
- 1,622 View
- 21 Download

- [Korean]
- Factors related to adolescent obesity and changes: a cross-sectional study based on the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Bora Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):363-375. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to identify factors associated with adolescent obesity, as well as any new factors that correlated with a change in the rate of obesity over time.
Methods
The study used 5-yearly data collected by the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey starting from the year 2006 up until 2021 (data from 2nd, 7th, 11th, and 17th surveys were analyzed). Factors such as demographics, dietary factors, health behavioral factors, and mental health factors were studied. All data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27.0, employing chi-square tests and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results
This study included data from a total of 255,200 participants. Factors contributing to obesity varied with time. Over the survey duration of 15 years, low academic achievement, parents with low levels of education, low frequency of fruit consumption, low frequency of fast food intake, long periods of being seated, and high levels of stress were significantly associated with a high rate of obesity. Factors that showed a new correlation with an increase in obesity rates included living with single parents, low frequency of muscle strengthening exercises, and experiencing intense sadness and despair in the past year. Factors that were correlated with a change in obesity rates over time included household economic status, frequency of carbonated beverage consumption, frequency of intense physical activity, and frequency of alcohol consumption. Breakfast intake and smoking were not significantly associated with obesity rates in the 15-year period.
Conclusions
While several factors associated with obesity remained consistent over time, several new factors have emerged in response to social, economic, and environmental changes contributed to a change in obesity rate over time. Therefore, to prevent and manage adolescent obesity, continuous research into the new emergent factors contributing to obesity is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,836 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Understanding consumer awareness and utilization of local food in Jecheon during the COVID-19 pandemic: a descriptive study
- Hye-ryeong Shin, Soojin Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):329-339. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to explore consumer awareness and usage patterns of local food in Jecheon city during the COVID-19 pandemic, contributing to the establishment of the Jecheon City Food Plan.
Methods
Surveys were conducted from July 24 to August 24, 2021, using a combination of web-link and self-administered methods for adults living in Jecheon city (n = 250). Descriptive analysis, t-test, importance and satisfaction analysis (ISA) of local food choice attributes were performed using SPSS Statistics.
Results
Participants prioritized freshness when purchasing agricultural products. The freshness of Jecheon local food was the selection attribute with the highest consumer satisfaction and could provide purchase motivation. Approximately 73.6% of respondents understood the concept of local food, and 70% were familiar with Jecheon's local food. Notably, 94.8% expressed an intention to purchase but held negative views on selling local food in other areas. The need to increase the supply of local food to vulnerable populations and public school catering was highly recognized. The ISA identified ‘affordable price’, ‘delivery service’, and ‘product information’ as areas requiring improvement. On the other hand, ‘freshness of products’, ‘quality for the price’, and ‘support for local farmers and economy’ were identified as attributes to be maintained and strengthened.
Conclusions
Consumers in Jecheon city recognized local foods as more than just 'consumer goods’. Our findings suggest the need for further research on local food revitalization and more comprehensive local food planning to enhance consumer satisfaction.
- 873 View
- 16 Download

- [Korean]
- Correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency and value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using dietary area: a descriptive study
- Yunhwa Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):317-328. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency, value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using the dietary area (CUDA).
Methods
Data were collected from 480 middle and high school students in Daegu, Gyeongbuk and Seoul, Gyeonggi using a self-administered five-point Likert scale questionnaire from May to July 2021. A questionnaire was used to investigate dietary safety management competency, awareness of convergence, recognition of the benefits, efficacy, and competency of CUDA.
Results
We conducted factor, reliability, correlation, and regression analyses using SPSS 25. The average scores for each factor were: dietary significance (3.68); dietary safety management knowledge (3.34); food selection and cooking (3.72); nutrition management (3.38); weight management (3.28); risk dietary management (3.13); CUDA interest (2.98); convergence necessity (3.50); benefits in specialized areas (3.31); benefits in everyday life (3.48); efficacy of science and technology convergence (3.35); convergence efficacy with humanities, social science, and arts (3.31); and CUDA competency (3.41). The score for interest in CUDA was lower than that for the recognition of CUDA benefits. Significant positive correlations were observed between all factors except between risk dietary management and both nutrition and weight management (P < 0.01). Interest in CUDA and recognition of the need for convergence exhibited a positive and significant effect on all factors of the perception of CUDA benefits and efficacy. The subgroup factors of dietary safety management competency and the recognition of CUDA had a positive effect on the CUDA competency (P < 0.001, R2= 0.58).
Conclusions
Strengthening dietary safety management competency and increasing the awareness of CUDA can enhance adolescents’ convergence competency. Therefore, CUDA and targeted education must be actively promoted among adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of elementary school pre-service teachers' perception of diet-related factors on their efficacy in creative dietary teaching
Yunhwa Kim, Ji Eun Kim, Kyoungae Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 153. CrossRef
- The impact of elementary school pre-service teachers' perception of diet-related factors on their efficacy in creative dietary teaching
- 1,048 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Changes in nutritional status of Korean older adults during COVID-19 Pandemic by household income and demographic factors -using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(2019-2020): a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):302-316. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to identify changes in the nutritional status of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic according to household income and demographic characteristics.
Methods
Study participants were 2,408 adults aged 65 and over who participated in the 2019–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). To examine changes in nutrient intake levels resulting from COVID-19, data of 2019 and of 2020 were compared. Study participants were divided into three groups based on household income level to compare these changes. The changes were compared according to household income level, age group, and household type.
Results
Percentages of recommended intakes for energy, protein, and most micronutrients were the lowest for the low-income group of both males and females in 2020. The Mean Adequacy Ratio (MAR) score was the lowest for the low-income group in both years. When comparing nutrient density for 2019 and 2020 by income group, the male low-income group experienced a decrease in nutrient densities of vitamin A, thiamine, calcium, and iron. For the same group, a decreased percentage for energy intake from protein was noted. Fruit intake was lowest in the low-income group for both males and females. Low-income males had the lowest intake levels for meat, fish, eggs, and legumes in both 2019 and 2020 and the lowest milk and milk product intake levels in 2020. Older adults living alone or single older adults with children had lower MAR scores than those living with a spouse. Older adults living alone experienced decreases in energy and thiamine and iron intake levels in 2020 compared to their intake levels in 2019.
Conclusions
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, nutrition intake levels worsened for older adult males in the low-income group and older adults living alone. This finding shows the need for a more systematic nutritional support strategy for the vulnerable older adults population in national disaster situations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
Yong-Seok Kwon, Dasol Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1973. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Comparison of nutrient intake and Korean Healthy Eating Index among the elderly in rural areas pre- and post- COVID-19 pandemic: the 2018–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Sangyeon Kim, Hye-Sook Hong, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(5): 496. CrossRef
- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
- 2,350 View
- 43 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Gender differences in dessert satisfaction and purchase behaviors among university students in Gwangju: a preliminary study
- Hyun-Jeong Na, Hyun-Young Jung, Joomin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):293-301. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.293
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the effect of eating habits and dietary attitudes on dessert consumption among university students in Gwangju Province, South Korea.
Methods
A survey was conducted from May to June 2022. Out of 300 distributed questionnaires, 261 valid responses were included in the analysis. The survey assessed dessert selection, satisfaction, consumer attitudes and behaviors, as well as factors influencing satisfaction.
Results
Both genders reported purchasing desserts 2 to 3 times per week, primarily after lunch, due to the convenience of dessert accessibility. Males favored ice cream, bakery items, and fruits, while females preferred bakery items, ice cream, and fruits in that sequence. ‘Having fun’ was identified as the most common motivation for dessert consumption post-meal. Notable gender disparities emerged regarding perceptions of dessert consumption, including its role in stress relief, potential for nutritional imbalance, positive effects, and preferences for seasonal menus. Significant gender-based differences also manifested in intentions to purchase dessert, responsiveness to price changes, and inclination to recommend desserts to others.
Conclusions
This study offers foundational data on university students’ dessert purchasing behaviors, perceptions, and satisfaction levels, intending to inform strategies promoting healthier dietary habits.
- 1,848 View
- 36 Download

- [English]
- Association between dietary intake, body measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):282-292. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Bone health in early adulthood, as individuals approach peak bone mass, plays a critical role in preventing osteoporosis later in life. This study aimed to investigate the associations between lifestyle and dietary factors, anthropometric measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 100 healthy Korean adults (50 men and 50 women) in their 20s and early 30s. Bone mineral density (BMD), anthropometric measurements, dietary intake (24-hour recall), and urinary bone resorption indicators (deoxypyridinoline and N-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen) were analyzed. Variables were compared between the osteopenia and osteoporosis groups (OSTEO group: 30% men and 60% women) and the healthy control group.
Results
Men in the OSTEO group were significantly taller than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Women in the OSTEO group had significantly lower body weight and body composition (muscle and body fat) than those in the normal group (P < 0.01). Men in the OSTEO group had a significantly higher intake of animal calcium (Ca) than those in the normal group (P < 0.05). Women in the OSTEO group had significantly higher dietary fiber, vitamin A, Ca, plant Ca, and potassium intake than did those in the normal group (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in caffeinated beverage consumption, eating habits, or urinary bone resorption indicators between the OSTEO and control groups of either sex.
Conclusions
In our study of young South Korean adults, we observed low bone density levels, with particularly low BMD in taller men and underweight women. We found a higher nutrient intake in the OSTEO group, indicating the possibility of reverse causality, a phenomenon often found in cross-sectional studies. Therefore, there is a need to further elucidate dietary factors related to osteoporosis in young adults through prospective cohort studies involving a larger population.
- 1,186 View
- 17 Download

- [English]
- The frequency of convenience food consumption and attitude of sodium and sugar reduction among middle and high school students in Seoul: a descriptive study
- Seoyeon Park, Yeonhee Shin, Seoyeon Lee, Heejung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):269-281. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.269
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the frequency of convenience food consumption at convenience stores (CVS) and the CVS usage patterns of middle and high school students as well as to understand students’ attitude toward sodium and sugar reduction.
Methods
We used an online questionnaire for data collection. The questionnaire comprised five distinct categories: general characteristics, CVS usage, frequency of consumption according to convenience food menus at CVS, attitude toward sodium and sugar reduction, and adherence to dietary guidelines.
Results
A total of 75 students from Seoul (14 middle school students and 61 high school students) participated in the study. Most respondents visit CVS 3-5 times a week. CVS are predominantly used during weekdays, mostly during lunch, and dinner. The students mostly checked the caloric content and expiration date as food labeling information. The participants were aware of the need to reduce their sugar and sodium intake. Among frequent CVS convenience food consumers, there was an increased consideration of the need to reduce their sugar and sodium consumption, despite their actual selection of foods with high sugar and sodium content. Additionally, they did not check the sugar and sodium levels indicated in food labeling. Further, the dietary action guide from the Ministry of Health and Welfare were poorly followed by most students.
Conclusions
There is a need for nutrition education specifically addressing the sugar and sodium content of the convenience foods predominantly consumed by students. Additionally, educating students with frequent convenience food consumption to actively check the sugar and sodium information on food labels could help promote healthier food choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 514. CrossRef
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- 3,908 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary sodium and potassium intake of Koreans estimated using 2 different sources of their contents in foods, Food & Nutrient Database and the Korean Total Diet Study : a comparative study
- Jee Yeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Soo Hyun Lee, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):235-244. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Based on the results from the Korean Total Diet Study (KTDS), the sodium (Na) and potassium (K) intake of Koreans were estimated and compared with intake estimates from the Food & Nutrient Database (FNDB), as in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) to verify the validity of these estimates.
Methods
One hundred and thirty-four representative foods (RFs) covering 92.5% of the total food intake of Koreans were selected, and 228 pairs of corresponding ‘RF x representative cooking method’ were derived by reflecting the methods used mainly in terms of frequency and quantity in their cooking. RF samples were collected from three cities with a larger population size in three regions (nine cities) nationwide, and six composite samples were made for each RF, considering its regional and/or seasonal characteristics. One thousand three hundred and sixty-eight ‘RF x representative cooking method’ pair samples were prepared, and the Na and K contents were assessed using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-MS). The Na and K intake of the Korean population was estimated by linking the content with the food intake data from the 7th KNHANES.
Results
The mean Na and K intake of Koreans were 2,807.4 mg and 2,335.0 mg per person per day, respectively. A comparison with the Na and K intake from KNHANES, including only RFs of KTDS, showed comparable results with less than 5% variation. While the contribution and ranking of food items to Na intake were similar between KNHANES and KTDS, there were differences in K intake. This was attributed to the large discrepancies in the K content of rice and coffee between KTDS results and the values in the 9th Revision of the National Food Composition Table used in KNHANES.
Conclusions
The Na and K intake of Koreans estimated based on the KTDS, which performed nutrient analysis on samples prepared to a ‘table-ready’ state using foods of the representative collection, was similar and comparable with that of KNHANES. This supports the validity and usefulness of FNDB-based nutrient intake estimation at the population level. The list of nutrients studied in KTDS is expected to be expanded, allowing for intake estimation of nutrients with currently insufficient or absent information in the FNDBs in use.
- 2,461 View
- 68 Download

- [Korean]
- Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
- Eunyoung Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):220-234. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.220
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the adherence to dietary guidelines among college students in the post-COVID-19 era and examine the changes in their dietary habits as the learning environment transitioned from remote to in-person classes.
Methods
We conducted a survey involving 327 college students in Daejeon from March to April 2023. The survey questionnaires included various factors, including age, gender, type of residence, frequency of use of delivery food, convenience food, and eating out. In addition, we investigated the extent of adherence to the dietary guidelines for Koreans and the degree of dietary changes following the post-COVID-19 shift in class format were investigated. For comparative analysis of the level of adherence to dietary guidelines in relation to dietary habit changes, an ANOVA and a post hoc Scheffe test were employed. We also performed a multiple linear regression analysis to identify dietary factors influencing the level of adherence to dietary guidelines.
Results
The study revealed a high rate of convenience food consumption and a low rate of homemade food intake among students. There was a marked increase in the consumption of processed foods, convenience foods, dining out, sweet foods, high-fat fried foods, beverages, and alcohol following the transition from online to in-person classes. When examining adherence to Korean dietary guidelines, the highest scored practice was ‘Hydration’, and the lowest was ‘Breakfast habit’. Increased consumption of convenience foods, late-night snacks, and dining out were negatively correlated with adherence levels to dietary guidelines, specifically correlating with ‘Healthy weight’, ‘Hydration’, ‘Breakfast habit’, and the total score of adherence. The adoption of ‘regular meals’ was positively associated with increased adherence levels to dietary guidelines.
Conclusions
The transition from remote to in-person classes post-COVID-19 led to increased intake of convenience foods, dining out, sweet foods, high-fat fried foods, and alcohol. The rise in convenience food and late-night snack consumption negatively influenced several aspects of the dietary guidelines adherence, thereby suggesting the need for strategies to encourage healthy dietary habits among college students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Attributes of multiple concurrent functional gastrointestinal disorders in female university students in South Korea
Hyo Kyung Kim, Hyunjung Kim, Aram Lee
Women & Health.2024; 64(8): 674. CrossRef - Impact of Social Media Use on Segmentation of Dining out Behavior Among Younger Generations: A Case Study in South Korea
Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim, Hyosun Jung
Foods.2024; 13(24): 4146. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef
- Attributes of multiple concurrent functional gastrointestinal disorders in female university students in South Korea
- 2,580 View
- 72 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



