Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
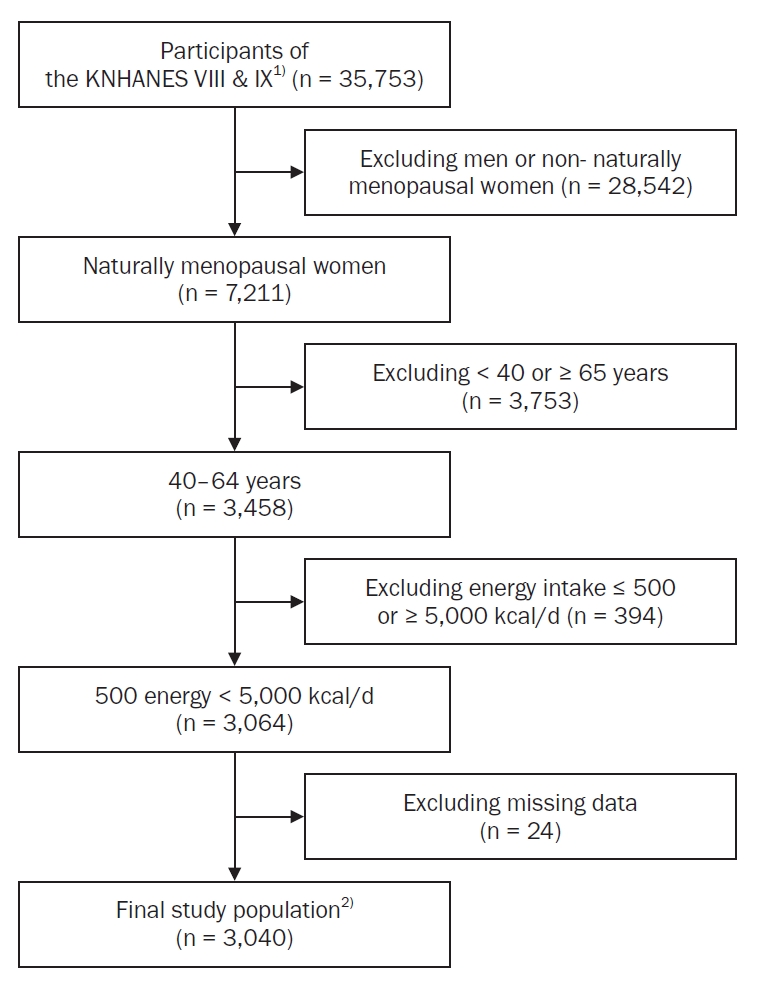
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 4,092 View
- 54 Download

- [English]
- Associations between the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease and dietary and lifestyle behavior among young Korean adults: a preliminary cross-sectional study
- Soheun Shim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):396-405. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00011

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a clinical condition caused by esophageal tissue damage resulting from the reflux of stomach or duodenal contents. An increasing number of GERD cases have been reported recently; however, research on this population, especially young adults, is lacking. This study aimed to investigate the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Methods: A total of 202 individuals (19–34 years old) living in Gwangju were surveyed using a questionnaire to examine their general characteristics, lifestyle, and dietary behaviors. GERD symptoms were investigated using the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GerdQ). The participants were grouped into normal (GerdQ score ≤ 4) and caution (GerdQ score ≥ 5), and their characteristics were analyzed according to the group. Results: The findings suggested 15 participants (7.4%) belonged to the GERD caution group. More non-office workers were in the caution group than in the normal group (P < 0.05). The participants’ smoking, physical activity, sleep duration, and pillow height were not significantly different between the GERD phenotypes; however, the caution group consumed alcohol more frequently than the normal group (P < 0.001). The analyses of the participants’ eating behaviors revealed that the frequency of overeating, late-night snacking and chocolate consumption was significantly higher in the caution group (P < 0.001). Conclusion: Lifestyle and dietary behaviors were associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Further studies with larger cohorts are required to confirm these findings.
- 5,961 View
- 75 Download

- [English]
- Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):173-188. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to analyze the regional differences in dietary protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome.
Methods
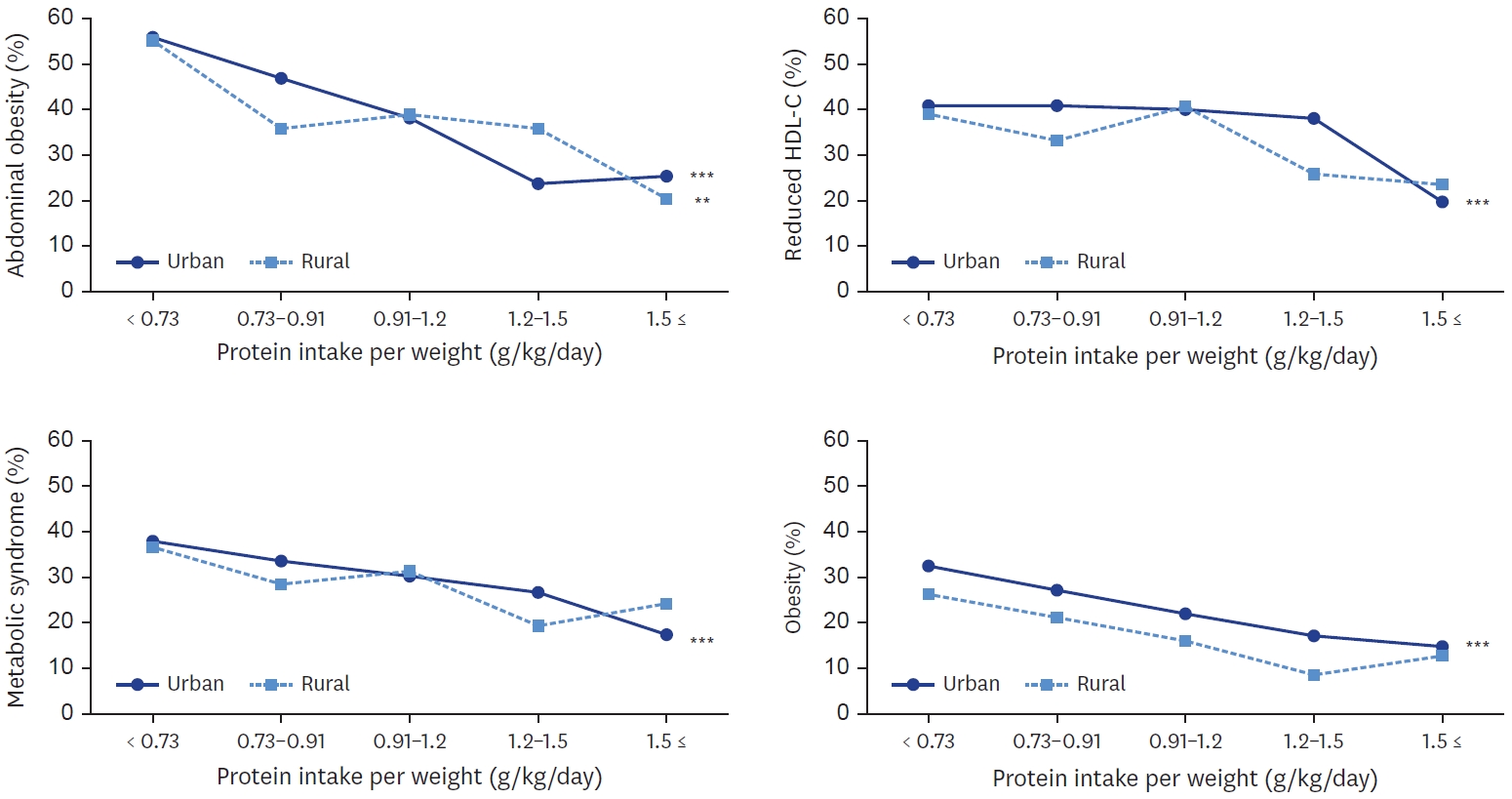
Study participants were 1,721 older adults aged 65 and over who participated in 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Using 24-hour recall dietary intake data, protein intake and their food sources were examined. The association between protein intake and metabolic syndrome, obesity, and abdominal obesity were analyzed by multiple logistic regression.
Results
Total protein and animal protein intakes were higher in urban area (60.0 g, 24.4 g, respectively) than in rural area (54.6 g, 19.6 g, respectively). With increase of protein intake level, animal to total protein proportion was increased in both areas. Total protein and plant protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity, abdominal obesity in both areas. Animal protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity in both areas, and with abdominal obesity only in urban area. In urban area, plant protein intake was also negatively associated with the risks of metabolic syndrome, elevated triglyceride, and reduced high density lipoprotein-cholesterol. In urban area, the risk of metabolic syndrome was decreased when their protein intake was more than 0.91 g/kg and was lowest when their protein intake was more than 1.5 g/kg (P for trend < 0.001).
Conclusions
Korean older adults showed inadequate protein intake and those in rural area showed lower animal protein intake than in urban area. The risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome was decreased with the increase of protein intake level. These findings may help develop effective nutrition support strategy for older adults to reduce regional health disparity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
Yea-Chan Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Soyoung Jeon, Yae-Ji Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2026; 50(1): 178. CrossRef - The association between dietary protein intake and metabolic syndrome: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Dorsa Ghazvineh, Ali Hosseinpour, Vahid Basirat, Elnaz Daneshzad
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between total, animal-based, and plant-based protein intake and cognitive decline in older adults
Maud Peperkamp, Margreet R. Olthof, Marjolein Visser, Hanneke A. H. Wijnhoven
European Journal of Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing Nutritional Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Diverse Statistical Tools
- 10,670 View
- 112 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
- Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):51-64. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between ultra-processed food (UPF) consumption and chronic diseases in elderly Koreans.
Methods
Data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were analyzed. Dietary intake and UPF consumption were assessed using the NOVA food classification based on 24-hour recall data from 3,790 participants (aged 65+ years). Participants were divided into 4 groups based on the quartile of energy intake from UPFs. Regions were classified as urban or rural. Multivariable logistic regression was employed to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) after controlling for potential confounders.
Results
Among the participants, 71.3% resided in urban and 28.7% in rural areas. Compared to the urban elderly, rural participants tended to be older, have lower education and income levels, be more likely to live in single-person households, and have a higher smoking rate (P < 0.05). Urban elderly consumed more UPFs daily (146.1 g) compared to rural residents (126.6 g; P < 0.05). “Sugar-sweetened beverages” were the most consumed category in both regions. “Sweetened milk and its products” and “traditional sauces” were prominent in urban areas, while rural elderly consumed more “traditional sauces” and “distilled alcoholic beverages.” Rural areas also had a higher carbohydrate-to-calorie ratio than urban areas. Compared to the lowest quartile of UPF intake, the highest quartile was significantly associated with impaired fasting glucose only in rural areas (AOR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.00–2.19; P for trend = 0.0014). No significant associations were observed for diabetes in either urban or rural areas.
Conclusions
This study suggests that high intake of UPFs is associated with increased odds of impaired fasting glucose in rural elderly. Further research is needed to elucidate the specific negative health effects of UPFs in different populations, and targeted efforts should promote healthy diets in both urban and rural areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
Nazlıcan Erdoğan Gövez, Eda Köksal
Current Nutrition Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study of the Chemosensory Properties of Commercial Processed Foods Using Electronic Sensors
Hyeonjin Park, Younglan Ban, Sojeong Yoon, Hyangyeon Jeong, Seong Jun Hong, Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 805. CrossRef - Analysis of Flavor and Taste Patterns of Various Processed Animal Foods: Using the Electronic Tongue and Nose
Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Younglan Ban, Hyeonjin Park, Sojeong Yoon, Na Eun Yang, Seong Jun Hong, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(12): 1267. CrossRef
- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
- 2,405 View
- 74 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Estimating and evaluating usual total fat and fatty acid intake in the Korean population using data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
- Gyeong-yoon Lee, Dong Woo Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):414-422. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.414
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated usual dietary intakes of total fat and fatty acids among the Korean population based on the revised Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2020 (2020 KDRIs).
Methods
This study utilized data from the eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES 2019–2021). We included 18,895 individuals aged 1 year and above whose 1-day 24-hour dietary recall data were available. To calculate the external variability using the National Cancer Institute 1-day method, data from the U.S. NHANES 2017-March 2020 Pre-pandemic dataset were employed. The total fat and fatty acid intake were evaluated based on the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDRs) and Adequate intake (AI) of 2020 KDRIs for each sex and age groups.
Results
Approximately 86% of the Korean population obtained an adequate amount of energy from total fat consumption (within the AMDRs), indicating an appropriate level of intake. However, the percentage of individuals consuming saturated fatty acids below the AMDR was low, with only 12% among those under 19 years of age and 52% aged 19 years and older. On a positive note, approximately 70% of the population showed adequate consumption of essential fatty acids, exceeding the AI. Nevertheless, monitoring the intake ratio of omega 3 (n-3) to omega 6 (n-6) fatty acids is essential to ensure an optimum balance.
Conclusions
This study explored the possibility of estimating the distribution of nutrient intake in a population by applying the external variability ratio. Therefore, if future KNHANES conduct multiple 24-hour recalls every few years-similar to the U.S. NHANES-even for a subset of participants, this may aid in the accurate assessment of the nutritional status of the population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef - The association between COVID-19 and changes in food consumption in Korea: analyzing the microdata of household income and expenditure from Statistics Korea 2019–2022
Haram Eom, Kyounghee Kim, Seonghwan Cho, Junghoon Moon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 153. CrossRef - Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2016–2021 KNHANES data
Enkhgerel Erdenetsetseg, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 144. CrossRef
- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- 2,878 View
- 49 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Changes in nutritional status of Korean older adults during COVID-19 Pandemic by household income and demographic factors -using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(2019-2020): a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):302-316. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to identify changes in the nutritional status of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic according to household income and demographic characteristics.
Methods
Study participants were 2,408 adults aged 65 and over who participated in the 2019–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). To examine changes in nutrient intake levels resulting from COVID-19, data of 2019 and of 2020 were compared. Study participants were divided into three groups based on household income level to compare these changes. The changes were compared according to household income level, age group, and household type.
Results
Percentages of recommended intakes for energy, protein, and most micronutrients were the lowest for the low-income group of both males and females in 2020. The Mean Adequacy Ratio (MAR) score was the lowest for the low-income group in both years. When comparing nutrient density for 2019 and 2020 by income group, the male low-income group experienced a decrease in nutrient densities of vitamin A, thiamine, calcium, and iron. For the same group, a decreased percentage for energy intake from protein was noted. Fruit intake was lowest in the low-income group for both males and females. Low-income males had the lowest intake levels for meat, fish, eggs, and legumes in both 2019 and 2020 and the lowest milk and milk product intake levels in 2020. Older adults living alone or single older adults with children had lower MAR scores than those living with a spouse. Older adults living alone experienced decreases in energy and thiamine and iron intake levels in 2020 compared to their intake levels in 2019.
Conclusions
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, nutrition intake levels worsened for older adult males in the low-income group and older adults living alone. This finding shows the need for a more systematic nutritional support strategy for the vulnerable older adults population in national disaster situations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
Yong-Seok Kwon, Dasol Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1973. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Comparison of nutrient intake and Korean Healthy Eating Index among the elderly in rural areas pre- and post- COVID-19 pandemic: the 2018–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Sangyeon Kim, Hye-Sook Hong, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(5): 496. CrossRef
- How Did the Dietary Behavior of Older Korean Adults Change During the COVID-19 Pandemic?
- 2,522 View
- 45 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Association between dietary intake, body measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):282-292. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Bone health in early adulthood, as individuals approach peak bone mass, plays a critical role in preventing osteoporosis later in life. This study aimed to investigate the associations between lifestyle and dietary factors, anthropometric measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 100 healthy Korean adults (50 men and 50 women) in their 20s and early 30s. Bone mineral density (BMD), anthropometric measurements, dietary intake (24-hour recall), and urinary bone resorption indicators (deoxypyridinoline and N-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen) were analyzed. Variables were compared between the osteopenia and osteoporosis groups (OSTEO group: 30% men and 60% women) and the healthy control group.
Results
Men in the OSTEO group were significantly taller than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Women in the OSTEO group had significantly lower body weight and body composition (muscle and body fat) than those in the normal group (P < 0.01). Men in the OSTEO group had a significantly higher intake of animal calcium (Ca) than those in the normal group (P < 0.05). Women in the OSTEO group had significantly higher dietary fiber, vitamin A, Ca, plant Ca, and potassium intake than did those in the normal group (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in caffeinated beverage consumption, eating habits, or urinary bone resorption indicators between the OSTEO and control groups of either sex.
Conclusions
In our study of young South Korean adults, we observed low bone density levels, with particularly low BMD in taller men and underweight women. We found a higher nutrient intake in the OSTEO group, indicating the possibility of reverse causality, a phenomenon often found in cross-sectional studies. Therefore, there is a need to further elucidate dietary factors related to osteoporosis in young adults through prospective cohort studies involving a larger population.
- 1,333 View
- 19 Download

- [Korean]
- Dietary sodium and potassium intake of Koreans estimated using 2 different sources of their contents in foods, Food & Nutrient Database and the Korean Total Diet Study : a comparative study
- Jee Yeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Soo Hyun Lee, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(3):235-244. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.3.235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Based on the results from the Korean Total Diet Study (KTDS), the sodium (Na) and potassium (K) intake of Koreans were estimated and compared with intake estimates from the Food & Nutrient Database (FNDB), as in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) to verify the validity of these estimates.
Methods
One hundred and thirty-four representative foods (RFs) covering 92.5% of the total food intake of Koreans were selected, and 228 pairs of corresponding ‘RF x representative cooking method’ were derived by reflecting the methods used mainly in terms of frequency and quantity in their cooking. RF samples were collected from three cities with a larger population size in three regions (nine cities) nationwide, and six composite samples were made for each RF, considering its regional and/or seasonal characteristics. One thousand three hundred and sixty-eight ‘RF x representative cooking method’ pair samples were prepared, and the Na and K contents were assessed using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-MS). The Na and K intake of the Korean population was estimated by linking the content with the food intake data from the 7th KNHANES.
Results
The mean Na and K intake of Koreans were 2,807.4 mg and 2,335.0 mg per person per day, respectively. A comparison with the Na and K intake from KNHANES, including only RFs of KTDS, showed comparable results with less than 5% variation. While the contribution and ranking of food items to Na intake were similar between KNHANES and KTDS, there were differences in K intake. This was attributed to the large discrepancies in the K content of rice and coffee between KTDS results and the values in the 9th Revision of the National Food Composition Table used in KNHANES.
Conclusions
The Na and K intake of Koreans estimated based on the KTDS, which performed nutrient analysis on samples prepared to a ‘table-ready’ state using foods of the representative collection, was similar and comparable with that of KNHANES. This supports the validity and usefulness of FNDB-based nutrient intake estimation at the population level. The list of nutrients studied in KTDS is expected to be expanded, allowing for intake estimation of nutrients with currently insufficient or absent information in the FNDBs in use.
- 2,626 View
- 70 Download

- [Korean]
- Comparison of blood biochemical characteristics and dietary intake by sex in gastric cancer patients over 40 years in Korea based on 7th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: a cross-sectional study
- Hyeon-Ju Lee, Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):48-60. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to compare the sex-associated differences in the dietary intake of gastric cancer patients in Korea.
Methods
Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) the 7th (2016-2018) were analyzed in the present study. The subjects included 122 gastric cancer patients aged over 40 years (75 male, 47 female). General characteristics (age, marital status, household income, education, food security, comorbidities, alcohol drinking, and smoking), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, body mass index, and blood pressure), blood biochemical characteristics [fasting plasma glucose (FPG), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, triglyceride, total cholesterol, and HDL-cholesterol)], and quantity and quality of dietary intake were compared between male and female participants.
Results
Males had higher rates of having a spouse, prevalence of hypertension, alcohol drinking, and smoking than females. The proportion of males with a normal range of FPG, BUN, and HDL-cholesterol was lower than that in females. The total cholesterol levels above the normal range were higher in females than in males. We also found that females had a higher percentage of intakes below the estimated energy requirement (EER) and intakes below the estimated average requirement (EAR) for carbohydrates, niacin, phosphorus, and iron than males. The index of nutritional quality (INQ) for phosphorus and folate, nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR) for vitamin C, thiamine, niacin, folate, calcium, and phosphorus, and the mean adequacy ratio (MAR) were lower in females than males.
Conclusions
In Korean gastric cancer patients, management of comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertriglyceridemia, lowering FPG, and raising HDL-cholesterol level management is required for males, whereas management of lowering total cholesterol and raising hematocrit is required for females. The quantitative and qualitative nutritional intakes were poor in gastric cancer patients, especially in females, who had a lower nutritional intake than males. We suggest that nutritional interventions are needed to improve the overall nutritional intake in both male and female gastric cancer patients. In particular, we propose that support is urgently needed for females whose nutritional intake is lower than that of males. In addition, family, social, and national support for nutritional management of female gastric cancer patients is highly necessary. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of coronary artery disease according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years and older: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition E
Areum Song, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 457. CrossRef
- Prevalence of coronary artery disease according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years and older: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition E
- 1,273 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Status of Iodine Intake and Comparison of Characteristics according to Iodine-sourced Food Intake Patterns of Chinese Adults: A Study Encompassing Three Regions with Different Iodine Nutritional Statuses
- Danying Zhang, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):503-514. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.503
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examines the status of iodine intake and compares the characteristics (region and thyroid disease prevalence) according to the iodine-sourced food intake pattern in Chinese adults.
Methods
An online survey was conducted by enrolling 437 Chinese adults aged 18-65 years, living in three regions with different iodine nutritional statuses: Sichuan, Chongqing, and Guangdong.
Results
The prevalence of thyroid diseases in Sichuan, Chongqing, and Guangdong were 12.5%, 8.5%, and 2.8%, respectively. Conversely, the proportion of people who received thyroid disease-related examinations was a mere 37.5%. Among the subjects who underwent thyroid examination, the prevalence of thyroid disease in the three regions was 32.2%, 21.8%, and 8.0%, respectively. No differences were obtained in the total iodine intake by region, but the type of iodine source foods differed. Regardless of the region, the highest iodine content was obtained from seaweed. However, the iodine content from iodized salt and other foods differed significantly by region. Factor analysis revealed three food intake patterns according to the iodine food source. The study further determined regional differences and differences in the prevalence of thyroid disease according to food intake patterns.
Conclusions
High salt intake can also increase iodine intake, which is thought to have an effect on the occurrence of iodine-excess thyroid disease. Hence, efforts focused on improving salty eating habits need to be implemented.
- 1,247 View
- 10 Download

- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):422-434. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.422
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With an increase in the population of the elderly in Korea, their nutritional status has become a cause for concern. This study was designed to compare the nutritional intake and health status of the Korean elderly according to their body mass index.
Methods
The subjects were 3,274 elderly people aged 65 and above who had participated in the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The subjects were divided into four groups: underweight, normal, overweight, and obese, based on their BMI. The general characteristics, daily energy, and nutrient intakes, nutrient intakes compared to the recommended nutrient intake, percentage of participants whose nutrient intake was lower than the estimated average requirement (EAR), index of nutrient quality, the mean adequacy ratio (MAR), intakes by food group, and health status of the four groups were compared.
Results
Underweight elderly people showed lower energy, lipids, dietary fiber, vitamin C, riboflavin, niacin, phosphorus, sodium, and potassium intake and MAR score (P < 0.001) compared to the normal or obese elderly. The mean protein, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin C, phosphorus, and iron intake of the underweight elderly was lower than the EAR (P < 0.05). Underweight elderly people also had a lower intake of vegetables and fats, oil and sweets food groups than the other groups (P < 0.001). The prevalence of diabetes and dyslipidemia was higher in the obese group, but the percentage of anemia was higher in the underweight group.
Conclusions
Underweight elderly people were vulnerable to undernutrition and were at a higher risk of anemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the Association Between Older Adults’ Body Mass Index and Their Fall Experience, Chronic Diseases, and Exercise Frequency: Evidence from Korea
Daekeun Kwon, Su-Yeon Roh, Jeonga Kwon
Medicina.2025; 61(9): 1622. CrossRef - Effect of physical activity on free fatty acids, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in obese older women
Woo-Hyeon Son, Min-Seong Ha, Tae-Jin Park
Physical Activity and Nutrition.2024; 28(2): 1. CrossRef - Determinants of Length of Stay for Medical Inpatients Using Survival Analysis
Jaekyeong Kim, Haegak Chang, Seiyoung Ryu, Ilyoung Choi, Angela Eunyoung Kwon, Haeyong Ji
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2024; 21(11): 1424. CrossRef - The Relationship of Pork Meat Consumption with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Biomarkers of Health Status in Korean Older Adults
Ah-Jin Jung, Anshul Sharma, Mei Chung, Taylor Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4188. CrossRef
- Exploring the Association Between Older Adults’ Body Mass Index and Their Fall Experience, Chronic Diseases, and Exercise Frequency: Evidence from Korea
- 3,526 View
- 53 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Blood Biochemical Characteristics, Dietary Intake, and Risk Factors Related to Poor HbA1c Control in Elderly Korean Diabetes Patients: Comparison between the 4 th (2007-2009) and the 7 th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):406-421. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.406
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the blood biochemical characteristics, comorbidities, dietary intake, and other risk factors leading to poor glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) control in elderly Korean diabetes patients over 65 years of age.
Methods
Data from the 4 th (2007-2009) and the 7 th 2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) were used. Socio-demographic characteristics (age, gender, region, household income, education level, marital status, nutrition education, diabetes duration and diabetes treatment), lifestyle characteristics (drinking, smoking, regular walking, and subjective health perception), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, and waist circumference), blood biochemical characteristics (HbA1c, high- density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, total cholesterol, blood urea nitrogen, and blood creatinine), co-morbidities (obesity, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and anemia), energy and nutrients intake, food group intake, and HbA1c control-related risk factors were compared.
Results
Compared to the 4 th survey, the 7 th survey showed an increase in diabetes prevalence among men, an increase in the prevalence of diabetes in the older patients, and an increase in the duration of diabetes. The energy ratio from carbohydrate consumption in the 7 th survey was lower than in the 4 th .Compared to the 4 th survey, thiamine and riboflavin intake had improved, and the intakes of vitamin A, vitamin C, and niacin had worsened in the 7 th . A comparison of food group intakes showed that there was a decrease in the consumption of whole grains, potatoes, and milk and an increase in the intake of beverages and alcoholic beverages. The risk factors for poor control of HbA1c were the duration of diabetes and co-morbid hypertriglyceridemia in the 4 th survey, whereas subjective health perception, obesity, and hypercholesterolemia as co-morbidities were found to be risk factors in the 7 th in addition to the risk factors highlighted in the 4 th survey.
Conclusions
For the future management of elderly Korean diabetes patients, greater care is indicated for men over 75 years, and those with low levels of education. It is necessary to increase the intake of milk and vegetables, and reduce the intake of beverages and alcoholic beverages. In addition, it is necessary to reduce the incidence of obesity, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertriglyceridemia for proper control of blood sugar. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the Dietary Behavior of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-sectional Study
Sohyun Jin, Youngshin Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 80. CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - Consistency of 1-day and 3-day average dietary intake and the relationship of dietary intake with blood glucose, hbA1c, BMI, and lipids in patients with type 2 diabetes
DaeEun Lee, Haejung Lee, Sangeun Lee, MinJin Lee, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(1): 20. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the Dietary Behavior of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-sectional Study
- 2,100 View
- 42 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary Iron Intake of Koreans Estimated using 2 Different Sources of Iron Contents are Comparable: Food & Nutrient Database and Iron Contents of Cooked Foods in the Korean Total Diet Study
- Jeeyeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Yoonjae Yeoh, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):245-253. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.245
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to find out if the dietary iron intake of Koreans estimated by 2 different methods (iron content sources) using the food intake data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) are comparable. One method was based on the KNHANES's Food & Nutrient Database (FND) derived mainly from the Korean Food Composition Table and the other used the iron content (IC) of food samples processed in the Korean Total Diet Study (KTDS).
Methods
Dietary intake data from the 2013-2016 KNHANES was used to select representative foods (RFs) in KTDS for iron analysis. Selection of the RFs and cooking methods for each RF (RF × cooking method pair) was performed according to the ‘Guidebook for Korean Total Diet Studies’ and resulted in a total of 132 RFs and 224 ‘RF × cooking method’ pairs. RFs were collected in 9 metropolitan cities nationwide once or twice (for those with seasonality) in 2018 and made into 6 composites each, based on the origin and season prior to cooking. Then, the RF composites prepared to a ‘table ready’ state for KTDS were analyzed by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Dietary iron intake of the Korean population was estimated using only RFs’ intake data based on the 2 sources of iron content, namely FND-KNHANES and IC-KTDS.
Results
RFs in KTDS covered 92.0% of total food intake of Koreans in the 2016-2018 KNHANES. Mean iron intake of Koreans was 7.77 mg/person/day by IC-KTDS vs 9.73 mg/person/day by FND-KNHANES. The major food groups contributing to iron intake were meats (21.7%), vegetables (20.5%), and grains & cereals (13.4%) as per IC-KTDS. On the other hand, the latter source (FND-KNHANES) resulted in a very different profile: grains & cereals (31.1%), vegetables (16.8%), and meats (15.3%). While the top iron source was beef, accounting for 8.6% in the former, it was polished rice (19.2%) in the latter. There was a 10-fold difference in the iron content of polished rice between 2 sources that iron intakes excluding the contribution by polished rice resulted in very similar values: 7.58 mg/person/day by IC-KTDS and 7.86 mg/person/day by FNDKNHANES.
Conclusions
This study revealed that the dietary iron intake estimated by 2 different methods were quite comparable, excluding one RF, namely polished rice. KTDS was thus proven to be a useful tool in estimating a ‘closer-to-real’ dietary intake of nutrients for Koreans and further research on various nutrients is warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrients and food intake according to atherogenic index of plasma in Korean postmenopausal women
Ye-Jin Lee, Sun Yung Ly
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 87. CrossRef - Iron Consumption and Colorectal Cancer in Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
Sukhong Min, Katherine De la Torre, Hyobin Lee, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Daehee Kang
Nutrients.2025; 17(8): 1309. CrossRef - Dietary sodium and potassium intake of Koreans estimated using 2 different sources of their contents in foods, Food & Nutrient Database and the Korean Total Diet Study: a comparative study
Jee Yeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Soo Hyun Lee, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 235. CrossRef
- Nutrients and food intake according to atherogenic index of plasma in Korean postmenopausal women
- 1,940 View
- 22 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Status in Korean Menopausal Women: Based on the 2016 ~ 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Pil-Sook Park, Mei-Sheng Li, Mi-Yeon Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):482-494. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.482
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated dietary behavior and nutritional status according to the metabolic syndrome status in Korean menopausal women.
Methods
The subjects were 1,392 menopausal women aged 50 to 64 who took part in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of 2016 and 2017. Subjects were classified into normal (NOR) group, pre-metabolic syndrome (Pre-MetS) group, and metabolic syndrome (MetS) groups according to the number of metabolic syndrome risk factors present.
Results
The overall prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 33.7%. Using the NOR group as a reference, the odds of belonging to the MetS group in Model 1 adjusted for age were higher at 53% (OR = 1.53, 95% CI:1.011-2.307) for ‘not used’ subjects compared to ‘used’ subjects of the nutrition labeling system. Using the NOR group as a reference, every 1g increase in the intake of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) decreased the odds of belonging to the MetS group in Model 1 adjusted for age by 3% (MUFA, OR = 0.97, 95% CI:0.946-0.991; PUFA, OR = 0.97, 95% CI:0.942-0.993).
Conclusions
These results suggest that to reduce the number of risk factors of metabolic syndrome in menopausal women, nutritional education should emphasize the adequate intake of riboflavin, unsaturated fatty acids, protein, and calcium, and also encourage the recognition and use of nutritional labeling. Results of this study are expected to be utilized as basic data for the health management of menopausal women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardiocerebrovascular Disease or Fatty Liver Incidence Associated with Pattern of Metabolic Risk Factors and Nutritional Status of Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
Pil Sook Park, Mei Sheng Li, Chong Yu Ding, Mi Yeon Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(2): 165. CrossRef - The Relationship Between the Korean Adults Diet Evaluated Using Dietary Quality Indices and Metabolic Risk Factors: Based on the 2016 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Chong-Yu Ding, Pil-Sook Park, Mi-Yeon Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 223. CrossRef
- Cardiocerebrovascular Disease or Fatty Liver Incidence Associated with Pattern of Metabolic Risk Factors and Nutritional Status of Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
- 1,556 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):467-481. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.467
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine the biochemical characteristics, intake of energy, and nutrients by household income levels of Korean adolescents aged 12 to 18 years.
Methods
Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES) were used for the study. A total of 1,839 (966 boys, 873 girls) subjects were included, and they were divided into four income groups according to their household income level. We examined general characteristics (gender, region of residence, skipping or not-skipping breakfast, lunch, dinner, frequency of eating-out), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, weight status), biochemical characteristics (fasting plasma glucose, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, triglycerides, cholesterol, HDLcholesterol, hemoglobin, and hematocrit), the quantitative intake of energy and nutrients using the Korean Dietary Reference Intakes (KDRI), and the qualitative intake evaluated by the nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean nutrition adequacy ratio (MAR) of the four groups.
Results
There were significant differences by income group within the region of residence and the rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, and dinner. The low-income group had a higher rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, and dinner. According to the income group, there was a difference in the height of boys, and there was no difference in the weight and obesity of boys and girls. In the biochemical characteristics, only the hematocrit of girls showed differences by income group. The quantitative intake of energy and nutrients compared with KDRI differed by income group. There were differences in energy, carbohydrates, proteins, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and phosphorus levels in boys and protein, vitamin A, niacin, and sodium levels in girls. The qualitative intake of energy and nutrients examined using NAR and MAR also differed according to the income group. The NAR showed differences in calcium in boys and vitamin C and calcium in girls. The MAR revealed differences in both boys and girls by income group.
Conclusions
Among adolescents in the low-income group, the rate of skipping meals was high, and the quantitative and qualitative intake of energy and some nutrients was low. It is suggested that the nutritional intake can be improved by lowering the rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, dinner. We suggest that even just providing breakfast in schools can be considered highly effective in improving the rate of avoidance of skipping meals and improving nutrient intake. Also, we suggest that it is necessary to improve the food environment, food availability, and food accessibility through national and social support for low-household income adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency and value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using dietary area: a descriptive study
Yunhwa Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 317. CrossRef - 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
민지 손, 은주 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 213. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of Changes in Adolescent Dietary Behavior during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Improvement Strategies for School-Provided Nutrition Counseling
Yeseul Na, Jieun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2023; 61(1): 39. CrossRef
- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,502 View
- 8 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
- Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):363-381. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the Korean elderly’s dietary intake status, subjective health-related perception and chronic disease prevalence among age groups. Associations of dietary quality with subjective health-related perception and chronic diseases were also examined.
Methods
Based on data from the 7th National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a total of 3,231 elderly were selected and categorized into 4 age groups of ‘65 ~ 69’, ‘70 ~ 74’, ‘75 ~ 79’ and ‘over 80’. Nutrient intakes, proportions of those with insufficient nutrient intakes, Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI), some subjective health-related perceptions and prevalence of major chronic diseases were compared according to the age groups. Differences in the subjective health-related perceptions and odds ratios of the chronic diseases according to the quartile levels of KHEI within the same age group were analyzed.
Results
With the increase of age, several nutrient intakes (P < 0.001) and KHEI scores significantly decreased (P < 0.01). In women, activity restriction increased (P < 0.05), and EQ-5D score decreased with age (P < 0.001). Prevalence of hypertension (P < 0.0001), hypercholesterolemia (P < 0.05) and anemia (P < 0.01) significantly increased, while hypertriglyceridemia (P < 0.01) significantly decreased only in men. Obesity prevalence decreased, while underweight prevalence increased (P < 0.05). Subjective health status, EQ-5D score and PHQ-9 score significantly improved as KHEI score increased in certain age groups of women (P< 0.05). Odds ratio of hypercholesterolemia significantly increased with the increase of KHEI score in 65 ~ 69-year-old women. However, hypertension and anemia significantly decreased with the increase of KHEI score in 75 ~ 79-year-old women (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
The study findings suggest that nutrition management and policy for the Korean elderly need to apply a segmented age standard that can better reflect their dynamic characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 359. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef - Blood Biochemical Characteristics, Dietary Intake, and Risk Factors Related to Poor HbA1c Control in Elderly Korean Diabetes Patients: Comparison between the 4th(2007-2009) and the 7th(2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 406. CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 422. CrossRef
- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
- 1,676 View
- 21 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Estimation of the Usual Food Intake Distribution Reflecting the Consumption Frequency and a Comparison of the Proportion of Non-consumers: Based on the KNHANES 2009
- Su Ji Ham, Dong Woo Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(4):296-306. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.4.296
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to estimate the distribution of the usual dietary intake of foods with respect to the probability of consumption derived from the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) of the 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
Methods
The intake quantity and frequency of 63 food items were assessed from the 2009 KNHANES which was completed by 7,708 participants. The participants completed one or two 24-h dietary recalls and one FFQ. The usual intake distribution was estimated using the multiple source method (MSM), and the proportion of nonconsumers was calculated through the usual intake distribution. This was then compared with the proportion of non-consumers from the 24-hour recall method.
Results
The difference in the proportion of non-consumers ranged from 2% to 82.9%, indicating that there is a very large difference based on food groups. The food groups in which the proportion of non-consumers did not differ was composed of foods consumed daily, such as ‘rice’, ‘cereal and barley’, and ‘Chinese cabbage and kimchi’, or foods with distinct palatability such as ‘coffee’ and ‘alcohol’. On the other hand, in the case of the food groups with a high difference in the proportion of non-consumers, most comprised fruits that emphasized seasonality.
Conclusions
In the case of foods or food groups that are occasionally consumed, it is desirable to use 2 recalls with additional FFQ data by combining the consumption frequency and the quantity consumed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Accuracy of 24-Hour Dietary Recalls among Free-Living Older Korean Adults: Validation against Weighed Intakes
Jieun Mun, Suyoung Kim, Kanghee Kim, Chaeyeon Nam, Sein Kim, Clara Y Park
The Journal of Nutrition.2025; 155(12): 4446. CrossRef - Fraction of cancer incidence and mortality attributable to dietary factors in Korea from 2015 to 2030
Hyun Jeong Cho, Jin Young Yoo, Ga-Eun Yie, An Na Kim, Soseul Sung, Sungji Moon, Youjin Hong, Sangjun Lee, Inah Kim, Kwang-Pil Ko, Sun-Seog Kweon, Jung Eun Lee, Sue K. Park
Epidemiology and Health.2025; 47: e2025065. CrossRef - Dietary Management of Obesity
Sang Hoon Lee, San Ha Kim, Sung Chul Park
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 83(3): 87. CrossRef
- Accuracy of 24-Hour Dietary Recalls among Free-Living Older Korean Adults: Validation against Weighed Intakes
- 1,851 View
- 17 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Sugar Reduction Perception and Sugary Food Intake among High School Students in Incheon
- Gyeong-Ja Bae, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):111-121. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.111
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined ways to promote desirable eating habits by choosing foods with low sugar contents and provide nutrition education in adolescents. Methods: This study was a cross-sectional survey. The sugar reduction perception and knowledge, sugary food preference, and intake frequency of 487 male and female high school students in Incheon were analyzed comparatively. Results: Approximately 94.9% and 94.5% of the subjects were unaware of the promotion of a sugar reduction policy and the sugar reduction in the basic guidelines for school meals, respectively. Approximately 95% of them had not received any sugar reduction nutrition education, and 90% were not interested in sugar reduction. The perception for sugar reduction was significantly higher in girls (3.43 out of 5 points) than in boys (3.16 out of 5 points) (P < 0.001). Knowledge about sugar was 3.65 out of 6 points in girls and 3.04 points in boys (P < 0.001). The preference and intake frequency for fruits of the total students were 4.24 out of 5 points and 2.56, respectively. For beverages, the preference was significantly higher in boys (3.97 points) than in girls (3.70 points) (P < 0.001), and the intake frequency was significantly higher in boys (2.26 points) than in girls (2.08 points) (P < 0.001). The preference for snacks was significantly higher for girls (4.19 points) than boys (4.02 points) (P < 0.01), and the intake frequency was 2.22 points in boys and 2.17 in girls, showing no significant difference. Sugar reduction perception and knowledge about sugar showed significant negative correlations with the snack intake frequency (r = -0.11, P < 0.05; -0.13, P < 0.05) after adjusting for gender, grade, and body mass index. Conclusions: The high school students' perception of sugar reduction was very low, and there was a significant correlation with sugary food intake, suggesting that the sugary food intake will decrease as the sugar reduction perception and knowledge about sugar increase. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Status of Sugar-Reduced Beverage Consumption according to Sex, among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju
Na-In Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Health-Related Factors according to the Frequency of Consumption of Sugar-Reduced Beverages among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju Area
Na-In Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 459. CrossRef - Sugar Intake and Perception of Sugar Reduction among University Students in Gwangju
Yeon-Ok Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1170. CrossRef - 충북지역 중등학생의 건강식생활 관련 식행동과 영양관리 정책에 대한 인식
은서 고, 영은 이
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 197. CrossRef
- Status of Sugar-Reduced Beverage Consumption according to Sex, among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju
- 1,188 View
- 16 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Estimation of Dietary Iodine Intake of Koreans through a Total Diet Study (TDS)
- Jeeyeon Lee, Yoonjae Yeoh, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(1):48-55. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.1.48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to estimate the dietary iodine intake of Koreans by a Total Diet Study (TDS) which provides ‘closer-to-real’ estimates of exposure to hazardous materials and nutrients through an analysis of table-ready (cooked) samples of foods. Methods: Dietary intake data from 2013-2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) was used to select representative foods (RFs) for iodine analysis. A total of 115 RFs were selected and 158 ‘RF × cooking method-combination’ pairs were derived by pairing each RF to corresponding cooking method(s) used more frequently. RFs were collected from 9 mega-markets in 9 metropolitan cities nationwide and mixed into composites prior to cooking preparation to a ‘table ready’ state for iodine analysis by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Iodine intake of Koreans was estimated based on the food intake data of the 2016-2018 KNHANES. Results: High iodine content was detected in seaweeds such as sea mustard and kelp. The mean iodine intake/capita/day was 418.4 ㎍ and the median value was 129.0 ㎍. Seaweeds contributed to 77.4% of the total iodine intake and the contribution by food item was as follows: sea mustard (44.0%), kelp (20.4%), laver (13.1%), milk (3.9%), egg (3.5%). Compared to the Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2020, the proportion of people with iodine intake exceeding the tolerable upper intake level or below the estimated average requirement was high in the physiologically vulnerable groups (infants, children, pregnant women, and lactating women). Conclusions: The results, drawn from a TDS, are regarded closer to real estimates for iodine intake of Koreans compared with values in existing literature, which were based on a very limited variety of foods. On the other hand, it seems necessary to seek out solutions for the problematic iodine intake among physiologically vulnerable groups through in-depth analyses on food intake data collected with significant scale & quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Radioactive Iodine Therapy in Patients with Hyperthyroidism
Kyeong Jin Kim, Eyun Song, Mijin Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Eu Jeong Ku, Hyun Woo Kwon, Jee Hee Yoon, Eun Kyung Lee, Won Woo Lee, Young Joo Park, Dong-Jun Lim, Sun Wook Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Jae Hoon Chung, Tae Yong Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Jee Soo Kim
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 65. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Radioactive Iodine Therapy in Patients with Hyperthyroidism
Kyeong Jin Kim, Eyun Song, Mijin Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Eu Jeong Ku, Hyun Woo Kwon, Jee Hee Yoon, Eun Kyung Lee, Won Woo Lee, Young Joo Park, Dong-Jun Lim, Sun Wook Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Jae Hoon Chung, Tae Yong Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Jee Soo Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 342. CrossRef - The association between iodine intake and thyroid disease in iodine-replete regions: the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Seon-Joo Park, Lulu Chen, Taylor C Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 554. CrossRef - Analysis and Risk Assessment of Total Iodine Content in Edible Seaweeds in South Korea
YoonMi Lee, Hyung June Park, Mira Jo, Kwang Soo Ha, Jong Soo Mok
Foods.2025; 14(16): 2865. CrossRef - Assessment of dietary iodine intake and its sources among Koreans: a cross-sectional analysis from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019–2021
Jee-Seon Shim, Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 728. CrossRef - Iodine intake from brown seaweed and the related nutritional risk assessment in Koreans
Sung Ok Kwon, Kwang-Il Kwon, Mi-Young Lee, Hye Young Lee, Cho-il Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(3): 412. CrossRef - Household Salt consumption and urinary iodine levels in Schoolchildren aged 8–10 in Darab City, Iran: 2022
Sakineh Hooshmand, Fatemeh Yousefian, Habibollah Rahimi, Mahdiyeh Mohammadzadeh, Rouhullah Dehghani
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Rising Incidence and Comorbidities of Endogenous Hypothyroidism in Republic of Korea from 2004 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
Chae Won Chung, Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(6): 891. CrossRef - High intakes of iodine among women during pregnancy and the postpartum period has no adverse effect on thyroid function
Dal Lae Ju, Sun Wook Cho, Chae Won Chung, Young Ah Lee, Gi Jeong Cheon, Young Joo Park, Choong Ho Shin, Jong Kwan Jun, June-Key Chung, Sue K. Park, YoonJu Song
European Journal of Nutrition.2023; 62(1): 239. CrossRef - Interactions between Polygenetic Variants and Lifestyle Factors in Hypothyroidism: A Hospital-Based Cohort Study
Da Sol Kim, Sunmin Park
Nutrients.2023; 15(17): 3850. CrossRef - Dietary sodium and potassium intake of Koreans estimated using 2 different sources of their contents in foods, Food & Nutrient Database and the Korean Total Diet Study: a comparative study
Jee Yeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Soo Hyun Lee, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 235. CrossRef - Dietary Iron Intake of Koreans Estimated using 2 Different Sources of Iron Contents are Comparable: Food & Nutrient Database and Iron Contents of Cooked Foods in the Korean Total Diet Study
Jeeyeon Lee, Sung Ok Kwon, Yoonjae Yeoh, Min Jeong Seo, Gae Ho Lee, Cho-il Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 245. CrossRef - Effect of iodine restriction on short-term changes in thyroid function in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism
Obin Kwon, Dong Yeob Shin, Eun Jig Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 250. CrossRef
- 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Radioactive Iodine Therapy in Patients with Hyperthyroidism
- 3,392 View
- 28 Download
- 13 Crossref

- [English]
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to the Frequency of Milk Consumption in Korean Adolescents: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ji Hyun Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):485-501. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine the biochemical characteristics and dietary intake of adolescents aged 12 to 18 years according to the frequency of milk consumption. Methods: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey was used for the study. The study examined adolescents’ (12~18 years) demographic characteristics (house income level, residence region, skipping or not-skipping of breakfast/lunch/dinner, eatingout frequency), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, weight status), biochemical characteristics (fasting plasma glucose, blood urea nitrogen, creatine, triglycerides, cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, hemoglobin, hematocrit) and nutrient intakes through quantitative and qualitative evaluation using the Korean Dietary Reference Intakes (KDRI), index of nutrition quality (INQ), nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) of 3 groups (< 1/week, 1~6/week, 1/day) according to the frequency of milk consumption. Results: There were significant differences in gender and income levels among the 3 groups. There were no differences in height, weight, and weight status among groups. There were differences in biochemical characteristics and nutrient intake. In boys, there were differences in the mean of BUN and HDL-cholesterol, in quantitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus, potassium by KDRI levels, in qualitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by INQ and riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by NAR among 3 groups. In girls, there were differences in the mean of blood urea nitrogen, creatine, HDL-cholesterol, in quantitative intakes of protein, riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by KDRI levels, in qualitative intakes of riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by INQ and riboflavin, calcium, phosphorus by NAR among the 3 groups. Conclusions: In Korean adolescents, boys had a higher frequency of milk consumption than girls, and higher the income level, higher the frequency of milk consumption. Consumption of milk appeared to have a positive association with triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, and indices related to muscle mass. Regular consumption of milk is an important factor in enhancing the intake of riboflavin, calcium, and phosphorus, which adolescents lack. The results of the study indicate a need to prepare an environment and education program to increase milk consumption in adolescents at home and school. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in Nutritional Status Through Low-Lactose Processed Milk Consumption in Korean Adults With Lactose Intolerance
Dong Hoon Jung, Gi Moon Nam, Chang Kyun Lee, Chul hong Kim, Hyun-San Lim, Ji Yeon Lee, Hee-Sook Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Quality in Children and Adolescents with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Using the Korean Nutrition Quotient Score
So Yoon Choi, Yoowon Kwon, Yoo Min Lee, In Hyuk Yoo, Tae Hyeong Kim, You Jin Choi, Su Jin Jeong
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2025; 28(4): 256. CrossRef - Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef
- Changes in Nutritional Status Through Low-Lactose Processed Milk Consumption in Korean Adults With Lactose Intolerance
- 1,479 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- A Comparisons of Nutritional Intake and Diet Quality Index-International in Gynecological Cancer Survivors and Normal Women - Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2016 -
- Bo-Young Seo, Eun-Sil Her
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):406-415. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.406
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to compare the nutritional intake and Diet Quality Index-International (DQI-I) of gynecological cancer survivors and normal women. Methods This study compared the anthropometric indices, dietary behavior, nutritional intake, and DQI-I in women with previous history of breast or uterine cancer [Gynecological cancer survivors group (GCSG, n=126)] and normal women [Normal control group (NCG, n=7,011)] using the 2013~2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data. Results Body mass index and waist circumference were lower in the GCSG compared the NCG. The frequency of skipping breakfast and eating out was higher in the NCG compared to GCSG. Energy and fat intake were significantly higher in the NCG than in the GCSG, whereas intake of all minerals and vitamins (excluding thiamine), and dietary fiber intake were higher in GCSG. It was observed that the fatty acid intake of the GCSG was significantly lower than that of the NCG. The diet quality evaluation using DQI-I results showed that GCSG was higher in the “within-group” diet variety and adequacy of vegetable group than the NCG, whereas the intake level of the fruit group was higher in NCG. Besides, protein, calcium, and vitamin C intake were higher in the GCSG than in the NCG. The GCSG showed higher levels of total fat and saturated fat moderation than the NCG, whereas cholesterol moderation showed the opposite results. The results of DQI-I comparison according to the cancer survival years showed that the overall score and scores related to diet adequacy and balance were higher in the below 5-year group, whereas the over 5-year group scored higher in terms of moderation of diet. Conclusions The results of this study suggest that a chronic disease based management approach is needed in cancer survivors. The study provides important data which can help in the preparation of guidelines for long-term lifestyle and diet management, in these patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effect of Vitamin Intake on the Relationship Between Depression and Health-related Quality of Life in Cancer Survivors (Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2020)
Min Ho Yun, Jong Eun Oh
Information.2024; 27(2): 131. CrossRef - Comparison of blood biochemical characteristics and dietary intake by sex in gastric cancer patients over 40 years in Korea based on 7th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: a cross-sectional study
Hyeon-Ju Lee, Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 48. CrossRef
- Mediating Effect of Vitamin Intake on the Relationship Between Depression and Health-related Quality of Life in Cancer Survivors (Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2020)
- 1,012 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Nutrient Intake between Hypercholesterolemic and Normal groups based on the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hyun-A Lee, Hyung-Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):396-405. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.396
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to compare the nutrient intake of normal healthy adults with those having hypercholesterolemia. Methods We analyzed data from the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VI). A total of 12,636 adults (5,223 males and 7,413 females) aged 19 or older were included in the study. Results Males with hypercholesterolemia were older and had a higher waist circumference, body mass index, fasting blood sugar levels (FBS) and serum triglyceride (TG) concentrations compared to the normal group. Females with hypercholesterolemia were older and had higher FBS levels and serum TG concentrations compared to the normal group. While comparing nutrient intake by the 24-hour recall method, the male normal group showed a higher intake of fat, saturated fatty acid (SFA), monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA), vitamin A and thiamin compared to the hypercholesterolemic group. However, the male normal group had a lower intake of iron and vitamin C compared to the hypercholesterolemic group. The female normal group had a higher intake of energy, protein, fat, SFA, MUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids, cholesterol, riboflavin, and niacin compared to the hypercholesterolemic group, but had a lower intake of iron compared to the hypercholesterolemic group. A comparison of nutrient intake by food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) showed the following: There was no significant difference in nutrient intake between the normal men and women and those with hypercholesterolemia. After adjustment for confounding factors, nutrient intake by FFQ of the male normal group showed higher levels of n-3 fatty acid and vitamin C compared to the group with hypercholesterolemia. However, there was no significant difference in nutrient intake between the two groups of women. Conclusions The average intake of n-3 fatty acids and vitamin C of the male group with hypercholesterolemia was lower than that of the normal group. However, since KNHANES is a cross-sectional study, prospective cohort studies are required to analyze the risk factors of hypercholesterolemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Blue Food Consumption and Its Relation to Nutrient Intake among Koreans
Yonghee Suk, Min June Lee, Sunny Ham
Nutrients.2024; 16(18): 3128. CrossRef - Comparison of blood biochemical characteristics and dietary intake by sex in gastric cancer patients over 40 years in Korea based on 7th (2016-2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: a cross-sectional study
Hyeon-Ju Lee, Sung-Won Oh, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 48. CrossRef - Analysis of Fruit Consumption and the Korean Healthy Eating Index of Adults Using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun A Choi, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(10): 1124. CrossRef
- Blue Food Consumption and Its Relation to Nutrient Intake among Koreans
- 1,135 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Validity of Estimating Sodium Intake using a Mobile Phone Application of 24-hour Dietary Recall with Meal Photos
- Seo-Yoon Kim, Sang-Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):317-328. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
The objective of this study was to verify the validity of a mobile phone application (app) that applies a 24-hour dietary recall with meal photos, as a means of being a more accurate method of estimating dietary sodium intake.
Methods
Of the 203 subjects enrolled, 172 subjects (84 males and 88 females) were selected for the final analysis, excluding those with an intake less than 500 kcal and urine output less than 500 ml. Dietary sodium assessment methods used for comparing with the 24-hour urinary sodium excretion are as follows: 1) face-to-face 24-hour dietary recall, 2) 24-hour dietary recall using the mobile app, 3) face-to-face 24-hour dietary recall considering liquid intakes from soup, stew, water kimchi and noodle, etc (liquid-based dishes), 4) 24-hour dietary recall using the mobile app considering liquid intakes from liquid-based dishes, and 5) food frequency questionnaire. Repeated ANOVA with Bonferroni method was used for comparing the average sodium intake, and Pearson’s correlation was applied to correlate the methods used.
Results
In women, no significant difference was observed in the average sodium intake between all methods. Moreover, analysis in men and total adults revealed no significant difference between the 24-hour urinary sodium secretion, and 24-hour dietary recall using the app and 24-hour dietary recall using the app considering liquid intakes. Sodium intake by food frequency questionnaire was significantly different when compared with the intake determined from 24-hour urinary sodium excretion. Sodium intake from all methods (except food frequency questionnaire) significantly correlated with values obtained from 24-hour urine sodium excretion.
Conclusions
Results of this study validated a mobile phone app using a 24-hour dietary recall with meal photos to better estimate dietary sodium intakes. It is believed that further studies in the future will enable the application as a tool to more accurately determine sodium intake.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Sodium and Fluid Restriction for Patients with Heart Failure
Eloisa Colin-Ramirez, Amitai Segev, Meghan Rozmahel, Justin Ezekowitz
Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine.2024; 26(12): 347. CrossRef - Comparison between 24-hour diet recall and 24-hour urine collection for estimating sodium and potassium intakes and their ratio among Korean adults
Taisun Hyun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Young-Ran Heo, Heekyong Ro, Young-Hee Han, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 284. CrossRef - Validity of Interviewer-Administered 24-h Dietary Recalls in Older Korean Women: A Pilot Study
Seunghee Kim, Clara Y. Park
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1757. CrossRef
- Dietary Sodium and Fluid Restriction for Patients with Heart Failure
- 1,137 View
- 10 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Low Hand Grip Strength with Protein Intake in Korean Female Elderly: based on the Seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII), 2016-2018
- Won Jang, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):226-235. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Decreasing muscle strength in old age has become a significant health problem because it increases the risk of falls or fractures and transfers to other diseases. The precise role of dietary protein intake in preventing or reducing muscle weakness is unclear. This study examined the relationship between handgrip strength and protein intake in Korean female elderly.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study that used data from the Seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) on female subjects aged 65 years and older. Low handgrip strength (LHGS) was defined as a handgrip strength below than 18 kg. Dietary intake data were obtained using the 1-day 24-hour recall method. Multiple regression was performed to test whether there is an independent relationship between the grip strength and protein intake, and the association between protein intake and LHGS was confirmed through multiple logistic regression.
Results
The mean age of the 2,083 elderly females was 73.3 ± 0.1 years, and the prevalence of LHGS was 35% (n=734). Elderly women with an LHGS consumed less energy, total protein, and animal-based protein than those in the normal group. A multiple regression analysis after adjusting for covariate revealed a significant positive association between the handgrip strength and energy, protein, and animal-based protein intake. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that the odds ratio (OR) of LHGS in female elderly with the highest quartiles of consumption of energy [OR, 0.65; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.43- 0.82; P for trend=0.004], and animal-based protein [OR, 0.59; CI, 0.40-0.87; P for trend= 0.037] were significantly lower than those in the lowest quartiles.
Conclusions
The energy intake and animal-based protein intake were negatively associated with the LHGS. These results suggest that adequate energy intake and protein intake, particularly those from animal-based sources, for elderly women in Korea are beneficial in lowering the risk of LHGS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between dietary protein and amino acid intake and handgrip strength in Korean adults: data from the 2014–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyunji Ham, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Nutrition Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Protein Intake and Physical Activity on Hand Grip Strength in the Older Adults Aged over 65 Years of Age: Using Data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Do-Yeon Kim, Byung-Sun Choi
Korean Journal of Geriatrics & Gerontology.2025; 26(1): 23. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment of Older Korean Adults by Level of Plant Protein Intake
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Jeong-Hun Song, Yangsuk Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1976. CrossRef - Association Between Protein Intake and Sarcopenia-Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Scoping Review
Minjee Han, Kyung-sook Woo, Kirang Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(3): 216. CrossRef - Association Between Serum High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels and Low Muscle Strength Among Korean Adults
Bo-Hyun Choi, Sunhye Shin
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2698. CrossRef - Associations Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Sarcopenia in South Korean Adults: Based on the 2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sunhye Shin, Mi Joung Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(20): 3292. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Association Between Dietary Fiber Intake and Low Muscle Strength Among Korean Adults
Sunhye Shin
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(1): 33. CrossRef - Health Outcome Comparison Based on Dietary Inflammatory Levels among Sample of Korean Elderly
Seul-Ki Koo, Hee-Sook Lim
Healthcare.2024; 12(10): 1003. CrossRef - Low dietary vitamin C intake is associated with low muscle strength among elderly Korean women
Chan Yoon Park, Sunhye Shin
Nutrition Research.2024; 127: 75. CrossRef - The Relationship of Pork Meat Consumption with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Biomarkers of Health Status in Korean Older Adults
Ah-Jin Jung, Anshul Sharma, Mei Chung, Taylor Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4188. CrossRef - Association of Protein Intake with Sarcopenia and Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Minjee Han, Kyungsook Woo, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2024; 16(24): 4350. CrossRef - Macronutrients intake and physical frailty in Korean older adults: A cohort‐based cross‐sectional study
Narae Yang, Yunhwan Lee, Mi Kyung Kim, Kirang Kim
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2023; 23(7): 478. CrossRef - The effect of combining nutrient intake and physical activity levels on central obesity, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic obesity: a population-based cross-sectional study in South Korea
Jong Eun Park, Seulgi Lee, Kirang Kim
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Anemia with Frailty and Nutritional Intake in Persons Age 65 and Older: The 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Heekyung Jeong, Chaeyoon Lee, So Yoon Han, Young-Jin Ko, Kyoung Jin Kim
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(1): 15. CrossRef - Association between seafood intake and frailty according to gender in Korean elderly: data procured from the Seventh (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Won Jang, Yeji Choi, Jung Hee Cho, Donglim Lee, Yangha Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 155. CrossRef - Association between plant protein intake and grip strength in Koreans aged 50 years or older: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2018
Sook-Hyun Jun, Jung Woo Lee, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Seung-Yeon Lee, Yookyung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(5): 969. CrossRef - Trends in Seafood Consumption and Factors Influencing the Consumption of Seafood Among the Old Adults Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009~2019
Won Jang, Jung-Hee Cho, Donglim Lee, Yangha Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 51(7): 651. CrossRef - Preparation of Mousse Type Pork Patties with Added Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae
Eunji Kim, Nami Joo
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(1): 63. CrossRef - Dietary Essential Amino Acid Intake Is Associated with High Muscle Strength in Korean Older Adults
Jihyun Im, Hyoungsu Park, Kyong Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3104. CrossRef - Handgrip Strength Assessment and Its Associated Factors among Hospitalized Elderly in Klang Valley Hospitals
Khairunisar-E-Rashim Mohammed Yusufirashim, Noraida Omar, Shazli Illyani Mohamad Shafie, Siti Hazimah Nor’hisham
Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences.2022; 18(6): 115. CrossRef - A study on the nutrient intake of the elderly in Korea based on activity limitations: data from the 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soyoung Kim, Youngmi Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(5): 543. CrossRef - Association between Sarcopenia and Energy and Protein Intakes in Community-dwelling Elderly
Woori Na, Dayoung Oh, Seohyeon Hwang, Bonghee Chung, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(4): 286. CrossRef - Dietary phytochemicals as a promising nutritional strategy for sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Hye Yun Jeong, Oran Kwon
Applied Biological Chemistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Interaction between Obesity and Grip Strength on Health-Related Quality of Life in Elderly: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Seungjae Hyun, Darae Woo, Sangshin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(1): 28. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef
- Relationship between dietary protein and amino acid intake and handgrip strength in Korean adults: data from the 2014–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 2,135 View
- 29 Download
- 26 Crossref

- [English]
- Estimation of Usual Meat Intake Distribution Considering Meat Content in Processed Foods: Based on the KNHANES 2009
- Yun-Jung Shin, Ae-Jung Kim, Dong Woo Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):150-158. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to estimate usual meat intake distribution, which may have been over/underestimated when estimations were made using only the third food codes of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
Methods
For this purpose, 24-hour recall data from the 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, which conducted a partial 2-day survey of food intake, were used. The Multiple Source Method (MSM) was used to estimate the distribution of the usual intake of red and processed meats.
Results
The results of this study show that the mean intake of red meat was 45.07 g while that of processed meat was 4.33 g. These results are slightly higher than the consumption calculated using only tertiary food code, and the difference was statistically significant. Furthermore, characteristics of the estimated usual intake distribution were a smaller standard deviation, increased lower percentiles, and decreased upper percentiles compared to the 2- day mean intake distribution for both red and processed meats. The proportion of individuals not consuming red meat decreased substantially from approximately 37% to 0.7%. The proportion of consumption that exceeded 90 g, which is the upper limit of red meat intake recommended by the National Health Service (NHS), was only approximately 10% in the distribution of usual intake.
Conclusions
As the consumption of processed foods is expected to continuously increase, caution is needed regarding the processes used to calculate food (group) intake to avoid over/underestimation. Moreover, use of KNHANES data to calculate the proportion of the population at risk of insufficiency or excess intake of certain nutrients or food (group), based on one day intake that does not address within-individual variation, may lead to biased estimates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Red meat and processed meat consumption and the risk of dyslipidemia in Korean adults: A prospective cohort study based on the Health Examinees (HEXA) study
Seong-Ah Kim, Sangah Shin
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(6): 1714. CrossRef
- Red meat and processed meat consumption and the risk of dyslipidemia in Korean adults: A prospective cohort study based on the Health Examinees (HEXA) study
- 1,329 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Analysis of Dietary Calcium and Phosphorus Intakes and Contribution Rates of Major Dish Groups according to Gender, Age, and Region in Korea
- Yeon Kyung Lee, Mi Kyeong Choi, Taisun Hyun, Eun Soon Lyu, Haeryun Park, Hee Kyong Ro, Young Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):32-47. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Calcium (Ca) is an insufficiently consumed nutrient, whereas phosphorus (P) intake has exceeded the recommended intake level in Korea over the past decade. The purpose of this study was to analyze dietary Ca and P intakes and their contribution rate according to dish groups.
METHODS
A 24-hour dietary recall survey of 640 healthy adults (aged 19–69 years) was undertaken twice in four Korean provinces. Dietary Ca and P intakes and their rates of contribution from 31 major dish groups were analyzed and compared by gender, age group, and region.
RESULTS
The average Ca and P intakes of the subjects were 542.1 ± 222.2 mg/d and 1,068.3 ± 329.0 mg/d, respectively. The intakes of Ca and P as percentages of recommended nutrients intake (RNI%) were 71.7 ± 29.8% and 152.6 ± 47%, respectively, and the percentages under the estimated average requirement were 60.3% for Ca and 3.8% for P. The RNI% of Ca was not significantly different between males and females, but was significantly higher in subjects in the sixties age group than in other age groups and was significantly lower in the Korean capital than in other regions. The RNI% of P did not significantly differ by gender or age groups, but it was significantly higher in the capital than in Gyeong-sang. The five major dish groups contributing to Ca intake (contribution rate) were milks/dairy products 69.2 ± 109.2 mg/d (12.6%), soups 55.6 ± 69.6 mg/d (10.1%), stir-fried foods 53.1 ± 70.7 mg/d (9.7%), stews 43.4 ± 85.4 mg/d (7.9%), and kimchi 38.4 ± 31.8 mg/d (7.0%). The five major dish group contributing to P intake (contribution rate) were cooked rice 160.7 ± 107.1 mg/d (14.9%), stir-fried foods 88.5 ± 89.4 mg/d (8.2%), soups 76.7 ± 85.8 mg/d (7.1%), one-dish meals 63.3 ± 94.4 mg/d (5.9%), and stews 62.6 ± 89.3 mg/d (5.8%). The dish groups contributing to Ca and P intakes differed somewhat by gender, age group, and region.
CONCLUSIONS
Programs to improve the nutritional status of Ca and P intakes should consider the differences in Ca and P contribution rates by dish groups as well as by gender, age group, and region. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Lactarius hatsudake fortification on
physicochemical, microbiological and antioxidant properties of stirred-type
yogurt during cold storage
Hanyu Zhu, Geqing Li, Huijing Liu, Weifeng Sun, Xiaoqian Yao, Rui Wu, Jiajia Hu, Qihui Yang
Food Science of Animal Resources.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Restructured Black Goat Jerky with
Various Types of Ultra-Ground Seaweed Powders
Ui-Bin Baek, Hack-Youn Kim
Food Science of Animal Resources.2024; 44(2): 483. CrossRef - Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Longitudinal Effects of Serum Calcium and Phosphate Levels and Their Ratio on Incident Ischemic Heart Disease among Korean Adults
Dong Hyuk Jung, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Biomolecules.2022; 12(1): 103. CrossRef - Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Bone Mineral Density in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients With Osteoporosis
Oh Chan Kwon, Ji Seon Oh, Min-Chan Park, Yong-Gil Kim
Frontiers in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of Lactarius hatsudake fortification on
physicochemical, microbiological and antioxidant properties of stirred-type
yogurt during cold storage
- 1,864 View
- 7 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Relation of Nutritional Intake and Allergic Rhinitis in Infants: Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2013~2016
- Eun Sil Her, Bo Young Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):321-330. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.321
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the relationship between the presence of allergic rhinitis and the nutritional intake levels of Korean infants.
METHODS
The study involved a total of 1,214 infant subjects aged 1~5 months from the 2013~2016 KNHNES (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey). The Subjects were classified into two groups based on the presence of allergic rhinitis: Non-allergic rhinitis infants (NARI, n=1,088) and allergic rhinitis infants (ARI, n=126). The general characteristics and family history of allergies, nutrient intake status, nutrient supplement intake, and breast milk and baby food start period data of the two groups were compared. All statistical analyses accounted for the complex sampling design effect and sampling weights.
RESULTS
The mean age was 0.5 years old in the ARI group compared to the NARI group. In the residence, the rate of urban was higher in ARI. The family history revealed a significant difference between the two groups, particularly those of mothers rather than fathers. The nutrient intake levels were high in energy, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, iron, riboflavin, niacin, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. Breastfeeding was significantly higher in the ARI group than in the NARI group. The baby food start period was 0.3 months earlier in NARI group than in ARI group. The height, body weight, and birth weight were higher in ARI group than NARI group. The result of Odds ratio analysis showed that excess energy, protein, calcium, phosphorus, iron, riboflavin, and niacin intake increases the risk of allergic rhinitis.
CONCLUSIONS
These results can be used as data to develop nutrition guidelines for allergic rhinitis infants. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between household income levels and nutritional intake of allergic children under 6 years of age in Korea: 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and application of machine learning
Seungpil Jeong, Yean Jung Choi
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge on complementary foods of mothers with young children and their perception of convenience complementary foods
Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang, Youngmin Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 16. CrossRef - Comparison of the growth and nutritional status of low birth weight and normal birth weight children
Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(6): 630. CrossRef - Association between depression, anemia and physical activity using isotemporal substitution analysis
Hee-kyoung Nam, Jungmi Park, Sung-il Cho
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Food and dish group diversity on menus of daycare centers provided by Center for Children’s Foodservice Management in Korea: a descriptive study
Youn-Rok Kang, Kyeong-Sook Lim, Hyung-Sook Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 449. CrossRef
- Association between household income levels and nutritional intake of allergic children under 6 years of age in Korea: 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and application of machine learning
- 1,692 View
- 11 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Nutrient Intakes of the Elderly according to Their Family Status: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2016
- Ji Hong Oh, Bok Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):309-320. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.309
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was undertaken to compare dietary life of the elderly living alone and in a family, and to compare differences based on gender, for the 2013-2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
The subjects included 2,612 elderly people aged over 65 years who participated in the health survey, health examination and nutrition survey. Subjects on a diet therapy were excluded. This study analyzed the general characteristics, dietary habits, daily energy and nutrient intakes, CPF ratio, estimated average requirement (EAR), nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean adequacy ratio (MAR), index of nutrient quality (INQ), and food consumption of the elderly living alone and in a family. We also compared the differences based on gender.
RESULTS
Daily intake of food, water, dietary fiber, potassium, retinol, and riboflavin were low in the male elderly subjects living alone. The elderly living with family revealed higher NAR and MAR as compared to the elderly living alone. Although all MAR values were <1, the elderly living alone had lower values. Considering the intake of food, the consumption of seaweed, fish and shellfish, and oils (animal) was higher in elderly men living with families, whereas women living with families consumed more vegetables, fruits, seaweeds and seafood, as compared to their counterparts living alone. Furthermore, analyzing the foods consumed by the elderly people living alone, female subjects consumed more seaweed, milk and animal oil as compared to male subjects.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study indicate that the elderly living alone have poor nutrient intake as compared to the elderly living with families. Based on this research data, we recommend that it is necessary to improve the health and nutritional status of the elderly living alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food insecurity and its associated characteristics of the elderly in Seoul: analysis of the data from the Seoul Food Survey 2023
Hyunjeong Park, Youngmin Nam, Linxi Huang, Youngmi Lee, Jihyun Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(1): 117. CrossRef - Profiling the socioeconomic characteristics, dietary intake, and health status of Korean older adults for nutrition plan customization: a comparison of principal component, factor, and cluster analyses
Kyungsook Woo, Kirang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2024; 46: e2024043. CrossRef - Evaluation on the Nutrition Quotient Scores of Elderly People Living Alone in Korea
Gyoungok Gang, Min Lee, Eun-hui Choi, Hye-Lim Lee, Hyun-Young Lee, Hye-Ja Chang, Jung-Hwa Choi, Na-Young Yi, Kyung-Eun Lee, Min-Jae Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak
Nutrients.2023; 15(17): 3750. CrossRef - Changes in nutritional status of Korean older adults during COVID-19 Pandemic by household income and demographic factors-using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(2019-2020): a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 302. CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 422. CrossRef - Comparison of the health and nutritional status of Korean elderly considering the household income level, using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 39. CrossRef - Social participation, health‐related behavior, and depression of older adults living alone in Korea
Seojin Won, Hyemee Kim
Asian Social Work and Policy Review.2020; 14(1): 61. CrossRef - Evaluation of the dietary quality and nutritional status of elderly people using the Nutrition Quotient for Elderly (NQ-E) in Seoul
Sun-Wook Ham, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 68. CrossRef - Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 502. CrossRef
- Food insecurity and its associated characteristics of the elderly in Seoul: analysis of the data from the Seoul Food Survey 2023
- 1,723 View
- 18 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of the Nutrition Status and Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence of the Members according to the Number of Household Members based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2014)
- Jin Young Lee, Soo Kyong Choi, Jung Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):232-244. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated the nutritional status and prevalence of metabolic syndrome of the people who participated in the KNHANES according to the number of household members. They were assessed by using information from the 2013~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
A total of 6,088 persons aged 19 years and over participated in 2013~2014 KNHANES, and they were classified into three groups according to the number of household members (single-person, two-person, three-person & over). The dietary behavior, nutritional status, health-related factors and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome of the subjects were investigated with using information from the survey questionnaires of KNHANES. The nutrient intake data of the subjects were obtained by the 24-hour recall method and this was analyzed for evaluating the nutrition adequacy ratio and the index of nutritional quality. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome among the subjects, and according to the study groups, was estimated using the blood and physical measurement data of the subjects.
RESULTS
As for EQ-5D index available for all the health states generated by the EQ-5D descriptive system, the single-person household member was the lowest among all the household types. The index of nutrition quality for protein, crude fiber, calcium, phosphorus, potassium, riboflavin and vitamin C in the single-person household was lower than that of the two-person or the three-person and over households (p<0.001). The mean adequacy ratio of single-person households was significantly decreased compared with that of the other types of households (p<0.001). The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was higher in the single-person households than that in the multiple-person households (p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
These results showed that dietary behaviors, nutrition status and health status might be influenced by the number of household members. The results from this study would be useful for improving Korean people's dietary life and health status by implementing evidence-based, specialized intervention for the members of diverse types of households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Beyond individual integration: Family systems, social support networks and living environment as health determinants among migrants in Germany
Franziska Reinhardt, Imad Maatouk
Journal of Migration and Health.2025; 12: 100368. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - The association of the Korean Healthy Eating Index with chronic conditions in middle-aged single-person households
EunJung Lee, Ji-Myung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 316. CrossRef - Analysis of Agrifood Consumer Competency and Dietary Satisfaction according to Household Type Using the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Meera Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(4): 414. CrossRef - An analysis of customer needs for the operation of unmanned food stores on a university campus
Se-Eun Kim, Min-Seo Park, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(5): 587. CrossRef - Assessment of Nutrient Intake and Dietary Quality of Korean Adults in Metabolic Syndrome Patients According to Taking Medical Care: Based on the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Juhee Lee, Kyungsuk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(4): 321. CrossRef - Relationships of Dietary Factors with Obesity, Hypertension, and Diabetes by Regional Type among Single-Person Households in Korea
Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1218. CrossRef - Living Environment Considerations on Obesity Prevention Behaviors and Self-Efficacy among Chinese Americans
Doreen Liou, Jessica A. Karasik
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(17): 9322. CrossRef - The Relationship between Meal Regularity and Oral Health and Metabolic Syndrome of Adults in Single Korean Households
Jin-Ah Jung, Hye-Won Cheon, On-Ju Ju
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 185. CrossRef - Association of Household Income Level with Vitamin and Mineral Intake
Haegyu Oh, Juyeon Kim, Yune Huh, Seung Hoon Kim, Sung-In Jang
Nutrients.2021; 14(1): 38. CrossRef - Nutritional status and metabolic syndrome risk according to the dietary pattern of adult single-person household, based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu Been Keum, Qi Ming Yu, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 23. CrossRef - Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Eun-Sun Park, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(6): 476. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 408. CrossRef
- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 2,937 View
- 9 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- Daily Water Consumption and its Contribution to Calcium Intake in Korean Adults
- Eun Sun Park, Yeon Kyung Lee, Mi Hyun Kim, Mi Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):18-23. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Although water is essential for life and can supply essential minerals, studies that evaluate calcium intake through drinking water are limited. The aim of this study was to assess calcium contents of natural mineral water (NMW) and its possible contribution to calcium intake in healthy adults.
METHODS
This study examined water consumption in 640 Korean adults with selfselected diet, analyzed the calcium content of 10 different brands of bottled NMWs sold in Korea, and assessed the amount of calcium intake from drinking water and its daily contribution to the recommended nutrient intake (RNI) of calcium.
RESULTS
Mean calcium content in 10 bottled NMWs was 20.9 mg/l. Daily water intakes from food composition database and calculated using energy intake based on 0.53 ml/kcal were 957.2 ml and 1109.8 ml for men and 848.3 ml and 951.6 ml for women, respectively, with a significant difference by gender (p < 0.001). Daily drinking water intake was significantly higher among men than women (1203.9 ml vs. 1004.3 ml, respectively, p < 0.001). Daily calcium intakes from foods were 564.0 mg for men and 534.2 mg for women. Daily possible calcium intakes from drinking bottled water were 25.2 mg for men and 21.0 mg for women (p < 0.001). The contribution of daily calcium intake from drinking bottled water to RNI of calcium was 3.3% for men and 2.9% for women without significant difference.
CONCLUSIONS
One half of the daily total water intake was consumed as drinking water, and possible calcium intake through drinking water was about 3% of RNI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing contribution of bottled water in nutrient absorption using the bottled water nutritional quality index (BWNQI) in Iran
Masoomeh Askari, Reza Saeedi, Ramin Nabizadeh, Ahmad Zarei, Maryam Ghani, Marzieh Ehsani, Mahmood Alimohammadi, Mehrnoosh Abtahi
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Variability of urinary creatinine, specific gravity, and osmolality over the course of pregnancy: Implications in exposure assessment among pregnant women
Gowoon Lee, Sunmi Kim, Hyunwoong Park, Jeonghwan Lee, Jung Pyo Lee, Younglim Kho, Gyuyeon Choi, Jiwon Park, Suwalee Worakhunpiset, Hyo-Bang Moon, Kyungho Choi
Environmental Research.2021; 198: 110473. CrossRef
- Assessing contribution of bottled water in nutrient absorption using the bottled water nutritional quality index (BWNQI) in Iran
- 3,684 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Accuracy of 24-hour Diet Recalls for Estimating Energy Intake in Elderly Men using the Doubly Labeled Water Method
- Ji Hye Jeon, Na Young Go, Mo Ran Lee, Didace Ndahimana, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):516-524. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.516
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study assessed the accuracy of the 24-hour diet recall method for estimating the energy intake of elderly men using the doubly labeled water as a reference method.
METHODS
Seventeen subjects (mean age 72.5 ± 3.9 years), who maintained the same body weight during the two weeks study period, were included in this study. Three 24-hour diet recalls (two weekdays and one weekend) were obtained over a 14 day period to estimate the mean energy intake. The total energy expenditure was measured over the same 14 days using the doubly labeled water method. The total energy intake and total energy expenditure were compared by paired t-test.
RESULTS
The total energy intake from the 24-hour diet recalls method was 2536.7 ± 350.6 kcal/day, and the total energy expenditure from the doubly labeled water method was 2659.8 ± 306.8 kcal/day. The total energy intake was slightly under-reported by −123.2 ± 260.8 kcal/day (−4.4%). On the other hand, no significant difference was observed between the total energy intake and total energy expenditure of the subjects (p=0.069). The percentage of accurate predictions was 64.7%. The correlation between the total energy intake and total energy expenditure was statistically significant (r=0.697, p < 0.005).
CONCLUSIONS
The present study supports the use of the 24-hour diet recall method to estimate the mean energy intake in elderly men group. More studies are needed to assess the validity of 24-hour diet recall method in other population groups, including elderly women, adults and children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Fibre Intake in Older Adults Is Inversely Associated With Serum Remnant Cholesterol Level: A Nationwide Population‐Based Study
Hye Jun Lee, Woo‐young Shin, Jung‐Ha Kim
Nutrition Bulletin.2025; 50(4): 656. CrossRef - Accuracy of 24-Hour Dietary Recalls among Free-Living Older Korean Adults: Validation against Weighed Intakes
Jieun Mun, Suyoung Kim, Kanghee Kim, Chaeyeon Nam, Sein Kim, Clara Y Park
The Journal of Nutrition.2025; 155(12): 4446. CrossRef - Health Outcome Comparison Based on Dietary Inflammatory Levels among Sample of Korean Elderly
Seul-Ki Koo, Hee-Sook Lim
Healthcare.2024; 12(10): 1003. CrossRef - Evaluation of Menopausal Syndrome Relief and Anti-Obesity Efficacy of the Korean Fermented Food Doenjang: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial
A Lum Han, Myeong Seon Ryu, Hee-Jong Yang, Do-Youn Jeong, Keum Ha Choi
Nutrients.2024; 16(8): 1194. CrossRef - Validation of a physical activity classification table in Korean adults and elderly using a doubly labeled water method
Hye-Ji Han, Ha-Yeon Jun, Jonghoon Park, Kazuko Ishikawa-Takata, Eun-Kyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 391. CrossRef - Validity of Interviewer-Administered 24-h Dietary Recalls in Older Korean Women: A Pilot Study
Seunghee Kim, Clara Y. Park
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1757. CrossRef - Comparison of total energy intakes estimated by 24-hour diet recall with total energy expenditure measured by the doubly labeled water method in adults
Eun-Kyung Kim, Justice Otoo Fenyi, Jae-Hee Kim, Myung-Hee Kim, Seo-Eun Yean, Kye-Wol Park, Kyungwon Oh, Sungha Yoon, Kazuko Ishikawa-Takata, Jonghoon Park, Jung-Hyun Kim, Jin-Sook Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(5): 646. CrossRef - A short education session increases the accuracy of estimated food records in young Korean women during a controlled-feeding study
Seunghee Kim, Bora Lee, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(5): 613. CrossRef - Accuracy of the 24-hour diet recall method to determine energy intake in elderly women compared with the doubly labeled water method
Kye-Wol Park, Na-Young Go, Ji-Hye Jeon, Didace Ndahimana, Kazuko Ishikawa-Takata, Jonghoon Park, Eun-Kyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(5): 476. CrossRef
- Dietary Fibre Intake in Older Adults Is Inversely Associated With Serum Remnant Cholesterol Level: A Nationwide Population‐Based Study
- 1,926 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Milk Intake Patterns with Lactose and Milk Fat in Korean Male Adults
- Jung Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, Sung Hee Min, Myung Hee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):488-495. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.488
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the milk intake patterns with lactose and milk fat in Korean male adults using the following variables: milk intake level, awareness of lactose, and milk fat, health problems, and necessity of milk intake. In addition, the factors affecting milk intake were analyzed by multiple regression analysis.
METHODS
The subjects were 532 males aged 20 years or older among the nationwide milk purchasing group. The subjects were 223 (41.9%) in the 20–29 year age group, 188 (35.3%) in the 30–49 year age group and 121(22.7%) in the over 50 year age group. The survey was conducted using ANOVA and multiple comparative analysis to examine the differences in age and multiple regression analysis was performed to investigate the factors affecting the intake of milk.
RESULTS
The intake of milk in the subjects was 538.14 ± 494.23 ml per week. There were statistically significant differences in the subjects' age according to processed milk, low fat, nonfat milk, cheese, and ice cream. The perception of milk and lactose and milk fat was recognized as a good food for skeletal health when milk was consumed. Among the milk nutrients, lactose was highly recognized at the age of 20–29, and milk fat was recognized in those over 50 years. In addition to lactose and milk fat, calcium was the most highly recognized among the milk nutrients. Health problems associated with milk were skeletal health, obesity, and lactose intolerance. The perception of lactose intolerance was related to lactose intolerance and fatness, and the dietary behavior was unaffected.
CONCLUSIONS
This study examined the milk intake patterns of adult Korean males. Many variables were found to be related to the intake of milk. In this study, the milk intake was high when there was no problem with the perception and dietary behaviors of milk nutrition (lactose and milk fat). This study focused on lactose and milk fat, which are major nutrients in milk, and it is a new perspective study among milk-related research. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of milk and dairy product consumption with the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular disease incidence in middle-aged and older Korean adults: a 16-year follow-up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Yeseung Jeong, Kyung Won Lee, Hyekyeong Kim, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1225. CrossRef
- Association of milk and dairy product consumption with the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular disease incidence in middle-aged and older Korean adults: a 16-year follow-up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
- 1,917 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Program on Obesity Index and Behavioral Modification in Moderate Obese Women
- Myung Hee Chang, Su Jin Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):318-332. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the behavioral modification of obese adults who underwent nutritional and physical activity education. Twenty obese females, aged 20–60 years old, with BMIs (Body Mass Index) >30 or body fat (%) >40 were subjected to this study.
METHODS
The physical activity education program consisted of doing exercise in a gymnasium together or home exercise. Dietary attitudes and dietary intakes were assessed using weight control, physical activity, and eating habits. The nutrition-exercise educational period was 12 weeks.
RESULTS
After the study period, there was significant improvement in physical activity and eating habits score. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the dietary intakes of fiber, iron, potassium, vitamin A, vitamin B6, and niacin. Blood pressure, blood glucose, and total cholesterol levels showed a tendency to decrease, but there was no significant difference. BMI, fat mass, abdominal circumference, and visceral fat levels were significantly reduced while muscle mass significantly increased.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that behavioral modification by nutrition and physical activity education with feedback has positive effects on dietary intake and anthropometric biomarkers in obese adults. Therefore, lifestyle interventions of this kind could be recommended as a method for obesity management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of tele-nutrition education on weight loss, energy intake, and fat adequacy among obese adults in Banyumas, Central Java, Indonesia
Teguh Jati Prasetyo, Izzati Nur Khoiriani, Sifa Aulia Wicaksari, Gumintang Ratna Ramadhan, A. Khomsan, E. Palupi, S.P. Loh, N. Mohd Esa
BIO Web of Conferences.2025; 153: 02013. CrossRef - Influence of Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention (LSI) Program on Health, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Middle-Aged Women
Su-Jin Jung, Seung-Ok Lee, Min-Jun Choi, Jun Heo, Soo-Wan Chae, Baik-Hwan Cho
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2022; 12(3): 127. CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef
- Effect of tele-nutrition education on weight loss, energy intake, and fat adequacy among obese adults in Banyumas, Central Java, Indonesia
- 1,647 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Effect of Nutrition Education on the Eating Habits and Quality of Life of Gastric Cancer Outpatients Undergoing Gastrectomy
- YoonHee Jung, Joomin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):162-173. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the effects of nutrition education on the nutritional status, including eating habits and quality of life in gastric cancer patients undergoing a gastrectomy.
METHODS
Thirty one out-gastric resection patients at C University Hospital in Gwangju, Korea were enrolled in this study. The patients received an individualized nutritional counseling session, and the effects were assessed before and after a 3-month nutrition education intervention. Nutrition education for gastric cancer outpatients included the dietary guidelines (e.g., food intake), the level of nutrient intake, and nutrition support.
RESULTS
The patients had significantly improved serum albumin and hematocrit levels after nutrition education. Of the dietary habits, the meal time and amount of food compared to the first education were increased significantly. Of the changes in the food intake frequency, fish and meat, and vegetables and fruits intake were increased, but not at a statistically significant level. The score of eating habits related to the gastrectomy was improved significantly after nutrition education from 31.7 to 34.5. The composite scores for the quality of life were also improved significantly after the nutrition education program.
CONCLUSIONS
The nutrition education for gastric cancer outpatients may be crucial and efficient for improving their lifestyle. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Irisin Levels in Cancer Anorexia Cachexia Syndrome and the Relationship between Nutrition Education and Quality of Life
Diler Us Altay, Duygu Mataracı Değirmenci, Salih Can Çelik, Abdullah Üner, Tevfik Noyan, Çağrı Akalın
Cumhuriyet Science Journal.2024; 45(4): 636. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Irisin Levels in Cancer Anorexia Cachexia Syndrome and the Relationship between Nutrition Education and Quality of Life
- 1,591 View
- 27 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Study of the Coverage of Nutrition Labeling System on the Nutrient Intake of Koreans - using the 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
- Ji Eun Park, Haeng Shin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):116-127. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.116
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to examine the coverage of the current mandatory nutrition labeling system on the nutrient intake of Koreans.
METHODS
KNHANES dietary intake data (2013) of 7,242 subjects were used in the analysis. KNHANES dietary intake data were collected by a 24-hour recall method by trained dietitians. For analysis, all food items consumed by the subjects were classified into two groups (foods with mandatory labeling and other foods). In the next step, all food items were reclassified into four groups according to the food type and nutrition labeling regulations: raw material food, processed food of raw material characteristics, processed foods without mandatory labeling, and processed foods with mandatory labeling. The intake of energy and five nutrients (carbohydrate, protein, fat, saturated fat, and sodium) of subjects from each food group were analyzed to determine the coverage of the mandatory nutrition labeling system among the total nutrient intake of Koreans.
RESULTS
The average intake of foods with mandatory labeling were 384g/day, which was approximately one quarter of the total daily food intake (1,544 g/day). The proportion of energy and five nutrients intake from foods with mandatory labeling was 18.1%~47.4%. The average food intake from the 4 food groups were 745 g/day (48.3%) for the raw food materials, 54 g/day (3.5%) for the processed food of raw material characteristics, 391 g/day (25.3%) for the processed foods without mandatory labeling, and 354 g/day (22.9%) for the processed foods with mandatory labeling.
CONCLUSIONS
Although nutrition labeling is a useful tool for providing nutritional information to consumers, the coverage of current mandatory nutrition labeling system on daily nutrient intake of the Korean population is not high. To encourage informed choices and improve healthy eating habits of the Korean population, the nutrition labeling system should be expanded to include more food items and foodservice menus.
- 1,320 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
- Mijin Jo, Young Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(1):38-47. Published online February 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to analyze the association between sodium excretion and obesity for healthy adults in the Gwangju area.
METHODS
The participants included 80 healthy adults aged 19 to 69 years in Gwangju. The dietary intake and sodium excretion were obtained using the 24-hour recall method and 24 hour urine collection. The participants were classified into two groups according to the amount of urinary sodium excretion: (≤ 141.75 mmol/dL, > 141.75 mmol/dL).
RESULTS
After adjusting for sex, age, smoking history, and income, the high excretion of sodium group was significantly higher for weight, body mass index, body fat mass, percent body fat, visceral fat area (VFA), waist circumference, hip circumference, and WHR. The energy and nutrients intake were significant after adjusting for sex, age, smoking history, and income. The LSE group had a significantly higher fat intake and Na/K intake ratio. The HSE group had significantly higher fiber intake, and K intake. As the amount of urinary sodium excretion increased, the risk of obesity before correction was 3.57 (95% CI: 1.13–11.25) times greater, and the risk of obesity of T3 increased significantly by 3.33 times (95% CI: 1.05–10.59). After correcting for sex and age, the obesity risk of T2 increased significantly by 4.23 times (95% CI: 1.11–16.06), and after correcting for sex, age, smoking history, and income, the obesity risk of T2 increased significantly by 6.81 times (95% CI: 1.44–32.19) the risk of obesity.
CONCLUSIONS
An association exists between sodium excretion and obesity in Korean adults. In this study, the high excretion of sodium group was obese and the risk of obesity was higher than the low excretion of sodium group. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preventive Effects of Whole Grain Cereals on Sarcopenic Obesity in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
Mi-Bo Kim, Sein Lee, Changhee Kim, Jae-Kwan Hwang
Food Engineering Progress.2018; 22(4): 358. CrossRef
- Preventive Effects of Whole Grain Cereals on Sarcopenic Obesity in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
- 1,285 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Nutrition Education Using Dietary Guidebook in Higher Grade Elementary Students of Jeonbuk Area
- Mi Ran Park, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(1):13-27. Published online February 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to examine the effects of nutrition education with a dietary guidebook for children on dietary attitude, nutrition knowledge and nutrient intakes.
METHODS
The subjects were 54 higher grade elementary students (27 educated vs. 27 non-educated). The educated group was provided individual and/or group lessons (40 min/lesson/week, 4 week) using a dietary guidebook of Children developed by The Korean Society of Community Nutrition (KSCN) & Korean Food and Drug Administration (KFDA). The contents were Balanced Diet, Smart Food Choices, Cooking a Healthy Snack and Building a Healthy Body. We examined the differences in nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes and dietary intake between the educated group and non-educated group.
RESULTS
After education, the educated group improved dietary attitude, nutrition knowledge and qualitative nutrient intakes compared to the non-educated group. Specifically, among dietary attitudes, ‘taking a meal with salty and spicy food’ increased, while among nutrition knowledge, ‘functions of protein’, ‘functions of fat’, ‘foods with carbohydrates’, ‘foods with fat’, ‘foods with vitamins’, and ‘foods with minerals’ were increased. Nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) scores for vitamin C, iron, and zinc were increased.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutrition education using a dietary guidebook for children developed by the KSCN & KFDA had positive effects on nutrition knowledge and qualitative nutrient intakes. These findings suggest that nutrition education focused on personalized daily energy and nutrient requirements may improve dietary attitude and quantitative nutrient intakes of children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 167. CrossRef - Development of Educational Board Game for Dietary Education; ‘Food-Bicycle’
Jung Hoon Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2018; 27(5): 411. CrossRef
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- 1,442 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Cholesterol Intake in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) VI (2013–2015)
- Myungsook Park, Sanghui Kweon, Kyungwon Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(6):520-528. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.6.520
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The aim of the study was to assess the intake of dietary cholesterol and its major food sources in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
A total of 20,671 nationally representative sample who had 24-hour recall data from the KNHANES VI (2013–2015) was included in this study. Mean cholesterol intake and the prevalence of subjects with cholesterol intake over the Intake Goal of the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) for Koreans were analyzed. Intakes of cholesterol by food groups or each food were calculated to find out the major food sources for cholesterol intake in Koreans.
RESULTS
The mean dietary cholesterol intake was 261.3 mg, which was higher in men (303.5 mg) compared to women (219.1 mg). Dietary cholesterol intake and the prevalence of subjects with cholesterol intake over the Intake Goal of DRIs were the highest in the 19-29 year old group. The eggs was the first major food group source for cholesterol intake in all age groups. Major food sources for cholesterol intake among Korean were egg, chicken, pork, squid and beef, which contributed 66.9% to total cholesterol intake.
CONCLUSIONS
Although the mean dietary cholesterol intake was under 300 mg, the prevalence of subjects with cholesterol intake over the Intake Goal of DRIs was about 30% in adults. Because both the mean intake and the prevalence of subjects with cholesterol intake over the Intake Goal of DRIs were higher in young adult groups, the dietary cholesterol intake was expected to be increased. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Analysis of Egg Yolk Fatty Acid and Phospholipid Composition by Breeding Type in Ogye and White Leghorn
Dain Lee, Eun-Ah Park, Ki-Teak Lee
Korean Journal of Poultry Science.2025; 52(4): 357. CrossRef - Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: accomplishments and future directions
Kyungwon Oh, Yoonjung Kim, Sanghui Kweon, Soyeon Kim, Sungha Yun, Suyeon Park, Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Youngtaek Kim, Ok Park, Eun Kyeong Jeong
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021025. CrossRef
- Comparative Analysis of Egg Yolk Fatty Acid and Phospholipid Composition by Breeding Type in Ogye and White Leghorn
- 2,055 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Risk of Metabolic Syndrome according to Intakes of Vegetables and Kimchi in Korean Adults: Using the 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2010–2011
- Jae Eun Yoo, Jin Su Kim, Sook Mee Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(6):507-519. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.6.507
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to examine the relations between total vegetable and Kimchi intakes and the risk of metabolic syndrome (Mets) in Korean adults.
METHODS
This study used dietary intake and health data of 6668 subjects aged 20 years and over from the 2010–2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Daily intakes of total vegetables and Kimchi were assessed by 24-hour recall data. The odds ratio of Mets risk according to daily intake of vegetables and Kimchi was analyzed, respectively.
RESULTS
The highest consumption of total vegetables was associated with a lower risk of abdominal obesity (multivariable adjusted OR=0.56, 95% CI: 0.33, 0.93) in men and lower risk of Mets (multivariable adjusted OR=0.67, 95% CI: 0.47, 0.94) in women. Kimchi consumption was not related to the risk of Mets in both men and in women. However, a higher intake of Kimchi was associated with an increased risk of elevated blood pressure (Q1 vs Q5, multivariable adjusted OR=1.34, 95% CI: 0.95, 1.90, P for trend= 0.0261) in women.
CONCLUSIONS
A higher intake of vegetables was associated with decreased risk of abdominal obesity and Mets in both men and women, respectively. A higher consumption of Kimchi was not related to the risk of Mets in both in men and in women. However, a higher intake of Kimchi was associated with an increased risk of elevated blood pressure in women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Causal effect of kimchi intake on HDL-cholesterol levels in middle aged Korean men: a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
Jaehee Cha, Seong-Hee Ko, Dayeon Shin
Genes & Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Phthalate Exposure and Frailty among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Repeated Panel Data Study
Hongsoo Kim, Seyune Lee, Young-Il Jung, Yun-Chul Hong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1985. CrossRef - Association of Korean fermented cabbage kimchi consumption with an incidence of metabolic syndrome: 10-year follow-up results of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Suk Hyeon Seo, Jiyoun Hong, Im Huei Son, Young Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 569. CrossRef - Risk of Metabolic Syndrome according to Intake of White Rice and Kimchi in Korean Adults: based on the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2013–2015
Jin-Su Kim, So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(6): 525. CrossRef
- Causal effect of kimchi intake on HDL-cholesterol levels in middle aged Korean men: a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- 1,458 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrient Intakes of Male College Combat Sport Athletes by Weight Control Status
- Ji Yeon Kim, Ji Seon Lee, Seong Suk Cho, Hyon Park, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(6):495-506. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.6.495
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Weight control practices are common in combat sport athletes. This study was performed to examine nutrient intakes of male college combat sport athletes (taekwondo, boxing, judo) by weight control (WC) status.
METHODS
Subjects were male combat sport athletes (n=90) from colleges in Gyeonggi Province. Survey was conducted during 2016. Questionnaire included general characteristics, weight control, and dietary intakes during the period of training, weight control, weigh-in ~ before competition and between competitions. Subjects were grouped into high- and normal WC groups. T-test, χ²-test, Fisher's exact test and ANCOVA were used to analyze the data.
RESULTS
During training, energy intake was 75.4% of EER and C:P:F ratio was 57.5:13.9:28.7. Iron and zinc intakes were different by WC groups (p<0.05). During weight control, energy intake was 44.7% of EER in normal WC and 30.5% in high WC group (p<0.05). C:P:F ratio was 69:11.1:19.5, and ratio from protein and fat was lower in the high WC group (p<0.05). Most nutrient intakes during weight control were less than 50% of 2015 KDRIs (RNI or AI), and intakes including thiamin (p<0.01), vitamin A, riboflavin, niacin, folate, calcium, potassium and zinc (p<0.05) were significantly lower in the high WC. Energy intake after weighing before the competition was 1,315 kcal, and energy (kcal/kg BW, p<0.05) and carbohydrate intakes (g/kg BW, p<0.01) were significantly higher in the high WC group. Energy intake between competitions was 691.1 kcal, with no difference by the WC group.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutrients intakes of combat sport athletes were inadequate. Dietary intakes during weight control were much below than the KDRIs, especially in the high WC group. It is needed to develop nutrition education programs for combat sport athletes to avoid severe energy restrictions and to apply specific dietary guides to each period of training and weight control. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight control practices, beliefs, self-efficacy, and eating behaviors in college weight class athletes
Ji Seon Lee, Seong Suk Cho, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(1): 45. CrossRef
- Weight control practices, beliefs, self-efficacy, and eating behaviors in college weight class athletes
- 1,406 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between Snack Intake and Oral Health Behavior of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Hyunsook Kang, Kyunghee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):336-346. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.336
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study was performed to investigate the relationship between snack intake and oral health behavior in middle school students in Gyeonggi-do area.
METHODS
The survey questionnaire was recorded by middle school students from July 6 to August 24, 2011. The questionnaire included items on general characteristics, snack intake status, and oral health behavior. Among collected survey questionnaire, a total of 620 questionnaires (320 males and 300 females) were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 program.
RESULTS
Frequencies of snack and beverage intakes were significantly higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). Oral health behavior was significantly higher in students with lower snack intake compared to those with higher or average snack intake (p < 0.05). Oral health behavior for tooth brushing and toothbrush care were significantly higher in females than in males (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Oral health behavior score that reflected better oral health of the subjects were higher as the snack intake was lower. Oral health behavior score was higher in females than in males. We conclude that the contents for oral health and nutrition education focused on snack intake need to be developed to induce changes in oral health behavior in middle school students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - Evaluation of frequency of consumption of cariogenic snacks by freshmen versus the senior dental students in Tehran and the related factors: a cross-sectional study
Mahdia Gholami, Simin Z Mohebbi, Milad Mafakheri, Houra Shahhosseini
BMJ Open.2024; 14(9): e086041. CrossRef
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,698 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutritional Adequacy Analysis of Recommended Menu in Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015
- Youngnam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):279-288. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.279
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Recommended Menu (RM) prepared according to the Target Pattern expected to meet the dietary reference intake (DRI) of nutrients. Nutritional adequacy of RM in ‘DRI for Koreans 2015’ were analyzed to verify whether such expectation was fulfilled.
METHODS
Dishes in RM are categorized by 5 food groups, and number and types of dishes for main meal and between-meals were analyzed. The energy and 12 nutrients (protein, dietary fiber, Ca, P, Fe, Na, K, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin and vitamin C) contents in 10 RMs were calculated using the food composition table (CD) in ‘DRI for Koreans’. Energy, energy contribution ratio, and nutrient contents in 10 RMs for 18 age groups were evaluated based on the ‘DRI for Koreans 2015’.
RESULTS
Number of dishes per meal were 4.83, and representative table setting consisted of cooked rice + soup (or stew) +3 side dishes. Energy contents of RM were 75~109% of estimated energy requirement (EER). None of the RM met the DRI of all 12 nutrients examined. Calcium was the most insufficient nutrient. Only 1-2 years' RM met the DRI, all the other RMs did not meet the calcium DRI. Dietary fiber and potassium contents were also insufficient in most RM. In adult male's RM, only 1 nutrient, i.e. calcium did not meet the DRI, but in female adult's RM, 5~6 nutrients did not meet the DRI. Energy contribution ratio of carbohydrate, protein, and fat in RM were 59.0~70.4%, 15.7~17.5%, 12.1~23.5%, respectively. And 4 RMs out of 10 exceeded the upper limit of acceptable macro-nutrient distribution range (AMDR) of carbohydrate and 3 RMs out of 10 RM were below the lower limit of fat AMDR. Contribution ratio of nutrients were ≥ 40% by food groups were as follows: grain group in energy and carbohydrate; meat·fish·egg·legume group in fat, protein, and niacin; vegetables group in dietary fiber, vitamin A, and vitamin C; milk·dairy products group in calcium.
CONCLUSIONS
RM prepared according to the Target Pattern did not meet nutritional adequacy as expected. Especially calcium, potassium, and dietary fiber contents are needed to be increased in many RMs. Further, energy content in RM needs to be adjusted for fat·sugar food group assigned in Target Pattern and condiment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Causal Relationship between Vitamin C Intake with Hyperglycemia and Metabolic Syndrome Risk: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Meiling Liu, Sunmin Park
Antioxidants.2022; 11(5): 857. CrossRef - Inverse association of a traditional Korean diet composed of a multigrain rice-containing meal with fruits and nuts with metabolic syndrome risk: The KoGES
Min Jung Kim, Haeng Jeon Hur, Dai Ja Jang, Myung-Sunny Kim, Sunmin Park, Hye Jeong Yang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Causal Relationship between Vitamin C Intake with Hyperglycemia and Metabolic Syndrome Risk: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
- 1,590 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Study on Sugar Consumption of Adult Workers According to Smoking Status
- Jung Yeon Yun, Boram Kim, Hee Sun Jeong, Nami Joo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(3):228-237. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.3.228
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the smoking status among adult workers, and current status of sugar intake.
METHODS
The survey included 500 men working in Gyeonggi-do from October to November in 2016. Questionnaire items covered their age, working status, smoking status, eating habits, eating behaviors, snack consumption status, habits and behaviors related to sugar intake. All data were analyzed by SPSS program (Ver. 23) and descriptive statistics was performed; a t-test, χ² test, One-way ANOVA and Scheffe test were used for post-hoc test.
RESULTS
The study results showed that eating habits and behaviors of non-smokers were better than those of smokers. The frequency of daily snack consumption was the highest in smokers compared to and non-smokers. The smokers' favorite taste after smoking was ‘Sweet’. The average score of sugar-related nutrition knowledge was higher in non-smokers compared to smokers. Non-smokers had better recognition of ‘sugar reduction’, and smokers were more likely to eat sweet foods, respectively. On the other hand, non-smokers could observe that they were trying to control themselves for health reasons. According to the results of the study, non-smokers showed better eating habits and dietary habits and consumed less sugar. Also, it was found that non-smokers tried to drink more water than beverages and refrain from eating sweets to reduce their sugar intake. Further, the most of the bread, coffee and beverages were also consumed at a lower frequency by non-smokers compared to smokers.
CONCLUSIONS
This study results showed that smoking and sugar consumption were closely related. Therefore, adult workers should actively promote and learn so that they can maintain healthy and suitable dietary habits through reduction of sugar consumption. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 120. CrossRef - Diet habits of employees in higher education
Hajnalka Požar, Sanja Šumonja, Nataša Sekulić, Nataša Čamprag-Sabo, Valentin Puškaš
Sestrinska rec.2023; 26(86): 5. CrossRef - Study on Cardiopulmonary Function, Maximal Oxygen Uptake, and Obesity Index according to Smoking Status in Middle-Aged and Older Office Workers
Deok-Ju Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2018; 9(3): 95. CrossRef
- Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
- 1,240 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Metabolic Syndrome Status of Chinese Workers and Their Physical Profiles, Lifestyle Scores, and Nutrient Intakes
- Chao Wang, Hokyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(1):63-73. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.1.63
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to survey the related factors of metabolic syndrome of Chinese workers aged 20 years and above.
METHODS
The study was conducted at three locations in Shandong, China, currently working and took the physical examination (PE) within one year in the area as target participants. Personal characteristics, physical and biochemical results based on the PE, lifestyle habits, and food intake of the participants were used to analyze the relationship with metabolic syndrome.
RESULTS
Results showed that overall, thirty-one subjects (22.5%) had metabolic syndrome, twenty males (32.7%) and eleven females (14.2%). Metabolic syndrome was related to age, gender, educational level and occupational type with more risk in male (P < 0.05), people of older age (P < 0.001), low educational level (P < 0.05) and nonoffice workers (P < 0.01). According to the life style scores, lifestyle evaluation showed specifically alcohol consumption and smoking (P < 0.001) and stress management (P < 0.05) as important factors that were associated with the metabolic syndrome. High calorie (P < 0.01) and carbohydrate (P < 0.01) intakes were observed on male participants with metabolic syndrome in comparison to the non-metabolic syndrome but no significant difference on female participants.
CONCLUSIONS
This results of this study can be used as significant supporting data to prevent and control metabolic syndrome in Chinese workers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychometric Properties of the Short-Form Revised Lifestyle Evaluation Scale for Metabolic Syndrome–Korean
Shinae Seo, Chun-Ja Kim, Se-Won Kang, Dae Jung Kim, Elizabeth A. Schlenk
The Science of Diabetes Self-Management and Care.2025; 51(6): 578. CrossRef
- Psychometric Properties of the Short-Form Revised Lifestyle Evaluation Scale for Metabolic Syndrome–Korean
- 1,063 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- High School Students' Sugar Intake Behaviors and Consumption of Sugary Processed Food Based on the Level of Sugar-related Nutrition Knowledge in Seoul Area
- Nami Joo, Shin Kyum Kim, Ji young Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(1):1-12. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The present study aimed to investigate high school students' sugar intake behaviors, the status of consuming sugary processed foods, the awareness of sugar, and the experience and interest in sugar-related education based on the level of sugar-related nutrition knowledge.
METHODS
In this study, five high schools were selected in Seoul, Korea, and a survey was conducted in 400 students on the level of sugar-related nutrition knowledge and sugar intake status. A total of 349 questionnaires were used for the final analysis. For statistical analysis, descriptive statistics was performed; a t-test, χ2 test, and Friedman test were used for comparative analysis.
RESULTS
The study results showed a positive association between the knowledge level of sugar and the appropriate sugar intake behavior and sugary food choices. The group with more nutrition knowledge on sugar was found to have good eating habits and to eat less sugary food. The main sources of sugar were beverages, confectionary, and bakery goods in the corresponding order, irrespective of the level of nutrition knowledge related to sugar. A significant difference was found in the groups' awareness of the sugar content of the drinks with 89.4% for the higher-knowledge group, and only 81.5% for the lower-knowledge group (p < 0.05). Results also showed that 43.9% of the higher-knowledge group and 36.4% of the lower knowledge group were interested in participating in education on sugar.
CONCLUSIONS
This study result indicated the need to help adolescents to avoid excessive sugar intake from only certain favorite foods. Therefore, it is necessary to seek a systematic foundation for participatory education in order for them to maintain a low sugar intake in daily life and lead healthy eating habits by increasing their level of sugar-related information and knowledge. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Xylitol Addition Enhances Generation Z Liking of Red Wine: A CATA and Penalty Analysis Approach
Christian Chervin, Julie Bornot, Olivier Geffroy
Journal of Sensory Studies.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Socioecological factors influencing sugar-sweetened beverage consumption among adolescents in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Jin Suk Ra, Sun Hwa Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(1): 28. CrossRef - Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 120. CrossRef - Sex-Based Differences in Factors Associated With Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Among Korean High School Students
Jin Suk Ra, Moonkyoung Park
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mobile application-based dietary sugar intake reduction intervention study according to the stages of behavior change in female college students
Yunjung Choi, Hyun-Sook Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 488. CrossRef - Study on Sugar Consumption of Adult Workers According to Smoking Status
Jung-Yeon Yun, Boram Kim, Hee Sun Jeong, Nami Joo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 228. CrossRef
- Xylitol Addition Enhances Generation Z Liking of Red Wine: A CATA and Penalty Analysis Approach
- 1,973 View
- 13 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- A Comparison of Sources of Sodium and Potassium Intake by Gender, Age and Regions in Koreans: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2010-2012
- Yang Hee Park, Sang Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):558-573. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.558
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the main sources of dietary sodium and potassium intake in Koreans by gender, age and regions.
METHODS
We used the data from 2010-2012 KNHANES. A total of 20,387 subjects aged 8 years and older were included. Intakes were compared by gender, age (8-18, 19-49 and >50 years) and geographical regions in Korea. Dishes were classified into 28 dish groups based on cooking methods. Statistical analysis was performed by using the SAS 9.3 and SUDAAN 11.0.1 software.
RESULTS
The mean sodium intake of Koreans was 4866.5 ± 35.9 mg/day, which was 2.4 times higher than the adequate intake (AI) of sodium for Koreans. We found that daily sodium intakes were significantly different by age, gender and regions. Men and aged over 50 years had significantly higher sodium intake than women and other age groups. The mean potassium intake in Koreans was 3002.2 ± 19.4 mg/day and daily potassium intakes were significantly different by age, gender and regions. Women and age 50 years and over had significantly higher potassium intakes than men and other age groups. The average Na/K ratio was 2.89 ± 0.01 and was highest in men and in the age group of 19-49 years. The major sources of dietary sodium were soup and stew, followed by Kimchi, noodles and dumpling, pickled vegetables and seasonings, which represented 63.1 % of total sodium intakes. Soup and stew or Kimchi were the primary sources of dietary sodium intake. The major sources of dietary potassium were cooked rice, followed by soup and stew, Kimchi, fruits and beverages.
CONCLUSIONS
Sodium and potassium intakes and the major sources of those were significantly different by gender, age groups and regions. Therefore, different approaches based on gender, age and regions are needed to decrease sodium intake and increase potassium intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 225. CrossRef - Dietary Habits of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer in Korea
Jaehoon Shin, Jiyeon Lee, Yooeun Yoon, Hye Sun Lee, Hyungmi Kim, Yu-Jin Kwon, Ji-Won Lee
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2024; 45(3): 149. CrossRef - Role of geographic characteristics in the spatial cluster detection of cancer: Evidence in South Korea, 1999–2013
Insang Song, Eun-Hye Yoo, Inkyung Jung, Jin-Kyoung Oh, Sun-Young Kim
Environmental Research.2023; 236: 116841. CrossRef - Development and application of the sodium index to estimate and assess sodium intake for Korean adults
Yeon-Kyung Lee, Taisun Hyun, Heekyong Ro, Young-Ran Heo, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(3): 366. CrossRef - Trends in sodium intake and major contributing food groups and dishes in Korea: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2017
Yeseung Jeong, Eui Su Kim, Jounghee Lee, Yuri Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(3): 382. CrossRef - Predictive Analysis of Food Behavior and Related Factors Using Spatial Analysis: Based on Community Health Survey Data 2016
Se-Mi Jeong, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(2): 189. CrossRef - The association of dietary patterns with insulin resistance in Korean adults: based on the 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
I Seul Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 247. CrossRef - Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
Na-Yeong Lee, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - Comparison of the sodium content of Korean soup-based dishes prepared at home, restaurants, and schools in Seoul
Yanghee Park, Jihyun Yoon, Sang-Jin Chung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 663. CrossRef - Designing optimized food intake patterns for Korean adults using linear programming (II): adjustment of the optimized food intake pattern by establishing stepwise intake goals of sodium
Kana Asano, Hongsuk Yang, Youngmi Lee, Meeyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(4): 342. CrossRef - The association between genetic variants of angiopoietin-like 3 and risk of diabetes mellitus is modified by dietary factors in Koreans
Clara Yongjoo Park, Jiyoung Moon, Garam Jo, Juhee Lee, Oh Yoen Kim, Hannah Oh, Hyunjung Lim, Min-Jeong Shin
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of biogenic amines and inorganic elements in Cheonggukjang
Min-Jeong Seo, Chang-Do Lee, Ji-Na Lee, Hee-Jong Yang, Do-Youn Jeong, Gae-Ho Lee
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2019; 26(1): 101. CrossRef - Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
Mijin Jo, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Diet-Related Risk Factors for Incident Hypertension During an 11-Year Follow-Up: The Korean Genome Epidemiology Study
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Nutrients.2018; 10(8): 1077. CrossRef - Study on the prevalence and incidence of urolithiasis in Korea over the last 10 years: An analysis of National Health Insurance Data
Joon Se Jung, Chang Hee Han, Sangrak Bae
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2018; 59(6): 383. CrossRef - Dietary status of young children in Korea based on the data of 2013 ~ 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eun-kyung Kim, Byengchun Song, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 330. CrossRef - Effects of Sodium Intake on the Association between the Salt-Sensitive Gene, Alpha-Adducin 1 (ADD1), and Inflammatory Cytokines in the Prevalence of Children Obesity
Mi-Young Park, Myoung-sook Lee
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2018; 7(2): 98. CrossRef - Dietary intakes of adolescents from food insecure households: analysis of data from the 6th(2013-2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mariam Nakitto, Kana Asano, Injoo Choi, Jihyun Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(6): 507. CrossRef
- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 3,963 View
- 9 Download
- 19 Crossref

- [English]
- Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Intake Ratio and Intake Pattern of Proteins in Middle-aged Men Based on the 2012-2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
- Minkyoung Jang, Eunsil Her, Kyunghea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):366-377. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.366
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to compare intake of energy nutrients, physical characteristics, and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome according to protein intake group.
METHODS
Subjects were 827 men aged 40-65 years. The results presented were based on data from the 2012-2013 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and analyzed using SPSS. The odds ratio (OR) of metabolic syndrome was assessed according to the protein intake group and intake pattern of protein-rich foods.
RESULTS
The mean of protein intake was 73.96 ± 0.71 g. According to level of protein intake, four groups (deficient, normal, excess 1, excess 2) were created and their percentages were 8.3%, 39.6%, 37.1%, and 15.0% respectively. The mean of daily energy intake was 2,312.33 ± 24.08 kcal. It was higher in excess group 2 than in the deficiency group (p < 0.001). Moreover, the intake of all energy nutrients increased significantly with protein intake group (p < 0.001). The main contribution to daily protein included mixed grains (10.96 ± 0.32 g), milled rice (7.14 ± 0.30 g), chicken (3.50 ± 0.21 g), and grilled pork belly (3.04 ± 0.16 g). With regard to physical characteristics, and blood pressure and blood test results, only body mass index increased significantly according to protein intake groups (p < 0.05). The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in subjects was 38.5%, and there was no significant correlation with protein intake group. The OR of metabolic syndrome increased with protein intake, and was higher 4.452 times in excess group 2 than in the normal group (p < 0.05). Conversely, the OR of metabolic syndrome according to the frequency of protein-rich food intake did not show a significant correlation.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study can be used as significant supporting data to establish guidelines for protein intake in middle-aged men. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of diet quality according to the eating-out patterns of preschoolers and school-aged children in South Korea: based on data from the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-na Ju, Youngmi Lee, Kyunghee Song, Yujin Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(2): 165. CrossRef - Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 112. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Dietary Fat Energy Ratio in Middle-aged Men - Using the 2012~2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data -
Eun-Sil Her
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 1030. CrossRef
- Evaluation of diet quality according to the eating-out patterns of preschoolers and school-aged children in South Korea: based on data from the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,385 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Quality of Diet and Nutritional Intake and Mortality Risk among South Korean Adults Based on 12-year Follow-up Data
- Hye Ryun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):354-365. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.354
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Studies that reported the association between diet quality/nutritional intake status and mortality have rarely used long-term follow-up data in Asian countries, including Korea. This study investigated the association between the risk of mortality (all-cause and cause-specific) and the diet quality/nutritional intake status using follow-up 12-year mortality data from a nationally representative sample of South Koreans.
METHODS
8,941 individuals who participated in 1998 and 2001 Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys were linked to mortality data from death certificates. Of those individuals, 1,083 (12.1%) had died as of December, 2012. Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the relative risks of mortality according to the level of diet quality and intakes of major nutrients. Indicators for diet quality index and nutritional intake status were assessed using MAR (mean adequacy ratio) and energy and protein intake level compared with the 2010 Korean DRI.
RESULTS
Higher diet quality/nutritional intake status were associated with lower mortality; the mortality risk (95% confidence interval) from all-cause of lowest MAR group vs highest was 1.66 (1.27 to 2.18) among ≥ 30 year old, and 1.98 (1.36 to 2.86) among 30~64 year old individuals. Those with below 75% of energy and protein intake of Korean DRI had higher mortality risks of all-cause mortality compared to the reference group. Diet quality/nutritional intake status was inversely associated with mortality from cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
CONCLUSIONS
Poor Diet quality/nutritional intake status were associated with a higher risk of mortality from all-cause and mortality from cardiovascular diseases and cancer among South Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of all-cause mortality is associated with multiple health-related lifestyle behaviors and does not differ between urban and rural areas in Korea
Seunghee Kim, Clara Yongjoo Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(4): 554. CrossRef - Development of an evaluation tool for dietary guideline adherence in the elderly
Young-Suk Lim, Ji Soo Oh, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Soymilk Intake on Diet Management and Blood Biochemistry in Diabetes Patients
Kyung-Ok Shin, Hyo-Jeong Hwang, Soon-Hee Park, Kwang-Jin Chon, Chung-Hwa Song, Dae-Gyun Moon
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(3): 154. CrossRef - The relationship between diet quality indices and odds of breast cancer in women: a case–control study
Mohammad Hassan Sohouli, Genevieve Buckland, Cain C. T. Clark, Heitor O. Santos, Felipe L. Athayde, Vahid Sanati, Leila Janani, Akram Sadat Sajadian, Mitra Zarrati
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Patterns and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Older Adults
Ae-Rim Seo, Tae-Yoon Hwang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3703. CrossRef - Do Where The Elderly Live Matter? Factors Associated with Diet Quality among Korean Elderly Population Living in Urban Versus Rural Areas
Sohyun Park, Hyun Ja Kim, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2020; 12(5): 1314. CrossRef - A Comparisons of Nutritional Intake and Diet Quality Index-International in Gynecological Cancer Survivors and Normal Women: Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2016
Bo-Young Seo, Eun-Sil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 406. CrossRef - Association between Breakfast Frequency and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Cross-Sectional Study of KNHANES Data, 2014–2016
Hyeon Ji Lee, Jieun Jang, Sang Ah Lee, Dong-Woo Choi, Eun-Cheol Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(10): 1853. CrossRef - Effect of nutrition care process-based nutrition intervention on improvement of intake in the elderly in-patients with malnutrition
Ji-Hyun Park, Min-Ji Kang, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 307. CrossRef
- Risk of all-cause mortality is associated with multiple health-related lifestyle behaviors and does not differ between urban and rural areas in Korea
- 1,507 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Recommended Intake and Dietary Intake of Vitamin A for Koreans by Unit of Retinol Activity Equivalent
- Youngnam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):344-353. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.344
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
New retinol activity equivalent (RAE) was introduced as vitamin A unit in Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) for Koreans 2015. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the adequacy of 2015 reference intake (RI) of vitamin A in RAE unit by the comparison with RI and dietary intake of vitamin A.
METHODS
Analyses on RI of vitamin A were based on the Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) for Koreans (1962~2000) and DRIs for Koreans (2005~2015). Analyses on Koreans dietary intake of vitamin A were based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES) reports (1969-2014). For recalculation of RI and dietary intake of vitamin A in RE to RAE, 2013 Koreans intake of retinol: carotenoids ratio of 13: 87 was applied.
RESULTS
RI of vitamin A was 600~750 RE for Korean adult, and 339~425 RAE when calculated by applying the retinol and carotenoids intake ratio. Vitamin A intakes of Koreans were <100% RI, 267~668 RE from 1969 to 2001. From 2005, vitamin A intake had increased to >700 RE, >100% RI. When vitamin A intake was converted from RE to RAE (2005~2014), 718~864 RE became 405.8~488.1 RAE, decreased to 56.5% level. The recent 2015 RI of vitamin A is 850 RAE, two times of 2005 & 2010 RI of 425 RAE for adult male.
CONCLUSIONS
When nutritional status of vitamin A was assessed for Koreans using the estimated average requirement (EAR) of 2015 (570, 460 RAE for male, female adults, respectively), ratio of deficient people increased significantly when judged based on the previous intake of Koreans, <490 RAE. We needs to examine the 2015 RI (EAR) of vitamin A, find a way to measure the accurate intake of dietary vitamin A, and to increase the dietary intake of this vitamin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in three types of Korean watery kimchi
Hyosun Park, Suna Kim, Jaecheol Kim, KyeongJin Lee, BoKyung Moon
Applied Biological Chemistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans: vitamin A
Yuri Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 201. CrossRef - Dynamics of Serum Retinol and Alpha-Tocopherol Levels According to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Status
Dongsub Jeon, Minkook Son, Juhyun Shim
Nutrients.2021; 13(5): 1720. CrossRef - Representative Nutrients Contents and Nutritional Adequacy Evaluation of Single-Dish Meal for Middle School Students
Gisun Lee, Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(2): 93. CrossRef
- Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in three types of Korean watery kimchi
- 2,464 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of a Dietary Fiber Composition Table and Intakes of Dietary Fiber in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
- Soyeong Yeon, Kyungwon Oh, Sanghui Kweon, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(3):293-300. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.293
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to develop a dietary fiber composition table (DFCT) and to assess dietary fiber intakes in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
METHODS
The DFCT was developed by compiling the food composition tables published by the agencies of Korea, United States, or Japan. When there was no available data from the same species or status (dried, boiled, etc.) of food, the values were imputed by estimating from the same species with different status or substituting familiar species in biosystematic grouping. Using KNHANES VI-2 (2014) microdata and DFCT, intake of dietary fiber of Koreans was estimated.
RESULTS
Among the 5,126 food items of DFCT, the proportion of items of which dietary fiber contents were taken from the analytical values of the same foods was 40.9%. The data from the domestic food composition tables was 37.5%, and the data from the foreign tables was 49.6%. The rest was assumed as zero, or estimated with recipe database and nutrition labeling. Mean daily intake of dietary fiber was 23.2 g, and mean intake per 1,000 kcal was 10.7 g in men and 12.6 g in women. The mean percentage of dietary fiber intake compared to adequate intake was higher than 100%. The major food groups contributing to dietary fiber intakes were vegetables and cereals, and the percent contribution were 32.9% and 23.0% of total dietary fiber intakes, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
This DFCT could serve as a useful database for assessing dietary fiber intakes and for investigating the association between dietary fiber intakes and non-communicable diseases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Resistant Starch on Metabolic Markers and Gut Microbiota in Women with Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Pilot Study
Kyu-Nam Kim, Min-Sook Kang, Nam-Seok Joo, Hyang-Rae Lee, Susie Jung, Seyoung Ju, Yong-Ju Lee, Kyucheol Lee, Soohwan Jung, Jisoon Im, Jiyoung Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(23): 3652. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Resistant Starch Intake with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
Min-Sook Kang, Kyeong-A Jang, Haeng-Ran Kim, SuJin Song
Nutrients.2024; 16(1): 158. CrossRef - Association between serum uric acid levels and dietary fiber intake in adults: the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES VII, 2016–2018)
Jinyoung Kim, Da Young Jung, Jin-Hee Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Hyeon Woo Yim, Su-Jin Moon
Nutrition & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Quality Characteristics of Allium victorialis var. platyphyllm Powder Based on the Blanching Conditions
Hye-Jeong Kwon, Jae-Gil Lim, Ji-Sun Park, Nam-Young Um, Su-Jeong Her
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 843. CrossRef - Development of a database to estimate dietary intake of resistant starch in Koreans
Kyeong-A. Jang, Hyun Ah Kim, Min-Sook Kang, Haeng-Ran Kim, Yong-Ju Lee, SuJin Song
Journal of Food Composition and Analysis.2023; 120: 105283. CrossRef - Differences in Growth and Dietary and Nutrient Intake Patterns by Breastfeeding Status Over One Year Among Korean Children Aged 24–35 Months
Jin A Sohn, Ju Young Chang, Sohee Oh, Jeana Hong
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities
of commercial tteokbokki sauce in Korea
Geon Oh, June Seok Lim, Geun-hee Cho, Sun-Il Choi, Xionggao Han, Xiao Men, Se-Jeong Lee, Sang Mi Jung, Min Hee Kwon, Yeong Rae Song, Ok-Hwan Lee, Moon Jin Ra
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2022; 29(7): 1150. CrossRef - Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: accomplishments and future directions
Kyungwon Oh, Yoonjung Kim, Sanghui Kweon, Soyeon Kim, Sungha Yun, Suyeon Park, Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Youngtaek Kim, Ok Park, Eun Kyeong Jeong
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021025. CrossRef - Chitosan alleviated menopausal symptoms and modulated the gut microbiota in estrogen-deficient rats
Xuangao Wu, Min Jung Kim, Hye Jeong Yang, Sunmin Park
European Journal of Nutrition.2021; 60(4): 1907. CrossRef - The association of dietary patterns with insulin resistance in Korean adults: based on the 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
I Seul Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 247. CrossRef - Namul, the driving force behind health and high vegetable consumption in Korea
Soon-Hee Kim, Dae Young Kwon, Donghwa Shin
Journal of Ethnic Foods.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Fiber Intake and the Prognosis of Amytrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Korea
Haelim Yu, Seung Hyun Kim, Min-Young Noh, Sanggon Lee, Yongsoon Park
Nutrients.2020; 12(11): 3420. CrossRef - Review of whole grain and dietary fiber recommendations and intake levels in different countries
Kevin Burke Miller
Nutrition Reviews.2020; 78(Supplement): 29. CrossRef - Estimated glycemic load (eGL) of mixed meals and its associations with cardiometabolic risk factors among Korean adults: data from the 2013 ~ 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Kyungho Ha, Kisun Nam, YoonJu Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(4): 354. CrossRef - High fiber and high carbohydrate intake and its association with the metabolic disease using the data of KNHANES 2013 ~ 2017
Heesoo Moon, Kyungho Ha, YoonJu Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 540. CrossRef - Designing optimized food intake patterns for Korean adults using linear programming (II): adjustment of the optimized food intake pattern by establishing stepwise intake goals of sodium
Kana Asano, Hongsuk Yang, Youngmi Lee, Meeyoung Kim, Jihyun Yoon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(4): 342. CrossRef - Designing optimized food intake patterns for Korean adults using linear programming (I): analysis of data from the 2010~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Kana Asano, Hongsuk Yang, Youngmi Lee, Jihyun Yoon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(1): 73. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Resistant Starch Prepared from Singil Rice Starch
Chae Eun Lee, Junhee No, Malshick Shin
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(6): 626. CrossRef - An iodine database establishment and iodine intake in Korean adults: Based on the 1998~2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu Mi Ko, Yong Seok Kwon, Yoo Kyoung Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(6): 624. CrossRef - Effects of Ultrasonication Treatment on Physical and Functional Characteristics of Fruits and Vegetables for Juice Production
Sohee Jeong, Heejeon Park, Malshick Shin, Chul Su Park, Ji-Young Song
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2017; 33(4): 387. CrossRef
- Effects of Resistant Starch on Metabolic Markers and Gut Microbiota in Women with Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Pilot Study
- 2,618 View
- 19 Download
- 20 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



