Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- The association between sodium index and the risk of obesity in Korean and Chinese university students: a cross-sectional study
- Linan Wang, Jin-Ah Seok, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):419-430. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
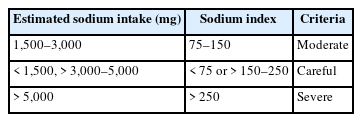
Korea and China have the highest sodium intakes globally. The sodium index is a quantitative measure of the estimated sodium intake, calculated using a regression equation with proven validity and reliability in individuals aged 19–69 years. This study aimed to compare the sodium index of Korean and Chinese university students and analyze the association between the sodium index and the risk of obesity.
Methods
A total of 218 university students—110 Korean (63 males, 47 females) and 108 Chinese (60 males, 48 females)—participated in this study in 2019. Sodium-related awareness, nutritional knowledge, and sodium index were compared between Korean and Chinese students. Obesity indicators were compared according to three criteria for the sodium index of Korean and Chinese students: “moderate,” “careful,” and “severe. ” The association between sodium index levels and risk of obesity was analyzed using multiple logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex.
Results
Overall, 84% of students recognized that they consumed large amounts of sodium. Korean students demonstrated higher nutritional knowledge scores than Chinese students. The average estimated sodium intake was 3,751 mg, and no significant difference was observed between Korean (3,857 mg) and Chinese (3,643 mg) students. The overall average sodium index was 187, which falls under the “careful” level. As the sodium index levels increased, the students’ body mass index, waist-hip ratio (WHR), and fat-related indicators significantly increased. At the “severe” level of the sodium index, Korean and Chinese students had 2.402-fold and 1.636-fold increases in the risk of obesity based on body fat percentage, and 3.682-fold and 1.622-fold increases based on WHR, respectively.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated an association between sodium index and obesity risk, showing that excessive sodium intake affects body fat-related indicators in university students.
- 402 View
- 20 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of clinical characteristics and dietary intakes according to phenotypes of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Jin Kim, Ji-Sook Park, Sung-Rae Cho, Daeung Yu, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):127-139. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Clinical nutrition treatment is the central part of diabetes management, such as prevention, treatment, and self-management of diabetes, and personalized clinical nutrition treatment, which enables improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study aimed to contribute to the improvement of appropriate nutrition management in personalized treatment for obese and non-obese diabetes patients.
Methods
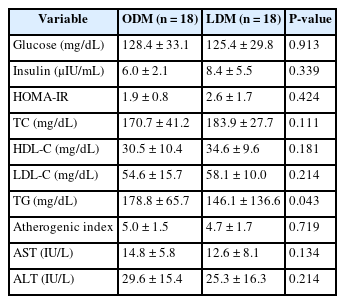
T2DM patients were recruited as participants, and 36 final participants were assigned to the lean diabetes mellitus group (LDM; body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and the obese diabetes mellitus group (ODM; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). We assessed the dietary intakes, body composition, dietary habits, the Korean version of obesity-related quality of life, and biochemical indices.
Results
According to the phenotype’s comparison, the ODM group had a high prevalence of T2DM complications and hypertension, had a dietary habit of less than 10 minutes of mealtime duration and preferred fast food intake, and had a low obesity-related quality of life. However, the LDM group had a high choice of Korean dishes at the time of eating out and a high intake of vitamin C, and iodine because of the intake of vegetables and seaweeds.
Conclusion
We observed differences in diet, nutrient intake, and clinical characteristics according to the phenotype of T2DM patients. In particular, obese diabetes patients have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, bad dietary habits, and low obesity-related quality of life. Therefore, personalized nutrition treatment is needed in consideration of the risk of cardiovascular disease and dietary habits for patients in the ODM group, as well as determining the energy requirements of Korean patients with T2DM.
- 2,292 View
- 33 Download

- [English]
- Serum branch chain amino acids and aromatic amino acids ratio and metabolic risks in Koreans with normal-weight or obesity: a cross-sectional study
- Ji-Sook Park, Kainat Ahmed, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.212
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Metabolic disease is strongly associated with future insulin resistance, and its prevalence is increasing worldwide. Thus, identifying early biomarkers of metabolic-related disease based on serum profiling is useful to control future metabolic disease. Our study aimed to assess the association of serum branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and aromatic amino acids (AAAs) ratio and metabolic disease according to body mass index (BMI) status among Korean adults.
Methods
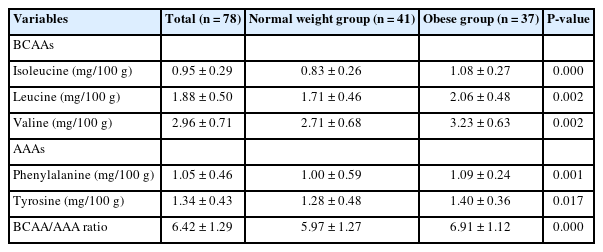
This cross-sectional study included 78 adults aged 20–59 years in Korea. We compared serum amino acid (AA) levels between adults with normal-weight and adults with obesity and investigated biomarkers of metabolic disease. We examined serum AA levels, blood profile, and body composition. We also evaluated the association between serum AAs and metabolic-related disease.
Results
The height, weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-hip-ratio, body fat mass, body fat percent, skeletal muscle mass, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure were higher in the group with obesity compared to normal weight group. The group with obesity showed significantly higher levels of BCAA, AAA, and BCAA and AAA ratio. Further, BCAA and AAA ratio were significantly positively correlated with triglyceride, body weight, and skeletal muscle mass. The evaluation of metabolic disease risks revealed an association between the ratios of BCAAs and AAAs, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome.
Conclusions
Our study is showed the associations between BCAA and AAA ratio, obesity, and obesity-related diseases using various analytical approaches. The elevated BCAA and AAA ratio could be early biomarkers for predicting future metabolic diseases in Korean population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
Apostolos Gkantzos, Stavros Kalogiannis, Olga Deda
Journal of Proteome Research.2025; 24(5): 2208. CrossRef - Current Data on the Role of Amino Acids in the Management of Obesity in Children and Adolescents
Diana Zamosteanu, Nina Filip, Laura Mihaela Trandafir, Elena Ţarcă, Mihaela Pertea, Gabriela Bordeianu, Jana Bernic, Anne Marie Heredea, Elena Cojocaru
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(15): 7129. CrossRef
- The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
- 2,382 View
- 26 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship of sodium index with the obesity indicators of university students in Daegu, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Young-Won Jang, Jian Ma, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):189-198. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The sodium index is an index that converts the estimated sodium intake calculated using a verified and reliable sodium estimation formula. This study aimed to determine the relationship between the sodium index and obesity indicators and the potential impact of excessive sodium consumption on obesity.
Methods
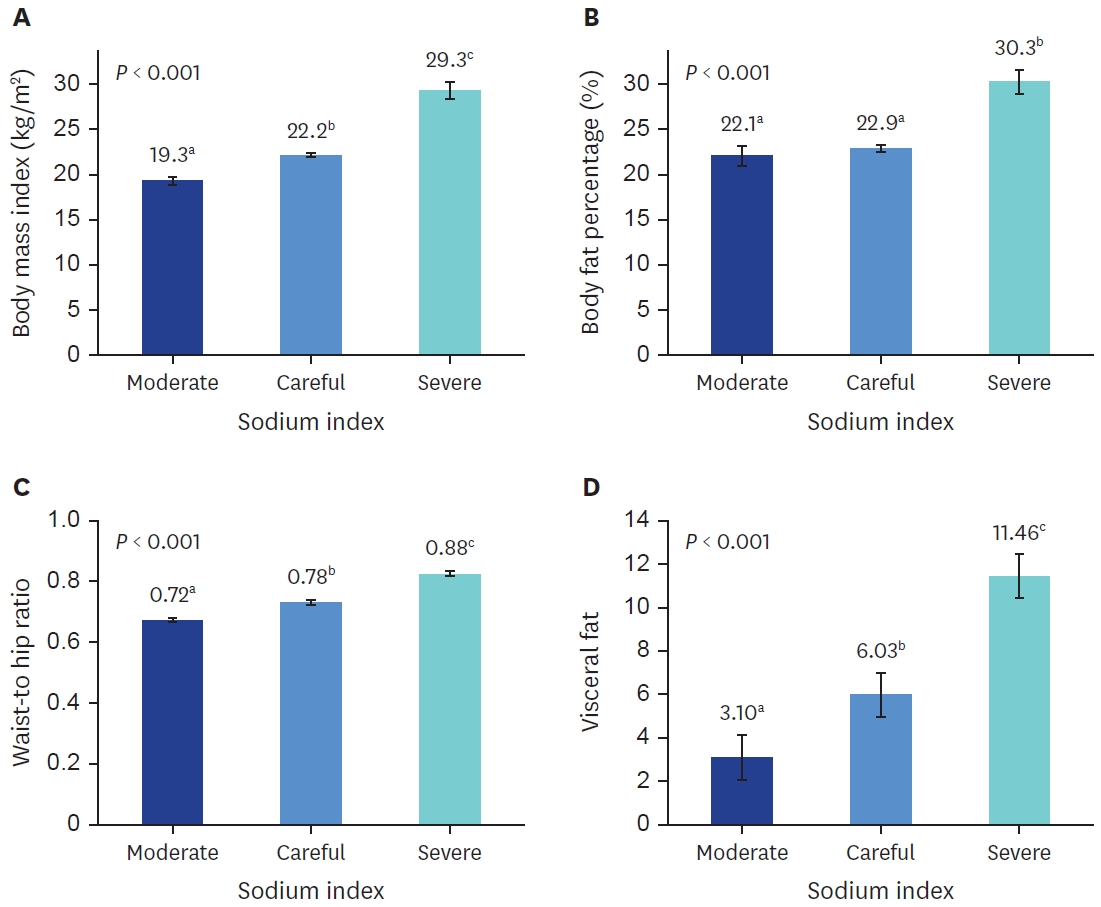
Obesity indicators, such as body mass index (BMI), body fat percentage, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), and visceral fat levels, were analyzed in 120 university students (60 men and 60 women). The sodium index was calculated by indexing the estimated sodium intake according to age, sex, BMI, salt-eating habits, and salt-eating behaviors. The relationship between sodium index and obesity indicators was analyzed using multiple logistic regression.
Results
The estimated sodium intake was 3,907.1 mg, with 76.7% of the participants categorized under the “careful” level of sodium index and 10.8% under the “moderate” level. As the sodium index increased, the BMI, body fat percentage, WHR, and visceral fat levels significantly increased. All obesity indicators significantly increased in patients with a “severe” sodium index than in those with a “moderate” sodium index. In addition, a strong positive correlation was identified between obesity indicators and sodium index. When the “severe” sodium index was compared with the “moderate” sodium index, the risk of obesity based on body fat percentage increased by 2.181 times (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.526–3.118), while the risk of obesity based on visceral fat level increased by 4.073 times (95% CI, 2.097–7.911).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest a correlation between excessive sodium intake and obesity. Moreover, the sodium index can be used to determine sodium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The association between sodium index and the risk of obesity in Korean and Chinese university students: a cross-sectional study
Linan Wang, Jin-Ah Seok, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 419. CrossRef
- The association between sodium index and the risk of obesity in Korean and Chinese university students: a cross-sectional study
- 5,557 View
- 42 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Facilitators and barriers to achieving dietary and physical activity goals : focus group interviews with city bus drivers and counseling dietitians
- Yongmin Jo, Suhyeun Cho, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):376-391. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.376
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Our previously published study showed that a workplace nutrition intervention program with personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling improved dietary habits and physical activity in city bus drivers who were overweight/obese. This study explored the facilitators and barriers that participants faced in achieving their dietary and physical activity goals six months after the intervention.
Methods
The study included bus drivers and dietitians who participated in the intervention program. Three focus group interviews were conducted with 10 bus drivers (divided by two groups based on their achievement of set goals) and five dietitians who had provided nutrition counseling.
Results
Willpower was the most important intrapersonal facilitator for drivers to achieve their goals. Other factors that promoted behavioral changes were nutrition counseling by dietitians, trackable physical activity using smartwatches, and setting of practical and achievable goals. Meanwhile, the most important barriers identified were occupational factors such as long driving hours, short breaks, and shift work. Other barriers were environmental factors such as availability of snackable food, accessibility to convenience stores, and cold weather. Family and colleagues were perceived as both facilitators and barriers. In addition, dietitians identified a lack of knowledge about healthy diet as one of the barriers.
Conclusions
Our results suggested that the workplace environment should be improved and that nutrition intervention programs at the workplace could encourage bus drivers to practice healthy eating habits. The facilitators and barriers identified in this study should be considered when planning a nutrition intervention program for bus drivers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 466. CrossRef
- Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
- 1,357 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Factors related to adolescent obesity and changes: a cross-sectional study based on the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Bora Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):363-375. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to identify factors associated with adolescent obesity, as well as any new factors that correlated with a change in the rate of obesity over time.
Methods
The study used 5-yearly data collected by the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey starting from the year 2006 up until 2021 (data from 2nd, 7th, 11th, and 17th surveys were analyzed). Factors such as demographics, dietary factors, health behavioral factors, and mental health factors were studied. All data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27.0, employing chi-square tests and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results
This study included data from a total of 255,200 participants. Factors contributing to obesity varied with time. Over the survey duration of 15 years, low academic achievement, parents with low levels of education, low frequency of fruit consumption, low frequency of fast food intake, long periods of being seated, and high levels of stress were significantly associated with a high rate of obesity. Factors that showed a new correlation with an increase in obesity rates included living with single parents, low frequency of muscle strengthening exercises, and experiencing intense sadness and despair in the past year. Factors that were correlated with a change in obesity rates over time included household economic status, frequency of carbonated beverage consumption, frequency of intense physical activity, and frequency of alcohol consumption. Breakfast intake and smoking were not significantly associated with obesity rates in the 15-year period.
Conclusions
While several factors associated with obesity remained consistent over time, several new factors have emerged in response to social, economic, and environmental changes contributed to a change in obesity rate over time. Therefore, to prevent and manage adolescent obesity, continuous research into the new emergent factors contributing to obesity is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,944 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review
- [English]
- Mercury exposure is associated with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jimin Jeon, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):192-205. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Previous studies have evaluated the association between mercury exposure and obesity but have yielded mixed conclusions. The aim of this study was to systematically review and summarize scientific evidence regarding the association between mercury exposure and obesity in the human population.
Methods
We conducted a systematic search of PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Science Direct for articles related to mercury exposure and obesity. Meta-analyses of the highest and lowest categories of mercury levels were evaluated using a random effects model. Begg’s test was used to detect publication bias.
Results
A total of 9 articles were included. The pooled random effects odds ratio (OR) for mercury exposure and obesity of all 9 studies was 1.66 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.16-2.38). This positive association was evident in adults (OR: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.02-2.54) and among studies with Asian populations (OR: 2.00, 95% CI: 1.53-2.59), but not among those with North America/African populations (OR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.50-1.65).
Conclusions
The present meta-analysis identified a positive association between mercury exposure and obesity. These findings suggest that toxic environmental metals such as mercury may be an important risk factor for obesity along with dietary habits and lifestyles. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Re-thinking the link between exposure to mercury and blood pressure
Xue Feng Hu, Allison Loan, Hing Man Chan
Archives of Toxicology.2025; 99(2): 481. CrossRef - Associations of Metal Mixtures During Early Pregnancy With Midlife Obesity and Body Composition: A Prospective Study
Mingyu Zhang, Izzuddin M. Aris, Andres Cardenas, Sheryl L. Rifas‐Shiman, Pi‐I Debby Lin, Long H. Ngo, Emily Oken, Stephen P. Juraschek, Marie‐France Hivert
Obesity.2025; 33(10): 1984. CrossRef - Association Between Heavy Metals Exposure and Elevated High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: Mediating Role of Body Mass Index
Seong-Uk Baek, Jin-Ha Yoon
Biomolecules.2025; 15(11): 1491. CrossRef - Association between heavy metal exposure and biomarkers for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adolescents
Dong-Wook Lee, Jongmin Oh, Yu Min Lee, Hyun-Joo Bae, Youn-Hee Lim
Heliyon.2024; 10(19): e37840. CrossRef
- Re-thinking the link between exposure to mercury and blood pressure
- 3,102 View
- 73 Download
- 4 Crossref

Research Articles
- [English]
- Nutritional status and dietary behavior of North Korean adolescent refugees based on Nutrition Quotient for Korean adolescents: a preliminary study
- Young Goh, Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeong Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):1-10. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the nutritional status and dietary behavior of adolescents from North Korean refugee (NKR) families residing in South Korea (SK), who are known to be at a higher risk of malnutrition due to their lower socioeconomic status and facing other psychological challenges.
Methods
A total of 178 adolescents (91 males and 87 females) from NKR families were included in the analysis, and their demographic details such as age, birthplace, parental nationality, and duration of their settlement in SK were collected through questionnaires. Anthropometric measurements were also taken to determine their growth and nutritional status according to the 2017 Korean National Growth Charts for children and adolescents. The study used the Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents (NQ-A) questionnaire to assess the dietary behavior of the participants.
Results
Approximately 11.8% and 10.1% of participants were identified with malnutrition and obesity, respectively. The total mean score for the NQ-A was 50.1. The mean scores for the individual factors of balance, diversity, moderation, environment, and practice were 49.2, 44.7, 43.8, 51.2, and 61.5, respectively. Approximately 47.2% of participants had a low NQ-A grade. However, there was no significant difference in the NQ-A scores according to their nutritional status or duration of time in SK.
Conclusions
Adolescents from NKR families exhibited both malnutrition and obesity. However, their dietary behavior, as assessed using the NQ-A, did not vary with their nutritional status. The unique challenges and related dietary behavior of North Korean adolescent refugees should be taken into consideration, when developing targeted strategies for nutritional education and health management programs.
- 2,132 View
- 24 Download

- [Korean]
- Program Evaluation using the RE-AIM Framework: A Systematic Review and Application to a Pilot Health Promotion Program for Children
- Ji-Eun Lee, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim, Jae-Heon Kang, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(4):296-308. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.4.296
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop evaluation criteria for the elementary-school-based health promotion program using the RE-AIM framework and to examine their feasibility.
Methods
Previous evaluation studies on health interventions for elementary-school students using the RE-AIM framework were reviewed systematically to identify appropriate evaluation criteria. A diet and physical activity intervention based on the transtheoretical model was implemented in a pilot study using the “Happy Me” application. The feasibility of using the RE-AIM framework to evaluate it was examined.
Results
The review yielded the following evaluation criteria: “reach,” the ratio of participants out of the total target population; “efficacy/effectiveness,” the difference in outcomes between the intervention and control groups, or between a pre- and post-test; “adoption,” the rate of use of the program and participation in the next stage of the program; “implementation,” the progress on the program components; “maintenance,” the participants’ and teachers’ intention to continue using the program. The pilot study reached 76.6% of the targeted population. The intake of sugar-sweetened beverages decreased (P < 0.0001), and the duration of walking increased (P < 0.0001). Other indicators could not be evaluated; therefore, potential indicators were suggested.
Conclusions
This study produced feasible evaluation criteria for elementary-school-based health promotion using the RE-AIM framework. Nevertheless, the feasibility needs to be validated with a broader range of studies and long-term interventions.
- 2,018 View
- 35 Download

- [English]
- The Changes in Obesity Prevalence and Dietary Habits in Korean Adults by Residential Area during the Last 10 Years – Based on the 4th (2007-2009) and the 7th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
- Da-Mee Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(1):37-47. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.1.37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to discover the changes in obesity prevalence and dietary habits in Korean adults residing in various residential areas during the last 10 years. Methods: Data on Korean adults aged 19 years and above was obtained from the 4th (2007-2009) and the 7th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The subjects were classified into metropolitan 4th : n=5,977, 7th : n=6,651), urban (4th : n=4,511, 7th : n=5,512) and rural (4th : n=3,566, 7th : n=2,570) based on their residence. The general characteristics, nutrient intake, intake amount, food groups, and healthy dietary factors were analyzed. The association between residential areas and obesity prevalence were analyzed by multiple logistic regression. Results: In urban and rural areas, the obesity rate increased in the 7th survey compared to the 4th survey, excluding the metropolitan area. The carbohydrate intake decreased, and lipid intake increased in the 7th survey compared to the 4th survey. Over the same period, the intake of cereals and vegetables decreased, and the intake of meat and processed foods increased. Rural residents had a higher intake of cereals and vegetables, and a lower intake of milk and processed foods than those in metropolitan areas and urban residents. The proportion of subjects who practiced a healthy diet increased in the 7th survey compared to the 4th survey. In the 4th survey, there was no relationship seen between the prevalence of obesity and the subject’s residential area, but in the 7th survey, the odds ratio of obesity was higher in rural areas than in the metropolitan areas, confirming the regional gap (OR: 1.16, 95% CI=1.00-1.36, p=0.044). Conclusions: This study showed that the obesity prevalence increased in rural residents compared to metropolitan residents, indicating a gap between the regions. The nutrient intake and intake of food groups changed in the 10 years under consideration, and there were differences seen between regions. Therefore, it is necessary to formulate a policy that will reduce obesity prevalence and health inequalities between regions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between chemotherapy and the risk of developing breast cancer-related lymphedema: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Sung Hoon Jeong, Seong Min Chun, Hyunji Lee, Miji Kim, Mira Choi, Ja-Ho Leigh
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality Characteristics and Antioxidant Activities of Morning Bread with the Addition of Whole Citron (Citrus junos seib) Powder
Eun Jung Kwak, Hyun-Joo Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2025; 36(3): 417. CrossRef - Long-Term Cancer Incidence Trends in Korea (2001–2020): An Age–Period–Cohort and Joinpoint Analysis with a Focus on Younger Cohorts
Hyungho Lee, Mingyu Kim, Geehyun Song, Jae Young Joung, Hokyung Seo, Jin-Ha Yoon, Jinsoo Chung
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2179. CrossRef - Ultra-processed food intake and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 410. CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer After Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis of the Korean National Sample Cohort
Sung Hoon Jeong, Kyungduk Hurh, Eun-Cheol Park, Ja-ho Leigh, Seung Hoon Kim, Sung-In Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - Association of heavy metal complex exposure and neurobehavioral function of children
Minkeun Kim, Chulyong Park, Joon Sakong, Shinhee Ye, So young Son, Kiook Baek
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Obesity Activity of Ethanol Extract of Veronica peregrina L.
Su Min Kim, Cheol Park, Yung Hyun Choi, Hye Jin Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 350. CrossRef - Effect of Type of Nutrition Labeling on the Healthfulness Evaluation and Purchase Intentions of Home Meal Replacements (HMR) in South Korea
Mee-Young Joe
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 387. CrossRef - Blood Biochemical Characteristics, Dietary Intake, and Risk Factors Related to Poor HbA1c Control in Elderly Korean Diabetes Patients: Comparison between the 4th(2007-2009) and the 7th(2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 406. CrossRef - Interactions between red and processed meat consumption and APOA5 gene variants associated with the incidence of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults
Woo Jeong Choi, Dayeon Shin
Genes & Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef - Regional Disparity in Adult Obesity Prevalence, and Its Determinants
Bongjeong Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(4): 410. CrossRef - Obese Frailty and Combined Exercise
Hae Sung Lee, Jong-Hee Kim
Exercise Science.2021; 30(4): 419. CrossRef
- Association between chemotherapy and the risk of developing breast cancer-related lymphedema: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
- 1,430 View
- 12 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between the Dietary Behavior of Young Children and Their Mothers in Daejeon, Korea Using the Nutrition Quotient for Preschoolers and Adults
- InYoung Jeong, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(1):12-22. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between the dietary behavior and weight status of preschool children and their mothers in Daejeon, Korea. Methods: A total of 301 mother–preschool children (aged 3~6 years) dyads were included in this study. The dietary behavior of children and their mothers was assessed using the Nutrition Quotient (NQ) questionnaire for preschoolers and adults, respectively. The NQ questionnaires were completed by the mothers. The overweight/ obesity status of children and their mothers was determined using data on height and body weight reported by the mothers. Multiple logistic regression was performed to examine the relationship between the dietary behavior and weight status of children and their mothers. Results: The mean NQ score was 58.9 ± 9.7 in children and 55.6 ± 9.2 in mothers. The NQ score was higher in boys than girls but did not vary by age. The prevalence of overweight/obesity was 27.5% in children and 46.5% in mothers. The physical activity level of mothers and their NQ scores were positively associated with the NQ scores of the children. After adjustment for covariates, the mothers in the highest tertile of NQ scores showed a lower odds ratio (OR) for the unhealthy dietary behavior of children (OR = 0.24, 95% CI = 0.11~0.53, P< 0.001) compared to those in the lowest tertile. The obese mothers showed a higher OR for children’s overweight/obesity (OR = 3.38, 95% CI = 1.68~6.80, P = 0.001) compared to normal weight mothers. Conclusions: The dietary behavior and weight status of young children and their mothers were closely linked. Nutrition education programs targeting mothers are necessary for improving maternal and child nutrition. Specifically, these programs need to be tailored to the socioeconomic characteristics or weight status of mothers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
Sil-Ah Kim, Min-Ah Kim, Seung-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 614. CrossRef -
Validation of the Korean Version of the Nutrition Screening Tool for Every Preschooler (NutriSTEP
®
): Using the Rasch Model
So Hyun Park, Youn-Jung Son, Hanjong Park
Journal of the American Nutrition Association.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
Sung-Mi Cha, Soo-Youn Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 541. CrossRef - Early childhood eating behaviors associated with risk of overweight and its socio-ecological determinants in Korean preschool children
Yeri Kim, Jiye Kim, Bomi Lee, Seungyoun Jung, Seo-Jin Chung, Hyekyeong Kim, Nana Shin, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(4): 717. CrossRef - Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Dietary Practices for Mothers in Japan
Lin Wu, Miao Wu, Akira Ishida
Women.2022; 2(3): 264. CrossRef - Use of mothers' home meal replacement and diet quality of their young children
Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 292. CrossRef
- Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
- 1,129 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Barriers of Obesity Management of Children Using Community Child Care Centers and Potential Possibility of Utilizing Mobile Phones: A Qualitative Study for Children and Caregivers
- Bo Young Lee, Mi-Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwan
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):189-203. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was performed to identify the current barriers of obesity management for children using Community Child Care Centers and their caregivers (parents and teachers working in the Centers). Further, this study explored the possibility of utilizing a mobile phone application for tailored obesity prevention and management programs to overcome the current difficulties associated with children's obesity management.
Methods
The qualitative data were collected through in-depth interviews with 20 obese and overweight children or children who wanted to participate in this study using Community Child Care Centers, 12 teachers working at the Centers, and a focus group interview with five parents of children using the Centers. Data were analyzed with a thematic approach categorizing themes and sub-themes based on the transcripts.
Results
The current barriers of obesity management of obese and overweight children using Community Child Care Centers were lack of self-directed motivation regarding obesity management (chronic obesity-induced lifestyles and reduced self-confidence due to stigma) and lack of support from households and Community Child Care Centers (latchkey child, inconsistency in dietary guidance between the Center and household, repetitive pressure to eat, and absence of regular nutrition education). Mobile phone applications may have potential to overcome the current barriers by providing handy and interesting obesity management based on visual media (real-time tracking of lifestyles using behavior records and social support using gamification), environmental support (supplementation of parental care and network-based education between the Community Child Care Center and household), and individualized intervention (encouragement of tailored and gradual changes in eating habits and tailored goal setting). It is predicted that the real-time mobile phone program will provide information for improving nutritional knowledge and behavioral skills as well as lead to sustainable children’s coping strategies regarding obesity management. In addition, it is expected that environmental factors may be improved by network-based education between the Community Child Care Centers and households using the characteristics of mobile phones, which are free from space and time constraints.
Conclusions
The tailored education program for children using Community Child Care Centers based on mobile phones may prevent and reduce childhood obesity by overcoming the current barriers of obesity management for children, providing environmental and individualized support to promote healthy lifestyles and quality of life in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
Jiyoung Park, Sein Hwang, Seolhyang Baek, Gill A. Ten Hoor
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2389. CrossRef
- An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
- 1,177 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Associated with Weight Status among Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: Using Data from the 2017–2018 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
- SuJin Song, Hyojune Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):465-475. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.465
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study investigated dietary and lifestyle factors associated with the weight status among Korean adolescents in multicultural families.
METHODS
This cross-sectional study analyzed 1,751 multicultural families' adolescents who participated in the 2017–2018 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Information on dietary and lifestyle factors was self-reported using a web-based questionnaire and this information included breakfast and foods consumption, perceived health status, alcohol drinking, smoking, physical activity, and weight control efforts. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated based on the self-reported height and body weight (kg/m²). Weight status was assessed according to the 2017 Korean National Growth Chart: underweight (weight-for-age <5(th) percentiles), overweight (85(th)≤ BMI-for-age <95(th) percentiles), and obese (BMI-for-age ≥95(th) percentiles). Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to examine the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with weight status after adjustment for covariates.
RESULTS
Among Korean adolescents from multicultural families, the prevalence of overweight/obesity was 20.9%, whereas about 7% of adolescents were underweight. The weight status did not show differences according to gender, school level, area of residence, and household income. Compared to adolescents who did not have breakfast during the previous week, those who had breakfast 3–4 days/week and ≥5 days/week had a 42% (p=0.021) and a 37% (p=0.009) lower prevalence of overweight/obesity, respectively. The adolescents who frequently consumed carbonated soft drinks (≥5 times/week) showed an odds ratio (OR) of 1.69 (95% CI=1.01–2.83) for overweight/obesity relative to those adolescents who did not consume carbonated soft drinks. The OR of being underweight for adolescents who ate fast food ≥3 times/week was 1.97 (95% CI=1.04–3.71) compared to those adolescents who had not eaten fast food during the previous week.
CONCLUSIONS
Dietary and lifestyle factors were associated with overweight/obesity as well as underweight among Korean adolescents in multicultural families. Our findings could be used to design and provide nutrition interventions for this specific population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Malnutrition and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents From Immigrant Families Living in Korea
Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeong Kim, Kyung-Ae Park
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(1): 29. CrossRef - Fruit Consumption and Mental Health in Adolescents from Multicultural and Non-multicultural Families: Data from Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web Based Survey 2021
Soohyun Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(2): 175. CrossRef - Identification of important features in overweight and obesity among Korean adolescents using machine learning
Serim Lee, JongSerl Chun
Children and Youth Services Review.2024; 161: 107644. CrossRef - Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 192. CrossRef - Effects of heavy metal, vitamin, and curry consumption on metabolic syndrome during menopause: a Korean community-based cross-sectional study
Hai Duc Nguyen, Min-Sun Kim
Menopause.2021; 28(8): 949. CrossRef - Association between levels of thiamine intake, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and depression in Korea: a national cross-sectional study
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, In Mo Yoon, Min-Sun Kim
Journal of Nutritional Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Antioxidant Vitamins, Curry Consumption, and Heavy Metal Levels on Metabolic Syndrome with Comorbidities: A Korean Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, Min-Sun Kim
Antioxidants.2021; 10(5): 808. CrossRef - Study on the Dietary Behavior of Adolescents in Multicultural Families Using the Nutrition Quotient and Their Changes in the Nutrition Knowledge and the Dietary Attitudes after Nutrition Education
Yoo-Jin Jung, Sung Hee Min, Min June Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(3): 208. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Malnutrition and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents From Immigrant Families Living in Korea
- 1,812 View
- 7 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- A Qualitative Study on the Potential Utilization of a Mobile Phone for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children : Parents Perspective
- Bo Young Lee, Mi Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(2):117-126. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.2.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the current difficulties surrounding children's obesity management and evaluate the application of a mobile phone as a tool to overcome such difficulties of obesity management from the perspective of main caregivers of elementary school students.
METHODS
The qualitative data were collected through 3 focus group interviews including 6 full-time housewives, 7 mothers with overweight children, and 4 working mothers. Data were analyzed using a thematic approach.
RESULTS
The limitations of current children's obesity management included difficulty in diet management and exercise as well as challenges of setting goals and lack of support at the household and school levels. Mobile technology may be useful to overcome the current problems by providing real-time knowledge on diet management and physical activity, online compensation scheme according to goal setting, and interactive environmental supports at both household and school levels for promoting overall health.
CONCLUSIONS
The mobile-based multiple support program may assist in overcoming the current limitations of child obesity management by providing tailored information and by creating a more supportive environment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Barriers of Obesity Management of Children Using Community Child Care Centers and Potential Possibility of Utilizing Mobile Phones: A Qualitative Study for Children and Caregivers
Bo Young Lee, Mi-Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 189. CrossRef - Consumers’ Impulse Buying Behavior on Instagram: Examining the Influence of Flow Experiences and Hedonic Browsing on Impulse Buying
Forough Shahpasandi, Azim Zarei, Mohsen Shafiei Nikabadi
Journal of Internet Commerce.2020; 19(4): 437. CrossRef
- Current Barriers of Obesity Management of Children Using Community Child Care Centers and Potential Possibility of Utilizing Mobile Phones: A Qualitative Study for Children and Caregivers
- 1,416 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Dietary Behaviors and Blood Clinical Indices in Underweight, Normal Weight, Normal Weight Obese and Obese Female College Students
- Su Bin Lee, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(5):431-443. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.5.431
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Normal weight obesity (NWO) is defined as excessive body fat in the context of a normal body mass index (BMI). This condition carries a greater risk of developing noncommunicable chronic disease and has been associated with early inflammation. This study was conducted to compare the anthropometric measurements, eating behaviors, and blood clinical indices among four groups: underweight, normal, normal weight obesity and obesity.
METHODS
The subjects included 215 female college students. A questionnaire was administered regarding general characteristics, dietary behaviors, food consumption frequency. Anthropometric measurements and blood clinical indices were also investigated.
RESULTS
The average BMI, body fat percentage, waist circumference, fat-free mass, and muscle mass were highest in the obesity group (p < 0.05). Most subjects had tried to lose weight and perceived that their health was worse than before they became college students. The ratio of students in the NWO group who thought their health was very poor was significantly higher than in the other three groups (p < 0.05). The obesity and NWO groups seemed to eat more and their eating speed was significantly faster than the other groups (pv0.001). The consumption frequency of caffeinated beverages was significantly higher in the NWO group than in the other three groups (p < 0.01). WBC was significantly higher in the obesity group (p < 0.05). Serum levels of TG and total cholesterol were also significantly higher in the obesity group (p < 0.05). Serum GPT was significantly higher in the obesity group (p < 0.05) while BUN level was highest in the NWO group (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The obesity group showed the most health problems while the NWO group seemed relatively healthy. However, NWO can lead to problems such as metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease in later life if poor dietary habits are maintained. Therefore, education in appropriate eating habits is needed for these subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on the perception of hand washing and health status in Korean adults
Soohee Park
Medicine.2021; 100(3): e24421. CrossRef - Gender Differences and Relationships among Lifestyle and Reproductive Health in University Students
Ju-Hee Nho, Hee Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 446. CrossRef
- A study on the perception of hand washing and health status in Korean adults
- 1,303 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Differences in Dietary Life and Health related Factors According to Obesity in Poor Urban Peruvian Adolescents
- Hye Kyung Chung, Hae Young Lee, Jin Ri Kim, Eun Woo Nam
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):302-318. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the differences in dietary life and health related factors, such as drinking behavior, exercise and leisure activities, mental health, and subjective perception for oneself according to obesity in poor urban Peruvian adolescents.
METHODS
A total of 1,532 Peruvian adolescents were selected from six schools in poor regions using stratified random sampling. The subjects were classified into two groups based on their BMI: ‘normal weight group (NW group=980)’ or ‘overweight and obese group (OWOB group=293)’. The differences in the general characteristics, dietary life, drinking behavior, physical activity and leisure, mental health and subjective perception of oneself in the two groups were compared. χ2 analysis and independent sample t-test were performed using the SPSS program ver. 24.
RESULTS
For the total and male students, the frequency of breakfast and dinner were significantly lower in the OWOB group than in the NW group (all p < 0.001). For total and female students, the percentage of subjects who received nutrition education was significantly higher in the OWOB group than in the NW group (all p < 0.05). For total students, the percentage of subject who exercised more than five days/week was lower in the OWOB group than in the NW group (p < 0.05). For the total and female students, the subjective health status was worse in the OWOB group than in the NW group (all p < 0.05). The subjective body image was significantly different between the OWOB group and NW group in the total, male and female subjects (all p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
The frequency of meals and exercise, and the subjective perceptions of the health status and body image differed according to obesity in poor urban Peruvian adolescents. Therefore, a school-based intervention program focused on regular meal and exercise, and adequate subjective perceptions for health status and body image need to be developed to prevent adolescent obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of perceived stress on obesity in South Korean adolescents using data from the 13th 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey
Hye Ja Gu
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(1): 29. CrossRef
- Influence of perceived stress on obesity in South Korean adolescents using data from the 13th 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey
- 1,243 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Status and Suggested Future Directions of Nutrition Intervention using Healthy School Tuck Shops: the Teenage Perspective
- Suhyun Oh, Kirang Kim, Ji Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):226-233. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the current status and to suggest future directions for health management of teenagers who use healthy school tuck shops to improve teenagers' eating habits while reducing and preventing obesity.
METHODS
A total of 29 students (16 middle school students and 13 high school students) took part in the interview for this study, and the interview was conducted for each school's focus group by using qualitative research methodology.
RESULTS
The current status of using healthy school tuck shops and suggested future directions were divided into two categories. Personal barriers such as discrepancies between personal perceptions and behaviors and lack of food choice suitable to individual tastes can be solved by rebuilding the operating system to provide intuitive promotion of behavior and customized products through improvements in existing products and new product development. A lack of consistent management from low utilization convenience and difficulty in maintaining a constant purchase price can be handled by establishing a solution to restricted physical access for products, as well as seeking profit by improving distribution costs via continuous cooperation between the school and community.
CONCLUSIONS
Continuous funding and a system that reflects the needs and preferences of healthy school tuck shop users should be applied for sustainable operation of healthy school tuck shops to improve teenagers' eating habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
Eun-Jin Choi, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 102. CrossRef
- Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
- 1,229 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationships between Obesity and Dietary Habits of Preschool Children and Their Parents in Dongducheon Based on the Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
- Ji Myung Kim, Hye Jeong Song, Young Ji Ahn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):216-225. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.216
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the associations between obesity and the children's Nutrition Quotient (NQ) and to further examine the relationships between NQ and mini dietary assessment (MDA) of their parents.
METHODS
The subjects were 355 children aged 3 to 5 years and their parents in Dongducheon. We collected parental-reported NQ questionnaires for children and MDA of parents. Anthropometric measurements, height, weight and BMI by BIA were measured in children. Overweight and obesity were determined according to age- and sex-specific BMI percentile from the 2007 Korean national growth chart. Statistical analyses consisted of the chi-squared test, ANOVA, partial correlations and logistic regression analysis adjustments for parents BMI.
RESULTS
Approximately 20.8% of preschool children were classified as overweight or obese. Underweight children showed a significantly higher score for balance than overweight children. The NQ of the children was 61.9 ± 11.6, and NQ scores and their parents' MDA did not exhibit any significant differences according to degree of obesity. After adjusting for parent's BMI, children's BMI was significantly correlated with balance and moderation among NQ factors. Parent's MDA showed significant correlation with their children's NQ, balance, diversity, moderation, regularity, practice and NQ grade, except for diversity of father. Additionally, NQ grade had a significantly increased (150.1%) odds ratio (OR) of being overweight (95% CI 1.008–2.234).
CONCLUSIONS
These results show that NQ for children is influenced by their parents' MDA and BMI. Furthermore, our findings support the association between overweight prevention and improvement of NQ grade among preschool children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the Causes of Obesity Among Adults in the Kurdish Regions of Iran: A Qualitative Study
Seyed Fahim Irandoost, Bahman Bayangani, Tahereh Dehdari, Javad Yousefi Lebni, Nafe Babasfari, Nafiul Mehedi, Mohammad Hosein Taghdisi
Community Health Equity Research & Policy.2023; 43(2): 183. CrossRef - Nutritional status and dietary behavior of North Korean adolescent refugees based on Nutrition Quotient for Korean adolescents: a preliminary study
Young Goh, Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeong Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 1. CrossRef - Dietary Behavior and Related Factors of Preschool Children in Seocheon-gun, Korea
Seung-Lim Lee, Sun-Im Won
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(1): 34. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary behaviors of preschool children in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do associated with the level of parents' health consciousness: using nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P)
Soo-Youn Kim, Sung-Mi Cha
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(2): 248. CrossRef - Association between Picky Eating Behavior, Growth, and Dietary Practices in Preschool Children
Jisun Kim, Sukyoung Kang, Seunghee Kye
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Relationship between the Dietary Behavior of Young Children and Their Mothers in Daejeon, Korea Using the Nutrition Quotient for Preschoolers and Adults
InYoung Jeong, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(1): 12. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary behavior and investigation of the affecting factors among preschoolers in Busan and Gyeongnam area using nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P)
Soo-Youn Kim, Sung-Mi Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 596. CrossRef - Assessment of dietary behaviors among preschoolers in Daejeon: using Nutrition Quotient for Preschoolers (NQ-P)
Hye-Jin Lee, Jin Hee Kim, SuJin Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(2): 194. CrossRef - Analysis of the types of eating behavior affecting the nutrition of preschool children: using the Dietary Behavior Test (DBT) and the Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
Hyeon Mi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 604. CrossRef
- Exploring the Causes of Obesity Among Adults in the Kurdish Regions of Iran: A Qualitative Study
- 1,424 View
- 14 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
- Mijin Jo, Young Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(1):38-47. Published online February 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to analyze the association between sodium excretion and obesity for healthy adults in the Gwangju area.
METHODS
The participants included 80 healthy adults aged 19 to 69 years in Gwangju. The dietary intake and sodium excretion were obtained using the 24-hour recall method and 24 hour urine collection. The participants were classified into two groups according to the amount of urinary sodium excretion: (≤ 141.75 mmol/dL, > 141.75 mmol/dL).
RESULTS
After adjusting for sex, age, smoking history, and income, the high excretion of sodium group was significantly higher for weight, body mass index, body fat mass, percent body fat, visceral fat area (VFA), waist circumference, hip circumference, and WHR. The energy and nutrients intake were significant after adjusting for sex, age, smoking history, and income. The LSE group had a significantly higher fat intake and Na/K intake ratio. The HSE group had significantly higher fiber intake, and K intake. As the amount of urinary sodium excretion increased, the risk of obesity before correction was 3.57 (95% CI: 1.13–11.25) times greater, and the risk of obesity of T3 increased significantly by 3.33 times (95% CI: 1.05–10.59). After correcting for sex and age, the obesity risk of T2 increased significantly by 4.23 times (95% CI: 1.11–16.06), and after correcting for sex, age, smoking history, and income, the obesity risk of T2 increased significantly by 6.81 times (95% CI: 1.44–32.19) the risk of obesity.
CONCLUSIONS
An association exists between sodium excretion and obesity in Korean adults. In this study, the high excretion of sodium group was obese and the risk of obesity was higher than the low excretion of sodium group. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preventive Effects of Whole Grain Cereals on Sarcopenic Obesity in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
Mi-Bo Kim, Sein Lee, Changhee Kim, Jae-Kwan Hwang
Food Engineering Progress.2018; 22(4): 358. CrossRef
- Preventive Effects of Whole Grain Cereals on Sarcopenic Obesity in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
- 1,285 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education at a Community Health Center on Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women in Jeonbuk Area-Focused on Personalized Daily Energy Requirement and Food Exchange Units
- Se Yeon Kim, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):307-322. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.307
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the effects of nutrition education focused on personalized daily energy requirement and food units using Food Exchange System on anthropometric, biochemical characteristics, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and nutrient intakes for overweight and obese in a public health center.
METHODS
The subjects were 60 overweight/obese women based on BMI (educated 30 vs. noneducated 30, 50~64 years). Educated group was provided individual and/or group lessons (40 min/ lesson/week, 5 week), ‘Introduction: obese & health’, ‘6 nutrients and 6 food groups’, ‘My obesity & daily needed energy’, ‘Meal planning for personalized daily energy and food units using Food Exchange Systems’, and ‘Smart food choices’. After education, we examined the differences in anthropometric/biochemical characteristics, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and nutrient intakes between educated group and non-educated group.
RESULTS
After nutrition education, in the educated group, there were improvements on anthropometric/biochemical characteristics, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and nutrient intakes in the educated group compared to the non-educated group. We observed a decrease in the mean weight, total cholesterol (TC) and the incidence of overweight/obesity and hypercholesterolemia and an increase in the mean lean body mass. The scores of nutrition knowledge, ‘Function of carbohydrate, protein, vitamin, mineral’ and ‘Food Sources of fat, vitamin, mineral’ were increased. The scores of dietary attitudes, ‘Taking a joyful meal, a leisurely meal, a balanced meal, a meal with sufficient vegetables, a meal with diversity, a meal with spicy foods, a meal with overeating’ were increased. The intakes of energy, carbohydrate, fat, protein, vitamin A, thiamin, Zn and cholesterol were decreased. The scores of INQ, protein, vitamin A, vitamin C, thiamin, riboflavin, vitamin B6, folate, Ca, P, Fe, Zn were increased.
CONCLUSIONS
The nutrition education focused on personalized daily energy requirement and food exchange unit using Food Exchange System for overweight and obese may improve food behavior, dietary intakes and symptoms of overweight and obese, even in a community health center. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Irisin Levels in Cancer Anorexia Cachexia Syndrome and the Relationship between Nutrition Education and Quality of Life
Diler Us Altay, Duygu Mataracı Değirmenci, Salih Can Çelik, Abdullah Üner, Tevfik Noyan, Çağrı Akalın
Cumhuriyet Science Journal.2024; 45(4): 636. CrossRef - Influence of Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention (LSI) Program on Health, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Middle-Aged Women
Su-Jin Jung, Seung-Ok Lee, Min-Jun Choi, Jun Heo, Soo-Wan Chae, Baik-Hwan Cho
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2022; 12(3): 127. CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Program on Obesity Index and Behavioral Modification in Moderate Obese Women
Myung-Hee Chang, Su-Jin Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(4): 318. CrossRef - Effects of an Intensive Management Program for Diabetic Patients on a Blood Biochemical Profile and Diabetes Knowledge
Su-Jeong Yeo, Bok-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(2): 148. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Irisin Levels in Cancer Anorexia Cachexia Syndrome and the Relationship between Nutrition Education and Quality of Life
- 1,260 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Leveraging Multimodal Supports using Mobile Phones for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children: Program Providers' Perspective from a Qualitative Study
- Mi Young Park, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim, Ji Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(3):238-247. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.3.238
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate providers' perspectives on current challenges in implementing a program for prevention and management of childhood obesity and adoption of mobile phone as a potential solution of leveraging multimodal delivery and support in a school setting.
METHODS
The qualitative data were collected through face-to-face in-depth interviews with 23 elementary-school teachers, 6 pediatricians, and 6 dieticians from community health centers and analyzed using a qualitative research methodology.
RESULTS
Current challenges and potential solutions of obesity-prevention and -management program for obesity program for elementary school children were deduced as two themes each. Lack of tailored intervention due to limited recipient motivation, lack of individualized behavioral intervention, and different environmental conditions can be solvable by mobile technology-based personalized intervention which brings about interactive recipient participation, customized behavioral intervention, and ubiquitous accessibility. Lack of sustainable management due to stigmatization, limited interactions between program providers and inconsistent administrative support can be handled by multimodal support based on school setting using mobile platform providing education of health promoting behaviors toward larger scale and interactive networking between program participants, and minimizing administrative burden.
CONCLUSIONS
Adoption of mobile-based health management program may overcome current limitations of child obesity program such as lack of tailored intervention and sustainable management via personalized intervention and multimodal supports although some concerns such as increased screen time need to be carefully considered in a further study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Qualitative Study on the Potential Utilization of a Mobile Phone for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children : Parents Perspective
Bo Young Lee, Mi-Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 117. CrossRef
- A Qualitative Study on the Potential Utilization of a Mobile Phone for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children : Parents Perspective
- 1,236 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review
- [English]
- Systematic Review on the Study of the Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in Korea: Dietary Risk Factors
- Eun Jeong Heo, Jae Eun Shim, Eun Young Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(3):191-206. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.3.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The present study systematically reviewed previous studies published in Korea regarding obesity status of children and adolescents in order to provide valid directions for future research and to help establish evidence-based prevention strategies.
METHODS
The articles were selected by searching the primary keyword ‘obesity’ and the secondary keywords ‘children’, ‘young children’, ‘adolescents’ or ‘kids’ on the KISS (Korean Studies Information Service System). Out of 503 articles excluding the overlap, 308 articles were selected with inclusion and exclusion criteria. Secular trends of obesity research, distribution of subjects, potential risk factors for obesity, and intervention method for obesity management were documented. The associations between obesity and dietary factors were summarized.
RESULTS
The overall number of research studies has increased since 2000 but obesity management studies have decreased in recent years. Most of the studies used a cross-sectional design. Research on preschool children were extremely limited. Intervention studies targeting males were prevalent. The most significant variables relevant to dietary habits were speed of eating, regular breakfast and snacking. The most significant food and nutrient intake factors were thiamin and iron. Intakes of cereals and animal foods were significantly higher in obese children than the counterparts.
CONCLUSIONS
The present review of locally published articles on the obesity status in children and adolescents suggested the need for well-designed further studies focused on risk factors of obesity and on a range of intervention methods conducive to the development of obesity prevention and management programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
Minji Kim, Meera Jang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 278. CrossRef - A systematic review and keyword network analysis of Korea Citation Index Journals (2004–2023)
Yunkyoung Oh, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 445. CrossRef - Trends in growth and nutritional status of Korean toddlers and preschoolers: a cross-sectional study using 2010–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Annisa Turridha, Jae Eun Shim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 480. CrossRef - Association of Infant Feeding Characteristics With Dietary Patterns and Obesity in Korean Childhood
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Moon-Kyung Shin
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(4): 338. CrossRef - Using methylome data to inform exposome-health association studies: An application to the identification of environmental drivers of child body mass index
Solène Cadiou, Mariona Bustamante, Lydiane Agier, Sandra Andrusaityte, Xavier Basagaña, Angel Carracedo, Leda Chatzi, Regina Grazuleviciene, Juan R. Gonzalez, Kristine B. Gutzkow, Léa Maitre, Dan Mason, Frédéric Millot, Mark Nieuwenhuijsen, Eleni Papadopo
Environment International.2020; 138: 105622. CrossRef - An Integrative Literature Review of Interventions for School-aged Overweight and Obese Children
Juhyun Jo, Sang-Youn Jang, Dajeong Kum, Jihee Lim, Jeongeun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2019; 16(2): 75. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study on the Potential Utilization of a Mobile Phone for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children : Parents Perspective
Bo Young Lee, Mi-Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 117. CrossRef - Effects of Sodium Intake on the Association between the Salt-Sensitive Gene, Alpha-Adducin 1 (ADD1), and Inflammatory Cytokines in the Prevalence of Children Obesity
Mi-Young Park, Myoung-sook Lee
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2018; 7(2): 98. CrossRef
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,679 View
- 14 Download
- 9 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Distribution and Exposure Prevalence of Carbohydrate-based Food Intake among Obese Korean Adults Based on the Health Examinees (HEXA) Study
- Yuri Han, Sung Ok Kwon, Sang Ah Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(2):159-170. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.2.159
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to estimate the distribution and exposure prevalence of total carbohydrate intake and the carbohydrate-based foods such as rice, noodles, sweet potatoes, sweet drinks, milk and fruits and to characterize intake patterns among obese Korean adults.
METHODS
Subjects included 137,363 adults aged 40 years or older who participated in a Health Examinees (HEXA) Study. Multiple regression analysis of data from Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire (SQFFQ) identified food sources of carbohydrates. Weight, height and waist circumstance (WC) were measured, and the body mass index (BMI) was calculated. Obesity was defined as BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 and abdominal obesity as WC ≥ 90 cm and ≥ 85 cm for males and females, respectively.
RESULTS
Obese adults appeared to have a higher total carbohydrate intake in the univariate analysis but had eaten less after adjustment for general and lifestyle factors, compared to normal weight adults (OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.73-0.82 for general obesity; OR 0.79, 95% CI 0.74-0.85, for abdominal obesity; P trend < 0.0001, respectively). Based on advance analysis for the food sources of carbohydrates, obese subjects had lower intake of rice (OR 0.86, 95% CI 0.68 -1.09 for general obesity; OR 0.87, 95% CI 0.67-1.13, for abdominal obesity; P trend < 0.0001, respectively) and higher intake of noodles (OR 1.21, 95% CI 1.16-1.27 for general obesity; OR 1.25, 95% CI 1.19-1.32, for abdominal obesity; P trend < 0.0001 respectively). With regard to other food sources of carbohydrates such as milk and fruits, intake was lower among obese compared to normal weight subjects.
CONCLUSIONS
In the Korean middle-aged and older obesity groups, the intake of carbohydrates and the related foods was lower than in normal weight subjects, except for noodles. We conclude that a higher intake of noodles may enhance weight-gain. Therefore, this study suggested that the guidelines should consider the types of carbohydrate sources and the amount consumed from foods in order to provide proper guidance with regard to control and prevent obesity among Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Calcium- and Sodium-Rich Food Intake among Koreans with and without Metabolic Syndrome: Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Byeonggeun Choi, Jiyoon Kim, Yeonjin Kim, Jiae Shin, Sang-Ah Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(15): 2439. CrossRef - In vitro safety and efficacy of probiotics mixture
on carbohydrate digestion inhibition
Eunsol Seo, Jang-Bin Woo, MinYeong Seo, Jeongmin Woo
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2023; 30(3): 538. CrossRef - Assessment of dietary quality and nutrient intake of obese children in Changwon area
Ji-Sook Park, Ha-Neul Choi, Jae-Young Kim, Sang-Hyuk Ma, Jung-Eun Yim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(6): 630. CrossRef - Comparison of the levels of energy intake from dish and food groups by gender and age among Korean obese adults: data obtained from the 2013-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Cheongmin Sohn, Woori Na, Chaeryeon Kim, Seunghee Choi, Oh Yoen Kim, Jounghee Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(6): 670. CrossRef - Relationship between Obesity and Dental Caries in Some University Students: A Pilot Study
SooJeong Hwang, Hoon Kim, MinSeock Seo
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(2): 127. CrossRef
- Calcium- and Sodium-Rich Food Intake among Koreans with and without Metabolic Syndrome: Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
- 1,281 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Diet Quality and Diversity according to Obesity Type among 19-64 year old Korean Adults
- Hyae Min Gu, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Mi Ah Han, Yeong Eun Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):545-557. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.545
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to compare the diet quality and diversity according to types of obesity categorized by body mass index and waist circumference among Korean adults aged 19-64 years.
METHODS
This study used the data of the 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES-V) and included 11,081 study participants. Type of obesity was categorized into 4 groups (Type 1: BMI obesity + abdominal obesity; Type 2: BMI obesity only; Type 3: abdominal obesity only; Type 4: Normal). To compare the diet quality and diversity according to obesity type, ANCOVA (Analysis of covariance) was used with stratification of age groups (19-44 years, 45-64 years).
RESULTS
With regard to comparative analysis of diet quality, there were significant differences between diet qualities in energy, protein, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, phosphorous and iron and type of obesity in the 19-44 age group, while there were significant differences between diet qualities on protein, vitamin C, phosphorous and type of obesity in the 45-64 age group. There was no significant difference between diet diversity score and type of obesity in Korean adults.
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that in Korean adults, diet qualities of some nutrients were different among obesity types, while diet diversity was not. These observations should be considered in an effort to improve intake of over-and deficient nutrients and in further studies to evaluate the effects of nutrient quality on obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of pre-obesity and above and its associated factors in adult women: an analysis of the 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyunju Chae
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(2): 117. CrossRef - The Factors Influencing the Bone Mineral Density in Korean Adult Men : Based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2011 Data
Hye-Sang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 136. CrossRef
- Prevalence of pre-obesity and above and its associated factors in adult women: an analysis of the 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,279 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Associations between Exposure to Unhealthy Food Outlets Within Residential District and Obesity: Using Data from 2013 Census on Establishments and 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoonjung Kim, Sung Nim Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(5):463-476. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.5.463
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Environmental, social and personal factors influence eating patterns. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between unhealthy food outlets within a residential area and obesity using nationally representative Korean survey data and data from the Census on Establishments.
METHODS
Data on the food intakes and socioeconomic variables of a total of 9,978 adults aged ≥ 19 years were obtained from the 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Geographic locations of restaurants were obtained from the 2013 Census on Establishments in Korea. Administrative area was categorized into tertiles of count of unhealthy food outlets based on the distribution of number of unhealthy food outlets among all urban (Dong) and rural (Eup or Myun) administrative districts in Korea. Multilevel logistic regressions model were used to assess the association between the number of unhealthy food outlets and obesity.
RESULTS
People living in the district with the highest count of unhealthy food outlets had higher intakes of fat (45.8 vs. 44.4 g/day), sodium (4,142.6 vs. 3,949.8 mg/day), and vitamin A (753.7 vs. 631.6 µgRE/day) compared to those living in the district with the lowest count of unhealthy food outlets. A higher count of unhealthy food outlets was positively associated with frequent consumption of instant noodles, pizza, hamburgers and sandwiches, sweets and sour pork or pork cutlets, fried chicken, snacks, and cookies. Higher exposure to unhealthy food outlets was associated with increased odds of obesity (1st vs. 3rd tertile; OR 1.689; 95% CI 1.098-2.599).
CONCLUSIONS
A high count of unhealthy food outlets within a residential area is positively associated with the prevalence of obesity in Korea. The results suggest that food environmental factors affects the health outcomes and interventions aiming to restrict the availability of unhealthy food outlets in local neighborhoods may be a useful obesity prevention strategy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity-Related Factors in Adult Women with Early Menarche
Hunha Cho, Jeong-Won Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(4): 557. CrossRef - Associations between adolescent dietary habits, obesity and food environment around schools in Seoul
Hyun-Jae Woo, Hong Lim Lee, Hae-Young Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(5): 55. CrossRef - Relationship between the Intake of Children's Favorite Foods and Policy based on Special Act on Safety Control of Children's Dietary Life
Taejung Woo, Jihye Yoo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 106. CrossRef
- Obesity-Related Factors in Adult Women with Early Menarche
- 1,552 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity and Their Association with Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Postmenopausal Women: Results for the 2008-2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Misung Kim, Cheongmin Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):378-385. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.378
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the association between sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity and cardiovascular disease risk in Korean postmenopausal women.
METHODS
We analyzed data of 2,019 postmenopausal women aged 50-64 years who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2008-2011 and were free of cardiovascular disease history. Blood pressure, height, and weight were measured. We analyzed the serum concentrations of glucose, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Waist circumference was used to measure obesity. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Sarcopenia was defined as the appendicular skeletal muscle mass/body weight<1 standard deviation below the gender-specific means for healthy young adults. The estimated 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease risk was calculated by Pooled Cohort Equation. Subjects were classified as non-sarcopenia, sarcopenia, or sarcopenic obesity based on status of waist circumference and appendicular skeletal muscle mass.
RESULTS
The prevalence of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity was 16.3% (n=317) and 18.3% (n=369), respectively. The 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease risk in the sarcopenic obesity group was higher (3.82 ± 0.22%) than the normal group (2.73 ± 0.09%) and sarcopenia group (3.17 ± 0.22%) (p < 0.000). The odd ratios (ORs) for the ≥7.5% 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease risk were significantly higher in the sarcopenic obesity group (OR 3.609, 95% CI: 2.030-6.417) compared to the sarcopenia group (OR 2.799, 95% CI: 1.463-5.352) (p for trend < 0.000) after adjusting for independent variables (i.e., exercise, period of menopausal, alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT) score, income, education level, calorie intake, %fat intake and hormonal replacement therapy).
CONCLUSIONS
Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity appear to be associated with higher risk factors predicting the 10-year risks of cardiovascular disease risk in postmenopausal women. These findings imply that maintaining normal weight and muscle mass may be important for cardiovascular disease risk prevention in postmenopausal women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Health Behavior Factors According to the Presence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged Men: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Junya Kang, In-Kyung Jung
Journal of Korean Association of Physical Education and Sport for Girls and Women.2024; 38(4): 201. CrossRef - The Impact of Possible Sarcopenia and Obesity on the Risk of Falls in Hospitalized Older Patients
Kahyun Kim, Dukyoo Jung
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2023; 26(1): 18. CrossRef - Association of Sarcopenia with Heart Rate Variability
Jeong-Min Ji, Hyun-Min Koh, Ji-Yong Jang, Jin-Sook Moon, Hye-Rang Bak, Hye-Jin Jang, An-Na Lee, Nak-Gyeong Ko
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2022; 12(5): 311. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Sarcopenia, Sarcopenic Obesity, and Sarcopenia Without Obesity in Older Adults
Seo-hyun Kim, Chung-hwi Yi, Jin-seok Lim
Physical Therapy Korea.2021; 28(3): 177. CrossRef - Association among the Prevalence of Sarcopenia without Obesity, Nonsarcopenic Obesity, Sarcopenic Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome in Cancer Survivors: Based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yoon J Park, Young M Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 679. CrossRef
- Comparison of Health Behavior Factors According to the Presence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged Men: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
- 1,506 View
- 7 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between Bone Mineral Density and Bone Metabolic Biochemical Markers and Diet Quality Index-International(DQI-I) in Postmenopausal Obese Women
- Yeonah Jeong, Misung Kim, Saeron Shin, Ahreum Han, Geomsuk Seo, Cheongmin Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(3):284-292. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.284
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study compared the differences of postmenopausal women's bone mineral density in relation to the degree of obesity, metabolism index and dietary factors that affect bone mineral density.
METHODS
The subjects included in the study are 39 postmenopausal women of normal weight with body mass index less than 25 kg/m2 and 32 postmenopausal who are obese. Anthropometry and biochemical analysis were performed and nutrient intakes and DQI-I were assessed.
RESULTS
Normal weight women were 56.03 ± 3.76 years old and obese women were 58.09 ± 5.13 years old and there was no significant difference in age between the two groups. The T-score of bone mineral density was 0.03 ± 1.06 in normal weight women and -0.60 ± 1.47 in obese women and this was significantly different between the two groups (p<0.05). Blood Leptin concentration was significantly lower in normal weight women (6.09 ± 3.37 ng/mL) compared to obese women in (9.01 ± 4.99 ng/mL) (p<0.05). The total score of diet quality index-international was 70.41±9.34 in normal weight women and 64.93 ± 7.82 in obese women (p<0.05). T-score of bone mineral density showed negative correlations with percentage of body fat (r = -0.233, p=0.05), BMI (r = -0.197, p=0.017), triglyceride (r = -0.281, p=0.020) and leptin (r = -0.308, p=0.011). The results of multiple regression analysis performed as the method of entry showed that with 22.0% of explanation power, percentage of body fat (β=-0.048, p<0.05), triglyceride (β=-0.005, p<0.05) and HDL-cholesterol (β=0.034, p<0.01), moderation of DQI-I (β=-0.231, p<0.05) affected T-score significantly.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of the study showed that obese women have less bone density than those with normal weight women. In addition, the factor analysis result that affect bone mineral density showed that intake of fat is a very important factor. Therefore, postmenopausal women need to maintain normal weight and manage blood lipid levels within normal range. They also need to take various sources of protein and reduce consumption of empty calorie foods that have high calories, fat, cholesterol and sodium.
- 1,136 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Associations between 24-hour Urine Sodium Excretion Level and Obesity-related Metabolic Risk Factors
- Hyun Woo Oh, Hyun Jung Kim, Dae Won Jun, Seung Min Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(6):460-467. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.460
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Excess sodium intake has been linked to obesity and obesity-related indices. However, the scientific evidence for this association is inadequate. The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between urinary sodium excretion and obesity-related indices among Korean adults.
METHODS
A convenience sample of 120 subjects (60 obese and 60 non-obese subjects) were recruited applying frequency matching for sex and age between two groups. Sodium intake level was assessed through 24-hour urine collection. Obesity-related metabolic risk factors, including fasting blood lipid indices, subcutaneous and visceral fat through computed tomography (CT), insulin resistance indices, blood pressure and liver enzymes were measured in all subjects. These obesity-related metabolic risk factors were compared between obese and non-obese group according to sodium excretion levels (<110 mEq/day, 110~180 mEq/day, >180 mEq/day).
RESULTS
After adjusting for age, gender, health behaviors (smoking, exercise, drinking), and energy intake, several obesity-related metabolic risk factors, including abdominal circumference, body fat percentage, subcutaneous and visceral fat, triglyceride, and systolic blood pressure were found to be significantly deteriorated as the sodium excretion level increases. In addition, multivariate adjusted-odds ratios of abdominal obesity, high blood triglyceride, and high blood pressure were found significantly higher in the highest sodium excretion group compared to the lowest group. The mean number of metabolic syndrome risk factors was also significantly greater in the highest sodium excretion group than in the lowest group.
CONCLUSIONS
The current study findings suggested that high sodium intake can affect obesity and metabolic syndrome risk negatively, implying the necessity of future research on low-sodium diet intervention in relation to obesity and related health problems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of sodium index with the obesity indicators of university students in Daegu, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Young-Won Jang, Jian Ma, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 189. CrossRef - Dietary salt intake and kidney function in rural Senegalese populations: a cross-sectional study
Ndongo Modou, Lot Nehemie Motoula Latou, Toure Maimouna, Amadou Diop Dia, Sidy Mohamed Seck
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiometabolic Risk of Visceral Fat Obesity and Factors Influencing Visceral Fat in Overweight or Obese Middle-Aged Korean Women: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sujin Kim, Nah-Mee Shin, Jiwon Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 320. CrossRef - The association between dietary sodium intake and obesity in adults by sodium intake assessment methods: a review of systematic reviews and re-meta-analysis
Jounghee Lee, Cheongmin Sohn, Oh-Yoen Kim, Young-Min Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Myoungsook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 175. CrossRef - Relationship between urinary sodium-creatinine ratios and insulin resistance in Korean children and adolescents with obesity
So Yoon Han, Nan Hee Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seon Mee Kim
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 31(4): 375. CrossRef - Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
Mijin Jo, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Relationship of sodium consumption with obesity in Korean adults based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2014
Se Young Cheon, Hye Won Wang, Hwa Jung Lee, Kyung Mi Hwang, Hae Seong Yoon, Yoon Jung Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 64. CrossRef - Associations of Obesity and Dyslipidemia with Intake of Sodium, Fat, and Sugar among Koreans: a Qualitative Systematic Review
Yoon Jung Kang, Hye Won Wang, Se Young Cheon, Hwa Jung Lee, Kyung Mi Hwang, Hae Seong Yoon
Clinical Nutrition Research.2016; 5(4): 290. CrossRef
- Relationship of sodium index with the obesity indicators of university students in Daegu, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 1,488 View
- 3 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effect of Obesity-Related Quality of Life on selecting a Goal for Weight Management in Overweight and Obese Patients
- Min Young Chun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(4):281-290. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.4.281
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Obesity is known to influence physical and mental health as well as the general quality of life. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of obesity related quality of life on selecting a goal for weight management in overweight and obese female patients.
METHODS
A total of 140 overweight or obese (Body mass index 23 kg/m2) female outpatients aged > or = 20 and < or = 60 years from one clinic participated in this study. Patients' desired weight (goal weight, ideal weight, satisfactory weight, acceptable weight and disappointed weight) and obesity related quality of life measures were evaluated. Univariate and multivariate analysis were performed to evaluate the effect of obesity related quality of life on goal weight reduction (%) and goal body mass index (BMI).
RESULTS
Mean BMI of overweight group, mild obesity group and severe obesity group were 62.0 +/- 4.8 kg, 68.5 +/- 5.5 kg and 83.5 +/- 9.6 kg, respectively. Mean weight loss expectations of the three groups were 16.4 +/- 4.7%, 19.5 +/- 5.3% and 30.2 +/- 6.8%, respectively and goal weight was significantly different among the three groups. Severe obesity group had a lower total quality of life score including physical, work-related, daily living domains than overweight or mild obesity groups. In univariate and multivariate regression analysis, psychosocial domain of quality of life had an effect on goal weight reduction (%) and goal BMI.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study demonstrated that the obese patients with poorer quality of life and psychosocial health tended to choose higher goal weight reduction and lower goal BMI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Search for Personalized Health and Beauty Care Using DTC Gene Analysis Data
Esther Choi, Myoung-Joo Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Cosmetology.2025; 31(1): 174. CrossRef - Effect on 12-week Intensive Dietary and Exercise Program on Weight Reduction and Maintenance in Obese Women with Weight Cycling History
Ha Nui Kwon, Sang-Seok Nam, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2017; 6(3): 183. CrossRef
- Search for Personalized Health and Beauty Care Using DTC Gene Analysis Data
- 1,290 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effects of Low-sodium Diet Education Program on Dietary Habits, Diet Quality and Obesity Index in Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women
- Soo Bin Jeong, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Jin Nam Kim, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):513-526. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.513
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of low sodium diet education program on dietary habits, diet quality, and measures of obesity in overweight or obese middle-aged women.
METHODS
Subjects were 81 individuals aged 45 years or over, who completed an 8-week nutrition education. The subjects were divided into a normal group (N = 30) and an overweight-obese group (N = 51) according to the BMI. The effects were evaluated by anthropometric measurement, biochemical analysis, questionnaire, and diet records before and after the program.
RESULTS
Overweight-obese group showed significant decreases in weight (p < 0.0001), BMI (p < 0.0001), percent of body fat (p = 0.0087), waist circumference (p < 0.0001), systolic (p = 0.0003) and diastolic blood pressure (p = 0.0261). Nutrients intakes were not different between the two groups and only sodium intake was decreased after education. Total score of general dietary habits, dietary behavior related to sodium intake, dietary diversity score (DDS), diet variety score (DVS), and diet quality index-international (DQI-I) were improved in both groups compared to the baseline. Overweight-obese group showed significant improvement in 'having fruits everyday', 'having fish everyday', 'trying to eat many kinds of food', 'eating less broth when eating soup, stew, and noodles', 'eating less kimchi and salt-fermented vegetable', and 'propensity to think that dishes should be pretty seasoned'. In addition, moderation of empty calories food (p = 0.0064) and macronutrient ratio (p = 0.0004) were improved in the overweigh-obese group, but in the normal group, the results did not reach statistical significance.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggested that low sodium diet education program may contribute to obesity management by improving diet quality and dietary habits in middle-aged women.
- 1,093 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Breast-feeding and Obesity in Early Childhood: Based on the KNHANES 2008 through 2011
- Miyong Yon, Haeng Shin Lee, Dohee Kim, Jeeyeon Lee, Jiwoon Nam, Gui Im Moon, Jinhwan Hong, Cho il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(6):644-651. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.6.644
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although there has been a significant increase in breast-feeding (BF) rate in Korea, it is plateaued since 2008 and still low compared with that of other countries. Because BF has been related to lower obesity prevalence in many studies and the increase in childhood obesity became evident in Korea, we wondered if a relatively lower BF rate has anything to do with this increase. Therefore, we looked into the relationship between mode & duration of BF during infancy and weight status of toddlers using the data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008 through 2011. Number of 2-3 year old toddlers with complete information on BF, anthropometry and normal birth weight was 674. While 87% of them were ever-breastfed, 6.2% each of them were either obese or overweight based on the Standard Growth Chart for Korean Children. Not only the obesity prevalence was different among groups of different mode of feeding, but also the mean duration of BF was significantly longer in normal weight group (9.2 mo.) compared with obese group (5.5 mo.). Accordingly, overweight and obesity prevalence of the toddlers breast-fed for 12 months or longer was significantly lower than that of the toddlers breast-fed for less than 12 months (OR 0.53, 95% CI 0.32-0.87). This study revealed that both BF and duration of BF affect the childhood obesity and, BF for 12 months or longer should be encouraged more aggressively as one of the main strategies to prevent and/or decrease childhood obesity in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the growth and nutritional status of low birth weight and normal birth weight children
Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(6): 630. CrossRef - Breastfeeding and impact on childhood hospital admissions: a nationwide birth cohort in South Korea
Jeong-Seon Lee, Jae Il Shin, Sunyeup Kim, Yong-Sung Choi, Youn Ho Shin, Jimin Hwang, Jung U Shin, Ai Koyanagi, Louis Jacob, Lee Smith, Han Eol Jeong, Yunha Noh, In-Sun Oh, Sang Youl Rhee, Chanyang Min, Seong Ho Cho, Steve Turner, Guillaume Fond, Laurent B
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Infant Feeding Characteristics With Dietary Patterns and Obesity in Korean Childhood
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Moon-Kyung Shin
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(4): 338. CrossRef - Feeding characteristics in infancy affect fruit and vegetable consumption and dietary variety in early childhood
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Moon-Kyung Shin
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 307. CrossRef - Relations among Maternal Employment, Depressive Symptoms, Breastfeeding Duration, and Body Mass Index Trajectories in Early Childhood
Jihyoung Kim
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2020; 24(2): 75. CrossRef - Knowledge and health beliefs about gestational diabetes and healthy pregnancy's breastfeeding intention
Seungmi Park, Jung Lim Lee, Jang In Sun, Youngji Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2018; 27(21-22): 4058. CrossRef - Exclusive breastfeeding and partial breastfeeding reduce the risk of overweight in childhood: A nationwide longitudinal study in Korea
Seon-Joo Park, Hae-Jeung Lee
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2018; 12(2): 222. CrossRef - Dietary status of young children in Korea based on the data of 2013 ~ 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eun-kyung Kim, Byengchun Song, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 330. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Breastfeeding Duration and Preschooler Problem Behavior:
The Mediating Role of Cognitive Development
Sujeong Kang, Yea-Ji Hong, Naya Choi, Kangyi Lee
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2017; 38(6): 63. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Obesity and Overweight in Korean Preschool Children: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013-2014
Inju Hwang, Kyung-Sook Bang
Child Health Nursing Research.2016; 22(4): 237. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Nutrient Intakes according to Feeding Method during Infant Period in Elementary School Students
Myung-Hwa Kang, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Hyun-Jin Kim, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(1): 57. CrossRef
- Comparison of the growth and nutritional status of low birth weight and normal birth weight children
- 1,380 View
- 6 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Classification of Obesity for Koreans based on the Articles in the Korean Journal of Community Nutrition: Articles Enlisted from 1996 to 2011
- Youngnam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(5):525-538. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.5.525
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to provide information on obesity assessment for Koreans. Among total of 1012 research papers enlisted in the Korean J Community Nutrition form 1996 to 2011, 248 articles were examined in which subjects were divided into more than 2 groups by obesity rate. About the method of anthropometric data collection, more than half of the research papers examined 52.5% and 28.7% of studies utilized the directly measured data and self-described data, respectively. About the utilization of obesity assessment methods, indirect methods of weight-height index (BMI, BMI percentile, and Rohrer index) and PIBW (WLR, Broca index, and KDA) were 62.4% and 23.2%, respectably, and the direct method of percent body fat assessment was only 9.3%. The most frequently utilized methods were WLR in under primary and primary school children, and BMI in the middle and high school students and in adults. For primary school students, WLR was the most frequently utilized method up to 2007, but it changed to BMI percentile afterward. Broca Index was no longer utilized since 2008. There were no articles utilizing BMI percentile and Rohrer index for obesity assessment in adults. Criteria for obesity assessment were not consistent among research papers: for example, % body fat, 19~40%; BMI, 20~30; BMI percentile, 85th or 95th. In the case of PIBW, 120% of ideal weight was the most frequently utilized criterion for obesity. Based on these findings, we suggest that proper methods and criteria of obesity assessment for each age group should be determined and proclaimed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Contributing to Diabetic Foot Ulcer among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Seo Jin Park, Taeyoung Yang, Jun Young Lee, Jinhee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 106. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Dietary and Weight Control Behavior of Female College Students in Korea and China
Li Song, Na Young An, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(4): 761. CrossRef
- Factors Contributing to Diabetic Foot Ulcer among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- 1,359 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Serum Adiponectin Levels According to Body Mass Index and Dietary Behaviors of Female University Students in Seoul
- Mi Joung Kim, Hyun Young Jun, Hye Bog Rha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(4):354-364. Published online August 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.4.354
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to determine whether dietary factors could be related with serum adiponectin concentrations in 243, year-three female university students living in Seoul. The mean of body mass index (BMI) and adiponectin levels of all subjects were 20.17 kg/m2 and 11.07 microg/ml, respectively. When the subjects were divided into 3 groups based on BMI (underweight: < 18.5, normal: 18.5 < or = < 23, overweight and obesity: > or = 23), serum adiponectin levels in underweight group was significantly higher than that in 'normal' or 'overweight and 'obesity' groups. Also when the subjects were divided into two groups by mean adequacy ratio (MAR), serum adiponectin concentration of the high MAR group (MAR > 75) was slightly higher than that the low MAR group (MAR < or = 75). Serum adiponectin levels showed a negative correlation with body weight (p < 0.01) or BMI (p < 0.001) and a positive correlation with intakes of of animal or total protein (please clarify) or vegetable protein.Among the dietary behaviors, serum adiponectin levels of females who answered 'yes' to the question about 'eating breakfast' was significantly higher than that of those who answered 'sometimes' or 'No' (p < 0.05) and serum adiponectin levels were higher among those who reported higher fruit intakes. Overall, our results suggested that healthy lifestyle including acceptable BMI, eating breakfast and higher fruit consumption might play an important role in the prevention of obesity and enhancement of blood adiponectin levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of nutritional status between adults with and without disabilities: a population-based cross-sectional study in South Korea
Jong Eun Park, Tae Hui Jang, So Young Kim, Jong Hyock Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(6): 967. CrossRef - A Study on Food Habits and Nutrient Intakes according to BMI in Food and Nutrition Major and Non-major Female Students in Kyungnam University
Eun-Hee Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 297. CrossRef - Relationships among Serum Adiponectin, Leptin and Vitamin D Concentrations and the Metabolic Syndrome in Farmers
Seo-Eun Yeon, Hee-Ryoung Son, Jung-Sook Choi, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(1): 12. CrossRef
- Comparison of nutritional status between adults with and without disabilities: a population-based cross-sectional study in South Korea
- 1,201 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- The study of Perception in Body Somatotype and Dietary Behaviors - The Comparative Study between Korean and Chinese College Students -
- Youngmee Lee, Lin Sun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(1):25-44. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.1.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study aimed to analyze about the perception in obesity and body somatotype of university students in Korea and in China. This study provides the basic data of nutrition education for university student healthy weight program in China. The subjects were selected 240 university students of Korea and China. Two types of qualitative and quantitative questionnaires were used to analyze the attitude and body somatotype of subjects. The results of this study were as follows: The average BMI of Korean and Chinese male students was 22.3 and 22.5, respectively while the average BMI of Korean and Chinese female students was 19.8 and 19.7, respectively. In the past three years, the weight gain of Chinese students was higher than that of Korean students. Chinese students preferred the overweight body somatotype more compared to the Korean students. The overweight and obese students had more obvious insufficiency in body somatotype perception. The overweight and obese students had higher tendency to 'eat more meat', 'drink carbonated beverages', 'eat convenience food', 'take fast food' and 'drink alcohol' than the normal and low weight group. The major reasons for Korean students to control weight were 'appearance' and 'self confidence', while the major reasons for Chinese students were 'health' and 'employment'. From the results of associative group analysis (AGA), Chinese students had different semantic value of 'obese' than Korean students. Considering of the food transition status in China, it may be necessary to develop more suitable education programs for weight control for Chinese university students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unhappy and Happy Obesity: A Comparative Study on the United States and China
Kazuma Sato
Journal of Happiness Studies.2021; 22(3): 1259. CrossRef - The Moderation of Obesity Penalty on Job Market Outcomes by Employment Efforts
Rosemary Ahn, Tae Hyun Kim, Euna Han
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(16): 2974. CrossRef - Comparison of body image perception, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes, and dietary habits between Korean and Mongolian college students
Zolzaya Erdenebileg, So Hyun Park, Kyung Ja Chang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(2): 149. CrossRef - University Students’ Eating Habit, Perception and Acceptance of Korean Food in Jeollabuk-do Province
Kyung Jin Min, Hwi-Jin Joung, Ye-Ji Lee, Moon Sook Kim, Il Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2017; 33(5): 588. CrossRef - Body mass index and self-rated health in East Asian countries: Comparison among South Korea, China, Japan, and Taiwan
Jin-Won Noh, Jinseok Kim, Youngmi Yang, Jumin Park, Jooyoung Cheon, Young Dae Kwon, Clemens Fürnsinn
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(8): e0183881. CrossRef - Comparisons of Health Related Lifestyle and Dietary Behaviors according to Gender, Ethnicity and Residence Type of University Students in Yanbian, China
Kyung Hee Hong, Unju Hwa Oh
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(4): 486. CrossRef - Breakfast Intake Status and Demand of School Breakfast Between High School Students Living in Dormitory and Family Home in Iksan City
Hyounhwa Go, Eunhee Hwang
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(1): 99. CrossRef - Comparison Study of Dietary Behavior, Nutrition Knowledge, and Body Weight Perception of Female High School Students in Jeonju, Korea and Jinan, China
Eun-Jung Joo, Eun-Sook Park
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(1): 121. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Dietary and Weight Control Behavior of Female College Students in Korea and China
Li Song, Na Young An, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(4): 761. CrossRef - Perceptions and practices of commensality and solo-eating among Korean and Japanese university students: A cross-cultural analysis
Wookyoun Cho, Wakako Takeda, Yujin Oh, Naomi Aiba, Youngmee Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(5): 523. CrossRef - Impact of body mass on job quality
Tae Hyun Kim, Euna Han
Economics & Human Biology.2015; 17: 75. CrossRef - Differences in Solo Eating Perceptions and Dietary Behaviors of University Students by Gender
Youngmee Lee, Yu Jin Oh, Wookyoun Cho, Pil Kyoo Jo
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(1): 57. CrossRef - Health-related Factors, Nutrition Knowledge and Dietary Habits among Nursing and Allied Health College Students
Su Ol Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2015; 28(3): 158. CrossRef - A comparative study on dietary behavior, nutritional knowledge and life stress between Korean and Chinese female high school students
Sohwan Son, Yoona Ro, Hwajin Hyun, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(2): 205. CrossRef - A comparative study on dietary behavior, nutritional knowledge and life stress between Korean and Chinese female high school students
Sohwan Son, Yoona Ro, Hwajin Hyun, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(2): 205. CrossRef - The Study of the Weight Control Experiences, Body Image Perception and Eating Disorder Status of High School Students in Yantai City, Shandong Province, China
Wen Jing Yu, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2013; 24(4): 447. CrossRef - A Study on the Intakes and Perceptions of Convenient Breakfast
Yeon-Seo Mun, Eun-Kyung Jung, Nami Joo, Ji-Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(5): 559. CrossRef
- Unhappy and Happy Obesity: A Comparative Study on the United States and China
- 1,259 View
- 0 Download
- 17 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on the Health and Nutritional Characteristics according to Household Income and Obesity in Korean Adults Aged over 50: Based on 2005 KNHANES
- So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(4):463-478. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.4.463
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the health and nutritional characteristics according to household income level and obesity in Koreans aged over 50 years based on the 2005 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Subjects were classified into 3 groups by average household income with reference to the minimum monthly living expenses (MLE): low (n = 319, < 100% MLE), middle (n = 222, < 200% MLE), high (n = 411, > or = 200% MLE) and each group was compared by BMI index. With increasing income level, the prevalence of systolic hypertension and hyperlipidemia was increased. In the low income group, serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, and fasting glucose were higher in the obese compared with the normal. In the middle and high income groups, the prevalence of hyperlipidemia and diastolic hypertension were higher in the obese. Subjects had nutritional imbalance, such as inadequate intake of calcium and potassium. With increasing income level, the percentages of protein and fat to total calorie were increased in addition to the intakes and density of nutrients. The obese in the low income group had higher intakes of energy, protein, phosphorus and higher consumption frequency of cereals and potatoes compared with the normal. It was shown that the obese of the middle and high income groups tended to have lower consumption frequency of Korean cabbage and higher frequency of fruits. The obese of high income group also had binge drinking habit. Therefore, this study suggests that specific approaches based on economic status should be considered in developing nutrition education program for the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Changes in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome before and after the COVID-19 pandemic according to household income levels
Hyunjung Kang, Dagyeong Lee, Junhee Park, Su-Min Jung
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2025; 46(1): 27. CrossRef - Comparison of the health and nutritional status of Korean elderly considering the household income level, using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 39. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef - Estimated dietary intake of vitamin A in Korean adults: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2012
Seong-Ah Kim, Shinyoung Jun, Hyojee Joung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(4): 258. CrossRef - Optimization of Extraction Conditions for Mixture of Camellia sinensis L. and Artemisia argyi by Response Surface Methodology
Young-Hyun Kim, Woo-Sik Kim, Jae-Min Kim, Sun-il Choi, Tae-Dong Jung, Jin-Ha Lee, Jong-Dai Kim, Jae Kag Lim, Ok-Hwan Lee
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2016; 31(4): 278. CrossRef - A study on nutritional intakes in middle income adults based on data from the 5thKorean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ji-Myung Kim, Hye Sook Kim, Ki Nam Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(4): 364. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Dietary Habit and Nutritional Status by Household Income in Female Adults over the Age of 20 - Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hee-Kyung Jang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 660. CrossRef
- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,337 View
- 1 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study of Glycemic Index, Glycemic Load and Food Sources according to Body Mass Index in Female College Students
- Jee Young Yeon, Eun Young Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(4):429-439. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.4.429
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate nutrients intakes, glycemic index (GI), glycemic load (GL) according to body mass index (BMI) in female college students (n = 320). The study subjects were divided into 3 groups based on their body mass index, an underweight group (BMI < 18.5 kg/m2, n = 55), a normal group (18.5 kg/m2 < or = BMI < 23 kg/m2, n = 231), and an overweight group (23 kg/m2 < or = BMI < 25 kg/m2, n = 34). The food and nutrition intake data obtained by administering a 3-day food record and were analyzed by using Can pro 3.0 software. Anthropometric measurements were collected from each subject. Body weights and BMI of the underweight group were 45.9 kg, 17.6 kg/m2, those of the normal group were 53.8 kg, 20.5 kg/m2, and those of overweight group were 62.6 kg, 23.8 kg/m2, respectively. The mean daily dietary GI of underweight, normal and overweight groups was 66.2, 65.8 and 66.5, respectively. These differences were statistically non-significant. The mean daily dietary GL of underweight, normal and overweight groups were 159.2, 149.4, and 148.9, respectively. The major food source of dietary GI and GL was rice in the three groups. Dietary GI and GL were not significantly correlated with obesity when adjusted for energy, carbohydrate and dietary fiber intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Utility of the Glycemic Index in Practical Diabetes Management
Jung Hwa Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2015; 16(2): 135. CrossRef
- Utility of the Glycemic Index in Practical Diabetes Management
- 1,429 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrient Intake and Anthropometric Parameters related to Obesity in Korean Female Adolescents according to Dietary Diversity Score: From the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 2007-2009
- Yun Jung Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(4):419-428. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.4.419
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate nutrient intake and anthropometric parameters related to obesity in Korean female adolescents according to dietary diversity score. We analyzed data from the combined 2007-2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). The subjects were 770 female adolescents. Nutrient intakes, Dietary Diversity Score (DDS) ) and Dietary Variety Score (DVS) were derived by using the data from the 24-recall method. The DDS was defined as the number of six food groups (cereals, meats, fruits, vegetables, dairy, fats and oils) consumed. The DVS was defined as the number of food items consumed. The average age of the subjects of the study was 15.02 years and the average height, weight, and BMI were 159.50 cm, 52.58 kg, 20.62 kg/m2, respectively. The energy and nutrients intakes, percent of the recommended intake for nutrients in DDS = 5~6 group were significantly higher than those of the other groups. Calcium and vitamin C INQ in DDS = 5~6 group were significantly higher than those of the other groups. The average DVS of the subjects was 29.33. The most frequent style of food pattern was CMDFVO (cereals, meats, dairy, fruits, vegetables, fats and oils) = 111011. In conclusion, in healthy Korean female adolescents, food diversity intake variety did beneficially affect the intakes of calcium and vitamin C. Further studies are needed to confirm these findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Dietary Nutrient Intake and Food Variety by Milk Consumption in Postmenopausal Korean Women: Data Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015
Ae Wha Ha, Woo Kyung Kim, Sun Hyo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 51(9): 912. CrossRef - Relationship between dietary diversity score and general health in female students
Azadeh AMINIANFAR, Fereydoun SIASSI, Mostafa QORBANI, Javad KARIMI, Gity SOTOUDEH, Yas KALIKIAS, Sanaz SOLTANI
Minerva Pediatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ) and the Risk of Obesity in Male Adolescents: a Case-Control Study
Maryam Gholamalizadeh, Samira Rastgoo, Saeid Doaei, Farhad Vahid, Hanieh Malmir, Narges Ashoori, Alireza Mosavi Jarrahi
Biological Trace Element Research.2021; 199(5): 1701. CrossRef - Relationship between dietary intakes and the double burden of malnutrition in adults of Malang, Indonesia: An exploratory study
Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(5): 426. CrossRef - Night eating status according to body mass index of Korean adolescents
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Yu-Jin Cho, Myung-Hee Kim, Yun Jung Bae
Nutrition & Food Science.2017; 47(1): 89. CrossRef - Systematic Review on the Study of the Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in Korea: Dietary Risk Factors
Eun Jeong Heo, Jae Eun Shim, Eun Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 191. CrossRef - Development of NQ-A, Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior
Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 142. CrossRef - Comparison of Diet Quality and Diversity according to Obesity Type among 19-64 year old Korean Adults
Hyae Min Gu, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Mi Ah Han, Yeong Eun Son
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(6): 545. CrossRef - Effects of brown rice-vegetable school meal program on subjective health status, BMI and hematological parameters among high school students
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7385. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Nutritional Value of Traditional Korean Noodles through Energy Density and Diversity
YoonKyoung Yang, SungOk Kim, Juhyeon Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 732. CrossRef - Effects of a Brown Rice and Vegetable Diet on the Defecation Conditions and Health Status of High School Students
Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(1): 179. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Dietary Nutrient Intake and Food Variety by Milk Consumption in Postmenopausal Korean Women: Data Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015
- 1,298 View
- 3 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- Development and Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Website for the Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity
- Miyong Yon, Chan Park, Kwan Hee Yoo, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(4):390-406. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.4.390
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Childhood obesity has rapidly increased worldwide and is one of the most serious health problems in this age group. In order to prevent and manage childhood obesity, we developed a nutrition education website. The website consisted of three parts. The first part was made for self-assessment with regard to obesity index, dietary habits, food frequency, dietary attitude, nutrition knowledge, nutrient intake, energy expenditure, and the stage of behavioral change, and tailored messages and advice according to the assessment results. A total of 612 real-size food photos as well as a nutrient database of 3,346 foods and 541 dishes were created to help children estimate nutrient intakes accurately. In addition, an energy expenditure database of 156 activities for children was established to calculate calorie consumption. The second part was made for setting long-term and short-term goals and keeping track of the changes in energy intake and expenditure in one's own page. The third part was made for education. Various types of nutrition information were provided; texts, pictures, calculators and games. The readability and design of the website were evaluated by 46 obese children. Usefulness, design and readability of the website were found to be desirable for children. This website is expected to be used by an obese child alone or with parents or nutrition teachers in order to control body weight through healthy dietary habits and physical activities. In addition, a non-obese child can also use this website for maintaining healthy dietary habits and preventing obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Education Materials as a Card News Format for Nutrition Management of Pregnant and Lactating Women
Young-Hee Han, Jung Hyun Kim, Min Jun Lee, Taeksang Yoo, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 248. CrossRef - Application and Evaluation of Web-based Food Frequency Questionnaire for Korean Adolescents
Jinhee Yum, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(5): 440. CrossRef - Development of Web-based u-Health Self-nutrition Management Program for Diabetic Patients
Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Hee-Seon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 372. CrossRef - A Study on the Development of a Metadata Schema for the Food Education Digital Library
Soojung Kim, Eunha Youn
Journal of the Korean Society for Library and Information Science.2014; 48(4): 323. CrossRef
- Development of Education Materials as a Card News Format for Nutrition Management of Pregnant and Lactating Women
- 1,423 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Diet Quality and Food Patterns of Obese Adult Women from Low Income Classes: Based on 2005 KNHANES
- Jin Sook Yoon, Heekyung Jang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):706-715. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.706
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study aims to identify the dietary patterns relevant to obesity of Korean women among low income classes. Adults 20-64 years were used as study subjects from the data of 2005 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. We compared obese and normal-weight women in terms of their nutrients intake, diet quality and food patterns. Diet quality was assessed by using the Nutritional Adequacy Ratio (NAR) and Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ). Our results showed higher prevalence of obesity among lower socioeconomic status women. In men, there were no significant associations with socioeconomic status and prevalence of obesity. Higher risk of nutritional inadequacy was observed among obese women compared to normal weight women. Obese women showed significantly lower INQ for nutrients such as Ca, Fe, Vitamin A, Thiamin, Riboflavin and Vitamin C compared to other women. They consumed significantly higher amount of rice (p < 0.05) and lower amount of vegetables (p < 0.01). By contrast, obese men from low income classes showed higher intake of those nutrients. Obese men also consumed significantly higher amount of meats than normal weight men. Therefore, this study suggests that genderspecific approaches based on economic situation should be considered in developing the intervention program for managing obesity for low income classes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of a health promotion program based on Community-based Participatory Research for older adults at risk for metabolic syndrome: a mixed methods study
Juhyeon Yang, Bohyun Park
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Food insecurity and adult weight abnormality risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sajjad Moradi, Atieh Mirzababaei, Alireza Dadfarma, Shahabeddin Rezaei, Hamed Mohammadi, Behrooz Jannat, Khadijeh Mirzaei
European Journal of Nutrition.2019; 58(1): 45. CrossRef - Effects of a Self-Care Reinforcement Program for Socially Vulnerable Elderly Women with Metabolic Syndrome in Korea
Mikyung Park, Kiwol Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(3): 271. CrossRef - Eating frequency is inversely associated with BMI, waist circumference and the proportion of body fat in Korean adults when diet quality is high, but not when it is low: analysis of the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANE
Sunmi Kim, Jeong Hee Yang, Gyeong-Hun Park
British Journal of Nutrition.2018; 119(8): 918. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Taste Preference, Food Consumption Frequency, and Nutrition Intake between the Elderly in Their 80's Living in Long Life Regions in Jeollanam-do and a Part of Seoul
Soon-Sil Chun, Eunju Yoon
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(1): 115. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - A study on nutritional intakes in middle income adults based on data from the 5thKorean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ji-Myung Kim, Hye Sook Kim, Ki Nam Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(4): 364. CrossRef - Major Foods and Nutrient Intake Quality According to Body Image Perception among Korean Women: Based on the 2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
Young Suk Lim, Soo Bin Jeon, Hee Mang Kim, So Yeon Jeong, Jae Young Ahn, Hae Ryun Park
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(2): 154. CrossRef - Associations between food insecurity and healthy behaviors among Korean adults
In-Ae Chun, So-Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Hee-Kyung Ro, Mi-Ah Han
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(4): 425. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Dietary Habit and Nutritional Status by Household Income in Female Adults over the Age of 20 - Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hee-Kyung Jang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 660. CrossRef - Calcium Status and Bone Mineral Density by the Level of Sodium Intake in Young Women
Jin-Sook Yoon, Mi Jung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(2): 125. CrossRef - A Study on the Health and Nutritional Characteristics according to Household Income and Obesity in Korean Adults Aged over 50 -Based on 2005 KNHANES-
So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son, Hye Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(4): 463. CrossRef
- Evaluation of a health promotion program based on Community-based Participatory Research for older adults at risk for metabolic syndrome: a mixed methods study
- 1,253 View
- 3 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Daily Sleep Duration with Obesity, Macronutrient Intake, and Physical Activity
- Inkyung Baik, Chol Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(3):315-323. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.3.315
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are a few studies that reported the association of sleep duration with calorie intake and energy expenditure. Using cross-sectional data from a population-based prospective study, we evaluated the association of sleep duration with indicators of obesity including body mass index and waist circumference, calorie intake and its proportion of macronutrients, and physical activity. The study subjects were 4,226 male and female adults, who were aged 40 to 69 years and were free of diagnosed cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia at baseline. Robust regression analysis was used to analyze associations. The study found that sleep duration is inversely associated with waist circumference, calorie intake, and percent of calories from fat intake and is positively associated with percent of calories from carbohydrate intake and physical activity. The inverse association between sleep duration and waist circumference was stronger among men than among women. The inverse association between sleep duration and calorie intake was stronger among women than among men and such association was also stronger among obese persons than those with a normal body mass index. The positive association between sleep duration and physical activity was strongly demonstrated regardless of sex or obesity. Physical activity is positively associated with sleep duration independent of potential confounding factors including age, sex, income, occupation, marital status, education, smoking status, waist circumference, calorie and macronutrient intake, and alcohol intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Anti-Stress and Sleep-Inducing Effects of a Zizyphus jujuba Mill.-Hypericum perforatum L. Mixture and Its Bioactive Compounds
June-Seok Lim, Yeon-Seok Seong, Geon Oh, Ji-Hyun Im, Xiaolu Fu, Min-Hye Kim, Jin-Ho Roh, Ok-Hwan Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(6): 489. CrossRef - A comparative study on eating habits and mental health of Korean middle school students according to their bedtime across regions: using data from the 2020–2022 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Sarim Kim, Jiyoung Jeong, Juyeon Kang, Jihye Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(2): 269. CrossRef - Grit in Community‐Dwelling Older Adults with Low Back Pain Is Related to Self‐Physical Training Habits
Tsubasa Kawasaki, Ryosuke Tozawa
PM&R.2020; 12(10): 984. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Dietary Habits according to Sleep Duration in Korean Adults Based on the 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(4): 237. CrossRef - The longitudinal influence of child maltreatment on child obesity in South Korea: The mediating effects of low self-esteem and depressive symptoms
Aely Park, Youngmi Kim
Children and Youth Services Review.2018; 87: 34. CrossRef - Dietary behavior status and its association with study-related factors in middle school students in Gyeonggi area
Myoung Sook Lee, Wha Jin Hyun, Kyung Hee Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 455. CrossRef - Relationship between Bone Mineral Density and Bone Metabolic Biochemical Markers and Diet Quality Index-International(DQI-I) in Postmenopausal Obese Women
Yeonah Jeong, Misung Kim, Saeron Shin, Ahreum Han, Geomsuk Seo, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 284. CrossRef - Difference in Sleep Circadian Rhythm and Sleep Quality between Normal-weight and Obese Group
Hyun Jin Suk, Yeon Kyung Na, Hae Sook Hong
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(4): 309. CrossRef - Experiences of Health Related Lifestyles in High Body Fat but Non-obese Female College Students in Korea
Jeongsoo Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5(1): 68. CrossRef - Predictors of Poor Sleep Quality among Nursing Students
Young Ran Chae, Dong Hee Choi, Su Jeong Yu
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(2): 98. CrossRef - Correlation between Sleep Quality and Snack Intake in Third Year Middle and High School Students in the Gwangju Area
Hyo Bok Kim, Yang Won Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(2): 212. CrossRef - A Study on the Correlation of the accompanying symptoms, Heart Rate Variability and Body Component Analysis in 350 Insomnia Patients
Ji-Won Ha, Bo-Kyung Kim, Jin-Hyeong Jung
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2012; 23(3): 47. CrossRef - Physical activity level, total daily energy expenditure, and estimated energy expenditure in normal weight and overweight or obese children and adolescents
Myung Hee Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(6): 511. CrossRef
- Analysis of Anti-Stress and Sleep-Inducing Effects of a Zizyphus jujuba Mill.-Hypericum perforatum L. Mixture and Its Bioactive Compounds
- 1,470 View
- 0 Download
- 13 Crossref

- [English]
- Implementation & Evaluation of Nutrition-Exercise Program on Weight Control for Obese Children
- Jeong min Lee, Ji young Yoon, Joo Hee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(6):727-739. Published online December 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the evaluation of nutrition and exercise education program on weight control for obese children. The subjects of this study were 28 obese children and their parents living in Geyongnam area. The weight control program consisted of exercises for children and nutrition education for both children and their parents. The BMI values of the children were significantly reduced from 27.96 kg/m2 to 27.22 kg/m2 after 11 weeks (p < 0.001) and to 27.65 kg/m2 after one year. Dietary habits and exercise patterns were also changed positively. For the children, while the frequency of eating breakfast and appropriate chewing habits were increased, the percentages of eating in inappropriate position and the frequency of buying snacks were decreased (p < 0.001). In terms of exercise, the proportion of doing exercise more than 30 minutes, participating in physical activity classes actively, and walking rather than taking a car were significantly increased. Nutrition knowledge of both the student and parent respondents were significantly increased when measured immediately after the education and even a year after compared to their knowledge status measured before the program (p < 0.001). Both the students (82.1%) and parents (96.4%) were satisfied with the overall weight control program. Exercise therapy was chosen as the most beneficial content. Reparticipation intention was comparable between the students (28.6%) and their parents (67.9%). A year after survey results revealed that 71.4% of students controlled their weight by doing regular exercises (55.0%) and controlling overeating (45%). Parents often applied healthy cooking methods (89.3%) and low calorie menus (64.3%), which they learned from nutrition education. Most parents perceived that the weight control program was helpful for their children (89.3%) and themselves (92.9%) as well.
- 354 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Association between hs-CRP Concentration of Blood and Metabolic Syndrome in the Residents of a Rural Community
- Jong Im Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(6):796-805. Published online December 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the correlations and risk distribution differences between high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and the diagnosis factors of metabolic syndrome among the residents of a rural community. Two thousand adults aged from 40 to 70 were recruited and 1,968 subjects were included in the study after excluding those with infectious disease or with hs-CRP higher than 10 mg/L in blood. The subjects were then divided into three groups of hs-CRP to examine the correlations and risk ratio with the risk factors of metabolic syndrome. There was a tendency of hs-CRP increasing according to the number of risk factors of metabolic syndrome. The risk ratio with hs-CRP according to metabolic syndrome significantly increased by 2.0 and 2.2 times in the intermediate and high risk group, respectively, compared with the low risk group. The risk ratio with the risk factors of metabolic syndrome according to hs-CRP rose in abdominal obesity, triglyceride, and W/Ht in the intermediate risk group of hs-CRP. The risk ratio also surged in high pressure, W/Ht, ex-drinking (1.7 times), exsmoking (2.0 times) and current smoking (2.0 times) in the high risk group. The results indicate that hs-CRP is related to the risk factors of metabolic syndrome and that it's very important to manage obesity including abdominal obesity and W/Ht and everyday habits including drinking and smoking.
- 335 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Health Status and Nutrient Intakes of 5th Grade Elementary Students in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
- Ok Hyun Kim, Hyun Ah Park, Young Gyu Cho, Kyoung Woo Kim, Yangim Hur, Ji Hyun Song, Jae Heon Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(6):717-726. Published online December 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate health status and nutrient intakes among 5th grade elementary students at Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2010. This study was cross-sectional study on 1,384 children (687 boys, 697 girls) from nine elementary schools located in Seoul and Gyeonggi province. The average height, weight and BMI were 145 cm, 40.6 kg 19.2 kg/m2 for boys and 145.4 cm, 38.2 kg, 18.0 kg/m2 for girls. The prevalence of overweight and obesity were 11.3%, 5.2%, respectively. Serum AST, ALT, glucose, HDL-Cholesterol and RBC levels were significantly higher, while TG levels was significantly lower for boys than for girls. The average energy intake was 1772.4 kcal, which was 98.7% of Estimated Energy Requirement (EER). The boys consumed more energy intake (1800.4 kcal) than the girls (1744.7 kcal). Also, they took insufficient calcium and folate (69.1% and 83.3% of Recommended Intake (RI)) and excess sodium (297.6% of Adequate Intake (AI)) and 85.1% of the subjects had breakfast everyday. In general, the proportion of the children who consumed fruits and vegetables at least once or more a day was low. There was a higher proportion of children in boys who had ramyun and milk with sufficient physical activity than those in girls. As a result of this study, we can find risk factors on obesity and metabolic disorders, and the results can be used for an evidence of nutrition education program and the intervention program.
- 385 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Assessment for Nutrient Intakes in Korean Women according to Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Hye Kyung Chung, Ju Hee Kang, Min Jeong Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(5):694-703. Published online October 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recent studies have reported that a subset of obese individuals who were metabolically healthy but obese had more favorable clinical outcomes than obese subjects with metabolic disturbances. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the distribution and agreement of obesity subtypes according to body mass index (BMI) and metabolic syndrome (MS). Furthermore, we examined the differences of nutrient intake among the groups. Data was analyzed for 1,095 female subjects older than 40 years using Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey in 2008. The degree of obesity was classified by two methods, using BMI (obese > or = 25 kg/m2, not obese < 25 kg/m2) and MS (meet > or = 3 criteria among 5 index: waist circumference, triglyceride, glucose, HDL-cholesterol and blood pressure). Subjects were divided into 4 groups according to 2x2 cross table: non-obese without MS, non-obese with MS, obese without MS and obese with MS. Nutrient intakes were compared among 4 groups. The results showed that the proportions of non-obese without MS, non-obese with MS, obese without MS and obese with MS were 47.6%, 13.6%, 16.6%, and 22.2% of total subjects, respectively. The agreement (kappa value) of two methods was 0.354 (fair) in total subjects, 0.365 (fair) in 40-60 year old subjects and 0.304 (fair) in > or = 61 year old subjects. In > or = 61 years old subjects, intakes of percentage energy from carbohydrate, percentage of energy from fat, calcium, phosphorous, sodium, vitamin A, carotene, thiamine, riboflavin and niacin were significantly different among the groups. In contrast, the subjects of 40-60 years old, no differences in nutrient intakes were observed. In conclusion, there were differences in nutrient intakes among the groups subdivided by obesity and MS, especially in elderly female subjects. Individualized dietary guideline for subtype of obesity will be needed to treat metabolic disturbance of obesity.
- 332 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Effects of Obesity, Body Image Dissatisfaction and Dietary Habits on the Risk of Disturbed Eating Attitudes among High School Students in Gyunggi Province, Korea
- Kyeong Sook Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(5):656-669. Published online October 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rapid shift to western dietary patterns and social drive of thinness would lead to increase the likelihood of developing eating disorders. This study was performed to analyze the associated factors between dietary pattern and self visualization in terms of body shape, which may increase the risk of disturbed eating attitudes among high school students in Korea. A cross-sectional study was conducted from 2009 to 2010 for high school students including both male and female students, from 6 schools in Gyunggi Province, Korea. A total of 766 students self-reported a questionnaire, including weight control practice, perceptions of self body image and ideal body image, dietary habit, and EAT-26 (Eating Attitude Test-26). Logistic regression analysis was used to fine the factors potentially associated with disturbed eating attitudes. Statistical analysis was conducted using SAS program (version 9.1). Results showed that disturbed eating attitudes were found in 8.7% of male high school students, and in 20.8% of female high school students. Experience of body weight control was reported by 56.2% of male students and by 87.3% of female students. According to multiple logistic regression analysis, obesity was independently associated with high risk of disturbed eating attitudes in male students [Odds Ratios (OR) 2.96, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) 0.90-9.71]. Body image dissatisfaction (OR 2.77, 95%CI 1.37-5.62) and extended family type (OR 2.70, 95%CI 1.05-6.90) were independently associated with high risk of disturbed eating attitudes, especially in female students. In conclusion, proper efforts in education for obesity and developing self-esteem to reduce the risks of disturbed eating attitudes should be implemented in high school nutrition program.
- 367 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Comparative Study on Nutrients Intake, Physical Activities and Bone Mineral Density of Specialized Game High School Students according to Obesity Level
- Yun Kyoung Oh, Cheongmin Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(3):393-402. Published online June 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was performed to evaluate the prevalence of overweight and to compare the dietary behaviors, nutrient intake and physical activities of specialized game high school students. Total of 163 subjects participated and their weight, height, waist circumference, hip circumference and bone status by a quantitative ultrasound method were measured. The subjects were surveyed by a self-administered questionnaire about general characteristics, dietary behaviors and physical activities. Nutrient intakes of the subjects were assessed by semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire. The subjects were divided into four groups on their obesity level by BMI. The prevalence of underweight, normal, overweight and obese group was 6%, 58%, 16%, and 20% respectively. BMI was negatively correlated with bone mineral density (p < 0.01) and positively correlated with WHR (p < 0.01). The dietary guideline compliance score for "Enjoy Korean rice food style" was 2.63, followed by "Prepare food sanitarily" 2.48, "Do not skip breakfast" 2.29, "Eat a variety of vegetables, fruits, dairy products daily" 2.25, "Drink water instead of beverage" 2.10, "Choose less fried foods" 2.09 and "Maintain healthy weight" 1.91. The exercise frequency of walking was not significantly different between groups; however, heavy exercise frequency was significantly lower in underweight group than the other groups (p < 0.05). The energy intake was 2153 kcal, which was 81.2% of the Estimate Energy Requirement, and the intake of calcium and vitamin B2 was 66.7% and 77.8% of KDRIs. Particularly, the intake of iron, vitamin A and vitamin C was about 59.4%, 52.2% and 55.4% of KDRIs and INQ was 0.71, 0.63 and 0.65 respectively, and intake of folic acid fell behind 39.1% of KDRIs and INQ was 0.46. Our study suggests that the systematic and continuous nutrition education will have to be provided at schools to improve dietary and health behaviors and prevent chronic metabolic disease for students of specialized game high school.
- 314 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of Different Dietary Habits by Classification of Body Mass Index of Middle School Male Students in Ulsan City
- Soon im Jung, Soon myung Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(3):342-350. Published online June 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigates differences in middle school male students' anthropometric variables and dietary habits using BMI (Body Mass Index) classifications. chi-square-test for frequency and ANOVA test for mean value and duncan value were used to analyze results. Averaged results of three groups of middle school male students' anthropometry including height (normal group 164.4 cm, overweight group 165.0 cm, obese group 167.0 cm), weight (normal group 56.0 kg, overweight group 70.0 kg, obese group 83.2 kg) and waist circumference (normal group 20.7 cm, overweight group 79.8 cm, overweight group 89.6 cm) were resulted. Classification of obese group was based upon 2007 growth charts using BMI criteria. This study indicates the normal weight group boys have over-eating related dietary habits and the obese groups have less calorie dietary habits. They answered oppositely to normal recognition. The obese group reflected dietary problems, such as preferences for sweet fruit rather than normal group males. Dinnertime of the groups were significantly different and obese group's earlier dinnertime can influence on their late night snack eating. Forty precent of obese male group like fruits as late night eating food. Three meal amount of three groups were significantly different, as obese group answered they ate same amount at every meal. It can mean obese group ate more amount of food in every meal. Overweight and obese male students have dietary problem of fast eating and answers of unbalanced eating were higher in normal group. These could mean obese group eats well in every food and fast eating habit could lead a lot of food eating habit. Obese group chooses out-going food of less calorie and frequency of fast food eating was lower than normal group. In result, obese group answered that they have less calorie related dietary habits, it could mean their answers were false or fixed dietary habit. Therefore, more researches should be followed.
- 331 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Changes of Obesity Index, Serum Lipid Profiles and Nutrient Intakes in Obese Children after the Weight Control Program of Nutrition Education
- Eun Ju Lee, Kyung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(1):61-72. Published online February 28, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of a weight control program on anthropometric values, serum lipid profiles and nutrient intakes. The subjects of this study were 38 obese children (boy : 17, girl : 21) with obesity index over 120%. The weight control program for obese children included nutritional education (50 min) and exercise (50 min) for 10 weeks. The nutrition intakes of the children were surveyed before and after the weight control program by 24hr recall test. The BMI, Rohrer Index, Obesity Index, WHR (Waist - Hip ratio) and body fat(%) were significantly decreased after completion of the weight control program. The total cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol of subjects were significantly increased after the weight control program. Distribution of serum lipid profiles was slightly changed. The energy intakes were significantly decreased (p < 0.001). from 1760.8 kcal to 1435.2 kcal. In addition, the intakes of P, Zn, retinol, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin E and niacin were significantly decreased. while intakes of vitamin C and folate were increased. Calcium and folic acid were upper 25% of subjects, under EAR(Estimated Average Requirements) intake before the weight control program. The distribution of energy intakes was significantly changed into positive status; fat percentage was decreased 26.3% to 22.1% (p < 0.01). Carbohydrate was increased 58.6% to 61.2% (p < 0.05). Meal distribution of energy intakes was changed; calorie percentage from lunch significantly increased from 32.2% to 38.3%. Calorie percentage from snack significantly decreased from 17.7% to 13.5%. In conclusion, weight control program for 10 weeks is effective in obesity index and nutrient intakes although serum lipid values were a little changed.
- 309 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Association of Serum Lipids and Dietary Intakes with Serum Adiponectin Level in Overweight and Obese Korean Women
- Mi Young Lee, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(1):27-35. Published online February 28, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was done to investigate the association of blood clinical parameters and dietary intakes with serum adiponectin level. Athropometric measurement, dietary intakes, serum lipids and adiponectin levels were examined in 160 overweight and obese women. The subjects were divided into 5 groups by quintile according to serum adiponectin level. Weight, BMI, waist circumferences and waist/hip ratio of the highest quintile group were significantly lower than those of the lowest quintile group. Serum lipid analysis showed a significant higher level of TG, LDL-cholesterol, LDL/HDL ratio, AI, and serum hs-CRP in the lowest quintile group. Similarly, correlation data also showed that serum adiponectin level was positively correlated with serum HDL-cholesterol level (p < 0.01) and was negatively correlated with BMI (p < 0.01), waist circumferences (p < 0.01), waist/hip ratio (p < 0.01), systolic (p < 0.01) and diastolic blood pressure (p < 0.05), TG (p < 0.01), LDL-cholesterol (p < 0.05), LDL/HDL ratio (p < 0.05), AI (p < 0.01), Homa-IR (p < 0.01), hs-CRP (p < 0.05) and leptin (p < 0.05). Dietary intake data showed that protein intake was significantly lower in the highest quintile group compared to the lower quintile groups while intakes of vitamin C was significantly higher in highest quintile group after adjustment by BMI, waist and energy intake, In addition, the highest quintile group had higher fiber intakes than the lower quintile groups. These results might suggest that a diet high in fiber and vitamin C and low in protein for obese patients would better be recommended to improve adiponectin level. However, further research is needed to elucidate the association of dietary intakes or dietary patterns and serum adiponectin level.
- 327 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Study of Food Intakes and Eating Patterns among Preschool Children in Daegu Area: Nutrient Intakes and Dietary Habits Associated with Body Weight Status
- Ju Young Seo, In Sook Lee, Bong Soon Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):710-721. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the body weight status (by WLI: Weight-Length Index) and dietary habits and to assess the nutritional status among preschool children in the Daegu area. Dietary habits including dietary attitude and behavior were investigated using questionnaire answered by mothers of 680 subjects aged 4 to 6 years old (508 completed). Also, dietary intake survey using 24-hour recall method was performed by mothers of the children. According to WLI, the underweight, normal, overweight and obesity level of subjects were 9.1, 62.0, 19.5, and 9.4%, respectively. As well, the number of girls was higher than boys in underweight, overweight, and obese group. There were significantly different on overeating, eating fast, and preferring eating-out by body weight status, and overweight group got higher score than underweight or normal-weight group (p < 0.01, p < 0.001). As well, there was significantly different on not moving around during mealtime by body weight status, and underweight group have lower score than obese group (p < 0.001). From the 24-hour recall survey, it was found that intakes of all the nutrients were higher than the %KDRI except energy, calcium and folate. The energy intake of underweight group of 4~5-year old (1338.2 kcal) and 6-year old was lower than Koreans %DRI for those age group. Folate and dietary fiber intakes of obese group were significantly lower than underweight (p < 0.01, p < 0.05). For 4~5-year old, vitamin B(6) intakes of obese group were significantly higher than obese group (p < 0.05). For 6-year old, obese group showed that intake of vitamin B(1) was significantly higher than the other three groups, and intake of vitamin B(1) of overweight group was significantly higher than the other three groups. Taken together, these results indicate that there were significant differences in the nutrient intake level and dietary habits of preschool children by body weight status in Daegu area. Therefore, parents (family) and caregivers should be aware of the prevalence of obesity and nutritional status of preschool children, and start nutrition education as soon as possible.
- 345 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



