Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- [English]
- Dietary factors and nutritional guidelines for sarcopenia in older adults: a narrative review
- Sumin Heo, Soo Jin Yang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):389-396. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00360
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Sarcopenia is a condition characterized by the loss of muscle mass and function and is often accompanied by aging and chronic diseases such as diabetes and obesity. It increases the risk of falls, frailty, disability, hospitalization, and mortality in older adults. Its global prevalence is estimated as approximately 10%–27% in adults aged > 60 years. This review analyzes evidence from research findings and recommendations to provide a comprehensive overview of dietary factors and nutritional strategies for preventing and managing sarcopenia in older adults.
Methods
Literatures were searched to integrate findings from observational studies, clinical trials, systematic reviews, and meta-analysis on dietary factors and nutritional guidelines for the prevention and management of sarcopenia. Particularly, points were emphasized on protein intake, micronutrient adequacy, dietary patterns, and combined lifestyle interventions relevant to older populations.
Results
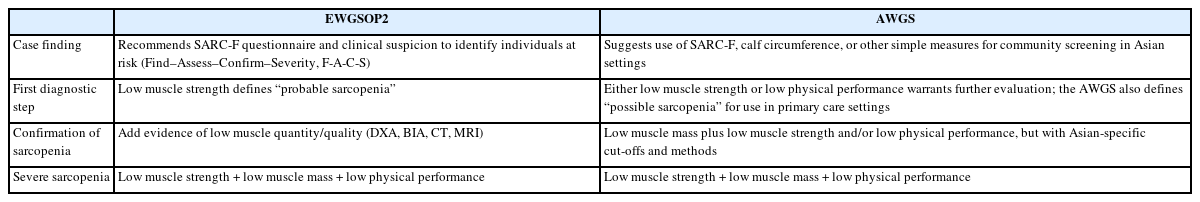
Sarcopenia develops through multifactorial mechanisms such as dysfunction in muscle protein synthesis, chronic inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging-related hormonal decline. Nutritional factors, particularly protein intake, play a central role in its development and management. Adequate protein intake is typically 1.0–1.2 g/kg/day for healthy older adults and more than 1.2 g/kg/day for individuals with sarcopenia or frailty. High-quality protein intake, sufficient leucine intake, and amino acids or β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate supplementation may help to counteract dysfunction in muscle protein synthesis. The adequacy of vitamin D supports musculoskeletal health. Dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean and Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension diets have been consistently associated with better muscle mass, strength, and function. Strong evidence has demonstrated synergistic benefits when optimized nutrition is combined with resistance exercise.
Conclusion
The comprehensive management of sarcopenia in older adults requires an integrated strategy that prioritizes adequate protein and energy intake, vitamin D adequacy, healthy dietary patterns, and regular resistance exercise.
- 245 View
- 14 Download

Research Articles
- [English]
- The association between sodium index and the risk of obesity in Korean and Chinese university students: a cross-sectional study
- Linan Wang, Jin-Ah Seok, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):419-430. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
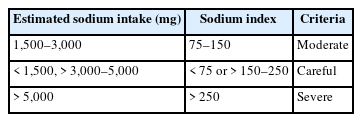
Korea and China have the highest sodium intakes globally. The sodium index is a quantitative measure of the estimated sodium intake, calculated using a regression equation with proven validity and reliability in individuals aged 19–69 years. This study aimed to compare the sodium index of Korean and Chinese university students and analyze the association between the sodium index and the risk of obesity.
Methods
A total of 218 university students—110 Korean (63 males, 47 females) and 108 Chinese (60 males, 48 females)—participated in this study in 2019. Sodium-related awareness, nutritional knowledge, and sodium index were compared between Korean and Chinese students. Obesity indicators were compared according to three criteria for the sodium index of Korean and Chinese students: “moderate,” “careful,” and “severe. ” The association between sodium index levels and risk of obesity was analyzed using multiple logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex.
Results
Overall, 84% of students recognized that they consumed large amounts of sodium. Korean students demonstrated higher nutritional knowledge scores than Chinese students. The average estimated sodium intake was 3,751 mg, and no significant difference was observed between Korean (3,857 mg) and Chinese (3,643 mg) students. The overall average sodium index was 187, which falls under the “careful” level. As the sodium index levels increased, the students’ body mass index, waist-hip ratio (WHR), and fat-related indicators significantly increased. At the “severe” level of the sodium index, Korean and Chinese students had 2.402-fold and 1.636-fold increases in the risk of obesity based on body fat percentage, and 3.682-fold and 1.622-fold increases based on WHR, respectively.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated an association between sodium index and obesity risk, showing that excessive sodium intake affects body fat-related indicators in university students.
- 117 View
- 9 Download

- [Korean]
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):441-456. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to clarify parental perceptions of dietary and nutritional education provided to young children, identify parental support needs, and suggest directions for improvement.
Methods
A mixed-method sequential explanatory design was followed. Quantitative data were collected through an online survey conducted nationwide that included 200 parents of children aged three to six years in South Korea. Qualitative data were subsequently obtained through focus group interviews with fifteen parents to explore their contextual insights and experiences.
Results
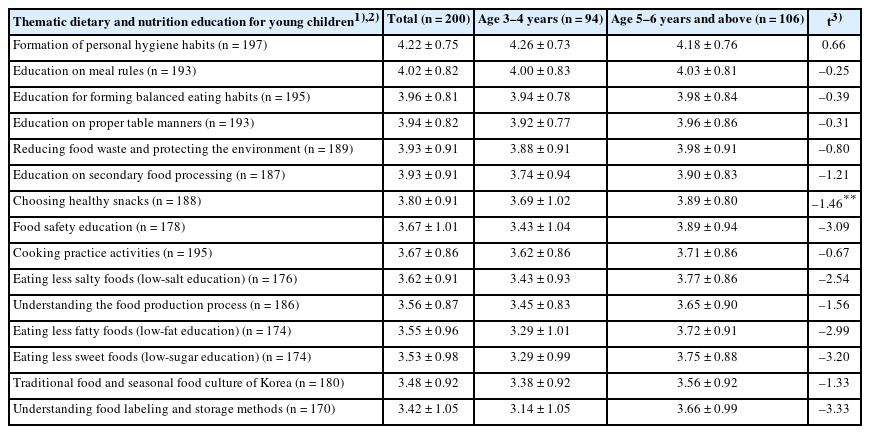
Needs ratings prioritized expanding activity-based/experiential education (3.65 ± 0.88), followed by strengthening home-school communication and connectivity (3.59 ± 0.84), diversifying topics and content (3.55 ± 0.88), and increasing instructional time (3.39 ± 0.94). Integrated with the focus group interview findings, multilevel barriers were revealed—individual level: strong preferences of children for sweet/processed foods; interpersonal level: strong parental modeling and peer effects counterbalancing limited teacher expertise/time; organizational level: insufficient effective event-based experiential activities, and resource gaps across institutions; community/policy level: infrequent external support, uneven access to local resources, lack of standardized guidance, and limited opportunities for parental participation. Parents favored short, interactive digital content and expressed concerns about overexposure. These convergent findings indicate needs to 1) formalize and extend experiential programs within the regular curriculum, 2) provide standardized guidelines and home resource kits, and 3) institutionalize parental involvement.
Conclusion
These findings reveal that dietary and nutritional education for young children should move beyond fragmented, event-based programs toward an integrated three-tiered model incorporating (1) a structured, experiential curriculum, (2) home-linked educational packages, and (3) safe and interactive digital content. Establishing standardized guidelines, enhancing educational infrastructure, and institutionalizing parental participation are essential for sustainable improvement of early childhood dietary education.
- 116 View
- 7 Download

- [English]
- Ultra-processed food intake and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):410-418. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the intake of ultra-processed foods (UPF) and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents.
Methods
This study used 24-hour dietary recall data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2023). In total, 1,720 adolescents aged 12–18 years were included in this study and categorized into quartiles based on the percentage of energy intake from the UPF. Nutritional status, contributing subgroups of UPF intake, and healthy dietary practices were examined using Health Plan 2030 indicators across quartiles of UPF intake.
Results
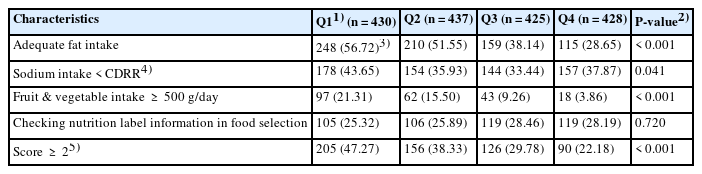
The nutrient intake of protein, vitamins (A, B1, B2, niacin), and minerals (iron, potassium) was the lowest in the fourth quartile of UPF intake compared with the first quartile (P for trend < 0.001), whereas calcium intake increased across quartiles, from 47.68% in the first quartile to 58.51% in the fourth quartile (P for trend < 0.001). The main contributing subgroups to UPF intake differed across quartiles of UPF intake, and the highest contributing subgroups were ‘instant noodles and dumplings,’ ‘desserts, cakes, and ice cream,’ and ‘sauces and seasonings.’ Healthy dietary practices were the lowest in the fourth quartile (22.18%, P < 0.001), and the proportions of appropriate fat and fruit/vegetable intake were significantly lower in the higher quartiles of UPF intake (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that a lower UPF intake was associated with better nutritional status and healthy dietary practices in Korean adolescents. These findings provide fundamental evidence for promoting healthier food choices and balanced dietary practices.
- 162 View
- 9 Download

- [English]
- Nutrition Quotient and nutrient intake among older adults in a rural Korean community: a cross-sectional study
- Ji-Sook Park, Hyeon-Mi Bae, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):397-409. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00283

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Korea is experiencing rapid population aging, with older adults forming a large proportion of rural communities. Aging leads to physiological and functional declines, resulting in lower physical activity, poor diet quality, and higher risk of chronic diseases. Although the Nutrition Quotient for the Elderly (NQ-E) is a validated tool to assess dietary quality, few studies have applied it to rural populations. This study aimed to compare nutrient intake and NQ-E scores by age and sex and examine their associations with lifestyle factors.
Methods
This study investigated the relationship between nutrient intake and NQ-E scores among older adults in rural Korean community, considering age, sex, and lifestyle factors. A cross-sectional study was conducted with 79 community-dwelling older adults (24 male and 55 female; mean age: 76.3 years) residing in Geochang-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. Participants were recruited from community centers and health posts between June 2024 and December 2024. Data collection included general characteristics, 24-hour dietary recalls, and NQ-E questionnaires.
Results
Female aged > 75 years had significantly lower intakes of energy, protein, fat, vitamin E, riboflavin, folate, and zinc than their male counterparts (P < 0.05). The mean NQ-E score was 55.01, which was lower than the national average reported for urban older adults (57.6). Participants with higher NQ-E grades had significantly higher intakes of dietary fiber, vitamin A, thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, potassium, and magnesium, and regular physical activity and dietary supplement use were positively associated with higher NQ-E grades (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
These findings suggest that older female in rural communities are particularly vulnerable to inadequate nutrient intake and lower dietary quality, and that the NQ-E is a useful screening tool for identifying nutritional risk in this population. Community-based nutrition interventions promoting physical activity, supplement use, and dietary diversity are warranted to improve dietary quality and support healthy aging.
- 100 View
- 8 Download

Educational Material
- [Korean]
- Development and evaluation of play-based food and nutrition education materials for early childhood through sensory experiences: a pre-post observational study
- Hyunjoo Ryou, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):471-483. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00276

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop play-based nutrition education (PBNE) materials for young children and to evaluate their applicability and effectiveness.
Methods
An online survey of 1,253 primary caregivers of preschool children was conducted, and the findings were used to develop age-specific utilization guides, slides, activity sheets, activity cards, posters, educational videos, and parent newsletters. Selected materials were implemented in child-care centers through the Children’s Foodservice Management Centers between October and November 2023. The effectiveness of the PBNE program was assessed by examining changes in mushroom consumption as well as food awareness and preferences, before and after the intervention.
Results
A total of eight media formats and 320 educational contents were developed, and mushrooms were as the pilot theme among the 12 possible food items. Following the intervention, children’s positive awareness of mushrooms increased, and > 96% of participants attempted to consume them. Teachers in child-care centers rated the appropriateness and applicability of the content, its contribution to behavioral improvement, and their overall satisfaction at > 4.9 out of 5 points.
Conclusion
This study developed experiential, PBNE materials aligned with the national standard child- and play-centered curriculum. The materials were effective in enhancing food awareness and promoting attempts at consumption. Future efforts should focus on developing additional experiential teaching tools that incorporate teacher feedback and on strengthening home-linked programs to support healthy seasonal food intake and positive dietary experiences in young children.
- 122 View
- 9 Download

Research Article
- [Korean]
- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
- Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):431-440. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00234

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this qualitative study was to explore and understand the behaviors and challenges of self-nutrition management from the perspective of elderly.
Methods
In May 2025, ten elderly aged 65–83 years with prior experience using digital devices were recruited through purposeful sampling. Data were collected via focus group interviews using a semi-structured questionnaire until saturation was reached, and all interviews were recorded, transcribed, and analyzed using traditional content analysis methods. The collected interview data were extracted focusing on phrases or sentences relevant to the research purpose, and various concepts derived through memo writing and the constant comparison were categorized based on common meanings. Subsequently, the categorized statements were deeply interpreted and reclassified into subcategories for final analysis.
Results
Under the overarching theme of development directions for a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly, three main categories and 13 subcategories were derived. The three main categories include: (1) processes of acceptance and utilization of digital technologies; (2) potential for applying digital self-nutrition management; and (3) strategies for implementing digital-based nutrition education.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that elderly face barriers to utilizing digital tools for self-nutrition management not only due to physical or technical limitations, but also because of the confusion arising from limited nutrition knowledge and information overload. To overcome the barriers that may arise during the digital-based education process for elderly, strategies (educational topics, delivery strategies, and operational strategies) were derived to vitalize a digital self-nutrition management education program. These results highlight the necessity of developing tailored digital nutrition education programs that reflect the characteristics of elderly, which may enhance their practical applicability and provide foundational evidence for establishing a digital–nutrition integrated care model within the senior customized care service.
- 131 View
- 15 Download

Review
- [English]
- Evaluation and standardized dietary strategies for dysphagia in older adults: a narrative review
- Jean Kyung Paik
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):323-330. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00290

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This review aimed to elucidate the characteristics of dysphagia and age-related swallowing changes (presbyphagia) in older adults and to comprehensively examine assessment tools and standardized meal management strategies applicable in community settings to propose effective meal management strategies for healthy longevity.
Methods
Domestic and international literatures were analyzed regarding the definition and causes of dysphagia, physiological and structural characteristics and clinical impacts of presbyphagia, assessment and diagnostic tools (K-EAT-10 and K-DRACE), and the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI).
Results
Dysphagia compromises safe swallowing and nutritional intake in older adults, leading to serious complications, such as aspiration pneumonia, dehydration, malnutrition, sarcopenia, and reduced quality of life. The K-EAT-10 and K-DRACE proved effective for rapid screening of dysphagia risk in community-dwelling older adults. Moreover, texture-modified meals and viscosity adjustments based on the IDDSI standards are useful for reducing the risk of aspiration and improving nutrient intake. Meals can be classified as liquidized, minced, chopped, or regular, allowing for individualized management.
Conclusion
Presbyphagia is a multidimensional problem, and the integrated use of assessment tools and standardized meals is crucial. Community-based dysphagia management programs and collaboration among dietitians and healthcare professionals are needed to improve the nutritional status and quality of life of older adults.
- 1,453 View
- 42 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Factors associated with nutritional risk among disabled persons in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study using 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel
- Seong-Ah Kim, Seul Ki Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):364-375. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Persons with disabilities face heightened nutritional risks due to barriers in dietary management, yet research remains limited. This study examined the nutritional health status and associated risk factors among disabled adults in Korea.
Methods
Data were drawn from the 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel, a nationally representative survey of registered disabled Koreans aged ≥ 20 years. Nutritional health was assessed using the Nutrition Screening Initiative checklist and categorized as low, moderate, or high risk. Multivariate multinomial logistic regression was applied to identify predictors of nutritional risk.
Results
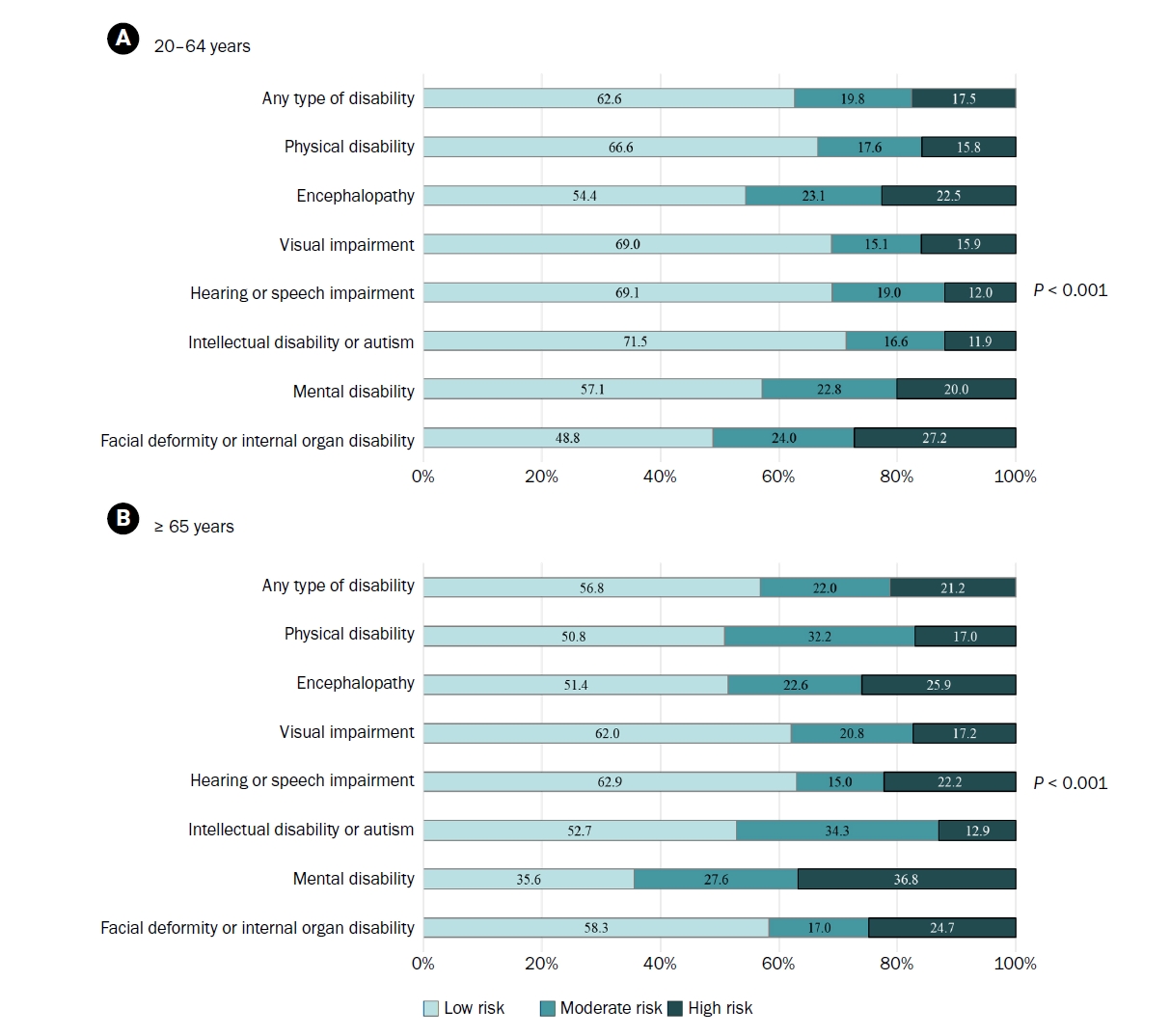
Among adults with disabilities aged 20–64 years, the prevalence of low, moderate, and high nutritional risk was 62.6%, 19.8%, and 17.5%, respectively. In the ≥ 65 years group, the distribution was 56.8% (low), 22.0% (moderate), and 21.2% (high). Moderate to high nutritional risk was most prevalent among individuals with facial deformity or internal organ disability (51.2%) in the 20–64 years group, and those with mental disabilities (61.7%) in the ≥ 65 years group. Significant predictors of high nutritional risk included living alone, lowest income quartile, chronic disease, depressive symptoms, and perceived underweight for both age groups. Compared with visual or speech impairments, facial deformity or internal organ disability (in the 20–64 years group) and physical disability (in the ≥ 65 years group) were significantly associated with moderate or high nutritional risk.
Conclusion
Nearly 40% of disabled Koreans are at nutritional risk. Tailored dietary interventions that address disability type, socioeconomic status, and health conditions are required to reduce disparities in nutritional health.
- 415 View
- 22 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):352-363. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The dietary habits of school-aged children play a critical role in their growth and development, and are strongly influenced by the home environment. Household income is closely associated with caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. This directly affects the nutritional status of children. This study aimed to provide evidence to inform policies and educational programs for improving dietary habits in children, and to establish a foundation for tailored support strategies for low-income families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 846 primary caregivers of school-aged children from 17 regions across Korea, recruited through an online survey. Household income, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment were assessed. Nutritional status in children was measured using the Nutrition Quotient for Children (NQ-C). Statistical analyses included descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), correlation analyses, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Caregivers from higher income households demonstrated significantly greater food literacy and social support (P < 0.001). Children from these households showed high balance scores and a large proportion of these children were in the “high” NQ-C grade. The NQ-C score in children was positively correlated with food literacy (r = 0.425), social support (r = 0.471), and the food environment (r = 0.235) (P < 0.001). Multiple regression analysis showed that food literacy (β = 0.256) and social support (β = 0.348) were significant predictors of nutritional status in children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that the nutritional status in children is not only determined solely by household income but is also mediated by caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. These findings highlighted the limitations of providing only economic support. The findings underscore the need for multifaceted interventions such as strengthening parental nutrition education, expanding social support networks, and improving access to healthy foods.
- 682 View
- 37 Download

- [English]
- Sex differences in the association between Korean Healthy Eating Index and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korean adults: a prospective cohort study
- Yeeun Park, Minji Kim, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):331-340. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Dietary quality is a modifiable determinant of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, evidence on the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI) and sex-specific differences in its association with T2DM risk remains limited. This study is to examine the longitudinal association between KHEI and incident T2DM in Korean adults, with a focus on potential sex differences.
Methods
We analyzed 56,000 adults (37,684 women and 18,316 men) from the Health Examinee cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Dietary intake was assessed using a validated semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire, and KHEI scores were constructed based on national guidelines. Incident T2DM was defined using physician diagnosis, treatment history, or biochemical criteria. Cox proportional hazards models and restricted cubic spline analyses were applied to evaluate associations, with adjustments for demographic, lifestyle, and clinical covariates.
Results
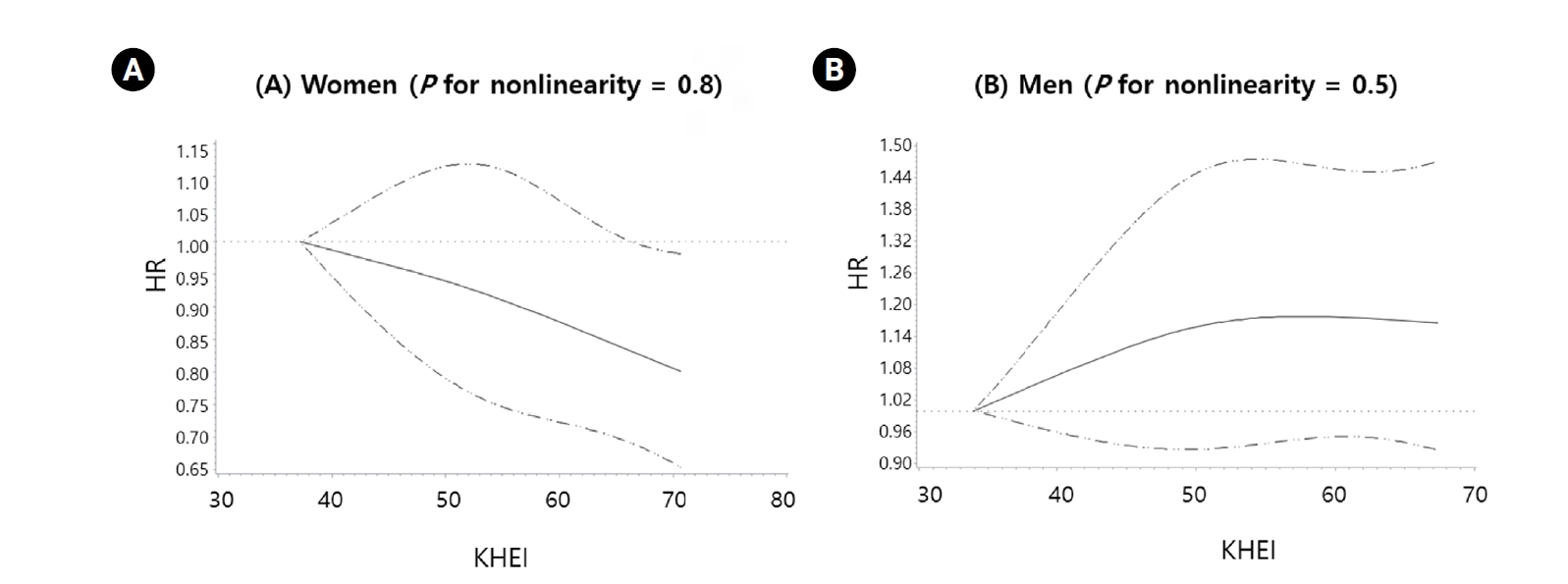
Over a median follow-up of 4.2 years, 2,252 women and 1,776 men developed T2DM. Women in the highest quartile of KHEI had a 18% lower risk of T2DM compared with those in the lowest quartile (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.82, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.71–0.93; P for trend = 0.007). In men, no significant association was observed (HR: 1.11, 95% CI: 0.95–1.29). The interaction by sex was statistically significant (P for interaction < 0.05). Spline analyses indicated a linear inverse association between KHEI and T2DM risk in women, whereas no trend was evident in men.
Conclusion
Higher diet quality, as measured by the KHEI, was associated with a reduced risk of T2DM in women but not in men, suggesting sex-specific effects of dietary patterns on diabetes prevention. These findings highlight the need for tailored nutritional strategies that consider biological and behavioral differences between women and men in Korea.
- 673 View
- 28 Download

- [Korean]
- A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Kyoung-Min Lee, Woo-jeong Kim, So-young Kim, Young-mi Park, Hwa-young Yoon, Min-Sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):376-388. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Individuals with disabilities require targeted interventions to ameliorate disability-related conditions and improve overall health status. Nutritional challenges and counseling needs vary according to the type of disability, necessitating comprehensive assessments of dietary habits, physical activity, and food intake. Compared to traditional education, nutrition counseling offers a more sustainable and environmentally adaptable approach that effectively addresses individualized nutritional issues. Therefore, this study aimed to develop and evaluate a practical nutrition counseling manual and meal guidelines for people with disabilities in Korea, addressing their diverse dietary needs and improving nutritional care in social welfare facilities.
Methods
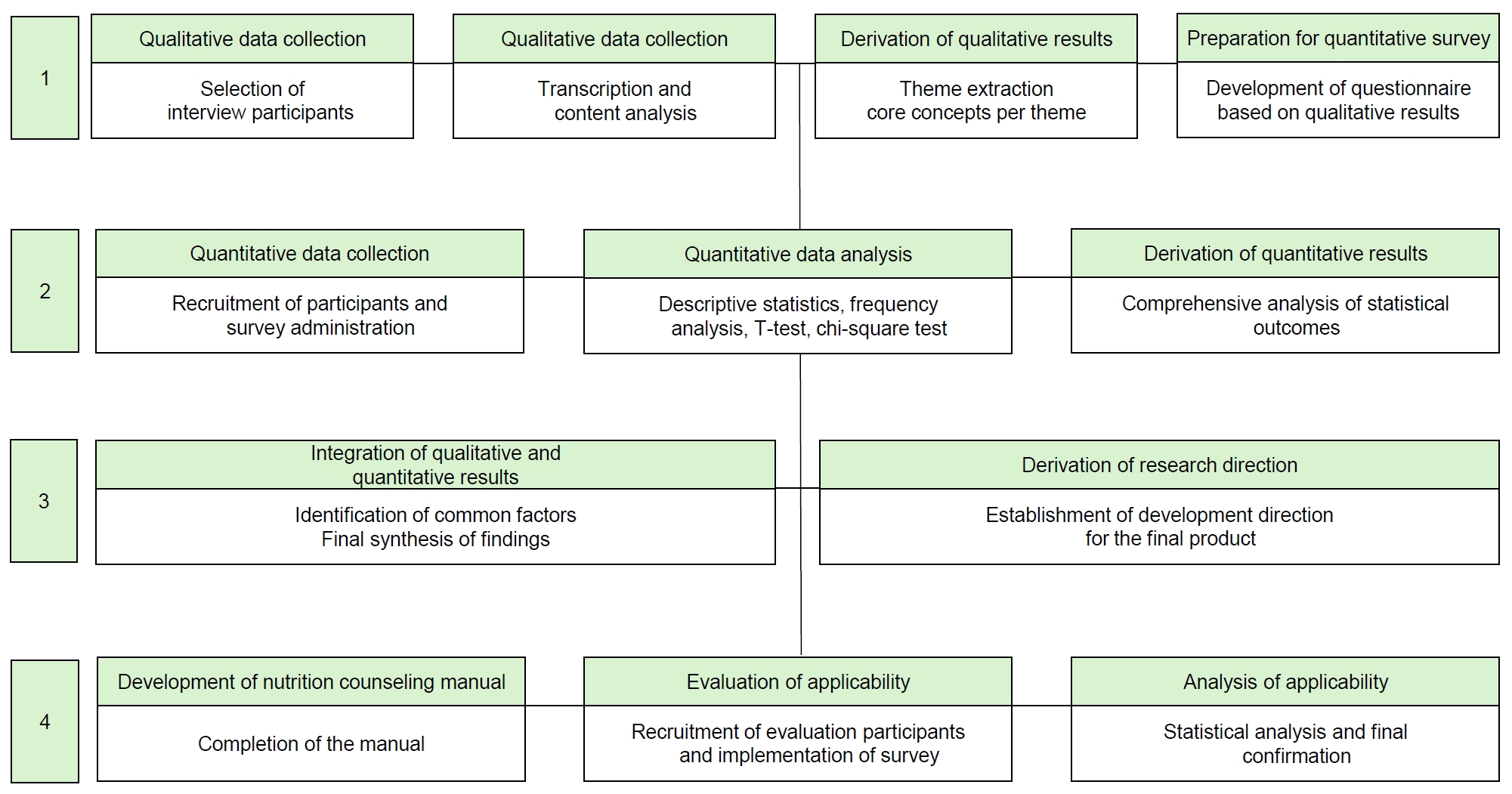
A four-stage integrated research design was employed. Stage 1 involved qualitative research through in-depth interviews with 11 facility staff. In Stage 2, a nationwide survey (n = 249) was conducted based on the results of the interviews. Stage 3 integrated both qualitative and quantitative findings. Stage 4 focused on developing and evaluating a nutrition counseling manual and five types of meal guidelines through feedback from 26 nutritionists at 24 Korean Centers for Social Welfare Foodservice Management.
Results
Six major nutrition counseling topics were identified: healthy eating, managing salt and sugar intake, dysphagia diet, appropriate intake, and hygiene. The manual and guidelines demonstrated high field usability, with average satisfaction scores of 3.98 and 3.99, respectively.
Conclusion
The integrated study resulted in the development of a specialized nutrition counseling manual and handbook for individuals with disabilities in Korean social welfare facilities. The materials were revised and improved based on practical evaluations by dietitians, enhancing their field applicability. These tools are expected to contribute to better dietary management and health promotion among facility residents. The developed materials reflect the real-world needs of people with disabilities and offer practical tools for effective nutrition counseling and dietary management in institutional settings.
- 350 View
- 14 Download

Research Note
- [English]
- Pilot evaluation of a cooking-based nutrition education program to promote vegetable intake among children in Seoul, South Korea: a single-group pre–post study
- Sil-Ah Kim, Su-Jin Lee, Min-Ah Kim, Ji-Eun Oh, Sohyun Park, Hyun-Joo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):249-260. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00220

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Food neophobia in children is often associated with limited exposure and familiarity to some foods. Cooking-based nutrition education (CBNE), which promotes acceptance through direct experience, may support the development of healthy eating habits. This study aimed to develop and implement a standardized CBNE program for school-aged children in Seoul, South Korea, and to evaluate its effectiveness by assessing changes in raw vegetable intake. Raw vegetable intake is an early indicator of the effectiveness of nutrition education on diverse topics in promoting healthy eating habits.
Methods
A single-group pre–post study was conducted with 37 children aged 6–11 years who participated in a 2-day CBNE program in October 2023. The participants completed pre- and post-education questionnaires and raw vegetable intake assessments. Four low-preference vegetables (bell pepper, carrot, cucumber, and tomato) were selected and served raw (25 g each) before and after the program. Intake changes were analyzed using paired t-tests, and Pearson’s correlation and hierarchical regression analyses were performed to identify predictors.
Results
Total raw vegetable intake significantly increased post-education (P = 0.008), particularly for carrots (P = 0.023). By subgroup, raw vegetable intake significantly increased in girls, upper-grade students, and those who consumed four or more vegetable side dishes per meal. Hierarchical regression analysis revealed that while vegetable preference was initially significant, vegetable-related experiences (β = 0.395, P = 0.026) and diversity of vegetable side dishes per meal (β = 0.403, P = 0.032) were stronger predictors in the final model (adj R2 = 0.333).
Conclusion
The CBNE program may enhance vegetable intake in children. Although preference remained the strongest individual factor, vegetable experience and the diversity of vegetable side dishes per meal had a greater combined effect. These findings underscore the importance of repeated and diverse exposure, not only by supporting previous studies that link such exposure to increased intake but also by suggesting that environmental support may be essential for sustaining healthy eating habits.
- 1,833 View
- 58 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Survey on consumer perceptions, health benefits and preferences of kindergarten and school foodservices in Korea, including related keywords reported in newspaper: a mixed-methods study
- Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Hyeja Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):309-320. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00199

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With the rapid development of social culture, the perception of kindergarten and school foodservice, as well as opinions on its health benefits, has changed significantly. However, research on this topic remains scarce. We conducted a survey in South Korea on consumers’ perceptions, healthiness, and preferences regarding kindergarten and school foodservice.
Methods
With the nationwide cooperation of 17 city and provincial education offices, online and offline surveys were conducted targeting the parents of kindergarten and lower-grade elementary school children, as well as upper-grade elementary, middle, and high school students. In addition, keywords in newspaper reports were analyzed using the Big Kinds platform. A total of 532 valid questionnaires were collected, and statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 27.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
The average age of the parents and students was 40 and 12.5 years, respectively, with 36.4% of the students attending schools in the Seoul and Gyeonggi areas. The main keywords reported in newspaper articles, as analyzed using the Big Kinds platform, were “eco-friendly agricultural products,” “food ingredients,” “safety,” and “marine products.” The perception of kindergarten and school foodservice was very positive, especially regarding the attributes of safe ingredient use (4.44), menu variety (4.29), cafeteria cleanliness (4.31), cleanliness of plates, spoons, and utensils (4.24), thorough hygiene management (4.2), nutritional excellence (4.24), and support for proper eating habits (4.18). The healthiness of school foodservice was highly rated, although there is still room for improvement in terms of “not serving fried foods more than twice a week”. In terms of preference for school meals, the most preferred items were meat side dishes, followed by chicken, noodles, fried food, beverages, and bread. In contrast, soybean paste soup, vegetables, and mixed-grain rice received relatively low preference.
Conclusion
The results described above may be used to develop educational programs or policies that inform students and parents about the goals of school foodservice and help address common misunderstandings.
- 2,262 View
- 34 Download

- [English]
- Safety education status and needs priorities of Korean military food service personnel using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model: a cross-sectional study
- Jeongeun Park, Eunsil Her
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):261-273. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00185

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Since the enactment of the Serious Accidents Punishment Act in Korea in 2021, the importance of safety management in food service facilities has increased. This study was conducted to examine the status of safety education and to identify educational needs for safety accident prevention among army food service personnel.
Methods
This study included 157 food service personnel from Army units located in Gyeongsangnam-do. Participants were divided into two groups based on the daily number of meals served. Demographic characteristics, the status of safety education, and priority for safety accident prevention education were evaluated.
Results
A total of 97.5% of participants received safety education, with 60.8% attending at least monthly. “Lecture” (63.4%) was the most commonly used educational method. The preferred educational methods were “Lecture” (23.5%) and “Counselling” (23.5%), showing significant group differences (P < 0.001). A total of 79.6% of participants reported applying the educational content in their performance. The mean importance score for safety accident prevention (4.78) was higher than the performance score (4.44), with significant differences between the two groups observed in the importance scores (P < 0.05). “Slip & burn” had the highest importance score, while “Electric shock and fire” had the highest performance score. The educational needs analysis revealed that the highest priority item for the < 100 meals group was “When moving heavy items, an assistive device or assistance from colleagues should be utilized”, while for the ≥ 100 meals group, it was “When using a vegetable cutter or grinder, use an exclusive stick.”
Conclusion
This study can serve as a foundational database for developing customized safety education programs tailored to Korean army food service personnel.
- 2,407 View
- 24 Download

- [English]
- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
- Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):274-285. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00157

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Although diet quality is known to be associated with environment and individuals’ characteristics, these have not been studied together. We determined the association of diet quality with regional factors stratified by individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics.
Methods
This study used nationally representative survey data on regional factors (2010–2020) and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data on individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics (2013–2018). Community-dwelling Koreans aged ≥ 20 were included (n = 26,853). Regions were categorized into metropolitan cities or provinces and subsequently according to regional factors (level of educational attainment, income per capita, food security status, physical activity facilities, time to the nearest large retailer, and internet use of the region). Individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics included age, education status, income, and number of household members. Diet quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI).
Results
In the entire population, education status of metropolitan cities was positively associated with the KHEI. Shorter time to retailers and higher internet use were positively associated with the KHEI in metropolitan residents with higher income levels but negatively associated with the KHEI in those with lower income status. Among provincial residents with a low education status or income, regional physical activity facilities were positively associated with the KHEI.
Conclusion
The association between diet quality and regional factors varied depending on the resident’s sociodemographic characteristics. Both regional and individual sociodemographic factors must be considered to address gaps in nutritional equity.
- 1,540 View
- 25 Download

- [Korean]
- A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
- Seo Young Choi, Hyun joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):286-295. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00143

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
In this study, we identified the current status of meal and nutritional management in elderly care facilities and analyzed the educational needs of employees, with the goal of proposing effective support strategies for nutritional management and to suggest directions for developing customized educational content.
Methods
Between May and June 2024, we conducted nine focus group interviews with 22 participants recruited from 10 cities across four major regions of Korea, including 13 employees of children and social welfare meal management support centers and nine employees of elderly care facilities.
Results
Our findings revealed that supporting algorithm-based dietary planning, improving communication with caregivers, and providing flexible, practical education tailored to facility conditions, are key elements for enhancing nutritional management in elderly care facilities. To facilitate the translation of these insights into practice, it will be necessary to strengthen collaboration between centers and facilities, combined with efforts to improve the operational environment for applying the algorithm and providing continuous educational support.
Conclusion
The findings of this study emphasize the importance of on-site education and sustainable support strategies based on the diet and nutritional management status and education needs of elderly care facilities. Strengthening practical education, communication systems, and center–facility collaboration is required, and future research needs to verify the efficacy of these measures and define a sustainable support system based on quantitative analysis.
- 1,398 View
- 64 Download

- [Korean]
- Adult consumers’ perception of plant-based meat substitutes and related factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Yun-A Lee, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):237-248. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We aimed to examine differences in experience, consumption, and perception of plant-based meat substitutes according to consumer characteristics, and to identify associated factors.
Methods
In this cross-sectional study, 410 adult consumers were surveyed regarding their eating habits, experience with and consumption of plant-based meat substitutes, and their intentions and perceptions of these products. Statistical analyses were conducted.
Results
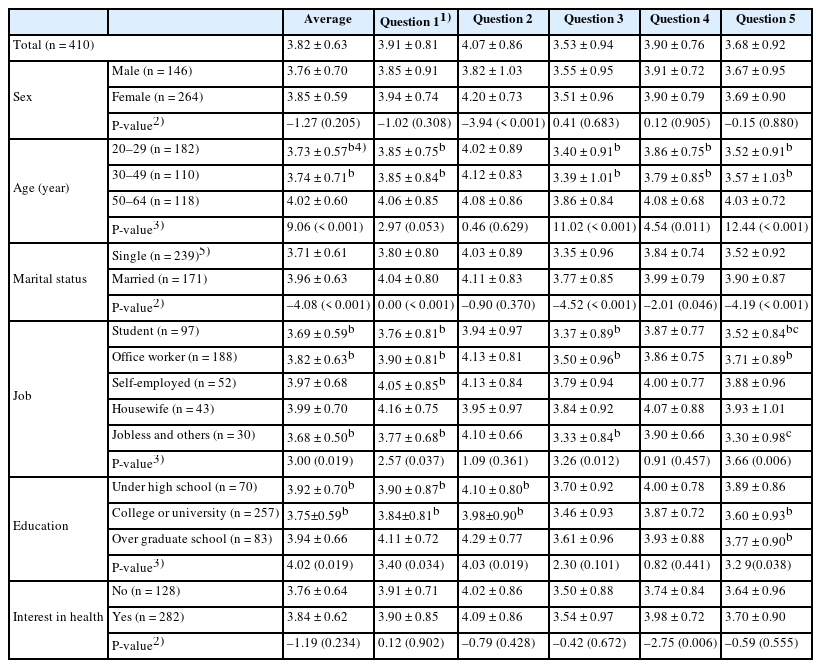
Approximately 84% of participants had heard of plant-based meat substitutes, most commonly through mass media and social media. Overall, 65.12% reported having consumed plant-based substitutes, with higher consumption observed among older and more health-conscious individuals. The most common reason for consumption was curiosity about new foods (36.33%), whereas the primary reason for non-consumption was lack of opportunity (61.54%). Additionally, 77.32% of respondents indicated willingness to try plant-based substitutes, with taste identified as the most influential factor in purchasing decisions. Perception of plant-based meat substitutes was rated 3.82 out of 5, with significantly higher awareness among individuals aged 50–64, married individuals, housewives, graduate students or graduates, and those with irregular meal times or infrequent dining out.
Conclusion
Older, married, more educated, and health-conscious individuals who dine out less frequently tend to have higher perception scores for plant-based meat substitutes, along with greater experience and stronger future use intention.
- 1,374 View
- 60 Download

- [Korean]
- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
- Ji-Won Kang, Su-Jin Lee, Sil-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):224-236. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00108

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To reduce urban carbon emissions, in this study, we aimed to suggest strategies for disseminating the planetary health diet (PHD) guidelines to adult cafeterias in a government worksite in Seoul based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB) and focus group interviews (FGI).
Methods
A total of 132 adults who worked at a government worksite in Seoul and used its cafeteria were included for a TPB-based survey. Factor analyses and multiple regression were used to investigate the relationships between attitude (cognitive•affective), subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control (PBC, internal•external) and the behavioral intention to adopt the PHD. To identify the contextual factors related to PHD dissemination, 14 participants underwent in-depth interviews.
Results
Affective attitudes and PBC (internal•external) constructs of the TPB were significantly related with the intention to adopt PHD: external PBC (β = 0.324, P < 0.001), internal PBC (β = 0.269, P < 0.01), and affective attitudes (β = 0.226, P < 0.05). The FGI results highlighted the insufficiency of simply providing healthy meals to encourage the adoption of PHDs, but that menu development and natural acceptance strategies are needed to increase palatability. In addition, the need for strategies to promote PHDs at an organizational level was identified, as it is directly influenced by the company of partners with whom one dines. Furthermore, users' perceptions of how “Meals for the Planet” are delivered and suggestions for its improvement were also interpreted.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that users' beliefs, convictions, and emotions are important while promoting or educating individuals about sustainable PHDs. Our findings are expected to help local governments or private group cafeterias that wish to introduce PHDs in the future, given the growing importance of environmentally conscious eating. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Planetary Health Diet Adherence in Korean Adults: Association with the Korean Healthy Eating Index
Su-Jin Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrients.2025; 17(19): 3060. CrossRef - Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 431. CrossRef
- Planetary Health Diet Adherence in Korean Adults: Association with the Korean Healthy Eating Index
- 1,231 View
- 55 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
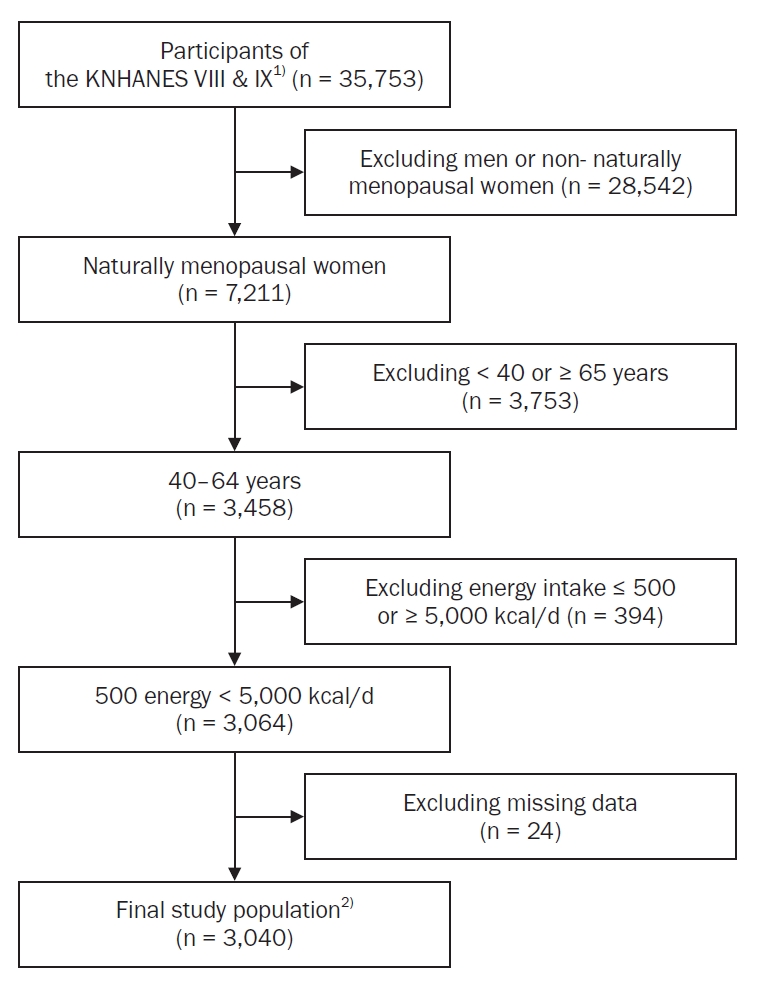
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 3,790 View
- 44 Download

- [English]
- Shifting social perceptions of dietitians in Korea after the legislation of nutrition teachers: a keyword network analysis of unstructured data
- Yunkyoung Oh, Eunsil Her
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):214-223. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
In Korea, dietitian licenses began to be issued in 1964, and they have been working to prevent diseases and promote people’s health in various fields according to the times. This study was conducted to compare differences in social perception of dietitian over time by collecting online unstructured data and analyzing the frequency and network structure of nutritionist-related keywords after the deployment of nutrition teachers began.
Methods
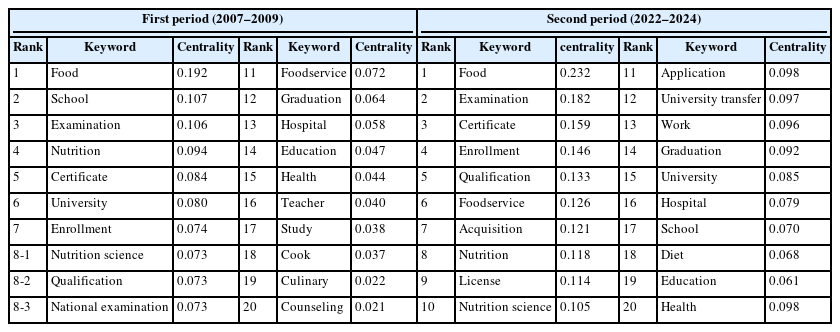
Using ‘dietitian’ as a keyword, we collected data from NAVER’s web, blogs, and news provided by Textom (2024, The IMC) and refined the data. We investigated the frequency ranking of keywords related to dietitians for each period, revealed the network structure using UCINET6 (Freeman) and Netdraw, and clustered similar concepts among keywords through CONCOR (CONvergence of iterated CORrelations) analysis to cluster-related concepts.
Results
Frequency analysis revealed that during the first period, keywords such as “School” and “Education” reflecting the institutionalization of nutrition teachers, were highly ranked. However, by the second period, these terms had dropped out of the top 10. Meanwhile, keywords related to healthcare, such as “Hospital”, consistently remained among the most prominent. In the second period, the rankings of the “License” and “University transfer” keywords increased significantly. Centrality analysis showed stronger connectivity between dietitians and keywords such as “Food”, “School”, “Examination”, and “Nutrition” in the second period compared to the first. CONCOR analysis further demonstrated that the “Major education” cluster of the first period was differentiated into the “Major education and qualification” and “professional competency certification process” clusters of the second period. In addition, the “Health and welfare” cluster of the first period was divided into the “Health and welfare regional service” clusters of the second period.
Conclusion
The results of this study will be used as basic data for identifying social perception and trends in the dietitian profession, further providing a scope for their improvement.
- 2,567 View
- 18 Download

- [English]
- Healthy eating intentions among adults in China: a cross-sectional study of northern and southern regions and city tiers based on the theory of planned behavior
- Yi Jiang, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):114-126. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The theory of planned behavior (TPB) has been widely employed to predict healthy eating intentions. Regional differences may affect dietary habits, health status, and personality traits, whereas variations in urbanization influence accessibility to fresh and healthy food, thereby impacting TPB components. This study aimed to explore whether regional differences between northern and southern China including city-tier development are associated with healthy eating intentions among Chinese adults.
Methods
The study included data from 2,114 Chinese adults aged 19–64 years collected between 2019 and 2023. Participants were categorized by geographic region (north or south) and city-tier status (first-tier or other).
Results
Compared to individuals from northern first-tier cities, those from southern regions exhibited stronger attitudes, perceived behavioral control (PBC), and intention to eat healthily. Participants from other cities in the north had more positive attitudes, subjective norms, PBC, and intentions to participate in healthy eating. Furthermore, residents of southern cities revealed weaker subjective norms than those of cities in the north. The adjusted odds ratio (OR) for compliance with intention to engage in healthy eating was higher among participants from other cities in both the north and south compared to those from northern first-tier cities (northern other cities: OR = 2.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.49–3.97, P < 0.001; southern other cities: OR = 1.95, 95% CI: 1.08–3.51, P = 0.027). No significant differences existed among the subjects from first-tier cities according to their geographic regions. These trends remained consistent even after including the interaction term between geographic regions and city-tier classification.
Conclusion
These findings underscore the complexity of regional variations influencing dietary intentions and indicate that tailored health promotion strategies should incorporate regional characteristics. Future research should explore underlying factors, including regional cultural influences, to better inform policies and interventions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
Md. Asaduzzaman Babu
Food and Humanity.2025; 5: 100779. CrossRef
- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
- 1,656 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Maternal home meal replacement use and attitudes, and young children’s preferences by usage frequency in meals for young children: a cross-sectional study
- Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):163-172. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00066
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With the increase in women’s workforce participation and changing family eating habits, home meal replacements (HMRs) have become more prevalent. However, research on how mothers incorporate HMR into meals of young children remains limited. This study examined mothers’ attitudes toward and use of HMR, as well as their association with young children’s HMR preferences.
Methods
A survey was conducted between June 1 and July 3, 2020, involving 337 mothers of 5-year-old children in Sejong, South Korea. The questionnaire assessed mothers’ perceptions of HMR, consumption patterns, and their children’s preferences for HMR.
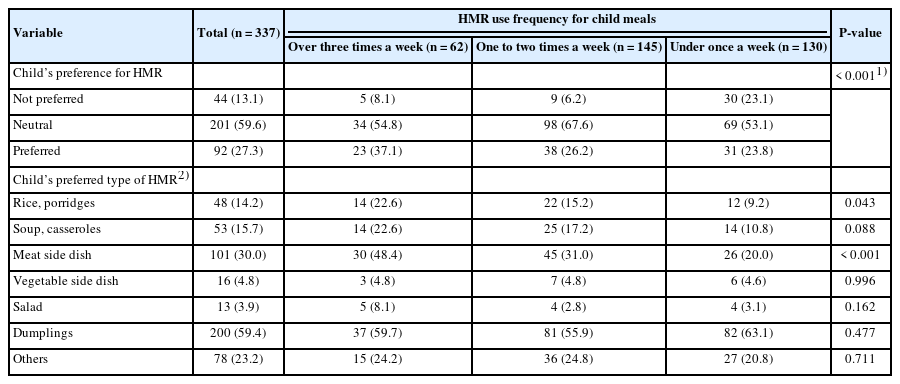
Results
The average age of participating mothers was 38.3 years, with 93.2% living in nuclear families. Full-time homemakers constituted 40.1% of the respondents and showed lower HMR usage among them. HMR was primarily consumed as late-night snacks, side dishes, and dinners, with large discount stores (81.6%) being the primary purchase location. The high HMR consumption group exhibited more positive attitudes toward HMR (P < 0.001). HMR types varied in consumption frequency. Among ready-to-eat foods, kimbap (38.3%) was the most common, followed by meat side dishes (11.3%) and salads (11.0%). Among the heat-and-eat items, dumplings were the most frequently consumed. Simple cooking kits for Korean street food were used by 56.5% of mothers in the high-frequency HMR group, compared to 38.6% and 29.2% in the lower consumption groups (P < 0.01). Children’s preference for HMR was significantly associated with maternal HMR consumption frequency (P < 0.001). The most preferred items among children were rice porridge (P < 0.05) and meat side dishes (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Higher maternal HMR consumption was associated with increased acceptance by children. Mothers who frequently used HMR exhibited more positive attitudes toward its palatability, convenience, nutritional value, and variety. While HMR offers diverse and tasty meal options, overreliance on processed foods warrants caution. Importantly, high HMR consumption during early childhood may influence long-term dietary behaviors, including a continued preference for HMRs.
- 1,310 View
- 34 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of clinical characteristics and dietary intakes according to phenotypes of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Jin Kim, Ji-Sook Park, Sung-Rae Cho, Daeung Yu, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):127-139. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Clinical nutrition treatment is the central part of diabetes management, such as prevention, treatment, and self-management of diabetes, and personalized clinical nutrition treatment, which enables improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study aimed to contribute to the improvement of appropriate nutrition management in personalized treatment for obese and non-obese diabetes patients.
Methods
T2DM patients were recruited as participants, and 36 final participants were assigned to the lean diabetes mellitus group (LDM; body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and the obese diabetes mellitus group (ODM; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). We assessed the dietary intakes, body composition, dietary habits, the Korean version of obesity-related quality of life, and biochemical indices.
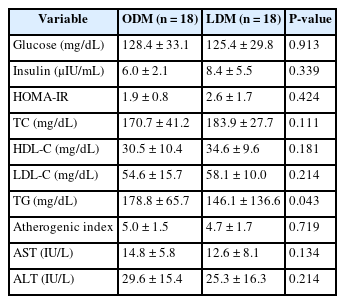
Results
According to the phenotype’s comparison, the ODM group had a high prevalence of T2DM complications and hypertension, had a dietary habit of less than 10 minutes of mealtime duration and preferred fast food intake, and had a low obesity-related quality of life. However, the LDM group had a high choice of Korean dishes at the time of eating out and a high intake of vitamin C, and iodine because of the intake of vegetables and seaweeds.
Conclusion
We observed differences in diet, nutrient intake, and clinical characteristics according to the phenotype of T2DM patients. In particular, obese diabetes patients have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, bad dietary habits, and low obesity-related quality of life. Therefore, personalized nutrition treatment is needed in consideration of the risk of cardiovascular disease and dietary habits for patients in the ODM group, as well as determining the energy requirements of Korean patients with T2DM.
- 2,037 View
- 32 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung–Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):150-162. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00038

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To determine the association between night eating habits and oral health in adolescents.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 were analyzed. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed the frequency of night eating per week, dietary habits, oral health characteristics, and factors affecting the presence of symptoms of poor oral health.
Results
Almost thirty-seven percent (36.6%) of Korean adolescents have eaten at night one to two times per week and 23.0% more than three times per week. An increased frequency of night eating was associated with poor dietary habits. Adolescents who consumed more at night were less likely to have breakfast, drink water, and eat fruit, while their consumption of fast food, sweet drinks, and high-caffeine drinks increased (P < 0.001). An increased frequency of night eating was also associated with poor oral health. In a logistic regression analysis, more frequent night eaters were significantly less likely to brush their teeth at least three times per day (odds ratio [OR], 0.78; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75–0.82; P for trend < 0.001), and brush their teeth before going to sleep (OR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.65–0.75; P for trend < 0.001), while they were more likely to experience sealant (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.13–1.26). More frequent night eaters were significantly more likely to have tooth fracture (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.30–1.53; P for trend < 0.001), tooth pain when eating (OR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.50–1.67; P for trend < 0.001), toothache (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.52–1.70), and bad breath (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.43–1.60).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that frequent night eating is linked to symptomatically poor oral health in adolescents. Therefore, oral health education programs related to dietary habits are necessary to reduce the potential of night eating to negatively influence dietary habits and oral health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Bo Young Park, Eun Bi Sim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(4): 370. CrossRef
- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,431 View
- 58 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):103-113. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00255
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors such as medication use, dietary supplementation, dietary habits, and physical activity among Koreans aged 20–60 years.
Methods
Data from a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) living in Seoul and Gyeonggi provinces in Korea were analyzed to assess the relationship between health behaviors and dietary supplements (DSs) related to self-care. Based on self-care levels, the participants were classified into three groups: low (LS, n = 124), medium (MS, n = 78), and high (HS, n = 98).
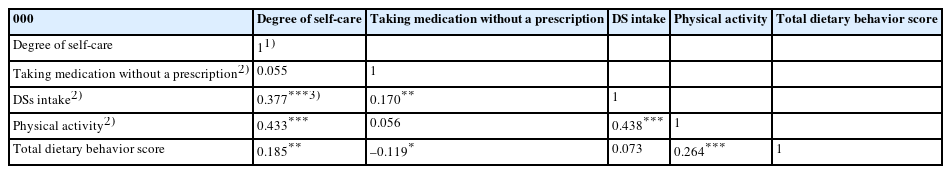
Results
DSs (P < 0.001), physical activity (P < 0.001), recognizing the perceived health benefits of self-care (P < 0.001), self-care when sick (P = 0.039), and the reasons for self-care (P = 0.028) differed among the self-care groups. Daily diet frequency (P = 0.001), breakfast frequency (P = 0.026), regular exercise (P < 0.001), DSs use rate (P < 0.001), DSs use frequency (P = 0.013), and total dietary behavior score (P < 0.001) also differed significantly depending on the degree of self-care. The degree of self-care was significantly and positively correlated with DSs intake (r = 0.377, P < 0.001), physical activity (r = 0.433, P < 0.001), and total dietary behavior score (r = 0.185, P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The results demonstrated that the degree of self-care was related to DSs, physical activity, and total dietary behavior scores in Korean adults. Additionally, self-care capacity should be increased through health-related behaviors based on health education programs.
- 2,276 View
- 55 Download

- [Korean]
- Development and applicability evaluation of a nutrition education program for residents and users of disability social welfare facilities in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Jin-kyung Kim, Kyoung-min Lee, Min-sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):64-74. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop a nutrition education program based on social cognitive theory to promote the health of individuals using facilities for people with disabilities. It also sought to evaluate the applicability of the educational materials through assessments by counselors at the Social Welfare Food Service Management Support Center.
Methods
A group of six experts developed the program based on a needs assessment of nutrition education in facilities for individuals with disabilities. Applicability was evaluated through an online survey of 26 counselors from Social Welfare Food Service Management Support Centers nationwide in July 2023, and the results were analyzed.
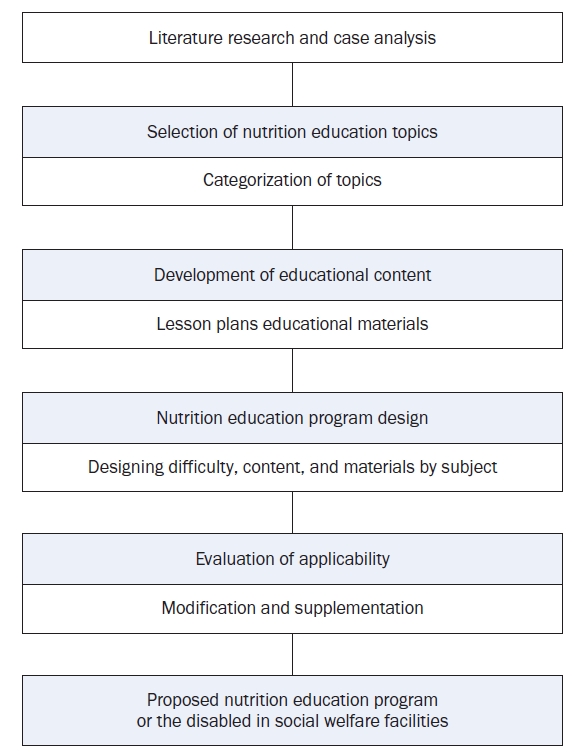
Results
The nutrition education program includes a basic course on personal hygiene, dining etiquette, picky eating prevention, and obesity management. The advanced course covers dietary management for chronic diseases, such as meal planning for hypertension, diabetes management, and dietary principles for dysphagia. Additionally, lecture PPTs, individual activity sheets, and experiential teaching aids were developed. Applicability evaluations showed high scores, with the teaching-learning plan and PPT averaging 4.15 and the experiential teaching aids scoring 4.17, all above 4.0.
Conclusion
This study developed a nutrition education program for individuals with disabilities and assessed its applicability and usability. Implementing this program in disability welfare institutions could enhance health promotion and improve the quality of life for individuals with disabilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
Su-Jin Lee, Ji-Won Kang, Sil Ah Kim, Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Hyunjoo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 498. CrossRef
- Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
- 2,624 View
- 78 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung Su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):53-63. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To apply a healthy dietary program with reduced sodium intake, developed using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), focusing on the sodium intake level and eating patterns.
Methods
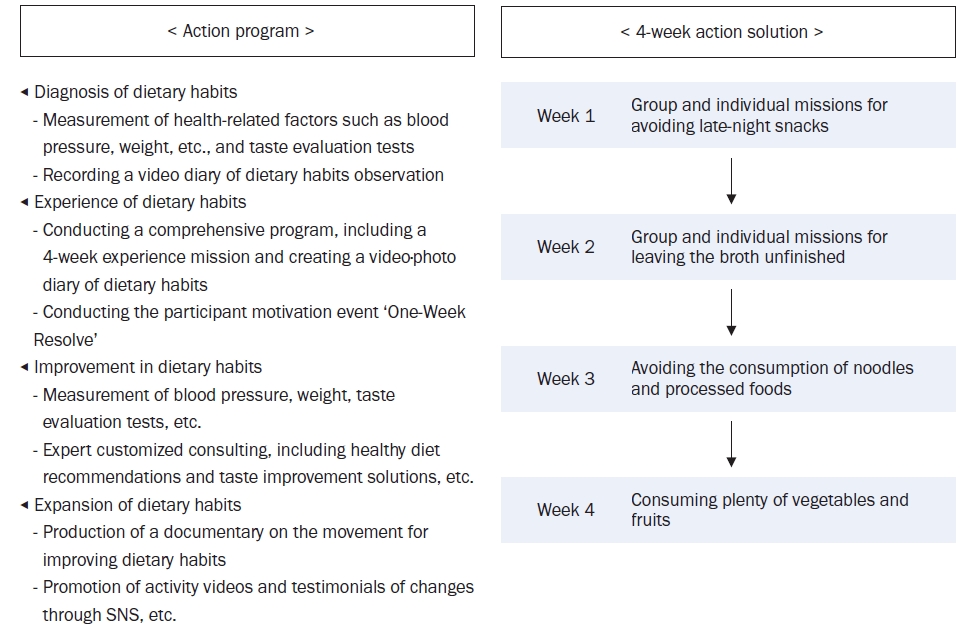
The program was implemented using a living lab model, an open innovation ecosystem for user-centered problem-solving. Analysis of the KNHANES data revealed that older age groups had a low energy intake but a high sodium intake, particularly among those who frequently dined out. The program was designed to improve sodium-reduction literacy and enhance practical competency. Over four weeks, 40 participants tracked their dietary intake and worked with a clinical nutritionist through a process of diagnosis, experience, improvement, and expansion. A self-administered survey was conducted before and after the program to assess effectiveness.
Results
Participants were four teenagers (10%), 26 in their twenties (65%), and 10 aged ≥ 30 years (25%), with eight males (20%) and 32 females (80%). Post-program analysis showed significant improvements in sodium-related nutrition knowledge (P < 0.01), with increased agreement on adopting low-sodium intake practices (e.g., interest in sodium content, choosing lower-sodium foods). Nutrient intake analysis showed a decrease in energy, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (P < 0.001), with sodium intake decreasing from 3,382.37 mg/d to 2,119.05 mg/d (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The community-based, living lab model for the sodium-reduction program effectively improved participant sodium-reduction literacy and practical competency, suggesting that step-by-step, autonomous learning, can reduce sodium intake and promote healthier eating habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
Wonyeong Park, Hae Jin Park, Suah Moon, Jieun Oh
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(6): 917. CrossRef
- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
- 1,818 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of the relationship between sugar intake and cancer prevalence: a cross-sectional study using the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hye-Ryun Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):89-102. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00339
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze the association between sugar intake and cancer risk among Korean adults aged 19 years and older.
Methods
A total of 13,016 adults aged 19 years and older who participated in the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2019 to 2021 were included. Sugar intake was assessed in terms of both absolute intake and sugar energy rate. Sugar intake was divided into quartiles, while sugar energy rate was categorized into three groups (< 10%, 10%–20%, > 20%) based on the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans and into two groups (< 10%, ≥ 10%) based on WHO recommendations. Cancer prevalence was determined using cancer-related survey questions. The association between sugar intake and cancer prevalence was analyzed by sex and cancer type using logistic regression. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS statistics 29.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
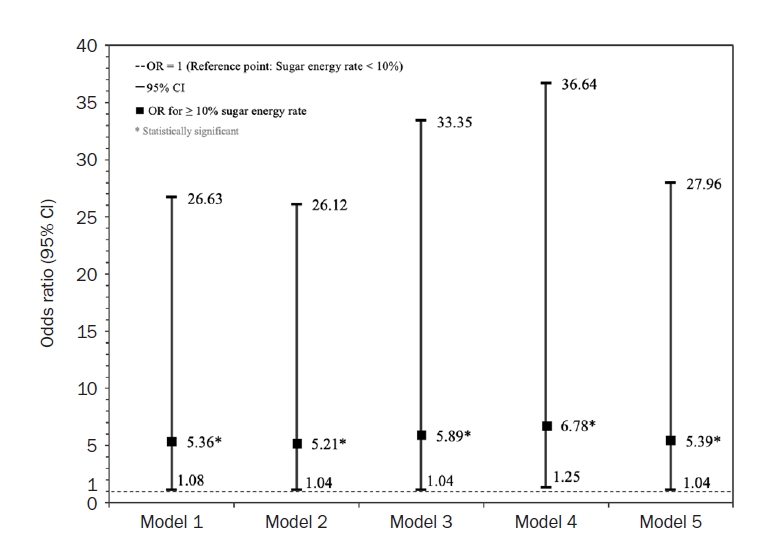
From 2019 to 2021, sugar intake significantly declined with age in both men and women (P for trend < 0.001), with the highest intake observed in the 19–29 age group (61.38 g). Men consumed significantly more sugar than women across all age groups except for the 50–64 and 65–74 groups (P < 0.05). However, the sugar energy rate was significantly higher in women than in men (P < 0.05). While the association between sugar intake and cancer prevalence varied across regression models and cancer types, cervical cancer consistently showed a significant association with sugar intake (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
The association between sugar energy rate and the prevalence of premenopausal cervical cancer was consistent and significant. Given that women had a higher sugar energy rate than men, the relationship between sugar intake and cancer prevalence in women warrants further investigation. Longitudinal studies with more detailed sugar intake assessments are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
Zhe Sun, Wookyoun Cho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 441. CrossRef - Influence of the Size of the Spoon on the Eating rate, Energy Intake and the Satiety Levels of Female College Students
Yang Hee Hong, Young Suk Kim, Hyun Jung Kwon, Do Seok Chang, Dong Geon Kim, Un Jae Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 375. CrossRef - Dietary behavior and nutritional status among Chinese female college students residing in Korea
Gaowei, Soyeon Kim, Namsoo Chang, Ki Nam Kim
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2013; 46(2): 177. CrossRef
- A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
- 2,684 View
- 93 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Jounghee Lee, Juhyun Lee, Wookyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):75-88. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to identify and analyze how different South Korean lifestyles impact attitudes towards pork consumption.
Methods
We implemented a cross-sectional survey targeting 705 adult consumers in South Korea using hierarchical and K-means cluster analyses. Respondents were classified into three relevant lifestyles: (1) domestic preference, (2) price-sensitive, and (3) quality-experience-oriented. The importance-performance analysis was employed to evaluate discrepancies between how they rated pork consumption using factors of “importance” and “satisfaction”. We employed Borich’s needs assessment and the Locus for Focus model to prioritize management areas.
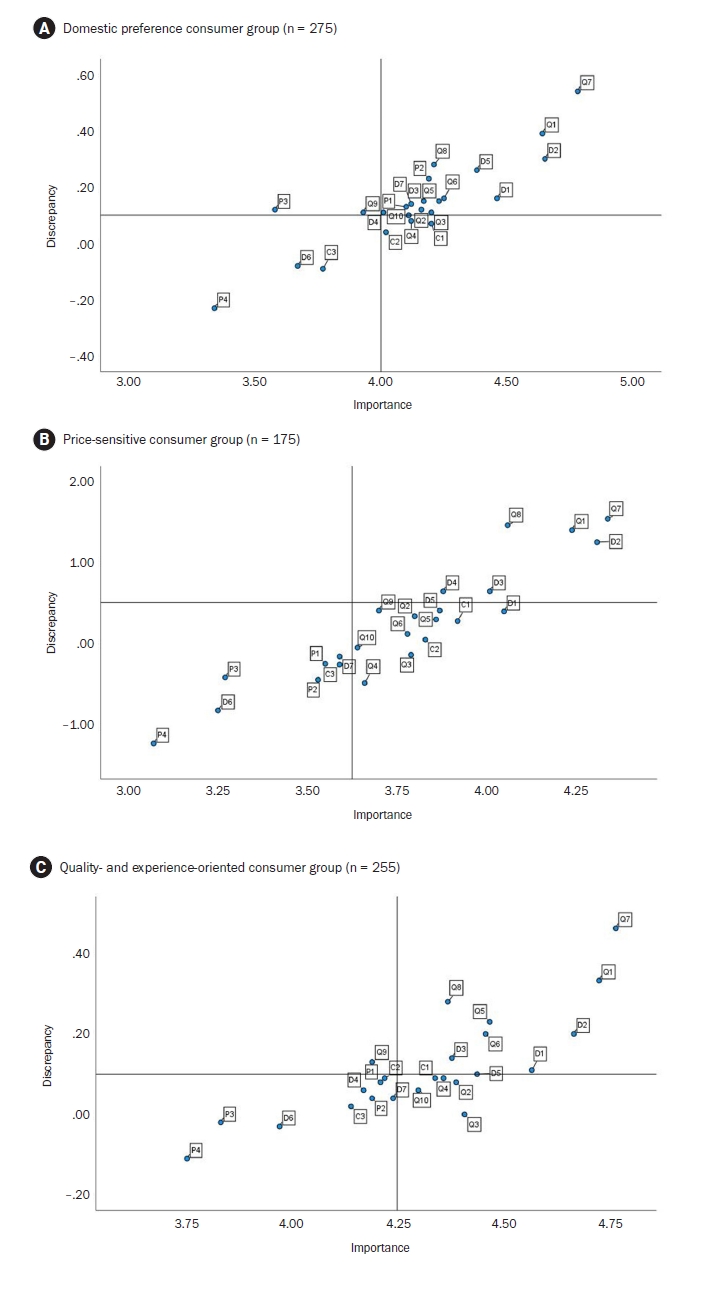
Results
The research findings highlight that unpleasant odor/smell (Q7) and hygiene (Q1) were common key areas for management across all consumer groups, emphasizing their importance in enhancing pork consumption satisfaction. Among the groups, the domestic preference group showed high importance-performance discrepancies in attributes like expiry date (D2), suggesting a need for strengthened trust in domestic pork distribution and information transparency. The price-sensitive group prioritized economic factors, with fat thickness (Q8) identified as an essential management area. The quality-experience-oriented group emphasized sensory qualities such as juiciness (Q6) and meat color (Q5), with off-flavors (Q7) displaying the largest discrepancy. These results show the significant role of sensory attributes in consumer satisfaction.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the multidimensional nature of pork consumption behavior, emphasizing the need for tailored strategies across consumer groups. Managing hygiene (Q1) and reducing off-flavors (Q7) are critical for all segments, while group-specific strategies include managing sensory quality for the quality-experience-oriented group, providing product information (D2) to increase trust for the domestic preference group, and emphasizing value for money for the price-sensitive group.
- 1,894 View
- 42 Download

- [English]
- Food and nutrient intake in pregnant women with singletons or multiples and post-delivery changes in intake in Korea: an observational study
- Cheawon Lee, Dahyeon Kim, Yoon Ha Kim, Myeong Gyun Choi, Jong Woon Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):1-15. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00325
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Nutrient intake during pregnancy and lactation is crucial for the health of both mother and offspring. Diet and nutrient metabolism potentially vary according to ethnicity and fetal number; nevertheless, recent studies validating this are inadequate. Furthermore, few studies have tracked changes in intake after delivery. We compared the food and nutrient intakes between pregnant women in Korea carrying singletons and multiples during late pregnancy and assessed their changes through postpartum.
Methods
Ninety-eight pregnant women were recruited from Chonnam National University Hospital between January 2019 and December 2023, and 48 responded to follow-up. Third trimester and postpartum intake were assessed via food frequency questionnaires and supplement questionnaires. Student’s t-test, Mann–Whitney U test, chi-square test, paired t-test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test was performed and adjustments were made for covariates.
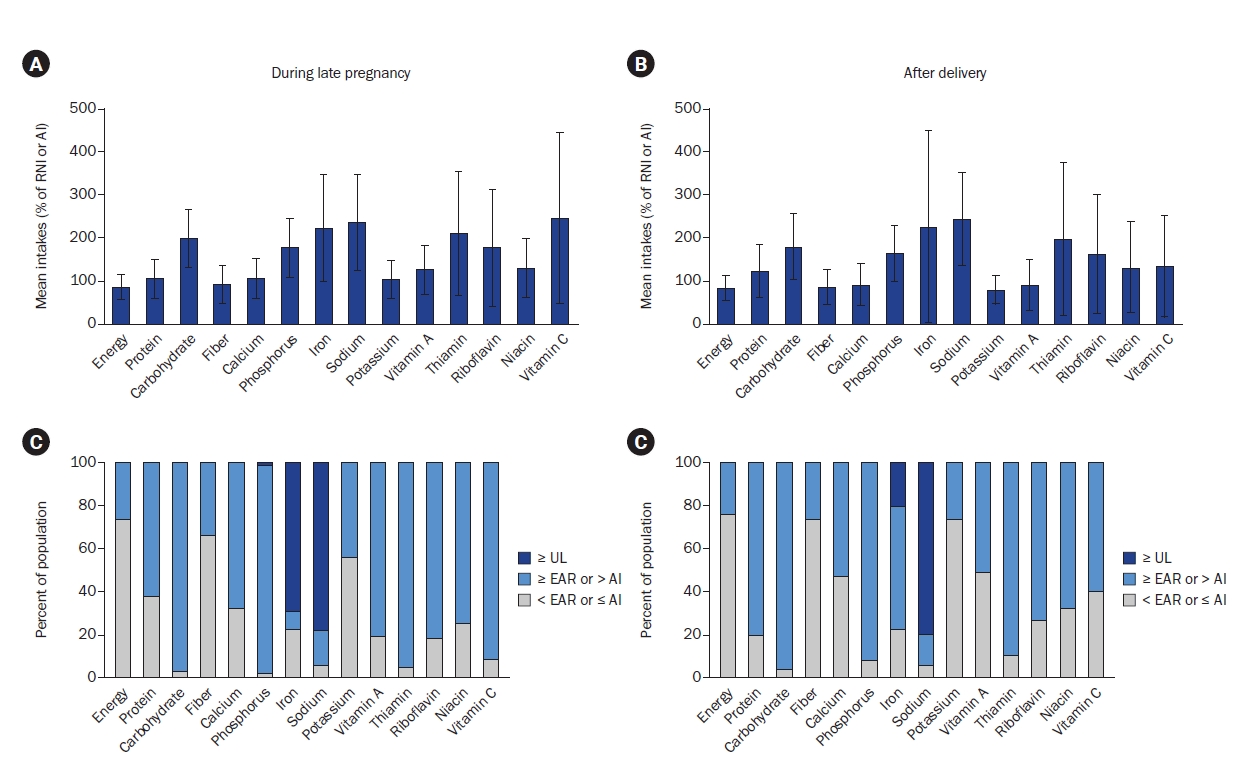
Results
Nutrient intake was generally adequate relative to the Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans, with no differences between singleton- and multiple-pregnancy women. Sixty-six of 98 (67%) pregnant women consumed meat, fish, vegetables, and fruit daily. Dairy intake was low, while the mean iron intake during pregnancy reached 54.2 ± 34.0 mg/d, exceeding the tolerable upper intake level, mainly owing to supplements. Postpartum fruit and vitamin C intake decreased, with no significant differences between breastfeeding and non-breastfeeding women.
Conclusion
Dietary intake did not significantly differ between Korean singleton- and multiple-pregnancy women. Dairy intake was low and iron intake was excessive. Fruit intake decreased after delivery; however, difference in dietary intake according to breastfeeding status was minimal. Nutritional education may be necessary to promote a balanced diet in pregnant and postpartum women. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier KCT0005118. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Placental cadmium and its association with maternal diet and offspring growth in Koreans
Dahyeon Kim, Cheawon Lee, Yoon Ha Kim, Myeong Gyun Choi, Jong Woon Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(3): 473. CrossRef
- Placental cadmium and its association with maternal diet and offspring growth in Koreans
- 7,188 View
- 63 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):16-26. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00311

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated the nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P) and analyzed the impact of key factors, such as caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment, on the eating habits of preschool children in Korea. This study also sought to provide foundational data for developing tailored nutrition education programs by identifying the nutrition education needs of caregivers.
Methods
This study was conducted among caregivers of preschool children (aged 0–6 years) using an online self-administered survey conducted from August 22 to August 28, 2023. A total of 1,116 survey responses were analyzed. This study assessed children’s NQ-P score, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and nutritional education needs. Data were analyzed using SPSS 29.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
The average NQ-P score for preschool children was 52, showing a tendency for the balance score to decrease and the moderation score to increase with age. Children from rural and low-income areas exhibited significantly lower NQ-P scores. Caregivers’ food literacy was higher in urban and higher-income groups. Multiple regression analysis revealed that social support, food literacy, income, and food environment significantly affected children's NQ-P scores. The effectiveness of nutrition education varied based on the income level, with nutrition education on healthy eating being the most preferred topic for preschool children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that caregivers’ food literacy and social support significantly affected preschool children’s nutritional status. This suggests a need for tailored nutritional education and dietary support policies, particularly for low-income and rural populations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 352. CrossRef
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- 3,105 View
- 60 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of a multi-component program based on partially hydrolyzed guar gum (Sunfiber®) on glycemic control in South Korea: a single-arm, pre-post comparison pilot clinical trial
- Hyoung Su Park, A-Hyun Jeong, Hyejung Hong, Hana Jang, Hye-Jin Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):40-52. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00276
- Correction in: Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to assess the impact of a multi-component program, including partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG, Sunfiber®) supplementation, on glycemic control, gut health, and nutritional status to support diabetes prevention and management among Korean adults.
Methods
A single-arm trial was conducted with 29 adults (aged 20-55 years) with fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 100 mg/dL. Over a six-week period, participants engaged in a multi-component program that incorporated the supplementation of PHGG (Sunfiber®, 12.5 g/day), weekly nutritional coaching, and the use of continuous glucose monitoring devices. The program’s effectiveness was evaluated by measuring FPG and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels through blood tests conducted before and after the intervention. Improvements in gut health were gauged using the Korean Gut Quotient Measurement Scales, while enhancements in nutritional status were assessed using the Nutrition Quotient (NQ) and surveys that evaluated improvements in gut health and nutritional status.
Results
Participants’ average age was 43.89 years, with approximately 80% being male. Most participants (about 75%) were classified as overweight or obese. After six-weeks, 17 participants who adhered closely to the program (meeting certification criteria) exhibited significant reductions in key blood glucose markers. FPG levels decreased from 113.06 ± 23.16 mg/dL to 106.24 ± 16.33 mg/dL (P < 0.05), and HbA1c levels decreased from 6.08% ± 0.81% to 5.87% ± 0.53% (P < 0.05). The NQ evaluation revealed significant increases in comprehensive nutrition scores, and in the balance and practice domain scores for all participants (P < 0.05). Furthermore, in the gut health survey, approximately 82.1% of all participants reported experiencing positive changes.
Conclusion
Among adults with elevated FPG levels, a multi-component intervention program that included PHGG (Sunfiber®) supplementation, structured dietary management, and the use of health-monitoring devices showed significant benefits in improving glycemic control, overall nutritional status, and gut health. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010049. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of dietary and lifestyle habits according to the prediabetic status in young adults
Joungyoon Seo, SeongHee Shin, Yuri Kim, Yoo Kyoung Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 468. CrossRef - Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Combined with a Low-Fat Diet Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites
Zhiqiang Cao, Hongxia Li, Quantao Cai, Li Chen, Liangzhong Liu, Yuhan Tang, Zhe Zhu, Ping Yao
Nutrients.2025; 17(23): 3746. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of dietary and lifestyle habits according to the prediabetic status in young adults
- 7,434 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):492-503. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00018
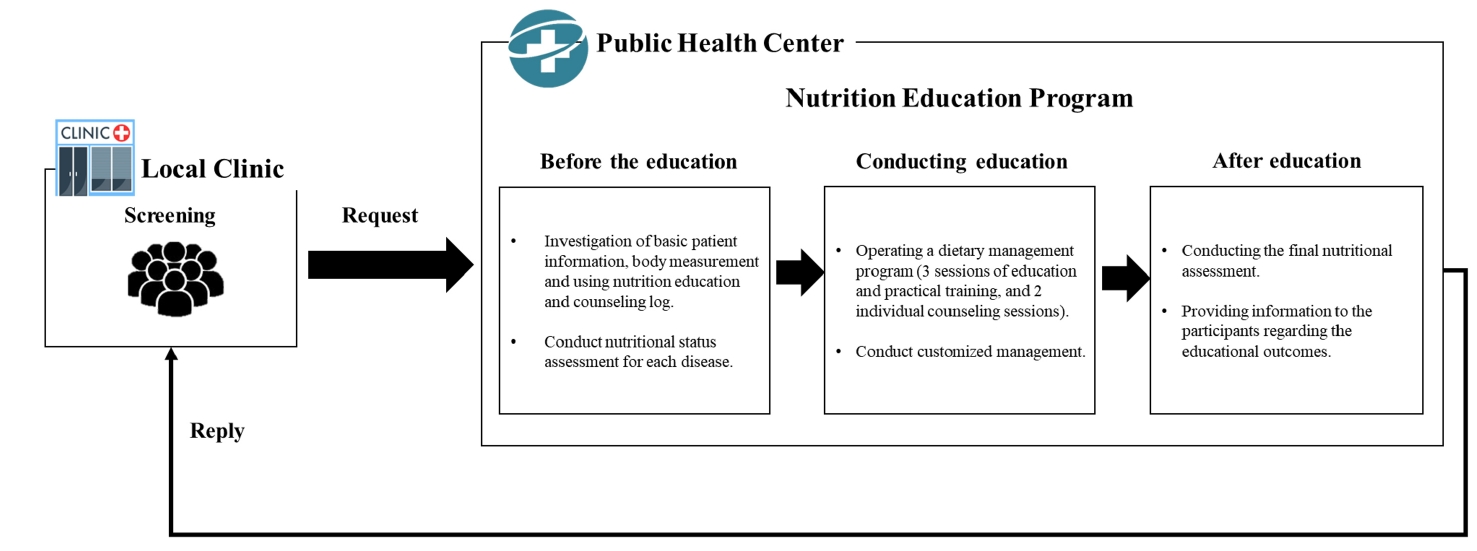
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We investigated the impact of an advanced “Nutrition Education Program” on patients with Diabetes mellitus, type 2 from public health centers enrolled in a primary health care-based chronic disease management project. This 12-week dietary management program was developed by the Korea Health Promotion and Development Institute. We assessed if this program improved glycemic control and other health indicators through dietary and nutritional improvements.
Methods
Seventeen patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2 were enrolled in the “Nutrition Education Program.” These patients were referred to public health centers for lifestyle management based on physician assessments at local clinics that were participating in a pilot project on primary health care-based chronic disease management. The participants attended the program comprising face-to-face basic, in-depth, and practical training sessions at the health center during the third, fifth, and seventh weeks, respectively. Anthropometric measurements, body composition analysis, blood biochemical characteristics, nutritional knowledge, and self-efficacy evaluation were performed before and after the program. Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 28.0.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 62 years, and most participants were female (14, 82.4%). No significant changes in patients’ anthropometric measurements or body composition were observed after the training. However, significant reductions were observed in the blood biochemical characteristics, including glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels. Additionally, patients’ nutritional knowledge and self-efficacy scores increased significantly.
Conclusions
The “Nutrition Education Program” helped in improving glycemic control and other health indicators in patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2. Further research is required to objectively confirm the long-term and sustained effects of the program in a controlled study. Trial Registration Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010010
- 2,354 View
- 85 Download

- [English]
- Health-related quality of life and nutrient intake of the elderly with type 2 diabetes according to comorbidity burden: a cross-sectional study
- Yejung Choi, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):418-430. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00014

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to explore the cross-sectional association between health-related quality of life (HRQoL) according to the number of comorbidities in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) using the Euro Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) index. Methods: This study included 3,553 participants aged ≥ 65 years from the 2008–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Dietary data were collected through 24-hour recall interviews by trained researchers, and demographic and lifestyle information via self-administered questionnaires. HRQoL was measured using a modified EQ-5D scale. Multivariable linear regression analyzed the associations between EQ-5D scores, nutrients and comorbidity, controlling for sociodemographic and health variables. Results: Most participants reported ‘no problems’ in the EQ-5D scores, although approximately 17% to 47% of participants reported ‘some problems’ or ‘extreme problems,’ depending on the dimension. As comorbidities increased, significant declines were observed across all dimensions, particularly in mobility, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/ depression. Nutrient intake analysis revealed that participants with three or more comorbidities consumed less carbohydrates, but more fat. Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that among older adults with T2DM, a higher number of comorbidities is associated with decreased HRQoL. Additionally, there are differences in nutrient intake patterns among those with more comorbidities, specifically decreased carbohydrate intake and increased fat intake. These results emphasize the need for comprehensive and tailored management strategies that consider both diabetes and the co-occurring health conditions. By addressing the complex healthcare needs of individuals with multiple comorbidities, it is possible to enhance their HRQoL and overall well-being.
- 2,047 View
- 32 Download

- [Korean]
- Food purchase patterns, food policy recognition, and food environment satisfaction among adults in Jeju, Korea, according to food security: a cross-sectional study
- Sumin Kim, Youjeong Jang, Hyunji Ham, Hanbin Ko, Insuk Chai, Kyungho Ha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):406-417. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00012

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Recently, food insecurity has been a major public health issue along with the food crisis caused by COVID-19, climate change, and the polarization of food supply due to socioeconomic disparities. Food insecurity is known to be related to the food choices and environment of the consumer. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the food security statuses of adults in Jeju and investigate their food purchase patterns, food policy recognition, and food environment satisfaction.
Methods
Based on data from the 2022 Jeju Food Survey, 346 adults aged ≥19 years in Jeju were classified into food security and insecurity groups (quantitatively and qualitatively) using the questionnaire. Food purchase patterns, including purchasing frequency, items, and reasons, were surveyed for local and eco-friendly foods. The recognition and necessity of several food policies and satisfaction with diet and food environment (availability, accessibility, affordability, accommodation, and acceptability) were measured using the Likert scale.
Results
Among the total participants, 47.4% were in the food insecurity group. The frequency of purchasing local and eco-friendly foods did not significantly differ by food security status. The insecurity group exhibited a higher recognition rate of basic rights to food (36.0%) than the security group (24.7%, P = 0.023). The recognition and necessity of specific food policies did not significantly differ by food security status, except for the policy of promoting food communities, for which the food security group exhibited higher recognition than the food insecurity group did (P = 0.004). The food insecurity group exhibited significantly lower scores regarding satisfaction toward diet and food environment factors (P < 0.05 for all).
Conclusions
Overall, the food security group reported higher satisfaction with their diet and food environment than the food insecurity group. Further in-depth studies to investigate the determinants of food insecurity and effective promotional strategies for food policies are needed.
- 2,106 View
- 50 Download

- [English]
- Associations between the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease and dietary and lifestyle behavior among young Korean adults: a preliminary cross-sectional study
- Soheun Shim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):396-405. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00011

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a clinical condition caused by esophageal tissue damage resulting from the reflux of stomach or duodenal contents. An increasing number of GERD cases have been reported recently; however, research on this population, especially young adults, is lacking. This study aimed to investigate the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Methods: A total of 202 individuals (19–34 years old) living in Gwangju were surveyed using a questionnaire to examine their general characteristics, lifestyle, and dietary behaviors. GERD symptoms were investigated using the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GerdQ). The participants were grouped into normal (GerdQ score ≤ 4) and caution (GerdQ score ≥ 5), and their characteristics were analyzed according to the group. Results: The findings suggested 15 participants (7.4%) belonged to the GERD caution group. More non-office workers were in the caution group than in the normal group (P < 0.05). The participants’ smoking, physical activity, sleep duration, and pillow height were not significantly different between the GERD phenotypes; however, the caution group consumed alcohol more frequently than the normal group (P < 0.001). The analyses of the participants’ eating behaviors revealed that the frequency of overeating, late-night snacking and chocolate consumption was significantly higher in the caution group (P < 0.001). Conclusion: Lifestyle and dietary behaviors were associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Further studies with larger cohorts are required to confirm these findings.
- 5,529 View
- 71 Download

- [Korean]
- The needs and prioritization of nutrition and dietary support for individuals with disabilities: an exploratory study
- Jong Eun Park, Yu Jin Kim, So Young Kim, Jong Hyock Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):431-443. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00009
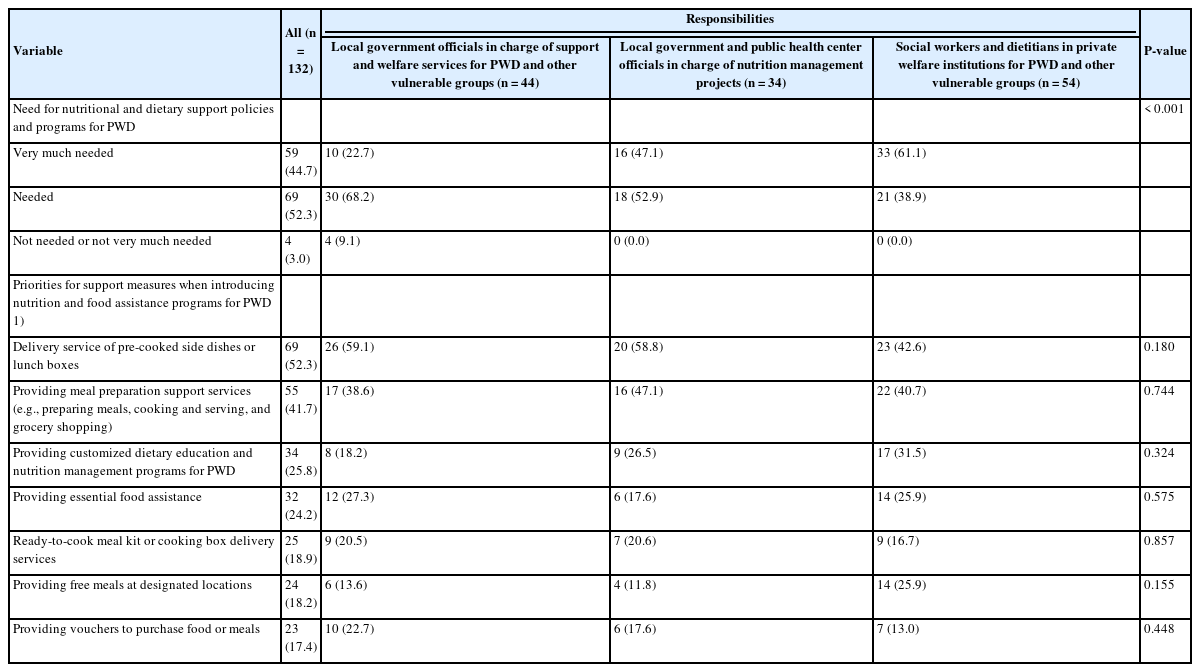
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Based on a survey of officers, social workers, and dietitians involved in managing nutrition and welfare policies or projects for vulnerable groups in local governments or private welfare institutions, this study aimed to assess the need for nutritional and dietary support policies and programs for persons with disabilities (PWD), as well as to identify appropriate support measures. Methods: An online survey was conducted from March 2 to 15, 2021. The survey included 20 questions exploring perspectives on the nutritional status of PWD, their need for nutritional and dietary support policies and programs, and the prioritization of appropriate support measures. A total of 132 responses were analyzed. Results: Approximately 68.9% of the respondents rated the nutritional status of PWD as “bad” or “very bad.” A substantial number identified “difficulty in purchasing ingredients, cooking, and preparing meals independently due to disability,” and “limited knowledge about nutrition and recipes necessary for maintaining a healthy and balanced diet” as the primary challenges in the dietary and nutritional management of this population. Additionally, 97.0% of the respondents deemed that the introduction of nutritional and dietary support policies and programs for PWD was “needed” or “very much needed.” Priority strategies to implement and strengthen these policies and systems included the “development of customized programs and services tailored to the needs and demands of the target population” and the “establishment of a dedicated department with specialized personnel.” Conclusion: Comprehensive nutritional and dietary support policies and programs should be actively implemented to ensure a healthy and stable diet for PWD, tailored to meet their actual needs and demands. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
Su-Jin Lee, Ji-Won Kang, Sil Ah Kim, Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Hyunjoo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 498. CrossRef - Factors associated with nutritional risk among disabled persons in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study using 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel
Seong-Ah Kim, Seul Ki Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 364. CrossRef
- Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
- 2,597 View
- 117 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- An educational needs analysis of sustainable dietary education for nutrition teachers: an application of the IPA, Borich needs assessment and The locus for focus model
- Eunseo Yang, Borham Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):372-381. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00008

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the importance and performance levels of sustainable dietary education across the health, environment, and society domains as perceived by nutrition teachers and evaluate the needs and priorities for sustainable dietary education.
Methods
An online survey was conducted for 151 nutrition teachers in Jeollanam-do. The survey included 20 questions across the health, environment, and society domains. The data were analyzed using a paired-sample t-test, the importance-performance analysis (IPA), the Borich needs assessment model, and the locus for focus model.
Results
Overall, the average importance levels of the 20 items of sustainable dietary education were significantly higher than their average performance levels (4.44 vs. 3.68). The examination of each educational domain revealed that although the importance of education in the health domain was recognized and actively practiced by the nutrition teachers, the performance was comparatively lower in the environment and society domains. The Borich needs assessment and the locus for focus model identified education on biodiversity conservation, plant-based protein, and the use of local food as the top-priority group in the environment domain along with fair and ethical food, food security, regional food culture, food policy and trade, and family dining culture as the second-priority group in the society domain.
Conclusions
The results of this study underscore the need to support the nutrition teachers’ perception and practice of sustainable dietary education in the environment and society domains. We believe that the educational needs and priorities proposed in this study will be considered in the future development and modification of sustainable dietary education programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Jounghee Lee, Juhyun Lee, Wookyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 75. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef - Analysis of students’ need for artificial intelligence content in the 「Digital education」 subject
SungAe Kim, Ji Won You
The Journal of Korean Association of Computer Education.2025; 28(7): 71. CrossRef - Safety education status and needs priorities of Korean military food service personnel using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model: a cross-sectional study
Jeongeun Park, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 261. CrossRef
- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 2,493 View
- 75 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Eating habits and dietary supplement utilization according to food-related lifestyle among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):253-264. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00017
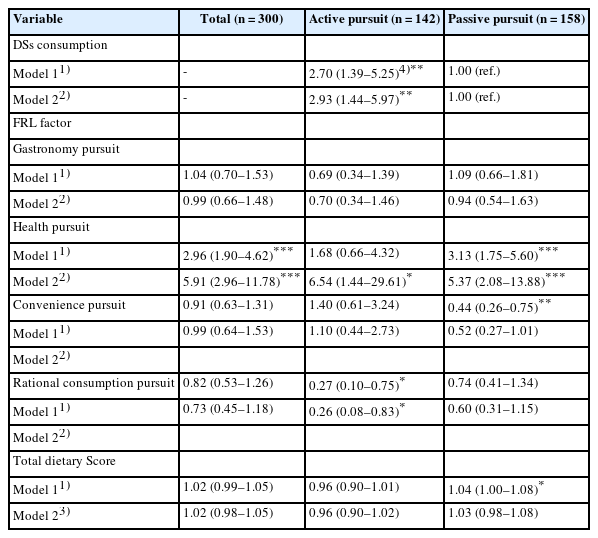
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the association between eating habits and the utilization of dietary supplements (DSs) according to food-related lifestyle (FRL) among Korean adults. Methods: This study included a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) in their 20s to 60s living in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province. We identified two groups by factor and cluster analysis: an ‘active pursuit’ group and a ‘passive pursuit’ group. Differences in eating habits and DS utilization between the two groups were analyzed by chi-square test and t-test. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the effect of variables on DS consumption according to FRL. Results: There were significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, alcohol drinking frequency, total dietary score, change in DS consumption after coronavirus disease 2019, and current DS consumption (P < 0.05). The proportion who perceived many health benefits of DSs was higher in the ‘active pursuit’ group than in the ‘passive pursuit’ group (P = 0.003). The most commonly consumed type of DSs was multivitamins & minerals for the ‘active pursuit’ group, and omega-3 fatty acids for the ‘passive pursuit’ group. The ‘an active pursuit’ group consumed DSs 2.93 times more (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.44–5.97) compared to the ‘passive pursuit’ group, after adjusting for confounders. In the ‘active pursuit’ group, the health pursuit (odds ratio [OR] = 6.54, 95% CI: 1.44– 29.61) and rational consumption pursuit factors (OR = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.08–0.83) were associated with DS consumption, whereas only the health pursuit factor had a significant association (OR = 5.37, 95% CI: 2.08–13.88) within the ‘passive pursuit’ group. However, total dietary score and DSs consumption did not show a relationship. Conclusions: By understanding the consumption characteristics of DSs according to FRL, this can serve as basic data necessary for promoting health through the utilization of DSs and healthy behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
Hongryul Ahn, Seungwon Kim, Jinmyung Jung, Chan Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(4): 618. CrossRef
- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
- 4,975 View
- 94 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Exploring the customer perceived value of online grocery shopping: a cross-sectional study of Korean and Chinese consumers using Means-End Chain theory
- Xinyu Jiang, Hyo Bin Im, Min A Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):318-335. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00007
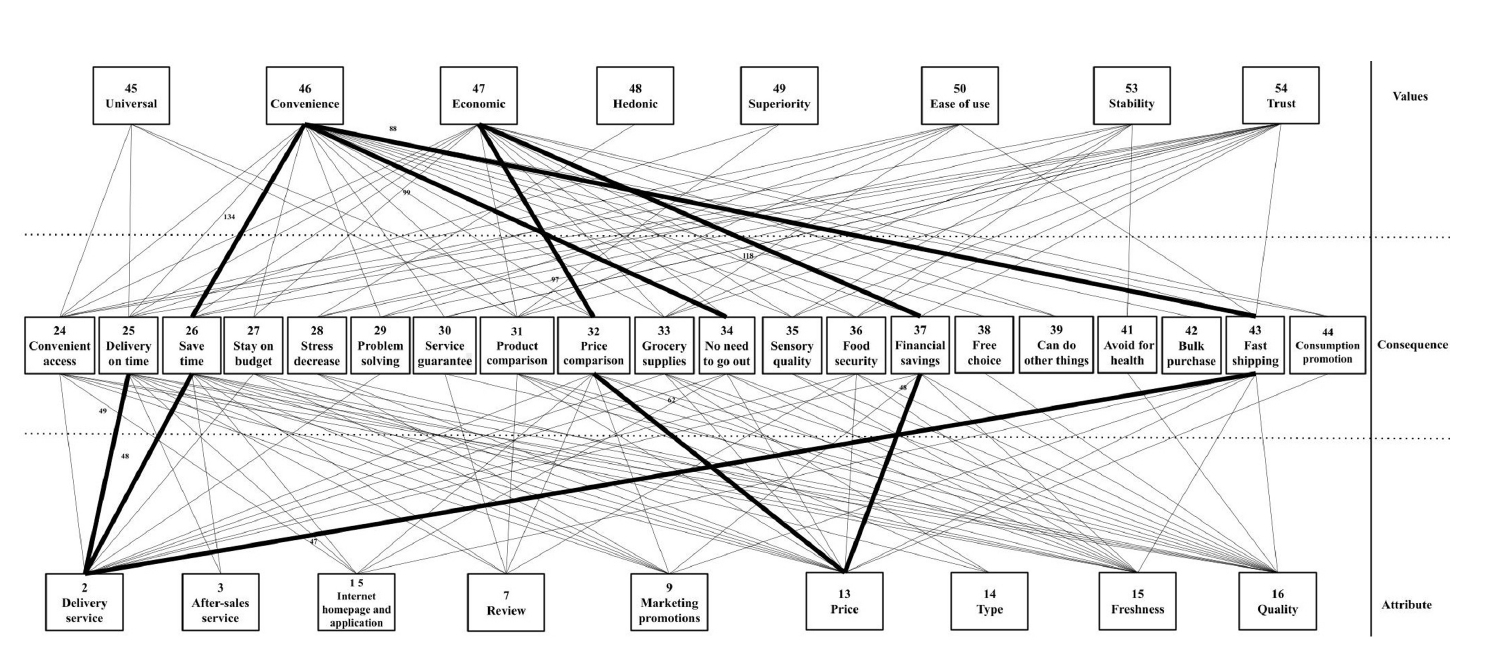
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Despite the growing market share of online grocery shopping, there is a need to understand customer perceived value due to the ongoing advancements in information technology. This study explores the connections between attributes, consequences, and values. Additionally, it conducts a cross-country comparison of consumers’ online grocery shopping behaviors to gain a deeper understanding of consumer market segments and any potential variations among them.
Methods
Data was collected through an online questionnaire survey conducted from May 1 to 15, 2024, targeting 400 consumers in Seoul, Korea, and Shanghai, China, who have experience with online grocery shopping. The survey utilized the Means-End Chain theory and association pattern technique hard laddering. Data collation and analysis were conducted using the IBM SPSS Statistics 28.0 program. The LadderUX software was employed to analyze the links between attributes, consequences, and values and create the consumer purchasing process’s implication matrix and hierarchical value map (HVM).
Results
The study identified key attributes that influence online grocery shopping decisions, including delivery service, price, freshness, and quality. Korean consumers demonstrated a higher sensitivity to price (19.0%) and delivery service (17.0%). In contrast, Chinese consumers prioritized delivery service (15.0%) and after-sales service (14.8%). Commonly cited consequences included time saving (12.6% for Koreans, 11.3% for Chinese), whereas prevalent values encompassed convenience (36.8% for Koreans, 19.6% for Chinese) and economic value (26.6% for Koreans, 14.7% for Chinese). The HVM underscored these insights, highlighting diverse consumer preferences and country-specific nuances.
Conclusions
The findings highlight the current state of online food consumption and consumers’ value systems, revealing variations among countries. These findings offer empirical insights that can be used to create customized global marketing strategies that resonate with various consumer preferences and market dynamics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the stage: how performing arts tourism shapes tourist perceptions and destination image
Islam Elbayoumi Salem, Mohammed Ali Bait Ali Sulaiman, Enrico di Bella, Sara Preti, Mohamed Kamal Abdien, Ahmed Magdy
Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights.2025; : 1. CrossRef
- Beyond the stage: how performing arts tourism shapes tourist perceptions and destination image
- 5,711 View
- 75 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
- Youngmin Nam, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):288-303. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00006
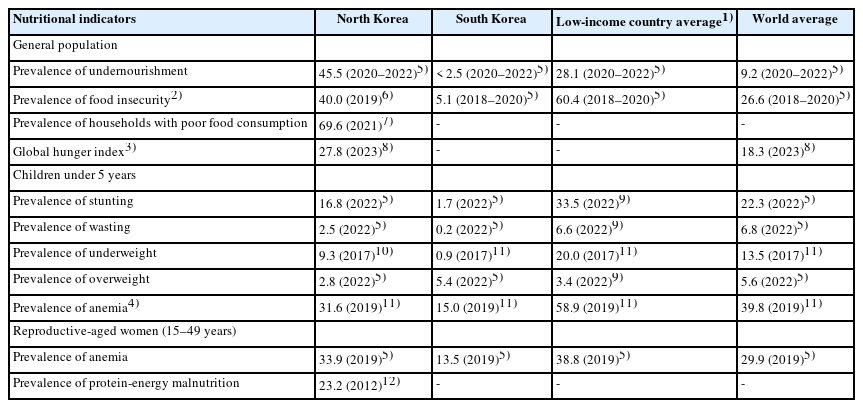
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
North Koreans have been facing chronic food shortages and malnutrition. This study examined the nutritional status of North Koreans and the perceptions of South Korean adults regarding their nutritional status.
Methods
The nutritional status was examined using nutritional indicators for the general population, children, and reproductive-aged women in North Korea. An online survey was conducted among 1,000 South Korean adults aged 19–69 years to investigate their perceptions regarding the nutritional status of North Koreans.
Results
Although the nutritional status of children in North Korea has consistently improved, significant progress in the general population and reproductive-aged women in the country remains elusive. The prevalence of malnutrition among North Korean children has decreased to a level that is not considered severe based on international standards, although it shows a substantial difference from that among South Korean children. The prevalence of undernourishment and food insecurity in North Korea remains over 40%. South Korean adults perceive the nutritional status of North Koreans as being more severe than it is in reality. Notably, a significant inconsistency exists between the perceived and actual nutritional status of North Korean children, with over 95% of South Korean adults perceiving North Korean children’s malnutrition as being more severe than it actually is. Moreover, South Korean adults in their 20s to 40s tended to perceive the nutritional status of North Koreans as being more severe than those in their 50s to 60s did.
Conclusions
The nutritional status of North Koreans is a matter of concern. The disparity between South Koreans’ perceptions of the nutritional status of North Koreans and the actual status highlights the need for accurate information dissemination to effectively address malnutrition in North Korea. These efforts could be instrumental in enhancing public awareness and fostering social consensus on food aid and nutritional support programs for North Korea.
- 3,866 View
- 72 Download

- [English]
- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
- Jiwoo Min, Youngmi Lee, Yunhee Chang, Yujin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):304-317. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00004
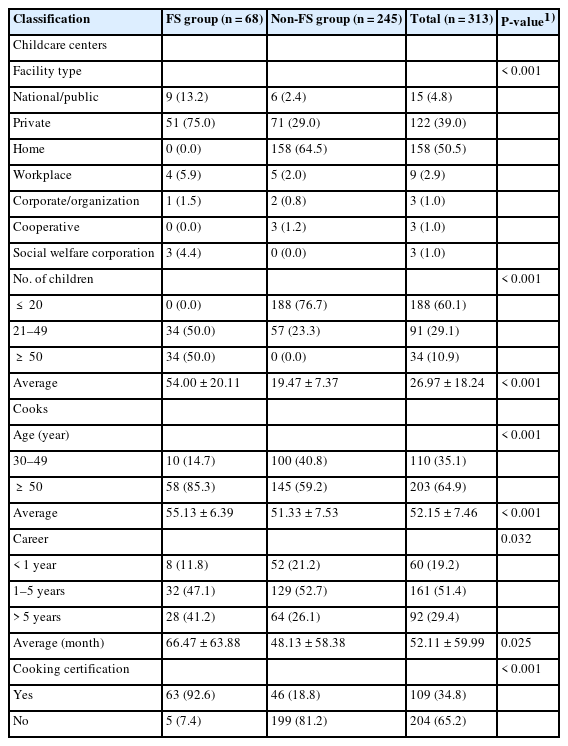
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the importance and performance of sodium reduction practices among childcare center cooks in the Yongin area before and after a 3-month salinometer support program.
Methods
In total, 313 cooks employed in childcare centers in Yongin were surveyed before and after participating in a salinometer support program. The survey included questions on general information, sodium-related dietary habits, and perceived importance and performance levels of sodium reduction approaches in the purchasing, cooking, and serving areas. The centers were divided into childcare centers registered as group-feeding facilities (FS group, n = 68) and those not registered as such (non-FS group, n = 245). The differences between the two groups were analyzed.
Results
The overall importance levels increased significantly after the program in both the FS-group (P < 0.001) and non-FS group (P = 0.005). The overall performance levels also increased significantly in both groups (P < 0.001 for all). Consequently, the significant difference between the importance and performance levels disappeared in both groups after the program. However, unlike the FS group, which showed no significant differences between the importance and performance levels after the program in all three areas, the non-FS group still demonstrated lower performance levels than importance levels in the purchasing (P = 0.011) and serving (P = 0.034) areas after the program.
Conclusions
The use of salinometers significantly enhanced the performance and importance of low-sodium management practices among cooks in childcare centers, especially in the FS group. The continuous monitoring of salinity measurements and tailored education specialized for the FS and non-FS groups are recommended.
- 1,631 View
- 26 Download

- [English]
- Sex differences in health-related quality of life among older Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
- Hyeonji Jeong, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):336-347. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00003
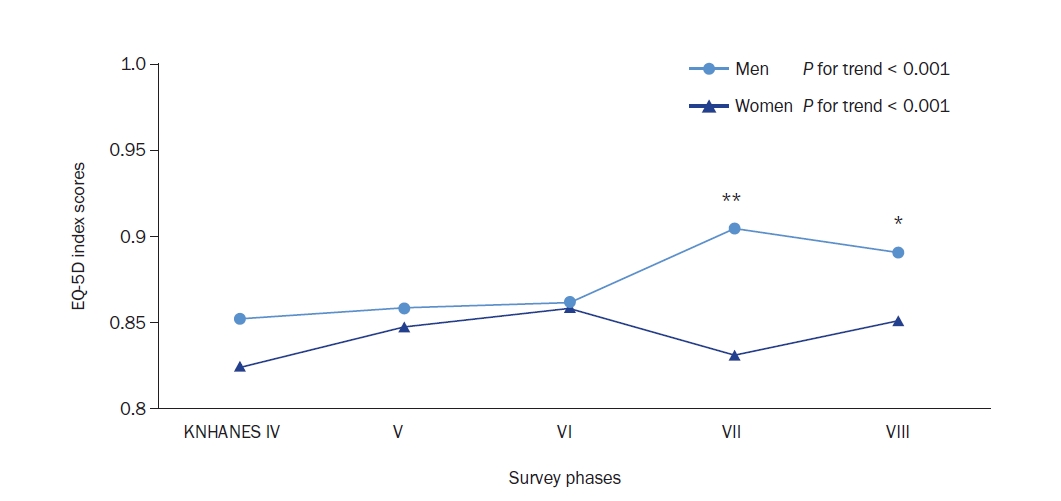
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This cross-sectional study examined sex differences in Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) among seniors with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2008–2020) were analyzed. The EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D), a measure of HRQoL, was used. It comprises five dimensions: mobility, self-care, usual activity, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression, each with three levels.
Results
Analysis of 3,826 older adults with T2DM showed a significant increasing trend in the EQ-5D Index from the 4th survey phase onwards (P for trend < 0.001 for both men and women). Men consistently reported higher EQ-5D levels than women across all survey years. Women’s EQ-5D levels remained lower than men’s, maintaining a decade-old disparity (P < 0.05). Men scored significantly higher (P < 0.05) in most EQ-5D domains, except for self-care and anxiety/depression, resulting in a higher total EQ-5D Index (P = 0.001). Increased comorbidities were strongly associated with lower EQ-5D levels in both sexes. Additionally, there was a negative correlation between the EQ-5D Index and refined grain intake for both sexes (P for trend < 0.001), with high-EQ-5D groups consuming fewer refined grains. Women in the high-EQ-5D group consumed more nuts, vegetables, and meat compared to men (P for trend < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our study highlights the sex disparities in HRQoL among older adults with T2DM. The findings suggest the need for tailored treatment guidelines aimed at improving the HRQoL of elderly T2DM patients, with a focus on their sex-specific characteristics. Implementing these tailored guidelines could enhance the HRQoL of older women with T2DM and promote more equitable healthcare outcomes. This underscores the importance of considering sex differences to comprehensively improve the well-being of this population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding Gender Disparities in Quality of Life Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Ethiopia: An Institutional‐Based Study
Enguday Demeke Gebeyaw, Girma Deshimo Lema
Lifestyle Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Understanding Gender Disparities in Quality of Life Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Ethiopia: An Institutional‐Based Study
- 2,524 View
- 40 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
- Minji Kim, Meera Jang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):278-287. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00002
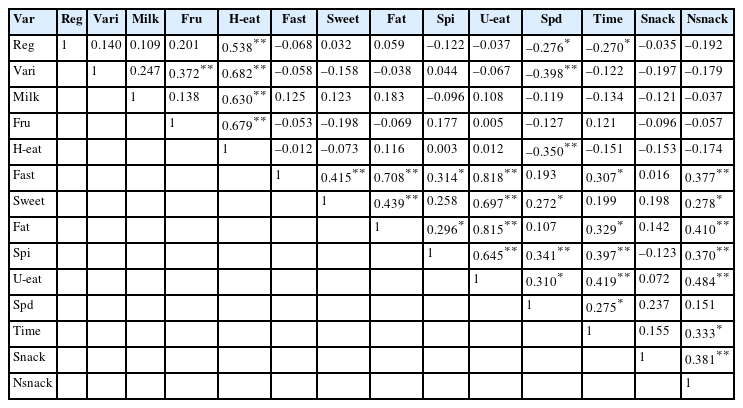
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigates the relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior among elementary school students. Methods: This survey was conducted on 4th- to 6th-grade students at elementary schools in Gangneung from September 6th to September 15th, 2023. Of the 129 copies of the questionnaire that were distributed to 5 schools, 66 copies (51.2%) were returned. Results: Compared to the nationwide statistics, the smartphone ownership rate of elementary school students in Gangneung was lower, but the rate of smartphone overdependence was higher. Smartphone dependence was 21.12 points for study subjects and 26.00 points for the overdependence risk group (Org). Compared to national statistics, the self-control failure factor was higher, so study participants in Gangneung City are thought to have great difficulty with self-control. The Org’s weekend smartphone use time of 7.54 hours was significantly more than the general user group (Gug)’s 4.06 hours. The number of days in which the Org consumed late-night snacks per week was 2.92 days, and the Gug had 2.15 days, but the difference was not significant. Eating fast food showed a positive correlation with eating sweet food, eating fatty food, and eating heavily seasoned food. It was found that frequent consumption of fast food is closely correlated with unhealthy eating behavior. Weekend smartphone use time showed a significant positive correlation with smartphone dependence and the number of days late-night snacks consumed per week. Conclusions: Study participants in Gangneung are more dependent on smartphones than national statistics. Smartphone dependence had a negative correlation with healthy eating behavior and a correlation with average unhealthy eating behavior.
- 3,601 View
- 53 Download

- [English]
- Total sugar intake and its contributed foods by age groups in Koreans using the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: a cross-sectional study
- Hyejin Yu, Sang-Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):222-233. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.222
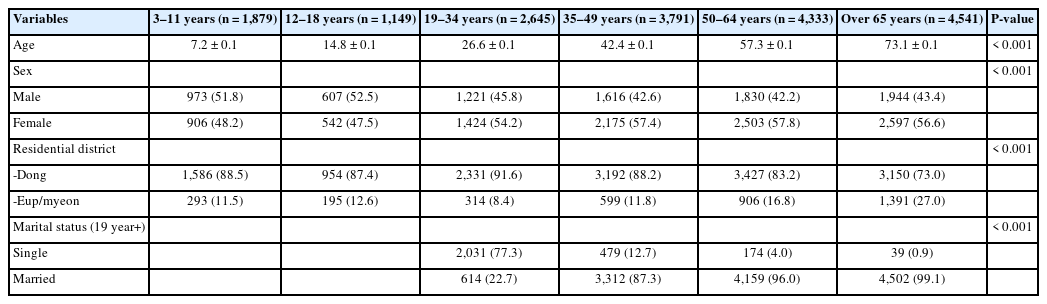
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to investigate the status of total sugar intake and contributing foods in Korea according to age groups.
Methods
This study used 24-hour dietary recall data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021) to investigate the nutritional and total sugar intake status among Koreans. A total of 18,338 research participants (≥3 years old) were included in this study. To analyze the types of foods contributing to total sugar intake, these foods were categorized into 15 types. Moreover, we examined the total sugar intake and ranked the most consumed foods by age groups (3–11 years, 12–18 years, 19–34 years, 35–49 years, 50–64 years, over 65 years). A survey procedure was employed for statistical analysis.
Results
The energy intake ratio from total sugars was approximately 12%–15%, which was within the recommended range. However, the proportion of individuals consuming total sugar exceeding 20% of their total caloric intake is nearly 20%, raising concerns about excessive sugar consumption. Furthermore, the percentage of participants whose intake of sugar from processed foods exceeded 10% of their total calories was highest in the 12–18 age group at 37.1%, followed by the 3–11 age group at 35.2%, and the 19–34 age group at 34.0%. Carbonated drinks, cola, and cider were the primary foods consumed by children and adolescents (3–18 years old) and young adults (19–34 years old). For middle-aged and older adults, mixed coffee with sugar and cream was a prominent contributor to sugar intake.
Conclusions
This study investigated sugar consumption patterns among Koreans, finding the principal foods contributing to this intake. Identifying these contributors is pivotal, given their potential impact on public health.
- 12,809 View
- 147 Download

- [English]
- Serum branch chain amino acids and aromatic amino acids ratio and metabolic risks in Koreans with normal-weight or obesity: a cross-sectional study
- Ji-Sook Park, Kainat Ahmed, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.212
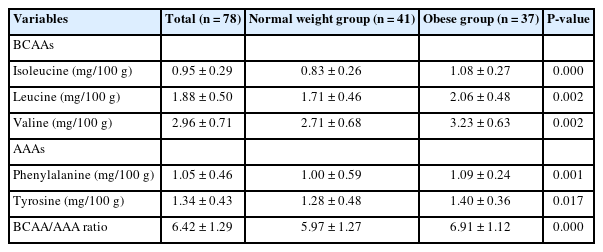
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Metabolic disease is strongly associated with future insulin resistance, and its prevalence is increasing worldwide. Thus, identifying early biomarkers of metabolic-related disease based on serum profiling is useful to control future metabolic disease. Our study aimed to assess the association of serum branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and aromatic amino acids (AAAs) ratio and metabolic disease according to body mass index (BMI) status among Korean adults.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 78 adults aged 20–59 years in Korea. We compared serum amino acid (AA) levels between adults with normal-weight and adults with obesity and investigated biomarkers of metabolic disease. We examined serum AA levels, blood profile, and body composition. We also evaluated the association between serum AAs and metabolic-related disease.
Results
The height, weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-hip-ratio, body fat mass, body fat percent, skeletal muscle mass, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure were higher in the group with obesity compared to normal weight group. The group with obesity showed significantly higher levels of BCAA, AAA, and BCAA and AAA ratio. Further, BCAA and AAA ratio were significantly positively correlated with triglyceride, body weight, and skeletal muscle mass. The evaluation of metabolic disease risks revealed an association between the ratios of BCAAs and AAAs, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome.
Conclusions
Our study is showed the associations between BCAA and AAA ratio, obesity, and obesity-related diseases using various analytical approaches. The elevated BCAA and AAA ratio could be early biomarkers for predicting future metabolic diseases in Korean population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
Apostolos Gkantzos, Stavros Kalogiannis, Olga Deda
Journal of Proteome Research.2025; 24(5): 2208. CrossRef - Current Data on the Role of Amino Acids in the Management of Obesity in Children and Adolescents
Diana Zamosteanu, Nina Filip, Laura Mihaela Trandafir, Elena Ţarcă, Mihaela Pertea, Gabriela Bordeianu, Jana Bernic, Anne Marie Heredea, Elena Cojocaru
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(15): 7129. CrossRef
- The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
- 2,173 View
- 24 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship of sodium index with the obesity indicators of university students in Daegu, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Young-Won Jang, Jian Ma, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):189-198. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.189
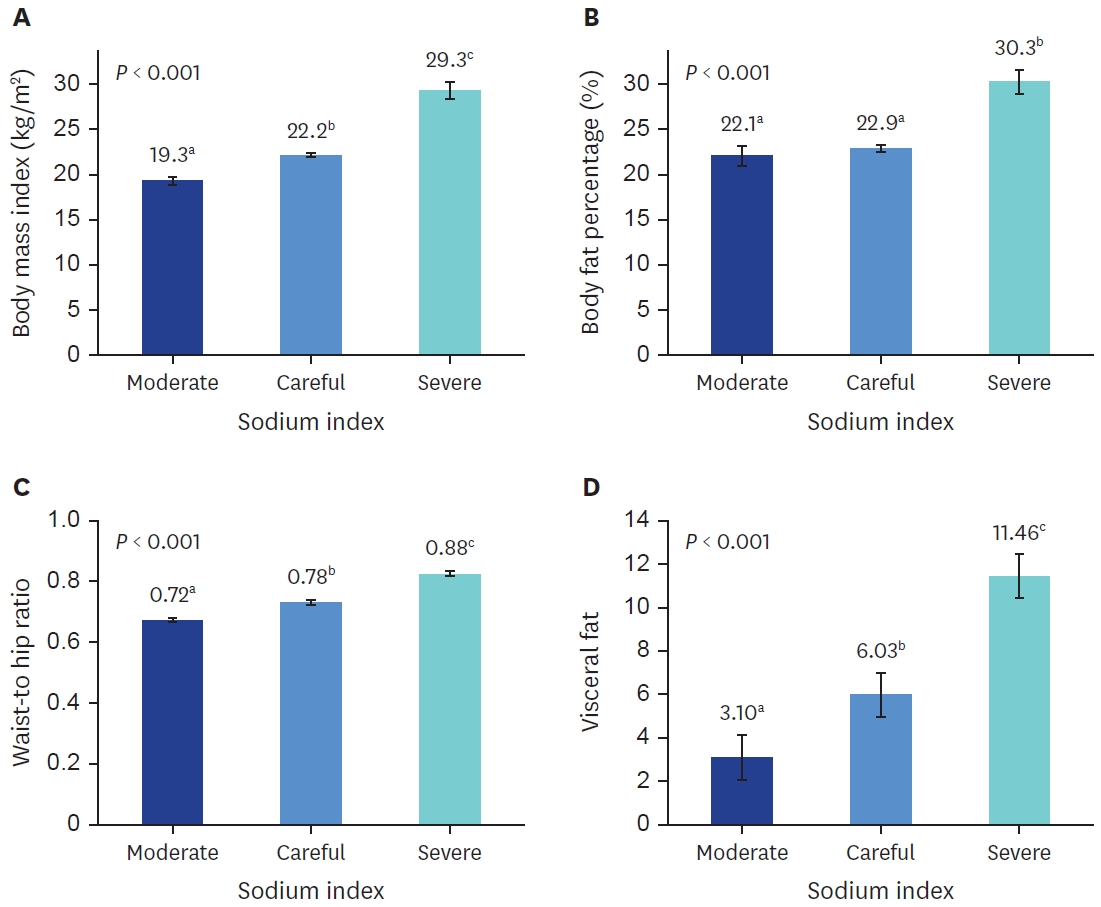
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The sodium index is an index that converts the estimated sodium intake calculated using a verified and reliable sodium estimation formula. This study aimed to determine the relationship between the sodium index and obesity indicators and the potential impact of excessive sodium consumption on obesity.
Methods
Obesity indicators, such as body mass index (BMI), body fat percentage, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), and visceral fat levels, were analyzed in 120 university students (60 men and 60 women). The sodium index was calculated by indexing the estimated sodium intake according to age, sex, BMI, salt-eating habits, and salt-eating behaviors. The relationship between sodium index and obesity indicators was analyzed using multiple logistic regression.
Results
The estimated sodium intake was 3,907.1 mg, with 76.7% of the participants categorized under the “careful” level of sodium index and 10.8% under the “moderate” level. As the sodium index increased, the BMI, body fat percentage, WHR, and visceral fat levels significantly increased. All obesity indicators significantly increased in patients with a “severe” sodium index than in those with a “moderate” sodium index. In addition, a strong positive correlation was identified between obesity indicators and sodium index. When the “severe” sodium index was compared with the “moderate” sodium index, the risk of obesity based on body fat percentage increased by 2.181 times (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.526–3.118), while the risk of obesity based on visceral fat level increased by 4.073 times (95% CI, 2.097–7.911).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest a correlation between excessive sodium intake and obesity. Moreover, the sodium index can be used to determine sodium intake.
- 5,122 View
- 42 Download

- [English]
- Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):173-188. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.173
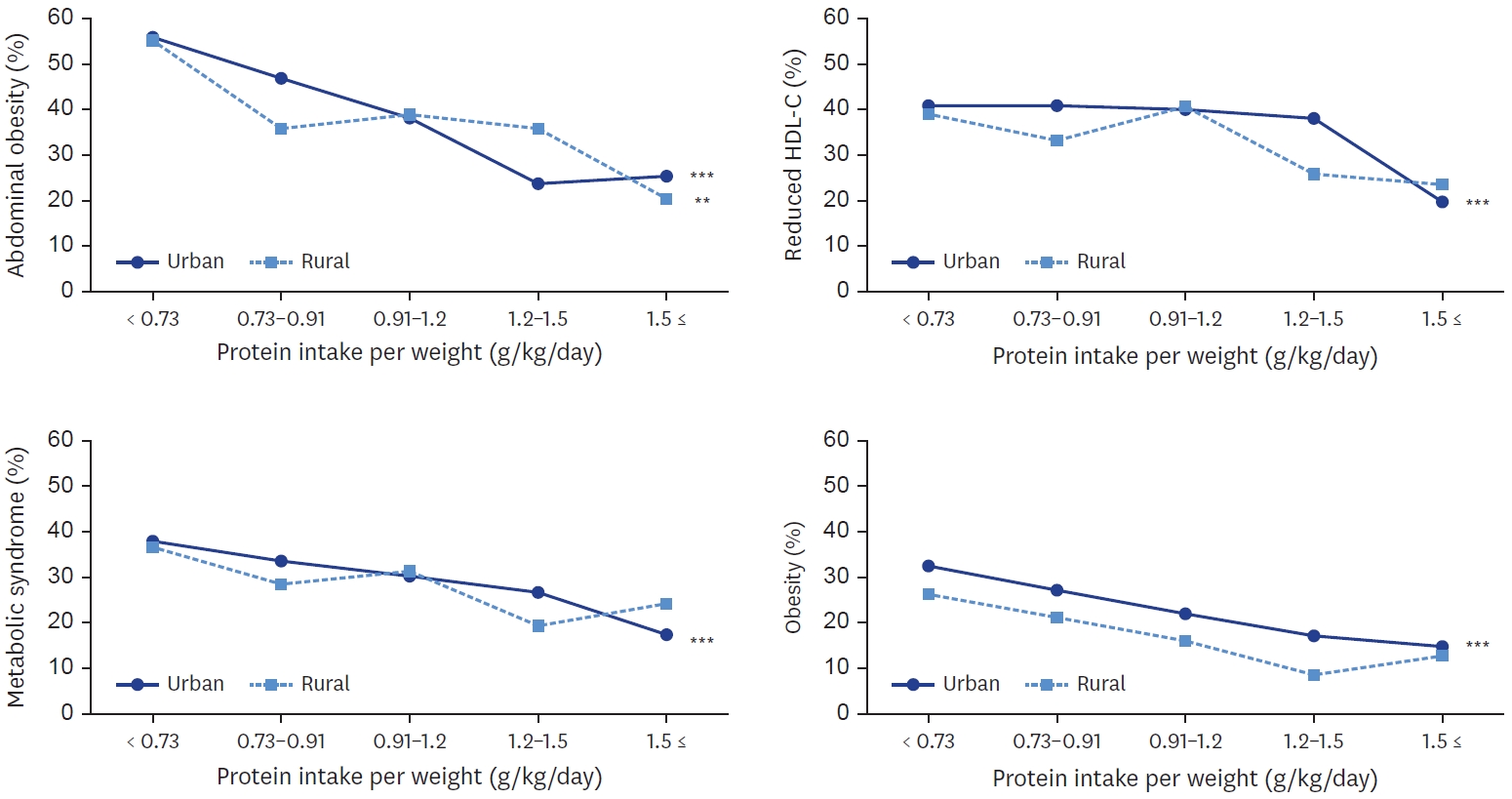
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to analyze the regional differences in dietary protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome.
Methods
Study participants were 1,721 older adults aged 65 and over who participated in 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Using 24-hour recall dietary intake data, protein intake and their food sources were examined. The association between protein intake and metabolic syndrome, obesity, and abdominal obesity were analyzed by multiple logistic regression.
Results
Total protein and animal protein intakes were higher in urban area (60.0 g, 24.4 g, respectively) than in rural area (54.6 g, 19.6 g, respectively). With increase of protein intake level, animal to total protein proportion was increased in both areas. Total protein and plant protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity, abdominal obesity in both areas. Animal protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity in both areas, and with abdominal obesity only in urban area. In urban area, plant protein intake was also negatively associated with the risks of metabolic syndrome, elevated triglyceride, and reduced high density lipoprotein-cholesterol. In urban area, the risk of metabolic syndrome was decreased when their protein intake was more than 0.91 g/kg and was lowest when their protein intake was more than 1.5 g/kg (P for trend < 0.001).
Conclusions
Korean older adults showed inadequate protein intake and those in rural area showed lower animal protein intake than in urban area. The risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome was decreased with the increase of protein intake level. These findings may help develop effective nutrition support strategy for older adults to reduce regional health disparity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
Yea-Chan Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Soyoung Jeon, Yae-Ji Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2026; 50(1): 178. CrossRef - The association between dietary protein intake and metabolic syndrome: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Dorsa Ghazvineh, Ali Hosseinpour, Vahid Basirat, Elnaz Daneshzad
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between total, animal-based, and plant-based protein intake and cognitive decline in older adults
Maud Peperkamp, Margreet R. Olthof, Marjolein Visser, Hanneke A. H. Wijnhoven
European Journal of Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
- 10,062 View
- 107 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Arterial stiffness index, physical activity and food and nutrient intake: cross-sectional study in adults aged 40 years and older
- Eun-A Kim, Yun-Mi Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):81-96. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate arterial stiffness index, physical activity, and food and nutrient intake in middle-aged adults over 40 years when the incidence of cardiovascular disease begins to increase.
Methods
This study included 106 subjects (48 males and 58 females) aged between 40 and 64 years. The arterial stiffness index (brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity [baPWV], and ankle-brachial index [ABI]) were measured using a blood pressure pulse wave testing device. Physical activity was assessed using the Korean version of the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire, and food and nutrient intake was calculated using the Food Frequency Questionnaire.
Results
The mean age of the subjects was 54.4 years. Although the ABI of the subjects was within the normal range, they were divided into tertiles to compare physical activity and food and nutrient intake. In males, the time spent on moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) was significantly higher in T3 (600.6 min/week) than in T1 (304.4 min/week). In females, the time spent in sedentary behavior was significantly lower in T3 (294.5 min/week) than in T1 (472.1 min/week). In addition, the frequency of fish consumption was significantly higher in T3 (1.27 frequency/day) than in T1 (0.64 frequency/day) in females. Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) and ω-3 fatty acid intake, adjusted for energy intake, were significantly positively correlated with ABI (r = 0.200 and r = 0.218, respectively).
Conclusions
High MVPA (in males), low sedentary behavior (in females), and PUFA and ω-3 fatty acid intake through fish consumption may be associated with low peripheral artery stiffness. Therefore, arteriosclerosis can be prevented through physical activity and proper dietary therapy.
- 1,310 View
- 38 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



