Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Ultra-processed food intake and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):410-418. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the intake of ultra-processed foods (UPF) and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents.
Methods
This study used 24-hour dietary recall data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2023). In total, 1,720 adolescents aged 12–18 years were included in this study and categorized into quartiles based on the percentage of energy intake from the UPF. Nutritional status, contributing subgroups of UPF intake, and healthy dietary practices were examined using Health Plan 2030 indicators across quartiles of UPF intake.
Results
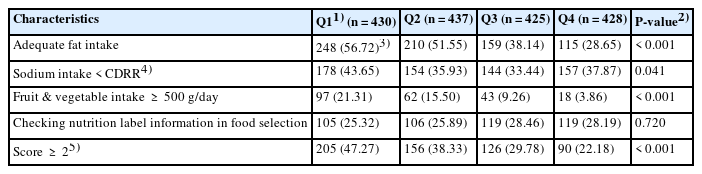
The nutrient intake of protein, vitamins (A, B1, B2, niacin), and minerals (iron, potassium) was the lowest in the fourth quartile of UPF intake compared with the first quartile (P for trend < 0.001), whereas calcium intake increased across quartiles, from 47.68% in the first quartile to 58.51% in the fourth quartile (P for trend < 0.001). The main contributing subgroups to UPF intake differed across quartiles of UPF intake, and the highest contributing subgroups were ‘instant noodles and dumplings,’ ‘desserts, cakes, and ice cream,’ and ‘sauces and seasonings.’ Healthy dietary practices were the lowest in the fourth quartile (22.18%, P < 0.001), and the proportions of appropriate fat and fruit/vegetable intake were significantly lower in the higher quartiles of UPF intake (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that a lower UPF intake was associated with better nutritional status and healthy dietary practices in Korean adolescents. These findings provide fundamental evidence for promoting healthier food choices and balanced dietary practices.
- 162 View
- 9 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung-Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):156-170. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the association between how often Korean adolescents watch Mukbang and Cookbang videos and their dietary habits.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 was analyzed for this study. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed various aspects, including demographics, frequency of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos per week, dietary habits, health behaviors, and mental health factors.
Results
Nearly a third (29.3%) of Korean adolescents watched Mukbang and Cookbang videos one to four times a week, while 13.5% watched them more than five times weekly. Females, those with lower academic achievement, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds were significantly more likely to be frequent viewers (P < 0.001). Increased viewing frequency was associated with poorer dietary habits. Adolescents who watched more frequently were less likely to eat breakfast and consume fruits and milk, while their consumption of fast food, high-caffeine drinks, sugary drinks, and late-night snacks increased (P < 0.001). Higher viewing frequency correlated with increased feelings of stress, depression, and loneliness (P < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis confirmed these associations. More frequent viewers were significantly less likely to eat breakfast (odds ratio (OR), 0.63; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.58–0.68), and more likely to consume fast food (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.69–2.02), high-caffeine drinks (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30–1.56), sugary drinks (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.41–1.67), and late-night snacks (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.25–1.51).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that frequent exposure to Mukbang and Cookbang content is linked to unhealthy dietary habits in adolescents. Educational programs may be necessary to mitigate the potential for these videos to negatively influence dietary choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
Seung Jae Lee, Yeseul Na, Kyung Won Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2652. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef
- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
- 3,609 View
- 103 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2016–2021 KNHANES data
- Enkhgerel Erdenetsetseg, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):144-155. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.144
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids in Korean adolescents.
Methods
This study was comprised of 3,932 adolescents (9–18 years) who participated in the 2016–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids, including alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and linoleic acid (LA) were evaluated using data obtained from one-day 24-hour dietary recall. The proportions of adolescents consuming ALA, EPA + DHA, and LA above or below the adequate intake (AI) of the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans were calculated. All statistical analyses accounted for the complex sampling design effect and appropriate sample weights.
Results
The mean intakes of ALA, EPA, DHA, and LA among Korean adolescents were 1.29 g/day, 69.6 mg/day, 166.0 mg/day, and 11.1 g/day, respectively. Boys had higher intakes of all essential fatty acids compared to girls. By age group, adolescents aged 15–18 years showed lower intakes of EPA and DHA compared to adolescents in younger age groups. The 9–11-year-old adolescents had lower intakes of ALA and LA than older adolescents. The proportions of adolescents who consumed more than AI were 35.7% for ALA, 30.4% for EPA + DHA, and 41.5% for LA. Adherence to the AI for ALA did not differ by sex or age group, although boys showed a lower adherence to the AI for EPA + DHA than girls. Major food sources for ALA and LA were plant-based oils, mayonnaise, pork, and eggs. Mackerel was the most significant contributor to EPA and DHA intake (EPA, 22.6%; DHA, 22.2%), followed by laver, squid, and anchovy.
Conclusions
The proportion of Korean adolescents who consumed EPA + DHA more than AI was low. Our findings highlight that nutrition education emphasizing an intake of essential fatty acids from healthy food sources is needed among Korean adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Harnessing dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids through gut microbiota to enhance ferroptosis in breast cancer therapy
Yara Adel Haroun, Abdulrahman Abdulla Alzyoud, Mohammad Taha Alizadeh, Nashwa Ahmed Mohamed, Riyad Bendardaf, Sameh S.M. Soliman
Nutrition Research.2025; 141: 10. CrossRef
- Harnessing dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids through gut microbiota to enhance ferroptosis in breast cancer therapy
- 3,829 View
- 58 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Factors related to adolescent obesity and changes: a cross-sectional study based on the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Bora Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):363-375. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to identify factors associated with adolescent obesity, as well as any new factors that correlated with a change in the rate of obesity over time.
Methods
The study used 5-yearly data collected by the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey starting from the year 2006 up until 2021 (data from 2nd, 7th, 11th, and 17th surveys were analyzed). Factors such as demographics, dietary factors, health behavioral factors, and mental health factors were studied. All data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27.0, employing chi-square tests and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results
This study included data from a total of 255,200 participants. Factors contributing to obesity varied with time. Over the survey duration of 15 years, low academic achievement, parents with low levels of education, low frequency of fruit consumption, low frequency of fast food intake, long periods of being seated, and high levels of stress were significantly associated with a high rate of obesity. Factors that showed a new correlation with an increase in obesity rates included living with single parents, low frequency of muscle strengthening exercises, and experiencing intense sadness and despair in the past year. Factors that were correlated with a change in obesity rates over time included household economic status, frequency of carbonated beverage consumption, frequency of intense physical activity, and frequency of alcohol consumption. Breakfast intake and smoking were not significantly associated with obesity rates in the 15-year period.
Conclusions
While several factors associated with obesity remained consistent over time, several new factors have emerged in response to social, economic, and environmental changes contributed to a change in obesity rate over time. Therefore, to prevent and manage adolescent obesity, continuous research into the new emergent factors contributing to obesity is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,835 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency and value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using dietary area: a descriptive study
- Yunhwa Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):317-328. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency, value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using the dietary area (CUDA).
Methods
Data were collected from 480 middle and high school students in Daegu, Gyeongbuk and Seoul, Gyeonggi using a self-administered five-point Likert scale questionnaire from May to July 2021. A questionnaire was used to investigate dietary safety management competency, awareness of convergence, recognition of the benefits, efficacy, and competency of CUDA.
Results
We conducted factor, reliability, correlation, and regression analyses using SPSS 25. The average scores for each factor were: dietary significance (3.68); dietary safety management knowledge (3.34); food selection and cooking (3.72); nutrition management (3.38); weight management (3.28); risk dietary management (3.13); CUDA interest (2.98); convergence necessity (3.50); benefits in specialized areas (3.31); benefits in everyday life (3.48); efficacy of science and technology convergence (3.35); convergence efficacy with humanities, social science, and arts (3.31); and CUDA competency (3.41). The score for interest in CUDA was lower than that for the recognition of CUDA benefits. Significant positive correlations were observed between all factors except between risk dietary management and both nutrition and weight management (P < 0.01). Interest in CUDA and recognition of the need for convergence exhibited a positive and significant effect on all factors of the perception of CUDA benefits and efficacy. The subgroup factors of dietary safety management competency and the recognition of CUDA had a positive effect on the CUDA competency (P < 0.001, R2= 0.58).
Conclusions
Strengthening dietary safety management competency and increasing the awareness of CUDA can enhance adolescents’ convergence competency. Therefore, CUDA and targeted education must be actively promoted among adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of elementary school pre-service teachers' perception of diet-related factors on their efficacy in creative dietary teaching
Yunhwa Kim, Ji Eun Kim, Kyoungae Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 153. CrossRef
- The impact of elementary school pre-service teachers' perception of diet-related factors on their efficacy in creative dietary teaching
- 1,047 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- The frequency of convenience food consumption and attitude of sodium and sugar reduction among middle and high school students in Seoul: a descriptive study
- Seoyeon Park, Yeonhee Shin, Seoyeon Lee, Heejung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):269-281. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.269
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the frequency of convenience food consumption at convenience stores (CVS) and the CVS usage patterns of middle and high school students as well as to understand students’ attitude toward sodium and sugar reduction.
Methods
We used an online questionnaire for data collection. The questionnaire comprised five distinct categories: general characteristics, CVS usage, frequency of consumption according to convenience food menus at CVS, attitude toward sodium and sugar reduction, and adherence to dietary guidelines.
Results
A total of 75 students from Seoul (14 middle school students and 61 high school students) participated in the study. Most respondents visit CVS 3-5 times a week. CVS are predominantly used during weekdays, mostly during lunch, and dinner. The students mostly checked the caloric content and expiration date as food labeling information. The participants were aware of the need to reduce their sugar and sodium intake. Among frequent CVS convenience food consumers, there was an increased consideration of the need to reduce their sugar and sodium consumption, despite their actual selection of foods with high sugar and sodium content. Additionally, they did not check the sugar and sodium levels indicated in food labeling. Further, the dietary action guide from the Ministry of Health and Welfare were poorly followed by most students.
Conclusions
There is a need for nutrition education specifically addressing the sugar and sodium content of the convenience foods predominantly consumed by students. Additionally, educating students with frequent convenience food consumption to actively check the sugar and sodium information on food labels could help promote healthier food choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 514. CrossRef
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- 3,907 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutritional status and dietary behavior of North Korean adolescent refugees based on Nutrition Quotient for Korean adolescents: a preliminary study
- Young Goh, Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeong Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):1-10. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the nutritional status and dietary behavior of adolescents from North Korean refugee (NKR) families residing in South Korea (SK), who are known to be at a higher risk of malnutrition due to their lower socioeconomic status and facing other psychological challenges.
Methods
A total of 178 adolescents (91 males and 87 females) from NKR families were included in the analysis, and their demographic details such as age, birthplace, parental nationality, and duration of their settlement in SK were collected through questionnaires. Anthropometric measurements were also taken to determine their growth and nutritional status according to the 2017 Korean National Growth Charts for children and adolescents. The study used the Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents (NQ-A) questionnaire to assess the dietary behavior of the participants.
Results
Approximately 11.8% and 10.1% of participants were identified with malnutrition and obesity, respectively. The total mean score for the NQ-A was 50.1. The mean scores for the individual factors of balance, diversity, moderation, environment, and practice were 49.2, 44.7, 43.8, 51.2, and 61.5, respectively. Approximately 47.2% of participants had a low NQ-A grade. However, there was no significant difference in the NQ-A scores according to their nutritional status or duration of time in SK.
Conclusions
Adolescents from NKR families exhibited both malnutrition and obesity. However, their dietary behavior, as assessed using the NQ-A, did not vary with their nutritional status. The unique challenges and related dietary behavior of North Korean adolescent refugees should be taken into consideration, when developing targeted strategies for nutritional education and health management programs.
- 1,929 View
- 24 Download

- [Korean]
- Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
- YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):192-204. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between dietary behaviors and perceived health status among Korean adolescents from multicultural families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 2,459 Korean adolescents from multicultural families (aged 13 ~ 18 years) who participated in the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Information on the sociodemographic variables, dietary behaviors, and lifestyle variables was selfreported using a web-based questionnaire. The dietary behaviors analyzed in this study were the breakfast and food intake frequencies, including fruit, vegetable, milk, fast food, carbonated drink, sweet drink, and high caffeine/energy drinks. The adolescents’ health perception was self-rated as healthy, average, or unhealthy. The dietary behaviors associated with health perception were examined using a multiple logistic regression after adjusting for the confounding variables.
Results
In this study population, 7.6% of adolescents perceived their health status as unhealthy, and 25.4% perceived it as average. The adolescents who were girls, middle school students, and in households with a low economic status showed significantly higher percentages of poor health perception (P-values < 0.001). Skipping breakfast was significantly associated with a negative health perception. Compared to the adolescents who consumed fruits every day, those who did not consume fruits during the previous week showed a higher odd ratio (OR) for a negative health perception [OR = 2.29, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.32–3.97]. The adolescents who frequently consumed carbonated drinks ( 5 times/week) perceived their health status as unhealthy relative to those who did not consume carbonated drinks (OR = 2.15, 95% CI = 1.25–3.71). Skipping breakfast was significantly associated with an increased OR for a negative health perception in girls but not in boys. Compared to adolescents with a normal weight, those with overweight/ obesity (OR = 1.75, 95% CI = 1.21–2.52) and underweight (OR = 2.19, 95% CI = 1.25–3.82) showed higher ORs for negative health perception. Positive associations of overweight/obesity and underweight with negative health perception were observed in boys but not in girls.
Conclusions
Dietary behaviors and weight status were associated with the health perception in Korean adolescents from multicultural families. These findings suggest that nutrition interventions on breakfast intake and healthy food choices for this population might effectively improve their weight and perceived health status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The unequal weight of COVID-19 pandemic: national trends in body mass index among Korean adolescents by immigrant-origin and gender from 2013 to 2022
Nari Yoo, Yumin Hong, Yoonyoung Choi
International Journal of Adolescence and Youth.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The unequal weight of COVID-19 pandemic: national trends in body mass index among Korean adolescents by immigrant-origin and gender from 2013 to 2022
- 1,203 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):467-481. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.467
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine the biochemical characteristics, intake of energy, and nutrients by household income levels of Korean adolescents aged 12 to 18 years.
Methods
Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES) were used for the study. A total of 1,839 (966 boys, 873 girls) subjects were included, and they were divided into four income groups according to their household income level. We examined general characteristics (gender, region of residence, skipping or not-skipping breakfast, lunch, dinner, frequency of eating-out), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, weight status), biochemical characteristics (fasting plasma glucose, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, triglycerides, cholesterol, HDLcholesterol, hemoglobin, and hematocrit), the quantitative intake of energy and nutrients using the Korean Dietary Reference Intakes (KDRI), and the qualitative intake evaluated by the nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean nutrition adequacy ratio (MAR) of the four groups.
Results
There were significant differences by income group within the region of residence and the rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, and dinner. The low-income group had a higher rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, and dinner. According to the income group, there was a difference in the height of boys, and there was no difference in the weight and obesity of boys and girls. In the biochemical characteristics, only the hematocrit of girls showed differences by income group. The quantitative intake of energy and nutrients compared with KDRI differed by income group. There were differences in energy, carbohydrates, proteins, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and phosphorus levels in boys and protein, vitamin A, niacin, and sodium levels in girls. The qualitative intake of energy and nutrients examined using NAR and MAR also differed according to the income group. The NAR showed differences in calcium in boys and vitamin C and calcium in girls. The MAR revealed differences in both boys and girls by income group.
Conclusions
Among adolescents in the low-income group, the rate of skipping meals was high, and the quantitative and qualitative intake of energy and some nutrients was low. It is suggested that the nutritional intake can be improved by lowering the rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, dinner. We suggest that even just providing breakfast in schools can be considered highly effective in improving the rate of avoidance of skipping meals and improving nutrient intake. Also, we suggest that it is necessary to improve the food environment, food availability, and food accessibility through national and social support for low-household income adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency and value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using dietary area: a descriptive study
Yunhwa Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 317. CrossRef - 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
민지 손, 은주 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 213. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of Changes in Adolescent Dietary Behavior during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Improvement Strategies for School-Provided Nutrition Counseling
Yeseul Na, Jieun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2023; 61(1): 39. CrossRef
- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,332 View
- 8 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Sugar Reduction Perception and Sugary Food Intake among High School Students in Incheon
- Gyeong-Ja Bae, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):111-121. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.111
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined ways to promote desirable eating habits by choosing foods with low sugar contents and provide nutrition education in adolescents. Methods: This study was a cross-sectional survey. The sugar reduction perception and knowledge, sugary food preference, and intake frequency of 487 male and female high school students in Incheon were analyzed comparatively. Results: Approximately 94.9% and 94.5% of the subjects were unaware of the promotion of a sugar reduction policy and the sugar reduction in the basic guidelines for school meals, respectively. Approximately 95% of them had not received any sugar reduction nutrition education, and 90% were not interested in sugar reduction. The perception for sugar reduction was significantly higher in girls (3.43 out of 5 points) than in boys (3.16 out of 5 points) (P < 0.001). Knowledge about sugar was 3.65 out of 6 points in girls and 3.04 points in boys (P < 0.001). The preference and intake frequency for fruits of the total students were 4.24 out of 5 points and 2.56, respectively. For beverages, the preference was significantly higher in boys (3.97 points) than in girls (3.70 points) (P < 0.001), and the intake frequency was significantly higher in boys (2.26 points) than in girls (2.08 points) (P < 0.001). The preference for snacks was significantly higher for girls (4.19 points) than boys (4.02 points) (P < 0.01), and the intake frequency was 2.22 points in boys and 2.17 in girls, showing no significant difference. Sugar reduction perception and knowledge about sugar showed significant negative correlations with the snack intake frequency (r = -0.11, P < 0.05; -0.13, P < 0.05) after adjusting for gender, grade, and body mass index. Conclusions: The high school students' perception of sugar reduction was very low, and there was a significant correlation with sugary food intake, suggesting that the sugary food intake will decrease as the sugar reduction perception and knowledge about sugar increase. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Status of Sugar-Reduced Beverage Consumption according to Sex, among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju
Na-In Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Health-Related Factors according to the Frequency of Consumption of Sugar-Reduced Beverages among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju Area
Na-In Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 459. CrossRef - Sugar Intake and Perception of Sugar Reduction among University Students in Gwangju
Yeon-Ok Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1170. CrossRef - 충북지역 중등학생의 건강식생활 관련 식행동과 영양관리 정책에 대한 인식
은서 고, 영은 이
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 197. CrossRef
- Status of Sugar-Reduced Beverage Consumption according to Sex, among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju
- 1,046 View
- 15 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to the Frequency of Milk Consumption in Korean Adolescents: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ji Hyun Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):485-501. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine the biochemical characteristics and dietary intake of adolescents aged 12 to 18 years according to the frequency of milk consumption. Methods: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey was used for the study. The study examined adolescents’ (12~18 years) demographic characteristics (house income level, residence region, skipping or not-skipping of breakfast/lunch/dinner, eatingout frequency), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, weight status), biochemical characteristics (fasting plasma glucose, blood urea nitrogen, creatine, triglycerides, cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, hemoglobin, hematocrit) and nutrient intakes through quantitative and qualitative evaluation using the Korean Dietary Reference Intakes (KDRI), index of nutrition quality (INQ), nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) of 3 groups (< 1/week, 1~6/week, 1/day) according to the frequency of milk consumption. Results: There were significant differences in gender and income levels among the 3 groups. There were no differences in height, weight, and weight status among groups. There were differences in biochemical characteristics and nutrient intake. In boys, there were differences in the mean of BUN and HDL-cholesterol, in quantitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus, potassium by KDRI levels, in qualitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by INQ and riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by NAR among 3 groups. In girls, there were differences in the mean of blood urea nitrogen, creatine, HDL-cholesterol, in quantitative intakes of protein, riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by KDRI levels, in qualitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by INQ and riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by NAR among the 3 groups. Conclusions: In Korean adolescents, boys had a higher frequency of milk consumption than girls, and higher the income level, higher the frequency of milk consumption. Consumption of milk appeared to have a positive association with triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, and indices related to muscle mass. Regular consumption of milk is an important factor in enhancing the intake of riboflavin, calcium, and phosphorus, which adolescents lack. The results of the study indicate a need to prepare an environment and education program to increase milk consumption in adolescents at home and school. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in Nutritional Status Through Low-Lactose Processed Milk Consumption in Korean Adults With Lactose Intolerance
Dong Hoon Jung, Gi Moon Nam, Chang Kyun Lee, Chul hong Kim, Hyun-San Lim, Ji Yeon Lee, Hee-Sook Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Quality in Children and Adolescents with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Using the Korean Nutrition Quotient Score
So Yoon Choi, Yoowon Kwon, Yoo Min Lee, In Hyuk Yoo, Tae Hyeong Kim, You Jin Choi, Su Jin Jeong
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2025; 28(4): 256. CrossRef - Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef
- Changes in Nutritional Status Through Low-Lactose Processed Milk Consumption in Korean Adults With Lactose Intolerance
- 1,288 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Association between Stress and Nutritional status of High School Students in Chungbuk using Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents
- In Young Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):361-373. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between stress levels and eating habits in adolescents. Methods A total of 453 male and female high school students were surveyed to ascertain their stress levels, Nutrition Quotients for Korean Adolescents (NQ-A), and stress-related eating behavior. Results The average age of the subjects was 18 and they were mostly from nuclear families. Their average daily conversation time with their parents was between 10 to 30 minutes. The average sleep time for female students was observed to be less than that of male students. The satisfaction level of academic achievement of female students was significantly lower than that of the male students (P < 0.001). The average stress level score for female students was 2.7 out of 5, which was significantly higher than the male student's score of 2.4 (P < 0.001). The eating speed of male students was related to stress levels. Both male and female students ate more and craved spicy food when under stress. All male and female students had significantly ascending NQ-A scores rising in the order of stress from ‘low level’ to ‘medium level’, to ‘high level’ (P< 0.001). There was a significant negative correlation between the stress score and the NQ-A score adjusted for general characteristics (r = −0.29, P < 0.001). Conclusions Since stress and NQ-A were negatively correlated in high school students, higher stress levels can be associated with irregular eating habits and negative eating behavior. Therefore, stress management and nutrition education focusing on stress status are needed for adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
Ho-Jung Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Yookyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 320. CrossRef - Development of evaluation items for adolescents’ dietary habits and nutritional practices reflecting eating behaviors and food environment
Jimin Lim, Hye Ji Seo, Jieun Oh
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 136. CrossRef - 충북지역 중등학생의 건강식생활 관련 식행동과 영양관리 정책에 대한 인식
은서 고, 영은 이
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 197. CrossRef - Revision of Nutrition Quotient for Korean adolescents 2021 (NQ-A 2021)
Ki Nam Kim, Hyo-Jeong Hwang, Young-Suk Lim, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Jung-Sug Lee, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 247. CrossRef - The Relationship between Lifestyle and Nutrition Quotient in Middle School Students
Ha Jin Park, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(2): 243. CrossRef
- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
- 1,449 View
- 28 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
- Eun-Jin Choi, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):102-111. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The frequency of eating out among adolescents seems to be connected to a high rate of skipping breakfast and be interrelated to various nutritional problems. The purpose of this study was to assess the dietary habits of breakfast and eating out and investigate their relationships in male adolescents.
Methods
This study conducted a cross-sectional survey. Dietary habits and eating out status were surveyed among 510 male students at a high school in Incheon and compared according to their breakfast skipping and breakfast type.
Results
The percentages of subjects in the breakfast skipping group and breakfast group were 41.0% and 59.0%, respectively, and the breakfast group comprised a Korean meal group (74%) and a convenience meal group (26%). In the breakfast skipping group, the percentage of subjects buying and eating snacks due to hunger was 39.7%. Reasons for eating breakfast among subjects who ate breakfast were because parents prepared breakfast (41.9%) and out of habit (31.5%) in the Korean meal group, in contrast to because parents prepared breakfast (36.7%) and due to hunger (29.1%) in the convenience meal group (P < 0.001). Breakfast preparer was mother (91.4%) in the Korean meal group, in contrast to mother (67.1%) and self (20.3%) in the convenience meal group (P < 0.001). A high proportion of the breakfast group woke up at 07~07:30 or 06:30-07, whereas a high proportion of the breakfast skipping group woke up at 07~07:30 or after 07:30, showing a significant difference according to breakfast skipping (P < 0.001). A high proportion of the breakfast group spent 10,000 won (32.5%) a week eating out while a high proportion of the breakfast skipping group spent 20,000 won or more (28.2%), showing a significant difference (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
About 40% of male high school students skipped breakfast and consumed snacks as a solution after breakfast skipping. The students who skipped breakfast spent more money on eating out. These results show that breakfast status may be related to eating out. Therefore, practical education on food choice and meal preparation along with regular breakfast instruction is needed in male adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analytic Hierarchy Process approach to estimate weights of menu management in the school foodservice
Hyo Bin Im, Seo Ha Lee, Hojin Lee, Lana Chung, Min A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 349. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - A prediction model for adolescents’ skipping breakfast using the CART algorithm for decision trees: 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun A Choi, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 300. CrossRef - Trends in Prevalence and the Differentials of Unhealthy Dietary Habits by Maternal Education Level among Korean Adolescents
Yunseo Chung, Kyunghee Jung-Choi, Bo Young Kim, Kyoung Ae Kong
The Ewha Medical Journal.2021; 44(4): 133. CrossRef
- Analytic Hierarchy Process approach to estimate weights of menu management in the school foodservice
- 1,593 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Associated with Weight Status among Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: Using Data from the 2017–2018 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
- SuJin Song, Hyojune Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):465-475. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.465
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study investigated dietary and lifestyle factors associated with the weight status among Korean adolescents in multicultural families.
METHODS
This cross-sectional study analyzed 1,751 multicultural families' adolescents who participated in the 2017–2018 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Information on dietary and lifestyle factors was self-reported using a web-based questionnaire and this information included breakfast and foods consumption, perceived health status, alcohol drinking, smoking, physical activity, and weight control efforts. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated based on the self-reported height and body weight (kg/m²). Weight status was assessed according to the 2017 Korean National Growth Chart: underweight (weight-for-age <5(th) percentiles), overweight (85(th)≤ BMI-for-age <95(th) percentiles), and obese (BMI-for-age ≥95(th) percentiles). Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to examine the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with weight status after adjustment for covariates.
RESULTS
Among Korean adolescents from multicultural families, the prevalence of overweight/obesity was 20.9%, whereas about 7% of adolescents were underweight. The weight status did not show differences according to gender, school level, area of residence, and household income. Compared to adolescents who did not have breakfast during the previous week, those who had breakfast 3–4 days/week and ≥5 days/week had a 42% (p=0.021) and a 37% (p=0.009) lower prevalence of overweight/obesity, respectively. The adolescents who frequently consumed carbonated soft drinks (≥5 times/week) showed an odds ratio (OR) of 1.69 (95% CI=1.01–2.83) for overweight/obesity relative to those adolescents who did not consume carbonated soft drinks. The OR of being underweight for adolescents who ate fast food ≥3 times/week was 1.97 (95% CI=1.04–3.71) compared to those adolescents who had not eaten fast food during the previous week.
CONCLUSIONS
Dietary and lifestyle factors were associated with overweight/obesity as well as underweight among Korean adolescents in multicultural families. Our findings could be used to design and provide nutrition interventions for this specific population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Malnutrition and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents From Immigrant Families Living in Korea
Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeong Kim, Kyung-Ae Park
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(1): 29. CrossRef - Fruit Consumption and Mental Health in Adolescents from Multicultural and Non-multicultural Families: Data from Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web Based Survey 2021
Soohyun Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(2): 175. CrossRef - Identification of important features in overweight and obesity among Korean adolescents using machine learning
Serim Lee, JongSerl Chun
Children and Youth Services Review.2024; 161: 107644. CrossRef - Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 192. CrossRef - Effects of heavy metal, vitamin, and curry consumption on metabolic syndrome during menopause: a Korean community-based cross-sectional study
Hai Duc Nguyen, Min-Sun Kim
Menopause.2021; 28(8): 949. CrossRef - Association between levels of thiamine intake, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and depression in Korea: a national cross-sectional study
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, In Mo Yoon, Min-Sun Kim
Journal of Nutritional Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Antioxidant Vitamins, Curry Consumption, and Heavy Metal Levels on Metabolic Syndrome with Comorbidities: A Korean Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, Min-Sun Kim
Antioxidants.2021; 10(5): 808. CrossRef - Study on the Dietary Behavior of Adolescents in Multicultural Families Using the Nutrition Quotient and Their Changes in the Nutrition Knowledge and the Dietary Attitudes after Nutrition Education
Yoo-Jin Jung, Sung Hee Min, Min June Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(3): 208. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Malnutrition and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents From Immigrant Families Living in Korea
- 1,673 View
- 6 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Differences in Dietary Life and Health related Factors According to Obesity in Poor Urban Peruvian Adolescents
- Hye Kyung Chung, Hae Young Lee, Jin Ri Kim, Eun Woo Nam
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):302-318. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the differences in dietary life and health related factors, such as drinking behavior, exercise and leisure activities, mental health, and subjective perception for oneself according to obesity in poor urban Peruvian adolescents.
METHODS
A total of 1,532 Peruvian adolescents were selected from six schools in poor regions using stratified random sampling. The subjects were classified into two groups based on their BMI: ‘normal weight group (NW group=980)’ or ‘overweight and obese group (OWOB group=293)’. The differences in the general characteristics, dietary life, drinking behavior, physical activity and leisure, mental health and subjective perception of oneself in the two groups were compared. χ2 analysis and independent sample t-test were performed using the SPSS program ver. 24.
RESULTS
For the total and male students, the frequency of breakfast and dinner were significantly lower in the OWOB group than in the NW group (all p < 0.001). For total and female students, the percentage of subjects who received nutrition education was significantly higher in the OWOB group than in the NW group (all p < 0.05). For total students, the percentage of subject who exercised more than five days/week was lower in the OWOB group than in the NW group (p < 0.05). For the total and female students, the subjective health status was worse in the OWOB group than in the NW group (all p < 0.05). The subjective body image was significantly different between the OWOB group and NW group in the total, male and female subjects (all p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
The frequency of meals and exercise, and the subjective perceptions of the health status and body image differed according to obesity in poor urban Peruvian adolescents. Therefore, a school-based intervention program focused on regular meal and exercise, and adequate subjective perceptions for health status and body image need to be developed to prevent adolescent obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of perceived stress on obesity in South Korean adolescents using data from the 13th 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey
Hye Ja Gu
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(1): 29. CrossRef
- Influence of perceived stress on obesity in South Korean adolescents using data from the 13th 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey
- 1,107 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Health Behavior Factors Associated with Sugar-sweetened Beverage Intake among Adolescents
- Hyae Min Gu, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):193-201. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to measure the intake rate of SSBs (sugar sweetened beverages) and examine the relationship between health behavior factors and SSBs intake by adolescents.
METHODS
This study used data from the 2016 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey, which included 65,528 study participants. SSBs intake frequency was measured by asking respondents if they consumed soda, high-caffeinated beverages, and sugary drinks during the previous week. Type of intake was categorized into three groups according to the number of consumed drinks [SSBs (0): None; SSBs (1–2): 1 or 2 consumed; SSBs (3): 3 consumed]. Multinomial logistic regression analysis was used to examine health behaviors that affected SSBs consumption.
RESULTS
Increased SSBs intake was significantly correlated with current smoking (OR=2.4, 95% CI=1.82–3.17), current drinking (OR=2.13, 95% CI=1.82–2.51), sedentary time increase (OR=1.31, 95% CI=1.15–1.49), three days or more physical activity per week (OR=1.12, 95% CI=1.02–1.24), < 8 hours sleep (OR=1.6, 95% CI=1.43–1.78), increased internet usage time (OR=1.44, 95% CI=1.25–1.65).
CONCLUSIONS
Sugar-sweetened beverages intake by Korean adolescents was associated with health behaviors such as smoking, drinking, sedentary time increase, more physical activity, poor sleeping time, and increased internet use time. Based on these results, it is necessary to recognize the influence of SSBs intake and to intervene to reduce consumption of SSBs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-Related Behaviors and Perceived Health Status According to Water and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Korean Adolescents
Yoon Sun Kim, Hyun Ja Kim
Nutrients.2024; 16(17): 3038. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef - Dietary behavior of school-going adolescents in Bhutan: Findings from the global school-based student health survey in 2016
Tshering Choeda, Kathiresan Jeyashree, Soundappan Kathirvel, Thinley Dorji, Kinley Dorjee, Karma Tenzin, Sangay Thinley, Tashi Tenzin, Mongal Singh Gurung
Nutrition.2021; 90: 111290. CrossRef - Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 350. CrossRef - Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and influencing factors in Korean adolescents: based on the 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Ayoung Kim, Jinhee Kim, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 465. CrossRef
- Health-Related Behaviors and Perceived Health Status According to Water and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Korean Adolescents
- 2,274 View
- 17 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Application and the Effect of Nutrition Education Program Based on the Social Cognitive Theory Among Middle School Girls
- Jihea Kim, Taejung Woo, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):497-508. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.497
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of nutrition education using materials based on social cognitive theory. Education topics focused on improving health-related and dietary self-awareness and behavior capability in adolescents.
METHODS
Participants were recruited from a middle school for girls; 67 students (educated group, n=34 and control group, n=33) participated. The education group received 12 lessons in club activity class. Self-administered surveys were conducted for each group before and after the nutrition education program. The questionnaires consisted of variables such as self-efficacy, outcome expectation, outcome expectancy, knowledge, and dietary practices based on the social cognitive theory. Education satisfaction was evaluated using a five-point Likert scale for two sections: a) teaching and learning and b) education results. The data were analyzed using a t-test and Chi Square-test (significance level: p < 0.05).
RESULTS
In the education group, post-education, there were significant differences in self-efficacy (p < 0.05), knowledge (p < 0.01), and dietary practices (p < 0.05), whereas outcome expectation and expectancy did not show any significant differences. None of the variables showed any significant differences in the control group. Educational satisfaction scores were 4.38 ± 0.12 (teaching and learning) and 4.14 ± 0.15 (education results).
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that improving adolescent's awareness and behavior capability has a positive effect on their dietary practices. Moreover, this study suggested that a theory-based determinant should be considered to improve dietary behavior among adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultivating health: the role of interventionist actions in promoting vegetable consumption among children
Letícia Malherbi Byczkovski, João Lucas Mota Nogueira da Costa, Daiana Novello
Caderno Pedagógico.2025; 22(12): e20716. CrossRef - Survey on consumer perceptions, health benefits and preferences of kindergarten and school foodservices in Korea, including related keywords reported in newspaper: a mixed-methods study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 309. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 167. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Education Experience (Home, School, and Mass Media) on Food Consumer Information literacy
Ji Eun Kim, Kyoung Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 363. CrossRef - Factors affecting preference of vegetable in elementary school students: based on social cognitive theory
Su Hyeon Cha, Ho Kyung Ryu
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(3): 285. CrossRef
- Cultivating health: the role of interventionist actions in promoting vegetable consumption among children
- 1,403 View
- 19 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Application and Evaluation of Web-based Food Frequency Questionnaire for Korean Adolescents
- Jinhee Yum, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(5):440-450. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.5.440
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
We previously developed a dish-based semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) for Korean adolescents and reported that it had reasonable reliability and validity. The objective of the current study was to construct a web-based dietary evaluation system applying the FFQ for Korean adolescents and examine its applicability in the context of reliability and validity.
METHODS
A web-based food frequency questionnaire system was designed using a comprehensive approach, incorporating not only dietary data survey but also up-to-date nutrition information and individualized eating behavior guidelines. A convenience sample of 50 boys and girls aged 12~18 years agreed to participate in the study and completed the FFQ twice and 3 days of dietary recall on the developed website during a two-month period. The FFQ’s reliability and validity was examined using correlation and cross classification analysis. We also measured participants’ subjective levels of the web site’s usability, visual effect, understanding, and familiarity.
RESULTS
Spearman correlation coefficients for reliability ranged from 0.74 (for vitamin A) to 0.94 (for energy). From cross-classification analyses, the proportion of subjects in the same intake quartile was highest for energy (82.0%) and lowest for vitamin A (56.0%). With regard to validity analysis, Spearman correlation coefficients ranged from 0.34 (for fiber) to 0.79 (for energy). The proportions of subjects in the opposite categories between the first FFQ and 3-day diet recall data were generally low from 0.00% (for fat) to 36.2% (for sodium). Average subjective levels of the website’s usability, visual effect, understanding, and familiarity were all found to be over 4 points out of 5 points.
CONCLUSIONS
The web-based dietary evaluation system developed can serve as a valid and attractive tool for administering FFQ to Korean adolescents.
- 1,016 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Gender Differences in Adolescents' Dietary Perceptions and Practices
- Taejung Woo, Hye Jin Lee, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(2):165-177. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.2.165
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study attempted to compare adolescents' dietary behaviors and perceptions by gender in order to recommend useful strategies for nutrition interventions.
METHODS
Subjects were 2,363 middle school (MS) and high school (HS) students. They completed a self-administered questionnaire on their interest in diet and health, dietary perceptions, nutrition knowledge, dietary practices, and dietary environment at home. Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, and simple regression analysis by gender and by school groups.
RESULTS
Overall, girls obtained higher scores than boys did for "interest" (MS: p<0.001; HS: p<0.01), "dietary perceptions" (MS: p<0.001; HS: p<0.01), and "knowledge" (MS: p<0.01; HS: p<0.001). Regarding "dietary practices," no gender differences were observed among MS students, however, among HS students, boys obtained higher scores-reflecting good practices-than girls did (p<0.01). In all subjects, dietary environment at home was strongly associated with dietary practice than other variables (MS boys: β=0.435, p<0.001; MS girls: β=0.492, p<0.001, HS boys: β=0.271, p<0.001; HS girls: β=0.429, p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
We observed gender differences in some of the variables such as knowledge and perception among adolescent students. Educational programs and core strategies that consider these gender differences need to be developed. Specifically, for girls, educational programs should focus on facilitating dietary recommendation adherence, whereas for boys, the program could focus on improving dietary knowledge and perceptions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Secular Trends in Dietary Patterns Among Korean Adolescents: Using Data From the 2007–2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunyoung Tak, Eugene Kang, Minji Kang
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(4): 270. CrossRef - Development of evaluation items for adolescents’ dietary habits and nutritional practices reflecting eating behaviors and food environment
Jimin Lim, Hye Ji Seo, Jieun Oh
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 136. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - Restaurant Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption Behavior according to Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyles
Yulee Shin, Minsook Kyung, Seonyeong Baek, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(3): 172. CrossRef - Association between Stress and Nutritional status of High School Students in Chungbuk using Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents
In Young Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 361. CrossRef - Development of NQ-A, Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior
Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 142. CrossRef - Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitudes, and Dietary Behaviors by Gender of High School Students in Incheon
Zolzaya Erdenebileg, So Hyun Park, Su Ji Park, Kyung Ja Chang
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2016; 31(6): 652. CrossRef - Adulterated Food Management Characteristics according to Dietary Lifestyles among Adolescents
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(6): 509. CrossRef - Application and the Effect of Nutrition Education Program Based on the Social Cognitive Theory Among Middle School Girls
Jihea Kim, Taejung Woo, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(6): 497. CrossRef
- Secular Trends in Dietary Patterns Among Korean Adolescents: Using Data From the 2007–2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,565 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Status and Need Assessment on Nutrition & Dietary Life Education among Nutrition Teachers in Elementary, Middle and High Schools
- Na Gyeong Oh, Su Jin Gwon, Kyung Won Kim, Cheong Min Sohn, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(2):152-164. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.2.152
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the status and need for nutrition and dietary life education among nutrition teachers at schools. These characteristics were analyzed if they were different between elementary schools and middle-high schools.
METHODS
Subjects were 151 nutrition teachers from 70 elementary schools, 41 middle schools and 40 high schools in 17 cities nationwide selected by two-stage stratified cluster sampling process. Survey questionnaires included the items on general characteristics, status and need assessment for nutrition and dietary life education. Chi-square test or t-test was used for data analysis by school groups.
RESULTS
Nutrition education was implemented at 65.7% of elementary schools and 51.9% of middle-high schools. Nutrition education was mainly performed in 'discretionary activities·extracurricular activities' at elementary school and through 'newsletters, school homepage, foodservice bulletin board' at middle-high school (p<0.001). The most needed topic for nutrition education in nutrition teachers was 'healthy dietary habits and table manners' and this was not significantly different by school groups. Responses on adequate frequency (p<0.01), methods used for nutrition education (p<001), materials for nutrition education (p<0.001), information sources for nutrition education (p<0.001) were significantly different by school groups. Major tasks for activating nutrition education included 'securing the time for implementing nutrition education by reducing work loads' and 'developing standardized nutrition education materials' in schools.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutrition education at schools might be activated by improving working conditions of nutrition teachers and developing the practical programs that reflect the needs of nutrition teachers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 16. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef - Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef - Nutrition teacher’s perception and current status of nutrition education for free learning semester program: a preliminary study
Mi Joo Park, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 24. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Need for Obesity Prevention Education Programs through Analysis of Factors Affecting Student Obesity Factors in Seoul during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Seoung Hi Kim, Seonyeong Baek, Min Jeong Choi, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 214. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 167. CrossRef - Analysis of the consumer perception and related education effect on the reduction of sugar for elementary school students in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do
Ki Nam Kim, Jung Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hae Kyung Chung, Hae Rang Chung, Moon-Jeong Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(3): 303. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Quality and Nutritional Status according to the Use of Nutrition Labeling and Nutrition Claims among University Students in Chungbuk Area: Based on Nutrition Quotient
Yun-Jung Bae, Seo Young Park, Hye-Rin Bak
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 179. CrossRef - What Are the Barriers at Home and School to Healthy Eating?: Overweight/Obese Child and Parent Perspectives
Hee Soon KIM, Jiyoung PARK, Yumi MA, Mihae IM
Journal of Nursing Research.2019; 27(5): e48. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Education Experience (Home, School, and Mass Media) on Food Consumer Information literacy
Ji Eun Kim, Kyoung Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 363. CrossRef - Status and Needs Assessment on Nutrition Management and Meal Service for Elementary · Middle · High School Athletes among Athlete's Parents
Jung Hyun Hwang, Ji Yeon Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 47. CrossRef - Status and needs of nutrition education for children's sugars intake reduction in elementary school
Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 433. CrossRef - Current status of dietary education in elementary, middle and high school in Gyeonggi province: Comparison according to school level and placement of nutrition teacher
Youngmi Lee, Soo Youn Kwon, Ji Hea Kim, Ok Sun Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(6): 645. CrossRef - Evaluation of educational school meal programs in Gyeonggi province, South Korea
Youngmi Lee, Oksun Kim, Uiok Lee, Sooyoun Kwon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 111. CrossRef - Needs Assessment for Dietary Education Program Focused on the Increase of HAN-SIK (Korean Food) Consumption in Children and Adolescents Living in Jeonbuk and Gyunggi Areas
Sang-Eun Lee, Yangsuk Kim, Eun Mi Ahn, Young Hwang, Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2016; 27(S): 609. CrossRef
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- 1,390 View
- 7 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education Providing School Lunch by Personalized Daily Needed Food Exchange Units for Adolescent Athletes in Jeonbuk Province
- Kang Mo Ko, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):25-36. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of nutrition education providing school lunch by personalized daily needed food exchange units using Food Exchange System for adolescent athletes.
METHODS
The subjects were 60 sports high school students (educated group, 30 vs. non-educated group 30). Nutrition education was provided for 4 weeks (40 min/lesson/week). In addition, personalized school lunch was served for 4 weeks, nutrition education period. The personalized lunch were provided Food Exchange Units according to personalized daily needed energy. The lessons were '5 Major nutrients, functions and foods', 'My daily needed energy and food exchange units by Food Exchange System', 'My meal plan by food exchange units according to my daily needed energy' and 'Smart choice of healthy snacks and eating outs'. After nutrition education, we examined the differences in anthropometric characteristics, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and dietary intake between the educated and the non-educated group.
RESULTS
We observed improvements in lean body mass in the educated group. With regard to nutrition knowledge, there were improvements in 'Functions of vitamins', 'Functions of minerals', 'Foods of fat', 'Foods of vitamin', and 'Foods of mineral' in the educated group. In relation to dietary attitude, there were improvements in 'Taking a meal with family and friend', 'Taking a meal at ease', 'Taking a meal with kimchi and vegetables', 'Taking a meal with three kinds of side dishes', 'Priority of choosing snacks' and 'Type of snacks' in the educated group. With regard to dietary intakes according to Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans, there were improvements in intakes levels of fiber, vitamin A, vitamin C, folate, calcium, iron and zinc. The index of nutrition quality, as indicated by nutrition adequacy ratio also improved in the educated group.
CONCLUSIONS
These results showed that a nutrition education program providing education lessons and personalized school lunch by food exchange units according to daily needed energy showed positive changes in nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and dietary intake of adolescent athletes. Nutrition education program providing personalized school lunch by Food Exchange Units may improve dietary behaviors and dietary intakes of adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition Quotient and Dietary Self-efficacy according to the Transtheoretical Model in Adolescent Athletes
Nahan Kim, Kwang-Seok Hong, In-Kyung Jung
Exercise Science.2022; 31(4): 499. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to the Frequency of Milk Consumption in Korean Adolescents: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ji Hyun Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 485. CrossRef - Status and Needs Assessment on Nutrition Management and Meal Service for Elementary · Middle · High School Athletes among Athlete's Parents
Jung Hyun Hwang, Ji Yeon Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 47. CrossRef - Evaluation of educational school meal programs in Gyeonggi province, South Korea
Youngmi Lee, Oksun Kim, Uiok Lee, Sooyoun Kwon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 111. CrossRef
- Nutrition Quotient and Dietary Self-efficacy according to the Transtheoretical Model in Adolescent Athletes
- 1,317 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- A comparison of Dietary Habits and Influencing Factors for Vegetable Preferences of Adolescents in Gyeongnam Province
- Suhyang Kwak, Taejung Woo, Kyoung Ae Lee, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(4):259-272. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.4.259
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
A higher consumption of vegetables is emphasized as the core component of most dietary guidelines. Thus, this research investigated the dietary habits and influencing factors of vegetable preferences of adolescents.
METHODS
This study was conducted by using a self-administered questionnaire. 400 students from two high schools in Gyeongnam (193 boys, 207 girls) participated in the survey. The questionnaire consisted of the following variables: dietary habit, dietary action guide and factors based on Social Cognitive Theory (SCT).
RESULTS
The dietary habits of subjects showed significant differences depending on whether they prefer vegetables or not. The subjects in the group who liked vegetables had better dietary habits than the other group. Also, the study determined that the most important reason for liking or disliking vegetables is due to the taste. In the practice of dietary guidelines, the group of subjects who liked vegetables followed dietary guidelines more closely than the other group (p < 0.001). When the factors based on SCT were analyzed, personal factors showed significant differences between the groups: outcome expectation (p < 0.001), self-efficacy (p < 0.001) and affective attitude (p < 0.001). Personal factors and rated vegetable preferences showed a significant correlation in multiple regression analysis (F=42.015, p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
These results showed that vegetable preference is associated with a key point of desirable dietary habits among subjects. In order to increase vegetable preference or consumption, it is important to focus on strengthening not only self-efficacy of students, but also affective attitude of vegetable. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of evaluation items for adolescents’ dietary habits and nutritional practices reflecting eating behaviors and food environment
Jimin Lim, Hye Ji Seo, Jieun Oh
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 136. CrossRef - Analysis of socio-demographic and dietary factors associated with fruit and vegetable consumption among Korean adolescents: use of data from the 7th and 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2019)
Bokyeong Yun, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 292. CrossRef - Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 120. CrossRef - Factors influencing the consumption of convenience foods among Korean adolescents: analysis of data from the 15th (2019) Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Seul Ki Park, Ji Hyun Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(3): 255. CrossRef - The Influence of Social Media Affinity on Eating Attitudes and Body Dissatisfaction in Philippine Adolescents
Shannen Tadena, So Ra Kang, Shin-Jeong Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2020; 26(1): 121. CrossRef - Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Eun-Sun Park, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 476. CrossRef - Relationships among Skeletal Muscle Mass, Health Related Factors, Nutrient Intake, and Physical Activities in Male Adolescents: Based on the 5th (2009-2011) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
In-Kyung Jung, Jung-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2018; 29(2): 185. CrossRef - Study on Perception and Preference of Vegetable Intake of Alienated Children in Gyeongbuk Area according to Gender and Grade
Won-Hui Choe, Eun-Soon Lyu, Kyung-A Lee
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(4): 394. CrossRef - Analysis of health habit and hair mineral nutrition status of media addicted adolescent
Hee-Sook Lim, Soon-Kyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 295. CrossRef - Development of NQ-A, Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior
Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 142. CrossRef - Factors affecting vegetable preference in adolescents: stages of change and social cognitive theory
Taejung Woo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(4): 340. CrossRef - Status of Dietary Life Related Knowledge, Self-Efficacy, Food Preference and Dietary Behavior of Preschoolers in Kyunggi Area
A Reum Lee, Ye Lee Yu, Hye Jin Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 274. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Adolescents' Dietary Perceptions and Practices
Taejung Woo, Hye-Jin Lee, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 165. CrossRef
- Development of evaluation items for adolescents’ dietary habits and nutritional practices reflecting eating behaviors and food environment
- 1,531 View
- 12 Download
- 13 Crossref

- [English]
- Revision of the Target Pattern based on Single Serving Size of Dishes for Korean Adolescent Meal Plan
- Mi Jin Park, Youngnam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(1):21-29. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Maintaining a balanced diet is very crucial for adolescents. However, adolescents, who may have a short notion about the amount of food, find it difficult to plan daily meals by applying the target pattern proposed by the Korean Nutrition Society. This study was carried out to revise the target pattern based on cooked dishes instead of raw material food groups as an easier way for Korean adolescents to plan their meals.
METHODS
Target pattern for Korean adolescents were revised based on the following: 1st, categorize dish groups, 2nd, calculate representative values of each dish based on the adolescent' intake amount. 3rd, assign the recommended number of intake for each dish. Validity of the target pattern for Korean adolescent meal plan was examined by the energy content, energy contribution ratio, and NAR & INQ of nutrients.
RESULTS
The 11 dish groups categorized were bab; gook.tang.gigae; side dishes of meat, fish, egg, legume, kimchi, vegetable, seaweed; and between meal of fruit, and milk.dairy product. Based on the representative energy values, recommended number of intake were assigned to each dish. For boys, bab and gook.tang.gigae: 3 each; meat, fish, egg, and legume: 1 each; kimchi and vegetable: 3 each; seaweed: 1; fruit and milk.dairy product: 2 each were assigned. For girls, bab and gook.tang.gigae: 2 each; meat, fish, egg, and legume: choice of 3 dishes, 1 each; kimchi and vegetable: 3 each; seaweed: 1; fruit and milk.dairy product: 2 each were assigned. Energy contents, energy contribution ratio of carbohydrate, protein, and fat for boys and girls were in adequate range. The NARs were 1.0 and INQs were > or = 1.0 for all nutrients examined.
CONCLUSIONS
Revised dish-based, instead of food-based adolescent target patterns for boys and girls were easier and a valid way of Korean adolescent meal planning. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Representative Nutrients Contents and Nutritional Adequacy Evaluation of Single-Dish Meal for Middle School Students
Gisun Lee, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(2): 93. CrossRef - Nutritional Adequacy Analysis of Recommended Menu in Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015
Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(4): 279. CrossRef - Proposition and Application of a Dish-Based Target Pattern for Korean Adolescent Girls
Mi Jin Park, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(2): 87. CrossRef - Validation of Nutrient Intake Estimation based on One Serving Size
Yi-Yeong Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(5): 871. CrossRef
- Representative Nutrients Contents and Nutritional Adequacy Evaluation of Single-Dish Meal for Middle School Students
- 1,067 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Revision and Application of the Target Pattern in Food Guidance System: Administered to 2nd grade middle school students
- Ha Yeon Lee, Youngnam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(3):274-282. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.3.274
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to revise the target pattern in food guidance system for adolescents' balanced menu planning.
METHODS
The food groups in the target pattern were divided into detailed food items, and intake number were assigned to each food items based on the revised standard food composition table. The validity of revised target pattern was examined. Menu planning according to the revised target pattern was made available to 305 male and female middle school students and the nutritional assessment of the menu plan were carried out using SPSS WIN 12.0.
RESULTS
The energy contents, energy contribution ratios of carbohydrate, fat, and protein, and 4 minerals' and 6 vitamins' contents of the revised target pattern were adequate. The average energy contents of the menu planned according to revised target pattern were 400~500 kcal higher than that of the revised target pattern when the revised standard food composition was applied. The energy contribution ratios of fat were 28.9%, close to maximum of acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) (30%), and that of carbohydrate were 54.5%, lower than minimum of AMDR (55%). The nutrient adequacy ratios (NARs) of calcium and vitamin C were less than 1.0. According to index of nutritional quality (INQ) of food items, kimchi, milkdairy products, and soybean curd were energy efficient source for calcium, kimchi, fruit, vegetable and seaweed were energy efficient source for vitamin C, with INQ of food items were higher or close to 2.0. Kimchi was the best energy efficient source of calcium and vitamin C.
CONCLUSIONS
Revised target pattern based on the adolescent's foods intake was not good enough for balanced menu planning by adolescents, because what they ate and what they wanted to eat were very much different. Detailed guidance for food selection is necessary in each food items. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Designing optimized food intake patterns for Korean adults using linear programming (I): analysis of data from the 2010~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Kana Asano, Hongsuk Yang, Youngmi Lee, Jihyun Yoon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(1): 73. CrossRef - Nutritional Adequacy Analysis of Recommended Menu in Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015
Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(4): 279. CrossRef - Proposition and Application of a Dish-Based Target Pattern for Korean Adolescent Girls
Mi Jin Park, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(2): 87. CrossRef - Revision of the Target Pattern based on Single Serving Size of Dishes for Korean Adolescent Meal Plan
Mi Jin Park, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 21. CrossRef
- Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
- 1,259 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Metabolic Abnormalities in Korea Children and Adolescents and Nutrient intakes: Using 2008 the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hang Me Nam, Mi Ja Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(2):133-141. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.2.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to estimate the prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MS), metabolic abnormalities, and nutrient intakes in Korea children and adolescents using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2008.
METHODS
A sample of 838 children and adolescent males (n = 442) and females (n = 396) aged 10-18 was used from the 2008 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination survey. The diagnosis of the metabolic syndrome subjects was adapted from modified National Cholesterol Education Program-Adult Treatment Panel III by Ford. To compare nutrient intakes, we used a judgment sampling. The first group was composed of all children and adolescents (n = 46) with MS. The second one along with the first group had children and adolescents with the same age, sex, and body mass index (BMI) but without MS (n = 46). The control group like the first two had children and adolescents with same sex and same age but with normal BMI and without MS (n = 46).
RESULTS
In this randomized controlled controlled trial, the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome was 5.8%. The risk factors was associated with the MS were abdominal obesity 9.4%, hypertriglyceridemia 25.0%, low HDL-cholesterol 10.3%, hypertension 23.4%, and hyperglycemia 7.1%. Among metabolic abnormalities, blood pressure was significantly affected by sex, age and obesity. On the other hand, HDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, and waist circumference were directly linked to obesity. There were no significant differences in nutrient intakes among the three groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The prevalence of MS was higher in children (10-11 years old) than in adolescents (12-18 years old). There was a difference in hypertension among risk factors by gender, and there were no significant differences in nutrient intakes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence Trends of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Children and Adolescents from a Population-Based Cross-Sectional Survey
Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Sub Lim
Life.2022; 12(9): 1404. CrossRef - Biochemical Index, Nutrition Label Use, and Weight Control Behavior in Female Adolescents: Using the 2010 and 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi-Ja Choi, Hyun-Ju Jo, Mi-Kyung Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2020; 9(1): 32. CrossRef - Socioeconomic and Behavioral Characteristics Associated With Metabolic Syndrome Among Overweight/Obese School-age Children
Ok Kyung Ham
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2017; 32(1): 30. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents According to the National Cholesterol Education Program, Adult Treatment Panel III and International Diabetes Federation
Seonho Kim, Wi-Young So
Nutrients.2016; 8(10): 588. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment and Factors Related to Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Youth: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2013
Yong-Suk Kwon, Yangsuk Kim, Eun-Mi Ahn, Hyun Ju Kang, Young-Hee Park, Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2016; 27(4): 875. CrossRef - Evaluation of nutrient intake and food variety by age in Korean adolescents: Based on 2010~2012 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(3): 236. CrossRef
- Prevalence Trends of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Children and Adolescents from a Population-Based Cross-Sectional Survey
- 1,143 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Wanting Extremely Low BMI May be Associated with Higher Depression and Undesirable Dietary Habits in High School Girls Who were Not Overweight
- Hyeyoung Park, Hongmie Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(4):344-353. Published online August 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.4.344
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The widespread pursuit for the thin physique may have detrimental impact on the wellbeing of the young generation, especially females. This study aimed to determine the effect of wanting very low body weight on dietary habits and psychological factors of female adolescents. Participants were 619 girls from 5 high schools in Kyeonggi, Korea. Information on dietary behaviors, psychological factors as well as current heights and weights and the desired weight for current height were obtained by questionnaire. Of total subjects, 38.1%, 35.5%, and 26.5% desired weights corresponding to normal (10~85 percentile), low (3~10 percentile) and very low BMI (< 3 percentile), respectively. The subjects who wanted to be very low weight had the average BMI of 18.57 kg/m2, which was significantly lower than 21.21 kg/m2 of those who wanted to be normal weight (p < 0.001). The subjects who desired very low weight had significantly higher scores for depression symptoms (p < 0.05), while there were no differences in obsession to lose weight and obesity stress. Moreover, more subjects in this group had undesirable dietary habits such as eating fast foods more than weekly (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that the desire for extreme thinness may lead female adolescents to have not only unreasonably similar obesity stress and obsession to lose weight but also higher depression symptoms, along with undesirable dietary habits. The findings suggest the potential harm from excessive weight concerns of female adolescents; thus efforts to teach this group about healthy weights are urgently needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Body Image Perception and Eating Behaviors among Male Middle and High School Students according to Weight Status in Seoul
Bo-Mi Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(2): 123. CrossRef - Agreement Between Actual and Perceived Body Weight in Adolescents and Their Weight Control Behaviors
Sun Mi Shin
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2017; 26(2): 138. CrossRef - Body Image Perception, Eating Disorder Risk, and Depression Level according to Dieting Experience of Female High School Students in Seoul
Jisun Min, Kyunghee Song, Hongmie Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(4): 241. CrossRef - The Associations between Discordance of Body Image and Physical Activities among Adults Aged 19 to 64 Years: Based on the Data from 2010 Community Health Survey
In Ae Chun, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Mi Ah Han, Seong Woo Choi, Dae Sik Ko
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2014; 23(4): 274. CrossRef
- Body Image Perception and Eating Behaviors among Male Middle and High School Students according to Weight Status in Seoul
- 1,196 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrient Intake and Meal Variety with Breakfast Eating in Korean Adolescents: Analysis of Data from the 2008~2009 National Health and Nutrition Survey
- Yun Jung Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(3):257-268. Published online June 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.3.257
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate nutrient intake and meal variety with breakfast eating in Korean adolescents using data from the 2008-2009 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The analysis included 1245 adolescents aged 12 to 18 years. The subjects were divided into two groups according to breakfast skipping (BS: breakfast skipping, n = 235, BE: breakfast eating, n = 1110). The BS group was significantly higher in its frequency of eating soda drinks, instant noodle, and ice cream than the BE group. The BS group consumed significantly lower quantities of plant calcium and plant protein per 1,000 kcal compared to the BE group. Also the intake of cereal and vegetables in the BS group was significantly lower than those in the BE group, however, the intake of beverage in the BS group was significantly higher than that in the BE group. The average number of foods of the BE and BS groups were 29.50 and 25.85, respectively and revealed a statistical significance (p < 0.0001). The snack intake and % energy from snack intake of the BS group were significantly higher than those of the BE group. Also, the fasting blood glucose concentrations were significantly higher in the BS group compared to the BE group. In conclusion, adolescents who skip breakfast may have lower meal variety and higher blood glucose concentrations. Therefore, in support of proper dietary management, it is necessary to promote and encourage breakfast eating.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparative study on eating habits and mental health of Korean middle school students according to their bedtime across regions: using data from the 2020–2022 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Sarim Kim, Jiyoung Jeong, Juyeon Kang, Jihye Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(2): 269. CrossRef - 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
민지 손, 은주 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 213. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Quality of Convenience Store Meal Boxes according to Store Company and Meal Price
Changgyu Cho, Youngmin Nam, Hye-Jong Yoo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 105. CrossRef - Recognition and preference of rice-based home meal replacement for breakfast among adolescents in the Jeonbuk area
Hae-Rim Oh, Hyunsuk Kim, Su-Jin Jung, Youn-Soo Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 262. CrossRef - Trends in Prevalence and the Differentials of Unhealthy Dietary Habits by Maternal Education Level among Korean Adolescents
Yunseo Chung, Kyunghee Jung-Choi, Bo Young Kim, Kyoung Ae Kong
The Ewha Medical Journal.2021; 44(4): 133. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary habits according to breakfast consumption in Korean adolescents: based on the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2013 ~ 2015
Hyun-Suk Kim, Ui-Suk Lee, Seon-Hyeong Kim, Youn-Soo Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(2): 217. CrossRef - Children's Food Intake and Nutrition Levels, and Obesity by Maternal Employment: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2015
Geunyeong Kang, Yoonna Lee, Mihyang UM, Seunghee Kye
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(4): 331. CrossRef - Ecological Factors Affecting Obesity Among Middle School Students in South Korea
Suhee Kim, Gwang Suk Kim
Journal of School Health.2019; 89(3): 181. CrossRef - Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and influencing factors in Korean adolescents: based on the 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Ayoung Kim, Jinhee Kim, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 465. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Nutritional Status of Young Women according to Breakfast Frequency in Seoul
Da-Mee Kim, Youl-Ri Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(2): 102. CrossRef - Study on Skipping Breakfast in Adolescents Classified by Household Type
Jaehong Park, Soye You
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2017; 28(2): 329. CrossRef - Development of NQ-A, Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior
Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 142. CrossRef - Importance and performance of food and nutrition labeling for school adolescents in Seoul
Jeong-Yoon Yoon, Ae Wha Ha, Seyoung Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(4): 383. CrossRef - A Study on nutritional status and dietary quality according to carbonated drink consumption in male adolescents: Based on 2007~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yun-Jung Bae, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(6): 488. CrossRef - Evaluation of nutrient intake and food variety by age in Korean adolescents: Based on 2010~2012 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(3): 236. CrossRef - Study on Nutritional Knowledge and Food Consumption Differences of Middle School Students living in Rural and Urban Areas of Inner Mongolia
Ying Li, Youngmi Lee, Nari Park, Haeryun Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(6): 933. CrossRef - Associations of Eating Habits with Obesity and Nutrition Knowledge for Middle and High School Adolescents in Shanghai and Heze China
Yang Song, Hyo-Jin Ahn, Ji-Hye Choi, Se-Young Oh
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(6): 648. CrossRef
- A comparative study on eating habits and mental health of Korean middle school students according to their bedtime across regions: using data from the 2020–2022 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,330 View
- 11 Download
- 17 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Relationship between Socio-demographic Factors and Food Consumption Frequencies among Adolescents in South Korea: Using the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey from 2011
- Ji Eun Jo, Hae Ryun Park, Soo Bin Jeon, Jin Sil Kim, Go Eun Park, Yang Li, Young Suk Lim, Jinah Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(2):165-176. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.2.165
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to analyze the influence of socio-demographic factors on food consumption frequencies among adolescents in Korea. Data were obtained from the Seventh Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (2011 KYRBS), a nationwide representative sample of 75,643 (37,873 males and 37,770 females) middle and high school students. It was carried out as a self-administered on-line survey. The frequency of eating breakfast was 4.8 times per week for middle school students and 4.6 times per week for high school students (p < 0.001). Higher levels of perceived household economic status, family affluence scale (FAS) and education attainment of mother were associated with more frequent breakfast eating. The frequencies of consumption of vegetables and milk were higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). The frequency of consumption fruits was higher in females than in males (p < 0.01). Higher levels of perceived household economic status, FAS and education attainment of mother were associated with more frequent consumption of vegetable, fruits and milk. The frequencies of consumption of soda, fast food and instant noodls were higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). The frequency of consumption of snacks was higher in females than in males. Adolescents with lower levels of FAS and education attainment of mother were at risk for skipping breakfast and consuming of soda, fast food and instant noodls more frequently. Whereas, adolescents with higher levels of FAS, education attainment of mother were more likely to be frequent consumers of vegetable, fruits and milk. These findings demonstrated that being high school students and belonging to lower level of socio-economic status (SES) were associated with undesirable food habits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - Changes in eating behaviors according to household income in adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic: findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Ah Lee, Ho Jung Lee, Bomi Park, Yoonhee Shin, Hyunjin Park, Hyesook Park
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022102. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef - Trends in Beverage Consumption and Related Demographic Factors and Obesity among Korean Children and Adolescents
Su Bin Hwang, SoHyun Park, Guang-Ri Jin, Jae Hyun Jung, Hyeon Ju Park, Su Hyun Lee, Sangah Shin, Bog-Hieu Lee
Nutrients.2020; 12(9): 2651. CrossRef - Convenience Store Use and the Health of Urban Adolescents in Seoul, South Korea
Nan-He Yoon, Changwoo Shon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(18): 6486. CrossRef - Factors influencing the consumption of convenience foods among Korean adolescents: analysis of data from the 15th (2019) Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Seul Ki Park, Ji Hyun Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(3): 255. CrossRef - Development of NQ-A, Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior
Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 142. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Adolescents' Dietary Perceptions and Practices
Taejung Woo, Hye-Jin Lee, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 165. CrossRef - Study on Nutritional Knowledge and Food Consumption Differences of Middle School Students living in Rural and Urban Areas of Inner Mongolia
Ying Li, Youngmi Lee, Nari Park, Haeryun Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(6): 933. CrossRef - Analysis of consumption frequencies of vegetables and fruits in Korean adolescents based on Korea youth risk behavior web-based survey (2006, 2011)
Yangsuk Kim, Yong-Suk Kwon, Young-Hee Park, Jeong-Sook Choe, Jin-Young Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(4): 411. CrossRef
- Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
- 1,359 View
- 3 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitude, and Dietary Behavior among Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
- Na Yeon Noh, So Young Nam, Hee Suk Kang, Ji Eun Lee, Soo Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(2):101-111. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.2.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Type 1 diabetes is on the rise worldwide. Although nutrition education for patients with diabetes has become a routine practice, specifics and impacts of such educations need to be more researched. This study examined the status of nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude, and dietary behavior among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (9-19 year-old) and explored factors influencing dietary behaviors related to diabetes by applying the Theory of Planned Behavior. Face-to-face interviews, using a pre-tested structured questionnaire, were conducted with 32 participants (11 boys and 21 girls) with type 1 diabetes followed by a diabetes clinic in a university hospital. This study found that the level of nutrition knowledge related to diabetes was generally low at 4 points out of a possible 10, however, the dietary attitude related to diabetes was found to be generally good at 26 points out of a possible 30. Participants were motivated to follow medical staff recommendations the most; however, their family was also important. Perceived behavioral control was low especially for eating-out and portion control. The dietary behavior related to blood glucose control showed low at 13 points out of a possible 20. Regression analysis showed that perceived behavioral control (p < 0.001) was significantly related to the dietary behavior related to blood glucose control. This rare study with children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes showed that nutrition education should include a component to improve perceived behavioral control through high-risk situation management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spatial Distribution of Diabetes Prevalence Rates and Its Relationship with the Regional Characteristics
Eun-Kyung Jo, Eun-Won Seo, Kwang-Soo Lee
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(1): 30. CrossRef
- Spatial Distribution of Diabetes Prevalence Rates and Its Relationship with the Regional Characteristics
- 1,191 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- The Relationship among Insulin Resistance, Blood Profiles and Nutrient Intake in Overweight or Obese Children and Adolescents
- Jae Hee Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(5):530-542. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.530
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purposes of this study were to investigate blood profiles and nutrient intakes of groups that are different in obese levels, and to find the credible predictor of insulin resistance. The subjects were classified as normal weight (%IBW < or = 110), obese without MS and obese with MS according to IDF definition of the risk group in metabolic syndrome (MS). Subjects of this study were included 137 (59 boys, 78 girls) free living children and adolescents (mean age 12.6 +/- 3.4 years) in Gangneung area, South Korea. %IBW of normal weight (94.9%), obese without MS (123.8%) and obese with MS (131.5%) were significantly different among groups. HOMA-IR had positive correlations with TG (r = 0.634), waist circumference (r = 0.553), atherogenic index (r = 0.513), %IBW (r = 0.453) and ALT (r = 0.360), but showed negative correlations with HDL cholesterol (r = -0.417, p < 0.001). HOMA-IR showed positive correlation with polyunsaturated fatty acid intake (p < 0.05). The energy intake of obese with MS was 1762 kcal/day which was not significantly different from those of normal weight and obese without MS. Total fatty acid intakes of two obese groups were significantly higher than that of normal weight. The results of this study suggest that waist circumference and ALT as well as TG, atherogenic index and weight can be credible indices to predict the insulin resistance in children and in adolescents. In addition, nutrition education and adequate diet should be provided to prevent MS in children and in adolescents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of dietary quality and nutrient intake of obese children in Changwon area
Ji-Sook Park, Ha-Neul Choi, Jae-Young Kim, Sang-Hyuk Ma, Jung-Eun Yim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(6): 630. CrossRef - Biochemical Index, Nutrition Label Use, and Weight Control Behavior in Female Adolescents: Using the 2010 and 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi-Ja Choi, Hyun-Ju Jo, Mi-Kyung Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2020; 9(1): 32. CrossRef - Factors associated with Obesity among Korean Adolescents based on the Seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016)
Hyun Young Koo, Eun Kyung Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(1): 28. CrossRef - Effects of interaction betweenSLC12A3polymorphism, salt-sensitive gene, and sodium intake on risk of child obesity
Joohyun Jung, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 32. CrossRef - Evaluation of Eating Behavior and Nutritional Status Using the Nutrition Quotient in Obese Children
Hee-Sook Lim, Soon-Kyung Kim, Yoon-Hyung Park, Young-Lim Shin
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2016; 25(4): 225. CrossRef
- Assessment of dietary quality and nutrient intake of obese children in Changwon area
- 1,100 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrient Intake and Anthropometric Parameters related to Obesity in Korean Female Adolescents according to Dietary Diversity Score: From the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 2007-2009
- Yun Jung Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(4):419-428. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.4.419
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate nutrient intake and anthropometric parameters related to obesity in Korean female adolescents according to dietary diversity score. We analyzed data from the combined 2007-2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). The subjects were 770 female adolescents. Nutrient intakes, Dietary Diversity Score (DDS) ) and Dietary Variety Score (DVS) were derived by using the data from the 24-recall method. The DDS was defined as the number of six food groups (cereals, meats, fruits, vegetables, dairy, fats and oils) consumed. The DVS was defined as the number of food items consumed. The average age of the subjects of the study was 15.02 years and the average height, weight, and BMI were 159.50 cm, 52.58 kg, 20.62 kg/m2, respectively. The energy and nutrients intakes, percent of the recommended intake for nutrients in DDS = 5~6 group were significantly higher than those of the other groups. Calcium and vitamin C INQ in DDS = 5~6 group were significantly higher than those of the other groups. The average DVS of the subjects was 29.33. The most frequent style of food pattern was CMDFVO (cereals, meats, dairy, fruits, vegetables, fats and oils) = 111011. In conclusion, in healthy Korean female adolescents, food diversity intake variety did beneficially affect the intakes of calcium and vitamin C. Further studies are needed to confirm these findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Dietary Nutrient Intake and Food Variety by Milk Consumption in Postmenopausal Korean Women: Data Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015
Ae Wha Ha, Woo Kyung Kim, Sun Hyo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 51(9): 912. CrossRef - Relationship between dietary diversity score and general health in female students
Azadeh AMINIANFAR, Fereydoun SIASSI, Mostafa QORBANI, Javad KARIMI, Gity SOTOUDEH, Yas KALIKIAS, Sanaz SOLTANI
Minerva Pediatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ) and the Risk of Obesity in Male Adolescents: a Case-Control Study
Maryam Gholamalizadeh, Samira Rastgoo, Saeid Doaei, Farhad Vahid, Hanieh Malmir, Narges Ashoori, Alireza Mosavi Jarrahi
Biological Trace Element Research.2021; 199(5): 1701. CrossRef - Relationship between dietary intakes and the double burden of malnutrition in adults of Malang, Indonesia: An exploratory study
Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(5): 426. CrossRef - Night eating status according to body mass index of Korean adolescents
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Yu-Jin Cho, Myung-Hee Kim, Yun Jung Bae
Nutrition & Food Science.2017; 47(1): 89. CrossRef - Systematic Review on the Study of the Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in Korea: Dietary Risk Factors
Eun Jeong Heo, Jae Eun Shim, Eun Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 191. CrossRef - Development of NQ-A, Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior
Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 142. CrossRef - Comparison of Diet Quality and Diversity according to Obesity Type among 19-64 year old Korean Adults
Hyae Min Gu, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Mi Ah Han, Yeong Eun Son
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(6): 545. CrossRef - Effects of brown rice-vegetable school meal program on subjective health status, BMI and hematological parameters among high school students
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7385. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Nutritional Value of Traditional Korean Noodles through Energy Density and Diversity
YoonKyoung Yang, SungOk Kim, Juhyeon Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 732. CrossRef - Effects of a Brown Rice and Vegetable Diet on the Defecation Conditions and Health Status of High School Students
Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(1): 179. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Dietary Nutrient Intake and Food Variety by Milk Consumption in Postmenopausal Korean Women: Data Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015
- 1,134 View
- 2 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- The Relationship between High Energy/Low Nutrient Food Consumption and Obesity among Korean Children and Adolescents
- Gyu Jin Heo, So Young Nam, Soo Kyung Lee, Sang Jin Chung, Ji hyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(2):226-242. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.2.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Consumption of foods with high energy and low nutrient values has been linked to various health issues including obesity and chronic diseases. This study investigated the high-energy/low-nutrient food consumption status and its relationship with obesity status and intake of energy and nutrients, using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) and the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (KYRBWS). The prevalence of overweight and obesity among 2-18 year-olds was 8.4% and 10.8% in 2008 and 8.5% and 9.0% in 2009, respectively, in KNHANES. The prevalence of obesity among 12-18 year-olds was 13.9% in 2008 and 11.4% in 2009 in KNHANES, while it was 8.1% in 2008 and 8.2% in 2009 in KYRBWS. Consumption patterns of high-energy/low-nutrient foods were diverse depending on the particular food type. High-energy/low-nutrient foods such as cookies were most often consumed more frequently (2~3 times per week), but fast food type foods were generally consumed less frequently (once per week or less). No significant relationships between high-energy/low-nutrient food consumption and level of energy and nutrient intakes were found in either datasets. Adolescents who were not obese more frequently consumed ramen (p < 0.001), cookies (p < 0.001) and fast food (p < 0.001) than those who were obese in KYRBWS, however, such relationships were not found in KNHANES. This direction of the relationship could be probably attributed to the cross-sectional nature of the datasets. This study was limited by the cross-sectional nature of the data, therefore, further longitudinal research using various study techniques would be necessary to understand the effects of high-energy/low-nutrient foods on child obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - Do types of snacks, sleep hours, and eating places affect nutritional intakes and its adequacy in adolescents?
Sora Kim, Jeonglee Kim, Hyeja Chang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(3): 396. CrossRef - Analysis on the Relationship between Eating Behavior, Physical Activities and Youth Obesity: Based on the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey for High School Students in 2016~2018
Seung-Hoo Lee, Jong-Ho Lee
Information.2020; 11(3): 169. CrossRef - Relationship between the Intake of Children's Favorite Foods and Policy based on Special Act on Safety Control of Children's Dietary Life
Taejung Woo, Jihye Yoo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 106. CrossRef - Diet and Physical Activity of Korean Female Adolescents in Their Peer Networks
Sophia Jihey Chung, Anne L. Ersig, Ann Marie McCarthy
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2019; 51(2): 147. CrossRef - Systematic Review on the Study of the Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in Korea: Dietary Risk Factors
Eun Jeong Heo, Jae Eun Shim, Eun Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 191. CrossRef - Development of NQ-A, Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior
Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 142. CrossRef - Food deserts in Korea? A GIS analysis of food consumption patterns at sub-district level in Seoul using the KNHANES 2008-2012 data
Dohyeong Kim, Chang Kil Lee, Dong Yeon Seo
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(5): 530. CrossRef - Dietary assessment according to frequency of food consumed away from home among children and adolescents: Based on the 2010~2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yong-Suk Kwon, Wan-Soo Hong, Seyoung Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(6): 471. CrossRef - Associations between Exposure to Unhealthy Food Outlets Within Residential District and Obesity: Using Data from 2013 Census on Establishments and 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yoonjung Kim, Sung Nim Han
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(5): 463. CrossRef - The awareness level and needs for education on reducing sugar consumption among mothers with preschool children
Younhee Lee, Nami Joo
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(2): 229. CrossRef - Analysis of consumption frequencies of vegetables and fruits in Korean adolescents based on Korea youth risk behavior web-based survey (2006, 2011)
Yangsuk Kim, Yong-Suk Kwon, Young-Hee Park, Jeong-Sook Choe, Jin-Young Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(4): 411. CrossRef - Evaluation of nutrient intake and food variety by age in Korean adolescents: Based on 2010~2012 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(3): 236. CrossRef - Influences of Korean Haw (Crataegus pinnatifida BUNGE) on Lipid Concentration in Hypercholesterolemia
Han-Soo Kim, Min-A Kim, Seong-Ho Jang
Journal of Environmental Science International.2014; 23(5): 793. CrossRef - Influences of Wild Haw (Crataegus pinnatifida BUNGE) on Lowering BUN and Creatinine Concentrations in Dyslipidemia
Han-Soo Kim, Min-A Kim, Yishan Duan, Seong-Ho Jang, Han-Jin Cho, Jae-Young Ryu, Sang-Woo Kim
Journal of Environmental Science International.2014; 23(6): 1029. CrossRef - Effects of Haw (Crataegus pinnatifida BUNGE) on Relaxation in the Lipid Components and Blood Glucose of Lipid Metabolism Syndrome
Han-Soo Kim, Min-A Kim, Yishan Duan, Seong-Ho Jang, Won-Ki Lee, Jae-Young Ryu
Journal of Environmental Science International.2014; 23(6): 1021. CrossRef - A Survey on the Calorie and Nutrient in Children-favored Food within Green Food Zone in Gwangju
Yongshik Yang, Jungmi Seo, Sujin Mun, Taesun Kim, Bokyung Kim, Sooyeon Choi, Baesik Cho, Dongryong Ha, Eunsun Kim
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2013; 28(4): 299. CrossRef - Characteristics of School Menus from the Daegu and Gyeongbuk Area
Seon Woo Ahn, Mi-Kyung Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(6): 983. CrossRef
- Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,232 View
- 1 Download
- 18 Crossref

- [English]
- Change of Children's Meal Structure in Terms of Temporal and Spatial Dimensions : Analysis of the Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys of 1998 and 2009
- Youngmi Lee, Jae Eun Shim, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(1):109-118. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.1.109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to characterize changes in the meal structure of Korean children in terms of temporal and spatial dimensions. The data of 1,891 and 1,627 school-aged children and adolescents extracted respectively from the 1998 and 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys were analyzed by gender, age group, and residential area. From 1998 to 2009, the total eating events increased from 4.3 to 4.6 (p = 0.001); the average number of meal intake decreased from 2.8 to 2.7 (p < 0.001) while that of snack intake increased from 1.5 to 1.9 (p < 0.001). The prevalence of "3 meals a day" pattern tended to decrease while that of "2 meals a day" pattern increased over the years. Especially, the "2 meals a day" pattern with "lunch + dinner" increased from 13% in 1998 to 20% in 2009. The percentage of eating breakfast or dinner at home decreased over the years. These results indicate that over the last decade, "destructuration" occurred in Korean children's meal structure in terms of temporal and spatial dimensions. Especially, such alteration was more distinctive in male than female and in the high school-aged group than the elementary or middle school-aged groups. Overall, the difference of meal structure between genders and residential areas became smaller while the difference among age groups became larger over the years.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescent According to the Meal Frequency: The 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yonghoon Ji, Junhee Park, Jun-Hyun Yoo
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2022; 12(3): 158. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Quality and Nutritional Status according to the Use of Nutrition Labeling and Nutrition Claims among University Students in Chungbuk Area: Based on Nutrition Quotient
Yun-Jung Bae, Seo Young Park, Hye-Rin Bak
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 179. CrossRef - Korean Adolescents’ Energy Intake of Selected Foods by Eating Place from 1998 to 2012 During Implementation of Two National School Nutrition Policies
Seul Ki Choi, Edward A. Frongillo, Christine E. Blake, James F. Thrasher
Journal of Hunger & Environmental Nutrition.2018; 13(1): 116. CrossRef - Associations between Exposure to Unhealthy Food Outlets Within Residential District and Obesity: Using Data from 2013 Census on Establishments and 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yoonjung Kim, Sung Nim Han
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(5): 463. CrossRef - Nutrient intakes and frequently consumed foods among Korean adults according to the intake frequency of Baechu (Chinese cabbage) kimchi: Based on the 2012~2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ae-Wha Ha, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(2): 125. CrossRef - Recognition and Usage of Nutrition Labeling for Processed Foods and Restaurant Meals according to the Effort Level of Healthy Dietary Behavior in 5th Grade Elementary School Girls
Jin-Ah Moon, Jung-Eun Kong, Gui-Im Moon, Baeg-Won Kang, Jee-Young Yeon
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(5): 849. CrossRef - Bite Force and Lip Closing Force Measurement in Preschool Children
Nayoung Cho, Hyeongun Kim, Jaegon Kim, Byeongju Baik, Yeonmi Yang
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2015; 42(3): 233. CrossRef - Assessment on Dietary Diversity According to Korean Dietary Pattern Score of Korean Adolescents and Children: Using 2007~2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
Yong-Suk Kwon, Yangsuk Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2015; 31(5): 660. CrossRef - Perception on Nutrition Labeling of the Processed Food among Elementary School Students and Parents in Daegu Area
Jung Mi Kim, Mi Hee Lee, Nan Hee Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(6): 1107. CrossRef - Evaluation of items for the food behavior checklist and nutrition quotient score on children in rural areas of Gyeongbuk
Jung-Sun Yoo, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(5): 427. CrossRef - Development of 'Children's Food Avatar' Application for Dietary Education
Joo-Han Cho, Sook-Bae Kim, Soon-Kyung Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Gap-Soo Kim, Se-Na Kim, So-Young Kim, Jeong-Weon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(4): 299. CrossRef - Current Status and Strategic Plan of Nutrition Education Comparing Nutrition Teachers with Dietitians in Schools, Gyeonggi Area
Young-sun Hong, Joung-hee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 233. CrossRef
- Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescent According to the Meal Frequency: The 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,189 View
- 2 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Associated with Hypertension in Korean Adolescents: Based on 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Killye Kim, Sook Mee Son, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(4):439-453. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.4.439
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to determine dietary and lifestyle factors associated with hypertension in Korean adolescents. Study subjects were 12~19 years (n = 521) adolescents who participated in the 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III). Subjects were divided into the hypertensive group (HG, n = 102) and normotensive group (NG, n = 419) by '2007 Korean children and adolescents growth standard' and the relationships between blood pressure and physical measurement, nutrients intakes, eating behaviors and health related factors were analyzed. HG showed significantly higher levels in weight, waist circumference and BMI than NG. The amount of nutrient intakes was not different between NG and HG. Index of nutritional quality (INQ) for phosphate was higher in HG compared with NG. In both male and female HG, INQ for iron was higher but INQ for vitamin B1 was lower than NG. HG revealed higher consumption frequencies of snack, yoghurt, and ice cream compared with NG. In eating and behavioral factors, 'dinner with family', 'eat proper amount', 'keep Korean traditional diet', alcohol drinking, and mean alcohol intake were significantly different between the two groups. By logistic regression method, risk factors for hypertension revealed in this study were gender (male), age (15~19 years), BMI (> or = 85 percentile), and not keeping Korean traditional diet. These results suggest that education program for hypertension prevention in adolescents should include eating habits improvement and lifestyle modification as well as weight control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef - Differences in SBP, BMI, and Stress with AUDIT Score in Adolescents
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2018; 12(1): 228. CrossRef - An analysis of long-term occurrence of renal complications following pediatric pyeloplasty
Hahn-Ey Lee, Kwanjin Park, Hwang Choi
Journal of Pediatric Urology.2014; 10(6): 1083. CrossRef - The Factors related to Dyslipidemia and Hypertension among Male Office Workers
Eun Kyung Lee, Ok Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(4): 432. CrossRef - A Study on Classification of Obesity for Koreans based on the Articles in the Korean Journal of Community Nutrition - Articles Enlisted from 1996 to 2011 -
Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(5): 525. CrossRef - Association of Bone Mineral Density and Blood Pressure, Calcium Intake among Adult Women in Seoul · Kyunggi Area - Based on 2011 KNHANES -
Jae Ok Koo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 269. CrossRef
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,173 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrition Label Use, Self-Efficacy, Snacking and Eating Behavior of Middle School Students in Kyunggi Area
- Seo Yeon Ko, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(4):513-524. Published online August 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to examine nutrition label use, self-efficacy, snacking and eating behaviors of middle school students, and to investigate if these characteristics were different by nutrition label use. A cross-sectional survey was conducted to 348 middle school students in Kyunggi, Korea. About a third of subjects read nutrition labels when they purchased snacks/packaged foods. Most nutrition label users were interested in reading information on calories, fat and trans-fat. Self-efficacy of eating/selecting snacks or general nutrition behavior was moderate (mean score: 44.4 out of 60), with significantly higher score in nutrition label users compared to nonusers (p < 0.001). Nutrition label users felt more confident in 9 items out of 15 items of self-efficacy, such as "taking fruits instead of cookies/candy for snack" (p < 0.001), "choosing milk instead of soft drink" (p < 0.01), "not having snacks after dinner" and "avoiding processed foods for snacks" (p < 0.05). Subjects had snacks 1.3 times a day, and nutrition label nonusers consumed snacks more frequently than the counterparts (p < 0.01). About 55% of nutrition label users and 64.7% of nonusers mainly purchased snacks for themselves (p < 0.05). Commonly purchased snacks by adolescents were ice cream, cookies/chips, breads and ramen. Major considerations in purchasing snacks were taste (46.9%) and price (34.6%). In selecting snacks, the influence of friends and parents was greater than the other sources. Based on eating frequency of snacks, nutrition label users were more likely to consume healthy snacks, such as fruit juices, vegetables, milk, yogurt, and potato/sweet potato than nonusers (p < 0.05). Eating behaviors measured by 15 items scored 33.6 out of 45. Nutrition label users showed better eating behaviors, such as "eating meals slowly", "eating foods cooked with plant oil", and "eating out less frequently" (p < 0.05). Study results showed that majority of adolescents did not read nutrition labels, selected snacks for themselves and had somewhat unhealthy foods for snacks. This study also showed the differences in self-efficacy, snacking and eating behaviors between nutrition label users and nonusers. In nutrition education, it is necessary to stress the importance and skills for reading nutrition labels. It is also needed to help adolescents to select healthy snacks and have desirable eating behaviors, as well as increasing self-efficacy.
- 369 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of Different Dietary Habits by Classification of Body Mass Index of Middle School Male Students in Ulsan City
- Soon im Jung, Soon myung Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(3):342-350. Published online June 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigates differences in middle school male students' anthropometric variables and dietary habits using BMI (Body Mass Index) classifications. chi-square-test for frequency and ANOVA test for mean value and duncan value were used to analyze results. Averaged results of three groups of middle school male students' anthropometry including height (normal group 164.4 cm, overweight group 165.0 cm, obese group 167.0 cm), weight (normal group 56.0 kg, overweight group 70.0 kg, obese group 83.2 kg) and waist circumference (normal group 20.7 cm, overweight group 79.8 cm, overweight group 89.6 cm) were resulted. Classification of obese group was based upon 2007 growth charts using BMI criteria. This study indicates the normal weight group boys have over-eating related dietary habits and the obese groups have less calorie dietary habits. They answered oppositely to normal recognition. The obese group reflected dietary problems, such as preferences for sweet fruit rather than normal group males. Dinnertime of the groups were significantly different and obese group's earlier dinnertime can influence on their late night snack eating. Forty precent of obese male group like fruits as late night eating food. Three meal amount of three groups were significantly different, as obese group answered they ate same amount at every meal. It can mean obese group ate more amount of food in every meal. Overweight and obese male students have dietary problem of fast eating and answers of unbalanced eating were higher in normal group. These could mean obese group eats well in every food and fast eating habit could lead a lot of food eating habit. Obese group chooses out-going food of less calorie and frequency of fast food eating was lower than normal group. In result, obese group answered that they have less calorie related dietary habits, it could mean their answers were false or fixed dietary habit. Therefore, more researches should be followed.
- 281 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation of Diet Quality of Children and Adolescents Based on Nutrient and Food Group Intake and Diet Quality Index-International (DQI-I)
- Mi Hyun Kim, Yun Jung Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(1):1-14. Published online February 28, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is suggested that evaluation of diet quality may be a great indicator of nutritional assessment. The aim of this study was to evaluate the diet quality of children and adolescents based on nutrient and food group intake and Diet Quality Index-International (DQI-I). This survey was conducted through questionnaires and diet record survey to 477 students (elementary school students; n = 131, middle school students; n = 136, and high school students; n = 210). The results showed that high school students were significantly more often to skip breakfast compared with the other groups. The middle and high school students consumed significantly higher intakes of food and energy compared to the elementary school students. Also the number of nutrients in Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ) < 1.0 of high school students were significantly higher than that of elementary and middle school students. The Korean's dietary diversity score (KDDS) of elementary school, middle school and high school students were 4.1, 4.4 and 4.3 respectively. The average DQI-I of elementary school, middle school and high school students were 66.7, 65.5, and 63.7, respectively and there was significant difference. Also, middle school students showed to have higher score in variety and adequacy category compared with the other groups, and elementary school students appeared to have higher score in moderation category. In conclusion, high school students appeared to have unhealthy dietary habits in terms of high frequency of skipping breakfast and lower INQ and DQI-I score compared to the elementary school and middle school students. Therefore, the proper dietary management should be needed for high school students.
- 348 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Interrelations Among Fast Food, Beverage Intake and Sociality, Anger Expression of Adolescents in the Busan Area
- Eun Soon Lyu, In Sook Chae, Kyung Hae Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(6):829-839. Published online December 31, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the relation of the fast food and beverage intake on sociality and anger expression of adolescents. Questionnaires were distributed to the adolescents of 599 middle and high school students in Busan. According to the results, the preference-intake frequency analysis (PEA) on fast food grid, high preference and high intake frequency were 'dukbokki', 'chicken' and 'mandu' and low preference and high intake frequency were 'ramyon', 'gimbab. PEA on beverage grid, high preference and high intake frequency were 'milk dairy product', 'fruit juice', 'isotonic beverage' and low preference and high intake frequency were 'carbonate drink'. The intake frequency of 'pizza', 'sandwich', 'udong', and 'dukbokki' had a positive relationship with sociality. 'Hamburger', 'chicken', 'french fry', 'gimbab', 'mandu', and 'ramyon' showed a positive relationship with anger-out. The intake frequency of 'carbonated drink' had a negative relationship with anger-control, but 'green tea' showed a positive relation with it. 'Carbonate drink', 'isotonic beverage', 'coffee', and 'milkshake' had a negative relationship with anger-out. The explanation power (R2) of intake of fast food and beverage on sociality was 0.019~0.038, and 'carbonated drink' and 'coffee' had a negative influence on sociality. The explanation power (R2) of intake of fast food and beverage on anger expression was 0.011~0.041, and 'carbonated drink' had a negative influence on angercontrol. 'Hamburger', 'carbonated drink', and 'coffee' showed a positive influence on anger-out. From these results, it was necessary to develop the practical eating-out habits program on proper fast food and beverage choice for adolescents.
- 270 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Interrelations Among Beverage Intake, Food Behavior and Personality in Adolescents
- Eun Sil Her, Kyung Hea Lee, Eun Young Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(2):189-198. Published online April 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the influences of the beverage intake on food behavior and personality for 1295 adolescents. The results were as follows. The favorite beverage was 'fruit juice', and preference of 'coffee' was the lowest. 'Milk and dairy product' was highest and 'milkshake' was lowest in intake frequency of beverage. The preference correlated positively(r = 0.391) with the intake frequency of beverage, especially high in 'green tea and black tea'(r = 0.622), 'coffee'(r = 0.581), 'carbonated drink'(r = 0.538), and 'milk and dairy product'(r = 0.501). The explanation power(R2) of beverage preference on beverage intake was 0.153. The explanation power(R(2)) of beverage intake on food behavior was 0.127, and 'carbonated drink' and 'coffee' as well as 'milkshake' had a negative influence on food behavior: however, 'milk and dairy product', 'green tea and black tea', and 'fruit juice' had a positive influence on food behavior. The relationship of beverage intake and sociality was very low(R(2)= 0.013), and 'isotonic drink' and 'green tea and black tea' had a positive influence on sociality. The relationship between beverage intake and anger expression was also very low. 'Coffee' showed a positive relationship with anger-in. 'Carbonated drink' and 'milkshake' showed a positive result with anger-out. 'Milkshake' showed a negative relation with anger-control, but 'green tea and black tea' and 'milk and dairy product' showed a positive relation. From these results, it was necessary to develop the practical nutritioneducation program on proper beverage choice for adolescents leading to better metal and physical status.
- 342 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Snacking Behaviors of Middle and High School Students in Seoul
- Seul Ki Choi, Hyeon Jeong Choi, Nam Soo Chang, Sung Hee Cho, Young Sun Choi, Hye Kyung Park, Hyo Jee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(2):199-206. Published online April 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate snacking behavior in adolescents. We selected one middle school and one high school in 11 school districts in Seoul. The subjects were 1,813 students (904 boys and 909 girls) in 21 schools (11 middle schools and 10 high schools). Subjects reported their snacking behavior: snack frequency, snack type, snack time, with whom to eat snack, place to purchase snack. The subjects were classified into four groups by gender and schooling. The mean snack frequency was 2.8. Girls ate snacks more frequently than boys (p < 0.001). More than half of subjects ate 1 to 3 snacks a day. Only 9.3% of them did not eat any snack. Tangerine was highly ranked in snack type. Each subject groups had different snack time (p < 0.01) and type of snack (p < 0.001). Most snack was consumed alone (46.6%), however they mainly ate fruits and other foods with family. 46.9% of snacks were purchased outside. A typical snack time was 'before dinner' for most snacks except fruits. Unhealthy foods like soft drinks, cookies, chips, candies, chocolates, ice creams had relatively high proportion in snack consumption with friends. In conclusion, adolescents had different snacking behaviors by their age and gender. These results indicate necessities of multi-dimensional efforts at home, school, media and government level considering adolescents' age and gender for their healthy snacking behavior.
- 373 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- A stydy on Nutritional Status and Eating Behaviors of Underweight Adolescent Boys Using 2001 NHANS of Korea
- Min kyung Kwon, Young sook Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(3):235-246. Published online June 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to identify nutritional status and eating behaviors of underweight male adolescents aged 15 to 19 years. The subjects selected by using the data of KNHANS-2001 were 32 underweight boys and 135 normalweight ones. We found that weight, waist and hip circumference of the underweight group were significantly different to normal-weight group, but height and waist-hip ratio were not. Their serum indices belonged within normal ranges and showed no difference between the two groups. Their energy and nutrient intakes were mostly poor. The level and proportion of the subjects below EAR, NAR and INQ of each nutrient were not significantly different between the two groups. There were no difference of frequencies of skipping meals, snacking and eating-out between the two groups, either. When comparing frequencies of food intakes, the underweight group consumed significantly more of fermented fishes and less milk than the normal-weight group. And the former had significantly more rest/sleep, nodoes and supplementation and less regular excercise than the latter. The underweight group perceived more correct self-images than the normal-weight group and they tried more to increase their body weight during weight control practice (p < 0.001). It was concluded that the underweight group showed no different biochemical indices, nutrient intakes, and dietary behaviors to the normal-weight group, but they revealed significantly higher non-active activities like rest and supplementations.
- 310 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Beverage Consumption and Related Factors among Adolescents in the Chungnam Urban Area
- Bok Sun Kang, Myoung Soon Park, Young Sun Cho, Joung Won Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(4):469-478. Published online August 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to investigate the adolescent's beverage drinking pattern and its related ecological factors, a questionnaire survey was conducted with the subjects of 920 middle and high-school students, 450 boys and 470 girls, residing in 4 cities of the Chungnam area. Of the subjects 65% liked, or liked very much, beverages and only 3.7% did not like beverages. They drank beverages 4.3 +/- 4.0 times a week on average, but 10.4% of them drank beverages more than twice a day. Male students drank more frequently than the females. The intake frequency of carbonated drinks was 1.7 +/- 2.3 a week, which was about 40% of the total beverages. However, more students drank mainly ion beverages (33.6%) than carbonated drinks (28.7%). As the students took more balanced food and ate more regularly, their beverage drinking frequency decreased and those taking carbonated drinks also tended to decrease. The more frequent the students took fast food, the more frequent they drank carbonated beverages. The drinking frequencies for beverages or carbonated beverages were also less in students eating cooked rice with sidedishes as breakfast than in students eating others. The drinking frequency for carbonated drinks showed significant correlations with the students' activities such as the time spent using computers and watching TV got longer, the drinking frequency for soft drinks was also higher. When nutritional knowledge was higher, drinking frequency for carbonated drinks got lower. In conclusion, to make the adolescents improve their attitudes toward drinking beverages and to prevent excessive drinking of carbonated drinks, they should be educated not only on the nutritional knowledge and the proper intake of beverages, but also on good dietary habits including balance, regularity, and types of meals. Proper snacking and fast food consumption also should be taught. Since ion beverages were taken more frequently than carbonated drinks among adolescents, further study is recommended on the impact of excessive intake of ion beverages.
- 345 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- A Study on Weight Control, Nutritional Knowledge, Dietary Attitudes and Eating Behaviors among High School Female Students
- Yun Ahn, Hyungmee Kim, Kyungwon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(2):205-217. Published online April 30, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to examine weight control, nutritional knowledge, dietary attitudes and eating behaviors of 370 high school girls and to investigate if there were differences in these variables by weight control status. The weight control attempters (65.1%) had significantly higher body weight and BMI (p<0.001). The difference between desired and current body weight was -9.1 kg in the attempters, showing a significantly higher difference than the counterparts (p<0.001). The attempters also showed more interest toward weight control (p<0.001), but were less satisfied with their body size (p<0.001). Most of subjects (88.1%), especially in the attempters (96.7%) responded that they would try to control their weights in the future. The regular exerciser was 22.9% in the attempters while the percentage of the counterparts was 11.9% (p<0.05). The use of internet or television watching was not significantly different by weight control status. Subjects scored 15.8 out of 20 on a nutritional knowledge scale, which showed a moderate level of knowledge. The nutritional knowledge score was 15.7 for the attempters and 15.8 for the counterparts. None of the nutritional knowledge items reached statistical significance, although the percentages of correct answers regarding weight control or balanced meals were slightly lower in the attempters. The attempters showed more favorable eating attitudes than the counterparts (p<0.001), especially in the attitudes of applying nutritional knowledge to daily life (p<0.01), attitudes for modifying diets (p<0.01) and importance of having adequate meals (p<0.01). The eating behavior was moderate, with mean scores of 31.1 (possible score: 15-45). Subjects showed problems in eating a variety of foods, eating meals regularly, eating slowly, eating breakfast and consumption of some food groups (e.g., dairy foods, fruits). The attempters consumed seaweeds more frequently than the counterparts (p<0.05). Although there were not many significant differences by weight control status, this study suggested that nutrition education for adolescent girls should be planned to provide nutrition information regarding desirable weight control as well as modifying diets and eating behaviors.
- 372 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Indices for Diet Quality Evaluation of Korean Adolescents by Residence Area and Body Size
- Min Young Park, Ji Sook Um, Hwa Jin Hyun, Hae Ryun Park, Young Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(2):180-190. Published online April 30, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to assess several indices of diet quality based on nutrient, food and food group intake of Korean adolescents based on several indices on diet quality according to residence area and body size. Using the data from the 1998 National Health and Nutrition Survey, twenty-four-hour-dietary recalls of a total of 1,110 Korean adolescents aged 13-19 years (male 543, female 567) were analyzed for nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR), index of nutritional quality (INQ), the number of foods (Dietary Variety Score, DVS) and food group consumed (Dietary Diversity Score, DDS). In doing that, it was attempted to apply only the minimum amount of solid foods of Kant's without inclusion of liquid foods because of the very limited variety in Korean foods. Based on weight length index, 13.1% of the subjects were categorized as obese, 14.2%, overweight, 44.4%, normal and 28.3%, underweight. Only vitamin B2 intake was higher in the obese group than in the underweight group. There was no meaningful difference in energy, protein and fat intakes according to the grade of the body size. In terms of residence area, intake of fat, niacin, vitamin B6 and folic acid were lower in the rural areas than in the metropolitan city. Only vitamin E intake was higher in the rural areas. Mean value of NARs (MAR) and INQs (mINQ) was also higher in the metropolitan city than in the rural areas, but there was no significant difference of these two values according to body size of the subjects. Mean DVS was 21.02 for total subjects, and has no difference between male and female and between metropolitan city and other medium-small city. But, the rural areas showed the lowest DVS of 19.05. Mean DDS in which five is a maximum score was 3.3 with no significant difference by sex and by residence area in male subjects. However, in female subjects, DDS in the rural areas was the lowest. According to body size of the subjects, there was no meaningful difference in both scores of DVS and DDS. In conclusion, most indices of nutrient intake and food and food group intake were not significantly different by body size of the subjects, while most indices were significantly different by residence areas: higher in the metropolitan city than in the rural area.
- 290 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study of Weight Control and Associated Factors among High School Female Students
- Yun Ahn, Hyungmee Kim, Kyungwon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(6):814-824. Published online December 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The study purpose was to examine weight control status and related factors among 370 high school girls in Seoul. Factors examined included interest toward weight control, body satisfaction, body image, beliefs regarding weight control and self-efficacy. 65.1% had attempted to control weight and were categorized into attempt group. Those in the attempt group had higher body weight (p<0.001) and BMI (p<0.001) than the counterparts. They tried to control weight 2.9 times on average (22.4 days each time). The major information sources for weight control were internet (62.8%), and TV/ radio (17.1%). Exercise was most commonly used for weight control, followed by reducing meal amount and skipping dinner. The attempt group was less satisfied with body size (p<0.001) and perceived their body sizs as heavier than the counterparts (p<0.001), but they showed more interest toward weight control (p<0.001). The ideal body size of society or the body size that they want was very thin in both groups. Twelve out of 20 beliefs regarding weight control were significantly different between the two groups. The attempt group believed more strongly on the advantages such as increased self-confidence, appearance, attractiveness (p<0.001) and 'good for making friends' (p<0.01). In contrast, the attempt group believed less strongly about the disadvantages including harmful effects on health (p<0.001), parents' dislike, feelings of discouragement (p<0.01) and becoming (p<0.05). The attempt group showed lower overall self-efficacy to control overeating (p<0.05) than the counterparts. Especially, the attempt group felt less control of overeating in situations such as eating-out, after school, when they are with family (p<0.01) or with friends, when they feel hungry, during examination periods and when others offer food (p<0.05). This study suggested that weight management education for adolescents include strategies for changing body image and beliefs regarding weight control, as well as increasing self-efficacy to control overeating.
- 349 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Effects of Smoking, Drinking, Exercise on Body Composition, Nutrient Intakes and Serum Lipids in Male High School Students
- Jung Hee Kim, Young In Chon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(1):19-28. Published online February 29, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was done to investigate effects of smoking, drinking and exercise on body composition, dietary intakes, serum lipids of male high school students in Seoul. Body Composition was analyzed by the Bioelectrical Impedance Fatness Analyzer. Dietary survey was conducted by 24-hour recall method and nutrient intakes were analyzed by the Computer Aided Nutritional analysis program for professional (CAN-Pro). All data were statistically analyzed by SAS PC package program. Mean and standard error were examined for each items. The significant difference was examined by student's t-test. Body composition data showed that protein mass, mineral mass and lean body mass of regular exercisers were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those of irregular exercisers. Energy and protein intakes of male high school students were 1868 kcal/day (69.2% RDA), 68 g/day (91.3% RDA), respectively. Ca, Fe and Vitamin B2 intakes were lower than 2000 RDA. Analysis of serum lipids showed that serum levels of HDL-cholesterol of drinkers were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those of nondrinkers. Overall results imply that smoking and alcohol drinking of adolescent males may not much influence on serum lipids levels because pack-years of smoking or the amount of alcohol drinking was not serious enough to be harmful to health.
- 287 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Factors Associated with Weight Control Experiences among Adolescents: Based on Self-esteem, Body-cathexis, Attitudes toward the Body, Anthropometric Characteristics and Perceptions of Body Shape
- Eun Sil Her, Hyun Jin Kang, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(5):658-666. Published online October 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to investigate among adolescents (total = 729) the relationship between their self-esteem, body-cathexis, their attitudes toward the importance of their bodies, their anthropometric characteristics, their perceptions of their body shapes and their experiences with weight control. The results are summarized as follows: The mean values for self-esteem and body-cathexis were generally low, but these values were significantly higher among boys than girls (p < 0.01 - 0.001). However the mean values for their attitudes toward the importance of their bodies were relatively high and were significantly higher among girls than boys (p < 0.01). The mean values for Percent Ideal Body Weight (PIBW) and Body Mass Index (BMI) were normal and no significant differences between the genders were observed. The distribution of the PIBW and the BMI values showed a higher rate for normal weights among the girlsand a higher rate for underweightedness and obesity among the boys (p < 0.01). With regard to their perception of their body image, among the boys, their current figures were almost identical with their idea of an ideal figure, but among the girls, their idea of an ideal figure was thinner than their current figure. The girls were more dissatisfied with their own body image than the boys (p < 0.001). Fifty-four percent of the subjects had previous weight control experience, and the girls had significantly more experience than the boys (p < 0.001). Their main reason for practising weight control was to lose weight (65.3%). Those who had more weight control experience had lower satisfaction with their body shapes, higher PIBW, higher BMIs or currently had fatter figures. Their standard image of their figures was influenced by TV (40.3%) and friends (36.9%). There was a weakly positive correlation between their self-esteem and their satisfaction with their body shapes, and a weakly negative correlation between their satisfaction with their body shapes and their attitudes toward the importance of their bodies. These results suggest the necessity for an educational program for adolescents as to foster a positive body image. Such a program should consider psychological factors such as selfesteem, satisfaction with body shape and attitudes toward the importance of the body
- 394 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Frequency of Instant Noodle (Ramyeon) Intake and Food Value Recognition, and their Relationship to Blood Lipid Levels of Male Adolescents in Rural Area
- Joung Won Lee, Yeon Ho Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(4):485-494. Published online August 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to investigate the ramyeon intake patterns, food value recognition, and their effects on blood pressure and blood lipid levels, a total of 385 male students aged 13-15 years living in rural area were sampled randomly, and they were surveyed using questionnaire. Blood pressure and fasting serum lipids levels of 123 subjects selected among the total were determined. Of the total subjects 80.3% either liked or liked very much ramyeon and 42.2% of them were eating ramyeon from 1 to 2 times a week,21.1% 5-6 times a week, while 11.7% more than once a day, and 13.1% less than once a month. They took ramyeon from one (56.8%) to two (25.4%) packs each time. Two-third of subjects consumed entire ramyeon soup or more than half of it. Mostly they added egg or onion to ramyeon and took along with kimchi, cooked rice, danmuji, or dried laver. The food value recognition score about ramyeon was 41.33 out of 100 full grade. Comparing to underweight or normal weight subjects, overweight students tended to take ramyeon more frequently when playing with friends and tended to consume less soup of ramyeon. There was a significant negative correlation between ramyeon intake frequencies and HDL-cholesterol levels (r=-.223 p < .05). Moreover, among the normal body weight students (n=72) adjusted with relative weight, ramyeon intake frequencies showed not only a significant negative correlation with HDL-cholesterol level (r=-.244 p < .05), but also significant positive correlations with atherogenic index (r: .249 p < .05) and systolic blood pressure (r: .259 p < .05) . These results suggested that frequent intake of ramyeon with limited sidedishes as a whole meal might have negative influences on blood pressure and serum lipid levels. Nutrition education is needed to have correct food value recognition and proper consumption of ramyeon along with the balanced diet.
- 353 View
- 8 Download

- [English]
- The Development and Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire to Assess Diets of Korean Adolescents
- Kyeong Sook Yim, Tae Young Lee, Hye Soon Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(2):149-159. Published online April 30, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to develop and evaluate the validity of a food frequency questionnaire for Korean adolescents (FFQ-A) which could be used in clinical and epidemiological studies of the lifestyle and health of young people. The FFQ-A was designed to reflect the eating pattern of Korean adolescents, and was based on the 1998 Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey Reports. The FFQ-A had 25 food categories. A total of 125 subjects (aged 13 to 15 years) was recruited from a randomly chosen middle school in a middle-income neighborhood in Anyang, South Korea. Each subject completed a FFQ-A, as well as a three-day dietary record. Data from 117 subjects (boys 47, girls 70) was used in the final analyses. Data on the nutrients was analyzed to estimate the Pearson correlations, Spearman rank-order correlations and agreement with categories. The validity of the FFQ-A was assessed relative to a three-day dietary record. The Pearson correlation coefficients for all the subjects were 0.94, 0.87, 0.77, 0.79, 0.49 and 0.68 for energy, carbohydrate, protein, fat, calcium, and iron, respectively. Similarly the Spearman rank-order correlation coefficients were 0.94, 0.85, 0.79, 0.81, 0.46, and 0.77 for energy, carbohydrate, protein, fat, calcium and iron, respectively. The Kappa values for energy, carbohydrate, protein, fat, calcium, and iron were 0.88, 0.67, 0.63, 0.67, 0.26, and 0.59, respectively. The percentage for misclassification of the lowest quartile into the highest quartile or vice versa ranged from 0% (energy, carbohydrate, or fat) to 16.7% (Vitamin C). Therefore the FFQ-A has a reasonable ability to assess the energy, carbohydrate, protein and fat intakes as estimated from a three-day dietary record of Korean adolescents.
- 377 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- A Study on Obesity and Food Habit of Adolescents in Yeosu, Jeonnam Area
- Bok Mi Jung, Il Su Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(2):129-137. Published online April 30, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was to investigate obesity and food habit of adolescents in Yosu, Chonnam area. It was surveyed using questionnaires with 551 adolescents consisted of 280 boys and 271 girls. The questionnaire included general characteristics, obesity index, eating behavior and snack intake pattern. The results were as follows. The proportion of obese subjects was 10% by Rohrer index but the rate of obesity by body mass index was 3.3%. The self perception of body shape were optimal (47.9%), fat (29.8%), slightly lean (14.5%), obese (4.7%) and lean (3.1%). Generally, the proportion of girls responded them as "fat" was greater than boys. The greater percentage of boys responded them as "lean" than girls. The subjects don't take breakfast regularly were 50.8% and the main reason for skipping breakfast was the lack of time (55.2%). The main type of breakfast was cooked rice (78.9%). The most favorite snacks turn out to be cookies (36.5%) and 45.7% of subjects take snacks during the rest. The reason for taking snacks was "feeling hungry" 52.6%) and the taste was the most important factor of snack choice. The results of this study showed that the most of subjects were not in a serious obesity condition, and their eating habits were generally satisfactory. Also, this study has found that it is necessary to educate the students the importance of regular intake of a balanced meal.
- 346 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



