Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Prevalence of coronary artery disease according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years and older: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Areum Song, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):457-470. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
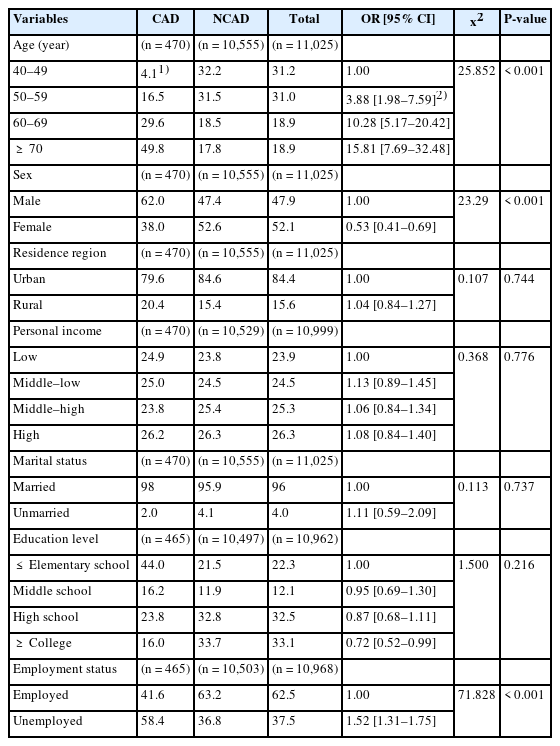
To examine the prevalence of coronary artery disease (CAD) according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years.
Methods
Data were derived from 11,025 participants aged ≥ 40 years in the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were assigned to a CAD group (n = 470) or a non-CAD group (n = 10,555). Socio-demographic characteristics (age, sex, residence, income, marital status, education level, and employment status), lifestyle characteristics (smoking, drinking, walking, strength training, sleep duration, stress level, and subjective health perception), energy and nutrient intakes, and comorbidities, including obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, stroke, cancer, depression, renal failure, cataract, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, and osteoporosis were analyzed.
Results
The prevalence of CAD was higher in older participants and in male. Participants with CAD had higher rates of smoking, engaged in less strength training, experienced higher stress, and had poorer perceived health. They had lower intakes of energy, fiber, folate and iron. The prevalence of obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, stroke, depression, renal failure, cataract, asthma, allergic rhinitis, osteoarthritis, or osteoporosis was significantly higher in the CAD group. The likelihood of having CAD was significantly higher among participants with renal failure (odds ratio [OR], 4.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.24–8.08), depression (OR, 2.14; 95% CI, 1.55–2.95), asthma (OR, 2.07; 95% CI 1.48–2.91), and dyslipidemia (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.69–2.44).
Conclusion
In Koreans aged 40 years, CAD was associated with unhealthy lifestyle habits, low nutrient intake, and increased comorbidities such as renal failure, depression, asthma, and dyslipidemia. These findings suggest the need for lifestyle management and intensive chronic disease management to reduce the risk of CAD.
- 94 View
- 10 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung–Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):150-162. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00038

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To determine the association between night eating habits and oral health in adolescents.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 were analyzed. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed the frequency of night eating per week, dietary habits, oral health characteristics, and factors affecting the presence of symptoms of poor oral health.
Results
Almost thirty-seven percent (36.6%) of Korean adolescents have eaten at night one to two times per week and 23.0% more than three times per week. An increased frequency of night eating was associated with poor dietary habits. Adolescents who consumed more at night were less likely to have breakfast, drink water, and eat fruit, while their consumption of fast food, sweet drinks, and high-caffeine drinks increased (P < 0.001). An increased frequency of night eating was also associated with poor oral health. In a logistic regression analysis, more frequent night eaters were significantly less likely to brush their teeth at least three times per day (odds ratio [OR], 0.78; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75–0.82; P for trend < 0.001), and brush their teeth before going to sleep (OR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.65–0.75; P for trend < 0.001), while they were more likely to experience sealant (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.13–1.26). More frequent night eaters were significantly more likely to have tooth fracture (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.30–1.53; P for trend < 0.001), tooth pain when eating (OR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.50–1.67; P for trend < 0.001), toothache (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.52–1.70), and bad breath (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.43–1.60).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that frequent night eating is linked to symptomatically poor oral health in adolescents. Therefore, oral health education programs related to dietary habits are necessary to reduce the potential of night eating to negatively influence dietary habits and oral health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Bo Young Park, Eun Bi Sim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(4): 370. CrossRef
- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,431 View
- 58 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of the relationship between sugar intake and cancer prevalence: a cross-sectional study using the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hye-Ryun Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):89-102. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00339
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze the association between sugar intake and cancer risk among Korean adults aged 19 years and older.
Methods
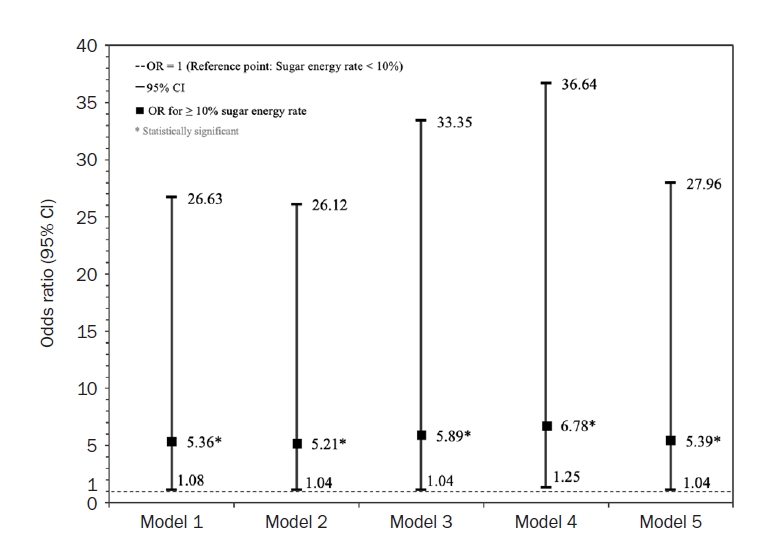
A total of 13,016 adults aged 19 years and older who participated in the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2019 to 2021 were included. Sugar intake was assessed in terms of both absolute intake and sugar energy rate. Sugar intake was divided into quartiles, while sugar energy rate was categorized into three groups (< 10%, 10%–20%, > 20%) based on the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans and into two groups (< 10%, ≥ 10%) based on WHO recommendations. Cancer prevalence was determined using cancer-related survey questions. The association between sugar intake and cancer prevalence was analyzed by sex and cancer type using logistic regression. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS statistics 29.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
From 2019 to 2021, sugar intake significantly declined with age in both men and women (P for trend < 0.001), with the highest intake observed in the 19–29 age group (61.38 g). Men consumed significantly more sugar than women across all age groups except for the 50–64 and 65–74 groups (P < 0.05). However, the sugar energy rate was significantly higher in women than in men (P < 0.05). While the association between sugar intake and cancer prevalence varied across regression models and cancer types, cervical cancer consistently showed a significant association with sugar intake (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
The association between sugar energy rate and the prevalence of premenopausal cervical cancer was consistent and significant. Given that women had a higher sugar energy rate than men, the relationship between sugar intake and cancer prevalence in women warrants further investigation. Longitudinal studies with more detailed sugar intake assessments are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
Zhe Sun, Wookyoun Cho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 441. CrossRef - Influence of the Size of the Spoon on the Eating rate, Energy Intake and the Satiety Levels of Female College Students
Yang Hee Hong, Young Suk Kim, Hyun Jung Kwon, Do Seok Chang, Dong Geon Kim, Un Jae Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 375. CrossRef - Dietary behavior and nutritional status among Chinese female college students residing in Korea
Gaowei, Soyeon Kim, Namsoo Chang, Ki Nam Kim
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2013; 46(2): 177. CrossRef
- A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
- 2,683 View
- 92 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Food and nutrient intake in pregnant women with singletons or multiples and post-delivery changes in intake in Korea: an observational study
- Cheawon Lee, Dahyeon Kim, Yoon Ha Kim, Myeong Gyun Choi, Jong Woon Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):1-15. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00325
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
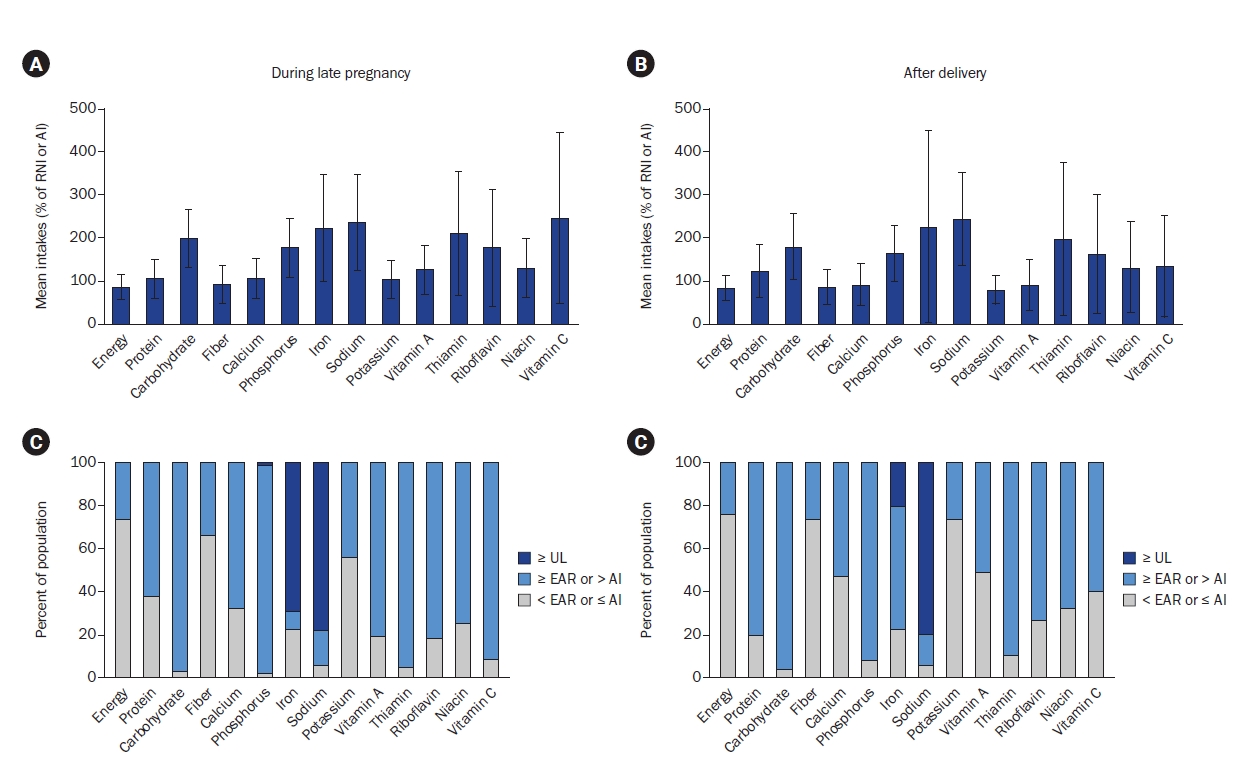
Nutrient intake during pregnancy and lactation is crucial for the health of both mother and offspring. Diet and nutrient metabolism potentially vary according to ethnicity and fetal number; nevertheless, recent studies validating this are inadequate. Furthermore, few studies have tracked changes in intake after delivery. We compared the food and nutrient intakes between pregnant women in Korea carrying singletons and multiples during late pregnancy and assessed their changes through postpartum.
Methods
Ninety-eight pregnant women were recruited from Chonnam National University Hospital between January 2019 and December 2023, and 48 responded to follow-up. Third trimester and postpartum intake were assessed via food frequency questionnaires and supplement questionnaires. Student’s t-test, Mann–Whitney U test, chi-square test, paired t-test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test was performed and adjustments were made for covariates.
Results
Nutrient intake was generally adequate relative to the Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans, with no differences between singleton- and multiple-pregnancy women. Sixty-six of 98 (67%) pregnant women consumed meat, fish, vegetables, and fruit daily. Dairy intake was low, while the mean iron intake during pregnancy reached 54.2 ± 34.0 mg/d, exceeding the tolerable upper intake level, mainly owing to supplements. Postpartum fruit and vitamin C intake decreased, with no significant differences between breastfeeding and non-breastfeeding women.
Conclusion
Dietary intake did not significantly differ between Korean singleton- and multiple-pregnancy women. Dairy intake was low and iron intake was excessive. Fruit intake decreased after delivery; however, difference in dietary intake according to breastfeeding status was minimal. Nutritional education may be necessary to promote a balanced diet in pregnant and postpartum women. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier KCT0005118. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Placental cadmium and its association with maternal diet and offspring growth in Koreans
Dahyeon Kim, Cheawon Lee, Yoon Ha Kim, Myeong Gyun Choi, Jong Woon Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(3): 473. CrossRef
- Placental cadmium and its association with maternal diet and offspring growth in Koreans
- 7,188 View
- 63 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):528-540. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine health-related characteristics and chronic disease risk in middle-aged Koreans based on their fat energy intake ratio.
Methods
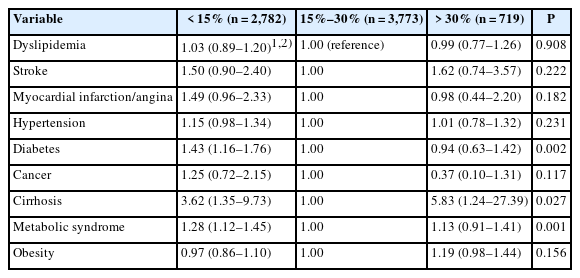
We analyzed data from 7,274 Koreans aged 40–64 years using the 7th (2016–2018) Koreans National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were classified into three groups based on their fat energy intake ratio: insufficient (< 15%), adequate (15%–30%), and excessive (> 30%). We assessed their socio-demographic characteristics; lifestyle characteristics; biochemical characteristics; quantitative and qualitative nutrient intakes, measured using dietary reference intakes for Koreans and index of nutrition quality (INQ); and chronic disease risk.
Results
Significant differences were observed between the groups in age, gender, income, education, and residence region. The insufficient group had the highest proportion of older adults, male, lower income, rural residents, and lower education levels. The groups differed significantly in lifestyle characteristics, with the insufficient group having the highest rates of no walking, heavy drinking, smoking, and poor subjective health perception. Biochemical characteristics in the insufficient group exhibited the lowest levels for fasting blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and triglycerides. Significant differences were found in both the quantitative and qualitative intake of nutrients. The insufficient group had the lowest intake of most nutrients except fiber, whereas the excessive group had the lowest fiber intake. Based on the INQ, vitamin A and Ca were the lowest in the insufficient group, and vitamin C and folic acid were the lowest in the excessive group. The risk of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome was highest in the deficient group, and the risk of liver cirrhosis was highest in the excessive group.
Conclusion
Insufficient or excessive fat energy intake ratio negatively affects nutrient intake and chronic disease risk. Fat energy intake of 15%–30% is important for improving nutrient intake and managing chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and liver cirrhosis. We suggest that education and an appropriate social environment are necessary to ensure this fat energy intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
Yu Hyeon Jo, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef
- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
- 1,536 View
- 50 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Health-related quality of life and nutrient intake of the elderly with type 2 diabetes according to comorbidity burden: a cross-sectional study
- Yejung Choi, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):418-430. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00014

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to explore the cross-sectional association between health-related quality of life (HRQoL) according to the number of comorbidities in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) using the Euro Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) index. Methods: This study included 3,553 participants aged ≥ 65 years from the 2008–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Dietary data were collected through 24-hour recall interviews by trained researchers, and demographic and lifestyle information via self-administered questionnaires. HRQoL was measured using a modified EQ-5D scale. Multivariable linear regression analyzed the associations between EQ-5D scores, nutrients and comorbidity, controlling for sociodemographic and health variables. Results: Most participants reported ‘no problems’ in the EQ-5D scores, although approximately 17% to 47% of participants reported ‘some problems’ or ‘extreme problems,’ depending on the dimension. As comorbidities increased, significant declines were observed across all dimensions, particularly in mobility, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/ depression. Nutrient intake analysis revealed that participants with three or more comorbidities consumed less carbohydrates, but more fat. Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that among older adults with T2DM, a higher number of comorbidities is associated with decreased HRQoL. Additionally, there are differences in nutrient intake patterns among those with more comorbidities, specifically decreased carbohydrate intake and increased fat intake. These results emphasize the need for comprehensive and tailored management strategies that consider both diabetes and the co-occurring health conditions. By addressing the complex healthcare needs of individuals with multiple comorbidities, it is possible to enhance their HRQoL and overall well-being.
- 2,046 View
- 32 Download

- [English]
- Associations between the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease and dietary and lifestyle behavior among young Korean adults: a preliminary cross-sectional study
- Soheun Shim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):396-405. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00011

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a clinical condition caused by esophageal tissue damage resulting from the reflux of stomach or duodenal contents. An increasing number of GERD cases have been reported recently; however, research on this population, especially young adults, is lacking. This study aimed to investigate the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Methods: A total of 202 individuals (19–34 years old) living in Gwangju were surveyed using a questionnaire to examine their general characteristics, lifestyle, and dietary behaviors. GERD symptoms were investigated using the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GerdQ). The participants were grouped into normal (GerdQ score ≤ 4) and caution (GerdQ score ≥ 5), and their characteristics were analyzed according to the group. Results: The findings suggested 15 participants (7.4%) belonged to the GERD caution group. More non-office workers were in the caution group than in the normal group (P < 0.05). The participants’ smoking, physical activity, sleep duration, and pillow height were not significantly different between the GERD phenotypes; however, the caution group consumed alcohol more frequently than the normal group (P < 0.001). The analyses of the participants’ eating behaviors revealed that the frequency of overeating, late-night snacking and chocolate consumption was significantly higher in the caution group (P < 0.001). Conclusion: Lifestyle and dietary behaviors were associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Further studies with larger cohorts are required to confirm these findings.
- 5,522 View
- 71 Download

- [Korean]
- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
- Youngmin Nam, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):288-303. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
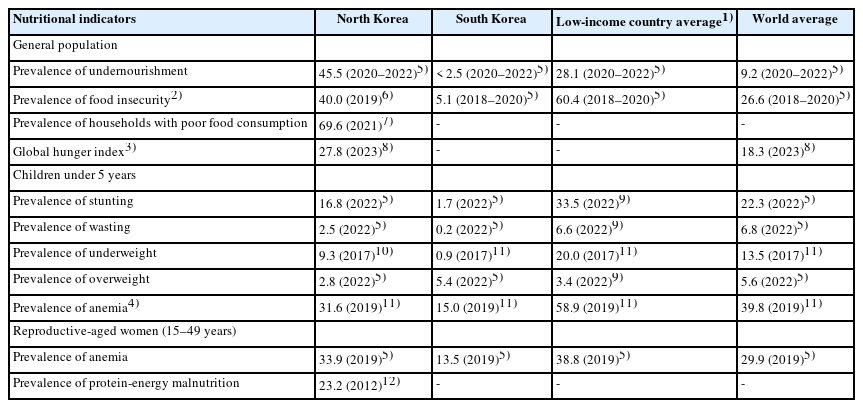
North Koreans have been facing chronic food shortages and malnutrition. This study examined the nutritional status of North Koreans and the perceptions of South Korean adults regarding their nutritional status.
Methods
The nutritional status was examined using nutritional indicators for the general population, children, and reproductive-aged women in North Korea. An online survey was conducted among 1,000 South Korean adults aged 19–69 years to investigate their perceptions regarding the nutritional status of North Koreans.
Results
Although the nutritional status of children in North Korea has consistently improved, significant progress in the general population and reproductive-aged women in the country remains elusive. The prevalence of malnutrition among North Korean children has decreased to a level that is not considered severe based on international standards, although it shows a substantial difference from that among South Korean children. The prevalence of undernourishment and food insecurity in North Korea remains over 40%. South Korean adults perceive the nutritional status of North Koreans as being more severe than it is in reality. Notably, a significant inconsistency exists between the perceived and actual nutritional status of North Korean children, with over 95% of South Korean adults perceiving North Korean children’s malnutrition as being more severe than it actually is. Moreover, South Korean adults in their 20s to 40s tended to perceive the nutritional status of North Koreans as being more severe than those in their 50s to 60s did.
Conclusions
The nutritional status of North Koreans is a matter of concern. The disparity between South Koreans’ perceptions of the nutritional status of North Koreans and the actual status highlights the need for accurate information dissemination to effectively address malnutrition in North Korea. These efforts could be instrumental in enhancing public awareness and fostering social consensus on food aid and nutritional support programs for North Korea.
- 3,864 View
- 72 Download

- [English]
- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middle-aged Korean adults: an intervention study
- Minji Kang, Young-Hee Park, Subeen Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Hyun Wook Baik, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):265-277. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
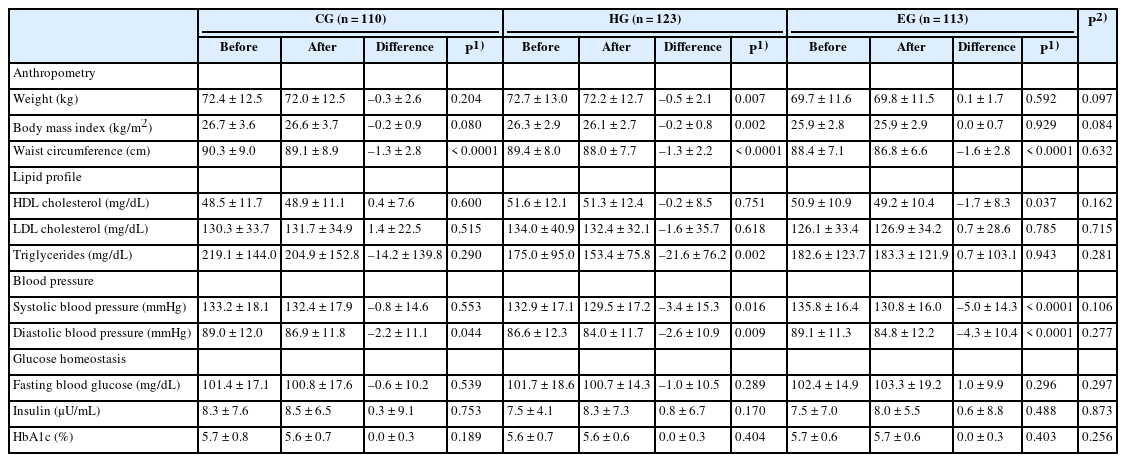
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 411 Korean adults 30–59 years of age were allocated randomly into three groups: the nutrition education group for promoting Han-sik consumption (HG), the nutrition education group for eating balanced diet (EG), and the control group (CG). The HG and EG received four face-to-face nutrition education sessions over 16 weeks to improve nutritional problems based on the individual’ usual diet. Effectiveness of the program was evaluated with the differences of self-reported dietary behaviors, dietary intakes, anthropometric measurements and biochemical indices between the baseline and the end of the nutrition education program. The changes within groups were analyzed using paired t-test and McNemar test and effectiveness among three groups was analyzed by repeated analysis of variance.
Results
After the nutrition education, the percentages of participants who achieved the recommended food group consumption in the Korean Food Guidance Systems significantly increased in HG (P = 0.022). Body weight (P = 0.007), body mass index (P = 0.002), and triglycerides (P = 0.002) significantly decreased in HG. Waist circumference and diastolic blood pressure decreased in all three groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
This study found that tailored nutrition education program for middle aged Korean adults showed beneficial effects on improving dietary behaviors and metabolic syndrome risk factors. Further studies are needed to assess the long-term effects of the nutrition education programs on metabolic syndrome risks.
- 4,186 View
- 85 Download

- [English]
- Sex differences in health-related quality of life among older Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
- Hyeonji Jeong, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):336-347. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
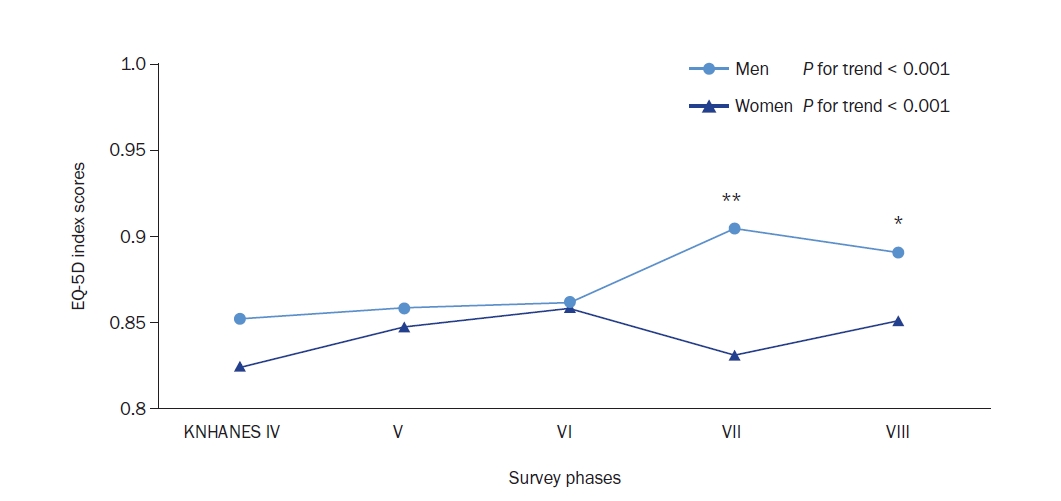
This cross-sectional study examined sex differences in Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) among seniors with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2008–2020) were analyzed. The EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D), a measure of HRQoL, was used. It comprises five dimensions: mobility, self-care, usual activity, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression, each with three levels.
Results
Analysis of 3,826 older adults with T2DM showed a significant increasing trend in the EQ-5D Index from the 4th survey phase onwards (P for trend < 0.001 for both men and women). Men consistently reported higher EQ-5D levels than women across all survey years. Women’s EQ-5D levels remained lower than men’s, maintaining a decade-old disparity (P < 0.05). Men scored significantly higher (P < 0.05) in most EQ-5D domains, except for self-care and anxiety/depression, resulting in a higher total EQ-5D Index (P = 0.001). Increased comorbidities were strongly associated with lower EQ-5D levels in both sexes. Additionally, there was a negative correlation between the EQ-5D Index and refined grain intake for both sexes (P for trend < 0.001), with high-EQ-5D groups consuming fewer refined grains. Women in the high-EQ-5D group consumed more nuts, vegetables, and meat compared to men (P for trend < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our study highlights the sex disparities in HRQoL among older adults with T2DM. The findings suggest the need for tailored treatment guidelines aimed at improving the HRQoL of elderly T2DM patients, with a focus on their sex-specific characteristics. Implementing these tailored guidelines could enhance the HRQoL of older women with T2DM and promote more equitable healthcare outcomes. This underscores the importance of considering sex differences to comprehensively improve the well-being of this population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding Gender Disparities in Quality of Life Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Ethiopia: An Institutional‐Based Study
Enguday Demeke Gebeyaw, Girma Deshimo Lema
Lifestyle Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Understanding Gender Disparities in Quality of Life Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Ethiopia: An Institutional‐Based Study
- 2,524 View
- 40 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Total sugar intake and its contributed foods by age groups in Koreans using the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: a cross-sectional study
- Hyejin Yu, Sang-Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):222-233. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
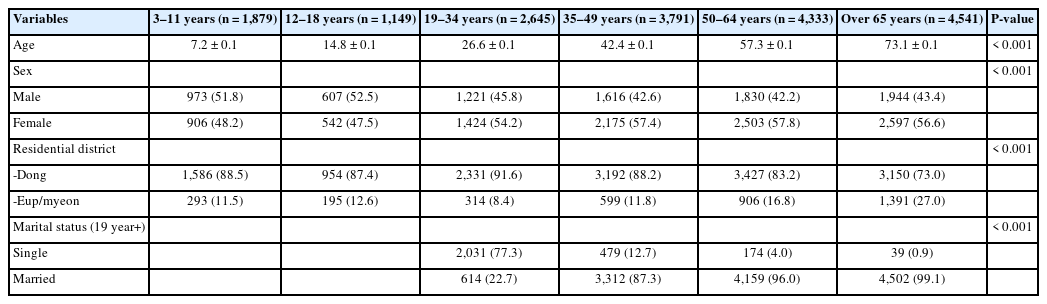
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to investigate the status of total sugar intake and contributing foods in Korea according to age groups.
Methods
This study used 24-hour dietary recall data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021) to investigate the nutritional and total sugar intake status among Koreans. A total of 18,338 research participants (≥3 years old) were included in this study. To analyze the types of foods contributing to total sugar intake, these foods were categorized into 15 types. Moreover, we examined the total sugar intake and ranked the most consumed foods by age groups (3–11 years, 12–18 years, 19–34 years, 35–49 years, 50–64 years, over 65 years). A survey procedure was employed for statistical analysis.
Results
The energy intake ratio from total sugars was approximately 12%–15%, which was within the recommended range. However, the proportion of individuals consuming total sugar exceeding 20% of their total caloric intake is nearly 20%, raising concerns about excessive sugar consumption. Furthermore, the percentage of participants whose intake of sugar from processed foods exceeded 10% of their total calories was highest in the 12–18 age group at 37.1%, followed by the 3–11 age group at 35.2%, and the 19–34 age group at 34.0%. Carbonated drinks, cola, and cider were the primary foods consumed by children and adolescents (3–18 years old) and young adults (19–34 years old). For middle-aged and older adults, mixed coffee with sugar and cream was a prominent contributor to sugar intake.
Conclusions
This study investigated sugar consumption patterns among Koreans, finding the principal foods contributing to this intake. Identifying these contributors is pivotal, given their potential impact on public health.
- 12,803 View
- 147 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung-Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):156-170. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the association between how often Korean adolescents watch Mukbang and Cookbang videos and their dietary habits.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 was analyzed for this study. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed various aspects, including demographics, frequency of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos per week, dietary habits, health behaviors, and mental health factors.
Results
Nearly a third (29.3%) of Korean adolescents watched Mukbang and Cookbang videos one to four times a week, while 13.5% watched them more than five times weekly. Females, those with lower academic achievement, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds were significantly more likely to be frequent viewers (P < 0.001). Increased viewing frequency was associated with poorer dietary habits. Adolescents who watched more frequently were less likely to eat breakfast and consume fruits and milk, while their consumption of fast food, high-caffeine drinks, sugary drinks, and late-night snacks increased (P < 0.001). Higher viewing frequency correlated with increased feelings of stress, depression, and loneliness (P < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis confirmed these associations. More frequent viewers were significantly less likely to eat breakfast (odds ratio (OR), 0.63; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.58–0.68), and more likely to consume fast food (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.69–2.02), high-caffeine drinks (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30–1.56), sugary drinks (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.41–1.67), and late-night snacks (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.25–1.51).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that frequent exposure to Mukbang and Cookbang content is linked to unhealthy dietary habits in adolescents. Educational programs may be necessary to mitigate the potential for these videos to negatively influence dietary choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
Seung Jae Lee, Yeseul Na, Kyung Won Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2652. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef
- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
- 3,609 View
- 103 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2016–2021 KNHANES data
- Enkhgerel Erdenetsetseg, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):144-155. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.144
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids in Korean adolescents.
Methods
This study was comprised of 3,932 adolescents (9–18 years) who participated in the 2016–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids, including alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and linoleic acid (LA) were evaluated using data obtained from one-day 24-hour dietary recall. The proportions of adolescents consuming ALA, EPA + DHA, and LA above or below the adequate intake (AI) of the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans were calculated. All statistical analyses accounted for the complex sampling design effect and appropriate sample weights.
Results
The mean intakes of ALA, EPA, DHA, and LA among Korean adolescents were 1.29 g/day, 69.6 mg/day, 166.0 mg/day, and 11.1 g/day, respectively. Boys had higher intakes of all essential fatty acids compared to girls. By age group, adolescents aged 15–18 years showed lower intakes of EPA and DHA compared to adolescents in younger age groups. The 9–11-year-old adolescents had lower intakes of ALA and LA than older adolescents. The proportions of adolescents who consumed more than AI were 35.7% for ALA, 30.4% for EPA + DHA, and 41.5% for LA. Adherence to the AI for ALA did not differ by sex or age group, although boys showed a lower adherence to the AI for EPA + DHA than girls. Major food sources for ALA and LA were plant-based oils, mayonnaise, pork, and eggs. Mackerel was the most significant contributor to EPA and DHA intake (EPA, 22.6%; DHA, 22.2%), followed by laver, squid, and anchovy.
Conclusions
The proportion of Korean adolescents who consumed EPA + DHA more than AI was low. Our findings highlight that nutrition education emphasizing an intake of essential fatty acids from healthy food sources is needed among Korean adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Harnessing dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids through gut microbiota to enhance ferroptosis in breast cancer therapy
Yara Adel Haroun, Abdulrahman Abdulla Alzyoud, Mohammad Taha Alizadeh, Nashwa Ahmed Mohamed, Riyad Bendardaf, Sameh S.M. Soliman
Nutrition Research.2025; 141: 10. CrossRef
- Harnessing dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids through gut microbiota to enhance ferroptosis in breast cancer therapy
- 3,829 View
- 58 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Comparative study on the health and dietary habits of Korean male and female adults before and after the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: utilizing data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
- Chaemin Kim, Eunjung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):65-80. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to compare changes in physical factors, health behaviors, eating habits, and nutritional intake among Korean male and female adults over a period of three years (2019–2021) before and after the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods
This study utilized raw data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021). The participants in this study included 6,235 individuals in 2019, 5,865 individuals in 2020, and 5,635 individuals in 2021. Individuals whose daily energy intake was less than 500 kcal or exceeded 5,000 kcal were excluded from the study.
Results
In comparison to 2019, overweight/obesity rates, weight, waist circumference, weekend sleep hours, and resistance exercise days/week increased in both male and female during the COVID-19 pandemic. Regarding eating habits, the proportions of people skipping breakfast, not eating out, consuming health supplements, and recognizing nutritional labels increased in 2020 and 2021, whereas the rate of skipping dinner decreased. Total energy intake has continued to decrease for the two years since 2019. A comparison of nutrient intake per 1,000 kcal before and after the outbreak of COVID-19 revealed that intake of nutrients, including protein, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, riboflavin, and niacin increased, while folic acid intake decreased. In male, calcium, phosphorus, riboflavin, and niacin intakes increased, whereas iron, vitamin C, and folic acid intakes decreased. In female, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, and riboflavin intake increased significantly, while protein and niacin intake decreased significantly.
Conclusions
After COVID-19, the obesity rate, breakfast skipping rate, health supplement intake, and nutritional label use increased, while the frequency of eating out, dinner skipping rate, and total energy intake decreased. These environmental changes and social factors highlight the need for nutritional education and management to ensure proper nutritional intake and reduce obesity rates in the post-COVID-19 era. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Status of Use of Protein Supplement Products according to the Health Concerns of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
Cho-In Oh, Bok-Mi Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 9. CrossRef - A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 140. CrossRef - How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
Yong-Seok Kwon, Dasol Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1973. CrossRef - Intake of energy and macronutrients according to household income among elementary, middle, and high school students before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study
Chae-Eun Jeong, Heejin Lee, Jung Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 234. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef
- Status of Use of Protein Supplement Products according to the Health Concerns of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
- 5,539 View
- 84 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
- Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):51-64. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between ultra-processed food (UPF) consumption and chronic diseases in elderly Koreans.
Methods
Data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were analyzed. Dietary intake and UPF consumption were assessed using the NOVA food classification based on 24-hour recall data from 3,790 participants (aged 65+ years). Participants were divided into 4 groups based on the quartile of energy intake from UPFs. Regions were classified as urban or rural. Multivariable logistic regression was employed to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) after controlling for potential confounders.
Results
Among the participants, 71.3% resided in urban and 28.7% in rural areas. Compared to the urban elderly, rural participants tended to be older, have lower education and income levels, be more likely to live in single-person households, and have a higher smoking rate (P < 0.05). Urban elderly consumed more UPFs daily (146.1 g) compared to rural residents (126.6 g; P < 0.05). “Sugar-sweetened beverages” were the most consumed category in both regions. “Sweetened milk and its products” and “traditional sauces” were prominent in urban areas, while rural elderly consumed more “traditional sauces” and “distilled alcoholic beverages.” Rural areas also had a higher carbohydrate-to-calorie ratio than urban areas. Compared to the lowest quartile of UPF intake, the highest quartile was significantly associated with impaired fasting glucose only in rural areas (AOR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.00–2.19; P for trend = 0.0014). No significant associations were observed for diabetes in either urban or rural areas.
Conclusions
This study suggests that high intake of UPFs is associated with increased odds of impaired fasting glucose in rural elderly. Further research is needed to elucidate the specific negative health effects of UPFs in different populations, and targeted efforts should promote healthy diets in both urban and rural areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
Nazlıcan Erdoğan Gövez, Eda Köksal
Current Nutrition Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study of the Chemosensory Properties of Commercial Processed Foods Using Electronic Sensors
Hyeonjin Park, Younglan Ban, Sojeong Yoon, Hyangyeon Jeong, Seong Jun Hong, Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 805. CrossRef - Analysis of Flavor and Taste Patterns of Various Processed Animal Foods: Using the Electronic Tongue and Nose
Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Younglan Ban, Hyeonjin Park, Sojeong Yoon, Na Eun Yang, Seong Jun Hong, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(12): 1267. CrossRef
- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
- 2,223 View
- 72 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Sustainable diets: a scoping review and descriptive study of concept, measurement, and suggested methods for the development of Korean version
- Sukyoung Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):34-50. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Transformation through a sustainable food system to provide healthy diets is essential for enhancing both human and planetary health. This study aimed to explain about sustainable diets and illustrate appropriate measurement of adherence to sustainable diets using a pre-existing index.
Methods
For literature review, we used PubMed and Google Scholar databases by combining the search terms “development,” “validation,” “sustainable diet,” “sustainable diet index,” “planetary healthy diet,” “EAT-Lancet diet,” and “EAT-Lancet reference diet.” For data presentation, we used data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2017–2018, among adults aged 20 years and older (n = 3,920). Sustainable Diet Index-US (SDI-US), comprising four sub-indices corresponding to four dimensions of sustainable diets (nutritional quality, environmental impacts, affordability, and sociocultural practices), was calculated using data from 24-hour dietary recall interview, food expenditures, and food choices. A higher SDI-US score indicated greater adherence to sustainable diets (range: 4–20). This study also presented SDI-US scores according to the sociodemographic status. All analyses accounted for a complex survey design.
Results
Of 148 papers, 16 were reviewed. Adherence to sustainable diets fell into 3 categories: EAT-Lancet reference diet-based (n = 8), Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) definition-based (n = 4), and no specific guidelines but including the sustainability concept (n = 4). Importantly, FAO definition emphasizes on equal importance of four dimensions of diet (nutrition and health, economic, social and cultural, and environmental). The mean SDI-US score was 13 out of 20 points, and was higher in older, female, and highly educated adults than in their counterparts.
Conclusions
This study highlighted that sustainable diets should be assessed using a multidimensional approach because of their complex nature. Currently, SDI can be a good option for operationalizing multidimensional sustainable diets. It is necessary to develop a Korean version of SDI through additional data collection, including environmental impact of food, food price, food budget, and use of ready-made products. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Do the Indices based on the EAT-Lancet Recommendations Measure Adherence to Healthy and Sustainable Diets? A Comparison of Measurement Performance in Adults from a French National Survey
Agustín R Miranda, Florent Vieux, Matthieu Maillot, Eric O Verger
Current Developments in Nutrition.2025; : 104565. CrossRef - Behavioral intention toward planetary health diet among adult users of government worksite cafeterias in Seoul, South Korea: a mixed-methods study based on the theory of planned behavior and focus groups interviews
Ji-Won Kang, Su-Jin Lee, Sil-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 224. CrossRef - Trends in sustainable dietary patterns in United States adults, 2007-2018
Sukyoung Jung, Heather A. Young, Barbara H. Braffett, Samuel J. Simmens, Eunice Hong Lim Lee, Cynthia L. Ogden
Epidemiology and Health.2025; 47: e2025045. CrossRef
- How Do the Indices based on the EAT-Lancet Recommendations Measure Adherence to Healthy and Sustainable Diets? A Comparison of Measurement Performance in Adults from a French National Survey
- 2,872 View
- 90 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Factors related to adolescent obesity and changes: a cross-sectional study based on the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Bora Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):363-375. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to identify factors associated with adolescent obesity, as well as any new factors that correlated with a change in the rate of obesity over time.
Methods
The study used 5-yearly data collected by the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey starting from the year 2006 up until 2021 (data from 2nd, 7th, 11th, and 17th surveys were analyzed). Factors such as demographics, dietary factors, health behavioral factors, and mental health factors were studied. All data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27.0, employing chi-square tests and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results
This study included data from a total of 255,200 participants. Factors contributing to obesity varied with time. Over the survey duration of 15 years, low academic achievement, parents with low levels of education, low frequency of fruit consumption, low frequency of fast food intake, long periods of being seated, and high levels of stress were significantly associated with a high rate of obesity. Factors that showed a new correlation with an increase in obesity rates included living with single parents, low frequency of muscle strengthening exercises, and experiencing intense sadness and despair in the past year. Factors that were correlated with a change in obesity rates over time included household economic status, frequency of carbonated beverage consumption, frequency of intense physical activity, and frequency of alcohol consumption. Breakfast intake and smoking were not significantly associated with obesity rates in the 15-year period.
Conclusions
While several factors associated with obesity remained consistent over time, several new factors have emerged in response to social, economic, and environmental changes contributed to a change in obesity rate over time. Therefore, to prevent and manage adolescent obesity, continuous research into the new emergent factors contributing to obesity is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,836 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary sodium and potassium intake of Koreans estimated using 2 different sources of their contents in foods, Food & Nutrient Database and the Korean Total Diet Study : a comparative study
- Jee Yeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Soo Hyun Lee, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):235-244. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Based on the results from the Korean Total Diet Study (KTDS), the sodium (Na) and potassium (K) intake of Koreans were estimated and compared with intake estimates from the Food & Nutrient Database (FNDB), as in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) to verify the validity of these estimates.
Methods
One hundred and thirty-four representative foods (RFs) covering 92.5% of the total food intake of Koreans were selected, and 228 pairs of corresponding ‘RF x representative cooking method’ were derived by reflecting the methods used mainly in terms of frequency and quantity in their cooking. RF samples were collected from three cities with a larger population size in three regions (nine cities) nationwide, and six composite samples were made for each RF, considering its regional and/or seasonal characteristics. One thousand three hundred and sixty-eight ‘RF x representative cooking method’ pair samples were prepared, and the Na and K contents were assessed using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-MS). The Na and K intake of the Korean population was estimated by linking the content with the food intake data from the 7th KNHANES.
Results
The mean Na and K intake of Koreans were 2,807.4 mg and 2,335.0 mg per person per day, respectively. A comparison with the Na and K intake from KNHANES, including only RFs of KTDS, showed comparable results with less than 5% variation. While the contribution and ranking of food items to Na intake were similar between KNHANES and KTDS, there were differences in K intake. This was attributed to the large discrepancies in the K content of rice and coffee between KTDS results and the values in the 9th Revision of the National Food Composition Table used in KNHANES.
Conclusions
The Na and K intake of Koreans estimated based on the KTDS, which performed nutrient analysis on samples prepared to a ‘table-ready’ state using foods of the representative collection, was similar and comparable with that of KNHANES. This supports the validity and usefulness of FNDB-based nutrient intake estimation at the population level. The list of nutrients studied in KTDS is expected to be expanded, allowing for intake estimation of nutrients with currently insufficient or absent information in the FNDBs in use.
- 2,460 View
- 68 Download

- [English]
- Nutritional status and dietary behavior of North Korean adolescent refugees based on Nutrition Quotient for Korean adolescents: a preliminary study
- Young Goh, Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeong Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):1-10. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the nutritional status and dietary behavior of adolescents from North Korean refugee (NKR) families residing in South Korea (SK), who are known to be at a higher risk of malnutrition due to their lower socioeconomic status and facing other psychological challenges.
Methods
A total of 178 adolescents (91 males and 87 females) from NKR families were included in the analysis, and their demographic details such as age, birthplace, parental nationality, and duration of their settlement in SK were collected through questionnaires. Anthropometric measurements were also taken to determine their growth and nutritional status according to the 2017 Korean National Growth Charts for children and adolescents. The study used the Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents (NQ-A) questionnaire to assess the dietary behavior of the participants.
Results
Approximately 11.8% and 10.1% of participants were identified with malnutrition and obesity, respectively. The total mean score for the NQ-A was 50.1. The mean scores for the individual factors of balance, diversity, moderation, environment, and practice were 49.2, 44.7, 43.8, 51.2, and 61.5, respectively. Approximately 47.2% of participants had a low NQ-A grade. However, there was no significant difference in the NQ-A scores according to their nutritional status or duration of time in SK.
Conclusions
Adolescents from NKR families exhibited both malnutrition and obesity. However, their dietary behavior, as assessed using the NQ-A, did not vary with their nutritional status. The unique challenges and related dietary behavior of North Korean adolescent refugees should be taken into consideration, when developing targeted strategies for nutritional education and health management programs.
- 1,929 View
- 24 Download

- [Korean]
- Problems Encountered in Analyzing the Market Size, Purchase, and Consumption of HMR in the Republic of Korea
- Sung Ok Kwon, Injoo Choi, Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):480-491. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.480
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the problems encountered when analyzing the market size, purchase, and consumption of HMR (home meal replacements) in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
The macro data relevant to the market size and purchase status of HMR were critically summarized. The micro data retrieved from the 2019 & 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) were analyzed to understand the consumption of HMR.
Results
The Korea Agro-Fisheries & Food Trade Corporation and the Ministry of Food and Drug Administration reported the market size of HMR, whereas the Korean Rural Economic Institute and the Rural Development Administration reported the purchase expense and frequencies of HMR. Since the values on the market size and purchase status were calculated or surveyed using different scopes of HMR, there have been reliability issues for the data presented. Additionally, lack of consensus on the use of Korean terms corresponding to HMR was found to be a problem. To examine the consumption of HMR, analysis of the food intake data from KNHANES presented results with very low validity due to the inappropriate survey and coding scheme not reflecting the inclusion of new food types.
Conclusions
Several problematic discrepancies were encountered in the statistics on HMR. The fundamental cause of these problems was the absence of agreement on the scope of HMR and the Korean terms corresponding to it. Considering the increasing importance of HMR in Korean diets, urgent cooperative efforts are required between the government and academia to derive an agreed Korean term and establish the scope of HMR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Human Resource Management in Emergencies: The Case of the Lithuanian Logistics Sector
Kristina Čižiūnienė, Gabrielė Voronavičiūtė, Dragan Marinkovic, Jonas Matijošius
Sustainability.2025; 17(6): 2591. CrossRef - Evaluation of Thermal Resistance in Geobacillus thermodenitrificans subsp. Calidus and Ureibacillus suwonensis Spores Isolated in Korea
Ju-Hee Nam, Du-Yeong Jung, Zi-On Choi, Hyun-Jung Jung, Jung-Beom Kim
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2025; 40(1): 13. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties and Quality Analysis of Miichthys miiuy Products Processed by Drying and Smoking
Yu-Jin Heo, Hayoun Kim, Hae-In Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 629. CrossRef - Survey on consumer perceptions, health benefits and preferences of kindergarten and school foodservices in Korea, including related keywords reported in newspaper: a mixed-methods study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 309. CrossRef - Eating behaviors, home meal replacement consumption, and nutrition quotient: a comparative study of male shift and non-shift workers in Chungcheong, Korea
Yeon Jin Lee, Munkyong Pae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 758. CrossRef - Usage and Quality Satisfaction of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores according to the Eating Behavior of University Students in Southern Gyeonggi Province
Se-In Oh, Ok-Sun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 492. CrossRef
- Sustainable Human Resource Management in Emergencies: The Case of the Lithuanian Logistics Sector
- 5,679 View
- 129 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Development of Korean NOVA Food Classification and Estimation of Ultra-Processed Food Intake Among Adults: Using 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hae Jin Park, Sohyun Park, Jee Young Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):455-467. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.455
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
In this study, we suggest a Korean NOVA food classification that can be applied to food consumption among Korean. Based on this suggestion, the nutritional intake of Korean adults from ultra-processed foods (UPFs) was estimated.
Methods
Korean commercial food was categorized based on the NOVA food classification criteria through the Korea Food Code and expert meetings. Then, the nutrient intake status of 6,991 participants in the 2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey was analyzed according to the food processing level. Then, 4,152 adult participants (age 19-65) were divided into quartiles on the basis of their intake of UPFs, and the nutrient intakes from UPFs were compared.
Results
Korean NOVA Food Classification defines with priority Group I (Unprocessed/ Minimally processed foods) and Group II (Processed culinary ingredients) foods based on the food cooking or consumption. Then, Group III (Processed foods) and Group IV (UPFs) are classified according to whether the characteristics of the raw materials used are maintained or whether the food was consumed before the 1970s. Our analysis results showed that most of the calories in the diet were consumed by Group I (52.7%), followed by Group IV (29.3%). After categorization of the adult participants into four groups according to their energy consumption from UPFs, we found that the highest consumption group (Q4) was younger and had higher percentage of men than women. The comparative analysis of the consumption of ultra-processed foods by Korean adults revealed that participants of a younger age and men consumed higher energy from UPFs than older participants and women, respectively (P < 0.01). Furthermore, the larger intake of UPFs was associated with an increasing trend for a higher intake of energy, sugar, saturated fat (P for trend < 0.001), total fat (P for trend = 0.021), and sodium (P for trend = 0.005), whereas the intake of carbohydrate, protein, and dietary fiber had a decreasing trend (P for trend < 0.001).
Conclusions
With the current increase in the consumption of processed and ultra-processed foods, it is important to carefully consider not only nutrient intake but also the level of food processing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Consumption of ultra-processed foods and major contributing foods according to the age group in Korean adults and older adults: using data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2019)
Seulgi Lee, Jee Young Kim, Kirang Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 59. CrossRef - Potential misclassification of ultra-processed foods across studies and the need for a unified classification system: a scoping review
Sukyoung Jung, Jee Young Kim, Sohyun Park, Jung Eun Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(3): 331. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Its Association with Obesity Among Korean Adults
Seung Jae Lee, Kyung Won Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 2027. CrossRef - Interaction between chronotype and ultra-processed food intake on triglyceride-glucose index in Korean adults
Sarang Jeong, Eunjin Jang, Sukyoung Jung, Jinhyun Kim, Minjeong Jeong, Dahye Han, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 591. CrossRef - Ultra-processed food intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: a pooled analysis of three prospective cohorts of Korean adults and an updated meta-analysis
Yujin Kim, Yoonkyoung Cho, Bonjae Koo, Zhangling Chen, Qi Sun, Hannah Oh
European Journal of Epidemiology.2025; 40(11): 1293. CrossRef - Sex Differences in the Association Between Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and NAFLD: An Analysis of KNHANES 2013–2021 Data
Byung Soo Kwan, Nak Gyeong Ko, Ji Eun Park
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(22): 7930. CrossRef - Associations of Ultra-Processed Food Intake with Body Fat and Skeletal Muscle Mass by Sociodemographic Factors
Sukyoung Jung, Jaehee Seo, Jee Young Kim, Sohyun Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(4): 780. CrossRef - Navigating Ultra-Processed Foods with Insight
Ji A Seo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(4): 713. CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - Sustainable diets: a scoping review and descriptive study of concept, measurement, and suggested methods for the development of Korean version
Sukyoung Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 34. CrossRef - Eating patterns in Korean adults, 1998–2018: increased energy contribution of ultra-processed foods in main meals and snacks
Sukyoung Jung, Jee Young Kim, Sohyun Park
European Journal of Nutrition.2024; 63(1): 279. CrossRef - Association Between Ultraprocessed Food Consumption and Metabolic Disorders in Children and Adolescents with Obesity
Gyeong-yoon Lee, Joo Hyun Lim, Hyojee Joung, Dankyu Yoon
Nutrients.2024; 16(20): 3524. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - Higher consumption of ultra-processed food is associated with cardiovascular risk in Korean adults: KNHANES 2016–2018
Sukyoung Jung, Eunjin Jang, Hyeongyeong Lee, Jee Young Kim, Sohyun Park
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Consumption of ultra-processed foods and major contributing foods according to the age group in Korean adults and older adults: using data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2019)
- 4,075 View
- 143 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between Sarcopenia and Energy and Protein Intakes in Community-dwelling Elderly
- Woori Na, Dayoung Oh, Seohyeon Hwang, Bonghee Chung, Cheongmin Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(4):286-295. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.4.286
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Sarcopenia is one of the most representative factors of senescence, and nutritional status is known to affect sarcopenia. This study was performed to analyze the relationships between energy and protein intake and sarcopenia.
Methods
The study subjects were 3,236 individuals aged ≥ 65 that participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2008 ~ 2011. General characteristics and anthropometric and 24-hour dietary recall data were analyzed. Sarcopenia was diagnosed using a formula based on appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM) and body weight. Logistic regression was performed to determine relationships between sarcopenia risk and energy and protein intakes.
Results
For energy intake, the odds ratio (OR) of sarcopenia in women was significantly higher those with the lowest intake [OR = 1.680, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.213-2.326] than those with the highest intake (P for trend = 0.001). Regarding protein intake per kg of body weight, the odds ratio of sarcopenia was significantly higher for those that consumed < 0.8 g/kg of protein daily than those that consumed > 1.2g/kg for men (OR = 2.459, 95% CI = 1.481-4.085) and women (OR = 2.178, 95% CI = 1.423-3.334).
Conclusions
This study shows a link between sarcopenia and energy and protein intake levels and suggests that energy and protein consumption be promoted among older adults to prevent sarcopenia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between Protein Intake and Sarcopenia-Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Scoping Review
Minjee Han, Kyung-sook Woo, Kirang Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(3): 216. CrossRef - Nutritional Approaches in Sarcopenia Management
Min-Yu Chung
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 565. CrossRef - The Present and Future of Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Exercise Interventions: A Narrative Review
Hongje Jang, Jeonghyeok Song, Jeonghun Kim, Hyeongmin Lee, Hyemin Lee, Hye-yeon Park, Huijin Shin, Yeah-eun Kwon, Yeji Kim, JongEun Yim
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(23): 12760. CrossRef - Design of contents for developing an intervention app for sarcopenia in older adults: A research study using the Delphi technique
Hee Jung Kim, Ju Young Ha
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(4): 370. CrossRef - Association of Protein Intake with Sarcopenia and Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Minjee Han, Kyungsook Woo, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2024; 16(24): 4350. CrossRef - Muscle Mass Changes After Daily Consumption of Protein Mix Supplemented With Vitamin D in Adults Over 50 Years of Age: Subgroup Analysis According to the Serum 25(OH)D Levels of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Yeji Kang, Namhee Kim, Yunhwan Lee, Xiangxue An, Yoon-Sok Chung, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2023; 12(3): 184. CrossRef
- Association Between Protein Intake and Sarcopenia-Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Scoping Review
- 2,552 View
- 67 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary Iron Intake of Koreans Estimated using 2 Different Sources of Iron Contents are Comparable: Food & Nutrient Database and Iron Contents of Cooked Foods in the Korean Total Diet Study
- Jeeyeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Yoonjae Yeoh, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):245-253. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.245
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to find out if the dietary iron intake of Koreans estimated by 2 different methods (iron content sources) using the food intake data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) are comparable. One method was based on the KNHANES's Food & Nutrient Database (FND) derived mainly from the Korean Food Composition Table and the other used the iron content (IC) of food samples processed in the Korean Total Diet Study (KTDS).
Methods
Dietary intake data from the 2013-2016 KNHANES was used to select representative foods (RFs) in KTDS for iron analysis. Selection of the RFs and cooking methods for each RF (RF × cooking method pair) was performed according to the ‘Guidebook for Korean Total Diet Studies’ and resulted in a total of 132 RFs and 224 ‘RF × cooking method’ pairs. RFs were collected in 9 metropolitan cities nationwide once or twice (for those with seasonality) in 2018 and made into 6 composites each, based on the origin and season prior to cooking. Then, the RF composites prepared to a ‘table ready’ state for KTDS were analyzed by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Dietary iron intake of the Korean population was estimated using only RFs’ intake data based on the 2 sources of iron content, namely FND-KNHANES and IC-KTDS.
Results
RFs in KTDS covered 92.0% of total food intake of Koreans in the 2016-2018 KNHANES. Mean iron intake of Koreans was 7.77 mg/person/day by IC-KTDS vs 9.73 mg/person/day by FND-KNHANES. The major food groups contributing to iron intake were meats (21.7%), vegetables (20.5%), and grains & cereals (13.4%) as per IC-KTDS. On the other hand, the latter source (FND-KNHANES) resulted in a very different profile: grains & cereals (31.1%), vegetables (16.8%), and meats (15.3%). While the top iron source was beef, accounting for 8.6% in the former, it was polished rice (19.2%) in the latter. There was a 10-fold difference in the iron content of polished rice between 2 sources that iron intakes excluding the contribution by polished rice resulted in very similar values: 7.58 mg/person/day by IC-KTDS and 7.86 mg/person/day by FNDKNHANES.
Conclusions
This study revealed that the dietary iron intake estimated by 2 different methods were quite comparable, excluding one RF, namely polished rice. KTDS was thus proven to be a useful tool in estimating a ‘closer-to-real’ dietary intake of nutrients for Koreans and further research on various nutrients is warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrients and food intake according to atherogenic index of plasma in Korean postmenopausal women
Ye-Jin Lee, Sun Yung Ly
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 87. CrossRef - Iron Consumption and Colorectal Cancer in Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
Sukhong Min, Katherine De la Torre, Hyobin Lee, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Daehee Kang
Nutrients.2025; 17(8): 1309. CrossRef - Dietary sodium and potassium intake of Koreans estimated using 2 different sources of their contents in foods, Food & Nutrient Database and the Korean Total Diet Study: a comparative study
Jee Yeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Soo Hyun Lee, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 235. CrossRef
- Nutrients and food intake according to atherogenic index of plasma in Korean postmenopausal women
- 1,746 View
- 22 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
- YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):192-204. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between dietary behaviors and perceived health status among Korean adolescents from multicultural families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 2,459 Korean adolescents from multicultural families (aged 13 ~ 18 years) who participated in the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Information on the sociodemographic variables, dietary behaviors, and lifestyle variables was selfreported using a web-based questionnaire. The dietary behaviors analyzed in this study were the breakfast and food intake frequencies, including fruit, vegetable, milk, fast food, carbonated drink, sweet drink, and high caffeine/energy drinks. The adolescents’ health perception was self-rated as healthy, average, or unhealthy. The dietary behaviors associated with health perception were examined using a multiple logistic regression after adjusting for the confounding variables.
Results
In this study population, 7.6% of adolescents perceived their health status as unhealthy, and 25.4% perceived it as average. The adolescents who were girls, middle school students, and in households with a low economic status showed significantly higher percentages of poor health perception (P-values < 0.001). Skipping breakfast was significantly associated with a negative health perception. Compared to the adolescents who consumed fruits every day, those who did not consume fruits during the previous week showed a higher odd ratio (OR) for a negative health perception [OR = 2.29, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.32–3.97]. The adolescents who frequently consumed carbonated drinks ( 5 times/week) perceived their health status as unhealthy relative to those who did not consume carbonated drinks (OR = 2.15, 95% CI = 1.25–3.71). Skipping breakfast was significantly associated with an increased OR for a negative health perception in girls but not in boys. Compared to adolescents with a normal weight, those with overweight/ obesity (OR = 1.75, 95% CI = 1.21–2.52) and underweight (OR = 2.19, 95% CI = 1.25–3.82) showed higher ORs for negative health perception. Positive associations of overweight/obesity and underweight with negative health perception were observed in boys but not in girls.
Conclusions
Dietary behaviors and weight status were associated with the health perception in Korean adolescents from multicultural families. These findings suggest that nutrition interventions on breakfast intake and healthy food choices for this population might effectively improve their weight and perceived health status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The unequal weight of COVID-19 pandemic: national trends in body mass index among Korean adolescents by immigrant-origin and gender from 2013 to 2022
Nari Yoo, Yumin Hong, Yoonyoung Choi
International Journal of Adolescence and Youth.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The unequal weight of COVID-19 pandemic: national trends in body mass index among Korean adolescents by immigrant-origin and gender from 2013 to 2022
- 1,204 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Trends in Dietary Protein Intake and Its Adequacy among Korean Adults: Data from the 2010 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
- Hyunji Ham, Kyungho Ha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(1):47-60. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.1.47
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate dietary protein intake and its adequacy among Korean adults during recent 10 years.
Methods
Based on the 2010 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) data, a total of 51,296 adults aged 19 years old or more who participated in a one-day 24-hr dietary recall were included. Dietary protein intake was estimated as percentages of total energy (% of energy) and grams per body weight (g/kg/ day) and compared with the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans to evaluate the adequacy of protein intake. In addition, proportions of people whose protein intakes were less than the estimated average requirement (EAR) and above the upper limit of the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) (> 20% of energy) were calculated according to sociodemographic characteristics.
Results
Protein intake was increased from 14.7% of energy in 2010 to 15.6% of energy in 2019 among Korean adults. However, there was no increase in protein intake relative to the recommended nutrient intake (% RNI) during the recent 10 years. Protein intake relative to the RNI was decreased from 130.2% in 2010 to 121.1% in 2019 (P for trend < 0.0001) among total participants, and a significant decreasing trend was observed in all age groups except for over 65 years old. However, protein intake relative to the RNI was lowest in the elderly (98.6%). Proportions of low protein intake (< EAR) and high protein intake (> AMDR) increased in the past 10 years (P for trend < 0.0001 for all), and these were associated with socioeconomic statuses, such as education and household income levels.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that protein adequacy in Korean adults has not been improved over the past decade compared with recommended levels. Nutritional education and intervention programs should consider different intake levels according to sociodemographic characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combined associations of protein intake and resistance exercise with handgrip strength in postmenopausal women
Jin Kyung Baek, Hae Rim Kim, Eun Jin Lee, Yun Soo Chung, Seok Kyo Seo
Maturitas.2026; 205: 108808. CrossRef - Status of Use of Protein Supplement Products according to the Health Concerns of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
Cho-In Oh, Bok-Mi Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 9. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment of Older Korean Adults by Level of Plant Protein Intake
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Jeong-Hun Song, Yangsuk Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1976. CrossRef - Trends in dietary amino acid intake and food sources among Korean adults: data from the 2010-2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sumin Kim, Hyunji Ham, Kyungho Ha
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 773. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef - High-Protein Products in 2013 and 2023: Shifts in Diverse Aspects Over the Last Ten Years
Hye Ran Lee, Ihyeon Cho, Hyejin Yi, Hee Jung Park
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 173. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
Hyoju Lee, Youjeong Jang, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 261. CrossRef - Association between Processed Meat Protein Consumption and Incident Osteoporosis in Adults Aged 50 Years and Older: A Prospective Cohort Study Based on Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study Data (2005–2020)
Dohee Lee, Soo Hyoung Lee, Ki Hyun Park, Kunhee Han, Eunjin Jeong
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2024; 45(5): 268. CrossRef - The Relationship of Pork Meat Consumption with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Biomarkers of Health Status in Korean Older Adults
Ah-Jin Jung, Anshul Sharma, Mei Chung, Taylor Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4188. CrossRef - Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - Relationship between protein intake and grip strength in qualitative and quantitative aspects among the elderly in Korea: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi‑Hyun Kim, Mi‑Kyeong Choi, Yun‑Jung Bae
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current status of nutrient intake in Korea: focused on macronutrients
Seung-Won Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(12): 801. CrossRef
- Combined associations of protein intake and resistance exercise with handgrip strength in postmenopausal women
- 7,357 View
- 198 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Regional Differences in Dietary Total Fat and Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Their Associations with Metabolic Diseases among Korean Adults: Using the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):495-507. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.495
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined regional differences in the intake of dietary total fat and saturated fatty acid (SFA) and their food sources among Korean adults. We also investigated the associations of SFA intake with metabolic diseases by region.
Methods
This study included 13,926 adults ( 19y) who participated in the 2016 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. The regions were divided into urban and rural areas according to the administrative districts where the participants lived. Using dietary data obtained from a 24-h recall, intake of total fat and SFA and their food sources were assessed by region. Metabolic diseases included obesity, abdominal obesity, and elevated total cholesterol and their association with SFA intake by region were examined using multiple logistic regression.
Results
Of the participants, 19.6% lived in rural areas. In urban areas, the total fat and SFA intakes were higher than in rural areas: 21.2% of energy (%E) came from total fat and 6.9%E from SFA in urban areas, whereas 18.0%E came from total fat and 5.8%E from SFA in rural areas. The percentage of participants who exceeded the dietary reference intakes for total fat and SFA in urban areas was 16.5% and 41.9%, respectively, but 43.4% of participants in rural areas showed lower intake levels for total fat compared to the reference level. Young adults did not show regional differences in fat intake, and the percentage of subjects who exceeded the reference for SFA was high both in urban (58.5%) and rural (55.7%) areas. Among middle-aged and older adults, intake of fatty acids except for n-3 fatty acid was significantly higher in urban areas than in rural areas. About 69% of older adults in rural areas showed a lower intake of total fat compared to the reference level. The food sources for total fat and SFA were meat, soybean oil, eggs, and milk in both areas. The intake of fat from eggs, milk, mayonnaise, and bread was higher in urban areas, but the intake of fat from white rice and coffee mix was higher in rural areas. The SFA intake was positively associated with elevated serum total cholesterol in urban areas (4th quartile vs. 1st quartile, OR: 1.22, 95% CI: 1.06-1.40, P for trend: 0.043), but not in rural areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 173. CrossRef - Association between the Korean Healthy Diet Score and Metabolic Syndrome: Effectiveness and Optimal Cutoff of the Korean Healthy Diet Score
Soo-Hyun Kim, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(19): 3395. CrossRef - Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Estimating and evaluating usual total fat and fatty acid intake in the Korean population using data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
Gyeong-yoon Lee, Dong Woo Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(5): 414. CrossRef - Associations of Dietary Intakes of Total and Specific Types of Fat with Blood Lipid Levels in the Filipino Women’s Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL)
Heejin Lee, Hyojin Kim, Sherlyn Mae P. Provido, Minji Kang, Grace H. Chung, Jae W. Lee, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Jung Eun Lee
Global Heart.2023; 18(1): 29. CrossRef - Regional Differences in Metabolic Risk in the Elderly in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, Yun-Jung Bae
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11675. CrossRef
- Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
- 1,662 View
- 20 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between Eating Alone Patterns and Mental Health Conditions by Region among Korean Adults
- Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):441-454. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the association between the frequency and pattern of eating alone and the mental health status according to region in Korean adults.
Methods
The data of 10,040 Korean adults aged ≥ 19 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2017 and 2019 were used. Participants were divided into 4 groups based on their frequency of eating alone: none (all meals together), 1, 2, and 3 meals/day alone. The regions were divided into urban and rural areas. Mental health status was assessed by stress recognition, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation. Multivariable logistic regressions were conducted to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) on the association of the frequency and pattern of eating alone with poor mental health after controlling for covariates.
Results
Among Korean adults, 74.1% ate more than one meal a day alone. Individuals having 3 meals a day alone tended to be less educated, single, single person households, or living in urban areas (all P < 0.05). In rural areas, those having 3 meals/ day alone had higher odds of stress recognition (AOR: 1.55, 95% CI: 1.02-2.35) than those having all meals together. In urban areas, individuals eating alone 3 times/day had higher odds of stress recognition (AOR: 1.60, 95% CI: 1.31-1.96), depressive symptoms (AOR: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.23-2.12), and suicidal ideation (AOR: 2.14, 95% CI: 1.42-3.22) compared to those having all meals together. Urban residents having dinner alone had higher odds of depressive symptoms (AOR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.05-1.58) and suicidal ideation (AOR: 1.66, 95% CI: 1.19-2.33) than those having dinner with others.
Conclusions
Our findings showed that the frequency and patterns of eating alone were differentially associated with increased odds of poor mental health according to region of residence. Nutrition education is needed for those frequently eating alone, particularly those living in urban areas, to highlight the advantages of eating together and to ensure that they have balanced and healthy meals even if they eat alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Social Activity Restrictions on Depression in Young Single-Person Households: The Moderating Effect of Eating Alone
Jiwon Kim, Youngye Park
Journal of Social Science.2025; 36(3): 27. CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - How Does the Frequency of Eating-Alone among Older People in Korea Affect Their Health and Dietary Behavior?
Yongseok Kwon, Kyung Hee Hong, Yoo-Kyung Park, Sohye Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2085. CrossRef - Impact assessment of a primary care physician counseling program for youth population
Yun-Su Kim, Shin-Ae Kim
Medicine.2022; 101(46): e31916. CrossRef
- The Impact of Social Activity Restrictions on Depression in Young Single-Person Households: The Moderating Effect of Eating Alone
- 2,219 View
- 39 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
- Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):363-381. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the Korean elderly’s dietary intake status, subjective health-related perception and chronic disease prevalence among age groups. Associations of dietary quality with subjective health-related perception and chronic diseases were also examined.
Methods
Based on data from the 7th National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a total of 3,231 elderly were selected and categorized into 4 age groups of ‘65 ~ 69’, ‘70 ~ 74’, ‘75 ~ 79’ and ‘over 80’. Nutrient intakes, proportions of those with insufficient nutrient intakes, Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI), some subjective health-related perceptions and prevalence of major chronic diseases were compared according to the age groups. Differences in the subjective health-related perceptions and odds ratios of the chronic diseases according to the quartile levels of KHEI within the same age group were analyzed.
Results
With the increase of age, several nutrient intakes (P < 0.001) and KHEI scores significantly decreased (P < 0.01). In women, activity restriction increased (P < 0.05), and EQ-5D score decreased with age (P < 0.001). Prevalence of hypertension (P < 0.0001), hypercholesterolemia (P < 0.05) and anemia (P < 0.01) significantly increased, while hypertriglyceridemia (P < 0.01) significantly decreased only in men. Obesity prevalence decreased, while underweight prevalence increased (P < 0.05). Subjective health status, EQ-5D score and PHQ-9 score significantly improved as KHEI score increased in certain age groups of women (P< 0.05). Odds ratio of hypercholesterolemia significantly increased with the increase of KHEI score in 65 ~ 69-year-old women. However, hypertension and anemia significantly decreased with the increase of KHEI score in 75 ~ 79-year-old women (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
The study findings suggest that nutrition management and policy for the Korean elderly need to apply a segmented age standard that can better reflect their dynamic characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 359. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef - Blood Biochemical Characteristics, Dietary Intake, and Risk Factors Related to Poor HbA1c Control in Elderly Korean Diabetes Patients: Comparison between the 4th(2007-2009) and the 7th(2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 406. CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 422. CrossRef
- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
- 1,548 View
- 21 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of a Zinc Database to Estimate the Zinc Intake Levels in the Korean Toddlers and Preschool Children
- Su-In Yoon, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):103-110. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to develop a zinc database (DB) to estimate the intake levels of zinc in Korean toddlers and preschool children using the data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Methods: A total of 3,361 food items for the DB representing the usual diet of Korean toddlers and preschool children were selected based on KNHANES (2009~2013) and the food composition table of Rural Development Administration (RDA). The existing values of zinc in foods were collected from the latest food composition tables of RDA (9th revision) and the US Department of Agriculture (legacy release). The zinc contents were filled preferentially with these collected values. The missing values were replaced with the calculated values or imputed values using the existing values of similar food items from the data source. The zinc intake levels of Korean toddlers and preschool children were estimated using KNHANES and zinc DB Results: A total of 1,188 existing values, 412 calculated values, and 1,727 imputed values were included in the zinc DB. The mean intake levels of zinc for 1-2-year-old children and 3-5-year-olds were 5.17 ± 2.94 mg/day and 6.30 ± 2.84 mg/day, respectively.There was no significant difference in the zinc intake levels between boys and girls in each group. Conclusions: This newly developed zinc DB would be helpful to assess the zinc nutritional status and investigate the association between the zinc intakes and related health concerns in Korean toddlers and preschool children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food sources of zinc and nutritional status with usual dietary zinc intake in Korean toddlers and preschool children
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1211. CrossRef
- Food sources of zinc and nutritional status with usual dietary zinc intake in Korean toddlers and preschool children
- 1,464 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Vegetable and Nut Food Groups are Inversely Associated with Hearing Loss- a Cross-sectional Study from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Sunghee Lee, Jae Yeon Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):512-519. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.512
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A cross-sectional study was conducted to investigate the associations between food groups and hearing loss. Methods: Data of 1,312 individuals were used from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013. Hearing loss was determined with a pure tone average (PTA) of greater than 25 dB in either ear. The PTA was measured as the average hearing threshold at speech frequencies of 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 kHz. The dietary intake was examined with a food frequency questionnaire with 112 food items. The food items were classified into 25 food groups. A weighted logistic regression was used to investigate the association. Results: Individuals in the highest tertile of vegetables and nuts food groups were less likely to have hearing loss than those in the lowest tertile [Odds Ratio (OR) = 0.58 (95% Confidence interval (CI) 0.38-0.91), P = 0.019; OR = 0.59 (95% CI 0.39-0.90), P = 0.020, respectively], after adjusting for confounding variables of age, sex, body mass index, drinking, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and physical activity. Conclusions: In this cross-sectional study, we observed that high intake of vegetables and nuts food groups revealed significant inverse associations with hearing loss, after adjusting for confounding variables among 1,312 participants.
- 957 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutritional Status of Vitamins and Minerals According to Consumption of Dietary Supplements in Korean Adults and the Elderly: Report Based on 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):329-339. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study was undertaken to evaluate the intake of vitamins and minerals from dietary supplements (DSs) in Korean adults and elderly.
Methods
Data for this study was generated from the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). We analyzed 4,204 individuals aged 19 years and older (2,579 users and 1,625 non-users). The survey included 24-h recall questions on food and DS intakes, as well as questions on DS use over the past year. The nutrient DSs evaluated were calcium, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and vitamin C. Total nutrient intakes were obtained by combining nutrient intakes of foods and DSs consumed by each subject.
Results
Most micronutrient intakes from food (except for thiamin) in adult users, and the four micronutrient intakes (iron, vitamin A, vitamin B2 and vitamin C) in elderly users, were significantly higher than values obtained in non-users. For total intake of nutrients and DSs, both adult and elderly users had a significantly higher intake than non-users. While proportions below Estimated Average Requirements for all micronutrients by adding respective DSs in users were significantly reduced in adults and elderly as compared to non-users, the proportions of above Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for calcium and vitamin A in adults, and vitamin A in elderly, were significantly increased. In the total subjects examined, consumption of DSs was associated with lower odds ratios of undernutrition of micronutrients, and with higher odds ratios of overnutrition of calcium, iron, and vitamin A, as compared to non-users of DSs.
Conclusions
Although DSs consumption by adults and the elderly improves the micronutrient status, it also increases the risk of excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 103. CrossRef - Folate intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey with newly established folate database
Eun-Ji Park, Inhwa Han, Kyoung Hye Yu, Sun Yung Ly
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(4): 418. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimated dietary vitamin D intake and major vitamin D food sources of Koreans: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 451. CrossRef - A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- 2,048 View
- 10 Download
- 5 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Relation between the Total Diet Quality based on Korean Healthy Eating Index and the Incidence of Metabolic Syndrome Constituents and Metabolic Syndrome among a Prospective Cohort of Korean Adults
- Saerom Shin, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):61-70. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the association of the total diet quality with the incidence risk of metabolic syndrome constituents and metabolic syndrome among Korean adults.
METHODS
Based on a community-based cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) from 2001 to 2014, data from a total of 5,549 subjects (2,805 men & 2,744 women) aged 40~69 years at the baseline with a total follow-up period of 38,166 person-years were analyzed. The criteria of the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel was employed to define metabolic syndrome. The total diet quality was estimated using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI). Hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for risk of metabolic syndrome constituents and metabolic syndrome in relation to KHEI quintile groups was calculated by multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model.
RESULTS
After adjusting for age, energy intake, income, education, physical activity, smoking, and drinking, the incidence of abdominal obesity and high blood pressure was significantly lower, by approximately 29.7% (P < 0.01) and 25.2% (P < 0.01), respectively, in the fifth KHEI quintile compared to the first quintile in men. A significant decreasing trend of the metabolic syndrome incidence was observed across the improving levels of KHEI (HRq5vs.q1: 0.775, 95% CIq5vs.q1: 0.619~0.971, P for trend < 0.01). In women, the incidence of abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome was significantly lower, by approximately 29.8% (P < 0.01) and 22.5% (P < 0.05), respectively, in the fifth KHEI quintile compared to the first quintile adjusting for multiple covariates. On the other hand, the linear trend of metabolic syndrome risk across the KHEI levels did not reach the significance level.
CONCLUSIONS
A better diet quality can prevent future metabolic syndrome and its certain risk factors among Korean men and women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The mediating effect of the Korean Healthy Eating Index on the relationship between lifestyle patterns and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Koreans: data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sori On, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 96. CrossRef - FTO rs9939609 polymorphism is associated with dietary quality in Korean females
Minjeong Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi
European Journal of Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender-specific association of diet with the risk of loss of muscle mass in Korean baby boomers: a prospective population-based cohort analysis
Eun-Hee Jang, Seungmin Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 635. CrossRef - Maternal Diet Quality Assessed Using the Korean Healthy Eating Index and Risk of Small-for-Gestational-Age Infants: Findings from the Mothers and Children’s Environmental Health (MOCEH) Study
Won Jang, Minji Kim, Eunhee Ha, Hyesook Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(19): 3056. CrossRef - Sex differences in the association between Korean Healthy Eating Index and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korean adults: a prospective cohort study
Yeeun Park, Minji Kim, Kyong Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 331. CrossRef - Association between Korean Healthy Eating Index and abdominal obesity in Korean adults: the mediating effect of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein
Jina Yoon, Dayeon Shin
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 88. CrossRef - Association between Dietary Quality and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korean Adults: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study Using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (2013–2021)
Seong-Uk Baek, Taeyeon Kim, Yu-Min Lee, Jong-Uk Won, Jin-Ha Yoon
Nutrients.2024; 16(10): 1516. CrossRef - TAS2R38 bitterness receptor genetic variation is associated with diet quality in Koreans
Hae Young Kim, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Appetite.2024; 200: 107561. CrossRef - Contents of Pantothenic Acid in Frequently Consumed Korean Vegetables and Fruits
Jihwan Kim, Jina Lee, Yoonjeong Kim, Eunji Park, Jinju Park, Youngmin Choi, Younghwa Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 816. CrossRef - Association of Social Jetlag with the Dietary Quality Among Korean Workers: Findings from a Nationwide Survey
Seong-Uk Baek, Jin-Ha Yoon
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4091. CrossRef - Association between green tea consumption and metabolic syndrome among Korean adults: results from the Health Examinees study
Hyeonjin Cho, Sunwoo Han, Jiwon Jeong, Hyein Jung, Sangah Shin
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(1): 70. CrossRef - Obesity-Status-Linked Affecting Factors of Dyslipidemia in Korean Young-Adult Men: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Min Kwon, Jinheum Kim, Eunjeong Cha
Healthcare.2023; 11(14): 2015. CrossRef - The association of the Korean Healthy Eating Index with chronic conditions in middle-aged single-person households
EunJung Lee, Ji-Myung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 316. CrossRef - Association between the Korean Healthy Eating Index and Serum Vitamin D Level in Korean Adults: 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
So-Yoon Choi, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(4): 218. CrossRef - Benefits of adherence to the Korea Healthy Eating Index on the risk factors and incidence of the metabolic syndrome: analysis of the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun A Choi, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 120. CrossRef - Prediction of metabolic and pre-metabolic syndromes using machine learning models with anthropometric, lifestyle, and biochemical factors from a middle-aged population in Korea
Junho Kim, Sujeong Mun, Siwoo Lee, Kyoungsik Jeong, Younghwa Baek
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrition Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Carrots and Parsnips
Yeon-Jin Park, So-Yeon Han, Jae-Joon Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(1): 83. CrossRef - Analysis of Fruit Consumption and the Korean Healthy Eating Index of Adults Using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun A Choi, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(10): 1124. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef - Association between frailty and dietary quality in community-dwelling elderly: data from the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2014–2015)
Woori Na, Hyeji Kim, Cheongmin Sohn
Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition.2021; 68(3): 268. CrossRef - Changes in Prevalence of Body Mass Index and Metabolic Syndrome during COVID-19 Lockdown Period
Ji Young Kwon, Sang-Wook Song, Ha-Na Kim, Sung Gu Kang
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2021; 11(4): 304. CrossRef
- The mediating effect of the Korean Healthy Eating Index on the relationship between lifestyle patterns and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Koreans: data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,799 View
- 52 Download
- 21 Crossref

- [English]
- Effect of Geographic Area on Dietary Quality across Different Age Groups in Korea
- Hyun Ja Kim, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):453-464. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.453
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to examine whether dietary quality varies among different age groups and geographic areas, and whether the difference between geographic areas varies across several age groups in Korea.
METHODS
The subjects were 14,170 subjects who participated in the 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The dietary quality was assessed using the Korean Health Eating Index (KHEI). Age groups were categorized into six groupings, and areas were categorized into urban and rural according to their administrative districts. The effect of area on the KHEI score was analyzed by multiple linear regression analysis.
RESULTS
The KHEI was the lowest in the 20-30s group (57.7 ± 0.4 score for 20s and 61.2 ± 0.3 score for 30s) and increased with age (p<0.001), showing the highest score in the 60s (67.9 ± 0.3 score), and then decreased again in the 70s and older (64.6 ± 0.3 score). As a result of comparing the KHEI score by area, the urban areas had higher KHEI scores than did the rural areas (63.5 ± 0.2 score for urban area and 62.2 ± 0.4 score for rural area, p=0.002). The difference between areas was dependent on the age group, showing a significant difference for subjects who were aged from 50s and older (p=0.002 for 50s, p<0.001 for 60s and p<0.001 for 70s and older). After adjusting for confounding factors, the effect of area on the KHEI score was only shown for those subjects in the over 60 years old group (p=0.035 for 60s and p<0.001 for 70s and older).
CONCLUSIONS
The dietary quality differed according to the age group and geographic area. The dietary quality was lower for younger people than that for older people, and in rural areas compared to that in urban areas, and especially for older adults. The area factor was a very important factor for the dietary quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary habits of Koreans aged 95 years and older residing in rural and metropolitan areas
Jieun Mun, Sein Kim, Suyoung Kim, Seunghee Kim, Sang Chul Park, Jae-Young Han, Kwangsung Park, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 66. CrossRef - Prediction model for identifying a high-risk group for food insecurity among elderly South Koreans
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual- and neighborhood-level factors influencing diet quality: a multilevel analysis using Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data, 2010-2019
Dahyun Park, Min-Jeong Shin, S V Subramanian, Clara Yongjoo Park, Rockli Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2025; 47: e2025043. CrossRef - Risk of all-cause mortality is associated with multiple health-related lifestyle behaviors and does not differ between urban and rural areas in Korea
Seunghee Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(4): 554. CrossRef - Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 173. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Perceived Community Food Accessibility Measurement Questionnaire for Korean Older Adults
Jisoo Hong, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(19): 4301. CrossRef - Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Regional Difference in the Effect of Food Accessibility and Affordability on Vegetable and Fruit Acquisition and Healthy Eating Behaviors for Older Adults
Dong Eun Lee, Kirang Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 14973. CrossRef - Regional Differences in Dietary Total Fat and Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Their Associations with Metabolic Diseases among Korean Adults: Using the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 495. CrossRef - Basic Concepts and Detailed Dimensions of Food Security and Related Indicators for Policy Development and Evaluation
Sohyun Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 429. CrossRef
- Dietary habits of Koreans aged 95 years and older residing in rural and metropolitan areas
- 1,305 View
- 7 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of the Nutrition Status and Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence of the Members according to the Number of Household Members based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2014)
- Jin Young Lee, Soo Kyong Choi, Jung Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):232-244. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated the nutritional status and prevalence of metabolic syndrome of the people who participated in the KNHANES according to the number of household members. They were assessed by using information from the 2013~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
A total of 6,088 persons aged 19 years and over participated in 2013~2014 KNHANES, and they were classified into three groups according to the number of household members (single-person, two-person, three-person & over). The dietary behavior, nutritional status, health-related factors and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome of the subjects were investigated with using information from the survey questionnaires of KNHANES. The nutrient intake data of the subjects were obtained by the 24-hour recall method and this was analyzed for evaluating the nutrition adequacy ratio and the index of nutritional quality. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome among the subjects, and according to the study groups, was estimated using the blood and physical measurement data of the subjects.
RESULTS
As for EQ-5D index available for all the health states generated by the EQ-5D descriptive system, the single-person household member was the lowest among all the household types. The index of nutrition quality for protein, crude fiber, calcium, phosphorus, potassium, riboflavin and vitamin C in the single-person household was lower than that of the two-person or the three-person and over households (p<0.001). The mean adequacy ratio of single-person households was significantly decreased compared with that of the other types of households (p<0.001). The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was higher in the single-person households than that in the multiple-person households (p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
These results showed that dietary behaviors, nutrition status and health status might be influenced by the number of household members. The results from this study would be useful for improving Korean people's dietary life and health status by implementing evidence-based, specialized intervention for the members of diverse types of households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Beyond individual integration: Family systems, social support networks and living environment as health determinants among migrants in Germany
Franziska Reinhardt, Imad Maatouk
Journal of Migration and Health.2025; 12: 100368. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - The association of the Korean Healthy Eating Index with chronic conditions in middle-aged single-person households
EunJung Lee, Ji-Myung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 316. CrossRef - Analysis of Agrifood Consumer Competency and Dietary Satisfaction according to Household Type Using the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Meera Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 414. CrossRef - An analysis of customer needs for the operation of unmanned food stores on a university campus
Se-Eun Kim, Min-Seo Park, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(5): 587. CrossRef - Assessment of Nutrient Intake and Dietary Quality of Korean Adults in Metabolic Syndrome Patients According to Taking Medical Care: Based on the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Juhee Lee, Kyungsuk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(4): 321. CrossRef - Relationships of Dietary Factors with Obesity, Hypertension, and Diabetes by Regional Type among Single-Person Households in Korea
Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1218. CrossRef - Living Environment Considerations on Obesity Prevention Behaviors and Self-Efficacy among Chinese Americans
Doreen Liou, Jessica A. Karasik
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(17): 9322. CrossRef - The Relationship between Meal Regularity and Oral Health and Metabolic Syndrome of Adults in Single Korean Households
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, On-Ju Ju
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 185. CrossRef - Association of Household Income Level with Vitamin and Mineral Intake
Haegyu Oh, Juyeon Kim, Yune Huh, Seung Hoon Kim, Sung-In Jang
Nutrients.2021; 14(1): 38. CrossRef - Nutritional status and metabolic syndrome risk according to the dietary pattern of adult single-person household, based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu Been Keum, Qi Ming Yu, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 23. CrossRef - Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Eun-Sun Park, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 476. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 408. CrossRef
- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 2,183 View
- 8 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Total Fat and Fatty Acids Intakes in the Korean Adult Population using Data from the 2016–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):223-231. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.223
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated dietary intakes of total fat and fatty acids among the Korean adult population.
METHODS
This cross-sectional study used the 2016–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data. A total of 10,772 subjects aged ≥19 y for which dietary data were available were selected. Data pertaining to energy and nutrient intakes were obtained by a 24-h recall method. Total fat and fatty acids intakes were evaluated based on the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDR) of 2015 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans by sex and age groups. All statistical analyses accounted for the complex sampling design effect and sampling weights.
RESULTS
The mean intakes of energy and total fat were 1,952 kcal (95% CI: 1928–1977) and 46.1 g (45.2–47.1), respectively, and about 21% of the energy was obtained from fat in this study population (21.7% in men and 20.2% in women). The mean percentages of energy from saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids were 6.4%, 6.7%, and 5.2%, respectively. About 18% of adults exceeded the AMDR for fat (30% of energy), whereas 37.6% exceeded the AMDR for saturated fatty acids (7% of energy). The proportions of subjects who consumed more than the AMDR for fat and saturated fatty acids decreased across age groups in both sexes. Among young adults (19–29 y), about 63% of the subjects obtained ≥7% of their energy from saturated fatty acids. About 61% of older adults obtained less than 15% of their energy from total fat.
CONCLUSIONS
Increased intake of fat energy was prominent in saturated fatty acids. Our findings suggest current information on total fat and fatty acids intakes in Korean adults and can be used to provide dietary guidelines for the improvement of public health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary patterns derived by reduced rank regression are associated with lipid disorders among Korean adults: a cross-sectional analysis
Hyun Ah Kim, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2016–2021 KNHANES data
Enkhgerel Erdenetsetseg, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 144. CrossRef - Nutrition and food intake status among adults in Jeju according to sociodemographic characteristics and obesity
Hyunji Ham, Hanbin Ko, Sumin Kim, Youjeong Jang, Jong-Seok Byun, Yoonsuk Jekal, Insuk Chai, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(6): 667. CrossRef - Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Content of Snacks for Smart Snack Choices
Chae Young Yoon, Eunju Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(4): 264. CrossRef - Trends in dietary intake and food sources of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids among Korean adults between 2007 and 2018
Jae Eun Shim, Youngmi Lee, SuJin Song
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023069. CrossRef - Diabetes and Dietary Fats
Jae Won Cho
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 154. CrossRef - Association of Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Its Food Sources With Hypercholesterolemia in Middle-Aged Korean Men and Women
In Young Jeong, Jae Eun Shim, SuJin Song
CardioMetabolic Syndrome Journal.2022; 2(2): 142. CrossRef - Increasing trends in dietary total fat and fatty acid intake among Korean children: using the 2007–2017 national data
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(2): 260. CrossRef - Substitution of Carbohydrates for Fats and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes among Korean Middle-Aged Adults: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Hye-Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(3): 654. CrossRef - Food behaviors accounting for the recent trends in dietary fatty acid profiles among Korean adults
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(3): 405. CrossRef - Current status of nutrient intake in Korea: focused on macronutrients
Seung-Won Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(12): 801. CrossRef - Regional Differences in Dietary Total Fat and Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Their Associations with Metabolic Diseases among Korean Adults: Using the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 495. CrossRef - The number of teeth is associated with diet quality in Korean adult population
Hye-Sun Shin
Archives of Oral Biology.2020; 118: 104882. CrossRef - Trends in Dietary Intake of Total Fat and Fatty Acids Among Korean Adolescents from 2007 to 2017
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrients.2019; 11(12): 3073. CrossRef
- Dietary patterns derived by reduced rank regression are associated with lipid disorders among Korean adults: a cross-sectional analysis
- 1,708 View
- 6 Download
- 15 Crossref

- [English]
- Analysis of the Difference in Nutrients Intake, Dietary Behaviors and Food Intake Frequency of Single- and Non Single-Person Households: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2014–2016
- Na Yeon Kang, Bok Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):1-17. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to compare the dietary life of single- and non single-person households in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
A nationally representative sample of 20,421 19-64-year-olds who had 24-hour recall data was taken from the 2014-2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Single- and non single-persons were compared for nutrient intake, dietary behaviors, food consumption patterns, nutrition education and confirm nutrition label.
RESULTS
The dietary intakes of dietary fiber and iron were lower in single-person households than in non single-person households. The lower the level of education and income, the lower the nutrient intake of single-person households. In the case of those aged 19 to 29, the breakfast skipping rate was higher in single-person households than in non single-person households. The higher the education level, the higher the breakfast skipping rate and the eating out frequency in the single-person households. In the food intake survey, the frequency of healthy food intake in single-person households was much lower than that of non single-person households. The confirmation rate of nutrition labeling was lower in single-person households than in non single-person households.
CONCLUSIONS
This study shows that single-person households have poorer health-nutritional behaviors than multi-person households. Therefore, a nutrition education program based on the data of this study needs to be developed for health promotion of single-person households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Cooking Fuel Choices on Household Food Security and Healthy Food Consumption in Indonesia
Moh Shadiqur Rahman, Sujarwoto Sujarwoto, Hery Toiba, Tri Wahyu Nugroho, Fahriyah Fahriyah, Mohammad Ilyas Shaleh, Tina Sri Purwanti, Bagus Andrianto
Review of Development Economics.2025; 29(4): 2242. CrossRef - A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 140. CrossRef - Generalized Anxiety Disorder Due to Household Type and Economic Status during COVID-19 Pandemic: Focusing on Gender Differences
Ye Eun Cha, Ju Yeong Hwang, Jin Young Nam
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(1): 89. CrossRef - Association of delivered food consumption with dietary behaviors and obesity among young adults in Jeju
Minjung Ko, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 336. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Diabetes Nutritional Management for Single-Person Households
Min Young Noh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(4): 236. CrossRef - Analysis of intake trends of kimchi, fruits and vegetables (1998–2020) and factors associated with the intake (2016–2020): based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jiwon Jeong, Jungmin Park, Yu Kyung Lee, Sung Wook Hong, Sangah Shin
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 404. CrossRef - The relationship between the prevalence of anemia and dietary intake among adults according to household types based on data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Won Kim, Ji-Myung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 510. CrossRef - Analysis of Agrifood Consumer Competency and Dietary Satisfaction according to Household Type Using the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Meera Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 414. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Associations of cooking practices and healthy eating habits among young Korean adults in their 20s
So-Young Kim, Ji Yu Choi
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2023; 31: 100644. CrossRef - Perception to the dietary guidelines for Koreans among Korean adults based on sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle
Yejin Yoon, Soo Hyun Kim, Hyojee Joung, Seoeun Ahn
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 742. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behaviors between Adults with Hypertension in Single- and Multi-Person Households: Based on the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yongjae Yu, Youn Huh, Sung Sunwoo
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
Ji Suk Yim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Association between eating alone and cardiovascular diseases in elderly women: a cross-sectional study of KNHANES 2016 data
Han-Gyo Choi, Hye-Jin Kim, Seok-Jung Kang
Menopause.2022; 29(1): 82. CrossRef - An analysis of customer needs for the operation of unmanned food stores on a university campus
Se-Eun Kim, Min-Seo Park, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(5): 587. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behaviors and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Single- and Multi-Person Households among Korean Adults
Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Healthcare.2021; 9(9): 1116. CrossRef - Nutritional status and metabolic syndrome risk according to the dietary pattern of adult single-person household, based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu Been Keum, Qi Ming Yu, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 23. CrossRef - Relationship between Eating Behavior and Healthy Eating Competency of Single-Person and Multi-Person Households by Age Group
Seung-Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 337. CrossRef - Current Trends in Nursing Research Across Five Locations: The United States, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, and Hong Kong
Eun‐Ok Im, Reiko Sakashita, Chia‐Chin Lin, Tae‐Hwa Lee, Hsiu‐Min Tsai, Jillian Inouye
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2020; 52(6): 671. CrossRef - Short-term Cudrania tricuspidata fruit vinegar administration attenuates obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice by improving fat accumulation and metabolic parameters
Jun-Hui Choi, Myung-Kon Kim, Soo-Hwan Yeo, Seung Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Healthy Eating Capability of One-person Households-The Effects of Eating Alone, Meal Types, and Dietary Lifestyles
Seonglim Lee, Ilsook Choi, Junghoon Kim
Family and Environment Research.2020; 58(4): 483. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 408. CrossRef - Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Eun-Sun Park, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 476. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Nutrition Status and Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence of the Members according to the Number of Household Members based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2014)
Jin-Young Lee, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 232. CrossRef
- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
- 2,184 View
- 24 Download
- 28 Crossref

- [English]
- Milk Intake Patterns with Lactose and Milk Fat in Korean Male Adults
- Jung Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, Sung Hee Min, Myung Hee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):488-495. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.488
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the milk intake patterns with lactose and milk fat in Korean male adults using the following variables: milk intake level, awareness of lactose, and milk fat, health problems, and necessity of milk intake. In addition, the factors affecting milk intake were analyzed by multiple regression analysis.
METHODS
The subjects were 532 males aged 20 years or older among the nationwide milk purchasing group. The subjects were 223 (41.9%) in the 20–29 year age group, 188 (35.3%) in the 30–49 year age group and 121(22.7%) in the over 50 year age group. The survey was conducted using ANOVA and multiple comparative analysis to examine the differences in age and multiple regression analysis was performed to investigate the factors affecting the intake of milk.
RESULTS
The intake of milk in the subjects was 538.14 ± 494.23 ml per week. There were statistically significant differences in the subjects' age according to processed milk, low fat, nonfat milk, cheese, and ice cream. The perception of milk and lactose and milk fat was recognized as a good food for skeletal health when milk was consumed. Among the milk nutrients, lactose was highly recognized at the age of 20–29, and milk fat was recognized in those over 50 years. In addition to lactose and milk fat, calcium was the most highly recognized among the milk nutrients. Health problems associated with milk were skeletal health, obesity, and lactose intolerance. The perception of lactose intolerance was related to lactose intolerance and fatness, and the dietary behavior was unaffected.
CONCLUSIONS
This study examined the milk intake patterns of adult Korean males. Many variables were found to be related to the intake of milk. In this study, the milk intake was high when there was no problem with the perception and dietary behaviors of milk nutrition (lactose and milk fat). This study focused on lactose and milk fat, which are major nutrients in milk, and it is a new perspective study among milk-related research. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of milk and dairy product consumption with the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular disease incidence in middle-aged and older Korean adults: a 16-year follow-up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Yeseung Jeong, Kyung Won Lee, Hyekyeong Kim, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1225. CrossRef
- Association of milk and dairy product consumption with the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular disease incidence in middle-aged and older Korean adults: a 16-year follow-up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
- 1,716 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Consumption of Han-sik and its Association with Socioeconomic Status among Filipino Immigrant Women: the Filipino Women's Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL)
- Nayeon Kim, Minji Kang, Grace Abris, Sherlyn Mae P Provido, Hyojee Joung, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):475-487. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.475
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the consumption of Han-sik and its association with the years of residence in Korea and the socioeconomic status among Filipino immigrant women of the Filipino Women's Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL).
METHODS
A total of 474 Filipino women married to Korean men were included in the analysis. Their dietary intake was assessed using a single-day 24-hour recall. The participants provided information on the demographics, socioeconomic, and health-related factors through face-to-face interviews. The generalized linear model and logistic regression model were used to examine the association between the socioeconomic status and consumption of Han-sik.
RESULTS
The mean age of the participants was 34.3 years old, and the average duration of residence in Korea was 8.2 years. Among 474 Filipino women, a total of 467 consumed Han-sik, with an average of 6.8 food items per day. The Han-sik foods that the participants consumed most frequently were rice, cabbage kimchi, mixed-grain rice, and fried eggs. The average ratio of Han-sik was 58.57%. The ratio of Han-sik showed no significant associations with the years of residence, years of living together with their husband, education levels, total annual family income, or linguistic competence of Korean. However, the ratio of Han-sik use was associated with cohabitation with parents-in-law; the odds ratio (95% confidence interval) was 2.41 (1.18–4.92, p-trend = 0.002) comparing the fourth quartile with the first quartile of the Han-sik ratio.
CONCLUSIONS
Filipino immigrant women in the FiLWHEL study consumed a larger number of Han-sik than Philippine foods. In addition, cohabitation with their parents-in-law was associated with the consumption of Han-sik. Further epidemiologic studies will be needed to determine how the diet affects the health and wellbeing of immigrant women in Korea.
- 1,100 View
- 13 Download

- [English]
- Development of 9(th) Revision Korean Food Composition Table and Its Major Changes
- Su Hui Park, Se Na Kim, Sang Hoon Lee, Jeong Sook Choe, Youngmin Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):352-365. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.352
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The Korean Food Composition Table (KFCT) was first published in 1970, and has since been updated every five years by the Rural Development Administration (RDA). This study was conducted to introduce the development strategies, features, and challenges of the 9th revision of the KFCT.
METHODS
Due to the increasing demands of nutrient database users and generators, the RDA started a new research project in 2013 to improve the quantity and quality of data for the 9th revision of the KFCT. Over 1,000 food items frequently consumed in Korea were selected as key foods using the results of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. About 200 raw materials and processed food items were collected and analyzed every year. Target nutrients that were analyzed by collaborative labs, such as, sugars, selenium, iodine, and biotin, were increased from 22 to 43. Analytical sample handling procedures and data quality evaluation systems were also established in collaboration with 10 contracted labs. Data were evaluated for data quality according to the FAO/INFOODS, CODEX, and AOAC guidelines.
RESULTS
The 9th revision contains data on 3,000 food items and up to 43 and 140 food nutrients for the printed table and the excel database file, respectively. Overall, 1,485 data items were newly added, 973 of which were provided by the RDA and 512 were cited from foreign nutrient databases. The remaining 1,515 food items were maintained as in the 8th revision.
CONCLUSIONS
The KFCT provides the basic infrastructure for food and nutrition policy, research, and dietary practice in South Korea. The use of the KFCT has increased exponentially in the past few years in both public and private sectors; accordingly, increased efforts should be paid to the preparation, improvement, and maintenance of KFCT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combined associations of protein intake and resistance exercise with handgrip strength in postmenopausal women
Jin Kyung Baek, Hae Rim Kim, Eun Jin Lee, Yun Soo Chung, Seok Kyo Seo
Maturitas.2026; 205: 108808. CrossRef - Impact of energy intake on the association between protein intake and the prevalence of frailty in older Korean adults: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2014–2018
Seokju Kang, Youri Jin, Yongsoon Park
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2025; 29(4): 100518. CrossRef - Dietary β-Carotene, Vitamin A, and Retinol Intake and Prevalence of Colorectal Adenoma: A Cross-Sectional Study and Meta-Analysis
Joowon Chung, Jioh Kang, Sang Hoon Kim, Min Kyu Jung, Dong Hyun Kim, Hyun Joo Song, Ki Bae Kim, Seung-Joo Nam, Hoon Jai Chun, Jung Eun Lee, Yun Jeong Lim
Gut and Liver.2025; 19(6): 845. CrossRef - Relationship between urinary sodium excretion and bone mineral density in pediatrics: population-based study from KNHANES V 2010–2011
In Kyung Lee, Yoo Mi Kim, Han Hyuk Lim
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 37(6): 553. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Questionnaire to Measure Adherence to a Mediterranean-Type Diet in Youth
Yu-Jin Kwon, Young-Hwan Park, Yae-Ji Lee, Li-Rang Lim, Ji-Won Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(16): 2754. CrossRef - Nutrition survey methods and food composition database update of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Seon-Joo Park, Jieun Lyu, Kyoungho Lee, Hae-Jeung Lee, Hyun-Young Park
Epidemiology and Health.2024; 46: e2024042. CrossRef - Fruits and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study Cohort
Hojun Yu, Cheol Min Lee, Seung-Won Oh
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2024; 45(1): 44. CrossRef - Ultra-Processed Food Intakes Are Associated with Depression in the General Population: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sunghee Lee, Myungjin Choi
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2169. CrossRef - Analyzing the Sugar Components of Domestic Agricultural Products for Establishing the National Standard Food Composition Data-Base
Eun-Ha Jang, Ki-Yeon Lee, Kyung-Dae Kim, Jae-Hee Lee, Ji-Sun Park, Jae-Gil Lim, Jin-Kwan Ham, Jin-Ju Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(1): 71. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the relationship between four hepatic steatosis indices and muscle mass
Taesic Lee, Tae-Ha Chung
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Parental BMI and Offspring’s Blood Pressure by Mediation Analysis: A Study Using Data From the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyowon Choi, Hunju Lee, Yeon-Soon Ahn
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(6): 533. CrossRef - Intake of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and fish associated with prevalence of low lean mass and muscle mass among older women: Analysis of Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008-2011
Yeji Kim, Yongsoon Park
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Protein Intake with Handgrip Strength and Its Relation to Strength Exercise in Korean Adults Aged over 60 Years in the KNHANES (2014-18)
Eun Young Choi
Nutrients.2023; 15(4): 1014. CrossRef - Analysis of Vitamin K Content in Commonly Consumed Foods in Korea
Seungjun Lee, Youngmin Choi, Minjoo Gu, Seungjoo Baik, Jeehye Sung, Heon Sang Jeong, Junsoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 51(12): 1272. CrossRef - The association between fruit and vegetable consumption and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: does multivitamin use matter?
Jihae Kim, Li-Juan Tan, Hyein Jung, Yumi Roh, Kyungjoon Lim, Sangah Shin
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022039. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Total Antioxidant Capacity with Cancer Recurrence and Mortality among Breast Cancer Survivors: A Prospective Cohort Study
Doyeon Han, Minsung Chung, Yongsoon Park
Nutrition and Cancer.2022; 74(9): 3253. CrossRef - Daily Walking Accompanied with Intermittent Resistance Exercise Prevents Osteosarcopenia: A Large Cohort Study
Sangyeob Lee, Ji-Seok Kim, Ki-Soo Park, Kyung-Wan Baek, Jun-Il Yoo
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2022; 29(4): 255. CrossRef - Comparison of multivariate linear regression and a machine learning algorithm developed for prediction of precision warfarin dosing in a Korean population
Van Lam Nguyen, Hoang Dat Nguyen, Yong‐Soon Cho, Ho‐Sook Kim, Il‐Yong Han, Dae‐Kyeong Kim, Sangzin Ahn, Jae‐Gook Shin
Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis.2021; 19(7): 1676. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Universal Protein Extraction Methodologies for Screening of Lipase Activity from Agricultural Products
Jisu Ha, Jun-Young Park, Yoonseok Choi, Pahn-Shick Chang, Kyung-Min Park
Catalysts.2021; 11(7): 816. CrossRef - Association of a Tobacco-specific Nitrosamine Carcinogen with Urinary Cotinine, Urinary Sodium Excretion, and Total Energy Intake in Adolescents and Children
Jong Weon Choi, Tatsuyoshi Fujii, Noriyoshi Fujii
Current Medical Science.2021; 41(2): 270. CrossRef - Development of an Unified Food Composition Database for the European Project “Stance4Health”
Daniel Hinojosa-Nogueira, Sergio Pérez-Burillo, Beatriz Navajas-Porras, Bartolomé Ortiz-Viso, Silvia Pastoriza de la Cueva, Fabio Lauria, Alexandra Fatouros, Kostas N. Priftis, Verónica González-Vigil, José Ángel Rufián-Henares
Nutrients.2021; 13(12): 4206. CrossRef - Total, bioavailable and free 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels as functional indicators for bone parameters in healthy children
You Joung Heo, Yun Jeong Lee, Kyunghoon Lee, Jae Hyun Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Young Ah Lee, Junghan Song, Dengshun Miao
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258585. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Total Antioxidant Capacity with Bone Mass and Osteoporosis Risk in Korean Women: Analysis of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2011
Donghyun Kim, Anna Han, Yongsoon Park
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1149. CrossRef - Association between Iron Intake and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes: Significance of Iron Intake and the Ratio between Iron Intake and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Intake
Kyuho Kim, YoonJu Song, Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Nutrients.2020; 12(11): 3365. CrossRef - Association between Dietary Patterns and Handgrip Strength: Analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data Between 2014 and 2017
Yunkoo Kang, Jieun Kim, Do-Yeon Kim, Seung Kim, Sowon Park, Hyunjung Lim, Hong Koh
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 3048. CrossRef - Comparison of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients’ dietary behaviors
Seon-Mi Kim, Byung Chin Kang, Hyun-Jung Kim, Min-Sook Kyung, Hyung Jung Oh, Jung-Hyun Kim, Oran Kwon, Dong-Ryeol Ryu
BMC Nephrology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Smartphone Application for Dietary Self-Monitoring
Jeong Sun Ahn, Dong Woo Kim, Jiae Kim, Haemin Park, Jung Eun Lee
Frontiers in Nutrition.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Combined associations of protein intake and resistance exercise with handgrip strength in postmenopausal women
- 4,272 View
- 50 Download
- 27 Crossref

- [English]
- Salinity of Representative Korean Foods High in Sodium from Home Meals, Foodservices, and Restaurants
- Lin Jiang, Damin Shin, Yeon Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):333-340. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to analyze the salinity of representative Korean foods high in sodium to generate data for use as a fundamental resource for setting salinity standards in foods.
METHODS
A total of 480 foods from 16 representative Korean foods high in sodium were collected from 10 households, 10 industry foodservice establishments, and 10 Korean restaurants in four regions (Capital area, Chungcheong Province, Gyeongsang Province, and Jeolla Province) and analyzed for salinity.
RESULTS
Among the foods, stir-fried anchovies (4.07~4.45%) showed the highest salinity, followed by pickled onion (1.86~2.62%), cabbage kimchi (1.83~2.2%), braised burdock and lotus root (1.79~2.17%), and sliced radish kimchi (1.78~1.89%) (p < 0.001). The salinity of kimchi from home meals (2.2%) was significantly higher than that of foodservice (1.83%) and restaurant (1.93%) kimchi (p < 0.05). Salinity in each group of food was highest in kimchi (1.83~2.04%), followed by braised dishes (1.54~1.78%), steamed dishes (1.0~1.22%), stir-fried dishes (1.02~1.18%), and soup or stew (0.74~1.02%) (p < 0.001). The salinity of soup and stew from restaurants (1.02%) was significantly higher than that of home meal (0.84%) and foodservice (0.74%) soup and stew.
CONCLUSIONS
Determination of the salinity of representative Korean foods known to be high in sodium by eating place is expected to be useful to establishing guidelines for reduction of salinity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 514. CrossRef - A Literature Review Study on Chronic Changes in Yukgaejang
Soon-Ah Choi, Bokyung Ryu, Lana Chung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 386. CrossRef - Comparison of the portion sizes of Korean adults across eating places: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2012–2016)
Hye-Sook Hong, Seon-Joo Park, Do-Kyung Lee, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 676. CrossRef - Development of standards for reducing the sodium content and salinity of Korean fermented soybean sauces and representative Korean foods high in sodium
Lin Jiang, Eun-Kyung Shin, Jung-Sook Seo, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(2): 185. CrossRef - Current status, perception and practicability of restaurant staffs related to reducing sodium use in Seongnam, Korea
So-Hyun Ahn, Jong Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Yoonna Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 475. CrossRef
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- 1,622 View
- 7 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Recognition and Propagation for Temple Food among University Students with Food-related Majors
- In Joon Huh, Sim Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):137-147. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the perspective and popularization of temple food among university students with food related majors, and to provide basic data for the popularization and the fostering of professional lecture in temple food.
METHODS
A self-administered questionnaire was applied to 453 university students at six universities with food related majors. The questionnaire was designed to examine interest, recognition, consumption, popularization and curriculum of temple food.
RESULTS
The study population consisted of 19.2% men, and 80.8% women, and the most common response to desired career after graduation was food related employment (53.9%). Overall, 49.0% replied that they had an interest in temple food, which was relatively low. 59.9% of respondents who had been known throw TV, Internet, newspaper, and magazines about temple food were showed the highest results. Additionally, as for the perception of temple food, ‘Prevention of lifestyle related disease’ was the highest score (4.10). Overall, 64.9% of the subjects had not tried temple food, and 84.7% of these responded that this was because they had not encountered temple food. Among subjects who had tried temple food, most had encountered it at a temple (73.0%), and 78.0% replied that the taste of temple food was suitable. The intention to try temple food was 73.3%, and 64.8% of respondents said there was a necessity to establishment curriculum regarding temple food. Finally, interest, popularization, and intention to try temple food were significantly positively corelated.
CONCLUSIONS
The results showed high interest in temple food and willingness to participate in education regarding temple food, as well as awareness of the need for popularization. Therefore, it is necessary to increase intake opportunities to raise interest in temple foods. This can be accomplished utilizing publicity materials, as well as by offering opportunities for temple food education through curriculum.
- 940 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- Study of the Coverage of Nutrition Labeling System on the Nutrient Intake of Koreans - using the 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
- Ji Eun Park, Haeng Shin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):116-127. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.116
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to examine the coverage of the current mandatory nutrition labeling system on the nutrient intake of Koreans.
METHODS
KNHANES dietary intake data (2013) of 7,242 subjects were used in the analysis. KNHANES dietary intake data were collected by a 24-hour recall method by trained dietitians. For analysis, all food items consumed by the subjects were classified into two groups (foods with mandatory labeling and other foods). In the next step, all food items were reclassified into four groups according to the food type and nutrition labeling regulations: raw material food, processed food of raw material characteristics, processed foods without mandatory labeling, and processed foods with mandatory labeling. The intake of energy and five nutrients (carbohydrate, protein, fat, saturated fat, and sodium) of subjects from each food group were analyzed to determine the coverage of the mandatory nutrition labeling system among the total nutrient intake of Koreans.
RESULTS
The average intake of foods with mandatory labeling were 384g/day, which was approximately one quarter of the total daily food intake (1,544 g/day). The proportion of energy and five nutrients intake from foods with mandatory labeling was 18.1%~47.4%. The average food intake from the 4 food groups were 745 g/day (48.3%) for the raw food materials, 54 g/day (3.5%) for the processed food of raw material characteristics, 391 g/day (25.3%) for the processed foods without mandatory labeling, and 354 g/day (22.9%) for the processed foods with mandatory labeling.
CONCLUSIONS
Although nutrition labeling is a useful tool for providing nutritional information to consumers, the coverage of current mandatory nutrition labeling system on daily nutrient intake of the Korean population is not high. To encourage informed choices and improve healthy eating habits of the Korean population, the nutrition labeling system should be expanded to include more food items and foodservice menus.
- 1,161 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Relation between Beverage Consumption Pattern and Metabolic Syndrome among Healthy Korean Adults
- Eun Ju Dennis, Minji Kang, Sung Nim Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(5):441-455. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.5.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study is to describe beverage patterns among healthy Korean adults and investigate their association with prevalence and components of metabolic syndrome.
METHODS
Subjects consisted of 6,927 Korean adults, aged 19-64 years in the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES, 2013-2015). Beverages were regrouped into twelve groups based on food codes and beverage intake (g/day) was assessed by 24-hour recall. Factor analysis was used to obtain beverage patterns. Waist circumference and body mass index (BMI) were used as anthropometric data; fasting blood glucose, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein (HDL), and blood pressure were used as biochemical indicators. The odds ratio (OR) for prevalence of metabolic syndrome and components of metabolic syndrome was assessed using logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS
Three beverage patterns were identified using factor analysis: 1) carbonated soft drinks 2) coffee (without added sugar or powdered creamer), and 3) alcoholic beverages. Subjects with high scores for the carbonated soft drink and coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer patterns were younger and subjects with high scores for the alcoholic beverage pattern were older. There were significant differences in gender distribution in all three beverage patterns, with men more likely to have high scores for carbonated soft drink and alcoholic beverage patterns. On the other hand, women were more likely to have higher scores for coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer pattern. Within each pattern, there were significant differences in sociodemographic and lifestyle characteristics such as education, household income, frequency of eating out, and smoking status according to the quartile of pattern scores. Alcoholic beverages and carbonated soft drinks patterns were associated with an increased levels of metabolic syndrome components, but coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer was not associated with any of metabolic syndrome components in healthy Korean adults after adjusting for age, sex, education, BMI, weight management, household income, smoking status, frequency of eating out, and energy intake.
CONCLUSIONS
Alcoholic beverages and carbonated soft drinks patterns are associated with increased levels of metabolic syndrome components while coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer pattern is not associated with any of metabolic syndrome components in healthy Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional and Health Status According to the Frequency of Carbonated Beverage Consumption among Adults in Their 20s : Based on the 2019-2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
You-Sin Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(3): 159. CrossRef - Calcium- and Sodium-Rich Food Intake among Koreans with and without Metabolic Syndrome: Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Byeonggeun Choi, Jiyoon Kim, Yeonjin Kim, Jiae Shin, Sang-Ah Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(15): 2439. CrossRef - Effects of Calamansi Soju and Other Alcoholic Beverages on Resin Restorations
Moon-Jin Jeong, Kyungwon Heo, Myoung-Hwa Lee, Myeong-Ju Jeong, Do-Seon Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(4): 251. CrossRef - Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 350. CrossRef - Association between Dietary Habits, Shift Work, and the Metabolic Syndrome: The Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Heeja Jung, Hyunju Dan, Yanghee Pang, Bohye Kim, Hyunseon Jeong, Jung Eun Lee, Oksoo Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7697. CrossRef - Exploring parenting variables associated with sweetness preferences and sweets intake of children
Taejung Woo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2019; 13(2): 169. CrossRef - Influence of beverage type and ingestion time on tooth corrosion
Jae-Deok Cheon, Eun-Ah Cho, Hyun-Bae Park, Yu-Jin Choi, Han-Ju Kim, Jung-Soo Lee, Eun-Jeong Bae
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2018; 45(3): 169. CrossRef
- Nutritional and Health Status According to the Frequency of Carbonated Beverage Consumption among Adults in Their 20s : Based on the 2019-2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
- 1,656 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Recognition, Preference and Popularization of Temple Food - Among Local and Foreign Restaurant Visitors
- Yang Su Moon, Sim Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(1):53-62. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.1.53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to identify factors that influence the consumption of temple food and to find systematic methods improving the popularization of temple food.
METHODS
A self-administered questionnaire was applied to 304 temple food restaurant visitors, including 232 local and 72 foreign individuals. The questionnaire was designed to investigate recognition, consumption, preference and popularization of temple food among restaurant visitors.
RESULTS
The study population consisted of 30.6% men, 69.4% women. 76.3% were Korean while 23.7% were foreigners. The responses on their impression on temple food contained the words, “vegetarian†(4.64), “plain and familiar†(4.19), and “good for dieting†(4.16). The most commont reason to favor temple food was its “mild taste†(63.0%) in the local group while foreigners preferred it because it is “good for health†(35.8%). The preferred kind of side dish of the local group was roasted dish (4.40), stir-fried dish (4.39), blanched vegetables (4.36), and food boiled with sauce (4.23); foreigner's high preference was for stir-fried (4.67), Jangachi (4.63), food boiled with sauce (4.56), and Buggak (4.55).. Most respondents thought that it is necessary to maintain the traditional form of temple food. While 43.5 percent of Koreans responded that “the five pungent vegetables†could be allowed, 62.8 percent of foreign respondents said it is permissible.
CONCLUSIONS
A systematic approach to improve the temple food that reflects both foreign and local preference while maintaining its originality is necessary for its globalization. Furthermore, restaurants specialized in temple food should be expanded and promoted through effective marketing strategies that would make the cuisine easily accessible and spread throughout the world. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on the Consumer Perception and Needs for Temple Food Meal Kits
Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 535. CrossRef - Sustainable and Religion Food Consumer Segmentation: Focusing on Korean Temple Food Restaurants
Junkyu Park, Mark A. Bonn, Meehee Cho
Sustainability.2020; 12(7): 3035. CrossRef - Recognition and Propagation for Temple Food among University Students with Food-related Majors
In-Joon Huh, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(2): 137. CrossRef
- A Study on the Consumer Perception and Needs for Temple Food Meal Kits
- 1,103 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Nutritional Status and Eating Behavior of Korean and Chinese Children using the Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
- Hua Ling, Hokyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(1):22-39. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the nutritional status and dietary behavior of Korean and Chinese elementary school children using Nutritional Quotient (NQ).
METHODS
The survey was conducted by distributing questionnaires to the parents of the child, after selecting four elementary schools located in Pusan city of Korea and three elementary schools located in Luoyang city, Henan Province of China, from Grade 1 to Grade 6 in each school.
RESULTS
The NQ scores of Korean children and Chinese children were 64.99 and 66.57, respectively, which did not show a statistically significant difference. Korean children significantly showed higher diversity score (p<0.001) than Chinese, but Chinese children significantly showed higher moderation (p < 0.001), regularity (p < 0.001) and practice score (p < 0.01) than Korean. NQ grades showed a statistically significant difference. According to food security of the household, NQ scores of the Chinese children of secure household were significantly higher than those of food insecurity household (p < 0.01). In particular, it showed a significant difference in the practice (p < 0.001), moderation (p < 0.05) and regularity score (p < 0.05). Korean children's NQ score showed a significant correlation with the score of following the Dietary Guidelines of parents, but Chinese did not show such a correlation.
CONCLUSIONS
There were differences in children's dietary behaviors and parents' impact to children's dietary attitude between Korean and Chinese. NQ developed for Korean could be successfully applied to Chinese. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the dietary quality among Chinese adults living in Shanghai and the Anhui Province using the Nutrition Quotient for adults
Ani Liu, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 117. CrossRef - Diet-Related Disparities and Childcare Food Environments for Vulnerable Children in South Korea: A Mixed-Methods Study
Jiyoung Park, Seolhyang Baek, Gahui Hwang, Chongwon Park, Sein Hwang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1940. CrossRef
- Assessment of the dietary quality among Chinese adults living in Shanghai and the Anhui Province using the Nutrition Quotient for adults
- 1,241 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Diet Quality and Diversity according to Obesity Type among 19-64 year old Korean Adults
- Hyae Min Gu, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Mi Ah Han, Yeong Eun Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):545-557. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.545
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to compare the diet quality and diversity according to types of obesity categorized by body mass index and waist circumference among Korean adults aged 19-64 years.
METHODS
This study used the data of the 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES-V) and included 11,081 study participants. Type of obesity was categorized into 4 groups (Type 1: BMI obesity + abdominal obesity; Type 2: BMI obesity only; Type 3: abdominal obesity only; Type 4: Normal). To compare the diet quality and diversity according to obesity type, ANCOVA (Analysis of covariance) was used with stratification of age groups (19-44 years, 45-64 years).
RESULTS
With regard to comparative analysis of diet quality, there were significant differences between diet qualities in energy, protein, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, phosphorous and iron and type of obesity in the 19-44 age group, while there were significant differences between diet qualities on protein, vitamin C, phosphorous and type of obesity in the 45-64 age group. There was no significant difference between diet diversity score and type of obesity in Korean adults.
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that in Korean adults, diet qualities of some nutrients were different among obesity types, while diet diversity was not. These observations should be considered in an effort to improve intake of over-and deficient nutrients and in further studies to evaluate the effects of nutrient quality on obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of pre-obesity and above and its associated factors in adult women: an analysis of the 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyunju Chae
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(2): 117. CrossRef - The Factors Influencing the Bone Mineral Density in Korean Adult Men : Based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010~2011 Data
Hye-Sang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 136. CrossRef
- Prevalence of pre-obesity and above and its associated factors in adult women: an analysis of the 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,088 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Associations between Exposure to Unhealthy Food Outlets Within Residential District and Obesity: Using Data from 2013 Census on Establishments and 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoonjung Kim, Sung Nim Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(5):463-476. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.5.463
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Environmental, social and personal factors influence eating patterns. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between unhealthy food outlets within a residential area and obesity using nationally representative Korean survey data and data from the Census on Establishments.
METHODS
Data on the food intakes and socioeconomic variables of a total of 9,978 adults aged ≥ 19 years were obtained from the 2013-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Geographic locations of restaurants were obtained from the 2013 Census on Establishments in Korea. Administrative area was categorized into tertiles of count of unhealthy food outlets based on the distribution of number of unhealthy food outlets among all urban (Dong) and rural (Eup or Myun) administrative districts in Korea. Multilevel logistic regressions model were used to assess the association between the number of unhealthy food outlets and obesity.
RESULTS
People living in the district with the highest count of unhealthy food outlets had higher intakes of fat (45.8 vs. 44.4 g/day), sodium (4,142.6 vs. 3,949.8 mg/day), and vitamin A (753.7 vs. 631.6 µgRE/day) compared to those living in the district with the lowest count of unhealthy food outlets. A higher count of unhealthy food outlets was positively associated with frequent consumption of instant noodles, pizza, hamburgers and sandwiches, sweets and sour pork or pork cutlets, fried chicken, snacks, and cookies. Higher exposure to unhealthy food outlets was associated with increased odds of obesity (1st vs. 3rd tertile; OR 1.689; 95% CI 1.098-2.599).
CONCLUSIONS
A high count of unhealthy food outlets within a residential area is positively associated with the prevalence of obesity in Korea. The results suggest that food environmental factors affects the health outcomes and interventions aiming to restrict the availability of unhealthy food outlets in local neighborhoods may be a useful obesity prevention strategy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity-Related Factors in Adult Women with Early Menarche
Hunha Cho, Jeong-Won Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(4): 557. CrossRef - Associations between adolescent dietary habits, obesity and food environment around schools in Seoul
Hyun-Jae Woo, Hong Lim Lee, Hae-Young Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(5): 55. CrossRef - Relationship between the Intake of Children's Favorite Foods and Policy based on Special Act on Safety Control of Children's Dietary Life
Taejung Woo, Jihye Yoo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 106. CrossRef
- Obesity-Related Factors in Adult Women with Early Menarche
- 1,388 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of a Korean Food Culture Education Textbook for Married Female Immigrants
- Jeong Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(5):415-425. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.5.415
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to develop a textbook of the integrated education of Korean food culture and language for married female immigrants.
METHODS
An analysis was conducted with the textbooks and researches for married female immigrants, and dietary life related contents were extracted. The contents were organized by activity oriented approach which is acquired the culture. The evaluation was conducted through depth interview with 6 married female immigrants through an analysis of the qualitative materials.
RESULTS
The text book comprised of 30 Korean food recipes with the target expressions and vocabularies. It also included Korean basic table setting, Korean table manner, main dishes and side dishes, basic cutting, seasoning and garnish, measure of the ingredients, symbolic food, regional food culture, choice of food ingredients, shopping, bargaining, taste expression, color expression, all sorts of spices, Korean traditional festival food, and seasonal customs and food. For intensifying communication, activity which is close to real life was added. Through cooking, married female immigrants expose words and sentence patterns and that allows to evaluate their level of understanding. We observed that the developed textbook is suited for married female immigrants' needs and cognitive level. The text book included a comparative study between Korean culture and their country's culture, which could provide the motive for accepting each other’s cultures. The study showed how to develop a textbook that integrates Korean language education and Korean food culture and how to apply the textbook in real life.
CONCLUSIONS
The correct understanding about Korean food culture could lead to improvements communication ability. Useful information which relates to Korean food, recipes, and food culture could increase daily life satisfaction. Conducting both cultural education and language education could increase the participation of married female immigrants in learning activities. Therefore this study could help these females to adapt Korean society and manage family dietary life effectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Korean Dietary Life Adaptation of Married Female Immigrants
Jeong-Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 103. CrossRef
- Analysis of Korean Dietary Life Adaptation of Married Female Immigrants
- 1,519 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Quality of Diet and Nutritional Intake and Mortality Risk among South Korean Adults Based on 12-year Follow-up Data
- Hye Ryun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):354-365. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.354
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Studies that reported the association between diet quality/nutritional intake status and mortality have rarely used long-term follow-up data in Asian countries, including Korea. This study investigated the association between the risk of mortality (all-cause and cause-specific) and the diet quality/nutritional intake status using follow-up 12-year mortality data from a nationally representative sample of South Koreans.
METHODS
8,941 individuals who participated in 1998 and 2001 Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys were linked to mortality data from death certificates. Of those individuals, 1,083 (12.1%) had died as of December, 2012. Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the relative risks of mortality according to the level of diet quality and intakes of major nutrients. Indicators for diet quality index and nutritional intake status were assessed using MAR (mean adequacy ratio) and energy and protein intake level compared with the 2010 Korean DRI.
RESULTS
Higher diet quality/nutritional intake status were associated with lower mortality; the mortality risk (95% confidence interval) from all-cause of lowest MAR group vs highest was 1.66 (1.27 to 2.18) among ≥ 30 year old, and 1.98 (1.36 to 2.86) among 30~64 year old individuals. Those with below 75% of energy and protein intake of Korean DRI had higher mortality risks of all-cause mortality compared to the reference group. Diet quality/nutritional intake status was inversely associated with mortality from cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
CONCLUSIONS
Poor Diet quality/nutritional intake status were associated with a higher risk of mortality from all-cause and mortality from cardiovascular diseases and cancer among South Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of all-cause mortality is associated with multiple health-related lifestyle behaviors and does not differ between urban and rural areas in Korea
Seunghee Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(4): 554. CrossRef - Development of an evaluation tool for dietary guideline adherence in the elderly
Young-Suk Lim, Ji Soo Oh, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Soymilk Intake on Diet Management and Blood Biochemistry in Diabetes Patients
Kyung-Ok Shin, Hyo-Jeong Hwang, Soon-Hee Park, Kwang-Jin Chon, Chung-Hwa Song, Dae-Gyun Moon
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(3): 154. CrossRef - The relationship between diet quality indices and odds of breast cancer in women: a case–control study
Mohammad Hassan Sohouli, Genevieve Buckland, Cain C. T. Clark, Heitor O. Santos, Felipe L. Athayde, Vahid Sanati, Leila Janani, Akram Sadat Sajadian, Mitra Zarrati
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Patterns and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Older Adults
Ae-Rim Seo, Tae-Yoon Hwang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3703. CrossRef - Do Where The Elderly Live Matter? Factors Associated with Diet Quality among Korean Elderly Population Living in Urban Versus Rural Areas
Sohyun Park, Hyun Ja Kim, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2020; 12(5): 1314. CrossRef - A Comparisons of Nutritional Intake and Diet Quality Index-International in Gynecological Cancer Survivors and Normal Women: Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2016
Bo-Young Seo, Eun-Sil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 406. CrossRef - Association between Breakfast Frequency and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Cross-Sectional Study of KNHANES Data, 2014–2016
Hyeon Ji Lee, Jieun Jang, Sang Ah Lee, Dong-Woo Choi, Eun-Cheol Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(10): 1853. CrossRef - Effect of nutrition care process-based nutrition intervention on improvement of intake in the elderly in-patients with malnutrition
Ji-Hyun Park, Min-Ji Kang, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 307. CrossRef
- Risk of all-cause mortality is associated with multiple health-related lifestyle behaviors and does not differ between urban and rural areas in Korea
- 1,347 View
- 6 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Status of Maternal Nutrition in South and North Korea
- Soh Yoon Yun, Young Hye Kwon, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(3):265-273. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study compared the nutritional status of child-bearing age women between the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) and the Republic of Korea (South Korea).
METHODS
The data presented in the DPRK Final Report of the National Nutrition Survey 2012 was utilized for the nutritional status and food intake of North Korean women. To produce the South Korean women's data comparable to those of North Korean women, the data from the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed and the data presented in the 2010 Report of the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards were utilized.
RESULTS
The prevalence of maternal anemia (blood hemoglobin < 12.0 g/dL) was over 30% in all the age groups of North Korean women and 8.9%, 14.2%, 16.4% in 20-29, 30-39, 40-49 year old South Korean women, respectively. The prevalence of maternal protein-energy malnutrition (Mid-Upper Arm Circumference < 22.5 cm) was 25.2%, 21.4%, 21.8% in 20-29, 30-39, 40-49 year old North Korean women, respectively and less than 10% in all the age groups of South Korean women. Result of dietary diversity comparison showed that North Korean women consumed less food than South Korean women at all food groups: grains, fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy. Percentage of North Korean women having consumed protein rich foods-meat and fish, eggs or dairy products-were much lower than those of South Korean women.
CONCLUSIONS
The striking disparity of nutritional status between South and North Korean women indicates that nutrition support for North Korean women is essential in the process of preparation for a unified nation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
Youngmin Nam, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 288. CrossRef - The Present and Future Status of Maternal and Child Health From the Perspective of Unification Medicine
Ji Young Kim, Eun Saem Choi, Ki Hoon Ahn
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(3): 132. CrossRef - Timely Initiation of Complementary Feeding and Associated Factors among Mothers of Children Aged 6–24 Months in Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia, 2019
Atsedemariam Andualem, Afework Edmealem, Belachew Tegegne, Lehulu Tilahun, Yitayish Damtie, C. S. Johnston
Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Systematic review of evidence on public health in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea
John J Park, Ah-Young Lim, Hyung-Soon Ahn, Andrew I Kim, Soyoung Choi, David HW Oh, Owen Lee-Park, Sharon Y Kim, Sun Jae Jung, Jesse B Bump, Rifat Atun, Hee Young Shin, Kee B Park
BMJ Global Health.2019; 4(2): e001133. CrossRef - Frequently covered diseases in North Korean internal medicine journal Internal Medicine [Naegwa]—Secondary publication
Shin Ha, Yo Han Lee
Science Editing.2019; 6(2): 99. CrossRef
- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
- 1,619 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



