Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Ultra-processed food intake and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):410-418. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the intake of ultra-processed foods (UPF) and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents.
Methods
This study used 24-hour dietary recall data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2023). In total, 1,720 adolescents aged 12–18 years were included in this study and categorized into quartiles based on the percentage of energy intake from the UPF. Nutritional status, contributing subgroups of UPF intake, and healthy dietary practices were examined using Health Plan 2030 indicators across quartiles of UPF intake.
Results
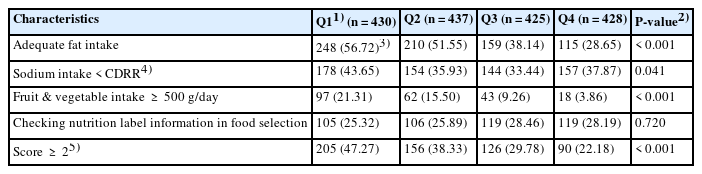
The nutrient intake of protein, vitamins (A, B1, B2, niacin), and minerals (iron, potassium) was the lowest in the fourth quartile of UPF intake compared with the first quartile (P for trend < 0.001), whereas calcium intake increased across quartiles, from 47.68% in the first quartile to 58.51% in the fourth quartile (P for trend < 0.001). The main contributing subgroups to UPF intake differed across quartiles of UPF intake, and the highest contributing subgroups were ‘instant noodles and dumplings,’ ‘desserts, cakes, and ice cream,’ and ‘sauces and seasonings.’ Healthy dietary practices were the lowest in the fourth quartile (22.18%, P < 0.001), and the proportions of appropriate fat and fruit/vegetable intake were significantly lower in the higher quartiles of UPF intake (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that a lower UPF intake was associated with better nutritional status and healthy dietary practices in Korean adolescents. These findings provide fundamental evidence for promoting healthier food choices and balanced dietary practices.
- 451 View
- 20 Download

- [English]
- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
- Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):274-285. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00157

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Although diet quality is known to be associated with environment and individuals’ characteristics, these have not been studied together. We determined the association of diet quality with regional factors stratified by individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics.
Methods
This study used nationally representative survey data on regional factors (2010–2020) and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data on individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics (2013–2018). Community-dwelling Koreans aged ≥ 20 were included (n = 26,853). Regions were categorized into metropolitan cities or provinces and subsequently according to regional factors (level of educational attainment, income per capita, food security status, physical activity facilities, time to the nearest large retailer, and internet use of the region). Individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics included age, education status, income, and number of household members. Diet quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI).
Results
In the entire population, education status of metropolitan cities was positively associated with the KHEI. Shorter time to retailers and higher internet use were positively associated with the KHEI in metropolitan residents with higher income levels but negatively associated with the KHEI in those with lower income status. Among provincial residents with a low education status or income, regional physical activity facilities were positively associated with the KHEI.
Conclusion
The association between diet quality and regional factors varied depending on the resident’s sociodemographic characteristics. Both regional and individual sociodemographic factors must be considered to address gaps in nutritional equity.
- 1,632 View
- 30 Download

- [Korean]
- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
- Ji-Won Kang, Su-Jin Lee, Sil-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):224-236. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00108

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To reduce urban carbon emissions, in this study, we aimed to suggest strategies for disseminating the planetary health diet (PHD) guidelines to adult cafeterias in a government worksite in Seoul based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB) and focus group interviews (FGI).
Methods
A total of 132 adults who worked at a government worksite in Seoul and used its cafeteria were included for a TPB-based survey. Factor analyses and multiple regression were used to investigate the relationships between attitude (cognitive•affective), subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control (PBC, internal•external) and the behavioral intention to adopt the PHD. To identify the contextual factors related to PHD dissemination, 14 participants underwent in-depth interviews.
Results
Affective attitudes and PBC (internal•external) constructs of the TPB were significantly related with the intention to adopt PHD: external PBC (β = 0.324, P < 0.001), internal PBC (β = 0.269, P < 0.01), and affective attitudes (β = 0.226, P < 0.05). The FGI results highlighted the insufficiency of simply providing healthy meals to encourage the adoption of PHDs, but that menu development and natural acceptance strategies are needed to increase palatability. In addition, the need for strategies to promote PHDs at an organizational level was identified, as it is directly influenced by the company of partners with whom one dines. Furthermore, users' perceptions of how “Meals for the Planet” are delivered and suggestions for its improvement were also interpreted.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that users' beliefs, convictions, and emotions are important while promoting or educating individuals about sustainable PHDs. Our findings are expected to help local governments or private group cafeterias that wish to introduce PHDs in the future, given the growing importance of environmentally conscious eating. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Planetary Health Diet Adherence in Korean Adults: Association with the Korean Healthy Eating Index
Su-Jin Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrients.2025; 17(19): 3060. CrossRef - Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 431. CrossRef
- Planetary Health Diet Adherence in Korean Adults: Association with the Korean Healthy Eating Index
- 1,343 View
- 57 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Healthy eating intentions among adults in China: a cross-sectional study of northern and southern regions and city tiers based on the theory of planned behavior
- Yi Jiang, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):114-126. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The theory of planned behavior (TPB) has been widely employed to predict healthy eating intentions. Regional differences may affect dietary habits, health status, and personality traits, whereas variations in urbanization influence accessibility to fresh and healthy food, thereby impacting TPB components. This study aimed to explore whether regional differences between northern and southern China including city-tier development are associated with healthy eating intentions among Chinese adults.
Methods
The study included data from 2,114 Chinese adults aged 19–64 years collected between 2019 and 2023. Participants were categorized by geographic region (north or south) and city-tier status (first-tier or other).
Results
Compared to individuals from northern first-tier cities, those from southern regions exhibited stronger attitudes, perceived behavioral control (PBC), and intention to eat healthily. Participants from other cities in the north had more positive attitudes, subjective norms, PBC, and intentions to participate in healthy eating. Furthermore, residents of southern cities revealed weaker subjective norms than those of cities in the north. The adjusted odds ratio (OR) for compliance with intention to engage in healthy eating was higher among participants from other cities in both the north and south compared to those from northern first-tier cities (northern other cities: OR = 2.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.49–3.97, P < 0.001; southern other cities: OR = 1.95, 95% CI: 1.08–3.51, P = 0.027). No significant differences existed among the subjects from first-tier cities according to their geographic regions. These trends remained consistent even after including the interaction term between geographic regions and city-tier classification.
Conclusion
These findings underscore the complexity of regional variations influencing dietary intentions and indicate that tailored health promotion strategies should incorporate regional characteristics. Future research should explore underlying factors, including regional cultural influences, to better inform policies and interventions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
Md. Asaduzzaman Babu
Food and Humanity.2025; 5: 100779. CrossRef
- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
- 1,798 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of clinical characteristics and dietary intakes according to phenotypes of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Jin Kim, Ji-Sook Park, Sung-Rae Cho, Daeung Yu, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):127-139. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Clinical nutrition treatment is the central part of diabetes management, such as prevention, treatment, and self-management of diabetes, and personalized clinical nutrition treatment, which enables improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study aimed to contribute to the improvement of appropriate nutrition management in personalized treatment for obese and non-obese diabetes patients.
Methods
T2DM patients were recruited as participants, and 36 final participants were assigned to the lean diabetes mellitus group (LDM; body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and the obese diabetes mellitus group (ODM; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). We assessed the dietary intakes, body composition, dietary habits, the Korean version of obesity-related quality of life, and biochemical indices.
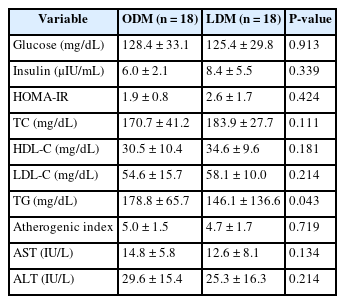
Results
According to the phenotype’s comparison, the ODM group had a high prevalence of T2DM complications and hypertension, had a dietary habit of less than 10 minutes of mealtime duration and preferred fast food intake, and had a low obesity-related quality of life. However, the LDM group had a high choice of Korean dishes at the time of eating out and a high intake of vitamin C, and iodine because of the intake of vegetables and seaweeds.
Conclusion
We observed differences in diet, nutrient intake, and clinical characteristics according to the phenotype of T2DM patients. In particular, obese diabetes patients have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, bad dietary habits, and low obesity-related quality of life. Therefore, personalized nutrition treatment is needed in consideration of the risk of cardiovascular disease and dietary habits for patients in the ODM group, as well as determining the energy requirements of Korean patients with T2DM.
- 2,184 View
- 32 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung–Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):150-162. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00038

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To determine the association between night eating habits and oral health in adolescents.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 were analyzed. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed the frequency of night eating per week, dietary habits, oral health characteristics, and factors affecting the presence of symptoms of poor oral health.
Results
Almost thirty-seven percent (36.6%) of Korean adolescents have eaten at night one to two times per week and 23.0% more than three times per week. An increased frequency of night eating was associated with poor dietary habits. Adolescents who consumed more at night were less likely to have breakfast, drink water, and eat fruit, while their consumption of fast food, sweet drinks, and high-caffeine drinks increased (P < 0.001). An increased frequency of night eating was also associated with poor oral health. In a logistic regression analysis, more frequent night eaters were significantly less likely to brush their teeth at least three times per day (odds ratio [OR], 0.78; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75–0.82; P for trend < 0.001), and brush their teeth before going to sleep (OR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.65–0.75; P for trend < 0.001), while they were more likely to experience sealant (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.13–1.26). More frequent night eaters were significantly more likely to have tooth fracture (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.30–1.53; P for trend < 0.001), tooth pain when eating (OR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.50–1.67; P for trend < 0.001), toothache (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.52–1.70), and bad breath (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.43–1.60).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that frequent night eating is linked to symptomatically poor oral health in adolescents. Therefore, oral health education programs related to dietary habits are necessary to reduce the potential of night eating to negatively influence dietary habits and oral health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Bo Young Park, Eun Bi Sim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(4): 370. CrossRef
- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,545 View
- 59 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
- Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):140-149. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to examine regional differences in dietary behavior and satisfaction between urban and rural residents in Korea, identifying key factors associated with dietary satisfaction in each group to deepen understanding of these variations.
Methods
The data were obtained from the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food 2022 by the Korea Rural Economic Institute. The analysis involved 6,365 adult participants, using the complex survey χ2-test and complex survey t-tests to compare dietary behavior across regions and complex survey regression analysis to explore factors related to dietary satisfaction. Data were analyzed with R 4.3.1 (for macOS; Posit PBC).
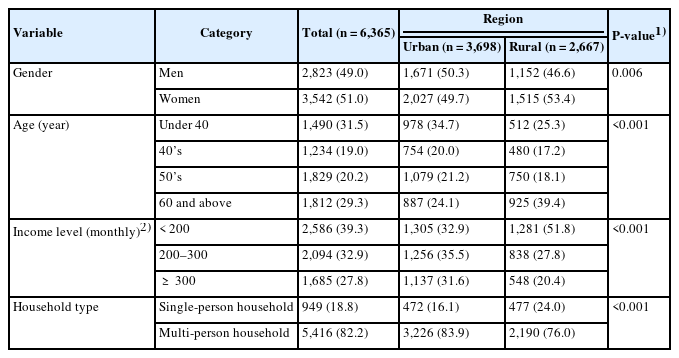
Results
Urban and rural areas differed in consumer characteristics such as gender, age, income, and household type, as well as in food consumption behaviors and in dietary competencies associated with purchasing and intake. Specifically, dining out and processed food consumption were more prevalent in urban areas, whereas home-cooked meals were more frequent in rural areas. Overall, dietary competencies were higher among urban residents. However, there was no significant difference in dietary satisfaction between the two regions. This finding suggests that satisfaction is based on subjective evaluations, with consumers in each region forming satisfaction in ways that align with their environment and lifestyle. Accordingly, the factors contributing to dietary satisfaction differed by region. In urban areas, information utilization competency and maintaining a balanced diet played a significant role in dietary satisfaction, whereas in rural areas, regular mealtimes were more influential. Urban consumers reported higher dietary satisfaction when meals provided a sense of appropriate convenience, whereas rural consumers showed greater satisfaction when meals were shared with family at home.
Conclusion
The findings indicate regional differences in food consumption behaviors and dietary competencies, as well as variations in how consumers achieve dietary satisfaction. These insights provide a foundation for developing dietary policies and programs aimed at improving dietary satisfaction.
- 1,518 View
- 52 Download

- [English]
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):103-113. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00255
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors such as medication use, dietary supplementation, dietary habits, and physical activity among Koreans aged 20–60 years.
Methods
Data from a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) living in Seoul and Gyeonggi provinces in Korea were analyzed to assess the relationship between health behaviors and dietary supplements (DSs) related to self-care. Based on self-care levels, the participants were classified into three groups: low (LS, n = 124), medium (MS, n = 78), and high (HS, n = 98).
Results
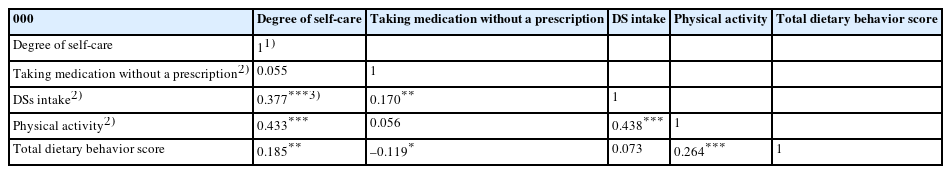
DSs (P < 0.001), physical activity (P < 0.001), recognizing the perceived health benefits of self-care (P < 0.001), self-care when sick (P = 0.039), and the reasons for self-care (P = 0.028) differed among the self-care groups. Daily diet frequency (P = 0.001), breakfast frequency (P = 0.026), regular exercise (P < 0.001), DSs use rate (P < 0.001), DSs use frequency (P = 0.013), and total dietary behavior score (P < 0.001) also differed significantly depending on the degree of self-care. The degree of self-care was significantly and positively correlated with DSs intake (r = 0.377, P < 0.001), physical activity (r = 0.433, P < 0.001), and total dietary behavior score (r = 0.185, P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The results demonstrated that the degree of self-care was related to DSs, physical activity, and total dietary behavior scores in Korean adults. Additionally, self-care capacity should be increased through health-related behaviors based on health education programs.
- 2,924 View
- 56 Download

- [English]
- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
- So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):27-39. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00031
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the differences in food purchase frequency among single-person households by gender and age group and explored the characteristics of single-person household groups according to their food purchase patterns.
Methods
Utilizing data from the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods conducted by the Korea Rural Economic Institute, this study examined food purchase frequencies among 966 single-person households. Data were analyzed using Rao-Scott chi-square tests, ANCOVA, ANOVA, and K-modes hierarchical cluster analysis.
Results
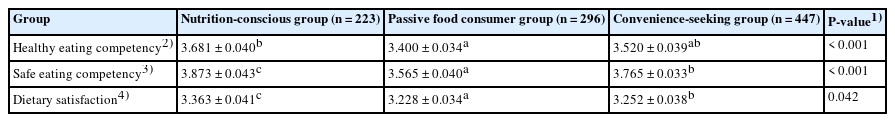
Significant differences were observed in the food purchase frequencies of single-person households for fresh and convenient food. Women displayed higher purchase frequencies for fish, vegetables, and fruits, whereas men showed higher purchase frequencies for convenient foods (P < 0.005). Single-person households aged 39 years and younger exhibited lower purchase frequencies for vegetables (P < 0.005) and fish (P < 0.001) and substantially higher frequencies of convenient food purchases (P < 0.001). Additionally, this study identified three distinct single-person household groups based on food purchase pattern: the “nutrition-conscious” group, which exhibited high purchase frequency for fresh foods; the “convenience-seeking” group, which showed high purchase frequency for all types of convenient foods; and the “passive food consumer” group, which displayed relatively low purchase frequency for both fresh foods and convenient foods. The socio-demographic characteristics of single-person households differed significantly across these three groups, with the “passive food consumer” group and “convenience-seeking” group exhibiting lower healthy eating competency (MN(nutrition-conscious group) = 3.68, MP(passive-food-consumer group) = 3.40, MC(convenience-seeking group) = 3.52, P < 0.001), safe eating competency (MN = 3.87, MP = 3.57, MC = 3.77, P < 0.001), and satisfaction (MN = 3.36, MP = 3.23, MC = 3.25, P = 0.04) than the “nutrition-conscious” group.
Conclusion
This study underscores the need for targeted nutrition programs to address the unique needs of single-person households depending on their characteristics. Specifically, this study highlights the importance of targeted interventions for “convenience-seeking” and “passive food consumer” to promote dietary competency and encourage healthy dietary behavior. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Secular trends in dietary patterns among Korean adults: using data from the 2007–2022 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey
Eunyoung Tak, Juhae Kim, Heejin Lee, Minji Kang
Nutrition Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Secular trends in dietary patterns among Korean adults: using data from the 2007–2022 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey
- 11,204 View
- 92 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Jounghee Lee, Juhyun Lee, Wookyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):75-88. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to identify and analyze how different South Korean lifestyles impact attitudes towards pork consumption.
Methods
We implemented a cross-sectional survey targeting 705 adult consumers in South Korea using hierarchical and K-means cluster analyses. Respondents were classified into three relevant lifestyles: (1) domestic preference, (2) price-sensitive, and (3) quality-experience-oriented. The importance-performance analysis was employed to evaluate discrepancies between how they rated pork consumption using factors of “importance” and “satisfaction”. We employed Borich’s needs assessment and the Locus for Focus model to prioritize management areas.
Results
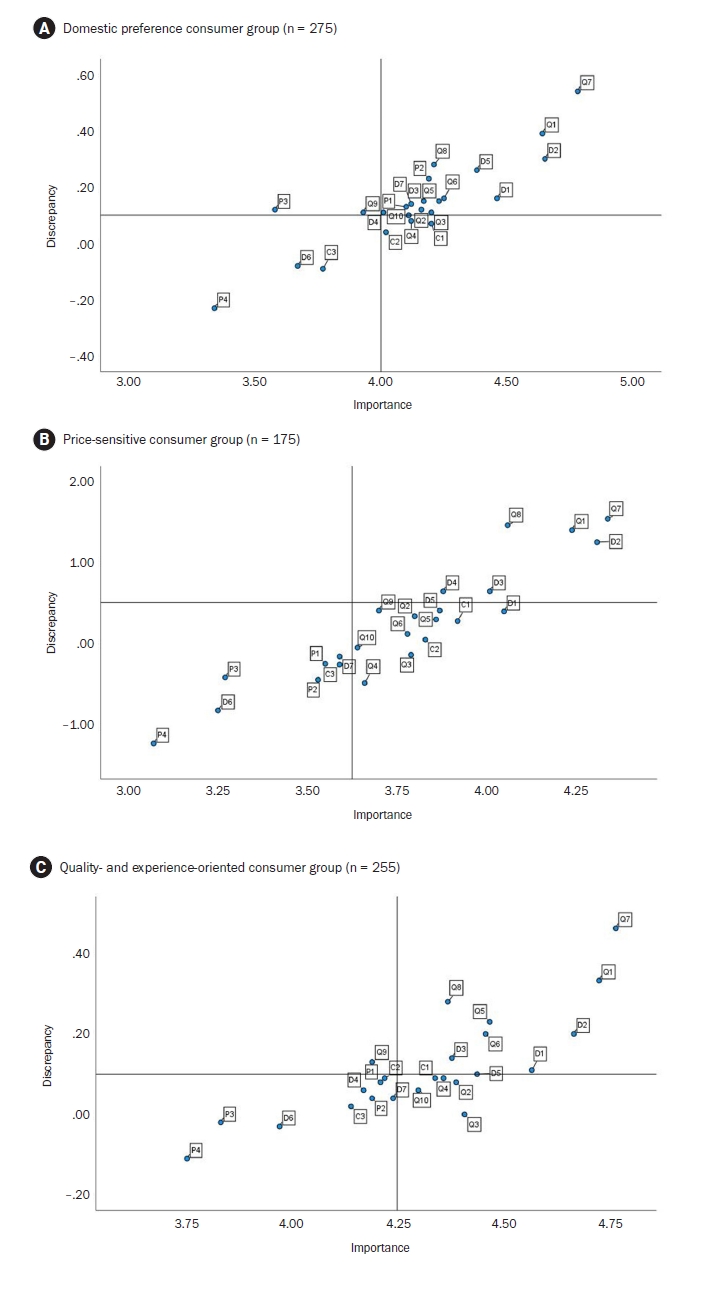
The research findings highlight that unpleasant odor/smell (Q7) and hygiene (Q1) were common key areas for management across all consumer groups, emphasizing their importance in enhancing pork consumption satisfaction. Among the groups, the domestic preference group showed high importance-performance discrepancies in attributes like expiry date (D2), suggesting a need for strengthened trust in domestic pork distribution and information transparency. The price-sensitive group prioritized economic factors, with fat thickness (Q8) identified as an essential management area. The quality-experience-oriented group emphasized sensory qualities such as juiciness (Q6) and meat color (Q5), with off-flavors (Q7) displaying the largest discrepancy. These results show the significant role of sensory attributes in consumer satisfaction.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the multidimensional nature of pork consumption behavior, emphasizing the need for tailored strategies across consumer groups. Managing hygiene (Q1) and reducing off-flavors (Q7) are critical for all segments, while group-specific strategies include managing sensory quality for the quality-experience-oriented group, providing product information (D2) to increase trust for the domestic preference group, and emphasizing value for money for the price-sensitive group.
- 1,976 View
- 43 Download

- [English]
- Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
- Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):382-395. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00010

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated whether outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors differed according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students. Methods: The participants were students recruited from nine universities in Seoul, Korea. An online survey was conducted, and data from 351 participants were analyzed. Participants were classified into pre-action and action stages based on adequate sodium intake. Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, analysis of covariance, and correlation analysis. Results: Participants in the action stage (22.8%) felt fewer disadvantages of eating sodium adequately compared to those in the pre-action stage (77.2%, P < 0.001) and perceived more self-efficacy for healthy eating behaviors (P < 0.001) and controlling sodium intake (P < 0.01). The participants in the action stage also showed more desirable eating behaviors than those in the pre-action stage, including general eating behaviors, behaviors related to sodium intake, and sodium checks (P < 0.001). The physical environment in the action stage was more supportive of adequate sodium intake (P < 0.05). Eating behaviors, self-efficacy, and outcome expectations were significantly correlated with the stages of change; however, some differences were noticed in the correlation of the subscales of variables with the stages of change when examined by sex. Conclusion: We observed differences in factors according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake. For the pre-action stage, nutrition education can be planned to modify negative expectations of eating adequate sodium, foster self-efficacy, and practice general eating behaviors and behaviors to gradually reduce sodium intake. It is also necessary to alter the physical environment to reduce sodium intake. In the action stage, support and reinforcement are needed to continually practice and maintain desirable eating behaviors. Nutrition education for women may be planned using multiple paths, whereas a simple strategy may be useful for men.
- 2,647 View
- 48 Download

- [English]
- Exploring the customer perceived value of online grocery shopping: a cross-sectional study of Korean and Chinese consumers using Means-End Chain theory
- Xinyu Jiang, Hyo Bin Im, Min A Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):318-335. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Despite the growing market share of online grocery shopping, there is a need to understand customer perceived value due to the ongoing advancements in information technology. This study explores the connections between attributes, consequences, and values. Additionally, it conducts a cross-country comparison of consumers’ online grocery shopping behaviors to gain a deeper understanding of consumer market segments and any potential variations among them.
Methods
Data was collected through an online questionnaire survey conducted from May 1 to 15, 2024, targeting 400 consumers in Seoul, Korea, and Shanghai, China, who have experience with online grocery shopping. The survey utilized the Means-End Chain theory and association pattern technique hard laddering. Data collation and analysis were conducted using the IBM SPSS Statistics 28.0 program. The LadderUX software was employed to analyze the links between attributes, consequences, and values and create the consumer purchasing process’s implication matrix and hierarchical value map (HVM).
Results
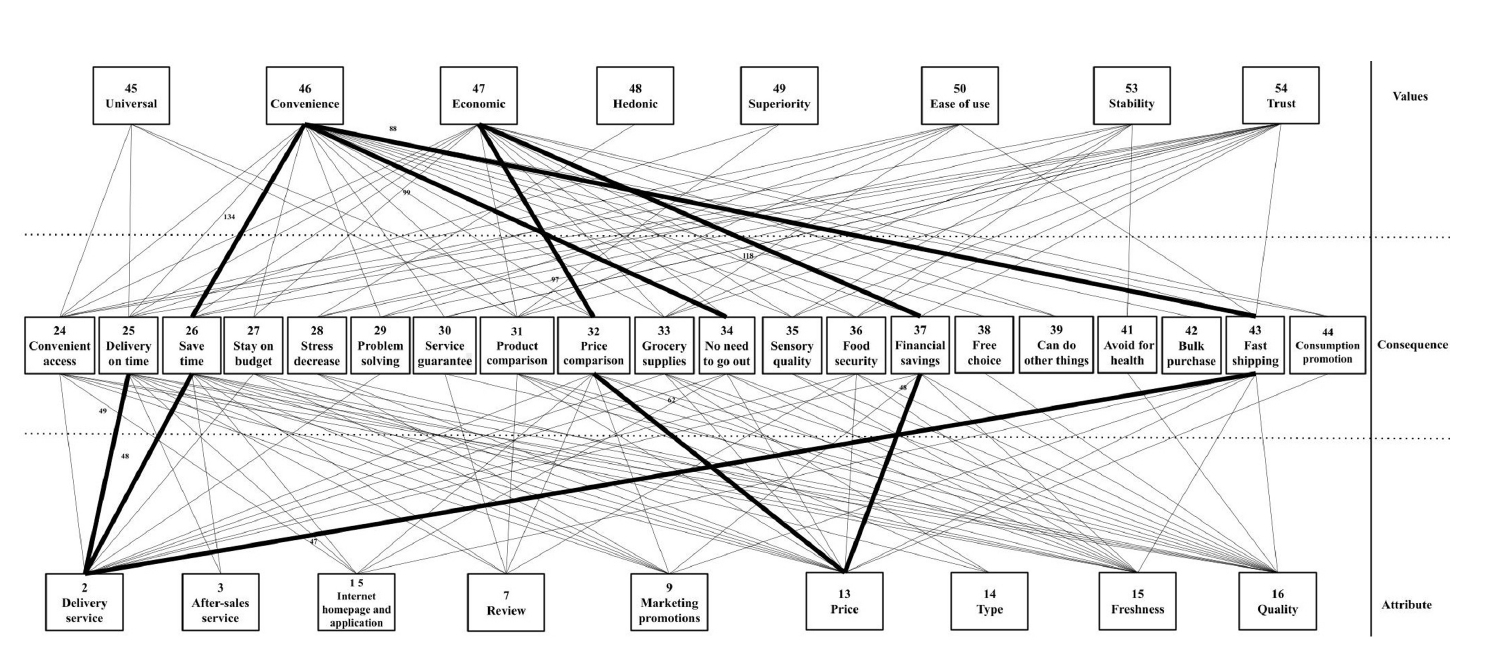
The study identified key attributes that influence online grocery shopping decisions, including delivery service, price, freshness, and quality. Korean consumers demonstrated a higher sensitivity to price (19.0%) and delivery service (17.0%). In contrast, Chinese consumers prioritized delivery service (15.0%) and after-sales service (14.8%). Commonly cited consequences included time saving (12.6% for Koreans, 11.3% for Chinese), whereas prevalent values encompassed convenience (36.8% for Koreans, 19.6% for Chinese) and economic value (26.6% for Koreans, 14.7% for Chinese). The HVM underscored these insights, highlighting diverse consumer preferences and country-specific nuances.
Conclusions
The findings highlight the current state of online food consumption and consumers’ value systems, revealing variations among countries. These findings offer empirical insights that can be used to create customized global marketing strategies that resonate with various consumer preferences and market dynamics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the stage: how performing arts tourism shapes tourist perceptions and destination image
Islam Elbayoumi Salem, Mohammed Ali Bait Ali Sulaiman, Enrico di Bella, Sara Preti, Mohamed Kamal Abdien, Ahmed Magdy
Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights.2026; 9(1): 375. CrossRef
- Beyond the stage: how performing arts tourism shapes tourist perceptions and destination image
- 5,936 View
- 77 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
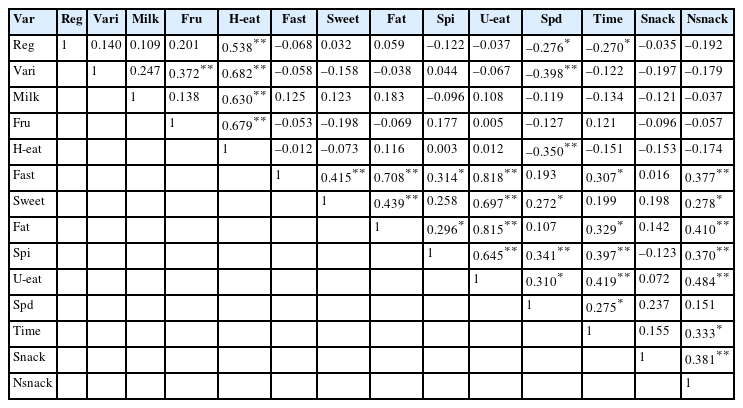
- The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
- Minji Kim, Meera Jang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):278-287. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigates the relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior among elementary school students. Methods: This survey was conducted on 4th- to 6th-grade students at elementary schools in Gangneung from September 6th to September 15th, 2023. Of the 129 copies of the questionnaire that were distributed to 5 schools, 66 copies (51.2%) were returned. Results: Compared to the nationwide statistics, the smartphone ownership rate of elementary school students in Gangneung was lower, but the rate of smartphone overdependence was higher. Smartphone dependence was 21.12 points for study subjects and 26.00 points for the overdependence risk group (Org). Compared to national statistics, the self-control failure factor was higher, so study participants in Gangneung City are thought to have great difficulty with self-control. The Org’s weekend smartphone use time of 7.54 hours was significantly more than the general user group (Gug)’s 4.06 hours. The number of days in which the Org consumed late-night snacks per week was 2.92 days, and the Gug had 2.15 days, but the difference was not significant. Eating fast food showed a positive correlation with eating sweet food, eating fatty food, and eating heavily seasoned food. It was found that frequent consumption of fast food is closely correlated with unhealthy eating behavior. Weekend smartphone use time showed a significant positive correlation with smartphone dependence and the number of days late-night snacks consumed per week. Conclusions: Study participants in Gangneung are more dependent on smartphones than national statistics. Smartphone dependence had a negative correlation with healthy eating behavior and a correlation with average unhealthy eating behavior.
- 3,695 View
- 54 Download

- [English]
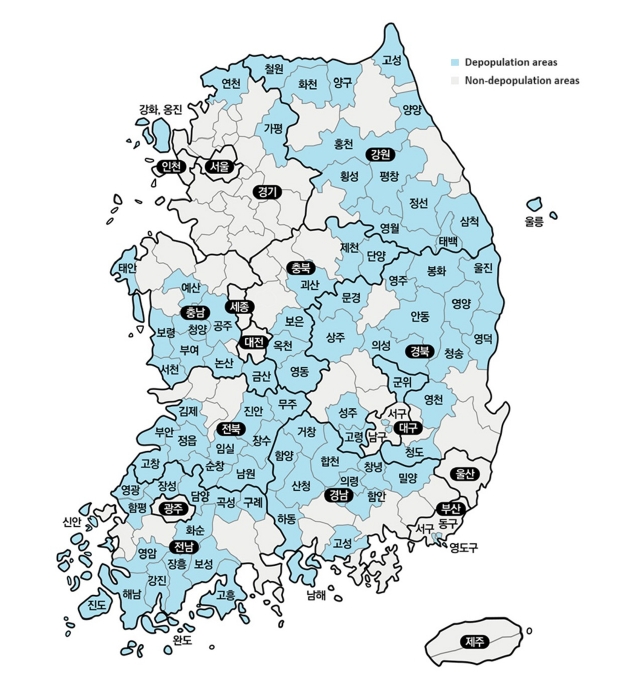
- Analysis of health behavior changes among residents in depopulation areas in Korea: a cross-sectional study based on Community Health Survey data from 2010 to 2019
- Miyong Yon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):348-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The total population of Korea began to decline in 2019; in particular, the population in rural areas has been rapidly decreasing and is aging. Therefore, the government has designated depopulation areas and is seeking ways to support them. To assess whether health disparities exist between areas with population decline and those without, this study used community health survey data to observe temporal changes in health behaviors between the two types of areas. Methods: The analysis used Community Health Survey data from 2010 to 2019, and regional classification was divided by depopulation areas designated by the Ministry of the Interior and Safety. Trends in health behavior and chronic disease prevalence between depopulation and non-depopulation areas were analyzed. All analyses were conducted using complex sample analysis procedures in SAS 9.4 software. Results: The smoking rate steadily decreased in both depopulation and non-depopulation areas, whereas the high-risk drinking rate increased slightly. The walking practice rate did not improve in depopulation areas compared to non-depopulation areas. Furthermore, nutritional labeling usage rate was consistently lower in depopulation areas than in non-depopulation areas, with the gap being the largest. The prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension showed that the gap between depopulation and non-depopulation areas is continuously increasing. Conclusions: Health behaviors in depopulation areas have not improved, and the prevalence of chronic diseases is increasing rapidly. Therefore, the demand for health care services that support healthy lifestyle practices and chronic disease management in these areas is expected to increase.
- 2,860 View
- 28 Download

- [English]
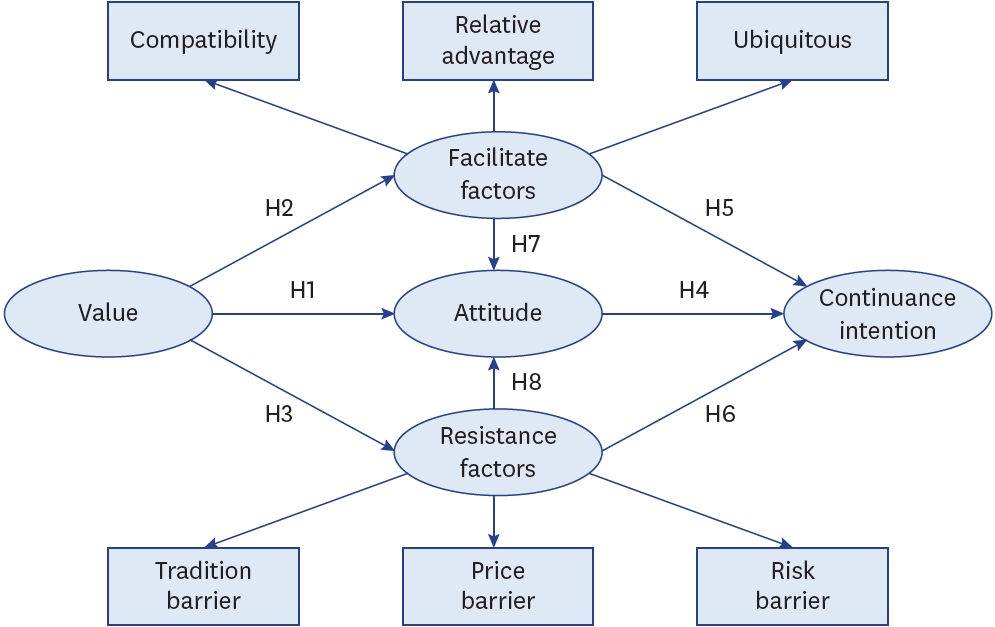
- Factors influencing consumers’ continuance intention in online grocery shopping: a cross-sectional study using application behavior reasoning theory
- Binglin Liu, Min A Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):199-211. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.199
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Online grocery shopping has gained traction with the digital transformation of retail. This study constructs a behavioral model combining values, attitudes, and reasons for behavior—specifically, facilitators and resistance—to provide a more novel discussion and further understand the relative influences of the various factors affecting continuance intention in online grocery shopping.
Methods
Data were collected through an online questionnaire from consumers who had engaged in online grocery shopping during the past month in Seoul, Korea. All collected data were analyzed using descriptive analysis, and model validation was performed using partial least squares structural equation modeling.
Results
Continuance intention is primarily driven by facilitative factors (compatibility, relative advantage, and ubiquity). Attitude can also positively influence continuance intention. Although resistance factors (price, tradition, and risk) do not significantly affect continuance intention, they negatively affect attitude. Values significantly influence consumers’ reasoning processes but not their attitude.
Conclusions
These findings explain the key influences on consumers’ online grocery shopping behavior in Seoul and provide additional discussion and literature on consumer behavior and market management. To expand the online grocery market, consumers should be made aware of the potential benefits of the online channel; the barriers they encounter should be reduced. This will help sustain online grocery shopping behavior. Furthermore, its positive impact on attitude will further strengthen consumers’ continuance intention. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Modelling the mass adoption potentials of fashion-augmented reality among the young consumers: evidence from an emerging economy
Mohima Akther, Mohammad Nurul Hassan Reza, Abdullah Al Mamun, Norzalita Abd Aziz, Marvello Yang
Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal.2025; 29(3): 459. CrossRef
- Modelling the mass adoption potentials of fashion-augmented reality among the young consumers: evidence from an emerging economy
- 7,548 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung-Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):156-170. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the association between how often Korean adolescents watch Mukbang and Cookbang videos and their dietary habits.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 was analyzed for this study. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed various aspects, including demographics, frequency of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos per week, dietary habits, health behaviors, and mental health factors.
Results
Nearly a third (29.3%) of Korean adolescents watched Mukbang and Cookbang videos one to four times a week, while 13.5% watched them more than five times weekly. Females, those with lower academic achievement, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds were significantly more likely to be frequent viewers (P < 0.001). Increased viewing frequency was associated with poorer dietary habits. Adolescents who watched more frequently were less likely to eat breakfast and consume fruits and milk, while their consumption of fast food, high-caffeine drinks, sugary drinks, and late-night snacks increased (P < 0.001). Higher viewing frequency correlated with increased feelings of stress, depression, and loneliness (P < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis confirmed these associations. More frequent viewers were significantly less likely to eat breakfast (odds ratio (OR), 0.63; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.58–0.68), and more likely to consume fast food (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.69–2.02), high-caffeine drinks (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30–1.56), sugary drinks (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.41–1.67), and late-night snacks (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.25–1.51).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that frequent exposure to Mukbang and Cookbang content is linked to unhealthy dietary habits in adolescents. Educational programs may be necessary to mitigate the potential for these videos to negatively influence dietary choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
Seung Jae Lee, Yeseul Na, Kyung Won Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2652. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef
- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
- 3,749 View
- 103 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Exploring factors of nutrition teachers’ intentions for sustainable dietary education in South Korea: an application of the theory of planned behavior
- Eunseo Yang, Borham Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):114-128. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the perception of nutrition teachers and the factors influencing their intention toward sustainable dietary education utilizing the theory of planned behavior (TPB).
Methods
The self-administered online survey was completed by nutrition teachers in Jeollanam-do, South Korea. A total of 151 valid questionnaires were analyzed. Factor analysis and multiple regressions were employed to test the research model.
Results
The study findings demonstrated that all TPB variables significantly influenced the sustainable dietary educational intention, with the degree of influence ranking as follows: external perceived behavioral control (β = 0.417), attitude (β = 0.240), internal perceived behavioral control (β = 0.207), and subjective norms (β = 0.181). For external perceived behavioral control, nutrition teachers and elementary schools exhibited higher levels compared to dietitians and middle/high schools, respectively. The participants in sustainable dietary education training programs exhibited a higher level of internal perceived behavioral control compared to those who did not participate. The highest perception levels were reported for attitude (4.26), followed by subjective norms (4.02), internal perceived behavioral control (3.67), and external perceived behavioral control (3.20).
Conclusions
This study affirmed that the TPB variables elucidated the sustainable dietary educational intentions of nutrition teachers. The significant impacts of external and internal perceived behavioral control, attitude, and subjective norms on educational intentions were confirmed. Consequently, proactive support from schools and governments is essential to enhance the facilitating factors and mitigate the barriers toward sustainable dietary education in schools. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
Ji-Won Kang, Su-Jin Lee, Sil-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 224. CrossRef - An educational needs analysis of sustainable dietary education for nutrition teachers: an application of the IPA, Borich needs assessment and The locus for focus model
Eunseo Yang, Borham Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 372. CrossRef
- Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
- 1,721 View
- 39 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Health behaviors and eating habits in people’s 20s and 30s according to food content usage level on social media: a cross-sectional study
- Seo-Yeon Bang, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):392-403. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.392
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was intended to investigate adults’ health behaviors and eating habits according to their levels of social media use.
Methods
From May 27 to July 11, 2022, an online survey was conducted of 452 male and female social media users in their 20s and 30s, and their eating habits and health behaviors were compared and analyzed according to their degree of social media use. For each of the three levels of food content use, the frequency of social media content use, and the total score range of average social media viewing time per day were divided into three parts, and a group with a score of less than 2 points was classified as low-use; a group with a score of 2 or more and less than 3 points was classified as middle-use; and a group with a score of 3 points or more was classified as high-use.
Results
The use of food content was higher in women than in men (P < 0.001), and higher in those in their 20s than in those in their 30s (P < 0.001). The group with a high level of food content use showed a higher rate of post-use hunger than the group with a low level (P < 0.01). The experience of eating after using food content was also higher in the group with a high level of use than in the group with a low level of use (P < 0.001). The group with a normal or high level of food content use had more negative eating habits than the group with a low level.
Conclusions
The study highlighted the need to provide desirable food content to people in their 20s and 30s with negative eating habits and to promote them so that they can use the right healthy nutrition–related content. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Eating Habits and Health Behaviors According to Long-Form and Short-Form Mukbang Viewing of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
Seogyong Go, Bok-Mi Jung, Yun-Jung Bae, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(6): 597. CrossRef - The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
Minji Kim, Meera Jang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 278. CrossRef
- Eating Habits and Health Behaviors According to Long-Form and Short-Form Mukbang Viewing of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
- 3,993 View
- 108 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Factors related to adolescent obesity and changes: a cross-sectional study based on the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Bora Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):363-375. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to identify factors associated with adolescent obesity, as well as any new factors that correlated with a change in the rate of obesity over time.
Methods
The study used 5-yearly data collected by the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey starting from the year 2006 up until 2021 (data from 2nd, 7th, 11th, and 17th surveys were analyzed). Factors such as demographics, dietary factors, health behavioral factors, and mental health factors were studied. All data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27.0, employing chi-square tests and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results
This study included data from a total of 255,200 participants. Factors contributing to obesity varied with time. Over the survey duration of 15 years, low academic achievement, parents with low levels of education, low frequency of fruit consumption, low frequency of fast food intake, long periods of being seated, and high levels of stress were significantly associated with a high rate of obesity. Factors that showed a new correlation with an increase in obesity rates included living with single parents, low frequency of muscle strengthening exercises, and experiencing intense sadness and despair in the past year. Factors that were correlated with a change in obesity rates over time included household economic status, frequency of carbonated beverage consumption, frequency of intense physical activity, and frequency of alcohol consumption. Breakfast intake and smoking were not significantly associated with obesity rates in the 15-year period.
Conclusions
While several factors associated with obesity remained consistent over time, several new factors have emerged in response to social, economic, and environmental changes contributed to a change in obesity rate over time. Therefore, to prevent and manage adolescent obesity, continuous research into the new emergent factors contributing to obesity is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,900 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Gender differences in dessert satisfaction and purchase behaviors among university students in Gwangju: a preliminary study
- Hyun-Jeong Na, Hyun-Young Jung, Joomin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):293-301. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.293
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the effect of eating habits and dietary attitudes on dessert consumption among university students in Gwangju Province, South Korea.
Methods
A survey was conducted from May to June 2022. Out of 300 distributed questionnaires, 261 valid responses were included in the analysis. The survey assessed dessert selection, satisfaction, consumer attitudes and behaviors, as well as factors influencing satisfaction.
Results
Both genders reported purchasing desserts 2 to 3 times per week, primarily after lunch, due to the convenience of dessert accessibility. Males favored ice cream, bakery items, and fruits, while females preferred bakery items, ice cream, and fruits in that sequence. ‘Having fun’ was identified as the most common motivation for dessert consumption post-meal. Notable gender disparities emerged regarding perceptions of dessert consumption, including its role in stress relief, potential for nutritional imbalance, positive effects, and preferences for seasonal menus. Significant gender-based differences also manifested in intentions to purchase dessert, responsiveness to price changes, and inclination to recommend desserts to others.
Conclusions
This study offers foundational data on university students’ dessert purchasing behaviors, perceptions, and satisfaction levels, intending to inform strategies promoting healthier dietary habits.
- 1,938 View
- 38 Download

- [Korean]
- Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
- Eunyoung Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):220-234. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.220
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the adherence to dietary guidelines among college students in the post-COVID-19 era and examine the changes in their dietary habits as the learning environment transitioned from remote to in-person classes.
Methods
We conducted a survey involving 327 college students in Daejeon from March to April 2023. The survey questionnaires included various factors, including age, gender, type of residence, frequency of use of delivery food, convenience food, and eating out. In addition, we investigated the extent of adherence to the dietary guidelines for Koreans and the degree of dietary changes following the post-COVID-19 shift in class format were investigated. For comparative analysis of the level of adherence to dietary guidelines in relation to dietary habit changes, an ANOVA and a post hoc Scheffe test were employed. We also performed a multiple linear regression analysis to identify dietary factors influencing the level of adherence to dietary guidelines.
Results
The study revealed a high rate of convenience food consumption and a low rate of homemade food intake among students. There was a marked increase in the consumption of processed foods, convenience foods, dining out, sweet foods, high-fat fried foods, beverages, and alcohol following the transition from online to in-person classes. When examining adherence to Korean dietary guidelines, the highest scored practice was ‘Hydration’, and the lowest was ‘Breakfast habit’. Increased consumption of convenience foods, late-night snacks, and dining out were negatively correlated with adherence levels to dietary guidelines, specifically correlating with ‘Healthy weight’, ‘Hydration’, ‘Breakfast habit’, and the total score of adherence. The adoption of ‘regular meals’ was positively associated with increased adherence levels to dietary guidelines.
Conclusions
The transition from remote to in-person classes post-COVID-19 led to increased intake of convenience foods, dining out, sweet foods, high-fat fried foods, and alcohol. The rise in convenience food and late-night snack consumption negatively influenced several aspects of the dietary guidelines adherence, thereby suggesting the need for strategies to encourage healthy dietary habits among college students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Attributes of multiple concurrent functional gastrointestinal disorders in female university students in South Korea
Hyo Kyung Kim, Hyunjung Kim, Aram Lee
Women & Health.2024; 64(8): 674. CrossRef - Impact of Social Media Use on Segmentation of Dining out Behavior Among Younger Generations: A Case Study in South Korea
Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim, Hyosun Jung
Foods.2024; 13(24): 4146. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef
- Attributes of multiple concurrent functional gastrointestinal disorders in female university students in South Korea
- 2,651 View
- 73 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Screen time, mealtime media use, and dietary behaviors in Korean preschoolers : a cross-sectional study
- Young-Hee Han, Saerom Shin, Eun Yeol Woo, Hye-Kyung Park, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):206-219. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Screen time refers to the time spent using screen media, such as televisions, smartphones, computers, or tablets. Excessive exposure to screen media has been reported to negatively impact young children’s health and development, including overweight, short sleep duration, and language delays. This study examined the association of screen time and mealtime media use with dietary behaviors among preschool children.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was conducted on parents of children aged three to five years using the online questionnaires of the Nutrition Quotient for Preschoolers (NQ-P) and the Dietary Screening Test (DST). Data from 261 children’s parents were analyzed.
Results
Of the 261 children, 96.9% used screen media, 55.6% used screen media for two hours or more daily, and 30.7% were exposed to screen media during meals. The NQ-P scores were significantly lower in the children with longer screen time and mealtime media use. Children who used screen media for two hours or more and those exposed to screen media during meals consumed kimchi less frequently and confectionery and sugar-sweetened beverages more frequently than children who used less than two hours and were not exposed to screen media during meals. In addition, they were more likely to be picky about food, refuse to eat, and less likely to feed themselves than children with shorter screen time and no mealtime media use.
Conclusions
This study reported an association between unhealthy dietary behaviors, feeding difficulties, and screen time and mealtime media use among preschool children. Further research should explore effective strategies for reducing children’s screen time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the impact of screen time, food advertising, and nutritional knowledge of parents on eating habits in preschoolers: a comprehensive review
P. Nagadharshini, Veena B. M., Shweatha H. E.
International Journal Of Community Medicine And Public Health.2025; 12(8): 3836. CrossRef
- Exploring the impact of screen time, food advertising, and nutritional knowledge of parents on eating habits in preschoolers: a comprehensive review
- 6,289 View
- 99 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between health financial capacity of local governments and health behaviors of local residents: a cross-sectional study
- Miyong Yon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):95-103. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The budget gap in the health sector of local governments affects the supply of health services, which can cause the health gap. This study classified local governments according to their financial characteristics, such as local financial independence and health budget level. It analyzed the health behaviors and disease prevalence of local residents to examine the effect of local government financial investment on the health of local residents.
Methods
To classify types according to the financial characteristics of local governments, financial independence and the health budget data for 17 local governments were collected from the local fiscal yearbook of the Ministry of Public Administration and Security. The prevalence of chronic diseases and healthy behavior was compared using the 16,333 data of adults between the ages of 30 and 65 years among the original data of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2020).
Results
Cluster analysis was used to classify local governments into five clusters according to the health financial capacity type. A comparison of the prevalence of local residents by cluster revealed a similar prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia. On the other hand, the obesity rate (P < 0.01), high-risk drinking rate (P < 0.01), aerobic physical activity rate (P < 0.001), and healthy eating practice rate (P < 0.001) were significantly different. In addition, an analysis of the odds ratio based on the Seoul area revealed a higher risk of health behavior of non-Seoul residents.
Conclusions
It is necessary to review the universal health promotion project budget considering the degree of regional financial vulnerability from the viewpoint of health equity to narrow the health gap among regions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of health equity-based Healthy City infrastructure on walking practice
Hyeyun Son, Changwoo Shon
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2025; 42(5): 99. CrossRef
- Influence of health equity-based Healthy City infrastructure on walking practice
- 1,375 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
- Jinkyung Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):468-479. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.468
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigates dietary supplement intakes by examining the characteristics of dietary and health-related behaviors. Data were obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Dietary and health-related behaviors were also examined before and after the occurrence of COVID-19 and household types (multi-members vs. single person).
Methods
Data used in this study were collected from the 2019-2020 KNHANES by including adults aged 19 to 64 years. Pregnant, lactating, and subjects consuming calories less than 500 and more than 5,000 were excluded. Differences in dietary and health-related behaviors before and after COVID-19, and between the two types of households were analyzed by Chi-square analyses using Rao-Scott. Logistic regression analyses were applied to determine which dietary and health-related behaviors affected the dietary supplement intakes. In addition, descriptive analysis was run for demographic characteristics.
Results
The dietary supplement intake rate differed significantly with respect to the gender, age, education, marital status, and household income. Dietary supplement intakes, frequency of eating out, obesity, and body weight changes were significantly different before and after COVID-19. In addition, meal evaluation, frequency of eating out, drinking, smoking, activity, subjective health evaluation, and body weight changes showed significant differences by household type. Attitude towards nutrition, activity, meal evaluation, obesity, and smoking were factors that affected the intake of dietary supplements.
Conclusions
While increased intake of dietary supplements is a prevalent phenomenon, this intake needs to be monitored and studied closely, considering the sociodemographic characteristics and dietary and health-related behaviors. Furthermore, the dietary supplement intake trend after COVID-19 needs to be studied along with food intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
Eunyoung Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 220. CrossRef
- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- 2,016 View
- 45 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
- YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):192-204. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between dietary behaviors and perceived health status among Korean adolescents from multicultural families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 2,459 Korean adolescents from multicultural families (aged 13 ~ 18 years) who participated in the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Information on the sociodemographic variables, dietary behaviors, and lifestyle variables was selfreported using a web-based questionnaire. The dietary behaviors analyzed in this study were the breakfast and food intake frequencies, including fruit, vegetable, milk, fast food, carbonated drink, sweet drink, and high caffeine/energy drinks. The adolescents’ health perception was self-rated as healthy, average, or unhealthy. The dietary behaviors associated with health perception were examined using a multiple logistic regression after adjusting for the confounding variables.
Results
In this study population, 7.6% of adolescents perceived their health status as unhealthy, and 25.4% perceived it as average. The adolescents who were girls, middle school students, and in households with a low economic status showed significantly higher percentages of poor health perception (P-values < 0.001). Skipping breakfast was significantly associated with a negative health perception. Compared to the adolescents who consumed fruits every day, those who did not consume fruits during the previous week showed a higher odd ratio (OR) for a negative health perception [OR = 2.29, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.32–3.97]. The adolescents who frequently consumed carbonated drinks ( 5 times/week) perceived their health status as unhealthy relative to those who did not consume carbonated drinks (OR = 2.15, 95% CI = 1.25–3.71). Skipping breakfast was significantly associated with an increased OR for a negative health perception in girls but not in boys. Compared to adolescents with a normal weight, those with overweight/ obesity (OR = 1.75, 95% CI = 1.21–2.52) and underweight (OR = 2.19, 95% CI = 1.25–3.82) showed higher ORs for negative health perception. Positive associations of overweight/obesity and underweight with negative health perception were observed in boys but not in girls.
Conclusions
Dietary behaviors and weight status were associated with the health perception in Korean adolescents from multicultural families. These findings suggest that nutrition interventions on breakfast intake and healthy food choices for this population might effectively improve their weight and perceived health status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The unequal weight of COVID-19 pandemic: national trends in body mass index among Korean adolescents by immigrant-origin and gender from 2013 to 2022
Nari Yoo, Yumin Hong, Yoonyoung Choi
International Journal of Adolescence and Youth.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The unequal weight of COVID-19 pandemic: national trends in body mass index among Korean adolescents by immigrant-origin and gender from 2013 to 2022
- 1,274 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association Between Health Literacy and Health Promoting Behavior (Eating Habits, Physical Activity, and Stress) of University Students
- Yoon-Sun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):94-104. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.94
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study attempted to examine the association between health literacy and health-promoting behavior, and identify the major variables that affect the health-promoting behavior of university students.
Methods
This was a descriptive correlation study that identified the degree of health literacy and health-promoting behavior of 248 university students (119 male and 129 female) and examined the correlation between the two and factors influencing them. The questionnaire covering health literacy comprised 66 questions, and that for health-promoting behavior comprised 10 questions covering eating habits, 3 questions about physical activity, and 10 questions involving stress.
Results
The score for health literacy was 41.56 ± 18.38 out of 66 points, and that for health-promoting behavior was 65.27 ± 11.21 points (27.61 ± 6.72 points for eating habits, 7.23 ± 2.56 points for physical activity, and 30.44 ± 5.61 points for stress). Health literacy and health-promoting behavior had a significant positive correlation (r = 0.175, P < 0.01). The perceived health status (β = 0.391,P < 0.001) was the most important variable in healthpromoting behavior, followed by health literacy (β = 0.236, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
It is necessary to develop a systematic educational strategy and implement educational programs to improve health literacy as well as encourage health-promoting behavior and thus increase the perceived health levels of university students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(2): 207. CrossRef
- Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
- 1,523 View
- 45 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Trends in Dietary Behavior Changes by Region using 2008 ~ 2019 Community Health Survey Data
- Yun-Hui Jeong, Hye-Young Kim, Hae-Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):132-145. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined trends in the health status and dietary behavior changes by region using the raw data from the 2008 ~ 2019 Community Health Survey.
Methods
This study analyzed the data of 2,738,572 people among the raw data of the Community Health Survey from 2008 to 2019. The regional differences in health status and dietary behavior were examined by classifying the regions into capital and non-capital regions, and the non-capital regions were classified into metropolitan cities and provinces. A chi-square test was conducted on the body mass index (BMI), diagnosis of diabetes and hypertension, frequency of eating breakfast, salty taste in usual diet, recognition of nutrition labeling, reading of nutrition labeling, and utilization of nutrition labeling.
Results
In determining obesity using the BMI, the normal weight by year decreased, and the obesity rate by year was 34.6% in 2019, which increased by 13% compared to 2008. In addition, the diabetes diagnosis rate and hypertension diagnosis rate continued to increase with the year. Both diabetes and hypertension diagnosis rates were higher in the non-capital regions than in the capital region. Eating breakfast five to seven times per week was most common and showed a significant decreasing trend by year (P < 0.001). The percentage of respondents who said they eat slightly bland foods increased from 19.5% in 2008 to 19.9% in 2010 and then to 22.1% in 2013. The percentage then decreased to 19.9% in 2019, but showed an overall increasing trend (P < 0.001). According to the region, the capital region had a higher percentage than the non-capital region. The nutrition labeling's recognition rate and utilization rate increased yearly, whereas the reading rate decreased.
Conclusions
The study results presented the primary data necessary to develop nutrition education programs and establish strategies for local nutrition management projects to improve disease prevention and dietary problems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Comparison of the levels of energy intake from dish and food groups by gender and age among Korean obese adults: data obtained from the 2013-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Cheongmin Sohn, Woori Na, Chaeryeon Kim, Seunghee Choi, Oh Yoen Kim, Jounghee Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(6): 670. CrossRef
- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
- 1,313 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
- Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):350-362. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.350
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated an association between sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) intake and the dietary quality of adults in Deagu, Korea.
Methods
A questionnaire survey was conducted in 1,022 adults aged 19 ~ 49 years (502 men and 520 women) in the Deagu area of Korea. Daily intake of SSB was obtained by the food frequency questionnaire, and the dietary quality was assessed using the nutrition quotient (NQ) for Korean adults. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to estimate the association between dietary quality and daily intake of SSB in adults.
Results
Daily intake of SSB was 463.6 mL/d for total subjects, and the highest intakes were sweetened coffees (192.7 mL/d), followed by carbonated drinks (77.1 mL/d). Higher intake of SSB was associated with higher intake frequency of fast food or sweet and greasy bread, processed beverage, ramyon, eating out or delivery food and night snack, and also associated with lower frequency of water, breakfast intake and nutrition label checking in men or women. Men and women who had a higher intake SSB had significantly greater odds for being in the low grade of NQ (P for trend = 0.0006 for men, P for trend = 0.0007 for women), especially in the moderation factor (P for trend < 0.0001 for men and women).
Conclusions
This study showed that high SSB intake was significantly associated with low dietary quality among adults. These study results suggest that nutrition education programs and guidelines should be provided to adults for improving their consumption of SSB and related diets. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the dietary quality among Chinese adults living in Shanghai and the Anhui Province using the Nutrition Quotient for adults
Ani Liu, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 117. CrossRef - Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - Nutritional and Health Status According to the Frequency of Carbonated Beverage Consumption among Adults in Their 20s : Based on the 2019-2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
You-Sin Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(3): 159. CrossRef - Study on the Dietary Behaviors and Eating Habits of University Students in the Gyeongnam Region in the Post-COVID-19 Era Using the Nutrition Quotient for Adults
Joo Sun Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 470. CrossRef - Nutritional status of Daejeon citizens and needs of community nutrition care services: a cross-sectional study
Dahye Lee, Minsun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 11. CrossRef - Sex-Based Differences in Factors Associated With Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Among Korean High School Students
Jin Suk Ra, Moonkyoung Park
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessment of the dietary quality among Chinese adults living in Shanghai and the Anhui Province using the Nutrition Quotient for adults
- 1,180 View
- 14 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Relationship between Eating Behavior and Healthy Eating Competency of Single-Person and Multi-Person Households by Age Group
- Seung-Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):337-349. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.337
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to analyse the relationship between eating behaviour and healthy dietary competency of single and multi-person households, to improve healthy eating behavior.
Methods
This study was conducted on 6,355 adult household members who participated in the Food Consumption Behavior Survey 2020. The subjects were divided into age groups comprising young people in their 20s and 30s, middle-aged people in their 40s and 50s, and the elderly in their 60s and above. The eating behavior and healthy dietary competency of single-person and multi-person households were then analyzed.
Results
The average age of the members in the single-person households was found to be higher. Single-person households were also found to have a lower marriage rate and lower monthly household income than multi-person households across the age groups of young, middle-aged, and elderly people (P < 0.05). Among each of the age groups, single-person households had significantly higher rates of skipping breakfast and eating breakfast, lunch, and dinner alone than multi-person households (P < 0.05). Young single-person households had lower average scores on healthy dietary competency than multi-person households (P = 0.032). When adjusted for age, gender, marriage, education, occupation, and household income, single-person households had a higher risk of delivery/take-out, eating out, or skipping meals compared to multi-person households (P < 0.05). In multi-person households, the risk of skipping meals, eating alone, eating out, or delivery/take-out decreased as healthy dietary competency improved (P< 0.05). On the other hand, in single-person households, as healthy dietary competency increased, the risk of delivery/take-out or eating alone decreased (P< 0.05).
Conclusions
The results of this study suggest that healthy dietary competency and eating practices can be improved by providing customized dietary education by age group for single and multi-person households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
Soyean Kang, Hae Sagong, Juyoung Lee
Public Health Nursing.2025; 42(3): 1182. CrossRef - Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Dietary status and the relationship between dietary competencies, cooking skills, and nutrition quotient of middle-aged adults living alone in Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Yun-Jung Bae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 257. CrossRef - A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 140. CrossRef - Antioxidant and Nutrition Facts Analysis of Konjac Jelly Stick Containing Pinus koraiensis Leaf Powder
Eunbin Park, Soo-In Ryu, Kyung Tae Jang, Jean Kyung Paik
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(5): 402. CrossRef - Comparative study on eating habits and health of single-person and multi-person households
Haerang Lee, Seon-Jip Kim, Minji Kang, Mi-So Shim
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0327763. CrossRef - The impact of flash continuous glucose monitoring and nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy and weight management in university students in Korea: a pre-post intervention study
Soojin Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 183. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics and Antioxidant Activities of Morning Bread with the Addition of Whole Citron (Citrus junos seib) Powder
Eun Jung Kwak, Hyun-Joo Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2025; 36(3): 417. CrossRef - Association between food-related media content and the eating behaviors of Korean adults according to household type
Ahyoung Yun, Hyein Jung, Byungmi Kim, Yoonjoo Choi
Frontiers in Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-Person Households: Insights from a Household Survey of Fruit and Vegetable Purchases
Andres Silva, Maripaz Rivera, Samuel Durán-Agüero, Maria Isabel Sactic
Nutrients.2024; 16(17): 2851. CrossRef - Association of delivered food consumption with dietary behaviors and obesity among young adults in Jeju
Minjung Ko, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 336. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Hazardous alcohol use is associated with food insecurity in adults living alone: Findings from a nationwide study in Korea
Seong-Uk Baek, Yu-Min Lee, Jin-Ha Yoon, Jong-Uk Won
Social Science & Medicine.2024; 362: 117468. CrossRef - Malnutrition risk, nutritional knowledge, and dietary intake in chronic kidney disease patients on hemodialysis: comparison according to coexisting diabetes
HyunJung Yoo, Sang Cheol Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(5): 481. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Associations of cooking practices and healthy eating habits among young Korean adults in their 20s
So-Young Kim, Ji Yu Choi
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2023; 31: 100644. CrossRef - 밀키트 이용 고객의 식생활 양식과 밀키트 선택속성이 밀키트 제품의 만족도에 미치는 영향 분석
세은 김, 현주 배
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 187. CrossRef - The relationship between the prevalence of anemia and dietary intake among adults according to household types based on data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Won Kim, Ji-Myung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 510. CrossRef - Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Perception to the dietary guidelines for Koreans among Korean adults based on sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle
Yejin Yoon, Soo Hyun Kim, Hyojee Joung, Seoeun Ahn
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 742. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef
- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
- 2,374 View
- 94 Download
- 22 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of Awareness, Knowledge, and Behavior about Food Hygiene·Safety Among the elderly
- Mi Sook Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):200-210. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.200
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to investigate the awareness, knowledge, and behavior about food hygiene·safety among the elderly, and to provide basic data on this for their healthy dietary life.
Methods
The study was conducted through a survey using a self-administered questionnaire on 473 elderly people over 60 years old living in Seoul and Gyeonggido. The questionnaire was designed to examine general characteristics, meal preparation status, the relation between awareness, knowledge, food hygiene behavior, and safety.
Results
Among the particpants, 44.2% of the total people surveyed were elderly married couples, and 14.0% were single-person households. For men, most of the meals were prepared by the spouse (74.1%), and among women, 93.8% prepared their meals themselves (P < 0.001). 61.3% of the total subjects answered that they were very interested in food hygiene and safety. Men (32.4%) thought it was more difficult to collect food hygiene·safety information compared to women (14.0%, P < 0.001). The knowledge score about food hygiene·safety was 0.60 (P < 0.05) and the behavior score was 3.70 (P < 0.001). The correlation coefficient between knowledge and behavior according to food hygiene·safety was 0.371 (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
The food hygiene·safety behavior of the elderly was associated with knowledge (P < 0.001). Therefore, food hygiene·safety education is necessary to ensure information availability and promote the health of the elderly. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the Impact of Food Safety Knowledge on Food Label Checking Behavior : The Mediating Role of Interest in Food Safety
DongYoung Kim, HeeSun Park, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(3): 171. CrossRef
- Understanding the Impact of Food Safety Knowledge on Food Label Checking Behavior : The Mediating Role of Interest in Food Safety
- 1,081 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- A Comparative Study of the Dietary Behavior of Adults Aged 20 and Over according to the Mukbang Viewing Time
- Ha-Yan Nam, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):93-102. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.93
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to investigate the relationship between watching Mukbang (eating broadcasts) and dietary and health behavior in adults who watch Mukbang Methods: The questionnaire was administered on a self-written basis through online and offline formats to 800 adults (400 men and 400 women). The contents of the survey consisted of general characteristics, Mukbang viewing time per week, breakfast intake frequency, preference for menus when viewing Mukbang , delivery food intake frequency per week, late meal intake frequency per week, and health behavior. The subjects were divided into three groups according to Mukbang viewing time.
Results
The body weight of viewers was significantly higher whenMukbang viewing time was over 14 hours for both men and women. In particular, based on the BMI (body mass index), those who watched Mukbang for more than 14 hours were found to be overweight. People with more than 14 hours of Mukbang viewing time per week were found to prefer mostly carbohydrate-rich food and meat, while those with less than 7 hours of Mukbang viewing time per week showed a higher preference for vegetables and fruits. An analysis of the frequency of breakfast eaten showed that the rate of skipping breakfast was the highest for those who watched Mukbang for more than 14 hours per week, and the rate of eating breakfast daily was the highest in the case of fewer than 7 hours of viewing. In the case of high Mukbang viewing time per week, the frequency of food delivery and night eating was high. When Mukbang viewing time was high, the viewer’s interest in health was low and the frequency of exercising too was low.
Conclusions
Viewers with high Mukbang viewing time showed undesirable health and eating behavior. Thus, it is believed that proper nutrition education on improving eating habits and raising the awareness of correct eating habits is necessary for such viewers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between food-related media content and the eating behaviors of Korean adults according to household type
Ahyoung Yun, Hyein Jung, Byungmi Kim, Yoonjoo Choi
Frontiers in Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary patterns and diet quality among adults in their 20s according to rice consumption: a co-occurrence network analysis using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2019–2021
Eun-kyung Kim, Jin-Young Lee, Yong-Seok Kwon, Minji Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(6): 571. CrossRef - Addictive symptoms of mukbang watching: A qualitative interview study using directed content analysis
Kagan Kircaburun, Filipa Calado, Andrew Harris, Mark D. Griffiths
Emerging Trends in Drugs, Addictions, and Health.2024; 4: 100147. CrossRef - Mukbang and Cookbang watching and dietary behavior in Korean adolescents
Jimin Sung, Jae-Young Hong, Jihong Kim, Jihye Jung, Seoeun Choi, Ji Yun Kang, Mi Ah Han
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(4): 523. CrossRef - Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef - Mukbang watching in Iran: a brief report validating the Persian version of the mukbang addiction scale and its relationship with disordered eating decisions and habits
Reza Shabahang, Sohee Kim, Xiuhan Chen, Mara S. Aruguete, Ágnes Zsila
Current Psychology.2024; 43(37): 29296. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef - Changes In the Activation of Supra-hyoid Muscles and Heart Rate of College Students During Food Intake According to Watching Mukbang
Byung-o Ahn, Sung-Min Son, Hyeong-Min Kim
American Journal of Health Behavior.2023; 47(4): 832. CrossRef - 밀키트 이용 고객의 식생활 양식과 밀키트 선택속성이 밀키트 제품의 만족도에 미치는 영향 분석
세은 김, 현주 배
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 187. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Watching Mukbang (Eating Show), Eating Behaviors, and Anthropometric Parameters in Iranian Female Students
Fatemeh Manafi Anari, Shahryar Eghtesadi
Journal of Research in Health Sciences.2023; 23(1): e00574. CrossRef - Health behaviors and eating habits in people’s 20s and 30s according to food content usage level on social media: a cross-sectional study
Seo-Yeon Bang, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(5): 392. CrossRef - Development and validation of Problematic Mukbang Watching Scale and Mukbang Watching Motives Scale: A cross-sectional study with adult mukbang watchers
Kagan Kircaburun, Andrew Harris, Filipa Calado, Mark D. Griffiths
Psychiatry Research Communications.2023; 3(3): 100138. CrossRef - Actual Status of Mukbang Viewing and Food Habits of University Students in Wonju Area
Seung-Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(4): 631. CrossRef - Uses and gratifications of problematic mukbang watching – The role of eating and social gratification: A pilot study
Kagan Kircaburun, Mustafa Savcı, Emrah Emirtekin, Mark D. Griffiths
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2022; 146: 28. CrossRef - Problematic video-streaming: a short review
Maryam Rahat, Juliette Mojgani, Grace Lethbridge, Hashim Al-Bya, Beth Patterson, Carolina Goldman Bergmann, Michael Van Ameringen
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences.2022; 48: 101232. CrossRef
- Association between food-related media content and the eating behaviors of Korean adults according to household type
- 2,447 View
- 57 Download
- 15 Crossref

- [English]
- The Study of Dietary Habits and Health Behaviors according to Physical Activity Type in Korean Adults -Based on the 2016~2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
- Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):122-133. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated the dietary habits and health behaviors of Korean adults according to their physical activity. Methods: Adults aged 19~64 years, who participated in the 2016~2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, were enrolled in this study. The subjects were classified into the physical inactivity group, aerobic physical activity group, strength exercise group, and combined exercise group. Results: Significant differences in skipping breakfast, frequency of eating out, dietary supplements, and alcohol drinking status were observed among physical activity groups (P < 0.001). The combined exercise group had the highest % KDRI of protein, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, calcium, potassium, and iron (P < 0.001). The physical inactivity group had the highest obesity rate (35.1%), and they perceived their body image type to be obese. In the combined exercise group, 47.8% of respondents said they were in good health (P < 0.001). The health-related quality of life score of the physical inactivity group was the lowest, with a score of 0.94. The metabolic syndrome risk rate of the combined exercise group was lower at 0.62 times (95% CI, 0.51-0.75) than the physical inactivity group. Conclusions: The physical activity type was associated with metabolic syndrome. These results can be useful for supporting dietary education and physical activity programs for adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
Soyean Kang, Hae Sagong, Juyoung Lee
Public Health Nursing.2025; 42(3): 1182. CrossRef - The Association between the Type and Level of Physical Activity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults Aged 40 Years and over: Results from the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Namkuk Son
The Korean Journal of Sports Medicine.2024; 42(2): 145. CrossRef - Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
Hyoju Lee, Youjeong Jang, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 261. CrossRef - 고령자의 신체건강 및 식생활 행태가 영양소 섭취량에 미치는 영향
하리 임, 다솔 김, 나미 주
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(6): 518. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef
- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
- 1,555 View
- 15 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between the Dietary Behavior of Young Children and Their Mothers in Daejeon, Korea Using the Nutrition Quotient for Preschoolers and Adults
- InYoung Jeong, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(1):12-22. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between the dietary behavior and weight status of preschool children and their mothers in Daejeon, Korea. Methods: A total of 301 mother–preschool children (aged 3~6 years) dyads were included in this study. The dietary behavior of children and their mothers was assessed using the Nutrition Quotient (NQ) questionnaire for preschoolers and adults, respectively. The NQ questionnaires were completed by the mothers. The overweight/ obesity status of children and their mothers was determined using data on height and body weight reported by the mothers. Multiple logistic regression was performed to examine the relationship between the dietary behavior and weight status of children and their mothers. Results: The mean NQ score was 58.9 ± 9.7 in children and 55.6 ± 9.2 in mothers. The NQ score was higher in boys than girls but did not vary by age. The prevalence of overweight/obesity was 27.5% in children and 46.5% in mothers. The physical activity level of mothers and their NQ scores were positively associated with the NQ scores of the children. After adjustment for covariates, the mothers in the highest tertile of NQ scores showed a lower odds ratio (OR) for the unhealthy dietary behavior of children (OR = 0.24, 95% CI = 0.11~0.53, P< 0.001) compared to those in the lowest tertile. The obese mothers showed a higher OR for children’s overweight/obesity (OR = 3.38, 95% CI = 1.68~6.80, P = 0.001) compared to normal weight mothers. Conclusions: The dietary behavior and weight status of young children and their mothers were closely linked. Nutrition education programs targeting mothers are necessary for improving maternal and child nutrition. Specifically, these programs need to be tailored to the socioeconomic characteristics or weight status of mothers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
Sil-Ah Kim, Min-Ah Kim, Seung-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 614. CrossRef -
Validation of the Korean Version of the Nutrition Screening Tool for Every Preschooler (NutriSTEP
®
): Using the Rasch Model
So Hyun Park, Youn-Jung Son, Hanjong Park
Journal of the American Nutrition Association.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
Sung-Mi Cha, Soo-Youn Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 541. CrossRef - Early childhood eating behaviors associated with risk of overweight and its socio-ecological determinants in Korean preschool children
Yeri Kim, Jiye Kim, Bomi Lee, Seungyoun Jung, Seo-Jin Chung, Hyekyeong Kim, Nana Shin, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(4): 717. CrossRef - Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Dietary Practices for Mothers in Japan
Lin Wu, Miao Wu, Akira Ishida
Women.2022; 2(3): 264. CrossRef - Use of mothers' home meal replacement and diet quality of their young children
Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 292. CrossRef
- Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
- 1,067 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
- Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):502-511. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.502
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the health and nutritional status of the elderly according to the number of chronic diseases, using data obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015. Methods: Data from a total of 2,310 individuals, aged 65 years and over, were used for the analysis. The elders were divided into 0 (n=375), 1 (n=673), 2 (n=637) and 3 or more (n=625) groups, by considering the number of chronic diseases. Results: Compared to other groups, the elderly subjects who were living with their spouse had the highest ratio in group 0 (P < 0.05), whereas subjects without economic activities had highest ratio in 3 or more group (P < 0.05). The EQ-5D index of subjects in the 0 group (0.90 ± 0.01) was higher than that in the 3 or more group (0.86 ± 0.01) (P< 0.05). After adjusting for confounding factors, the energy intake of subjects was determined to be lowest in the 3 or more group (P < 0.05). Protein (P < 0.05) and riboflavin (P < 0.05) intakes of the 3 or more group were also lower than other groups. Conclusions: This study indicates that multimorbidity of the elderly is associated with their health and nutritional status. The nutrients intake of the elderly, especially energy, protein and riboflavin, tended to be lowest in the 3 or more group. Further research is required to elucidate the risk factors related to presence of multimorbidity in the elderly. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Duration Is Associated with the Risk of Tooth Loss, Chewing Difficulty, and Undernutrition among Older Korean Women: Results of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2013–2015
Ye Rang Jo, Yoo Kyoung Park, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2023; 15(24): 5024. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,333 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Analysis of Factors Affecting Breakfast Eating Behavior of Children in Indonesia: An Application of the Health Belief Model
- Ran Yi Kang, Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):1-12. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study investigates the current state of consuming breakfast among elementary school students residing in Malang, East Java, Indonesia, and to identify factors that influence breakfast behavior.
METHODS
The research model was set up as per the health belief model, and slightly modified by adding the subjective normative factors of the theory of planned behavior. The survey was conducted from July 17 to August 15, 2017 using a questionnaire, after receiving the permission PNU IRB (2017_60_HR).
RESULTS
The subjects were 77 boys (49.4%) and 79 girls (50.6%) suffering from malnutrition with anemia (21.2%) and stunting ratio of Height for Age Z Score (HAZ) (11.5%). Furthermore, moderate weakness (14.8%) and overweight and obesity (12.3%) by Body Mass Index for Age Z Score (BMIZ) were coexistent. According to the results obtained for breakfast, 21.8% did not eat breakfast before school, with 18.8% of the reasons for skipping breakfast being attributed to lack of food. Even for subjects partaking breakfast, only about 10% had a good balanced diet. The average score of behavioral intention on eating breakfast was 2.60 ± 0.58. The perceived sensitivity, perceived severity, perceived benefits, and self-efficacy of the health belief model correlated with breakfast behavior. Of these, self-efficacy (β=0.447, R²=0.200) and perceived sensitivity (β=0.373, R²=0.139) had the greatest effect on breakfast behavior. Mother was the largest impact person among children.
CONCLUSIONS
In order to increase the level of breakfast behavior intention among children surveyed in Indonesia, we determined the effectiveness by focus on education which helps the children recognize to be more likely to get sick when they don't have breakfast, and increase their confidence in ability to have breakfast on their own. We believe there is a necessity to seek ways to provide indirect intervention through mothers, as well as impart direct nutrition education to children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The School Food Environment in Ghana is Associated With Dietary Diversity and Anemia: Findings From the 2022 National Nutrition and Health Survey of In-School Adolescents
Mica Jenkins, Esi Foriwa Amoaful, Mutala Abdulai, Veronica Quartey, Porbilla Ofosu-Apea, Jevaise Aballo, Maku E. Demuyakor, Maria Elena D. Jefferds, Nancy J. Aburto, Usha Ramakrishnan, Reynaldo Martorell, O. Yaw Addo
Food and Nutrition Bulletin.2025; 46(2-3): 78. CrossRef - Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
Sung-Mi Cha, Soo-Youn Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 541. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary behavior and investigation of the affecting factors among preschoolers in Busan and Gyeongnam area using nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P)
Soo-Youn Kim, Sung-Mi Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 596. CrossRef - Psychoactive substance use among Chinese non-engaged youth: The application of the Health Belief Model
Phoenix Kit-han Mo, Joseph Tak Fai Lau
Children and Youth Services Review.2020; 113: 105008. CrossRef
- The School Food Environment in Ghana is Associated With Dietary Diversity and Anemia: Findings From the 2022 National Nutrition and Health Survey of In-School Adolescents
- 2,428 View
- 47 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
- Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(5):408-421. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.5.408
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study compared the dietary behaviors of single-person households when eating alone according to the employment pattern and age.
METHODS
A total of 566 people aged 20~59 years old were collected from the status of workers and classified into three groups according to their employment pattern (regular, non-regular workers and business owner). The subjects were collected by purposive quota sampling on a Gallup panel from June to November in 2017. The dietary behavior and perception of eating alone of the subjects were surveyed via online and self-reported questionnaires.
RESULTS
The frequency of eating alone was significantly higher in the regular group than the non-regular group and business group (p<0.01). The place of eating alone was significantly higher in the regular and non-regular group in the convenience store, and business group in the office (p<0.001). Ramen, the menu when eating alone, was significantly higher in the non-regular group than the other groups (p<0.01). The preference for eating alone was lower in the older age group (p<0.05). The young aged group (aged 20~30) ate more fast food and felt more convenience than the older aged group aged 40~50 years (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Single-person households with a non-regular job have poorer dietary behavior in eating alone than those who had regular employment. In a situation of an increasing number of non-regular workers aged in their 20s and 30s, there is a high likelihood of social problems, such as health and poverty. This study highlights the need for a healthy food selection environment to improve the dietary life of single-person households with non-regular jobs for the diverse types of single-person households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The de-structuration of eating models in East Asia under compressed food modernity: An empirical synthesis
Haruka Ueda, Yu-Chan Chiu
Appetite.2024; 203: 107680. CrossRef - Analysis of the Effect Size of Insect Foods on Metabolic Syndrome-Related Indicators
Chan-Hwi Lee, Ae-Jung Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 860. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Analysis of Agrifood Consumer Competency and Dietary Satisfaction according to Household Type Using the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Meera Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 414. CrossRef - Association between Prediabetes and Meal Patterns Related to Meal Sharing among Korean Young Adults: Eighth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2019–2020
Saebom Kim, Sehee Kim, Youngmin Kim, Seonmi Seo, Yu Jin Chung, Sam Cheol Kim
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(3): 179. CrossRef - Impact assessment of a primary care physician counseling program for youth population
Yun-Su Kim, Shin-Ae Kim
Medicine.2022; 101(46): e31916. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Habits and Health-Related Factors According to the Employment in Women in Early Adulthood - Based on the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yun-Jung Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(4): 249. CrossRef - Gender and age group differences in nutrition intake and dietary quality of Korean adults eating alone: based on Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data, 2013–2016
Yoonjin Ahn, Youngmi Lee, Haeryun Park, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(1): 66. CrossRef
- The de-structuration of eating models in East Asia under compressed food modernity: An empirical synthesis
- 1,963 View
- 14 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between Dietary Behaviors and Life Stress of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Kyung Ae Park, Myoung Sook Lee, Kyung Hee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(5):384-394. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.5.384
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study was performed to examine the dietary behaviors and life stress of middle school students in the Gyeonggi area.
METHODS
A total of 580 middle school students (295males, 285 females) in the Gyeonggi area participated in the study between July and August in 2011. The study was a questionnaire-based survey that included dietary habits, dietary behaviors, and life stress.
RESULTS
For dietary habits, the score for drinking milk was higher in male students than in female students, whereas the score for eating fruits was higher in female students compared to male students. There were significant differences in foods eaten and preferred under stress between male and female students. Male students showed significantly less changes in the number of meals, amount of meal intake, number of snacks, snack intake, frequency of overeating, and appetite during stress than female students. Life stress score of students largely came from academic factors, and female students showed higher stress levels in personal and surrounding environment factors than male students. Life stress score was significantly lower in students with high and moderate levels of dietary habits than in students with a low level of dietary habits. Total score for dietary habits and scores for eating adequate amounts of foods for each meal, considering a combination of food groups at each meal and eating green and orange vegetables, were significantly negatively correlated with life stress score. Life stress score was significantly negatively correlated with meal regularity and positively with the level of overeating.
CONCLUSIONS
This study may provide basic information on dietary habits and life stress according to gender and the relationship between dietary behaviors and life stress of middle school students, and it suggests gender-based nutrition education programs to solve undesirable dietary habits and dietary behaviors in students with higher stress. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Life stress, dietary attitudes, and frequency of snack intake for college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi area: the difference between male and female students
Hyun Seung Oh, Yu bin Kim, Soyoung Park, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(1): 91. CrossRef
- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
- 1,308 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Consumer Innovativeness and Consumption Behavior of New Sauce Products for the Japanese Consumer
- Su Jin Kim, Seon Young You, Min A Lee, Eunju Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(5):374-383. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.5.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study analyzed Japanese consumers on their sauce consumption, and assessed the relationship between consumer innovativeness and consumption behavior for new sauce products.
METHODS
The survey was completed by local consumers visiting Korean restaurants in Osaka, Japan, in September 2018. The demographic characteristics, consumption of sauce, consumer innovativeness, and factors of theory of planned behavior were evaluated. Totally, 150 collected data were analyzed using the IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0 Program (IBM SPSS INC, Armonk, NY, USA).
RESULTS
Results of the survey indicate that Japanese consumers purchase a sauce by considering the taste and food utilization. Sauce purchases were maximum at mega markets and supermarkets. The consumer innovativeness for Japanese consumers was based on 3 factors: ‘Purchasing adventurous products (3.51 ± 0.96)’, ‘Active information seeking (4.36 ± 1.11)’, and ‘Interactive information seeking (4.33 ± 1.02)’, where the tendency of ‘Active information seeking’ was the highest innovativeness factor. Furthermore, higher values of perceived behavior control (4.68 ± 1.21), attitude (4.66 ± 1.41) and subjective norm (4.39 ± 1.28) were revealed, when assessing for theory of planned behavior factors. Correlating the variables of consumer innovation and factors of planning behavior theory, ‘Active information seeking’ is a positive attribute for attitude (p<0.016), subjective norm (p<0.001), and perceived behavior control (p<0.002). These 3 factors also had significantly positive effects on purchase intention for new sauce product (p<0.000, p<0.000, and p<0.002, respectively). Attitude was determined to be another very influential variable for purchase intention of a new sauce product (B=0.484, t=6.881).
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study determine the consumption patterns of sauce for the Japanese consumer, and the relationship between consumer innovativeness and consumption behavior for Korean traditional sauces. We believe the data generated from this study will help determine a marketing strategy to enter the Japanese market.
- 1,281 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Comparison Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Nutrient Intakes of the Elderly according to Their Family Status: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2016
- Ji Hong Oh, Bok Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):309-320. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.309
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was undertaken to compare dietary life of the elderly living alone and in a family, and to compare differences based on gender, for the 2013-2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
The subjects included 2,612 elderly people aged over 65 years who participated in the health survey, health examination and nutrition survey. Subjects on a diet therapy were excluded. This study analyzed the general characteristics, dietary habits, daily energy and nutrient intakes, CPF ratio, estimated average requirement (EAR), nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean adequacy ratio (MAR), index of nutrient quality (INQ), and food consumption of the elderly living alone and in a family. We also compared the differences based on gender.
RESULTS
Daily intake of food, water, dietary fiber, potassium, retinol, and riboflavin were low in the male elderly subjects living alone. The elderly living with family revealed higher NAR and MAR as compared to the elderly living alone. Although all MAR values were <1, the elderly living alone had lower values. Considering the intake of food, the consumption of seaweed, fish and shellfish, and oils (animal) was higher in elderly men living with families, whereas women living with families consumed more vegetables, fruits, seaweeds and seafood, as compared to their counterparts living alone. Furthermore, analyzing the foods consumed by the elderly people living alone, female subjects consumed more seaweed, milk and animal oil as compared to male subjects.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study indicate that the elderly living alone have poor nutrient intake as compared to the elderly living with families. Based on this research data, we recommend that it is necessary to improve the health and nutritional status of the elderly living alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food insecurity and its associated characteristics of the elderly in Seoul: analysis of the data from the Seoul Food Survey 2023
Hyunjeong Park, Youngmin Nam, Linxi Huang, Youngmi Lee, Jihyun Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 117. CrossRef - Profiling the socioeconomic characteristics, dietary intake, and health status of Korean older adults for nutrition plan customization: a comparison of principal component, factor, and cluster analyses
Kyungsook Woo, Kirang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2024; 46: e2024043. CrossRef - Evaluation on the Nutrition Quotient Scores of Elderly People Living Alone in Korea
Gyoungok Gang, Min Lee, Eun-hui Choi, Hye-Lim Lee, Hyun-Young Lee, Hye-Ja Chang, Jung-Hwa Choi, Na-Young Yi, Kyung-Eun Lee, Min-Jae Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak
Nutrients.2023; 15(17): 3750. CrossRef - Changes in nutritional status of Korean older adults during COVID-19 Pandemic by household income and demographic factors-using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(2019-2020): a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 302. CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 422. CrossRef - Comparison of the health and nutritional status of Korean elderly considering the household income level, using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 39. CrossRef - Social participation, health‐related behavior, and depression of older adults living alone in Korea
Seojin Won, Hyemee Kim
Asian Social Work and Policy Review.2020; 14(1): 61. CrossRef - Evaluation of the dietary quality and nutritional status of elderly people using the Nutrition Quotient for Elderly (NQ-E) in Seoul
Sun-Wook Ham, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 68. CrossRef - Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 502. CrossRef
- Food insecurity and its associated characteristics of the elderly in Seoul: analysis of the data from the Seoul Food Survey 2023
- 1,633 View
- 18 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effect of Consumers' Factors of Food Choices on Replacing Soft Drinks with Carbonated Water
- Seoyoung Park, Dongmin Lee, Jaeseok Jeong, Junghoon Moon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):300-308. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.300
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This research was conducted to identify the consumers' food choice factors that affect the consumers' replacement of soft drinks with carbonated water.
METHODS
The present study used secondary data from a consumer panel survey conducted by the Rural Development Administration of Korea, and the data included the panel members' purchase records based on their monthly spending receipts. The survey asked the participants about their food choice factors and their personal responsibility for their health. This survey included independent variables for the consumers' food purchase factors. As a dependent variable, two types of groups were defined. The replacement group included those people who increased their purchase of carbonated water and decreased their purchase of soft drinks. The non-replacement group included those people who did not change their purchase patterns or they increased their purchase of soft drinks and they decreased their purchase of carbonated water. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to determine the consumers' food choice factors that were associated with replacing soft drinks with carbonated water.
RESULTS
The replacement group was significantly associated with (1) a younger age (OR=0.953), (2) being a housewife (OR=2.03), (3) higher income (OR=1.001) and (4) less concern about price (OR=0.819) when purchasing food. This group also showed (5) higher enjoyment (OR=1.328) when choosing food and (6) they took greater responsibly for their personal health (OR=1.233).
CONCLUSIONS
This research is the first study to mainly focus on soft drinks and carbonated water. The result of this research showed that young, health-conscious consumers with a higher income and who are more interested in food have more possibilities to replace soft drinks with carbonated water. These research findings may be applied to consumers who have characteristics that are similar to the young health-conscious consumers and the results can help to suggest ways to reduce sugar intake and improve public health. However, this research has a limitation due to the application of secondary data. Therefore, a future study is needed to develop detailed survey questions about food choice factors and to extend these factors to all beverages, including soft drinks made with sugar substitutes, so as to reflect the growth of alternative industries that use artificial sweeteners or different types of sugar to make commercially available drinks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Dietary Behavior-Related Consumer Competency on the Purchase Satisfaction of Fresh Food via Early-Morning Delivery Service
Soon-Ok Lee, Ji-Young Kim, Seung-Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(6): 612. CrossRef
- Effects of the Dietary Behavior-Related Consumer Competency on the Purchase Satisfaction of Fresh Food via Early-Morning Delivery Service
- 1,392 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Analysis of Dietary Behaviors, Food Consumption Frequency and Blood Clinical Indices by Residence Types of Female College Students in Seoul
- Ru Zi Lee, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):183-196. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.183
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
College is an important time for students to establish their identity as an independent subjects and develop a foundation to maintain a healthy adulthood. However, after female students become college students, their eating habits are likely to become more irregular and they may experience various health problems because of excessive weight control. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the dietary behaviors and blood clinical indices of female college students by residence types.
METHODS
A total of 374 subjects were classified as home group, self-boarding group or boarding group according to residence type. Dietary habits, frequency of food intake, and eating attitudes were examined through questionnaires and anthropometric measurements and blood clinical indices were analyzed.
RESULTS
The meal most frequently skipped by female college students was breakfast, and the frequency of skipping breakfast was significantly lower in the home group than other groups. Most college students recognized that their eating habits had worsened since becoming college students, with the self-boarding group in particular feeling that their eating habits changed negatively. The consumption frequencies of protein foods, fruits, dairy products, seaweed, and fatty meats were significantly lower in the self-boarding group than other groups. The home group ate food cut into smaller pieces, while the self-boarding group tried new and rich foods. Residence types did not affect blood clinical indices.
CONCLUSIONS
The self-boarding group had inadequate dietary habits compared to the home group. Although residence type did not affect the blood clinical indices, the students still had poor dietary habits. Therefore, proper nutrition education is needed to improve the nutritional status of college students, especially those that self-board. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(2): 207. CrossRef - Usage and Quality Satisfaction of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores according to the Eating Behavior of University Students in Southern Gyeonggi Province
Se-In Oh, Ok-Sun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 492. CrossRef - Beliefs, self-efficacy, subjective norms, and eating behaviors according to the breakfast frequency among female university students in South Korea
Hye Jin Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1170. CrossRef - A Franchise Hamburger Menu for University Students Determined by Identifying Selection Attributes Using Conjoint Analysis
Yu-Ni Choi, Sung-Suk Chung, Jeong-Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(4): 250. CrossRef - Analysis of Usage, Preference, and Satisfaction for Convenience
Store Dessert among University Students in Chungbuk Area
Go Eun Lee, Hye-In Yang, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Biotechnology and Bioindustry.2021; 9: 63. CrossRef - Comparison of consumption behaviors and development needs for the home meal replacement among Chinese college students studying abroad in Korea, Chinese college students in China, and Korean college students in Korea
Mi Ae Bae, So Hyun Park, Siyao Cheng, Kyung Ja Chang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(6): 747. CrossRef
- Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
- 1,726 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Dietary Behaviors and Blood Clinical Indices in Underweight, Normal Weight, Normal Weight Obese and Obese Female College Students
- Su Bin Lee, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(5):431-443. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.5.431
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Normal weight obesity (NWO) is defined as excessive body fat in the context of a normal body mass index (BMI). This condition carries a greater risk of developing noncommunicable chronic disease and has been associated with early inflammation. This study was conducted to compare the anthropometric measurements, eating behaviors, and blood clinical indices among four groups: underweight, normal, normal weight obesity and obesity.
METHODS
The subjects included 215 female college students. A questionnaire was administered regarding general characteristics, dietary behaviors, food consumption frequency. Anthropometric measurements and blood clinical indices were also investigated.
RESULTS
The average BMI, body fat percentage, waist circumference, fat-free mass, and muscle mass were highest in the obesity group (p < 0.05). Most subjects had tried to lose weight and perceived that their health was worse than before they became college students. The ratio of students in the NWO group who thought their health was very poor was significantly higher than in the other three groups (p < 0.05). The obesity and NWO groups seemed to eat more and their eating speed was significantly faster than the other groups (pv0.001). The consumption frequency of caffeinated beverages was significantly higher in the NWO group than in the other three groups (p < 0.01). WBC was significantly higher in the obesity group (p < 0.05). Serum levels of TG and total cholesterol were also significantly higher in the obesity group (p < 0.05). Serum GPT was significantly higher in the obesity group (p < 0.05) while BUN level was highest in the NWO group (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The obesity group showed the most health problems while the NWO group seemed relatively healthy. However, NWO can lead to problems such as metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease in later life if poor dietary habits are maintained. Therefore, education in appropriate eating habits is needed for these subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on the perception of hand washing and health status in Korean adults
Soohee Park
Medicine.2021; 100(3): e24421. CrossRef - Gender Differences and Relationships among Lifestyle and Reproductive Health in University Students
Ju-Hee Nho, Hee Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 446. CrossRef
- A study on the perception of hand washing and health status in Korean adults
- 1,204 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Program on Obesity Index and Behavioral Modification in Moderate Obese Women
- Myung Hee Chang, Su Jin Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):318-332. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the behavioral modification of obese adults who underwent nutritional and physical activity education. Twenty obese females, aged 20–60 years old, with BMIs (Body Mass Index) >30 or body fat (%) >40 were subjected to this study.
METHODS
The physical activity education program consisted of doing exercise in a gymnasium together or home exercise. Dietary attitudes and dietary intakes were assessed using weight control, physical activity, and eating habits. The nutrition-exercise educational period was 12 weeks.
RESULTS
After the study period, there was significant improvement in physical activity and eating habits score. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the dietary intakes of fiber, iron, potassium, vitamin A, vitamin B6, and niacin. Blood pressure, blood glucose, and total cholesterol levels showed a tendency to decrease, but there was no significant difference. BMI, fat mass, abdominal circumference, and visceral fat levels were significantly reduced while muscle mass significantly increased.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that behavioral modification by nutrition and physical activity education with feedback has positive effects on dietary intake and anthropometric biomarkers in obese adults. Therefore, lifestyle interventions of this kind could be recommended as a method for obesity management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of tele-nutrition education on weight loss, energy intake, and fat adequacy among obese adults in Banyumas, Central Java, Indonesia
Teguh Jati Prasetyo, Izzati Nur Khoiriani, Sifa Aulia Wicaksari, Gumintang Ratna Ramadhan, A. Khomsan, E. Palupi, S.P. Loh, N. Mohd Esa
BIO Web of Conferences.2025; 153: 02013. CrossRef - Influence of Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention (LSI) Program on Health, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Middle-Aged Women
Su-Jin Jung, Seung-Ok Lee, Min-Jun Choi, Jun Heo, Soo-Wan Chae, Baik-Hwan Cho
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2022; 12(3): 127. CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef
- Effect of tele-nutrition education on weight loss, energy intake, and fat adequacy among obese adults in Banyumas, Central Java, Indonesia
- 1,537 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Consumption Behaviors of Energy Drinks and Comparison of Associated Factors Among College Students in Gwangju
- DaWun Seo, Bok Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):289-301. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.289
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to examine the current status of consumption of energy drinks among college students and investigate the effects of general environmental factors, health behavior factors, caffeine knowledge levels, and perceived stress levels on consumption of energy drinks.
METHODS
A survey was conducted among a total of 479 college students in Gwangju, using self-administered questionnaires. The questionnaire consisted of items about general environmental factors, health behavior, caffeine knowledge, perceived stress, and energy drink consumption behaviors.
RESULTS
69.1% of participants experienced consumption of energy drinks, and specifically 82.8% of male students and 54.1% of female students experienced consumption of energy drinks (p < 0.001). The reasons for drinking energy drinks were found to be recovery from fatigue, curiosity, taste, habit, thirst relief, and stress relief. In addition, 40.7% of participants experienced drinking energy drinks mixed with alcohol, and specifically 48.6% of male students and 27.4% of female students reported drinking energy drinks with alcohol (p < 0.001). Moreover, 51.5% of participants responded that they experienced the effects of energy drinks, 31.9% reported experiencing adverse effects, and 41.1% were found to perceive the health risks. As a result of the assessment of caffeine knowledge, the participants showed a high level of knowledge of the arousal effect (77.7%) and the concentration increasing effect (70.8%) of caffeine, whereas they exhibited a low level of understanding of the health problems due to caffeine (32.6%) and adequate caffeine intake levels (24.4%). The higher levels of consumption experience of energy drinks was associated with higher body mass indexes (BMI) (p < 0.01), higher academic years (p < 0.01), lower levels of interest in health (p < 0.05), smoking (p < 0.001), alcohol consumption (p < 0.05), and higher levels of perceived stress (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The risk groups related to consumption of energy drinks among college students were identified as male students rather than female students, students in the third or fourth year of study associated with increased stress levels, and students with negative health behaviors. Therefore, support for diverse health and nutrition education for college students is required along with the improvement of internal and external environments of schools in order for college students to manage increased stress levels due to the schoolwork and preparation for employment and maintain positive health behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Caffeine Intake and Eating Disorders among College Students according to Whether an Examination was Imminent or Not
Eun-Ji Lee, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2023; 34(1): 47. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - A Study on the Perception and Intake of Caffeinated Beverages in Adults Aged 20 to 30 Years
Bo-Ra Seo, Sim-Yeol Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 545. CrossRef
- Analysis of Caffeine Intake and Eating Disorders among College Students according to Whether an Examination was Imminent or Not
- 1,578 View
- 16 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Health Behavior Factors Associated with Sugar-sweetened Beverage Intake among Adolescents
- Hyae Min Gu, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):193-201. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to measure the intake rate of SSBs (sugar sweetened beverages) and examine the relationship between health behavior factors and SSBs intake by adolescents.
METHODS
This study used data from the 2016 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey, which included 65,528 study participants. SSBs intake frequency was measured by asking respondents if they consumed soda, high-caffeinated beverages, and sugary drinks during the previous week. Type of intake was categorized into three groups according to the number of consumed drinks [SSBs (0): None; SSBs (1–2): 1 or 2 consumed; SSBs (3): 3 consumed]. Multinomial logistic regression analysis was used to examine health behaviors that affected SSBs consumption.
RESULTS
Increased SSBs intake was significantly correlated with current smoking (OR=2.4, 95% CI=1.82–3.17), current drinking (OR=2.13, 95% CI=1.82–2.51), sedentary time increase (OR=1.31, 95% CI=1.15–1.49), three days or more physical activity per week (OR=1.12, 95% CI=1.02–1.24), < 8 hours sleep (OR=1.6, 95% CI=1.43–1.78), increased internet usage time (OR=1.44, 95% CI=1.25–1.65).
CONCLUSIONS
Sugar-sweetened beverages intake by Korean adolescents was associated with health behaviors such as smoking, drinking, sedentary time increase, more physical activity, poor sleeping time, and increased internet use time. Based on these results, it is necessary to recognize the influence of SSBs intake and to intervene to reduce consumption of SSBs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-Related Behaviors and Perceived Health Status According to Water and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Korean Adolescents
Yoon Sun Kim, Hyun Ja Kim
Nutrients.2024; 16(17): 3038. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef - Dietary behavior of school-going adolescents in Bhutan: Findings from the global school-based student health survey in 2016
Tshering Choeda, Kathiresan Jeyashree, Soundappan Kathirvel, Thinley Dorji, Kinley Dorjee, Karma Tenzin, Sangay Thinley, Tashi Tenzin, Mongal Singh Gurung
Nutrition.2021; 90: 111290. CrossRef - Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 350. CrossRef - Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and influencing factors in Korean adolescents: based on the 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Ayoung Kim, Jinhee Kim, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 465. CrossRef
- Health-Related Behaviors and Perceived Health Status According to Water and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Korean Adolescents
- 2,364 View
- 17 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Daily Stress on Dietary Pattern among Elementary School Children in Seongnam City
- Sunra Kim, Seunghee Kye
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(6):475-484. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.6.475
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study was conducted to investigate the relationship between several stress measures in everyday life, emotional eating behavior, and dietary pattern (snacks, fatty foods, sweet beverages, fruits and vegetables) in school-aged children.
METHODS
One hundred and ninety-four students of an elementary school located in Seongnam City participated in the study. The students responded to the survey questionnaire by self-report, which consisted of items regarding general characteristics, height, weight, dietary habits, frequency of consuming healthy (fruits and vegetables) and unhealthy foods (snacks, fatty foods, and sweet beverages), emotional eating behavior, and daily stress. Correlational analysis was performed to examine the relationship between stress, emotional eating behavior, and dietary pattern, and Poisson and logistic regression analyses were conducted to investigate the effects of stress on dietary pattern.
RESULTS
Positive correlations were found between all stress factors and emotional eating behavior and between the friend and personal factor (one of the stress factors) and the consumption of sweet beverages. The frequency of consuming sweet beverages was 2.6 times higher in the high stress group than in the low stress group (95% CI).
CONCLUSIONS
Children's daily stress was associated with emotional eating behavior and undesirable dietary pattern such as consumption of sweet beverages. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ACADEMIC STRESS IS ASSOCIATED WITH EMOTIONAL EATING BEHAVIOR AMONG ADOLESCENT
Nadia Ramadhani, Trias Mahmudiono
Media Gizi Indonesia.2021; 16(1): 38. CrossRef - Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and influencing factors in Korean adolescents: based on the 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Ayoung Kim, Jinhee Kim, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 465. CrossRef
- ACADEMIC STRESS IS ASSOCIATED WITH EMOTIONAL EATING BEHAVIOR AMONG ADOLESCENT
- 1,288 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Dietary Behavior and Food Preference of Sramanera·Sramanerika Monks in Nationwide Buddhist Monk's Universities
- Su Jin Han, Sim Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(5):387-400. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.5.387
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was designed to find out factors that are needed to be improved for the Buddhist training environment of Sramanera·Sramanerika monks, who have been newly adapted for their life style after becoming a monk, and to provide basic data for the development of the standard diet in Buddhist temples.
METHODS
A self-administered questionnaire was applied to 365 Sramanera·Sramanerika monks at 11 Buddhist monk universities. The questionnaire was designed to investigate their dietary habits, dietary evaluation, satisfaction of food service, and food preferences.
RESULTS
The study population consisted of 52.6% men, and 47.4% women. The subjects who had a vegetarian diet before joining the Buddhist priesthood were 27.7% women, and 13.5% men (p<0.01). 42.2% of the total subjects felt that they are healthy now and 19.4% felt weak. The most difficulty of dieting adaptation as soon as entering the priesthood was the strict diet rules (42.9%). The subjects considered health or nutrition (40.0%) highly when having meals. 94.8% women, 84.1% men ate breakfast every day (p<0.001). Women (55.4%) frequently ate snacks more than men (26.6%) (p<0.001). The results of the dietary evaluation indicated that the intake of milk, soy milk or dairy products and beans or tofu received lower than 3 points and women had lower point result than men (p<0.001). Foods with higher preference were grilled mushrooms, grilled laver, miso stew, sweet and sour mushrooms, steamed tofu with seasoning.
CONCLUSIONS
Women were more interested in their health than men but they also required to improve the nutritional eating habits. It appeared that the lower intake rates of the calcium containing food (milk and dairy), and proteins (beans and tofu) could result in nutritional imbalance. Therefore, it is necessary to offer food based on the standard menu plan with consideration given to their food preferences in order to maintain their health and desirable dietary habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behavior and Food Preferences of Buddhist Monks in Korean Temples
Choong-Sun Lim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(4): 331. CrossRef - Vegetarianism as a protective factor for asymptomatic colonic diverticulosis in Asians: a retrospective cross-sectional and case-control study
Jihun Bong, Hyoun Woo Kang, Hyeki Cho, Ji Hyung Nam, Dong Kee Jang, Jae Hak Kim, Jun Kyu Lee, Yun Jeong Lim, Moon-Soo Koh, Jin Ho Lee
Intestinal Research.2020; 18(1): 121. CrossRef
- Dietary Behavior and Food Preferences of Buddhist Monks in Korean Temples
- 1,430 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Use of Dietary Supplements and Determinants of Taking Dietary Supplements by Gender in the Korean Population: Using the 4(th) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007-2009)
- Yun Jung Lee, Minji Kang, Hee Young Paik, YoonJu Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):347-355. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.347
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Although dietary supplements use in Korea has been rapidly increasing and women are more likely to take dietary supplements more than men, only a few studies have been conducted to investigate factors contributing to gender differences in dietary supplement use in the Korean population. The aim of this study is to evaluate the prevalence of dietary supplement use and also identify gender-specific key factors that contribute to it using the data of the 4th KNHANES.
METHODS
Subjects were divided into user and non-user groups according to the answer given to the question that asked whether they had used any dietary supplement for more than 2 weeks on a regular basis during the previous year. Factors related to dietary supplement use were examined by general characteristics, health behavior and eating behavior.
RESULTS
Prevalence of dietary supplement use was 13.6% for men and 20.6% for women. Users were more likely to be middle-aged, have higher income and education, have a spouse, or reside in dong areas in both men and women. Regarding health behaviors, men with desirable lifestyle behavior were more likely to take dietary supplements, while men who smoked were less likely to take dietary supplements. Regarding disease history, both men and women with a current disease had higher odds of taking supplements. With regard to dietary behavior, frequent eating out and nutrition attitude were associated with higher odds of taking supplements in both men and in women.
CONCLUSIONS
Health or dietary behavior related factors that were associated with taking supplements differed by gender. These findings can be useful for planning gender-specific dietary education and health programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight management strategies and food supplement intake among Bulgarian adults: results of a national survey
Radiana Staynova, Vesselina Yanachkova
Pharmacia.2023; 70(4): 1119. CrossRef - A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef - COVID-19 Salgını Sürecinde Yetişkinlerde Gıda Takviyesi Kullanımı ve İlişkili Etmenler
Kevser TARI SELÇUK, Nursel ŞAHİN
Turkish Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 15(4): 751. CrossRef - Dietary supplements consumption and its association with socioeconomic factors, obesity and main non-communicable chronic diseases in the north of Iran: the PERSIAN Guilan Cohort Study (PGCS)
Marjan Mahdavi-Roshan, Arezoo Rezazadeh, Farahnaz Joukar, Yasaman Khorshidi, Mohammadreza Naghipour, Fariborz Mansour-Ghanaei
BMC Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Status of Vitamins and Minerals According to Consumption of Dietary Supplements in Korean Adults and the Elderly: Report Based on 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(4): 329. CrossRef - Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 112. CrossRef
- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- 1,544 View
- 7 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between Snack Intake and Oral Health Behavior of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Hyunsook Kang, Kyunghee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):336-346. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.336
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study was performed to investigate the relationship between snack intake and oral health behavior in middle school students in Gyeonggi-do area.
METHODS
The survey questionnaire was recorded by middle school students from July 6 to August 24, 2011. The questionnaire included items on general characteristics, snack intake status, and oral health behavior. Among collected survey questionnaire, a total of 620 questionnaires (320 males and 300 females) were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 program.
RESULTS
Frequencies of snack and beverage intakes were significantly higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). Oral health behavior was significantly higher in students with lower snack intake compared to those with higher or average snack intake (p < 0.05). Oral health behavior for tooth brushing and toothbrush care were significantly higher in females than in males (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Oral health behavior score that reflected better oral health of the subjects were higher as the snack intake was lower. Oral health behavior score was higher in females than in males. We conclude that the contents for oral health and nutrition education focused on snack intake need to be developed to induce changes in oral health behavior in middle school students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - Evaluation of frequency of consumption of cariogenic snacks by freshmen versus the senior dental students in Tehran and the related factors: a cross-sectional study
Mahdia Gholami, Simin Z Mohebbi, Milad Mafakheri, Houra Shahhosseini
BMJ Open.2024; 14(9): e086041. CrossRef
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,582 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship among Life Stress, Dietary Behaviors and High-fat Snack Intake in High School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Seorin Doo, Youngmi Lee, Haeryun Park, Kyunghee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):289-297. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.289
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Stress during adolescence is related to undesirable nutritional intake and negatively affects the growth and development. This study was performed to investigate the relationship among life stress, dietary behaviors and the intake of high-fat containing snacks in male and female high school students in Gyeonggi-do area.
METHODS
The subjects were 700 high school students (350 males, 350 females) in Gyeonggi-do from July to September 2014 and the survey was performed by using questionnaire that included general characteristics, dietary behaviors, high-fat containing snacks intake, and daily life stress.
RESULTS
There was a gender difference in health-related life style and dietary behaviors, and the life stress was significantly higher in female students than in male students. For health-related life style, exercise frequency, hours of sleep and conversation time with parents had significantly negative correlations with life stress, while smoking and perceived stress had significantly positive correlations with life stress. For dietary behaviors, the frequency of eating-out had a significantly negative correlation with life stress, while the changes in amount of meal intake under stress had a significantly positive correlation with life stress. The fat intake of ‘high-stress group’ was significantly higher and high-fat containing snacks consumed by this group consisted of cookies, honey bread and fried foods.
CONCLUSIONS
It is necessary to develop appropriate programs for the emotional stability and stress relief of adolescents that provide continuous nutrition education focused on proper snack intake, desirable dietary behaviors and nutritional aspects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef - Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
Ho-Jung Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Yookyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 320. CrossRef - Life stress, dietary attitudes, and frequency of snack intake for college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi area: the difference between male and female students
Hyun Seung Oh, Yu bin Kim, Soyoung Park, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(1): 91. CrossRef - Actual Status of Mukbang Viewing and Food Habits of University Students in Wonju Area
Seung-Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(4): 631. CrossRef - Assessment of Sugar and Sodium Contents and Their Intakes in Snack Food Groups : A Focus on Cookies, Nuts, Fruits, Dairy Products, and Beverages
Yun-Jung Bae, Kyoung-A Choi, Yu-Mi Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(4): 263. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Dietary Behavior of Adults Aged 20 and Over according to theMukbangViewing Time
Ha-Yan Nam, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(2): 93. CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Habits, Life Stress and Nutrition Knowledge of High School Students in Gyeonggi Area
Kyung Ae Park, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 126. CrossRef - Association between Stress and Nutritional status of High School Students in Chungbuk using Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents
In Young Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 361. CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Behaviors and Life Stress of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
Kyung Ae Park, Myoung Sook Lee, Kyung Hee Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 384. CrossRef - Body Image Perception and Eating Behaviors among Male Middle and High School Students according to Weight Status in Seoul
Bo-Mi Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(2): 123. CrossRef
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,265 View
- 1 Download
- 10 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



