Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
- Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):431-440. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00234

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this qualitative study was to explore and understand the behaviors and challenges of self-nutrition management from the perspective of elderly.
Methods
In May 2025, ten elderly aged 65–83 years with prior experience using digital devices were recruited through purposeful sampling. Data were collected via focus group interviews using a semi-structured questionnaire until saturation was reached, and all interviews were recorded, transcribed, and analyzed using traditional content analysis methods. The collected interview data were extracted focusing on phrases or sentences relevant to the research purpose, and various concepts derived through memo writing and the constant comparison were categorized based on common meanings. Subsequently, the categorized statements were deeply interpreted and reclassified into subcategories for final analysis.
Results
Under the overarching theme of development directions for a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly, three main categories and 13 subcategories were derived. The three main categories include: (1) processes of acceptance and utilization of digital technologies; (2) potential for applying digital self-nutrition management; and (3) strategies for implementing digital-based nutrition education.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that elderly face barriers to utilizing digital tools for self-nutrition management not only due to physical or technical limitations, but also because of the confusion arising from limited nutrition knowledge and information overload. To overcome the barriers that may arise during the digital-based education process for elderly, strategies (educational topics, delivery strategies, and operational strategies) were derived to vitalize a digital self-nutrition management education program. These results highlight the necessity of developing tailored digital nutrition education programs that reflect the characteristics of elderly, which may enhance their practical applicability and provide foundational evidence for establishing a digital–nutrition integrated care model within the senior customized care service.
- 131 View
- 15 Download

Review
- [Korean]
- Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
- Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):175-182. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00094
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study analyzes the status of nutrition education media among Korean older adults based on the transtheoretical model (TTM) and their food literacy to propose effective strategies for the development and utilization of educational media.
Methods
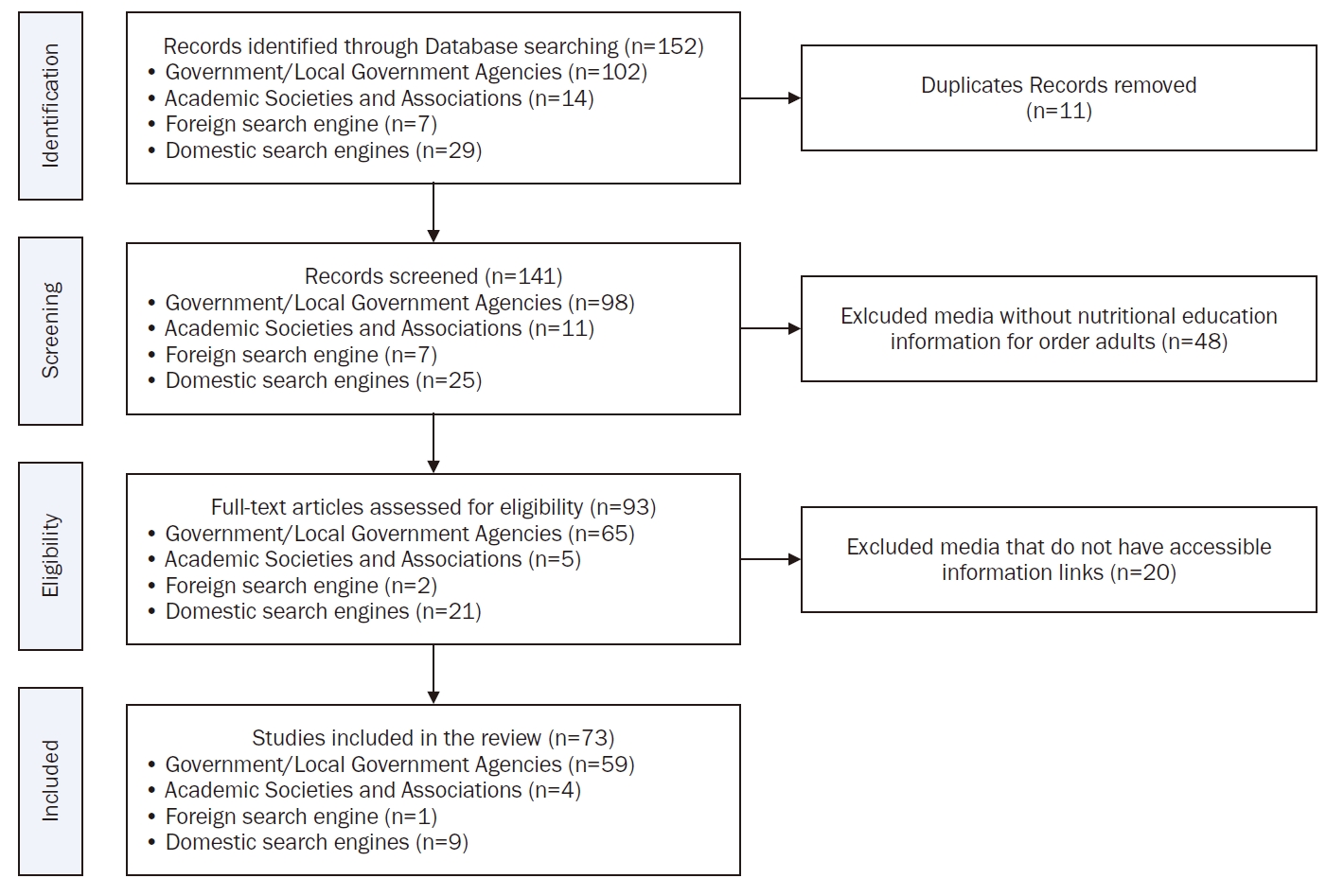
A literature review was conducted using The Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) protocol. The literature search was performed using government and local government agency websites, as well as those of affiliated institutions, health and nutrition-related academic societies, and academic search engines. A total of 144 studies were identified, and after a cross-evaluation by two reviewers based on the literature selection criteria, 73 studies were included in the final analysis.
Results
Among the types of nutrition education media, card news had the highest proportion, followed by video media. The development and distribution of nutrition education media for older adults were primarily carried out by government and local government agencies, as well as related affiliated institutions, accounting for 80.8% (n = 59) of the total. When nutrition education topics in the media were categorized according to the stages of behavior change in the TTM, the largest proportion, 64.6% (n = 61), was applicable to the precontemplation and contemplation stages. When categorized by food literacy domains, all topics fell under the categories of nutrition and safety.
Conclusion
Nutrition education media for older adults were found to be primarily focused on knowledge acquisition and information delivery, making them mostly applicable to the precontemplation and contemplation stages of behavior change. The concept of food literacy addressed in the different types of media was limited to the domains of nutrition and safety, with no content covering the cultural and relational domains or the social and ecological domains. For tailored nutrition education, it is necessary to develop diverse educational materials that comprehensively reflect each stage of the TTM and all aspects of food literacy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 431. CrossRef
- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
- 1,721 View
- 82 Download
- 1 Crossref

Research Articles
- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 3,790 View
- 44 Download

- [Korean]
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):528-540. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine health-related characteristics and chronic disease risk in middle-aged Koreans based on their fat energy intake ratio.
Methods
We analyzed data from 7,274 Koreans aged 40–64 years using the 7th (2016–2018) Koreans National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were classified into three groups based on their fat energy intake ratio: insufficient (< 15%), adequate (15%–30%), and excessive (> 30%). We assessed their socio-demographic characteristics; lifestyle characteristics; biochemical characteristics; quantitative and qualitative nutrient intakes, measured using dietary reference intakes for Koreans and index of nutrition quality (INQ); and chronic disease risk.
Results
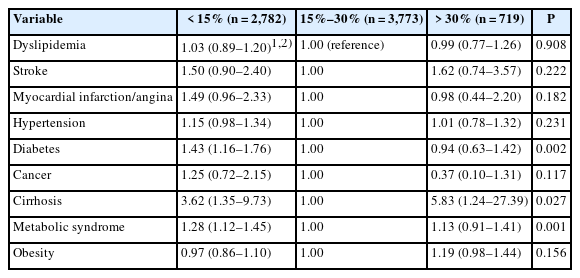
Significant differences were observed between the groups in age, gender, income, education, and residence region. The insufficient group had the highest proportion of older adults, male, lower income, rural residents, and lower education levels. The groups differed significantly in lifestyle characteristics, with the insufficient group having the highest rates of no walking, heavy drinking, smoking, and poor subjective health perception. Biochemical characteristics in the insufficient group exhibited the lowest levels for fasting blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and triglycerides. Significant differences were found in both the quantitative and qualitative intake of nutrients. The insufficient group had the lowest intake of most nutrients except fiber, whereas the excessive group had the lowest fiber intake. Based on the INQ, vitamin A and Ca were the lowest in the insufficient group, and vitamin C and folic acid were the lowest in the excessive group. The risk of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome was highest in the deficient group, and the risk of liver cirrhosis was highest in the excessive group.
Conclusion
Insufficient or excessive fat energy intake ratio negatively affects nutrient intake and chronic disease risk. Fat energy intake of 15%–30% is important for improving nutrient intake and managing chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and liver cirrhosis. We suggest that education and an appropriate social environment are necessary to ensure this fat energy intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
Yu Hyeon Jo, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef
- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
- 1,536 View
- 50 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Health-related quality of life and nutrient intake of the elderly with type 2 diabetes according to comorbidity burden: a cross-sectional study
- Yejung Choi, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):418-430. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00014

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to explore the cross-sectional association between health-related quality of life (HRQoL) according to the number of comorbidities in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) using the Euro Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) index. Methods: This study included 3,553 participants aged ≥ 65 years from the 2008–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Dietary data were collected through 24-hour recall interviews by trained researchers, and demographic and lifestyle information via self-administered questionnaires. HRQoL was measured using a modified EQ-5D scale. Multivariable linear regression analyzed the associations between EQ-5D scores, nutrients and comorbidity, controlling for sociodemographic and health variables. Results: Most participants reported ‘no problems’ in the EQ-5D scores, although approximately 17% to 47% of participants reported ‘some problems’ or ‘extreme problems,’ depending on the dimension. As comorbidities increased, significant declines were observed across all dimensions, particularly in mobility, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/ depression. Nutrient intake analysis revealed that participants with three or more comorbidities consumed less carbohydrates, but more fat. Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that among older adults with T2DM, a higher number of comorbidities is associated with decreased HRQoL. Additionally, there are differences in nutrient intake patterns among those with more comorbidities, specifically decreased carbohydrate intake and increased fat intake. These results emphasize the need for comprehensive and tailored management strategies that consider both diabetes and the co-occurring health conditions. By addressing the complex healthcare needs of individuals with multiple comorbidities, it is possible to enhance their HRQoL and overall well-being.
- 2,046 View
- 32 Download

- [English]
- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
- Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):359-371. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00013

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate and compare factors associated with malnutrition according to the presence or absence of dementia in community-dwelling elderly people.
Methods
Needs assessment data from 311 long-term care insurance (LTCI) recipients (dementia group 203; non-dementia group 108) that participated in the second pilot program of the integrated care model in community care settings under the Korean LTCI system were used. Descriptive statistical analysis, independent t-test, and analysis of variance were conducted on the sociodemographic characteristics, health and functional status, and nutritional status of the dementia and non-dementia groups. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify factors associated with malnutrition in the dementia and non-dementia groups.
Results
Malnutrition occurred in 33.5% and 26.9% of participants in the dementia and non-dementia groups, respectively. In the dementia group, living with family rather than living alone (odds ratio [OR]: 3.81; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.50–9.66; P = 0.031), increase in Korean Activities of Daily Living (K-ADL) score (OR: 1.35; 95% CI: 1.17–1.55; P < 0.001), and increase in the Neuropsychiatric Inventory-Questionnaire score (OR: 1.02; 95% CI: 1.01–1.03; P = 0.005) were associated with a higher risk of malnutrition. In the non-dementia group, the risk of malnutrition increased as the K-ADL score increased (OR: 1.20; 95% CI: 1.04–1.39; P = 0.011) and in the depressed group (OR: 2.84; 95% CI: 1.04–7.74; P = 0.042).
Conclusions
The study results confirmed the necessity of nutritional management for community-dwelling LTCI recipients. When developing a nutritional management program, considering the differences in factors related to malnutrition between the dementia and non-dementia groups is important. This study proposes policies for improving the LTCI system in terms of nutritional management and the utilization of community resources.
- 2,078 View
- 68 Download

- [English]
- Associations between the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease and dietary and lifestyle behavior among young Korean adults: a preliminary cross-sectional study
- Soheun Shim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):396-405. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00011

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a clinical condition caused by esophageal tissue damage resulting from the reflux of stomach or duodenal contents. An increasing number of GERD cases have been reported recently; however, research on this population, especially young adults, is lacking. This study aimed to investigate the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Methods: A total of 202 individuals (19–34 years old) living in Gwangju were surveyed using a questionnaire to examine their general characteristics, lifestyle, and dietary behaviors. GERD symptoms were investigated using the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GerdQ). The participants were grouped into normal (GerdQ score ≤ 4) and caution (GerdQ score ≥ 5), and their characteristics were analyzed according to the group. Results: The findings suggested 15 participants (7.4%) belonged to the GERD caution group. More non-office workers were in the caution group than in the normal group (P < 0.05). The participants’ smoking, physical activity, sleep duration, and pillow height were not significantly different between the GERD phenotypes; however, the caution group consumed alcohol more frequently than the normal group (P < 0.001). The analyses of the participants’ eating behaviors revealed that the frequency of overeating, late-night snacking and chocolate consumption was significantly higher in the caution group (P < 0.001). Conclusion: Lifestyle and dietary behaviors were associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Further studies with larger cohorts are required to confirm these findings.
- 5,525 View
- 71 Download

- [English]
- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middle-aged Korean adults: an intervention study
- Minji Kang, Young-Hee Park, Subeen Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Hyun Wook Baik, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):265-277. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
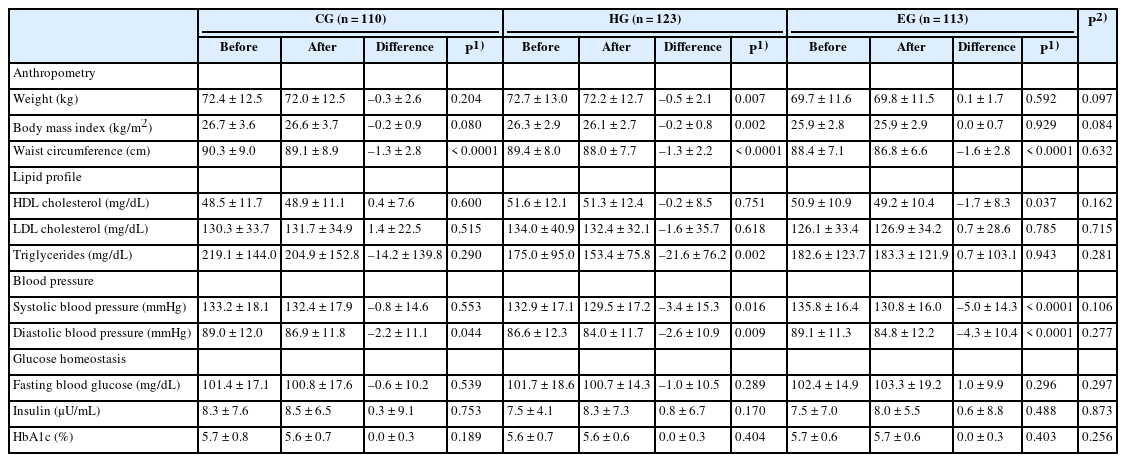
A total of 411 Korean adults 30–59 years of age were allocated randomly into three groups: the nutrition education group for promoting Han-sik consumption (HG), the nutrition education group for eating balanced diet (EG), and the control group (CG). The HG and EG received four face-to-face nutrition education sessions over 16 weeks to improve nutritional problems based on the individual’ usual diet. Effectiveness of the program was evaluated with the differences of self-reported dietary behaviors, dietary intakes, anthropometric measurements and biochemical indices between the baseline and the end of the nutrition education program. The changes within groups were analyzed using paired t-test and McNemar test and effectiveness among three groups was analyzed by repeated analysis of variance.
Results
After the nutrition education, the percentages of participants who achieved the recommended food group consumption in the Korean Food Guidance Systems significantly increased in HG (P = 0.022). Body weight (P = 0.007), body mass index (P = 0.002), and triglycerides (P = 0.002) significantly decreased in HG. Waist circumference and diastolic blood pressure decreased in all three groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
This study found that tailored nutrition education program for middle aged Korean adults showed beneficial effects on improving dietary behaviors and metabolic syndrome risk factors. Further studies are needed to assess the long-term effects of the nutrition education programs on metabolic syndrome risks.
- 4,186 View
- 85 Download

- [Korean]
- Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
- Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):466-479. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.466
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A mobile health intervention program was provided for employees with overweight and obesity for 12 weeks, and a process evaluation was completed at the end of the program. We investigated participant engagement based on app usage data, and whether engagement was associated with the degree of satisfaction with the program.
Methods
The program involved the use of a dietary coaching app and a wearable device for monitoring physical activity and body composition. A total of 235 employees participated in the program. App usage data were collected from a mobile platform, and a questionnaire survey on process evaluation and needs assessment was conducted during the post-test.
Results
The engagement level of the participants decreased over time. Participants in their 40s, high school graduates or lower education, and manufacturing workers showed higher engagement than other age groups, college graduates, and office workers, respectively. The overall satisfaction score was 3.6 out of 5. When participants were categorized into three groups according to their engagement level, the upper group was more satisfied than the lower group. A total of 71.5% of participants answered that they wanted to rejoin or recommend the program, and 71.9% answered that the program was helpful in improving their dietary habits. The most helpful components in the program were diet records and a 1:1 chat with the dietary coach from the dietary coaching app. The barriers to improving dietary habits included company dinners, special occasions, lack of time, and eating out. The workplace dietary management programs were recognized as necessary with a need score of 3.9 out of 5.
Conclusions
Participants were generally satisfied with the mobile health intervention program, particularly highly engaged participants. Feedback from a dietary coach was an important factor in increasing satisfaction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 53. CrossRef
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- 1,300 View
- 64 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Food and dish group diversity on menus of daycare centers provided by Center for Children’s Foodservice Management in Korea: a descriptive study
- Youn-Rok Kang, Kyeong-Sook Lim, Hyung-Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):449-465. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.449
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze menu patterns and food group diversity in daycare centers managed by the Center for Children's Foodservice Management in South Korea.
Methods
Data from 18 Center for Children's Foodservice Management centers across various provinces (excluding Jeju Island) were analyzed. We examined 8,796 meals served in February, May, August, and December 2021, focusing on seasonal lunch and snack menus for children aged 3-5. Foods were categorized into 19 groups for lunch and 21 for snacks. The frequency of food groups and dietary patterns were assessed using the Dietary Diversity Score. Analyses were conducted using Excel 2016 and IBM SPSS Statistics version 28.
Results
Most lunch menus (89%) included five menu items, with a ratio of grain, meat, and vegetables at 88%. Snack menus typically had one item (57%), with significantly more items in the afternoon compared to the morning (P < 0.001). Regarding snack patterns, 75.2% of morning snacks and 61.1% of afternoon snacks contained only one solid food and drink (P < 0.001). Fruit and milk (22.4%) was the most prevalent pattern in morning snacks, while grain and milk (31%) dominated afternoon snacks (P < 0.001). Only 48% of daycare center menus (all snacks and lunch) included all five food groups (grain, meat, vegetables, fruit, and milk). Notably, only 83% included milk and 57% included fruit.
Conclusions
These findings highlight the need to improve food variety and diversity in the Center for Children’s Foodservice Management-managed daycare center menus. Developing more detailed guidelines for menu structure and food composition is crucial to ensure children receive balanced and diverse nutrition. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 225. CrossRef
- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,360 View
- 33 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effectiveness of a mobile health intervention on weight loss and dietary behavior changes among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
- Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young-Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):141-159. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.141
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to determine whether a mobile health (mhealth) intervention is effective in reducing weight and changing dietary behavior among employees with overweight and obesity. The study also investigated whether engagement with the intervention affected its effectiveness.
Methods
The intervention involved the use of a dietary coaching app, a wearable device for monitoring physical activity and body composition, and a messenger app for communicating with participants and an intervention manager. A total of 235 employees were recruited for a 12-week intervention from eight workplaces in Korea. Questionnaire surveys, anthropometric measurements, and 24-h dietary recalls were conducted at baseline and after the intervention.
Results
After the intervention, significant decreases in the mean body weight, body mass index, body fat percentage, and waist circumference were observed. Furthermore, the consumption frequencies of multigrain rice and legumes significantly increased, whereas those of pork belly, instant noodles, processed meat, carbonated beverages, and fast food significantly decreased compared with those at baseline. The mean dietary intake of energy and most nutrients also decreased after the intervention. When the participants were categorized into three groups according to their engagement level, significant differences in anthropometric data, dietary behaviors, and energy intake were observed following the intervention, although there were no differences at baseline, indicating that higher engagement level led to greater improvements in weight loss and dietary behavior.
Conclusions
The intervention had positive effects on weight loss and dietary behavior changes, particularly among employees with higher engagement levels. These results indicate the importance of increasing the level of engagement in the intervention to enhance its effectiveness. The mhealth intervention is a promising model for health promotion for busy workers with limited time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 466. CrossRef - Systematic Review on the Study of the Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in Korea: Dietary Risk Factors
Eun Jeong Heo, Jae Eun Shim, Eun Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 191. CrossRef
- Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
- 1,923 View
- 64 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
- Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):38-47. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between the experience of disease management education and the use of nutrition labels according to the sociodemographic characteristics and health behaviors of people diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes living in the community.
Methods
Among the participants from the Community Health Survey (2018), 74,283 individuals diagnosed with hypertension or diabetes were included in the study population. According to gender, this study evaluated nutrition label use by the experience of disease management education, individual sociodemographic characteristics, and health behavior. Finally, using multiple logistic regression analysis, the association between disease management education and nutrition labels was calculated using the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results
Males (24.5%) experienced more disease management education than females (22.6%). In addition, younger age, higher education level, and higher equalized personal income experienced more disease management education (P < 0.001). The educational experience rate was higher in the male subjects who did not smoke or were involved in high-risk alcohol consumption (P < 0.001). In addition, the rate of disease management education experience was significantly higher for both men and women who exercised by walking (P < 0.001). The use of nutrition labels was higher in females (9.9%) than males (5.8%), and both males and females were significantly higher in young age, high education, high income, and professional and office positions (P < 0.001). The utilization rate of nutrition labels was high in non-smoking male subjects and high-risk-drinking female subjects. In addition, the utilization rate of nutrition labels was significantly higher in males and females who exercised by walking and those who experienced disease management education (P < 0.001). After adjusting for individual sociodemographic characteristics, health behavior, and disease management education, the use of nutrition labels was high among females (OR 3.19, 95% CI 2.85-3.58), high income (Q4; OR 1.62, 95% CI 1.41-1.87, Q5; OR 1.58, 95% CI 1.37-1.84) and highly educated (high school; OR 2.87, 95% CI 2.62-3.14, above college; OR 5.60, 95% CI 5.02-6.23) while it was low in the elderly (OR 0.43, 95% CI 0.40-0.47), and economically inactive (OR 0.86, 95% CI 0.76-0.96). The use of nutrition labels was high in non-smokers (OR 1.29, 95% CI 1.13-1.48), non-high-risk drinkers (OR 1.22, 95% CI 1.08-1.38), and subjects who exercised walking (OR 1.44, 95% CI 1.34-1.54). There was no difference in the utilization rate of nutrition labels according to obesity, and the utilization rate of nutrition labels was significantly higher in subjects who had experienced disease education (OR 1.34, 95% CI 1.24-1.44).
Conclusions
Education on the use of nutrition labels, which contributes to food selection for healthy eating, might be a tool for dietary management. Moreover, the utilization rate can be a good indicator for predicting the proportion of the population practicing the guide for disease management. Improving the utilization rate of nutrition labels through disease management education can be a useful intervention for people with chronic diseases who need healthy eating habits for disease management and preventing complications, particularly those diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Nutrition Label Utilization and Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: Using the Data of the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2021)
Ae-Seul Lee, Seong Woo Choi, So Yeon Ryu
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(3): 249. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Status and Life Satisfaction According to Food Security in Single-Person Households of Elderly Population
Dong Hoon Jung, Jae Won Han, Wonha Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(1): 42. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Dietary Behavior of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-sectional Study
Sohyun Jin, Youngshin Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 80. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Participation in Hypertension Management Education Among Diagnosed Hypertensive Patients in Busan: Utilizing the 2021 Community Health Survey
Hye Jung Jun, Kyoung Mi Kim
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 424. CrossRef - An association between socioeconomic status and preventive screening for diabetic eye and kidney complications among individuals with type 2 diabetes
Changwoo Shon, Jongnam Hwang
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(5): 27. CrossRef
- Association between Nutrition Label Utilization and Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: Using the Data of the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2021)
- 3,528 View
- 63 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Foodservice Status and Perception regarding Foodservice Management in Kindergartens attached to Elementary Schools in Seoul
- Ranmi Jung, Gun-Hee Kim, Jieun Oh, Sunny Ham, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):492-502. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.492
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examines the foodservice status of kindergartens attached to elementary schools in Seoul. We further determine the perception of elementary school principals and kindergarten assistant principals on the foodservice management for kindergartens.
Methods
This survey was conducted from July 17 to 23, 2019, enrolling 207 kindergartens attached to elementary schools in Seoul. Questionnaires were sent to principals of elementary schools and assistant principals of kindergartens, and the data obtained from 89 kindergartens were included in the analysis. The questionnaire consisted of four parts: general information on subjects, foodservice management status, foodservice management status during elementary school vacations, and the perception of principals of elementary schools and assistant principals of kindergartens on foodservice management. Data are presented as frequency and percentage or mean and standard deviation. Statistical comparison between principals of elementary schools and assistant principals of kindergartens was conducted by paired t-test, chi-square test, and Pearson's correlation analysis.
Results
A separate menu (10.1%) or recipe (20.2%) that considers preschooler characteristics was rarely used for foodservice at kindergartens attached to elementary schools. Most kindergartens did not have a separate dining space (3.4%) or a dedicated cook (93.3%). Although most kindergartens (92.1%) had operational foodservice during elementary school vacations, non-professional staff and non-nutrition teacher were mainly in charge of organizing the menu and purchasing ingredients (34.1% and 41.5%, respectively). The rate of using a contract catering company (28.0%, 23.2%) was also high. Both elementary school principals and assistant principals of kindergartens showed a high perception of the necessity for providing responsibility allowances for nutrition teachers and improving the cooking environment for kindergartens during elementary school vacations.
Conclusions
There is a need for policies and administrative support measures to improve the quality of foodservices for kindergartens attached to elementary schools. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef - A Study on the Menu Patterns and Menu Diversity of Bibimbap Meals Served by Elementary School Foodservices in the Jeonbuk Area
Sun A Choi, Chohee Mun, Jieun Go, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 444. CrossRef
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- 1,003 View
- 12 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- The Consumption Pattern of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and its Comparison with Body Composition Change from a Four-Week Time-Restricted Eating Intervention in Korean Young Adults
- SuJeong Park, YoonJu Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(1):36-46. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.1.36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the consumption pattern of sugarsweetened beverages (SSB) and compare body composition changes by SSB consumption based on 28 days of dietary records from a four-week time-restricted eating intervention among young adults in Korea.
Methods
A total of 33 participants completed the four-week dietary intervention with 8-hour time-restricted eating (TRE). The body composition was measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis at baseline, and daily dietary records were collected for 28 days during the intervention after 4 weeks.
Results
Based on 924 days of dietary records, the average eating occasion of SSB was 0.9 times per day, and the average amount of SSB was 205.8 g/times. Based on an individual’s usual intake of 28 days, the average eating frequency of SSB was 16.6 times out of 28 days, and the average amount of SSB was 184.0 g/day. The average energy intake from SSB was 131.0 kcal /day (8.7% of energy), and sugar intake from SSB was 18.2 g/day (4.9% of energy). The sugar intake was 2.6% of energy from sweetened dairy products, followed by 2.0% from coffee drinks, 0.5% from soda and juice and 0.2% from others. When subjects were divided into high (14 days or more) and low (less than 14 days) SSB groups based on eating frequency, the weight change in the low SSB group was -2.0 kg over 4 weeks, which was significantly lower than -0.7 kg in the high SSB group. However, no significant difference was found in muscle mass, fat mass and body fat percent between the two groups.
Conclusions
This study suggests that low consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages is more desirable in weight management despite having the dietary intervention of timerestricted eating without counting calories. Thus, further longitudinal studies on the association between SSB and obesity in Korean adults are necessary. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitude, and Dietary Behavior among Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Na-Yeon Noh, So-Young Nam, Hee-Suk Kang, Ji-Eun Lee, Soo-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(2): 101. CrossRef - Needs Assessment for Web-based Self-management Program by the Nutrition Knowledge Levels of Diabetic Patients
Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Jung Eun Youn, Hee-Seon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(1): 155. CrossRef
- Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitude, and Dietary Behavior among Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
- 1,534 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Management of Food Allergy in the Facilities Registered at Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Gangdong-gu
- Soon Mi Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):396-407. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.396
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We examined the common allergenic foods, symptoms and management of food allergies in children attending the facilities registered at Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Gangdong-gu, Korea. Methods: The survey was conducted among the directors or head teachers of 186 children’s food service facilities with 7,591 children in 2019. The questionnaire consisted of three parts, including general information about food service facilities, information related to food allergies and allergenic foods and symptoms in individual children. Results: The number of children with food allergy was 271 (3.6%), and the proportion decreased with the increase of age. There were 91 children (33.6%) with a medical certificate, and these children had a significantly higher number of allergenic foods and symptoms than those without a medical certificate. Allergenic food groups included meat, fish, eggs and legumes (59.1%), fruits (12.4%), milk and dairy products (8.9%), cereals (7.8%), vegetables (6.2%), processed foods (3.8%) and oils and sugars (1.9%). Eggs accounted for 22.1%, followed by peanut and tree nuts (18.6%), fruits (12.4%), milk and dairy products (8.9%), shellfish (8.6%), vegetables (6.2%), fish (5.7%), cereals (4.3%) and meat (1.1%). The common allergenic foods were eggs, peanuts, walnuts, kiwi, shrimp, milk, tomatoes, mackerel, blue-green fish, peaches, shellfish (clams and abalone), buckwheat, wheat and soybeans. The most common allergic symptoms were skin and mucous membrane symptoms, such as hives, rash, itching and oral angioedema. Meal management for children with food allergies showed different trends depending on the causative food. Conclusions: The objective diagnosis by an allergist should be done for food allergy management in children's catering facilities. A system for systematic meal management of causative foods should be prepared. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Knowledge and management of food allergy by parents of preschool children who experience food allergies
Seung Hui Kim, Seung-Min Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 184. CrossRef - Knowledge of atopic dermatitis and food allergies, as well as health information literacy, among North Korean refugee mothers: a descriptive survey study
In-Sook Lee, Jeong-Hee Jeon
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(4): 300. CrossRef
- Knowledge and management of food allergy by parents of preschool children who experience food allergies
- 1,878 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
- Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):363-381. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the Korean elderly’s dietary intake status, subjective health-related perception and chronic disease prevalence among age groups. Associations of dietary quality with subjective health-related perception and chronic diseases were also examined.
Methods
Based on data from the 7th National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a total of 3,231 elderly were selected and categorized into 4 age groups of ‘65 ~ 69’, ‘70 ~ 74’, ‘75 ~ 79’ and ‘over 80’. Nutrient intakes, proportions of those with insufficient nutrient intakes, Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI), some subjective health-related perceptions and prevalence of major chronic diseases were compared according to the age groups. Differences in the subjective health-related perceptions and odds ratios of the chronic diseases according to the quartile levels of KHEI within the same age group were analyzed.
Results
With the increase of age, several nutrient intakes (P < 0.001) and KHEI scores significantly decreased (P < 0.01). In women, activity restriction increased (P < 0.05), and EQ-5D score decreased with age (P < 0.001). Prevalence of hypertension (P < 0.0001), hypercholesterolemia (P < 0.05) and anemia (P < 0.01) significantly increased, while hypertriglyceridemia (P < 0.01) significantly decreased only in men. Obesity prevalence decreased, while underweight prevalence increased (P < 0.05). Subjective health status, EQ-5D score and PHQ-9 score significantly improved as KHEI score increased in certain age groups of women (P< 0.05). Odds ratio of hypercholesterolemia significantly increased with the increase of KHEI score in 65 ~ 69-year-old women. However, hypertension and anemia significantly decreased with the increase of KHEI score in 75 ~ 79-year-old women (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
The study findings suggest that nutrition management and policy for the Korean elderly need to apply a segmented age standard that can better reflect their dynamic characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 359. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef - Blood Biochemical Characteristics, Dietary Intake, and Risk Factors Related to Poor HbA1c Control in Elderly Korean Diabetes Patients: Comparison between the 4th(2007-2009) and the 7th(2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 406. CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 422. CrossRef
- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
- 1,548 View
- 21 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
- Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):350-362. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.350
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated an association between sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) intake and the dietary quality of adults in Deagu, Korea.
Methods
A questionnaire survey was conducted in 1,022 adults aged 19 ~ 49 years (502 men and 520 women) in the Deagu area of Korea. Daily intake of SSB was obtained by the food frequency questionnaire, and the dietary quality was assessed using the nutrition quotient (NQ) for Korean adults. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to estimate the association between dietary quality and daily intake of SSB in adults.
Results
Daily intake of SSB was 463.6 mL/d for total subjects, and the highest intakes were sweetened coffees (192.7 mL/d), followed by carbonated drinks (77.1 mL/d). Higher intake of SSB was associated with higher intake frequency of fast food or sweet and greasy bread, processed beverage, ramyon, eating out or delivery food and night snack, and also associated with lower frequency of water, breakfast intake and nutrition label checking in men or women. Men and women who had a higher intake SSB had significantly greater odds for being in the low grade of NQ (P for trend = 0.0006 for men, P for trend = 0.0007 for women), especially in the moderation factor (P for trend < 0.0001 for men and women).
Conclusions
This study showed that high SSB intake was significantly associated with low dietary quality among adults. These study results suggest that nutrition education programs and guidelines should be provided to adults for improving their consumption of SSB and related diets. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the dietary quality among Chinese adults living in Shanghai and the Anhui Province using the Nutrition Quotient for adults
Ani Liu, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 117. CrossRef - Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - Nutritional and Health Status According to the Frequency of Carbonated Beverage Consumption among Adults in Their 20s : Based on the 2019-2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
You-Sin Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(3): 159. CrossRef - Study on the Dietary Behaviors and Eating Habits of University Students in the Gyeongnam Region in the Post-COVID-19 Era Using the Nutrition Quotient for Adults
Joo Sun Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 470. CrossRef - Nutritional status of Daejeon citizens and needs of community nutrition care services: a cross-sectional study
Dahye Lee, Minsun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 11. CrossRef - Sex-Based Differences in Factors Associated With Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Among Korean High School Students
Jin Suk Ra, Moonkyoung Park
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessment of the dietary quality among Chinese adults living in Shanghai and the Anhui Province using the Nutrition Quotient for adults
- 1,117 View
- 13 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A Study on the Dietary and Lifestyle Changes of Middle-Aged Women in the Gwangju Area in the COVID-19 Era
- Moon-Soon Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(4):259-269. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.4.259
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the changes in the eating habits and lifestyle of middle-aged women in Gwangju during the COVID-19 pandemic. Methods: A total of 428 middle-aged women aged between 40 and 60 participated in a survey relating to general information, food and lifestyle, health functional food, and menopausal symptoms. The correlation between the variables was analyzed. Results: In the positive habits, the intake of nutritional supplements for immunity enhancement increased the most, followed by the use of media to learn healthy eating tips, and diets including healthy food. Negative habits increased in the order of frequency of taking delivery orders, levels of stress or anxiety, and time spent sitting or watching movies. In the case of recommended foods, the intake increased the most in the order of eggs, fruits, vegetables, milk/dairy products, and seaweed. Non-recommended foods increased in the order of meat, bread, rice, and noodles. The awareness of health functional foods was in the increasing order of interest, knowledge, consumption experience, and purchase amount. The type of health functional food intake was in the increasing order of probiotics, multivitamin and mineral supplements, vitamin C, collagen, and omega-3. Menopausal symptoms were in the increasing order of bone and joint pain, poor sleep quality, emotional ups and downs, loneliness, and feeling of emptiness. In the correlation of major variables, positive habits showed a significant positive correlation with recommended food intake and the recognition of health functional foods. Negative habits showed a significant positive correlation with non-recommended food intake and a significant positive correlation with menopausal symptoms. Recommended food intake showed a significant positive correlation with health functional food recognition and intake and menopausal symptoms. Conclusions: This study suggests that it is necessary to establish social measures to reduce the negative effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on middle-aged women and to ensure effective self-management through a healthy lifestyle since the pandemic has a long-term impact. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial
Ingyeong Kang, Hyunsook Jang, Minchul Gim, Sang Eun Bae, Yu Jin Lee, Chai Sun Leem, Yoo Kyoung Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(17): 2801. CrossRef - Comparative study on the health and dietary habits of Korean male and female adults before and after the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: utilizing data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Chaemin Kim, Eunjung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 65. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics of Staple Breads Based on Baking Methods
Eun-Hee Doo
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 77. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
Eunyoung Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 220. CrossRef - Changes in dietary habits and chronic diseases before and after COVID-19 by regions using data from the 2018-2020 Korea Community Health Survey and Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods: a cross-sectional study
Surim Park, Eun-hee Jang, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(2): 124. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - Consumers’ perceptions of dietary supplements before and after the COVID-19 pandemic based on big data
Eunjung Lee, Hyo Sun Jung, Jin A Jang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 330. CrossRef - Self-rated health according to change of lifestyle after COVID-19: Differences between age groups
Dan Bi Lee, Jung Hyun Ahn, Jin Young Nam
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(2): 1. CrossRef - Factors Related to Changes of Daily Life during COVID-19
Kyungjin Min, Pilhan Yun, Sangshin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(4): 297. CrossRef - Dietary Behavior and Diet Quality in the Korean Adult Population by Income Level before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic: Using the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2020)
Hye-Min Na, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(3): 397. CrossRef
- Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial
- 1,361 View
- 10 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Status of Sanitary and Nutritional Food Service in Elderly Day Care Center
- Jeong hyeon Woo, Yoo Kyoung Park, Mi-Hyun Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee, Kyung hee Song, Hye-Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):374-385. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to examine the status of foodservice management, with special interest on sanitary and nutritional food service in elderly day care centers. Methods A total of 79 employees who managed foodservice facilities in elderly day care centers were included in the survey. The contents of the questionnaire consisted of general characteristics, importance and performance of sanitary and nutrition management, the reasons for poor performance, factors necessary for improvement, and the employee's demand for support. Data analysis was conducted using the SPSS v25.0. Results Sanitary management showed an average importance score of 4.84 ± 0.40 and a performance score of 4.70 ± 0.61 (t-value: 8.260). The item with the lowest performance score was personal sanitary management (4.58 ± 0.71). In nutrition management, the average importance score was 4.52 ± 0.68, and the performance score was 4.20 ± 1.00 (t-value: 9.609). There were significant differences between the average score of importance and performance in both areas. As a result of an Importance-Performance Analysis, items that were recognized as important but had relatively low performance was “personal hygiene”, “ventilation” and “food storage”. Also in the nutritional management area, “menu planning for disease management” and “checking the saltiness in the soup” etc. had very low performance with low importance recognition. The items shown in the “low priority” quadrant were those that required professional management skills. In the areas that demanded support in foodservice management, education about sanitary and safe institutional food service had the highest score (4.42 ± 0.74), and all other items showed a demand of 4 points or more. Conclusions Foodservice managers recognize the importance of foodservice facility management but performance is relatively low. Institutional support is, therefore, needed to improve performance. For items with low importance, it seems necessary to improve awareness of the necessity of these items and to provide education in this regard. To gradually improve foodservice management, continuous provision of education and training in these areas are of great importance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
Do Hee Kim, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(4): 421. CrossRef - A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
Seo Young Choi, Hyun joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 286. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Snack Provision Practice in Long-Term Care Hospitals and Facilities in Korea
Dayeong Yeo, Hae Jin Kang, Hyejin Ahn, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(2): 108. CrossRef - Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 359. CrossRef - Sanitation Management Performance According to the Characteristics of Coffee Franchise Shops and Sanitation Knowledge According to the Characteristics of Employees
Suk-Kyoung Gu, Sunyoon Jung, Inyong Kim, Yoonhwa Jeong
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(11): 1248. CrossRef - Analysis of Awareness, Knowledge, and Behavior about Food Hygiene·Safety Among the elderly
Mi Sook Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 200. CrossRef
- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
- 1,020 View
- 13 Download
- 7 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
- Na Yeong Lee, Yeon Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):13-20. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the salinity of soups provided at childcare centers by measuring the salinity for three years and providing basic data for sodium reduction.
METHODS
The soup salinity was measured using a Bluetooth salinity meter from January 2015 to December 2017 at 80 childcare foodservice establishments enrolled in the Suseong Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Daegu.
RESULTS
An analysis of the soup salinity each year showed that the salinity decreased significantly from 0.48% in 2015 to 0.41% in 2017, particularly in clear soups and soybean soups compared to other soups (P < 0.05). The salinity and sodium content in seafood soups (0.45% and 179.1 mg/100 g, respectively) were highest, followed by soybean soups (0.44%, 175.2 mg/100 g), with perilla seed soups containing the lowest (0.42%, 167.2 mg/100 g) (P < 0.05). The salinity was significantly higher in institutional foodservice establishments than small foodservice establishments (P < 0.001). The salinity and sodium content were the highest in foodservice establishments with a small number of measurements, and the salinity was the lowest in foodservice establishments with salinity measurements performed an average of 151 times each year (three times a week) or more (P < 0.05). The soup salinity was low in the order of winter, spring, summer, and autumn, and the salinity decreased significantly year by year in all seasons. (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The soup salinity was significantly lower in foodservice establishments where the salinity was measured more than three times a week, indicating that continuous salinity management is effective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
Do Hee Kim, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(4): 421. CrossRef - Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 386. CrossRef
- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
- 1,474 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Effect of Geographic Area on Dietary Quality across Different Age Groups in Korea
- Hyun Ja Kim, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):453-464. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.453
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to examine whether dietary quality varies among different age groups and geographic areas, and whether the difference between geographic areas varies across several age groups in Korea.
METHODS
The subjects were 14,170 subjects who participated in the 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The dietary quality was assessed using the Korean Health Eating Index (KHEI). Age groups were categorized into six groupings, and areas were categorized into urban and rural according to their administrative districts. The effect of area on the KHEI score was analyzed by multiple linear regression analysis.
RESULTS
The KHEI was the lowest in the 20-30s group (57.7 ± 0.4 score for 20s and 61.2 ± 0.3 score for 30s) and increased with age (p<0.001), showing the highest score in the 60s (67.9 ± 0.3 score), and then decreased again in the 70s and older (64.6 ± 0.3 score). As a result of comparing the KHEI score by area, the urban areas had higher KHEI scores than did the rural areas (63.5 ± 0.2 score for urban area and 62.2 ± 0.4 score for rural area, p=0.002). The difference between areas was dependent on the age group, showing a significant difference for subjects who were aged from 50s and older (p=0.002 for 50s, p<0.001 for 60s and p<0.001 for 70s and older). After adjusting for confounding factors, the effect of area on the KHEI score was only shown for those subjects in the over 60 years old group (p=0.035 for 60s and p<0.001 for 70s and older).
CONCLUSIONS
The dietary quality differed according to the age group and geographic area. The dietary quality was lower for younger people than that for older people, and in rural areas compared to that in urban areas, and especially for older adults. The area factor was a very important factor for the dietary quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary habits of Koreans aged 95 years and older residing in rural and metropolitan areas
Jieun Mun, Sein Kim, Suyoung Kim, Seunghee Kim, Sang Chul Park, Jae-Young Han, Kwangsung Park, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 66. CrossRef - Prediction model for identifying a high-risk group for food insecurity among elderly South Koreans
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual- and neighborhood-level factors influencing diet quality: a multilevel analysis using Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data, 2010-2019
Dahyun Park, Min-Jeong Shin, S V Subramanian, Clara Yongjoo Park, Rockli Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2025; 47: e2025043. CrossRef - Risk of all-cause mortality is associated with multiple health-related lifestyle behaviors and does not differ between urban and rural areas in Korea
Seunghee Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(4): 554. CrossRef - Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 173. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Perceived Community Food Accessibility Measurement Questionnaire for Korean Older Adults
Jisoo Hong, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(19): 4301. CrossRef - Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Regional Difference in the Effect of Food Accessibility and Affordability on Vegetable and Fruit Acquisition and Healthy Eating Behaviors for Older Adults
Dong Eun Lee, Kirang Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 14973. CrossRef - Regional Differences in Dietary Total Fat and Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Their Associations with Metabolic Diseases among Korean Adults: Using the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 495. CrossRef - Basic Concepts and Detailed Dimensions of Food Security and Related Indicators for Policy Development and Evaluation
Sohyun Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 429. CrossRef
- Dietary habits of Koreans aged 95 years and older residing in rural and metropolitan areas
- 1,305 View
- 7 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
- Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(5):408-421. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.5.408
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study compared the dietary behaviors of single-person households when eating alone according to the employment pattern and age.
METHODS
A total of 566 people aged 20~59 years old were collected from the status of workers and classified into three groups according to their employment pattern (regular, non-regular workers and business owner). The subjects were collected by purposive quota sampling on a Gallup panel from June to November in 2017. The dietary behavior and perception of eating alone of the subjects were surveyed via online and self-reported questionnaires.
RESULTS
The frequency of eating alone was significantly higher in the regular group than the non-regular group and business group (p<0.01). The place of eating alone was significantly higher in the regular and non-regular group in the convenience store, and business group in the office (p<0.001). Ramen, the menu when eating alone, was significantly higher in the non-regular group than the other groups (p<0.01). The preference for eating alone was lower in the older age group (p<0.05). The young aged group (aged 20~30) ate more fast food and felt more convenience than the older aged group aged 40~50 years (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Single-person households with a non-regular job have poorer dietary behavior in eating alone than those who had regular employment. In a situation of an increasing number of non-regular workers aged in their 20s and 30s, there is a high likelihood of social problems, such as health and poverty. This study highlights the need for a healthy food selection environment to improve the dietary life of single-person households with non-regular jobs for the diverse types of single-person households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The de-structuration of eating models in East Asia under compressed food modernity: An empirical synthesis
Haruka Ueda, Yu-Chan Chiu
Appetite.2024; 203: 107680. CrossRef - Analysis of the Effect Size of Insect Foods on Metabolic Syndrome-Related Indicators
Chan-Hwi Lee, Ae-Jung Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 860. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Analysis of Agrifood Consumer Competency and Dietary Satisfaction according to Household Type Using the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Meera Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 414. CrossRef - Association between Prediabetes and Meal Patterns Related to Meal Sharing among Korean Young Adults: Eighth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2019–2020
Saebom Kim, Sehee Kim, Youngmin Kim, Seonmi Seo, Yu Jin Chung, Sam Cheol Kim
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(3): 179. CrossRef - Impact assessment of a primary care physician counseling program for youth population
Yun-Su Kim, Shin-Ae Kim
Medicine.2022; 101(46): e31916. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Habits and Health-Related Factors According to the Employment in Women in Early Adulthood - Based on the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yun-Jung Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(4): 249. CrossRef - Gender and age group differences in nutrition intake and dietary quality of Korean adults eating alone: based on Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data, 2013–2016
Yoonjin Ahn, Youngmi Lee, Haeryun Park, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(1): 66. CrossRef
- The de-structuration of eating models in East Asia under compressed food modernity: An empirical synthesis
- 1,844 View
- 14 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Status and Needs Assessment on Nutrition Management and Meal Service for Elementary · Middle · High School Athletes among Athlete's Parents
- Jung Hyun Hwang, Ji Yeon Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):47-59. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.47
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Young athletes require adequate nutrition to maintain their athletic performance, growth and health. This study examined the status and needs of nutrition management and meal services for student athletes among the athlete's parents.
METHODS
The subjects were parents of elementary, middle, and high school athletes (n=323) from 18 schools participating mainly in the Sports Food Truck. The questionnaire included general characteristics, status and needs on nutrition management and meal service for student athletes, and satisfaction with the Food Truck. The survey was done during 2018. The data were analyzed according to the school groups using a χ2-test or ANOVA.
RESULTS
Approximately 45% of subjects had difficulty in the nutrition management of athletes, and 87.1% had not received nutrition education. Approximately 74% wanted nutrition education held for athletes, and mainly wanted topics on nutrition management for health and eating for athletic performance. The preferred methods were lectures and cooking activity. The responses on the necessity of nutrition education for athletes, desired education topics, and desired times for education differed significantly according to the school groups (p < 0.05). Most subjects also wanted nutrition information mainly through SNS. In the athlete's meal, breakfast and snacks were highlighted as the meal to supplement. Approximately 90.3% responded that providing a meal service is necessary. The subjects preferred snacks before/after exercise and dinner if a meal service was provided. They preferred Korean food, followed by snacks, and a dish meal. As the meal type, the subjects wanted the Food Truck and packed meal. The responses on necessity of a meal service (p < 0.05), preferred food (p < 0.001), and meal type (p < 0.001) in the meal service differed significantly according to the school groups. Approximately 43% were satisfied with the Food Truck and 50.8% responded as average. They made suggestions for the Food Truck in terms of foods, operations and frequency.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the study results, nutrition education and meal service may support nutrition for student athletes considering the needs of the parents according to the school groups.
- 1,054 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- The Effect of Personality Type and Job Performance on Emotional Exhaustion and Job Satisfaction - Staff of the Center for Children's foodservice management -
- Kyung Min Lee, Min Sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):496-505. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.496
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the relationship between the personality traits and job performance of Centers for Children's Foodservice Management (CCFSM) staff on emotional exhaustion and job satisfaction. In addition, the characteristics of the center organization were examined to provide practical guidelines for the operation of the center. The aim was to determine management implications with an important meaning in human resource management to enhance the efficiency of the operation of Centers for Children's Foodservice Management (CCFSM).
METHODS
Out of 207 centers, there were 1,057 employees at 173 centers who agreed to participate in the study, the questionnaire was mailed on February 17, 2017 and collected by mail on March 31, 2017. Finally, 81 centers (46.82%) participated in the survey and 493 questionnaires were used.
RESULTS
Neuroticism among the five personality factors had a positive (+) influence on ‘cynicism’ and ‘exhaustion’ among the three subordinate factors of emotional exhaustion, negative (−) effects on the ‘job’ among the six subscales of job satisfaction. In addition, openness showed a negative (−) effect on ‘loss of professional confidence’ of emotional exhaustion and positive (+) relationship with the ‘job’ of job satisfaction. Agreeableness appeared to have a negative (−) effect on all factors of emotional exhaustion and a positive (+) influence on all factors of job satisfaction. As a result of analyzing the effects of job performance on emotional exhaustion and job satisfaction, the planning and operations management team showed a positive (+) influence on all factors of emotional exhaustion and negative (−) influence on all factors of job satisfaction. On the other hand, the nutrition management team showed a negative (−) influence on all emotional exhaustion factors and a positive (+) influence on the factors of job satisfaction. The hygiene management team showed a positive (+) relationship with ‘Emotional exhaustion’ among the subordinate factors of emotional exhaustion and a negative (−) influence on the ‘Educational opportunity’ of job satisfaction.
CONCLUSIONS
The personality type and job performance of Centers for Children's foodservice management (ccfsm) staff significantly affected the emotional exhaustion and job satisfaction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the relationship between employee perception of overqualification, job burnout, and impulsive buying behavior
Li Chaoyang, Fang Yuanhan, Yu Zengyuan, Li Huitao
Current Psychology.2025; 44(6): 5238. CrossRef
- Study on the relationship between employee perception of overqualification, job burnout, and impulsive buying behavior
- 854 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Cost-benefit Analysis of Nutrition Management Program for Children Aged Under 5 Years in DR Congo
- Tae Ho Lee, Chae Eun Lee, Eun Woo Nam
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(5):385-396. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study aims to evaluate the economic efficiency of a nutrition management program for children under 5 years of age in Kenge, Kwango District, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DR Congo) from 2014 to 2016.
METHODS
The economic efficiency of a nutrition management program for children under 5 years of age who have recovered from malnutrition status was evaluated using a cost-benefit analysis. The costs were analyzed according to the executed budget incurred during the project period. The benefits were estimated as the monetary value of the saved lives of children under 5 years of age. The economic efficiency of the program was determined by the Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR). The BCR was calculated by dividing the total discounted benefit by the total discounted costs. The project is economically efficient when the BCR is greater than 1.
RESULTS
The costs of the nutrition management program were calculated as 1,677,609,648 Korean Won (KRW). A total of 2,466 children survived with improved malnutrition status through this program. The benefit for the reduction of mortality for children under 5 years of age was estimated to be 6,814,354,467 KRW, the estimated value of life for 2,466 children. The BCR was 4.06.
CONCLUSIONS
The nutrition management program for children under 5 years of age in DR Congo was found to be a cost-effective project. Successful and efficient Official Development Assistance (ODA) for a health project requires integrated and comprehensive strategies and specialized international development consulting to improve efficiency. Future nutrition management programs should take into account the national health program to maintain the sustainability of the project. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of Public Physical Therapy Infrastructure on Community Health Impact Costs : A Comparison of Metropolitan and Rural Cities
Chong Yeob Kim, Jung-Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academy of Physical Therapy Science.2025; 32(2): 75. CrossRef
- The effect of Public Physical Therapy Infrastructure on Community Health Impact Costs : A Comparison of Metropolitan and Rural Cities
- 1,676 View
- 15 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Field Application and Evaluation of Health Status Assessment Tool based on Dietary Patterns for Middle-Aged Women
- Hye Jin Lee, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):277-288. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.277
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to verify the validity and judgment criteria setting of a health status assessment tool based on dietary patterns for middle-aged women.
METHODS
A total of 474 middle-aged women who visited the Comprehensive Medical Examination Center at Hanmaeum Hospital in Changwon were enrolled (IRB 2013-0005). The validity was verified using clinical indicators for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome (MS), and it was used to set the criteria for the tool. A logistic regression analysis was performed for validation. The area under-receiver operation (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and Youden Index were calculated through ROC curve analysis. Statistical analysis was performed by SPSS 21, and p value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
The mean score of the group with no MS (73.3 points) was significantly higher compared to the group with MS (65.7 points) (p < 0.001). An analysis of the association between the tool scores and risk of MS showed a 0.15-fold reduction in the risk of MS every time the tool's score increased by one point. As the result of the ROC curve analysis, the assessment reference point was set to 71 points, indicating 77.0% sensitivity and 61.0% specificity. Risk of MS was significantly higher in the group with a score of less than 71.0 than a group with more than 71 points (OR=5.28, p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
This study was the first attempt to develop a health status assessment tool based on the dietary patterns for middle-aged women, and this tool has proven its usefulness as an MS assessment tool through the application of middle-aged women in the field of health screening. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of milk and dairy product consumption with the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular disease incidence in middle-aged and older Korean adults: a 16-year follow-up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Yeseung Jeong, Kyung Won Lee, Hyekyeong Kim, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1225. CrossRef
- Association of milk and dairy product consumption with the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular disease incidence in middle-aged and older Korean adults: a 16-year follow-up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
- 1,096 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Status and Suggested Future Directions of Nutrition Intervention using Healthy School Tuck Shops: the Teenage Perspective
- Suhyun Oh, Kirang Kim, Ji Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):226-233. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the current status and to suggest future directions for health management of teenagers who use healthy school tuck shops to improve teenagers' eating habits while reducing and preventing obesity.
METHODS
A total of 29 students (16 middle school students and 13 high school students) took part in the interview for this study, and the interview was conducted for each school's focus group by using qualitative research methodology.
RESULTS
The current status of using healthy school tuck shops and suggested future directions were divided into two categories. Personal barriers such as discrepancies between personal perceptions and behaviors and lack of food choice suitable to individual tastes can be solved by rebuilding the operating system to provide intuitive promotion of behavior and customized products through improvements in existing products and new product development. A lack of consistent management from low utilization convenience and difficulty in maintaining a constant purchase price can be handled by establishing a solution to restricted physical access for products, as well as seeking profit by improving distribution costs via continuous cooperation between the school and community.
CONCLUSIONS
Continuous funding and a system that reflects the needs and preferences of healthy school tuck shop users should be applied for sustainable operation of healthy school tuck shops to improve teenagers' eating habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
Eun-Jin Choi, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 102. CrossRef
- Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
- 1,080 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Health Behavior Factors Associated with Sugar-sweetened Beverage Intake among Adolescents
- Hyae Min Gu, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):193-201. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to measure the intake rate of SSBs (sugar sweetened beverages) and examine the relationship between health behavior factors and SSBs intake by adolescents.
METHODS
This study used data from the 2016 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey, which included 65,528 study participants. SSBs intake frequency was measured by asking respondents if they consumed soda, high-caffeinated beverages, and sugary drinks during the previous week. Type of intake was categorized into three groups according to the number of consumed drinks [SSBs (0): None; SSBs (1–2): 1 or 2 consumed; SSBs (3): 3 consumed]. Multinomial logistic regression analysis was used to examine health behaviors that affected SSBs consumption.
RESULTS
Increased SSBs intake was significantly correlated with current smoking (OR=2.4, 95% CI=1.82–3.17), current drinking (OR=2.13, 95% CI=1.82–2.51), sedentary time increase (OR=1.31, 95% CI=1.15–1.49), three days or more physical activity per week (OR=1.12, 95% CI=1.02–1.24), < 8 hours sleep (OR=1.6, 95% CI=1.43–1.78), increased internet usage time (OR=1.44, 95% CI=1.25–1.65).
CONCLUSIONS
Sugar-sweetened beverages intake by Korean adolescents was associated with health behaviors such as smoking, drinking, sedentary time increase, more physical activity, poor sleeping time, and increased internet use time. Based on these results, it is necessary to recognize the influence of SSBs intake and to intervene to reduce consumption of SSBs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-Related Behaviors and Perceived Health Status According to Water and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Korean Adolescents
Yoon Sun Kim, Hyun Ja Kim
Nutrients.2024; 16(17): 3038. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef - Dietary behavior of school-going adolescents in Bhutan: Findings from the global school-based student health survey in 2016
Tshering Choeda, Kathiresan Jeyashree, Soundappan Kathirvel, Thinley Dorji, Kinley Dorjee, Karma Tenzin, Sangay Thinley, Tashi Tenzin, Mongal Singh Gurung
Nutrition.2021; 90: 111290. CrossRef - Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 350. CrossRef - Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and influencing factors in Korean adolescents: based on the 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Ayoung Kim, Jinhee Kim, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 465. CrossRef
- Health-Related Behaviors and Perceived Health Status According to Water and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Korean Adolescents
- 2,275 View
- 17 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Development and User Satisfaction of a Mobile Phone Application for Image-based Dietary Assessment
- Seo Yoon Kim, Sang Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(6):485-494. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.6.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to develop mobile phone application for image-based dietary assessment and evaluate satisfaction regarding respondent's use of the mobile phone application.
METHODS
We developed a mobile phone application to assess dietary intakes using 24 hour dietary recall. After initial development, application was reviewed by ten adults and revised based on their comments. We recruited 192 volunteers (92 males, 100 females) to use the mobile phone application and to respond to a satisfaction survey. Participants were instructed to use the mobile phone application with fiducial marker five centimeter in width, length and two centimeter height at each eating occasion during designated 4 days, capturing 45° angle and 90° angle images of all food and beverage items before and after consumption. After using the mobile phone application for 4 days, participants were asked to complete an online questionnaire on the satisfaction of the mobile phone app. User satisfaction items composed of 12 questions of application user interface, 8 questions of emotional response, 9 questions of eating behavior in 5 likert scale. Participants were also asked to provide additional open-ended comments on the use of mobile phone application. Statistical analysis was performed by using the SPSS 23.0 (Statistical Package for the Social Science).
RESULTS
The average user interface score was 2.82 ± 1.08, which was close to the ‘normal’ response. Responses for emotion and eating behavior also were borderline to the ‘normal’.
CONCLUSIONS
This study found that the mobile phone application using 24-hour recall was acceptable to be used to assess dietary intakes for several days. However, there should be a need for such technology to be user-oriented instead of researcher-oriented. Easy and cost-effective new technology is needed for estimating the amounts of food eaten automatically when the photos are taken. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diet status of college students evaluated by applying the photographic analysis method
Chae Hong Lee, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 439. CrossRef - Validity of Estimating Sodium Intake using a Mobile Phone Application of 24-hour Dietary Recall with Meal Photos
Seo-Yoon Kim, Sang-Jin Chung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(4): 317. CrossRef
- Diet status of college students evaluated by applying the photographic analysis method
- 1,174 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Relation between Beverage Consumption Pattern and Metabolic Syndrome among Healthy Korean Adults
- Eun Ju Dennis, Minji Kang, Sung Nim Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(5):441-455. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.5.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study is to describe beverage patterns among healthy Korean adults and investigate their association with prevalence and components of metabolic syndrome.
METHODS
Subjects consisted of 6,927 Korean adults, aged 19-64 years in the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES, 2013-2015). Beverages were regrouped into twelve groups based on food codes and beverage intake (g/day) was assessed by 24-hour recall. Factor analysis was used to obtain beverage patterns. Waist circumference and body mass index (BMI) were used as anthropometric data; fasting blood glucose, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein (HDL), and blood pressure were used as biochemical indicators. The odds ratio (OR) for prevalence of metabolic syndrome and components of metabolic syndrome was assessed using logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS
Three beverage patterns were identified using factor analysis: 1) carbonated soft drinks 2) coffee (without added sugar or powdered creamer), and 3) alcoholic beverages. Subjects with high scores for the carbonated soft drink and coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer patterns were younger and subjects with high scores for the alcoholic beverage pattern were older. There were significant differences in gender distribution in all three beverage patterns, with men more likely to have high scores for carbonated soft drink and alcoholic beverage patterns. On the other hand, women were more likely to have higher scores for coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer pattern. Within each pattern, there were significant differences in sociodemographic and lifestyle characteristics such as education, household income, frequency of eating out, and smoking status according to the quartile of pattern scores. Alcoholic beverages and carbonated soft drinks patterns were associated with an increased levels of metabolic syndrome components, but coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer was not associated with any of metabolic syndrome components in healthy Korean adults after adjusting for age, sex, education, BMI, weight management, household income, smoking status, frequency of eating out, and energy intake.
CONCLUSIONS
Alcoholic beverages and carbonated soft drinks patterns are associated with increased levels of metabolic syndrome components while coffee without added sugar or powdered creamer pattern is not associated with any of metabolic syndrome components in healthy Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional and Health Status According to the Frequency of Carbonated Beverage Consumption among Adults in Their 20s : Based on the 2019-2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
You-Sin Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(3): 159. CrossRef - Calcium- and Sodium-Rich Food Intake among Koreans with and without Metabolic Syndrome: Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Byeonggeun Choi, Jiyoon Kim, Yeonjin Kim, Jiae Shin, Sang-Ah Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(15): 2439. CrossRef - Effects of Calamansi Soju and Other Alcoholic Beverages on Resin Restorations
Moon-Jin Jeong, Kyungwon Heo, Myoung-Hwa Lee, Myeong-Ju Jeong, Do-Seon Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(4): 251. CrossRef - Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 350. CrossRef - Association between Dietary Habits, Shift Work, and the Metabolic Syndrome: The Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Heeja Jung, Hyunju Dan, Yanghee Pang, Bohye Kim, Hyunseon Jeong, Jung Eun Lee, Oksoo Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7697. CrossRef - Exploring parenting variables associated with sweetness preferences and sweets intake of children
Taejung Woo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2019; 13(2): 169. CrossRef - Influence of beverage type and ingestion time on tooth corrosion
Jae-Deok Cheon, Eun-Ah Cho, Hyun-Bae Park, Yu-Jin Choi, Han-Ju Kim, Jung-Soo Lee, Eun-Jeong Bae
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2018; 45(3): 169. CrossRef
- Nutritional and Health Status According to the Frequency of Carbonated Beverage Consumption among Adults in Their 20s : Based on the 2019-2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
- 1,656 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- Qualitative Study on Improvement of Operating System and Tailored Nutrition Education Program for Marriage Immigrants to Korea: Program Providers' Perspective
- Mee Young Joe, Ji Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):323-335. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.323
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study is to analyze the current status of nutrition education programs for multicultural families and to provide policy suggestions for improvement.
METHODS
In-depth interviews of a total of 21 multicultural experts were conducted; 15 people were interviewed individually, while 6 people were interviewed in groups of three.
RESULTS
In-depth interviews revealed various problems related to the operation of nutrition education programs. The causes of problems were analyzed and categorized as four factors: systemic, practical, environmental and cultural. As for the systematic factors, insufficient linkage between related organizations and duplicate performance of several projects were identified as concerns Establishment of a control tower and strengthening the linkage among the related organizations may be needed to address this concern. With regard to practical factors, the study identified that language barriers, and lack of nutritional education media and tools translated into multicultural languages were limiting factors. These limitations the development of nutrition education materials that aretranslated into multiple languages, implementation of education programs that are different from the Korean education, and by providing interpreters. As for the environmental factors, low educational level and poor nutritional knowledge of multicultural women made it difficult for them to understand the contents of the education. Demonstration, practical training and urgent education on pregnancy and childbirth nutrition were identified as needs to address these concerns. Withregard to cultural factors, food culture conflict with Korean families, and difficulties in home practices were detected as concerns. Participants in the study suggested that getting education with family and facilitation of weekend and nighttime programs health of this community.
CONCLUSIONS
Further studies are needed to adopt more effective and efficient nutrition intervention to promote the healthy eating of the married immigrant women based on the study results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
Sil-Ah Kim, Min-Ah Kim, Seung-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 614. CrossRef - Study on the Dietary Behavior of Adolescents in Multicultural Families Using the Nutrition Quotient and Their Changes in the Nutrition Knowledge and the Dietary Attitudes after Nutrition Education
Yoo-Jin Jung, Sung Hee Min, Min June Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(3): 208. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Education Experience (Home, School, and Mass Media) on Food Consumer Information literacy
Ji Eun Kim, Kyoung Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 363. CrossRef
- Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
- 1,200 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education at a Community Health Center on Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women in Jeonbuk Area-Focused on Personalized Daily Energy Requirement and Food Exchange Units
- Se Yeon Kim, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):307-322. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.307
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the effects of nutrition education focused on personalized daily energy requirement and food units using Food Exchange System on anthropometric, biochemical characteristics, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and nutrient intakes for overweight and obese in a public health center.
METHODS
The subjects were 60 overweight/obese women based on BMI (educated 30 vs. noneducated 30, 50~64 years). Educated group was provided individual and/or group lessons (40 min/ lesson/week, 5 week), ‘Introduction: obese & health’, ‘6 nutrients and 6 food groups’, ‘My obesity & daily needed energy’, ‘Meal planning for personalized daily energy and food units using Food Exchange Systems’, and ‘Smart food choices’. After education, we examined the differences in anthropometric/biochemical characteristics, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and nutrient intakes between educated group and non-educated group.
RESULTS
After nutrition education, in the educated group, there were improvements on anthropometric/biochemical characteristics, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude and nutrient intakes in the educated group compared to the non-educated group. We observed a decrease in the mean weight, total cholesterol (TC) and the incidence of overweight/obesity and hypercholesterolemia and an increase in the mean lean body mass. The scores of nutrition knowledge, ‘Function of carbohydrate, protein, vitamin, mineral’ and ‘Food Sources of fat, vitamin, mineral’ were increased. The scores of dietary attitudes, ‘Taking a joyful meal, a leisurely meal, a balanced meal, a meal with sufficient vegetables, a meal with diversity, a meal with spicy foods, a meal with overeating’ were increased. The intakes of energy, carbohydrate, fat, protein, vitamin A, thiamin, Zn and cholesterol were decreased. The scores of INQ, protein, vitamin A, vitamin C, thiamin, riboflavin, vitamin B6, folate, Ca, P, Fe, Zn were increased.
CONCLUSIONS
The nutrition education focused on personalized daily energy requirement and food exchange unit using Food Exchange System for overweight and obese may improve food behavior, dietary intakes and symptoms of overweight and obese, even in a community health center. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Irisin Levels in Cancer Anorexia Cachexia Syndrome and the Relationship between Nutrition Education and Quality of Life
Diler Us Altay, Duygu Mataracı Değirmenci, Salih Can Çelik, Abdullah Üner, Tevfik Noyan, Çağrı Akalın
Cumhuriyet Science Journal.2024; 45(4): 636. CrossRef - Influence of Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention (LSI) Program on Health, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Middle-Aged Women
Su-Jin Jung, Seung-Ok Lee, Min-Jun Choi, Jun Heo, Soo-Wan Chae, Baik-Hwan Cho
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2022; 12(3): 127. CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Program on Obesity Index and Behavioral Modification in Moderate Obese Women
Myung-Hee Chang, Su-Jin Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(4): 318. CrossRef - Effects of an Intensive Management Program for Diabetic Patients on a Blood Biochemical Profile and Diabetes Knowledge
Su-Jeong Yeo, Bok-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(2): 148. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Irisin Levels in Cancer Anorexia Cachexia Syndrome and the Relationship between Nutrition Education and Quality of Life
- 1,103 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Food Allergy Awareness and Nutritional Management by Preschooler's Faculty Members of Child Care Facilities
- Soo Bin Kim, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):298-306. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.298
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the awareness and nutritional management of food allergy (FA) by preschooler's faculty members in child care centers.
METHODS
A questionnaire survey was conducted among faculty members of child care centers in Seoul. The questionnaire was designed to identify the prevalence of food allergies, requirements of food allergy support and differences in food management depending on the presence of allergic diseases. After excluding incomplete responses, the data of 171 faculties in 137 child care centers (95.0%) were used for statistical analysis.
RESULTS
According to the 137 collected questionnaires, 96 child care centers asked parents about their children's allergic disease and 151 children from 66 child care centers had food allergies. A reported 89 children from 43 child care centers had food restrictions. However, 9 child care centers (21.0%) were not aware of food restriction for children with food allergies. Only 6 child care centers (14.0%) supplied substitute foods with the same amount and type of nutrients. Forty eight faculties (28.1%) received training about food allergies. Although there were some differences according to institution type, most of the faculty members wanted food allergy-related support.
CONCLUSIONS
This study identified a lack of food allergy training for faculty members in child care centers. For proper management, it is necessary for faculty members of child care centers to be educated on overall food allergies. Food allergy-related support such as menus without allergenic ingredients, guidelines on emergency care for food allergies and anaphylaxis should be provided for faculty members in child care centers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Knowledge and management of food allergy by parents of preschool children who experience food allergies
Seung Hui Kim, Seung-Min Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 184. CrossRef - Risk factors for food allergy among children in Seoul: focusing on dietary habits and environmental factors
Mijung Jang, KyooSang Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 559. CrossRef - Study on the snack menu pattern, food diversity and satisfaction of parent provided by Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Jeonbuk area
Eun-Byul Sym, Jeong-Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 501. CrossRef
- Knowledge and management of food allergy by parents of preschool children who experience food allergies
- 1,182 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Feasibility Study on the Dietary Improvement Program Development for Senior Citizens
- Sung Hee Kim, Boram Kim, Nami Joo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(3):218-227. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.3.218
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to develop dietary change program items that could be used to improve dietary life of the elderly and investigate their validity.
METHODS
The survey was were analyzed by SPSS program (Ver. 21) and descriptive statistics was performed; a t-test, χ² test, One-way ANOVA and Friedman test were used to determine the priority.
RESULTS
Programs for feeding senior citizens that need to be newly established are largely divided into two fields, namely, application of welfare facilities and application of home care, classified into large, medium and sub-classes. The large class was divided into nutrition management, sanitary control, and other health management. The medium class of nutrition management was divided into nutrition education, nutrition intervention, and menu management and supply. The sub-class was composed of division into application of welfare facilities for the elderly and application of home care for the same age group. Responses showed high rate saying that all the categorized items were necessary and valid. With respect to expectation effect on a community program for old people feeding, ‘yes’ was 65 people (55.6%) showing very high expectation toward the question whether a community program for old people feeding are newly set up.
CONCLUSIONS
It is believed that nutrition for the aged will be improved and it will be a help not only to a small facilities without obligation of employing a dietician but also to the aged at home if a community program for old people feeding are newly established.
- 878 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Needs for Development of IT-based Nutritional Management Program for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Chan Jung Han, Sun Young Lim, Eunsuk Oh, Yoon Hee Choi, Kun Ho Yoon, Jin Hee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(3):207-217. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.3.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to examine self-management status, nutritional knowledge, barrier factors in dietary management and needs of nutritional management program for women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM).
METHODS
A total of 100 women with GDM were recruited from secondary and tertiary hospitals in Seoul. The questionnaire composed of general characteristics, status of self-management, dietary habits, nutrition knowledge, barrier factors in dietary management, needs for nutrition information contents and nutritional management programs. Data were collected by a self-administered questionnaire. All data were statistically analyzed using student's t-test and chi-square test using SAS 9.3.
RESULTS
About 35% of the subjects reported that they practiced medical nutrition and exercise therapy for GDM control. The main sources of nutrition information were ‘internet (50.0%)’ and ‘expert advice (45.0%)’. More than 70% of the subjects experienced nutrition education. The mean score of nutrition knowledge was 7.5 point out of 10, and only about half of the subjects were reported to be correctly aware of some questions such as ‘the cause of ketosis’, ‘the goal of nutrition management for GDM’, ‘the importance of sugar restriction on breakfast’. The major obstructive factors in dietary management were ‘eating more than planned when dining out’, ‘finding the appropriate menu when dining out’. The preferred nutrition information contents in developing management program were ‘nutritional information of food’, ‘recommended food by major nutrients’, ‘the relationship between blood glucose and food’, ‘tips on menu selection at eating out’. The subjects reported that they need management program such as ‘example of menu by calorie prescription’, ‘recommended weight gain guide’, ‘meal recording and dietary assessment’, ‘expert recommendation’, ‘sharing know-how’.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of this study, it is necessary to develop a program that provide personalized information by identifying the individual characteristics of the subjects and expert feedback function through various information and nutrition information contents that can be used in real life. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chronically ailing or failing chronically: a typology of South African diners living with diabetes
Adam Viljoen, Martinette Kruger
International Journal of Spa and Wellness.2024; 7(2): 109. CrossRef - Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Thickness During Pregnancy
Moon Sook Hwang, Eunjeong Song, Jeonghee Ahn, Seungmi Park
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(9): 479. CrossRef - Current Status and Effects of Nutrition Education Programs for Diabetic Patients in Korea
Hae Jin Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(2): 106. CrossRef
- Chronically ailing or failing chronically: a typology of South African diners living with diabetes
- 1,150 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Analysis of Korean Dietary Life Adaptation of Married Female Immigrants
- Jeong Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(2):103-114. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.2.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study aims to investigate the married female immigrants' experience on Korean dietary life adaptation, especially identifying the symbolic meaning and nature of experiences.
METHODS
This study was conducted with six married female immigrants through an analysis of the qualitative materials which consisted of in-depth interviews, field notes and materials. Data was analyzed using Giorgi's phenomenological research methods.
RESULTS
The results were deduced as 116 significant statements, 17 formulated meanings (sub-theme), and 6 theme clusters. Six theme clusters comprised of lack of preliminary knowledge and information, conflict and support in relationships, Korean food culture which is different from homeland, adaptation attitudes of Korean food culture according to situation, sharing of homeland food culture, and practical difficulty and expectative service. The participants started Korean life in the dark about Korea and Korean food culture, so they were subjected to trial and error. The conflict between Korean mother-in-law and foreign daughter-in-law came from lack of consideration of daughter-in-law's cultural background. Some participants were hurt because of misunderstanding and nitpicking. They were learning about cooking method, ingredient, seasoning, table setting and manner. Some participants integrated Korean food culture and their homeland food culture. Some of them assimilated with Korean food culture. One of them maintained homeland food culture. The participants who adapted Korean food culture well could share homeland food amicably. They sometimes didn't apply the services which were offered by the government, because the services did not fit their needs. Some of them didn't know the usage route of the services or information. They had resistance about home teaching and it showed that outreach service was not always effective.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggested that it is necessary to develop a practical support plan which covers married female immigrants' real needs and system improvement measures.
- 892 View
- 4 Download

- [English]
- A Comparison of Sources of Sodium and Potassium Intake by Gender, Age and Regions in Koreans: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2010-2012
- Yang Hee Park, Sang Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):558-573. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.558
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the main sources of dietary sodium and potassium intake in Koreans by gender, age and regions.
METHODS
We used the data from 2010-2012 KNHANES. A total of 20,387 subjects aged 8 years and older were included. Intakes were compared by gender, age (8-18, 19-49 and >50 years) and geographical regions in Korea. Dishes were classified into 28 dish groups based on cooking methods. Statistical analysis was performed by using the SAS 9.3 and SUDAAN 11.0.1 software.
RESULTS
The mean sodium intake of Koreans was 4866.5 ± 35.9 mg/day, which was 2.4 times higher than the adequate intake (AI) of sodium for Koreans. We found that daily sodium intakes were significantly different by age, gender and regions. Men and aged over 50 years had significantly higher sodium intake than women and other age groups. The mean potassium intake in Koreans was 3002.2 ± 19.4 mg/day and daily potassium intakes were significantly different by age, gender and regions. Women and age 50 years and over had significantly higher potassium intakes than men and other age groups. The average Na/K ratio was 2.89 ± 0.01 and was highest in men and in the age group of 19-49 years. The major sources of dietary sodium were soup and stew, followed by Kimchi, noodles and dumpling, pickled vegetables and seasonings, which represented 63.1 % of total sodium intakes. Soup and stew or Kimchi were the primary sources of dietary sodium intake. The major sources of dietary potassium were cooked rice, followed by soup and stew, Kimchi, fruits and beverages.
CONCLUSIONS
Sodium and potassium intakes and the major sources of those were significantly different by gender, age groups and regions. Therefore, different approaches based on gender, age and regions are needed to decrease sodium intake and increase potassium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 225. CrossRef - Dietary Habits of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer in Korea
Jaehoon Shin, Jiyeon Lee, Yooeun Yoon, Hye Sun Lee, Hyungmi Kim, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2024; 45(3): 149. CrossRef - Role of geographic characteristics in the spatial cluster detection of cancer: Evidence in South Korea, 1999–2013
Insang Song, Eun-Hye Yoo, Inkyung Jung, Jin-Kyoung Oh, Sun-Young Kim
Environmental Research.2023; 236: 116841. CrossRef - Development and application of the sodium index to estimate and assess sodium intake for Korean adults
Yeon-Kyung Lee, Taisun Hyun, Heekyong Ro, Young-Ran Heo, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(3): 366. CrossRef - Trends in sodium intake and major contributing food groups and dishes in Korea: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2017
Yeseung Jeong, Eui Su Kim, Jounghee Lee, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(3): 382. CrossRef - Predictive Analysis of Food Behavior and Related Factors Using Spatial Analysis: Based on Community Health Survey Data 2016
Se-Mi Jeong, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(2): 189. CrossRef - The association of dietary patterns with insulin resistance in Korean adults: based on the 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
I Seul Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 247. CrossRef - Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
Na-Yeong Lee, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - Comparison of the sodium content of Korean soup-based dishes prepared at home, restaurants, and schools in Seoul
Yanghee Park, Jihyun Yoon, Sang-Jin Chung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 663. CrossRef - Designing optimized food intake patterns for Korean adults using linear programming (II): adjustment of the optimized food intake pattern by establishing stepwise intake goals of sodium
Kana Asano, Hongsuk Yang, Youngmi Lee, Meeyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(4): 342. CrossRef - The association between genetic variants of angiopoietin-like 3 and risk of diabetes mellitus is modified by dietary factors in Koreans
Clara Yongjoo Park, Jiyoung Moon, Garam Jo, Juhee Lee, Oh Yoen Kim, Hannah Oh, Hyunjung Lim, Min-Jeong Shin
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of biogenic amines and inorganic elements in Cheonggukjang
Min-Jeong Seo, Chang-Do Lee, Ji-Na Lee, Hee-Jong Yang, Do-Youn Jeong, Gae-Ho Lee
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2019; 26(1): 101. CrossRef - Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
Mijin Jo, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Diet-Related Risk Factors for Incident Hypertension During an 11-Year Follow-Up: The Korean Genome Epidemiology Study
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Nutrients.2018; 10(8): 1077. CrossRef - Study on the prevalence and incidence of urolithiasis in Korea over the last 10 years: An analysis of National Health Insurance Data
Joon Se Jung, Chang Hee Han, Sangrak Bae
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2018; 59(6): 383. CrossRef - Dietary status of young children in Korea based on the data of 2013 ~ 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eun-kyung Kim, Byengchun Song, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 330. CrossRef - Effects of Sodium Intake on the Association between the Salt-Sensitive Gene, Alpha-Adducin 1 (ADD1), and Inflammatory Cytokines in the Prevalence of Children Obesity
Mi-Young Park, Myoung-sook Lee
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2018; 7(2): 98. CrossRef - Dietary intakes of adolescents from food insecure households: analysis of data from the 6th(2013-2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mariam Nakitto, Kana Asano, Injoo Choi, Jihyun Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(6): 507. CrossRef
- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 3,720 View
- 6 Download
- 19 Crossref

- [English]
- Adulterated Food Management Characteristics according to Dietary Lifestyles among Adolescents
- Yunhwa Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):509-519. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.509
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Adulterated food education in adolescence period is very important because dietary management related to food safety is not made in a short period. This study aimed to identify dietary lifestyle factors which drive adulterated food management among middle and high school students.
METHODS
Data was collected from 270 middle and high school students in Daegu using a self-administered questionnaire in March and April of 2015. Data was analyzed using frequency analysis, one-way analysis of variance, χ²-test, factor analysis, reliability analysis, regression analysis, and cluster analysis.
RESULTS
The results of factor analysis indicated that adulterated food management awareness was classified into necessity, difficulty, and food purchasing anxiety. The adulterated food management capability was sub-grouped into environmental grasp, food identification, cooking hygiene, and situation management. The adulterated food management efficacy composed of management confidence, action intention, and knowledge. Dietary lifestyle comprised of gustation, family, and health factors after factor analysis, and it consisted of all seeking group, gustation seeking group, family seeking group, health seeking group, and family and health seeking group after cluster analysis. The gustation, family and health factors were significantly affected the factors of awareness, capability and efficacy of adulterated food management (p < 0.05). The frequency of health conditions, helping with meal preparation, and the times of eating out were significantly different according to seeking groups of dietary lifestyle (p < 0.01). The scores of awareness, capability and efficacy of adulterated food management of family and health seeking group were significantly higher than the other seeking groups (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that adulterated food management education programs should account for gustation, family and health factors of dietary lifestyle to be effective for adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Dietary safety management competency for the sustainable health management of adolescents
Yunhwa Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(3): 406. CrossRef - Restaurant Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption Behavior according to Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyles
Yulee Shin, Minsook Kyung, Seonyeong Baek, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(3): 172. CrossRef - Predicting adolescents’ behavioural intentions in adulterated food management
Yunhwa Kim
British Food Journal.2019; 122(1): 258. CrossRef - Survey on Foodservice Satisfaction and Dietary Education needs for Improvement of School Foodservice in Middle School Students in Seoul
Kyung-Hee Shin, Youngmee Lee, Wookyoun Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 127. CrossRef
- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
- 1,162 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Factors Affecting the Frequency of Skipping Meals of Prime-Aged Mothers with Children : Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2010-2011
- Mi Yeon Park, Pil Sook Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(5):451-462. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.5.451
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was designed with the goal of understanding the factors affecting the frequency of skipping meals of prime-aged mothers with children as well as their nutritional status.
METHODS
Utilizing data from the 2010-2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey, the frequency of skipping meals of mothers aged between 30 to 49 years with children aged between 3 to 11 years during a two day period was statistically analyzed. The number of meals skipped calculated and categorized into skipping no meals, skipping one meal, skipping two meals or more.
RESULTS
Compared to subjects who corresponded to mean nutrient adequacy ratio(MAR) of 4 quartile, subjects who corresponded to MAR of 2 quartile had 2.766 (95% CI: 1.552-4.931) probability of being in the 1 meal skippers group, while the probability of being in the more than 2 meals skippers group was 2.743(95% CI: 1.353-5.564). Also, compared to subjects who corresponded to MAR of 4 quartile, subjects who corresponded to MAR of 1 quartile had 3.471 (95% CI: 1.871-6.442) probability of being in the 1 meal skippers group, while the odds ratio for being in the more than 2 meals skippers group was 5.258(95% CI: 2.642-10.466).
CONCLUSIONS
The results have the advantage of being generalized because the study selected subjects from probability sampling of the female population of Korea. The research results showed that the elements influencing skipping meals of prime-aged mothers with children were mean nutrient adequacy ratio and the number of nutrients, under estimated average requirement intake, and others. Therefore, to encourage dietary behaviors in the right direction, an integrated approach that considers the associated factors must be realized. Future studies are needed to understand how the frequency of skipping meals of mothers affects their children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescent According to the Meal Frequency: The 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yonghoon Ji, Junhee Park, Jun-Hyun Yoo
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2022; 12(3): 158. CrossRef
- Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescent According to the Meal Frequency: The 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,117 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Food Allergy Awareness and Nutritional Management by the Parents of Preschool Children
- Soo Bin Kim, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(5):426-439. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.5.426
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to measure the food allergy (FA) awareness and management by the parents of preschool children.
METHODS
A questionnaire survey was conducted with the parents of preschool children. The questionnaire was designed to identify the prevalence of food allergies, requirements of food allergy support and differences in food management according to the presence or absence allergic diseases, using a modified International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) questionnaire. After excluding incomplete responses, the data of 158 parents of preschool children (90.3%) was used for statistical analysis.
RESULTS
The rate of the preschool children who had experienced food allergy (FA, ever) was 38.6% while diagnosed for food allergy by doctor (Diagnosis of FA, ever) was 17.7%. Forty nine preschool children (80.3%) had food restriction, and twenty three of them (37.7%) had self-restriction without diagnosis. The consumption frequencies of allergenic foods in FA group, such as ramyeon, noodles, bread, eggs, yogurt and ice cream were significantly (p<0.001) lower than those of the other two groups. The major allergenic foods were eggs, milk, wheat and processed foods in FA group. The overall food allergy-related knowledge level of parents was insufficient. Only 26 parents (16.5%) had received training about food allergies. All parents wanted to receive food allergy-related supports. In addition, most of parents wanted information on substitute menu for children with food allergy.
CONCLUSIONS
This study identified a lack of food allergy training for the parents of preschool children and the necessity for food allergy education. Food allergy-related supports, such as menus without allergenic ingredients, guidelines for managing food allergy & anaphylaxis emergency care plan etc, should be provided to the parents in order to avoid events related to food allergies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The status of food allergy and parental burden of preschoolers in Jeju area
Jeong Eun Oh, Eunyoung Kim, Yunkyoung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 664. CrossRef - Study on the snack meal management for infants and toddlers and the demand for snack products according to the sustainable dietary style of mothers in Jeonbuk area
Ji-Eun Lee, Jeong-Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 39. CrossRef - Study on the status of food allergy management and importance-performance analysis about precautions of food allergy in school foodservice according to the school types in Jeonbuk area
Ji Yeon Kim, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(3): 329. CrossRef - Study on the snack menu pattern, food diversity and satisfaction of parent provided by Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Jeonbuk area
Eun-Byul Sym, Jeong-Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 501. CrossRef - Food Allergy-related Awareness and Performance of Dietitians at Children's Hospitals in Korea: Comparison of Certificate Possession among Clinical Dietitians
Hye-Ran Shin, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 512. CrossRef - Food Allergy Awareness and Nutritional Management by Preschooler's Faculty Members of Child Care Facilities
Soo Bin Kim, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(4): 298. CrossRef
- The status of food allergy and parental burden of preschoolers in Jeju area
- 1,298 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Intake Ratio and Intake Pattern of Proteins in Middle-aged Men Based on the 2012-2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
- Minkyoung Jang, Eunsil Her, Kyunghea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):366-377. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.366
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to compare intake of energy nutrients, physical characteristics, and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome according to protein intake group.
METHODS
Subjects were 827 men aged 40-65 years. The results presented were based on data from the 2012-2013 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and analyzed using SPSS. The odds ratio (OR) of metabolic syndrome was assessed according to the protein intake group and intake pattern of protein-rich foods.
RESULTS
The mean of protein intake was 73.96 ± 0.71 g. According to level of protein intake, four groups (deficient, normal, excess 1, excess 2) were created and their percentages were 8.3%, 39.6%, 37.1%, and 15.0% respectively. The mean of daily energy intake was 2,312.33 ± 24.08 kcal. It was higher in excess group 2 than in the deficiency group (p < 0.001). Moreover, the intake of all energy nutrients increased significantly with protein intake group (p < 0.001). The main contribution to daily protein included mixed grains (10.96 ± 0.32 g), milled rice (7.14 ± 0.30 g), chicken (3.50 ± 0.21 g), and grilled pork belly (3.04 ± 0.16 g). With regard to physical characteristics, and blood pressure and blood test results, only body mass index increased significantly according to protein intake groups (p < 0.05). The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in subjects was 38.5%, and there was no significant correlation with protein intake group. The OR of metabolic syndrome increased with protein intake, and was higher 4.452 times in excess group 2 than in the normal group (p < 0.05). Conversely, the OR of metabolic syndrome according to the frequency of protein-rich food intake did not show a significant correlation.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study can be used as significant supporting data to establish guidelines for protein intake in middle-aged men. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of diet quality according to the eating-out patterns of preschoolers and school-aged children in South Korea: based on data from the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-na Ju, Youngmi Lee, Kyunghee Song, Yujin Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(2): 165. CrossRef - Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 112. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Dietary Fat Energy Ratio in Middle-aged Men - Using the 2012~2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data -
Eun-Sil Her
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 1030. CrossRef
- Evaluation of diet quality according to the eating-out patterns of preschoolers and school-aged children in South Korea: based on data from the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,189 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Status of Maternal Nutrition in South and North Korea
- Soh Yoon Yun, Young Hye Kwon, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(3):265-273. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study compared the nutritional status of child-bearing age women between the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) and the Republic of Korea (South Korea).
METHODS
The data presented in the DPRK Final Report of the National Nutrition Survey 2012 was utilized for the nutritional status and food intake of North Korean women. To produce the South Korean women's data comparable to those of North Korean women, the data from the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed and the data presented in the 2010 Report of the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards were utilized.
RESULTS
The prevalence of maternal anemia (blood hemoglobin < 12.0 g/dL) was over 30% in all the age groups of North Korean women and 8.9%, 14.2%, 16.4% in 20-29, 30-39, 40-49 year old South Korean women, respectively. The prevalence of maternal protein-energy malnutrition (Mid-Upper Arm Circumference < 22.5 cm) was 25.2%, 21.4%, 21.8% in 20-29, 30-39, 40-49 year old North Korean women, respectively and less than 10% in all the age groups of South Korean women. Result of dietary diversity comparison showed that North Korean women consumed less food than South Korean women at all food groups: grains, fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy. Percentage of North Korean women having consumed protein rich foods-meat and fish, eggs or dairy products-were much lower than those of South Korean women.
CONCLUSIONS
The striking disparity of nutritional status between South and North Korean women indicates that nutrition support for North Korean women is essential in the process of preparation for a unified nation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
Youngmin Nam, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 288. CrossRef - The Present and Future Status of Maternal and Child Health From the Perspective of Unification Medicine
Ji Young Kim, Eun Saem Choi, Ki Hoon Ahn
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(3): 132. CrossRef - Timely Initiation of Complementary Feeding and Associated Factors among Mothers of Children Aged 6–24 Months in Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia, 2019
Atsedemariam Andualem, Afework Edmealem, Belachew Tegegne, Lehulu Tilahun, Yitayish Damtie, C. S. Johnston
Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Systematic review of evidence on public health in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea
John J Park, Ah-Young Lim, Hyung-Soon Ahn, Andrew I Kim, Soyoung Choi, David HW Oh, Owen Lee-Park, Sharon Y Kim, Sun Jae Jung, Jesse B Bump, Rifat Atun, Hee Young Shin, Kee B Park
BMJ Global Health.2019; 4(2): e001133. CrossRef - Frequently covered diseases in North Korean internal medicine journal Internal Medicine [Naegwa]—Secondary publication
Shin Ha, Yo Han Lee
Science Editing.2019; 6(2): 99. CrossRef
- Nutritional status of North Koreans and related perceptions among South Korean adults
- 1,619 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- A study on the Needs for Nutrition Management Program for Elderly Who use Welfare Facilities
- Min June Lee, Jung Hyun Kim, Ok Jin Park, Young Mi Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):65-74. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to investigate the nutritional status, health conditions, eating habits and experience and demand for nutrition.dietary management of senior citizens. And these data are formed foundation of development of nutrition.dietary management education program and contents in welfare facilities for the aged.
METHODS
We visited 3 public health centers, 3 senior citizens centers, and 4 welfare centers in Seoul, Gyeonggi-do, Chungnam province, and Daejeon area and carried out interview by semi-structured questionnaire for senior citizens older than 65 years who use those facilities.
RESULTS
The study included 17%, 30.7% and 52.3% of senior citizens from public health centers, seniorcitizen centers and and welfare centers, respectively. The age range of 43.9% of the population was 65-74 years and and 56.1% were older than 75 years. We observed that 83.2% of subjects took some medicines due to diseases that they have and 58.0% took prescription medicines for hypertension. The thing that they considered the most when selecting food was 'the taste'(p<0.05). Regarding the level of practice to keep the dietary life, they answered more than 'average' for most of items but answered less than 'average' for lot of salt intake, drinking, exercise. For the experience of nutritionddietary life education, only 19.8% answered 'Yes' and the service for nutritionddietary life management showed the highest score in the demand for 'provide nutritious food'. For the size of consulting group for nutrition/dietary life education, the public health center and welfare center preferred a larger group size but the senior citizens center preferred a smaller group. With regard to who will carry out the consulting, the demand for dietitian was the highest and the operation type showed the high demand in the order of consulting, education. The contents that they want to have consultation in nutritionddietary life education were diet therapy for diseases and the ordinary diet therapy for health.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggested the management of nutritionddietry life necessitates qualitative measures according to the different types of welfare facilities. For these, it is in need of development of counseling and education program included therapy for disease. Above all, the policy to secure dietitian of welfare facilities for the aged to perform these should be achived. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spatial pattern and influencing factors of urban elderly meal assistance facilities: a case study from Beijing, China, based on multi-source data
Tuke Zheng, Xidong Ma, Xiaoqing Cheng
Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering.2025; : 1. CrossRef - A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
Seo Young Choi, Hyun joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 286. CrossRef - Snack Provision Practice in Long-Term Care Hospitals and Facilities in Korea
Dayeong Yeo, Hae Jin Kang, Hyejin Ahn, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(2): 108. CrossRef - Effectiveness of NQ-E index-based individual nutrition counseling for community-care elderly: an intervention study on improving nutritional status, complex chronic diseases, and quality of life
Yoonjeong Choi, Jihyun Lee, Heesook Lim, Yoo Kyoung Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 480. CrossRef - Evaluation on the Nutrition Quotient Scores of Elderly People Living Alone in Korea
Gyoungok Gang, Min Lee, Eun-hui Choi, Hye-Lim Lee, Hyun-Young Lee, Hye-Ja Chang, Jung-Hwa Choi, Na-Young Yi, Kyung-Eun Lee, Min-Jae Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak
Nutrients.2023; 15(17): 3750. CrossRef - Effects of nutrition and hygiene education program on healthy eating habits and behavior of the elderly in Chungbuk
Je-ok Yeon, Byung-chun Song, Kyung-Jin Yeum, Myoung-sook Kim, Mi-young Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(3): 390. CrossRef - Dietary quality of lunches in senior leisure service facilities in South Korea: analysis of data from the 2013–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Daeun Choi, Youngmi Lee, Haeryun Park, Kyunghee Song, Jinah Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(2): 266. CrossRef - Future Perspective of the Elderly Food in a Super-Aged Society
Weon-Sun Shin
Journal of the Korean Dysphagia Society.2021; 11(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of a Person-Centered Nursing Intervention for Frailty among Prefrail Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Jiyeon Ha, Yeon-Hwan Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(18): 6660. CrossRef - Socio-Economic Factors are Associated with Risk of Inadequate Protein Intake among Korean Elderly: Based on the Seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES Ⅶ), 2016-2018
Won Jang, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2020; 31(2): 215. CrossRef - Current Status of Sanitary and Nutritional Food Service in Elderly Day Care Center
Jeonghyeon Woo, Yoo Kyoung Park, Mi-Hyun Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee, Kyunghee Song, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 374. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of dietary behavior and nutrient intake of elderly in urban and rural areas for development of “Village Lunch Table” program: Based on 2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Youngmi Lee, Yourim Choi, Hae Ryun Park, Kyung Hee Song, Kyung Eun Lee, Chang Hee Yoo, Young Suk Lim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 171. CrossRef - Food Safety and Nutrition Education Program for Elderly and Assessment of Program Effectiveness Based on Health Belief Model
Jung-Hwa Choi, Eun-Sil Lee, Yoon-Jin Lee, Hye-Sang Lee, Hye-Ja Chang, Kyung-Eun Lee, Na-Young Yi, Yoon Ahn, Tong-Kyung Kwak
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2016; 45(9): 1366. CrossRef
- Spatial pattern and influencing factors of urban elderly meal assistance facilities: a case study from Beijing, China, based on multi-source data
- 1,360 View
- 6 Download
- 13 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Behavior of Marriage Migrant Women according to Their Nationality in Multicultural Families
- Jung Hyun Kim, Myung Hee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):53-64. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Nowadays, the multicultural families make up significant portion of Korean population and communities. Successful re-settling in a new country can be difficult, particularly when there are disparities in dietary behavior compared to home country. The objective of the study was to investigate the dietary behavior of marriage migrant women according to their nationality in multicultural families.
METHODS
The primary research was conducted targeting 94 marriage migrant women who came from China (40.4%), Vietnam (26.6%), and other countries except for Japan (33.0%). We investigated their dietary behavior, such as eating attitude and food choice behavior for Korea acculturation. We also studied dietary behavior among 14 selected subjects who had high level of integration and assimilation acculturation patterns by administering the Focus Group Interview (FGI).
RESULTS
The multicultural families had more integration acculturation patterns, which could have been influenced by their nationality. Vietnamese origin has the highest cultural adaptation as marginalization pattern. The common types of Korea acculturation were integration (3.03 +/- 1.08), separation (3.10 +/- 0.59), marginalization (3.10 +/- 0.58), followed by assimilation (2.84 +/- 0.51). There were significant differences in the four types of acculturation by marriage immigrant women's country of origin (p<0.05). According to dietary behavior, 'eliminating hunger' was the most important value in a meal. Chinese marriage migrant women, who had higher level of food intake attitude significantly, also considered 'being healthy' an important value. Regarding food choice behavior, Vietnamese had lowest frequency of homeland food intake. Most of marriage immigrant women were satisfied with the Korean food, and need for education was very high with interest for cooking, good nutrition, and managing their children's dietary life.
CONCLUSIONS
Coping with a change in dietary behavior is one of the biggest transitional difficulties, and family members may need support to find their familiar food items and to continue their cultural food choice behavior in the local areas. Further researches with quantitative and qualitative analysis are needed to understand the effect of dietary behavior for acculturation in multicultural families. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Economic Aspirations and Vietnamese Interest in Korean Matrimony
Nguyen Duy Quynh, Nguyen Nghi Thanh
Journal of Lifestyle and SDGs Review.2025; 5(2): e03215. CrossRef - Development and Application of Customized Nutrition Education Content Using Personas for Married Immigrant Women: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Social Cognitive Theory
Sil-Ah Kim, Min-Ah Kim, Seung-Ah Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 614. CrossRef - Prejudice and discrimination experienced by high-skilled migrants in their daily lives: Focus group interviews with Tokyo metropolitan area residents
Jiwon Shin, Hwajin Lim, Jiyeon Shin
Asian Journal of Social Science.2024; 52(1): 17. CrossRef - Analysis of eating behavior of Indonesian women from multicultural and non-multicultural families
Ulya Ardina, Su-In Yoon, Jin Ah Cho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 228. CrossRef - A relationship between food environment and food insecurity in households with immigrant women residing in the Seoul metropolitan area
Sung-Min Yook, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 264. CrossRef - Experience of reorganizing life in married immigrant women with chronic disease; With three Asian countries at the center
Soon-Mi Cheon
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(1): 15. CrossRef - The Food Delivery App Information Design Suggestion for Foreigners in
South Korea
Diana Iziiatullina, Jinyeon Shin, Aygul Akhmetova, Soojin Park
Journal of Multimedia Information System.2022; 9(4): 327. CrossRef - Analysis of Korean Dietary Life Adaptation of Married Female Immigrants
Jeong-Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 103. CrossRef - Effects of the Culturally Sensitive Education of Perinatal Care on Knowledge, Skills, and Self-Efficacy among Korean Husbands and Vietnamese Wives
Youngmee Kim, Kap-Chul Cho
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(4): 515. CrossRef - Qualitative Consumer Preference Studies on Korean-style Kimchi in Chinese Living in Korea
Mi-Ai Lee, Yun-Jeong Choi, Mina K. Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(2): 185. CrossRef - Food intake and nutritional status of female marriage immigrants residing in Gwangju, Korea
Eun Ju Yang, Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(5): 358. CrossRef - Dietary behaviors of female marriage immigrants residing in Gwangju, Korea
Eun Ju Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(3): 179. CrossRef
- Economic Aspirations and Vietnamese Interest in Korean Matrimony
- 1,330 View
- 5 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Health Status Assessment Tool Development based on Dietary Patterns in Middle-Aged Women
- Hye Jin Lee, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(1):37-52. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.1.37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was performed to develop an assessment tool for middle aged women's health status based on dietary patterns, which will have practical applications in the working field of health and hygiene, aiming at improving the middle aged women's quality of life through their health improvement.
METHODS
As a first step, a literature review was conducted and the original data of '2008~2009 Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Survey' were reanalyzed. This analysis identified 65 preliminary questions that may be relevant to the study. After verifying the content validity by experts, the 65 questions were reduced into 51 questions. In order to secure higher validity of the candidate items, verification of their clinical validity was conducted among women aged between 45 and 60 years. Finally, an assessment tool was developed by applying weight and scoring.
RESULTS
Selected 51 questions were used to verify clinical validity and the results showed that 20 questions were relevant, nine questions ('regular meal time', 'regular amount of meal', 'intake frequency of dairy products', 'intake frequency of fruits', 'intake frequency of meat products', 'intake frequency of high cholesterol foods', 'intake frequency of salty foods', 'appetite', 'eat breakfast everyday') were related to dietary life. Eleven other questions ('self-rated health status', 'deep sleep', 'smoking', 'frequency of drinking', 'stress levels', 'health-related fitness levels', 'pounding of the heart', 'strange feelings on the skin', 'interfere with daily life', 'menopause will bring you a chance to see the life in a different perspective', and 'body mass index') were selected as valid questions. For the response scale for each question, 5 point Likert scale was used to make total 100 point score.
CONCLUSIONS
This study is the first attempt to develop a health status assessment tool for middle aged women based on their dietary patterns. We conclude that this tool is expected to be a useful and practical tool in the field. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food consumption frequency of Korean adults based on whether or not having chewing difficulty using 2013–2016 KNHANES by sex-stratified comparative analysis
Mi Jeong Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(6): 637. CrossRef - Field Application and Evaluation of Health Status Assessment Tool based on Dietary Patterns for Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(4): 277. CrossRef
- Food consumption frequency of Korean adults based on whether or not having chewing difficulty using 2013–2016 KNHANES by sex-stratified comparative analysis
- 1,263 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- The Current State of Food Allergy of Preschool Childcare Facilities in Hanam
- Wookyoun Cho, Jinah Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(4):251-258. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.4.251
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate how to manage food allergy of pre-school children, focusing on the current status of the food allergy in childcare facilities in Hanam which have less than 100 children.
METHODS
Targeting 159 preschool childcare facilities, survey was carried out for a month in March, 2015. Recovery rate was 66.7%. 106 surveys out of 159 were available for analysis using SPSS statistical program version 19.0.
RESULTS
Among 106 facilities, 58 (54.7%) reported that none of their children had a food allergy and 48 (45.3%) reported one more children had a food allergy. Total number of children having a food allergy was 71. Among them, the occurrences of food allergy in males were significantly more than that of the females (p < 0.001). Further, children under 2 years of age had significantly more food allergy than the other ages (p < 0.001). The allergic inducing foods were nuts (23.3%), egg (17.8%), milk and dairy products (16.4%), fish and shellfish (13.7%), instant foods (12.3%), fruits (8.2%), soybean (4.1%), meat (2.7%), and cereals (1.4%) in order, and 6 children out of 71 were allergic to more than 2 food items. The clinical symptoms of the food allergy were a skin reaction (87.9%) and an oropharyngeal & respiratory reaction (12.1%). Majority of childcare facilities (80.3%) didn't serve alternative foods for children with food allergy. Necessity for food allergy education was significantly higher in facilities with food allergy issues than without such issues.
CONCLUSIONS
The Center for Children's Foodservice Management need to educate workers of childcare facilities and parents about managing food allergy and enforce a plan to provide alternative menu to children with food allergies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Knowledge and management of food allergy by parents of preschool children who experience food allergies
Seung Hui Kim, Seung-Min Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 184. CrossRef - Cleaning Methods to Effectively Remove Peanut Allergens from Food Facilities or Utensil Surfaces
Sol-A Kim, Jeong-Eun Lee, Jaemin Shin, Won-Bo Shim
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2023; 38(4): 228. CrossRef - Risk factors for food allergy among children in Seoul: focusing on dietary habits and environmental factors
Mijung Jang, KyooSang Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 559. CrossRef - Study on the snack menu pattern, food diversity and satisfaction of parent provided by Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Jeonbuk area
Eun-Byul Sym, Jeong-Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 501. CrossRef - Food allergic reactions in the community: a questionnaire survey of caregivers
An Deok Seo, Jun Yeol Lee, Song I Yang, Hye Ran Lee, So-Yeon Lee
Allergy, Asthma & Respiratory Disease.2017; 5(1): 27. CrossRef
- Knowledge and management of food allergy by parents of preschool children who experience food allergies
- 1,304 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Analysis of Weight Control Behaviors by Body Image Perception among Korean Women in Different Age Groups: Using the 2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
- Young Suk Lim, Na Ri Park, Su Bin Jeon, So Yeon Jeong, Zuunnast Tserendejid, Hae Ryun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(2):141-150. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.2.141
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Self perceived body image among women is drawing a lot of attention in Korea due to their unhealthy weight control behaviors. To determine the relationship between self-perceived body image and dietary behaviors among Korean women, the discrepancy between actual body size and body image perception, weight control behaviors were assessed based on age groups using the 2010 KNHANES data.
METHODS
A total of 1,747 subjects were selected after eliminating those of likely changing their diet recently using the 2010 KNHANES data. The subjects were divided into 3 groups, self-underweight, self-normal, and self-obese according to their perception of body image. The BMI and weight control behaviors were assessed based on age groups according to the body image perception.
RESULTS
The younger, the higher ratio of underweight, women perceived their body size as normal or overweight. Exercise and reduced food intakes were dominant among various weight control methods but unhealthy methods were dominant among self perceived overweight group.
CONCLUSIONS
Incorrect body image perception and unhealthy weight control behaviors can cause nutritional problems. Nutritional education should emphasize the importance of healthy weight and proper body image perception for Korean women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction model of weight control experience in men with obesity in their 30 s and 40 s using decision tree analysis
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of weight loss diet programs on anemia, nutrient deficiencies, and organ dysfunction markers among university female students: A cross-sectional study
Osama Y. Althunibat, Sultan Ayesh Mohammed Saghir, Saleem Hmoud Aladaileh, Atikah Rawadieh
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2023; 20(1): em436. CrossRef - Obesity-Status-Linked Affecting Factors of Dyslipidemia in Korean Young-Adult Men: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Min Kwon, Jinheum Kim, Eunjeong Cha
Healthcare.2023; 11(14): 2015. CrossRef - Physical Activity and Quality of Life in Adult Men and Women with Distorted Perception of Weight Status: Nationwide Surveys (KNHANES 2016–2018)
Su-Jin Lee, Min-Gyu Lim, Jung hee Kim, Chulyong Park, YoungJi Ko, Myung-Gwan Kim, Chul-Hyun Kim, Aeryoung Kim, Jong-Moon Hwang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 10417. CrossRef - Consumption of Weight-control or Health Functional Foods, Dietary Habits, and Weight Perceptions According to the Body Mass Index of Adult Women in the Chungcheong Area
Gayoung Seong, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 81. CrossRef - What are the correlates of body image distortion and dissatisfaction among school-adolescents?
Houda Ben Ayed, Sourour Yaich, Maissa Ben Jemaa, Mariem Ben Hmida, Maroua Trigui, Jihene Jedidi, Imen Sboui, Raouf Karray, Habib Feki, Yosra Mejdoub, Mondher Kassis, Jamel Damak
International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Biochemical Index, Nutrition Label Use, and Weight Control Behavior in Female Adolescents: Using the 2010 and 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi-Ja Choi, Hyun-Ju Jo, Mi-Kyung Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2020; 9(1): 32. CrossRef - The effects of body mass index and body shape perceptions of South Korean adults on weight control behaviors; Correlation with quality of sleep and residence of place
Nam E Kang, Seung Ju Kim, Yoon Sin Oh, Se-Eun Jang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(2): 160. CrossRef - Factors influencing disordered eating behavior based on the theory of triadic influence
Jee Hee Han, Sun Ah Kim, Sue Kim, Jin Young Park
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2019; 55(3): 366. CrossRef - Comparison of factors affecting weight control experiences by perception types of body shape
Yeo Jeong Gu, Jae Yeon Jeong, Ji Yun Jeong, Hae Jong Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(4): 77. CrossRef - Relationships between Obesity, Body Image Perception, and Weight Control in Adult Women
Hyunju Chae
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(2): 129. CrossRef - Relationship between body image and weight status in east Asian countries: comparison between South Korea and Taiwan
Jin-Won Noh, Young Dae Kwon, Youngmi Yang, Jooyoung Cheon, Jinseok Kim
BMC Public Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association of Food Label Use with Objective and Subjective Obesity among a Korean Population
In Sook Lee, Kowoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(3): 262. CrossRef - The association of body image distortion with weight control behaviors, diet behaviors, physical activity, sadness, and suicidal ideation among Korean high school students: a cross-sectional study
Jounghee Lee, Youngmin Lee
BMC Public Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight Control Behaviors, Health-related Quality of Life and Nutritional Status by Overestimation of Body Image among Young Korean Females: Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2010-2011
Seulki Park, Taisun Hyun, Hongmie Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 362. CrossRef - A Comparison of Body Image and Dietary Behavior in Middle and High School girls in Gyeongbuk Area
Hye-Jin Kim, Kyung-A Lee
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2015; 31(4): 497. CrossRef - The Influence of Self-resilience on Dietary Management in Middle School Students
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(6): 399. CrossRef
- Prediction model of weight control experience in men with obesity in their 30 s and 40 s using decision tree analysis
- 2,105 View
- 10 Download
- 17 Crossref

- [English]
- An Evaluation of Chronic Disease Risk Based on the Percentage of Energy from Carbohydrates and the Frequency of Vegetable Intake in the Korean Elderly: Using the 2007-2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yoon Suk Suh, Min Seon Park, Young Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(1):41-52. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Korean elderly people are known to consume diets high in carbohydrates low in vegetables compared to other age groups. This study evaluated the chronic disease risks and nutritional status in this group based on the percentage of energy from carbohydrates and the frequency of vegetable intake.
METHODS
Using the 2007~2009 Korean National Health Nutrition Examination Survey data, except those who were undergoing treatment for chronic disease, final 1,487 subjects aged 65 and older were divided into 4 groups: moderate carbohydrate energy ratio of 55~70% and low frequency of vegetable intake defined as less than 5 times per day (MCLV), moderate carbohydrate ratio and high frequency of vegetable intake more than 5 times (MCHV), high carbohydrate energy ratio above 70% and low frequency of vegetable intake less than 5 times (HCLV), and high carbohydrate ratio and high frequency of vegetable intake more than 5 times (HCHV). All data were analyzed after the application of weighted value, using a general linear model or logistic regression.
RESULTS
More than half of Korean elderly consumed diets with HCLV, and this group showed poor nutritional status and lower frequency of intake of most food items, but with no risk of chronic disease such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, cardiovascular disease or anemia probably due to low intake of energy. On the contrary, MCHV group with a high percentage of energy from fat and protein showed the highest intake of energy and most nutrients, the highest frequency of intake of most of food items and a tendency of high risk of abdominal obesity, being followed by the MCLV group. Meanwhile, HCHV group showed a tendency of high risk of hypertension, followed by HCLV group with low frequency of intake of vegetables compared with the two moderate carbohydrate groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggested that the percentage of energy from carbohydrate and the frequency of vegetable intake affected the nutritional status, but not significantly affected the risk of chronic disease in Korean elderly. Further studies using more detailed category of % energy from carbohydrates and of type and amount of vegetables with consideration of individual energy intake level, excessive or deficient, are needed to confirm the results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef - Energy big data acquisition and application based on service portfolio quality
Pingping Sun, Lingang Gu
Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments.2021; 45: 101134. CrossRef - Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 502. CrossRef - Analyzing the Relative Importance for the Development Plan of the Public Health Care System
You Ho Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(4): 300. CrossRef - The Quality of a Traditional Dietary Pattern in Relation to Metabolic Syndrome in Elderly South Koreans
Chorong Oh, Jaekyung No
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2018; 27(4): 254. CrossRef - Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Estimation of Usual Intake and Assessment of Nutrient Intake for Korean Adolescents: Analysis of the 2010-2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Meeyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
Family and Environment Research.2017; 55(4): 385. CrossRef
- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
- 1,174 View
- 0 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- The Risk of Metabolic Syndrome by Dietary Patterns of Middle-aged Adults in Gyeonggi Province
- You Sin Lee, Moo Yong Lee, Sim Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):527-536. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.527
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to assess how nutrient intakes are related to risk factors for metabolic syndrome according to dietary patterns in the middle-aged adults.
METHODS
The subjects (n = 187; 47 men, 140 women) consisted of middle-aged adults over 30 years old in Ilsan area. The metabolic syndrome was diagnosed according to the data collected from each subject, including anthropometric measurements and blood analyses. The dietary patterns were derived from the average of two-day dietary intake data.
RESULTS
Factor analysis identified three major dietary patterns which were "Meats and alcohol", "Mixed grains, vegetables and fruits", and "Rice, Kimchi and fish & shellfish". The daily intakes of energy, protein, and sodium increased across quartiles of "Meats and alcohol" pattern scores (p < 0.05), whereas the intakes of carbohydrates, potassium, calcium, and fiber increased across quartiles of "Mixed grains, vegetables and fruits" pattern scores (p < 0.001). The "Meats and alcohol" pattern scores were positively correlated with protein and sodium intakes but inversely correlated with carbohydrates, fiber and potassium intakes which were adjusted for age, sex and energy (p < 0.05). The highest quartile pattern score of "Meats and alcohol" pattern had elevated odds ratio of abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome (p < 0.05). The risk of hypertriglyceridemia decreased in the highest quartile of "Mixed grains, vegetables and fruits" pattern (OR 0.35, 95% CI 0.12-1.00).
CONCLUSIONS
Our results suggested that reducing the consumption of meat and alcohol along with increasing fruits, vegetables and mixed grains would be helpful for preventing the metabolic syndrome and chronic diseases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between the Korean Healthy Diet Score and Metabolic Syndrome: Effectiveness and Optimal Cutoff of the Korean Healthy Diet Score
Soo-Hyun Kim, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(19): 3395. CrossRef - The Relationship between Meal Regularity and Oral Health and Metabolic Syndrome of Adults in Single Korean Households
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, On-Ju Ju
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 185. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Dietary Fat Energy Ratio in Middle-aged Men - Using the 2012~2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data -
Eun-Sil Her
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 1030. CrossRef - Reduction of Plasma Triglycerides and Cholesterol in High Fat Diet-Induced Hyper-Lipidemic Mice by n-3 Fatty Acid from Bokbunja (Rubus coreanus Miquel) Seed Oil
Hyelin Jeon, Su-Jin Oh, Hyun Soo Nam, Yoon Seok Song, Kyung-Chul Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(7): 961. CrossRef
- Association between the Korean Healthy Diet Score and Metabolic Syndrome: Effectiveness and Optimal Cutoff of the Korean Healthy Diet Score
- 999 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effects of Low-sodium Diet Education Program on Dietary Habits, Diet Quality and Obesity Index in Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women
- Soo Bin Jeong, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Jin Nam Kim, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(6):513-526. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.6.513
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of low sodium diet education program on dietary habits, diet quality, and measures of obesity in overweight or obese middle-aged women.
METHODS
Subjects were 81 individuals aged 45 years or over, who completed an 8-week nutrition education. The subjects were divided into a normal group (N = 30) and an overweight-obese group (N = 51) according to the BMI. The effects were evaluated by anthropometric measurement, biochemical analysis, questionnaire, and diet records before and after the program.
RESULTS
Overweight-obese group showed significant decreases in weight (p < 0.0001), BMI (p < 0.0001), percent of body fat (p = 0.0087), waist circumference (p < 0.0001), systolic (p = 0.0003) and diastolic blood pressure (p = 0.0261). Nutrients intakes were not different between the two groups and only sodium intake was decreased after education. Total score of general dietary habits, dietary behavior related to sodium intake, dietary diversity score (DDS), diet variety score (DVS), and diet quality index-international (DQI-I) were improved in both groups compared to the baseline. Overweight-obese group showed significant improvement in 'having fruits everyday', 'having fish everyday', 'trying to eat many kinds of food', 'eating less broth when eating soup, stew, and noodles', 'eating less kimchi and salt-fermented vegetable', and 'propensity to think that dishes should be pretty seasoned'. In addition, moderation of empty calories food (p = 0.0064) and macronutrient ratio (p = 0.0004) were improved in the overweigh-obese group, but in the normal group, the results did not reach statistical significance.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggested that low sodium diet education program may contribute to obesity management by improving diet quality and dietary habits in middle-aged women.
- 968 View
- 3 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



