Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):441-456. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
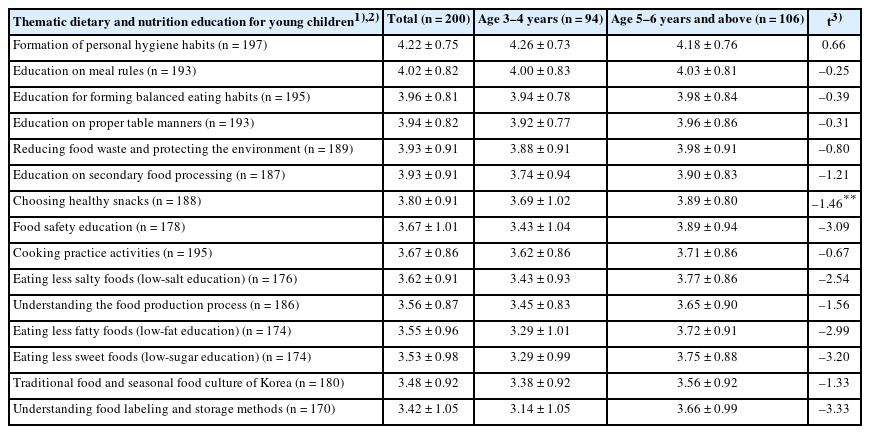
This study aimed to clarify parental perceptions of dietary and nutritional education provided to young children, identify parental support needs, and suggest directions for improvement.
Methods
A mixed-method sequential explanatory design was followed. Quantitative data were collected through an online survey conducted nationwide that included 200 parents of children aged three to six years in South Korea. Qualitative data were subsequently obtained through focus group interviews with fifteen parents to explore their contextual insights and experiences.
Results
Needs ratings prioritized expanding activity-based/experiential education (3.65 ± 0.88), followed by strengthening home-school communication and connectivity (3.59 ± 0.84), diversifying topics and content (3.55 ± 0.88), and increasing instructional time (3.39 ± 0.94). Integrated with the focus group interview findings, multilevel barriers were revealed—individual level: strong preferences of children for sweet/processed foods; interpersonal level: strong parental modeling and peer effects counterbalancing limited teacher expertise/time; organizational level: insufficient effective event-based experiential activities, and resource gaps across institutions; community/policy level: infrequent external support, uneven access to local resources, lack of standardized guidance, and limited opportunities for parental participation. Parents favored short, interactive digital content and expressed concerns about overexposure. These convergent findings indicate needs to 1) formalize and extend experiential programs within the regular curriculum, 2) provide standardized guidelines and home resource kits, and 3) institutionalize parental involvement.
Conclusion
These findings reveal that dietary and nutritional education for young children should move beyond fragmented, event-based programs toward an integrated three-tiered model incorporating (1) a structured, experiential curriculum, (2) home-linked educational packages, and (3) safe and interactive digital content. Establishing standardized guidelines, enhancing educational infrastructure, and institutionalizing parental participation are essential for sustainable improvement of early childhood dietary education.
- 439 View
- 36 Download

- [Korean]
- Toward the development of a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly: findings from focus groups study
- Hae-song Yoo, Jin-myong Lee, Min-sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):431-440. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00234

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this qualitative study was to explore and understand the behaviors and challenges of self-nutrition management from the perspective of elderly.
Methods
In May 2025, ten elderly aged 65–83 years with prior experience using digital devices were recruited through purposeful sampling. Data were collected via focus group interviews using a semi-structured questionnaire until saturation was reached, and all interviews were recorded, transcribed, and analyzed using traditional content analysis methods. The collected interview data were extracted focusing on phrases or sentences relevant to the research purpose, and various concepts derived through memo writing and the constant comparison were categorized based on common meanings. Subsequently, the categorized statements were deeply interpreted and reclassified into subcategories for final analysis.
Results
Under the overarching theme of development directions for a digital self-nutrition management education program for elderly, three main categories and 13 subcategories were derived. The three main categories include: (1) processes of acceptance and utilization of digital technologies; (2) potential for applying digital self-nutrition management; and (3) strategies for implementing digital-based nutrition education.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that elderly face barriers to utilizing digital tools for self-nutrition management not only due to physical or technical limitations, but also because of the confusion arising from limited nutrition knowledge and information overload. To overcome the barriers that may arise during the digital-based education process for elderly, strategies (educational topics, delivery strategies, and operational strategies) were derived to vitalize a digital self-nutrition management education program. These results highlight the necessity of developing tailored digital nutrition education programs that reflect the characteristics of elderly, which may enhance their practical applicability and provide foundational evidence for establishing a digital–nutrition integrated care model within the senior customized care service.
- 435 View
- 42 Download

Review
- [English]
- Evaluation and standardized dietary strategies for dysphagia in older adults: a narrative review
- Jean Kyung Paik
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):323-330. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00290

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This review aimed to elucidate the characteristics of dysphagia and age-related swallowing changes (presbyphagia) in older adults and to comprehensively examine assessment tools and standardized meal management strategies applicable in community settings to propose effective meal management strategies for healthy longevity.
Methods
Domestic and international literatures were analyzed regarding the definition and causes of dysphagia, physiological and structural characteristics and clinical impacts of presbyphagia, assessment and diagnostic tools (K-EAT-10 and K-DRACE), and the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI).
Results
Dysphagia compromises safe swallowing and nutritional intake in older adults, leading to serious complications, such as aspiration pneumonia, dehydration, malnutrition, sarcopenia, and reduced quality of life. The K-EAT-10 and K-DRACE proved effective for rapid screening of dysphagia risk in community-dwelling older adults. Moreover, texture-modified meals and viscosity adjustments based on the IDDSI standards are useful for reducing the risk of aspiration and improving nutrient intake. Meals can be classified as liquidized, minced, chopped, or regular, allowing for individualized management.
Conclusion
Presbyphagia is a multidimensional problem, and the integrated use of assessment tools and standardized meals is crucial. Community-based dysphagia management programs and collaboration among dietitians and healthcare professionals are needed to improve the nutritional status and quality of life of older adults.
- 2,005 View
- 57 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
- Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):352-363. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The dietary habits of school-aged children play a critical role in their growth and development, and are strongly influenced by the home environment. Household income is closely associated with caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. This directly affects the nutritional status of children. This study aimed to provide evidence to inform policies and educational programs for improving dietary habits in children, and to establish a foundation for tailored support strategies for low-income families.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 846 primary caregivers of school-aged children from 17 regions across Korea, recruited through an online survey. Household income, caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment were assessed. Nutritional status in children was measured using the Nutrition Quotient for Children (NQ-C). Statistical analyses included descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), correlation analyses, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Caregivers from higher income households demonstrated significantly greater food literacy and social support (P < 0.001). Children from these households showed high balance scores and a large proportion of these children were in the “high” NQ-C grade. The NQ-C score in children was positively correlated with food literacy (r = 0.425), social support (r = 0.471), and the food environment (r = 0.235) (P < 0.001). Multiple regression analysis showed that food literacy (β = 0.256) and social support (β = 0.348) were significant predictors of nutritional status in children.
Conclusion
This study confirmed that the nutritional status in children is not only determined solely by household income but is also mediated by caregivers’ food literacy, social support, and food environment. These findings highlighted the limitations of providing only economic support. The findings underscore the need for multifaceted interventions such as strengthening parental nutrition education, expanding social support networks, and improving access to healthy foods.
- 834 View
- 43 Download

- [English]
- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
- Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):274-285. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00157

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Although diet quality is known to be associated with environment and individuals’ characteristics, these have not been studied together. We determined the association of diet quality with regional factors stratified by individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics.
Methods
This study used nationally representative survey data on regional factors (2010–2020) and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data on individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics (2013–2018). Community-dwelling Koreans aged ≥ 20 were included (n = 26,853). Regions were categorized into metropolitan cities or provinces and subsequently according to regional factors (level of educational attainment, income per capita, food security status, physical activity facilities, time to the nearest large retailer, and internet use of the region). Individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics included age, education status, income, and number of household members. Diet quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI).
Results
In the entire population, education status of metropolitan cities was positively associated with the KHEI. Shorter time to retailers and higher internet use were positively associated with the KHEI in metropolitan residents with higher income levels but negatively associated with the KHEI in those with lower income status. Among provincial residents with a low education status or income, regional physical activity facilities were positively associated with the KHEI.
Conclusion
The association between diet quality and regional factors varied depending on the resident’s sociodemographic characteristics. Both regional and individual sociodemographic factors must be considered to address gaps in nutritional equity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Among Rural Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Changhee Lee, Kyeongmin Jang
Journal of Ageing and Longevity.2026; 6(1): 22. CrossRef
- Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Among Rural Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,747 View
- 33 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
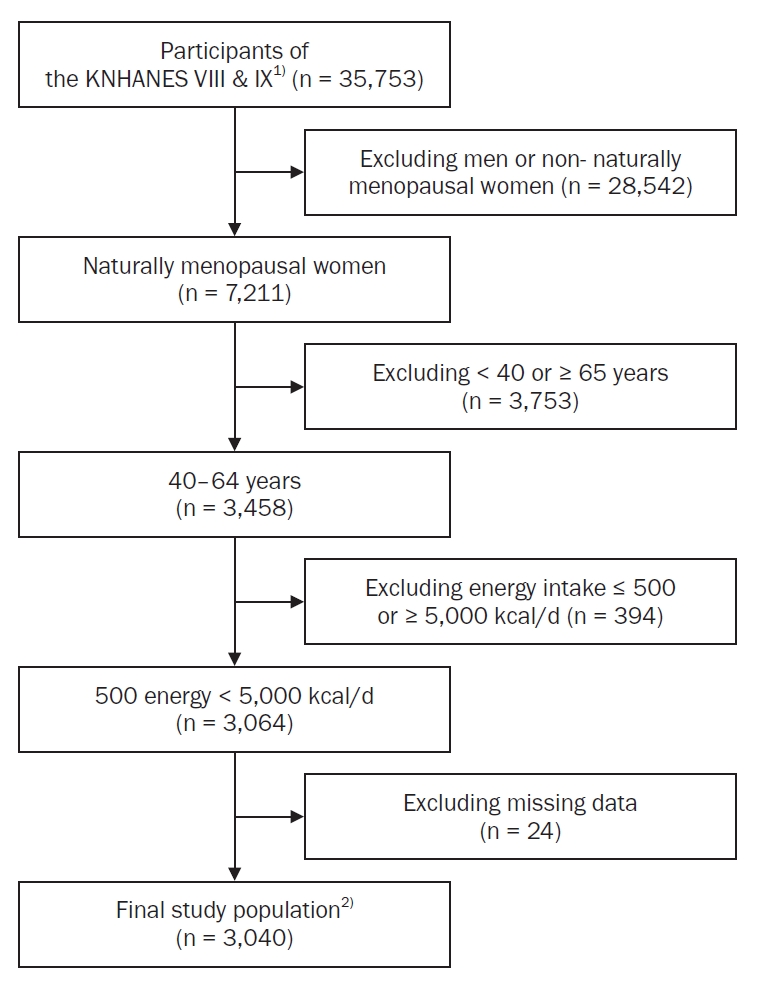
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 4,092 View
- 54 Download

- [Korean]
- Maternal home meal replacement use and attitudes, and young children’s preferences by usage frequency in meals for young children: a cross-sectional study
- Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):163-172. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00066
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With the increase in women’s workforce participation and changing family eating habits, home meal replacements (HMRs) have become more prevalent. However, research on how mothers incorporate HMR into meals of young children remains limited. This study examined mothers’ attitudes toward and use of HMR, as well as their association with young children’s HMR preferences.
Methods
A survey was conducted between June 1 and July 3, 2020, involving 337 mothers of 5-year-old children in Sejong, South Korea. The questionnaire assessed mothers’ perceptions of HMR, consumption patterns, and their children’s preferences for HMR.
Results
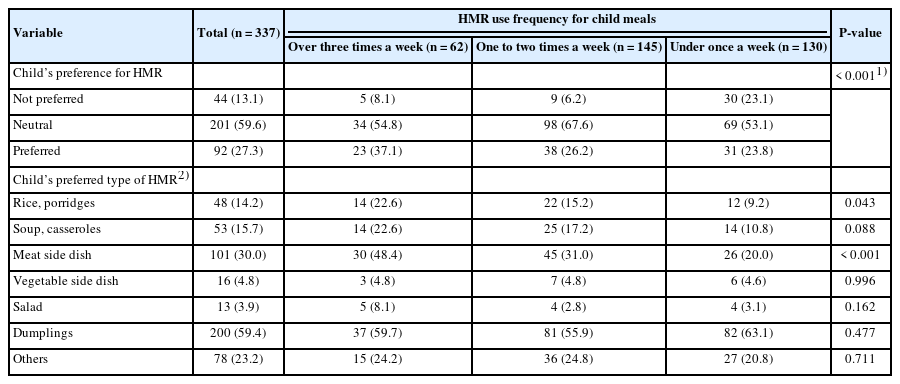
The average age of participating mothers was 38.3 years, with 93.2% living in nuclear families. Full-time homemakers constituted 40.1% of the respondents and showed lower HMR usage among them. HMR was primarily consumed as late-night snacks, side dishes, and dinners, with large discount stores (81.6%) being the primary purchase location. The high HMR consumption group exhibited more positive attitudes toward HMR (P < 0.001). HMR types varied in consumption frequency. Among ready-to-eat foods, kimbap (38.3%) was the most common, followed by meat side dishes (11.3%) and salads (11.0%). Among the heat-and-eat items, dumplings were the most frequently consumed. Simple cooking kits for Korean street food were used by 56.5% of mothers in the high-frequency HMR group, compared to 38.6% and 29.2% in the lower consumption groups (P < 0.01). Children’s preference for HMR was significantly associated with maternal HMR consumption frequency (P < 0.001). The most preferred items among children were rice porridge (P < 0.05) and meat side dishes (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Higher maternal HMR consumption was associated with increased acceptance by children. Mothers who frequently used HMR exhibited more positive attitudes toward its palatability, convenience, nutritional value, and variety. While HMR offers diverse and tasty meal options, overreliance on processed foods warrants caution. Importantly, high HMR consumption during early childhood may influence long-term dietary behaviors, including a continued preference for HMRs.
- 1,424 View
- 35 Download

- [Korean]
- A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
- Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):140-149. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to examine regional differences in dietary behavior and satisfaction between urban and rural residents in Korea, identifying key factors associated with dietary satisfaction in each group to deepen understanding of these variations.
Methods
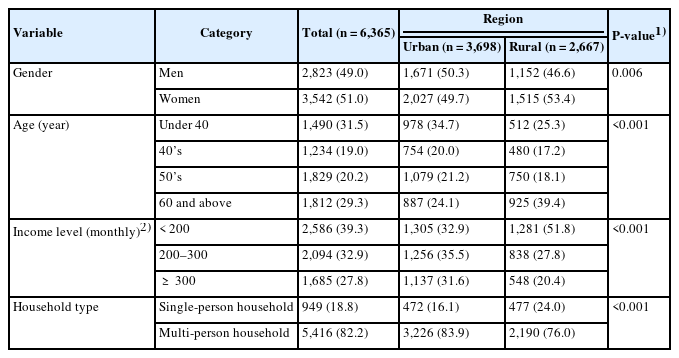
The data were obtained from the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food 2022 by the Korea Rural Economic Institute. The analysis involved 6,365 adult participants, using the complex survey χ2-test and complex survey t-tests to compare dietary behavior across regions and complex survey regression analysis to explore factors related to dietary satisfaction. Data were analyzed with R 4.3.1 (for macOS; Posit PBC).
Results
Urban and rural areas differed in consumer characteristics such as gender, age, income, and household type, as well as in food consumption behaviors and in dietary competencies associated with purchasing and intake. Specifically, dining out and processed food consumption were more prevalent in urban areas, whereas home-cooked meals were more frequent in rural areas. Overall, dietary competencies were higher among urban residents. However, there was no significant difference in dietary satisfaction between the two regions. This finding suggests that satisfaction is based on subjective evaluations, with consumers in each region forming satisfaction in ways that align with their environment and lifestyle. Accordingly, the factors contributing to dietary satisfaction differed by region. In urban areas, information utilization competency and maintaining a balanced diet played a significant role in dietary satisfaction, whereas in rural areas, regular mealtimes were more influential. Urban consumers reported higher dietary satisfaction when meals provided a sense of appropriate convenience, whereas rural consumers showed greater satisfaction when meals were shared with family at home.
Conclusion
The findings indicate regional differences in food consumption behaviors and dietary competencies, as well as variations in how consumers achieve dietary satisfaction. These insights provide a foundation for developing dietary policies and programs aimed at improving dietary satisfaction.
- 1,601 View
- 55 Download

- [English]
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):103-113. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00255
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors such as medication use, dietary supplementation, dietary habits, and physical activity among Koreans aged 20–60 years.
Methods
Data from a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) living in Seoul and Gyeonggi provinces in Korea were analyzed to assess the relationship between health behaviors and dietary supplements (DSs) related to self-care. Based on self-care levels, the participants were classified into three groups: low (LS, n = 124), medium (MS, n = 78), and high (HS, n = 98).
Results
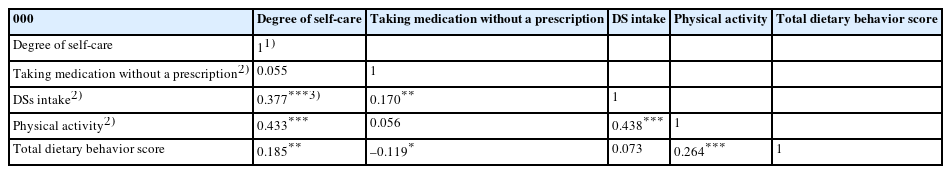
DSs (P < 0.001), physical activity (P < 0.001), recognizing the perceived health benefits of self-care (P < 0.001), self-care when sick (P = 0.039), and the reasons for self-care (P = 0.028) differed among the self-care groups. Daily diet frequency (P = 0.001), breakfast frequency (P = 0.026), regular exercise (P < 0.001), DSs use rate (P < 0.001), DSs use frequency (P = 0.013), and total dietary behavior score (P < 0.001) also differed significantly depending on the degree of self-care. The degree of self-care was significantly and positively correlated with DSs intake (r = 0.377, P < 0.001), physical activity (r = 0.433, P < 0.001), and total dietary behavior score (r = 0.185, P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The results demonstrated that the degree of self-care was related to DSs, physical activity, and total dietary behavior scores in Korean adults. Additionally, self-care capacity should be increased through health-related behaviors based on health education programs.
- 3,040 View
- 57 Download

- [English]
- Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
- Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):359-371. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00013

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate and compare factors associated with malnutrition according to the presence or absence of dementia in community-dwelling elderly people.
Methods
Needs assessment data from 311 long-term care insurance (LTCI) recipients (dementia group 203; non-dementia group 108) that participated in the second pilot program of the integrated care model in community care settings under the Korean LTCI system were used. Descriptive statistical analysis, independent t-test, and analysis of variance were conducted on the sociodemographic characteristics, health and functional status, and nutritional status of the dementia and non-dementia groups. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify factors associated with malnutrition in the dementia and non-dementia groups.
Results
Malnutrition occurred in 33.5% and 26.9% of participants in the dementia and non-dementia groups, respectively. In the dementia group, living with family rather than living alone (odds ratio [OR]: 3.81; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.50–9.66; P = 0.031), increase in Korean Activities of Daily Living (K-ADL) score (OR: 1.35; 95% CI: 1.17–1.55; P < 0.001), and increase in the Neuropsychiatric Inventory-Questionnaire score (OR: 1.02; 95% CI: 1.01–1.03; P = 0.005) were associated with a higher risk of malnutrition. In the non-dementia group, the risk of malnutrition increased as the K-ADL score increased (OR: 1.20; 95% CI: 1.04–1.39; P = 0.011) and in the depressed group (OR: 2.84; 95% CI: 1.04–7.74; P = 0.042).
Conclusions
The study results confirmed the necessity of nutritional management for community-dwelling LTCI recipients. When developing a nutritional management program, considering the differences in factors related to malnutrition between the dementia and non-dementia groups is important. This study proposes policies for improving the LTCI system in terms of nutritional management and the utilization of community resources.
- 2,224 View
- 70 Download

- [English]
- Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
- Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):382-395. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00010

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated whether outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors differed according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students. Methods: The participants were students recruited from nine universities in Seoul, Korea. An online survey was conducted, and data from 351 participants were analyzed. Participants were classified into pre-action and action stages based on adequate sodium intake. Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, analysis of covariance, and correlation analysis. Results: Participants in the action stage (22.8%) felt fewer disadvantages of eating sodium adequately compared to those in the pre-action stage (77.2%, P < 0.001) and perceived more self-efficacy for healthy eating behaviors (P < 0.001) and controlling sodium intake (P < 0.01). The participants in the action stage also showed more desirable eating behaviors than those in the pre-action stage, including general eating behaviors, behaviors related to sodium intake, and sodium checks (P < 0.001). The physical environment in the action stage was more supportive of adequate sodium intake (P < 0.05). Eating behaviors, self-efficacy, and outcome expectations were significantly correlated with the stages of change; however, some differences were noticed in the correlation of the subscales of variables with the stages of change when examined by sex. Conclusion: We observed differences in factors according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake. For the pre-action stage, nutrition education can be planned to modify negative expectations of eating adequate sodium, foster self-efficacy, and practice general eating behaviors and behaviors to gradually reduce sodium intake. It is also necessary to alter the physical environment to reduce sodium intake. In the action stage, support and reinforcement are needed to continually practice and maintain desirable eating behaviors. Nutrition education for women may be planned using multiple paths, whereas a simple strategy may be useful for men.
- 2,747 View
- 48 Download

- [Korean]
- An educational needs analysis of sustainable dietary education for nutrition teachers: an application of the IPA, Borich needs assessment and The locus for focus model
- Eunseo Yang, Borham Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):372-381. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00008

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the importance and performance levels of sustainable dietary education across the health, environment, and society domains as perceived by nutrition teachers and evaluate the needs and priorities for sustainable dietary education.
Methods
An online survey was conducted for 151 nutrition teachers in Jeollanam-do. The survey included 20 questions across the health, environment, and society domains. The data were analyzed using a paired-sample t-test, the importance-performance analysis (IPA), the Borich needs assessment model, and the locus for focus model.
Results
Overall, the average importance levels of the 20 items of sustainable dietary education were significantly higher than their average performance levels (4.44 vs. 3.68). The examination of each educational domain revealed that although the importance of education in the health domain was recognized and actively practiced by the nutrition teachers, the performance was comparatively lower in the environment and society domains. The Borich needs assessment and the locus for focus model identified education on biodiversity conservation, plant-based protein, and the use of local food as the top-priority group in the environment domain along with fair and ethical food, food security, regional food culture, food policy and trade, and family dining culture as the second-priority group in the society domain.
Conclusions
The results of this study underscore the need to support the nutrition teachers’ perception and practice of sustainable dietary education in the environment and society domains. We believe that the educational needs and priorities proposed in this study will be considered in the future development and modification of sustainable dietary education programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Jounghee Lee, Juhyun Lee, Wookyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 75. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef - Analysis of students’ need for artificial intelligence content in the 「Digital education」 subject
SungAe Kim, Ji Won You
The Journal of Korean Association of Computer Education.2025; 28(7): 71. CrossRef - Safety education status and needs priorities of Korean military food service personnel using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model: a cross-sectional study
Jeongeun Park, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 261. CrossRef
- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 2,754 View
- 79 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Eating habits and dietary supplement utilization according to food-related lifestyle among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):253-264. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
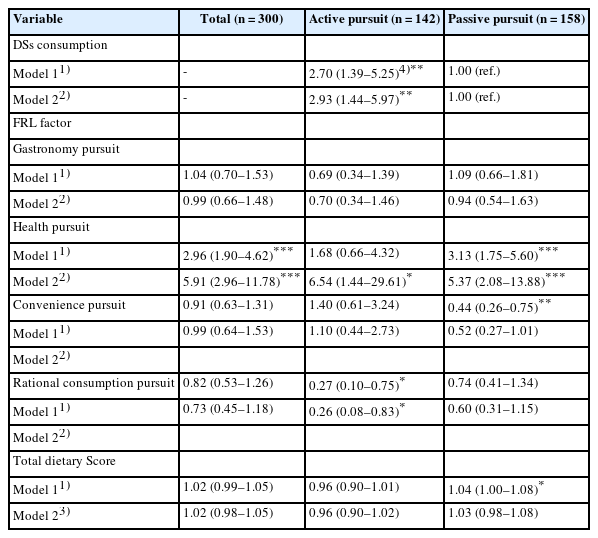
This study investigated the association between eating habits and the utilization of dietary supplements (DSs) according to food-related lifestyle (FRL) among Korean adults. Methods: This study included a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) in their 20s to 60s living in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province. We identified two groups by factor and cluster analysis: an ‘active pursuit’ group and a ‘passive pursuit’ group. Differences in eating habits and DS utilization between the two groups were analyzed by chi-square test and t-test. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the effect of variables on DS consumption according to FRL. Results: There were significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, alcohol drinking frequency, total dietary score, change in DS consumption after coronavirus disease 2019, and current DS consumption (P < 0.05). The proportion who perceived many health benefits of DSs was higher in the ‘active pursuit’ group than in the ‘passive pursuit’ group (P = 0.003). The most commonly consumed type of DSs was multivitamins & minerals for the ‘active pursuit’ group, and omega-3 fatty acids for the ‘passive pursuit’ group. The ‘an active pursuit’ group consumed DSs 2.93 times more (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.44–5.97) compared to the ‘passive pursuit’ group, after adjusting for confounders. In the ‘active pursuit’ group, the health pursuit (odds ratio [OR] = 6.54, 95% CI: 1.44– 29.61) and rational consumption pursuit factors (OR = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.08–0.83) were associated with DS consumption, whereas only the health pursuit factor had a significant association (OR = 5.37, 95% CI: 2.08–13.88) within the ‘passive pursuit’ group. However, total dietary score and DSs consumption did not show a relationship. Conclusions: By understanding the consumption characteristics of DSs according to FRL, this can serve as basic data necessary for promoting health through the utilization of DSs and healthy behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
Hongryul Ahn, Seungwon Kim, Jinmyung Jung, Chan Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(4): 618. CrossRef - Demographic and behavioral correlation of red ginseng consumption in Korea
DeYu Tian, KeunOh Choi, Yong-ung Kim, YoungJoo Lee
Integrative Medicine Research.2025; : 101287. CrossRef
- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
- 5,248 View
- 95 Download
- 2 Crossref

Educational Materialses
- [Korean]
- Systematization of food and nutrition education content based on national kindergarten curriculum: a qualitative formative study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Eunyoung Baik
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):509-522. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.509
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study is intended to develop a curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aimed at preschool children, reflecting government policy and meeting the demands of preschool settings.
Methods
Existing educational materials were analyzed, and key elements of the 2019 Revised Nuri Curriculum (“Nuri Curriculum”) and Guidelines for Nutrition and Food Education in Kindergartens, Elementary, Middle, and High Schools (“Guidelines”) were examined as foundational information for developing the curriculum for food and nutrition education.
Results
Basing ourselves on the five domains of the Nuri Curriculum, “Physical Activity and Health,” “Communication,” “Social Relationships,” “Art Experience,” and “Natural Science Inquiry,” we integrated three areas from the Guidelines, namely “Dietary Habits and Health,” “Dietary Habits and Safety,” and “Dietary Habits and Culture,” to structure the curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education. Three specific domains, “Nutrition and Health,” “Food and Culture,” and “Safe Dietary Practices,” were tailored for preschool children, each comprising core concepts, content elements, and educational materials. In the “Nutrition and Health” domain, core concepts such as “nutrition” were addressed through content elements such as “balanced eating” and “vegetables and fruit,” while “health” included elements such as “eating regularly” and “nutrients for disease prevention,” each with two educational content components. The “Food and Culture” domain focused on “food” with content on “local foods (vegetable-garden experience)” and “food culture” with content on “our dining table (rice and side dishes),” “our agricultural products,” “global cuisine (multiculture),” and “considerate dietary practices,” each with four educational content components. The “Safe Dietary Practices” domain included core concepts such as “hygiene” with content on “hand-washing habits” and “food poisoning management,” and “safety” with content on “food labeling.”
Conclusions
The systematized curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aligns with the Nuri Curriculum and is interconnected with the Guidelines. This curriculum can be used as foundational material for developing educational resources tailored to the characteristics of preschoolers, contributing to effective implementation in early childhood education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 441. CrossRef
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- 1,190 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
- Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):495-508. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.495
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop a campus-based intervention program to enhance food literacy (FL) among university students.
Methods
In the initial phase, we conducted a literature review of FL intervention studies and held in-depth interviews with university students to identify facilitators and barriers to improving and practicing FL. Expert counseling sessions were conducted with nutrition education, marketing, and service design professionals. The results of this phase led to the creation of an initial curriculum draft. In the second phase, a follow-up survey was conducted with young adults to assess the acceptability of the developed curriculum. After the follow-up survey, additional meetings were conducted with the aforementioned experts, and the curriculum was further refined based on their input.
Results
An 11-week FL intervention program was devised using constructs from the Social Cognitive Theory. The weekly curriculum consisted of 90-min theory-based and 90-min hands-on experience sessions. Three primary aspects of FL were covered: nutrition and food safety, cultural and relational dimensions, and socio-ecological aspects. Program highlights included cooking sessions for crafting traditional Korean desserts, lectures on animal welfare, insights into zero-waste practices, and communal eating experiences. Based on the study team’s previous research, the program also addressed mindful eating, helping participants understand the relationship with their eating habits, and providing strategies to manage negative emotions without resorting to food. Yoga sessions and local farm visits were incorporated into the curriculum to promote holistic well-being.
Conclusions
This study elucidated the comprehensive process of creating a campus-based curriculum to enhance FL among university students, a group particularly susceptible to problematic eating behaviors and low FL levels. The developed program can serve as a blueprint for adaptation to other campuses seeking to bolster students’ FL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of nutrition class with cooking lab on college students’ eating behaviors and well-being in the United States: a mixed-methods study
Borham Yoon, Kyungyul Jun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 305. CrossRef - The Dragon Fruit Advantage: Exploring University Students’ Experiences and Perceptions of a Targeted Nutrition Education Module
Adelfa Silor, Faith Stephanny C. Silor
Seminars in Medical Writing and Education.2025; 4: 924. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of a food literacy pilot program for university students: using a mixed-methods research approach
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(6): 885. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef
- Effects of nutrition class with cooking lab on college students’ eating behaviors and well-being in the United States: a mixed-methods study
- 2,636 View
- 78 Download
- 4 Crossref

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
- Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):466-479. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.466
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A mobile health intervention program was provided for employees with overweight and obesity for 12 weeks, and a process evaluation was completed at the end of the program. We investigated participant engagement based on app usage data, and whether engagement was associated with the degree of satisfaction with the program.
Methods
The program involved the use of a dietary coaching app and a wearable device for monitoring physical activity and body composition. A total of 235 employees participated in the program. App usage data were collected from a mobile platform, and a questionnaire survey on process evaluation and needs assessment was conducted during the post-test.
Results
The engagement level of the participants decreased over time. Participants in their 40s, high school graduates or lower education, and manufacturing workers showed higher engagement than other age groups, college graduates, and office workers, respectively. The overall satisfaction score was 3.6 out of 5. When participants were categorized into three groups according to their engagement level, the upper group was more satisfied than the lower group. A total of 71.5% of participants answered that they wanted to rejoin or recommend the program, and 71.9% answered that the program was helpful in improving their dietary habits. The most helpful components in the program were diet records and a 1:1 chat with the dietary coach from the dietary coaching app. The barriers to improving dietary habits included company dinners, special occasions, lack of time, and eating out. The workplace dietary management programs were recognized as necessary with a need score of 3.9 out of 5.
Conclusions
Participants were generally satisfied with the mobile health intervention program, particularly highly engaged participants. Feedback from a dietary coach was an important factor in increasing satisfaction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 53. CrossRef
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- 1,413 View
- 64 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Food and dish group diversity on menus of daycare centers provided by Center for Children’s Foodservice Management in Korea: a descriptive study
- Youn-Rok Kang, Kyeong-Sook Lim, Hyung-Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):449-465. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.449
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze menu patterns and food group diversity in daycare centers managed by the Center for Children's Foodservice Management in South Korea.
Methods
Data from 18 Center for Children's Foodservice Management centers across various provinces (excluding Jeju Island) were analyzed. We examined 8,796 meals served in February, May, August, and December 2021, focusing on seasonal lunch and snack menus for children aged 3-5. Foods were categorized into 19 groups for lunch and 21 for snacks. The frequency of food groups and dietary patterns were assessed using the Dietary Diversity Score. Analyses were conducted using Excel 2016 and IBM SPSS Statistics version 28.
Results
Most lunch menus (89%) included five menu items, with a ratio of grain, meat, and vegetables at 88%. Snack menus typically had one item (57%), with significantly more items in the afternoon compared to the morning (P < 0.001). Regarding snack patterns, 75.2% of morning snacks and 61.1% of afternoon snacks contained only one solid food and drink (P < 0.001). Fruit and milk (22.4%) was the most prevalent pattern in morning snacks, while grain and milk (31%) dominated afternoon snacks (P < 0.001). Only 48% of daycare center menus (all snacks and lunch) included all five food groups (grain, meat, vegetables, fruit, and milk). Notably, only 83% included milk and 57% included fruit.
Conclusions
These findings highlight the need to improve food variety and diversity in the Center for Children’s Foodservice Management-managed daycare center menus. Developing more detailed guidelines for menu structure and food composition is crucial to ensure children receive balanced and diverse nutrition. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 225. CrossRef
- Nutrient intake and food consumption of Korean preschool children: a comparison between a daycare meal group and non-daycare meal group using the data from the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,483 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between health financial capacity of local governments and health behaviors of local residents: a cross-sectional study
- Miyong Yon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):95-103. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The budget gap in the health sector of local governments affects the supply of health services, which can cause the health gap. This study classified local governments according to their financial characteristics, such as local financial independence and health budget level. It analyzed the health behaviors and disease prevalence of local residents to examine the effect of local government financial investment on the health of local residents.
Methods
To classify types according to the financial characteristics of local governments, financial independence and the health budget data for 17 local governments were collected from the local fiscal yearbook of the Ministry of Public Administration and Security. The prevalence of chronic diseases and healthy behavior was compared using the 16,333 data of adults between the ages of 30 and 65 years among the original data of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2020).
Results
Cluster analysis was used to classify local governments into five clusters according to the health financial capacity type. A comparison of the prevalence of local residents by cluster revealed a similar prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia. On the other hand, the obesity rate (P < 0.01), high-risk drinking rate (P < 0.01), aerobic physical activity rate (P < 0.001), and healthy eating practice rate (P < 0.001) were significantly different. In addition, an analysis of the odds ratio based on the Seoul area revealed a higher risk of health behavior of non-Seoul residents.
Conclusions
It is necessary to review the universal health promotion project budget considering the degree of regional financial vulnerability from the viewpoint of health equity to narrow the health gap among regions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of health equity-based Healthy City infrastructure on walking practice
Hyeyun Son, Changwoo Shon
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2025; 42(5): 99. CrossRef
- Influence of health equity-based Healthy City infrastructure on walking practice
- 1,435 View
- 27 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Effectiveness of a mobile health intervention on weight loss and dietary behavior changes among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
- Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young-Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):141-159. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.141
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to determine whether a mobile health (mhealth) intervention is effective in reducing weight and changing dietary behavior among employees with overweight and obesity. The study also investigated whether engagement with the intervention affected its effectiveness.
Methods
The intervention involved the use of a dietary coaching app, a wearable device for monitoring physical activity and body composition, and a messenger app for communicating with participants and an intervention manager. A total of 235 employees were recruited for a 12-week intervention from eight workplaces in Korea. Questionnaire surveys, anthropometric measurements, and 24-h dietary recalls were conducted at baseline and after the intervention.
Results
After the intervention, significant decreases in the mean body weight, body mass index, body fat percentage, and waist circumference were observed. Furthermore, the consumption frequencies of multigrain rice and legumes significantly increased, whereas those of pork belly, instant noodles, processed meat, carbonated beverages, and fast food significantly decreased compared with those at baseline. The mean dietary intake of energy and most nutrients also decreased after the intervention. When the participants were categorized into three groups according to their engagement level, significant differences in anthropometric data, dietary behaviors, and energy intake were observed following the intervention, although there were no differences at baseline, indicating that higher engagement level led to greater improvements in weight loss and dietary behavior.
Conclusions
The intervention had positive effects on weight loss and dietary behavior changes, particularly among employees with higher engagement levels. These results indicate the importance of increasing the level of engagement in the intervention to enhance its effectiveness. The mhealth intervention is a promising model for health promotion for busy workers with limited time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 466. CrossRef - Systematic Review on the Study of the Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in Korea: Dietary Risk Factors
Eun Jeong Heo, Jae Eun Shim, Eun Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 191. CrossRef
- Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
- 2,119 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Changes in dietary habits and chronic diseases before and after COVID-19 by regions using data from the 2018-2020 Korea Community Health Survey and Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods: a cross-sectional study
- Surim Park, Eun-hee Jang, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):124-140. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.124
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the changes in dietary habits, the prevalence of chronic diseases, and mental health problems in the regional areas of the Republic of Korea before and after the COVID-19 pandemic to provide evidence of the status of regional health inequalities.
Methods
This study analyzed Korean adults aged 19 or older who participated in the Korea Community Health Survey (n = 686,708) and Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods (n = 19,109) from 2018 to 2020. The participants were classified according to their residence area (Seoul metropolitan area, Metropolitan cities, Provinces); 2018-2019 were defined as before COVID-19, and 2020 as after COVID-19. The dietary behaviors, chronic diseases, and mental health problems were measured using a self-report questionnaire.
Results
After COVID-19, the eating-out usage rate in the Seoul metropolitan area and Provinces decreased compared to before COVID-19 (P < 0.001), and when responding that they eat out, the frequency of eating out with household members in the Seoul metropolitan area increased (P = 0.024). The deliveries/takeout usage rate in the Provinces decreased after COVID-19 compared to before (P < 0.001). After COVID-19, the prevalence of obesity decreased in all regions (P < 0.001), and the prevalence of hypertension increased significantly in the Provinces (P = 0.015). The prevalence of diabetes mellitus increased continuously before and after COVID-19 in all regions (P < 0.002). High-risk subjective stress levels increased significantly in the Seoul metropolitan area (P < 0.001), and sleep duration significantly increased in all regions (P < 0.001). Major depressive disorder was reduced significantly in Metropolitan cities (P = 0.042) and Provinces (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
After the COVID-19 pandemic, the prevalence of chronic diseases and mental health problems showed regional differences along with changes in dietary habits. It is necessary to reflect the regional differences in dietary habits in future policies resolving regional health inequalities.
- 1,257 View
- 16 Download

- [Korean]
- Association between eating habits, sweet taste assessment, and high-sugar food consumption among elementary school students in Daegu: a descriptive study
- Min-Jung Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):104-113. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to analyze high-sugar food consumption habits frequency among elementary school students, and their correlations with eating habits and sweet taste assessment.
Methods
The participants of the study were 164 elementary school students in Daegu, in the fifth or sixth grade, along with their parents. A questionnaire investigated eating habits, high-sugar food consumption habits and frequency, and sweet taste assessment.
Results
The average eating habits score for elementary school students was determined to be 71.7 out of 100. Students with higher eating habits scores had lower high-sugar food consumption habits and frequency compared to those with lower eating habits scores. Sweet taste assessment revealed that students who preferred less sweetness chose a 5% sugar concentration, those with a preference for normal sweetness chose a 10% sugar concentration, and those who preferred sweeter tastes chose a 20% sugar concentration. Sweet taste assessment showed that students who tended to prefer less sweetness had the highest eating habits scores and the lowest scores for high-sugar food consumption habits and frequency. In addition, eating habits scores were found to be negatively correlated with high-sugar food consumption habits, high-sugar food consumption frequency, and sweet taste assessment. The sweet taste assessment was positively correlated with high-sugar food consumption habits and frequency.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that students with good eating habits had more desirable overall sugar intake habits, and when the preference for sweetness was high, the frequency of high-sugar food consumption was also high. Our study highlights the importance of educating elementary school students and their parents about the harmful effects of excessive sugar consumption, as well as the benefits of adopting healthy eating habits and creating supportive environments.
- 1,211 View
- 32 Download

- [Korean]
- The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
- Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):38-47. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between the experience of disease management education and the use of nutrition labels according to the sociodemographic characteristics and health behaviors of people diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes living in the community.
Methods
Among the participants from the Community Health Survey (2018), 74,283 individuals diagnosed with hypertension or diabetes were included in the study population. According to gender, this study evaluated nutrition label use by the experience of disease management education, individual sociodemographic characteristics, and health behavior. Finally, using multiple logistic regression analysis, the association between disease management education and nutrition labels was calculated using the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results
Males (24.5%) experienced more disease management education than females (22.6%). In addition, younger age, higher education level, and higher equalized personal income experienced more disease management education (P < 0.001). The educational experience rate was higher in the male subjects who did not smoke or were involved in high-risk alcohol consumption (P < 0.001). In addition, the rate of disease management education experience was significantly higher for both men and women who exercised by walking (P < 0.001). The use of nutrition labels was higher in females (9.9%) than males (5.8%), and both males and females were significantly higher in young age, high education, high income, and professional and office positions (P < 0.001). The utilization rate of nutrition labels was high in non-smoking male subjects and high-risk-drinking female subjects. In addition, the utilization rate of nutrition labels was significantly higher in males and females who exercised by walking and those who experienced disease management education (P < 0.001). After adjusting for individual sociodemographic characteristics, health behavior, and disease management education, the use of nutrition labels was high among females (OR 3.19, 95% CI 2.85-3.58), high income (Q4; OR 1.62, 95% CI 1.41-1.87, Q5; OR 1.58, 95% CI 1.37-1.84) and highly educated (high school; OR 2.87, 95% CI 2.62-3.14, above college; OR 5.60, 95% CI 5.02-6.23) while it was low in the elderly (OR 0.43, 95% CI 0.40-0.47), and economically inactive (OR 0.86, 95% CI 0.76-0.96). The use of nutrition labels was high in non-smokers (OR 1.29, 95% CI 1.13-1.48), non-high-risk drinkers (OR 1.22, 95% CI 1.08-1.38), and subjects who exercised walking (OR 1.44, 95% CI 1.34-1.54). There was no difference in the utilization rate of nutrition labels according to obesity, and the utilization rate of nutrition labels was significantly higher in subjects who had experienced disease education (OR 1.34, 95% CI 1.24-1.44).
Conclusions
Education on the use of nutrition labels, which contributes to food selection for healthy eating, might be a tool for dietary management. Moreover, the utilization rate can be a good indicator for predicting the proportion of the population practicing the guide for disease management. Improving the utilization rate of nutrition labels through disease management education can be a useful intervention for people with chronic diseases who need healthy eating habits for disease management and preventing complications, particularly those diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Nutrition Label Utilization and Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: Using the Data of the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2021)
Ae-Seul Lee, Seong Woo Choi, So Yeon Ryu
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(3): 249. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Status and Life Satisfaction According to Food Security in Single-Person Households of Elderly Population
Dong Hoon Jung, Jae Won Han, Wonha Kim, Hee-Sook Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(1): 42. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Dietary Behavior of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-sectional Study
Sohyun Jin, Youngshin Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 80. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Participation in Hypertension Management Education Among Diagnosed Hypertensive Patients in Busan: Utilizing the 2021 Community Health Survey
Hye Jung Jun, Kyoung Mi Kim
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 424. CrossRef - An association between socioeconomic status and preventive screening for diabetic eye and kidney complications among individuals with type 2 diabetes
Changwoo Shon, Jongnam Hwang
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(5): 27. CrossRef
- Association between Nutrition Label Utilization and Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: Using the Data of the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2021)
- 3,667 View
- 66 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Foodservice Status and Perception regarding Foodservice Management in Kindergartens attached to Elementary Schools in Seoul
- Ranmi Jung, Gun-Hee Kim, Jieun Oh, Sunny Ham, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):492-502. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.492
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examines the foodservice status of kindergartens attached to elementary schools in Seoul. We further determine the perception of elementary school principals and kindergarten assistant principals on the foodservice management for kindergartens.
Methods
This survey was conducted from July 17 to 23, 2019, enrolling 207 kindergartens attached to elementary schools in Seoul. Questionnaires were sent to principals of elementary schools and assistant principals of kindergartens, and the data obtained from 89 kindergartens were included in the analysis. The questionnaire consisted of four parts: general information on subjects, foodservice management status, foodservice management status during elementary school vacations, and the perception of principals of elementary schools and assistant principals of kindergartens on foodservice management. Data are presented as frequency and percentage or mean and standard deviation. Statistical comparison between principals of elementary schools and assistant principals of kindergartens was conducted by paired t-test, chi-square test, and Pearson's correlation analysis.
Results
A separate menu (10.1%) or recipe (20.2%) that considers preschooler characteristics was rarely used for foodservice at kindergartens attached to elementary schools. Most kindergartens did not have a separate dining space (3.4%) or a dedicated cook (93.3%). Although most kindergartens (92.1%) had operational foodservice during elementary school vacations, non-professional staff and non-nutrition teacher were mainly in charge of organizing the menu and purchasing ingredients (34.1% and 41.5%, respectively). The rate of using a contract catering company (28.0%, 23.2%) was also high. Both elementary school principals and assistant principals of kindergartens showed a high perception of the necessity for providing responsibility allowances for nutrition teachers and improving the cooking environment for kindergartens during elementary school vacations.
Conclusions
There is a need for policies and administrative support measures to improve the quality of foodservices for kindergartens attached to elementary schools. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef - A Study on the Menu Patterns and Menu Diversity of Bibimbap Meals Served by Elementary School Foodservices in the Jeonbuk Area
Sun A Choi, Chohee Mun, Jieun Go, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 444. CrossRef
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
- 1,116 View
- 12 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
- Jinkyung Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):468-479. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.468
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigates dietary supplement intakes by examining the characteristics of dietary and health-related behaviors. Data were obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Dietary and health-related behaviors were also examined before and after the occurrence of COVID-19 and household types (multi-members vs. single person).
Methods
Data used in this study were collected from the 2019-2020 KNHANES by including adults aged 19 to 64 years. Pregnant, lactating, and subjects consuming calories less than 500 and more than 5,000 were excluded. Differences in dietary and health-related behaviors before and after COVID-19, and between the two types of households were analyzed by Chi-square analyses using Rao-Scott. Logistic regression analyses were applied to determine which dietary and health-related behaviors affected the dietary supplement intakes. In addition, descriptive analysis was run for demographic characteristics.
Results
The dietary supplement intake rate differed significantly with respect to the gender, age, education, marital status, and household income. Dietary supplement intakes, frequency of eating out, obesity, and body weight changes were significantly different before and after COVID-19. In addition, meal evaluation, frequency of eating out, drinking, smoking, activity, subjective health evaluation, and body weight changes showed significant differences by household type. Attitude towards nutrition, activity, meal evaluation, obesity, and smoking were factors that affected the intake of dietary supplements.
Conclusions
While increased intake of dietary supplements is a prevalent phenomenon, this intake needs to be monitored and studied closely, considering the sociodemographic characteristics and dietary and health-related behaviors. Furthermore, the dietary supplement intake trend after COVID-19 needs to be studied along with food intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
Eunyoung Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 220. CrossRef
- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- 2,088 View
- 46 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Effect of Type of Nutrition Labeling on the Healthfulness Evaluation and Purchase Intentions of Home Meal Replacements (HMR) in South Korea
- Mee-Young Joe
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):387-396. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.387
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of the types of nutrition labeling on the processing fluency, health evaluation and purchase intentions of home meal replacements.
Methods
This online experimental study was conducted from December 29 to 31, 2019 and included 134 participants. The research design was 2 (Objective nutrition labeling: present vs. absent) X 2 (Evaluative nutrition labeling: present vs. absent) and each participant was randomly assigned to one of four groups. As stimuli, five types of ready-to-heat foods sold in the market were used.
Results
Processing fluency (4.91 points) and purchase intention (4.13 points) were significantly high when both evaluative nutrition labeling and objective nutrition labeling were presented, and healthfulness evaluation (4.47 points) was significantly high when only evaluative nutrition labeling was presented. All three variables were measured to be high when evaluative nutrition labeling was presented. The evaluative nutrition labeling that visually represented nutritional values was found to be more effective for processing fluency, healthfulness evaluation, and purchase intention than the objective nutrition labeling representing the nutritional value of the product in numbers and proportions.
Conclusions
These results show that it is necessary to develop various types of evaluative nutrition labeling to enable consumers to choose and purchase healthful home meal replacements. Also, consumer education and public campaigns are needed to encourage consumers to select healthier home-cooked meals using nutrition labeling. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Sustainable Dietary Life Competency in Families According to Parents’ Dietary Lifestyle: Using the 2021 Korea Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1179. CrossRef - Study on the consumption practices and Importance-Satisfaction Analysis of meal-kit selection attributes among adults in their 20s and 30s
Se-Eun Kim, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 315. CrossRef
- Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Sustainable Dietary Life Competency in Families According to Parents’ Dietary Lifestyle: Using the 2021 Korea Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
- 1,212 View
- 18 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between Sarcopenia and Energy and Protein Intakes in Community-dwelling Elderly
- Woori Na, Dayoung Oh, Seohyeon Hwang, Bonghee Chung, Cheongmin Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(4):286-295. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.4.286
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Sarcopenia is one of the most representative factors of senescence, and nutritional status is known to affect sarcopenia. This study was performed to analyze the relationships between energy and protein intake and sarcopenia.
Methods
The study subjects were 3,236 individuals aged ≥ 65 that participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2008 ~ 2011. General characteristics and anthropometric and 24-hour dietary recall data were analyzed. Sarcopenia was diagnosed using a formula based on appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM) and body weight. Logistic regression was performed to determine relationships between sarcopenia risk and energy and protein intakes.
Results
For energy intake, the odds ratio (OR) of sarcopenia in women was significantly higher those with the lowest intake [OR = 1.680, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.213-2.326] than those with the highest intake (P for trend = 0.001). Regarding protein intake per kg of body weight, the odds ratio of sarcopenia was significantly higher for those that consumed < 0.8 g/kg of protein daily than those that consumed > 1.2g/kg for men (OR = 2.459, 95% CI = 1.481-4.085) and women (OR = 2.178, 95% CI = 1.423-3.334).
Conclusions
This study shows a link between sarcopenia and energy and protein intake levels and suggests that energy and protein consumption be promoted among older adults to prevent sarcopenia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between Protein Intake and Sarcopenia-Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Scoping Review
Minjee Han, Kyung-sook Woo, Kirang Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(3): 216. CrossRef - Nutritional Approaches in Sarcopenia Management
Min-Yu Chung
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 565. CrossRef - The Present and Future of Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Exercise Interventions: A Narrative Review
Hongje Jang, Jeonghyeok Song, Jeonghun Kim, Hyeongmin Lee, Hyemin Lee, Hye-yeon Park, Huijin Shin, Yeah-eun Kwon, Yeji Kim, JongEun Yim
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(23): 12760. CrossRef - Design of contents for developing an intervention app for sarcopenia in older adults: A research study using the Delphi technique
Hee Jung Kim, Ju Young Ha
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(4): 370. CrossRef - Association of Protein Intake with Sarcopenia and Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Minjee Han, Kyungsook Woo, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2024; 16(24): 4350. CrossRef - Muscle Mass Changes After Daily Consumption of Protein Mix Supplemented With Vitamin D in Adults Over 50 Years of Age: Subgroup Analysis According to the Serum 25(OH)D Levels of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Yeji Kang, Namhee Kim, Yunhwan Lee, Xiangxue An, Yoon-Sok Chung, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2023; 12(3): 184. CrossRef
- Association Between Protein Intake and Sarcopenia-Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Scoping Review
- 2,810 View
- 75 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Consumption of Weight-control or Health Functional Foods, Dietary Habits, and Weight Perceptions According to the Body Mass Index of Adult Women in the Chungcheong Area
- Gayoung Seong, Munkyong Pae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):81-93. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to investigate the experience and perception among adult women regarding weight control and the consumption of weight-control foods or health functional foods based on their body mass index (BMI).
Methods
The subjects were 634 adult women from the Chungcheong province, Korea, and data were collected through a self-administered questionnaire from July 2021 through September 2021. The subjects were divided into four groups based on their BMI status: underweight (< 18.5 kg/㎡ , 7.6%), normal weight (18.5 ~ 22.9 kg/㎡ , 53.3%), overweight (23 ~ 24.9 kg/㎡ , 19.7%), and obese ( ≥ 25 kg/㎡ , 19.4%).
Results
Over the past 3 years, almost two-thirds (68.6%) of the adult women had tried weight control measures, despite the fact that a significant proportion of them were normal or underweight. More importantly, 57.6% of subjects reported the consumption of weightcontrol foods, with a lower proportion in the underweight (35.4%) group compared to the normal (56.2%), overweight (62.4%), and obese (65.0%) groups. The food items used for weight control were mostly salads, chicken breasts, low fat (soy) milk, slimming tea, protein shakes, low-calorie cereals, and energy/protein bars among others. In addition, one-third (31.1%) of the subjects reported the use of health functional foods containing ingredients for fat reduction. A significantly higher proportion of these was from the overweight (36.0%) and obese (38.2%) groups compared to the underweight (20.8%) and normal weight (28.1%) groups. Products containing Garcinia cambogia extract, green tea, or Cissus extract, were popular among users. Subjects who were obese had a poorer perception of their health and body. Most subjects felt the need for correct information regarding weight control, but this number was significantly more in the higher BMI groups.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that the use of weight-control foods or health functional foods is popular among adult women, especially those who are obese. Thus, nutrition education courses covering facts about weight control and practice need to be developed and provided based on the BMI status of subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coffee Consumption Patterns According to Health Behavior and Dietary Factors among Young Adults : From the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2021
Hyun-Ju Jo, Hyun-Kyoung Bang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(4): 369. CrossRef - Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
Hyoju Lee, Youjeong Jang, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 261. CrossRef - Prediction model of weight control experience in men with obesity in their 30 s and 40 s using decision tree analysis
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on Diet Perceptions and Trends Before and After COVID-19 Using Big Data Analysis
Eunjung Lee, Hyosun Jung, Jina Jang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(6): 659. CrossRef - A Narrative Approach to the Diet History of Female College Students : Focusing on the Role of SNS and Social Media Influencers and Individuals’ Motivation for Dieting
Kyungbo Kim
Korean Journal of Journalism & Communication Studies.2022; 66(3): 139. CrossRef
- Coffee Consumption Patterns According to Health Behavior and Dietary Factors among Young Adults : From the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2021
- 1,786 View
- 34 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Dietary Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Status in Korean Menopausal Women: Based on the 2016 ~ 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Pil-Sook Park, Mei-Sheng Li, Mi-Yeon Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):482-494. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.482
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated dietary behavior and nutritional status according to the metabolic syndrome status in Korean menopausal women.
Methods
The subjects were 1,392 menopausal women aged 50 to 64 who took part in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of 2016 and 2017. Subjects were classified into normal (NOR) group, pre-metabolic syndrome (Pre-MetS) group, and metabolic syndrome (MetS) groups according to the number of metabolic syndrome risk factors present.
Results
The overall prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 33.7%. Using the NOR group as a reference, the odds of belonging to the MetS group in Model 1 adjusted for age were higher at 53% (OR = 1.53, 95% CI:1.011-2.307) for ‘not used’ subjects compared to ‘used’ subjects of the nutrition labeling system. Using the NOR group as a reference, every 1g increase in the intake of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) decreased the odds of belonging to the MetS group in Model 1 adjusted for age by 3% (MUFA, OR = 0.97, 95% CI:0.946-0.991; PUFA, OR = 0.97, 95% CI:0.942-0.993).
Conclusions
These results suggest that to reduce the number of risk factors of metabolic syndrome in menopausal women, nutritional education should emphasize the adequate intake of riboflavin, unsaturated fatty acids, protein, and calcium, and also encourage the recognition and use of nutritional labeling. Results of this study are expected to be utilized as basic data for the health management of menopausal women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardiocerebrovascular Disease or Fatty Liver Incidence Associated with Pattern of Metabolic Risk Factors and Nutritional Status of Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
Pil Sook Park, Mei Sheng Li, Chong Yu Ding, Mi Yeon Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(2): 165. CrossRef - The Relationship Between the Korean Adults Diet Evaluated Using Dietary Quality Indices and Metabolic Risk Factors: Based on the 2016 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Chong-Yu Ding, Pil-Sook Park, Mi-Yeon Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 223. CrossRef
- Cardiocerebrovascular Disease or Fatty Liver Incidence Associated with Pattern of Metabolic Risk Factors and Nutritional Status of Korean Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
- 1,556 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between Eating Alone Patterns and Mental Health Conditions by Region among Korean Adults
- Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):441-454. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the association between the frequency and pattern of eating alone and the mental health status according to region in Korean adults.
Methods
The data of 10,040 Korean adults aged ≥ 19 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2017 and 2019 were used. Participants were divided into 4 groups based on their frequency of eating alone: none (all meals together), 1, 2, and 3 meals/day alone. The regions were divided into urban and rural areas. Mental health status was assessed by stress recognition, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation. Multivariable logistic regressions were conducted to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) on the association of the frequency and pattern of eating alone with poor mental health after controlling for covariates.
Results
Among Korean adults, 74.1% ate more than one meal a day alone. Individuals having 3 meals a day alone tended to be less educated, single, single person households, or living in urban areas (all P < 0.05). In rural areas, those having 3 meals/ day alone had higher odds of stress recognition (AOR: 1.55, 95% CI: 1.02-2.35) than those having all meals together. In urban areas, individuals eating alone 3 times/day had higher odds of stress recognition (AOR: 1.60, 95% CI: 1.31-1.96), depressive symptoms (AOR: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.23-2.12), and suicidal ideation (AOR: 2.14, 95% CI: 1.42-3.22) compared to those having all meals together. Urban residents having dinner alone had higher odds of depressive symptoms (AOR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.05-1.58) and suicidal ideation (AOR: 1.66, 95% CI: 1.19-2.33) than those having dinner with others.
Conclusions
Our findings showed that the frequency and patterns of eating alone were differentially associated with increased odds of poor mental health according to region of residence. Nutrition education is needed for those frequently eating alone, particularly those living in urban areas, to highlight the advantages of eating together and to ensure that they have balanced and healthy meals even if they eat alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Social Activity Restrictions on Depression in Young Single-Person Households: The Moderating Effect of Eating Alone
Jiwon Kim, Youngye Park
Journal of Social Science.2025; 36(3): 27. CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - How Does the Frequency of Eating-Alone among Older People in Korea Affect Their Health and Dietary Behavior?
Yongseok Kwon, Kyung Hee Hong, Yoo-Kyung Park, Sohye Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2085. CrossRef - Impact assessment of a primary care physician counseling program for youth population
Yun-Su Kim, Shin-Ae Kim
Medicine.2022; 101(46): e31916. CrossRef
- The Impact of Social Activity Restrictions on Depression in Young Single-Person Households: The Moderating Effect of Eating Alone
- 2,447 View
- 40 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Management of Food Allergy in the Facilities Registered at Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Gangdong-gu
- Soon Mi Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):396-407. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.396
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We examined the common allergenic foods, symptoms and management of food allergies in children attending the facilities registered at Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Gangdong-gu, Korea. Methods: The survey was conducted among the directors or head teachers of 186 children’s food service facilities with 7,591 children in 2019. The questionnaire consisted of three parts, including general information about food service facilities, information related to food allergies and allergenic foods and symptoms in individual children. Results: The number of children with food allergy was 271 (3.6%), and the proportion decreased with the increase of age. There were 91 children (33.6%) with a medical certificate, and these children had a significantly higher number of allergenic foods and symptoms than those without a medical certificate. Allergenic food groups included meat, fish, eggs and legumes (59.1%), fruits (12.4%), milk and dairy products (8.9%), cereals (7.8%), vegetables (6.2%), processed foods (3.8%) and oils and sugars (1.9%). Eggs accounted for 22.1%, followed by peanut and tree nuts (18.6%), fruits (12.4%), milk and dairy products (8.9%), shellfish (8.6%), vegetables (6.2%), fish (5.7%), cereals (4.3%) and meat (1.1%). The common allergenic foods were eggs, peanuts, walnuts, kiwi, shrimp, milk, tomatoes, mackerel, blue-green fish, peaches, shellfish (clams and abalone), buckwheat, wheat and soybeans. The most common allergic symptoms were skin and mucous membrane symptoms, such as hives, rash, itching and oral angioedema. Meal management for children with food allergies showed different trends depending on the causative food. Conclusions: The objective diagnosis by an allergist should be done for food allergy management in children's catering facilities. A system for systematic meal management of causative foods should be prepared. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Knowledge and management of food allergy by parents of preschool children who experience food allergies
Seung Hui Kim, Seung-Min Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 184. CrossRef - Knowledge of atopic dermatitis and food allergies, as well as health information literacy, among North Korean refugee mothers: a descriptive survey study
In-Sook Lee, Jeong-Hee Jeon
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(4): 300. CrossRef
- Knowledge and management of food allergy by parents of preschool children who experience food allergies
- 2,008 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
- Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):382-395. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.382
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the nutritional status according to frailty status in the elderly at home. Methods: The participants were a total of 76 elderly at home living in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea. The nutritional status and frailty status were analyzed using the Nutrition Quotient for Elderly (NQ-E) and the Korean version of the Fatigue, Resistance, Ambulation, Illnesses and Loss of weight Scale (K-FRAIL), respectively. Results: The distribution of frailty status was robust (17.1%), pre-frailty (38.2%) and frailty (44.7%), and its distribution was significantly different in genders, age groups and the number of medications. The mean NQ-E score was 47.0 for total subjects, indicating a low grade. The scores of balance, diversity and dietary behavior factors were within the low grade, while the score of the moderation factor was within the medium-high grade. According to the frailty status, pre-frailty and frailty showed significantly higher scores for sugar-added beverages intake in the moderation constructs than robust. Robust showed significantly higher scores for the exercise hours and perception level for one’s health than pre-frailty and frailty. Conclusions: These results suggest that nutrition status is associated with frailty status. Regular nutrition education and visiting nutrition service should be established to improve the balance and diversity of food intake and improve the dietary behavior of the elderly at home. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Dietary Status among Mild Dementia Elderly Using the Nutrition Quotient for Elderly (NQ-E) in Daegu
Hyun-Kyoung Bang, Mi-Ok Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(4): 343. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary quality using elderly nutrition quotient depending on the consumption of healthy functional foods
Jieun Lee, Hyo-Jeong Hwang, Hye-Young Kim, Jung-Sug Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 483. CrossRef
- The Dietary Status among Mild Dementia Elderly Using the Nutrition Quotient for Elderly (NQ-E) in Daegu
- 1,411 View
- 19 Download
- 2 Crossref

Research Note
- [Korean]
- Development of 3D Printed Snack-dish for the Elderly with Dementia
- Ji-Yeon Lee, Cheol-Ho Kim, Kug-Weon Kim, Kyong-Ae Lee, Kwangoh Koh, Hee-Seon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):327-336. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to create a 3D printable snack dish model for the elderly with low food or fluid intake along with barriers towards eating. Methods: The decision was made by the hybrid-brainstorming method for creating the 3D model. Experts were assigned based on their professional areas such as clinical nutrition, food hygiene and chemical safety for the creation process. After serial feedback processes, the grape shape was suggested as the final model. After various concept sketching and making clay models, 3D-printing technology was applied to produce a prototype. Results: 3D design modeling process was conducted by SolidWorks program. After considering Dietary reference intakes for Koreans (KDRIs) and other survey data, appropriate supplementary water serving volume was decided as 285 mL which meets 30% of Adequate intake. To consider printing output conditions, this model has six grapes in one bunch with a safety lid. The FDM printer and PLA filaments were used for food hygiene and safety. To stimulate cognitive functions and interests of eating, numbers one to six was engraved on the lid of the final 3D model. Conclusions: The newly-developed 3D model was designed to increase intakes of nutrients and water in the elderly with dementia during snack time. Since dementia patients often forget to eat, engraving numbers on the grapes was conducted to stimulate cognitive function related to the swallowing and chewing process. We suggest that investigations on the types of foods or fluids are needed in the developed 3D model snack dish for future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 3D Printing Technology : Food Tech Analysis
Yuri Kim, Hyun-Jung Yun, Bum-Keun Kim, Hee-Don Choi, Yun-Sang Choi
Resources Science Research.2022; 4(1): 1. CrossRef
- 3D Printing Technology : Food Tech Analysis
- 1,292 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Crossref

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Dietary and Lifestyle Changes of Middle-Aged Women in the Gwangju Area in the COVID-19 Era
- Moon-Soon Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(4):259-269. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.4.259
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the changes in the eating habits and lifestyle of middle-aged women in Gwangju during the COVID-19 pandemic. Methods: A total of 428 middle-aged women aged between 40 and 60 participated in a survey relating to general information, food and lifestyle, health functional food, and menopausal symptoms. The correlation between the variables was analyzed. Results: In the positive habits, the intake of nutritional supplements for immunity enhancement increased the most, followed by the use of media to learn healthy eating tips, and diets including healthy food. Negative habits increased in the order of frequency of taking delivery orders, levels of stress or anxiety, and time spent sitting or watching movies. In the case of recommended foods, the intake increased the most in the order of eggs, fruits, vegetables, milk/dairy products, and seaweed. Non-recommended foods increased in the order of meat, bread, rice, and noodles. The awareness of health functional foods was in the increasing order of interest, knowledge, consumption experience, and purchase amount. The type of health functional food intake was in the increasing order of probiotics, multivitamin and mineral supplements, vitamin C, collagen, and omega-3. Menopausal symptoms were in the increasing order of bone and joint pain, poor sleep quality, emotional ups and downs, loneliness, and feeling of emptiness. In the correlation of major variables, positive habits showed a significant positive correlation with recommended food intake and the recognition of health functional foods. Negative habits showed a significant positive correlation with non-recommended food intake and a significant positive correlation with menopausal symptoms. Recommended food intake showed a significant positive correlation with health functional food recognition and intake and menopausal symptoms. Conclusions: This study suggests that it is necessary to establish social measures to reduce the negative effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on middle-aged women and to ensure effective self-management through a healthy lifestyle since the pandemic has a long-term impact. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial
Ingyeong Kang, Hyunsook Jang, Minchul Gim, Sang Eun Bae, Yu Jin Lee, Chai Sun Leem, Yoo Kyoung Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(17): 2801. CrossRef - Comparative study on the health and dietary habits of Korean male and female adults before and after the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: utilizing data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Chaemin Kim, Eunjung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 65. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics of Staple Breads Based on Baking Methods
Eun-Hee Doo
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 77. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
Eunyoung Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 220. CrossRef - Changes in dietary habits and chronic diseases before and after COVID-19 by regions using data from the 2018-2020 Korea Community Health Survey and Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods: a cross-sectional study
Surim Park, Eun-hee Jang, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(2): 124. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - Consumers’ perceptions of dietary supplements before and after the COVID-19 pandemic based on big data
Eunjung Lee, Hyo Sun Jung, Jin A Jang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 330. CrossRef - Self-rated health according to change of lifestyle after COVID-19: Differences between age groups
Dan Bi Lee, Jung Hyun Ahn, Jin Young Nam
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(2): 1. CrossRef - Factors Related to Changes of Daily Life during COVID-19
Kyungjin Min, Pilhan Yun, Sangshin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(4): 297. CrossRef - Dietary Behavior and Diet Quality in the Korean Adult Population by Income Level before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic: Using the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2020)
Hye-Min Na, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(3): 397. CrossRef
- Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial
- 1,512 View
- 10 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Dietary Habits and Health-Related Factors According to the Employment in Women in Early Adulthood - Based on the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yun-Jung Bae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(4):249-258. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.4.249
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to compare the factors of dietary and health behavior according to the employment in women in early adulthood and to analyze their relationship. Methods: In this study, adult women aged 20~29 who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2016~2019 were classified into two groups depending on their permanent worker status, namely tenured employees (n = 254) and temporary employees (n = 377). Dietary habits (prevalence of skipping meals, food nutrition label use, etc.), nutrient intake, and metabolic syndrome factors were analyzed. Results: The tenured employees' group showed a significantly lower proportion of subjects who skipped breakfast (P = 0.0254) and significantly higher daily energy intake (P = 0.0264) than the temporary employees' group. However, there were no significant differences in the intake of energy nutrients and most of the micronutrients per 1,000 kcal of energy intake between the two groups. The proportion of subjects who consumed energy nutrients under 75% of the estimated energy requirement (EER) was 38.11% in the tenured employees' group, which was significantly lower than the 48.30% in the temporary employees' group (P = 0.0159). In economically active women aged 19~29 years, the odds ratio of low HDL-cholesterolemia prevalence was 1.80 times higher (95% CI, 1.06-3.06) in the temporary employees' group compared to that in the tenured employees' group after adjustment for confounding factors (P = 0.0295). Conclusions: In conclusion, among Korean adult women in their twenties, temporary employees showed inappropriate eating habits such as skipping breakfast, and had abnormal blood lipid levels. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temporary Employment Is Associated with Poor Dietary Quality in Middle-Aged Workers in Korea: A Nationwide Study Based on the Korean Healthy Eating Index, 2013–2021
Seong-Uk Baek, Myeong-Hun Lim, Yu-Min Lee, Jong-Uk Won, Jin-Ha Yoon
Nutrients.2024; 16(10): 1482. CrossRef
- Temporary Employment Is Associated with Poor Dietary Quality in Middle-Aged Workers in Korea: A Nationwide Study Based on the Korean Healthy Eating Index, 2013–2021
- 1,367 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Can Dining Alone Lead to Healthier Menu Item Decisions than Dining with Others? The Roles of Consumption Orientation and Menu Nutrition Information
- EunSol Her, Carl Behnke, Barbara Almanza
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):155-166. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.155
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Driven by a growth of single-person households and individualized lifestyles, solo dining in restaurants is an increasingly recognizable trend. However, a research gap exists in the comparison of solo and group diners’ menu-decision making processes. Based on the self-control dilemma and the temporal construal theory as a theoretical framework, this study compared the ordering intentions of solo vs. group diners with healthy vs. indulgent (less healthy) entrées. The mediating role of consumption orientation and the moderating role of amount of menu nutrition information were further explored to understand the mechanism and a boundary condition.
Methods
A scenario-based online survey was developed using a 2 (dining social context: solo vs. with others) × 3 (amount of menu nutrition information: no nutrition information vs. calories vs. calories/fat/sodium), between-subjects, experimental design. Consumers’ level of nutrition involvement was controlled. A nationwide survey data (n = 224) were collected from a crowdsourcing platform in the U.S. Data were analyzed using multivariate analysis of covariance, independent t-test, univariate analysis of covariance, and moderated mediation analyses.
Results
Findings reveal that solo (vs. group) diners have less (vs. more) intentions to order indulgent menu items due to a more utilitarian (vs. more hedonic) consumption orientation in restaurant dining. Findings also show that solo (vs. group) diners have more (vs. less) intentions to order healthy menu items when the restaurant menu presented nutrition information including calories, fat, and sodium.
Conclusions
The findings contribute to the literature of foodservice management, healthy eating, and consumer behavior by revealing a mechanism and an external stimuli of solo vs. group diners’ healthy menu-decision making process in restaurants. Furthermore, the findings provide restauranteurs and health professionals with insights into the positive and negative impacts of menu nutrition labelling on consumers’ menu-decisions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Eating contexts encourage sustainable food choices: The mediating role of the symbolic meanings of foods
Chujun Wang, Xiaoang Wan
Appetite.2025; 207: 107896. CrossRef - A systematic review of solo dining research
Huiling Huang, Scarlett Sijia Feng, IpKin Anthony Wong
International Journal of Hospitality Management.2025; 130: 104226. CrossRef
- Eating contexts encourage sustainable food choices: The mediating role of the symbolic meanings of foods
- 1,927 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref

Review
- [English]
- Defining Food Literacy and Its Application to Nutrition Interventions: A scoping Review
- Hye lim Yoo, Eun bin Jo, Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):77-92. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Food literacy (FL) can be an important concept that embodies the nutritional capabilities of individuals. The purpose of this study was to introduce the definition and core elements of FL from previous literature, to summarize measurement tools and intervention programs with FL, and to suggest the direction of future research and programs to integrate the concept of FL. Methods: The literature review was conducted through PubMed and Google Scholar databases by combining the search term ‘food literacy’ with ‘definition’, ‘measurement’, ‘questionnaire’, ‘intervention’, and ‘program’. Among the 94 papers primarily reviewed 31 manuscripts that suited the purpose of the study were used for analyses. Results: There is no consensus on the definition of FL that encompasses the multidimensional aspects of the concept. The definitions of FL were slightly different depending on the authors, and the interpretation of the core elements also varied. Based on the review, we propose a framework of FL that is in line with the current discussion among international researchers. This focuses on the core elements adapted from health literacy, namely functional, interactive, and critical FL. Specifically, we suggest some detailed elements for interactive and critical FL, which were often the subject of divergent views among researchers in previous literature. We found that most of the tools in the reviewed literature provided information on validity and reliability and were developed for a specific target population. Also, most of the tools were focused on functional FL. Similarly, most of the interventions targeted functional FL. Conclusions: This study reviewed the definition and core elements of FL, available measurement tools, and intervention programs using validated tools. We propose the development of tools with sound reliability and validity that encompass the three core elements of FL for different age groups. This will help to understand whether improving food literacy can translate into better nutritional intake and health status among individuals and communities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A qualitative study of facilitators and barriers to healthy eating among older adults in China based on nutritional literacy and the capability opportunity motivation behaviour model
Qian Li, Qian Wang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 175. CrossRef - How food literacy levels shape healthy eating intentions: a cross-sectional study of adults in Shandong Province, China, using the theory of planned behavior
Baicai Xu, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 566. CrossRef - The Concept and Application of the Healing Industry: A Scoping Review
Ji Seong Yi, Sung Yee Yoon, Jae Soo Kim
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2025; 28(4): 537. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - Development of an evaluation tool for dietary guideline adherence in the elderly
Young-Suk Lim, Ji Soo Oh, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - The development, psychometric properties and refinement of a food literacy scale for specific and general application
Hennie Fisher, Marietjie Potgieter
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2024; 35: 100862. CrossRef - Status of Food Literacy and Association with the Nutrition Quotient among Korean Adults
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Human Ecology Research.2024; 62(3): 399. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of a food literacy pilot program for university students: using a mixed-methods research approach
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(6): 885. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Who has a high level of food literacy, and who does not?: a qualitative study of college students in South Korea
Hyelim Yoo, Eunbin Jo, Hyeongyeong Lee, Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1155. CrossRef - Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 495. CrossRef - Food literacy and its relationship with food intake: a comparison between adults and older adults using 2021 Seoul Food Survey data
Seulgi Lee, Sohyun Park, Kirang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023062. CrossRef - Nutrition and Food Literacy in the MENA Region: A Review to Inform Nutrition Research and Policy Makers
Hala Mohsen, Yonna Sacre, Lara Hanna-Wakim, Maha Hoteit
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 10190. CrossRef - Development of a Food Literacy Assessment Tool for Healthy, Joyful, and Sustainable Diet in South Korea
Hyelim Yoo, Eunbin Jo, Hyeongyeong Lee, Sohyun Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(7): 1507. CrossRef - Effects of University Students’ Perceived Food Literacy on Ecological Eating Behavior towards Sustainability
Yoojin Lee, Taehee Kim, Hyosun Jung
Sustainability.2022; 14(9): 5242. CrossRef - The Relationships between Food Literacy, Health Promotion Literacy and Healthy Eating Habits among Young Adults in South Korea
Yoojin Lee, Taehee Kim, Hyosun Jung
Foods.2022; 11(16): 2467. CrossRef
- A qualitative study of facilitators and barriers to healthy eating among older adults in China based on nutritional literacy and the capability opportunity motivation behaviour model
- 3,174 View
- 94 Download
- 17 Crossref

Research Articles
- [English]
- Use of Weight-control or Health Functional Foods, Associated Weight-control Behavior and Perception among University Students in Cheongju
- Gayong Kim, Munkyong Pae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(1):23-36. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.1.23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study sought to assess the prevalence and duration of weight-control or health functional food use, associated weight-control behavior, perception, and knowledge among university students. Methods: The subjects were 442 university students in Cheonju, Korea, and data was collected by a self-administered questionnaire. Both X2 and t-tests were conducted for categorical and mean comparisons. Results: An estimated 62.7% (female 69.0%, male 54.8%) had ever attempted weightcontrol. Among these, an estimated 59.2% of females and 38.9% of males had used weight-control or health functional foods with significant gender difference. The weightcontrol foods commonly used included chicken breast, protein powder, low-fat milk and soymilk, and meal replacement drinks, while garcinia cambogia extract and green tea extract were frequently used as health functional foods. One of 10 (10.3%) consumers of weight-control foods reported ≥ 7 months use, with less frequent long-term consumption of health functional foods (4.2%). The average degree of satisfaction was 3.24 ± 0.92 for weight-control foods and 2.72 ± 0.97 for health functional foods on a 5-point scale, meaning ‘slightly satisfied’ and ‘slightly dissatisfied’, respectively. Females or students with an experience of weight-control reported poorer perceptions of their health and body image as well as a higher need for weight control. Besides, both male and female subjects felt a high need for correct information regarding weight-control methods. Conclusions: Our results provide a better understanding of the characteristics associated with the use of weight-control or health functional foods among university students and will be useful in developing a nutrition education program by incorporating correct body image, knowledge, and practical yet desirable practices for weight control. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
Hyoju Lee, Youjeong Jang, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 261. CrossRef - Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(2): 207. CrossRef - Effects of Consumers’ Dietary Lifestyles on Preference for Alternative Noodle Products : Protein-Enhanced vs. Calorie-Reduced Products
Hyunju Song, Haram Eom, Junghoon Moon
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(4): 569. CrossRef - Association between weight loss agents and elevated liver enzymes: a population-based cross-sectional study
Ye-Jee Kim, Seo Young Kang, Mi-Sook Kim, Joongyub Lee, Bo Ram Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A study on the weight control behavior according to cluster types of the motivation to use social media among university students in the Jeonbuk area
Jiyoon Lee, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 203. CrossRef - Relationship between Grip Strength, Skeletal Muscle Mass, and
Nutrition Quotient among University Students in the Chungbuk
Region
Ji-Won Kang, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Biotechnology and Bioindustry.2023; 11: 53. CrossRef - A Narrative Approach to the Diet History of Female College Students : Focusing on the Role of SNS and Social Media Influencers and Individuals’ Motivation for Dieting
Kyungbo Kim
Korean Journal of Journalism & Communication Studies.2022; 66(3): 139. CrossRef - Consumption of Weight-control or Health Functional Foods, Dietary Habits, and Weight Perceptions According to the Body Mass Index of Adult Women in the Chungcheong Area
Gayoung Seong, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 81. CrossRef - Relationship among Health Interest, Depression and Dietary Habits of College Students according to Sex in Seoul and Gyeonggi Areas
Kyung Ae Park, Jiwon Kim, Onjeong Cho, Kyunghee Song
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(4): 213. CrossRef - Body Image Perception, Weight Control and Dietary Behavior of University Students in Daejeon
Joon Ho Lee, Wei Hu
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2017; 26(4): 353. CrossRef - Weight Control Behaviors, Health-related Quality of Life and Nutritional Status by Overestimation of Body Image among Young Korean Females: Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2010-2011
Seulki Park, Taisun Hyun, Hongmie Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 362. CrossRef - Estimated dietary flavonoids intake of Korean adolescent: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2012
Seong-Ah Kim, Shinyoung Jun, Hyojee Joung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(6): 496. CrossRef - A Study on Food Habits and Nutrient Intakes according to BMI in Food and Nutrition Major and Non-major Female Students in Kyungnam University
Eun-Hee Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 297. CrossRef - A Study on Dietary Habits, Body Satisfaction and Nutritional Knowledge by Body Image of Middle School Girl Students in Chungbuk Area
Jee-Young Yeon, Ki-Yong Shin, Soon-Kyu Lee, Hye-Young Lee, Baeg-Won Kang, Hye-Kyung Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(5): 442. CrossRef
- Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
- 1,726 View
- 16 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [English]
- E-commerce Food Purchases by Adult Women according to their Household Types
- Yu-Jin Park, Yu-Mi Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):464-473. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.464
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to compare and analyze e-commerce food purchase behavior and the perceptions of adult women according to their household types. Methods: The e-commerce food purchases of 318 adult women were surveyed and analyzed according to their household types (one-person or couple household (OCH); a household with children (HC); a household with parents (HP)). Results: The total amount of food purchases over 6 months through e-commerce according to household types was in the descending order of OCH (60.3%), HC (57%), and HP (55.1%) thus showing a significant difference (P < 0.05) in behavior between household types. The reasons for purchasing food through e-commerce included: a lower price than offline (30.8%), convenient delivery and transportation (30.2%), and food diversity (21.1%). When purchasing food online, the most important factor was price and quality, followed by quick and accurate delivery for OCH, exact information given about the product for HC, and recommendation from other consumers for HP (P < 0.01). The main foods purchased through e-commerce were coffee, tea (42.1%), instant and frozen foods (39.9%), water, beverages, dairy products (37.7%), snacks, bread, rice cakes (31.5%), and functional foods (27.4%). The percentage of respondents who were very satisfied or satisfied with their ecommerce food purchases was HP (84.1%), OCH (69.9%), and HC (65.6%) in that order (P < 0.05), and 96.5% of all subjects stated that they would be willing to purchase food through e-commerce in the future. The advantages of purchasing food through e-commerce were seen to be the highest in order and payment convenience with 4.1 points out of 5, followed by low price (4.0), variety of products (3.9), and ease of food purchase (3.9).Among the disadvantages listed, concerns about product damage and deterioration during delivery and differences between the displayed product and the delivered product were the highest with 3.7 points. Conclusions: The characteristics and perceptions of female consumers according to household types are important factors in enhancing the reach of e-commerce, and in preparing guidelines for food selection through e-commerce. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Perceived Quality and Attitude on Satisfaction in Online Fresh Food Shopping
Jin-Yi Jeong, Yoon-Ji Choi, Hye-Sung Chae, Jung Shin Choi, Joo-Lee Son
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 202. CrossRef - Examination the Factors that Influence Online Food Purchase Intention : An Empirical Study Based on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
Jin-Yi Jeong, Yoon-Ji Choi, Hye-Sung Chae, Jung Shin Choi, Joo-Lee Son
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(5): 320. CrossRef
- Effects of the Perceived Quality and Attitude on Satisfaction in Online Fresh Food Shopping
- 1,063 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Status of Sanitary and Nutritional Food Service in Elderly Day Care Center
- Jeong hyeon Woo, Yoo Kyoung Park, Mi-Hyun Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee, Kyung hee Song, Hye-Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):374-385. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to examine the status of foodservice management, with special interest on sanitary and nutritional food service in elderly day care centers. Methods A total of 79 employees who managed foodservice facilities in elderly day care centers were included in the survey. The contents of the questionnaire consisted of general characteristics, importance and performance of sanitary and nutrition management, the reasons for poor performance, factors necessary for improvement, and the employee's demand for support. Data analysis was conducted using the SPSS v25.0. Results Sanitary management showed an average importance score of 4.84 ± 0.40 and a performance score of 4.70 ± 0.61 (t-value: 8.260). The item with the lowest performance score was personal sanitary management (4.58 ± 0.71). In nutrition management, the average importance score was 4.52 ± 0.68, and the performance score was 4.20 ± 1.00 (t-value: 9.609). There were significant differences between the average score of importance and performance in both areas. As a result of an Importance-Performance Analysis, items that were recognized as important but had relatively low performance was “personal hygiene”, “ventilation” and “food storage”. Also in the nutritional management area, “menu planning for disease management” and “checking the saltiness in the soup” etc. had very low performance with low importance recognition. The items shown in the “low priority” quadrant were those that required professional management skills. In the areas that demanded support in foodservice management, education about sanitary and safe institutional food service had the highest score (4.42 ± 0.74), and all other items showed a demand of 4 points or more. Conclusions Foodservice managers recognize the importance of foodservice facility management but performance is relatively low. Institutional support is, therefore, needed to improve performance. For items with low importance, it seems necessary to improve awareness of the necessity of these items and to provide education in this regard. To gradually improve foodservice management, continuous provision of education and training in these areas are of great importance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
Do Hee Kim, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(4): 421. CrossRef - A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
Seo Young Choi, Hyun joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 286. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Snack Provision Practice in Long-Term Care Hospitals and Facilities in Korea
Dayeong Yeo, Hae Jin Kang, Hyejin Ahn, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(2): 108. CrossRef - Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 359. CrossRef - Sanitation Management Performance According to the Characteristics of Coffee Franchise Shops and Sanitation Knowledge According to the Characteristics of Employees
Suk-Kyoung Gu, Sunyoon Jung, Inyong Kim, Yoonhwa Jeong
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(11): 1248. CrossRef - Analysis of Awareness, Knowledge, and Behavior about Food Hygiene·Safety Among the elderly
Mi Sook Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 200. CrossRef
- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
- 1,174 View
- 13 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutritional Status of Vitamins and Minerals According to Consumption of Dietary Supplements in Korean Adults and the Elderly: Report Based on 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):329-339. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study was undertaken to evaluate the intake of vitamins and minerals from dietary supplements (DSs) in Korean adults and elderly.
Methods
Data for this study was generated from the 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). We analyzed 4,204 individuals aged 19 years and older (2,579 users and 1,625 non-users). The survey included 24-h recall questions on food and DS intakes, as well as questions on DS use over the past year. The nutrient DSs evaluated were calcium, phosphorus, iron, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and vitamin C. Total nutrient intakes were obtained by combining nutrient intakes of foods and DSs consumed by each subject.
Results
Most micronutrient intakes from food (except for thiamin) in adult users, and the four micronutrient intakes (iron, vitamin A, vitamin B2 and vitamin C) in elderly users, were significantly higher than values obtained in non-users. For total intake of nutrients and DSs, both adult and elderly users had a significantly higher intake than non-users. While proportions below Estimated Average Requirements for all micronutrients by adding respective DSs in users were significantly reduced in adults and elderly as compared to non-users, the proportions of above Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for calcium and vitamin A in adults, and vitamin A in elderly, were significantly increased. In the total subjects examined, consumption of DSs was associated with lower odds ratios of undernutrition of micronutrients, and with higher odds ratios of overnutrition of calcium, iron, and vitamin A, as compared to non-users of DSs.
Conclusions
Although DSs consumption by adults and the elderly improves the micronutrient status, it also increases the risk of excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 103. CrossRef - Folate intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey with newly established folate database
Eun-Ji Park, Inhwa Han, Kyoung Hye Yu, Sun Yung Ly
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(4): 418. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimated dietary vitamin D intake and major vitamin D food sources of Koreans: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019
Ki Nam Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Mi Ock Yoon, Hyun Sook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 451. CrossRef - A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef
- Relationship between self-care and health-related behaviors among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- 2,250 View
- 10 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Qualitative Study of Compliance with Nutritional Management in Colorectal Cancer Patient Undergoing Chemotherapy
- Heejung Park, Hyonson Kil, Wookyoun Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):303-316. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.303
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
The nutritional status of cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy is closely related to the compliance of nutrition education. However, as chemotherapy is conducted repeatedly, compliance with nutrition management is lowered, leading to malnutrition. Malnutrition is related directly to the quality of life after surgery in cancer patients. Therefore, this study examined the factors related to compliance with nutrition management during chemotherapy.
Methods
In this study, five subjects with colorectal cancer undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy were interviewed in-depth using the Giorgi study method. The contents of the nutrition education visits and in-depth interviews were transcribed in the language of the subject after recording, and the appropriateness of the data was improved by reflecting the subject’s actions and facial expressions.
Results
After conducting the in-depth interviews for each subject, the experience of the subject’s diet and adjuvant chemotherapy was drawn into two domains, six elements, and 26 sub-elements. In the cognitive domain, the patients experienced physical and psychological changes, and the need for nutrition management was recognized by analyzing the dietary causes of the diseases. In the domain of practice, a knowing-doing gap was formed, unlike the patient’s will. Factors that inhibited compliance with nutritional management included digestive problems, sensory changes, loss of appetite, and social interaction stress.
Conclusions
Dietary management is very important for patients receiving periodic anticancer therapy, and step-by-step training and personal monitoring based on the chemotherapy order is necessary to maintain the patient’s will and social and environmental support.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Continuous Nutrition Care on Nutritional Status and Dietary Habits of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Surgery
Jina Son, Ha I Kang, Eun young Jung, Hae won Ryu, Kyung-Ha Lee
Clinical Nutrition Research.2023; 12(2): 99. CrossRef
- Effects of Continuous Nutrition Care on Nutritional Status and Dietary Habits of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Surgery
- 1,327 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutritional Content in Convenience Store Lunchboxes by Meal Type, Price, and Store Brand
- Jin-Seon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):280-290. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study investigated the menu and nutritional contents of convenience store lunchboxes, and evaluated the nutritional content by meal type, price, and store brand.
Methods
In September 2019, 93 convenience store lunchboxes from the top five franchise stores were purchased. Relevant information on price, food weight, food ingredients, cooking methods, and nutrition labeling were subsequently collected. Nutritional content was evaluated based on the daily value (DV) and Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ), and energy contribution of carbohydrate, protein, fat, saturated fat and sugar was compared with the recommended range.
Results
Most lunchboxes included the food groups; grains/starches, meats/fish/eggs/ legumes, and vegetables. However, none provided fruits, and only a few lunchboxes provided milk/milk products. Stir-frying, deep-frying, and pan-frying were the most frequent methods of cooking. The average energy content of the lunchboxes was 736.6 kcal, whereas the average contents of protein, fat and saturated fat were higher than 40% of the DV, and sodium content was 66.8% of the DV. The contents of most nutrients in traditional type lunchboxes were higher, as compared to nutrients in onedish type lunchboxes. Considering pricing of lunchboxes, protein and sodium contents were higher in the higher-priced lunchboxes as compared to lower-priced lunchboxes, but there were no differences in the INQs. The contents of energy, protein, fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol significantly differed by brand.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that convenience store lunchboxes contain high levels of protein, fat, saturated fat, and sodium. The nutritional contents differed by meal type, price, and store brand, and higher price did not imply higher nutritional quality. We propose the need to educate consumers to check nutrition labels and purchase appropriate lunchboxes. Manufacturers also need to make efforts to reduce the amounts of fat, saturated fat, and sodium, and not provide protein in excess.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A nutritional evaluation of convenience store meal boxes in South Korea
Jinkyung Choi, Yunseon Choe
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2025; 42: 101332. CrossRef - Eating behaviors, home meal replacement consumption, and nutrition quotient: a comparative study of male shift and non-shift workers in Chungcheong, Korea
Yeon Jin Lee, Munkyong Pae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 758. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Quality of Convenience Store Meal Boxes according to Store Company and Meal Price
Changgyu Cho, Youngmin Nam, Hye-Jong Yoo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 105. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Convenience Food Choices based on the Health Consciousness of Chinese Students in South Korea
SongLin Bai, Youngmi Lee, Kyounghee Song, Yujin Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 169. CrossRef - Studies of Selection Attributes for Lunch Boxes (Dosirak) Using Conjoint Analysis among Single Men
A Reum Han, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(8): 884. CrossRef
- A nutritional evaluation of convenience store meal boxes in South Korea
- 4,067 View
- 21 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutritional Status among Primary School Children in Uganda: Comparison of Urban and Rural Areas
- Ji-Yeon Lee, Hye-Jung Park, Min Yu, Ha-Yeong Hwang, Jung-Rim Sung, Hee-Seon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):91-101. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate dietary intakes and nutritional status among Uganda primary school children from two selected schools in urban and rural areas.
Methods
Data were collected from 350 pupils (6-14 years) in Mpigi district, Uganda. All participants were offered a school lunch meal (usually maize porridge and boiled beans). Dietary survey was conducted in October 2016. Data for dietary intake levels were collected by the 24-hour recall method with trained school staffs. The data were converted into nutrient intakes using the CAN-Pro 5.0 Program and compared with KDRIs to evaluate the nutritional status of the subjects. Diet quality indexes such as nutrient density, nutrient adequacy ratio (NAR), mean adequacy ratio (MAR), and index of nutritional quality (INQ) and a diet diversity index such as diet diversity score (DDS) were calculated to evaluate nutritional status among subjects. Data were analyzed using SPSS statistical programs.
Results
Results show that the intakes of most nutrients were significantly different by schools. The nutritional status of micro-nutrients was very low in both schools according to analysis of nutritional indexes such as NARs and INQs. Students from both schools should improve intakes of micro-nutrients related to child growth such as calcium, Vitamin B6, zinc and folate. According to the analysis of dietary diversity, there was difference in dietary patterns by schools presumably due to their locations.
Conclusions
This suggests that current meals could not provide adequate nutrients for the subjects and urgent nutrition interventions for school food services are needed to improve their nutritional well-being. New foods supplements based on local cuisine are also needed to ensure dietary diversity and sustainable development plans.
- 1,049 View
- 18 Download

- [English]
- Qualitative Study on the Perception of Community Food-accessibility Environment among Urban Older Adults
- Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):137-149. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study explored the community food environmental factors affecting food purchasing using a qualitative research methodology for the elderly as well as the various food environments under their socioeconomic diversity.
Methods
For the qualitative data collection, this study interviewed 20 elderly people aged 65 years or more, who participated in a public health program or lunch services operated by the senior welfare center in Seoul. Five dimensions, such as availability, physical accessibility, affordability, acceptability, and accommodation suggested in previous studies, were used to identify the community food environmental factors.
Results
The elderly participants showed overall similarities to the concepts derived from existing studies on the five dimensions of food accessibility environment. In addition, other important food accessibility environmental factors that were not present in previous studies, such as acceptability for a product of domestic origin, delivery service to home, and small-packaged food sales, were derived. On the other hand, the concept of some subjects differed depending on the household income and specifically for the physical accessibility concept. This showed that the close distance factor from a grocery store at home might not apply to older adults in low-income households in Korea.
Conclusions
This study found that five dimensions of the food environment suggested by previous studies could also be applied to vulnerable older adults in Korea. On the other hand, the socioeconomic characteristics of individuals and households would affect the perspectives of their local food environments differently. The findings of this study could help in the development of tools for evaluating the community food environment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 16. CrossRef - Spatial inequalities and driving factors in food accessibility: Integrating online and offline grocery services in South Korea
Hyebin Kim, Minkyu Kim, Sugie Lee
Applied Geography.2025; 185: 103777. CrossRef - Effects of primary caregivers’ food literacy, social support, food environment, and household income on the nutritional status of school-aged children: a cross-sectional study
Seyeon Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sohyun Park, Hyun Joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 352. CrossRef - Spatial Disparity of Neighborhood Food Environment by Socioeconomic Status: Application of Urban Network Analysis
Taekyung Seong, Sugie Lee
Land.2024; 13(6): 865. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Perceived Community Food Accessibility Measurement Questionnaire for Korean Older Adults
Jisoo Hong, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(19): 4301. CrossRef - A relationship between food environment and food insecurity in households with immigrant women residing in the Seoul metropolitan area
Sung-Min Yook, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 264. CrossRef - Regional Difference in the Effect of Food Accessibility and Affordability on Vegetable and Fruit Acquisition and Healthy Eating Behaviors for Older Adults
Dong Eun Lee, Kirang Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 14973. CrossRef - Analysis of Accessibility Changes to Neighborhood Food Environment and Food Desert Phenomenon in Seoul, Korea : Focused on the High-density Areas of Low-income Older Adults
Taekyung Seong, Sugie Lee
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2021; 56(1): 137. CrossRef - Effects of Perceived Food Store Environment on Malnutrition and Frailty among the Food-Insecure Elderly in a Metropolitan City
Yu-Mi Kim, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2021; 13(7): 2392. CrossRef - Analyzing Socio-Economic and Geographical Factors that Affect the Health of the Elderly
Zacharias Dermatis, Athina Lazakidou, Athanasios Anastasiou, Panagiotis Liargovas
Journal of the Knowledge Economy.2021; 12(4): 1925. CrossRef - Analysis of Awareness, Knowledge, and Behavior about Food Hygiene·Safety Among the elderly
Mi Sook Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 200. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- 1,727 View
- 19 Download
- 12 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
- Na Yeong Lee, Yeon Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):13-20. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the salinity of soups provided at childcare centers by measuring the salinity for three years and providing basic data for sodium reduction.
METHODS
The soup salinity was measured using a Bluetooth salinity meter from January 2015 to December 2017 at 80 childcare foodservice establishments enrolled in the Suseong Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Daegu.
RESULTS
An analysis of the soup salinity each year showed that the salinity decreased significantly from 0.48% in 2015 to 0.41% in 2017, particularly in clear soups and soybean soups compared to other soups (P < 0.05). The salinity and sodium content in seafood soups (0.45% and 179.1 mg/100 g, respectively) were highest, followed by soybean soups (0.44%, 175.2 mg/100 g), with perilla seed soups containing the lowest (0.42%, 167.2 mg/100 g) (P < 0.05). The salinity was significantly higher in institutional foodservice establishments than small foodservice establishments (P < 0.001). The salinity and sodium content were the highest in foodservice establishments with a small number of measurements, and the salinity was the lowest in foodservice establishments with salinity measurements performed an average of 151 times each year (three times a week) or more (P < 0.05). The soup salinity was low in the order of winter, spring, summer, and autumn, and the salinity decreased significantly year by year in all seasons. (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The soup salinity was significantly lower in foodservice establishments where the salinity was measured more than three times a week, indicating that continuous salinity management is effective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
Do Hee Kim, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(4): 421. CrossRef - Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 386. CrossRef
- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
- 1,659 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Analysis of Factors Affecting Breakfast Eating Behavior of Children in Indonesia: An Application of the Health Belief Model
- Ran Yi Kang, Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(1):1-12. Published online February 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study investigates the current state of consuming breakfast among elementary school students residing in Malang, East Java, Indonesia, and to identify factors that influence breakfast behavior.
METHODS
The research model was set up as per the health belief model, and slightly modified by adding the subjective normative factors of the theory of planned behavior. The survey was conducted from July 17 to August 15, 2017 using a questionnaire, after receiving the permission PNU IRB (2017_60_HR).
RESULTS
The subjects were 77 boys (49.4%) and 79 girls (50.6%) suffering from malnutrition with anemia (21.2%) and stunting ratio of Height for Age Z Score (HAZ) (11.5%). Furthermore, moderate weakness (14.8%) and overweight and obesity (12.3%) by Body Mass Index for Age Z Score (BMIZ) were coexistent. According to the results obtained for breakfast, 21.8% did not eat breakfast before school, with 18.8% of the reasons for skipping breakfast being attributed to lack of food. Even for subjects partaking breakfast, only about 10% had a good balanced diet. The average score of behavioral intention on eating breakfast was 2.60 ± 0.58. The perceived sensitivity, perceived severity, perceived benefits, and self-efficacy of the health belief model correlated with breakfast behavior. Of these, self-efficacy (β=0.447, R²=0.200) and perceived sensitivity (β=0.373, R²=0.139) had the greatest effect on breakfast behavior. Mother was the largest impact person among children.
CONCLUSIONS
In order to increase the level of breakfast behavior intention among children surveyed in Indonesia, we determined the effectiveness by focus on education which helps the children recognize to be more likely to get sick when they don't have breakfast, and increase their confidence in ability to have breakfast on their own. We believe there is a necessity to seek ways to provide indirect intervention through mothers, as well as impart direct nutrition education to children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The School Food Environment in Ghana is Associated With Dietary Diversity and Anemia: Findings From the 2022 National Nutrition and Health Survey of In-School Adolescents
Mica Jenkins, Esi Foriwa Amoaful, Mutala Abdulai, Veronica Quartey, Porbilla Ofosu-Apea, Jevaise Aballo, Maku E. Demuyakor, Maria Elena D. Jefferds, Nancy J. Aburto, Usha Ramakrishnan, Reynaldo Martorell, O. Yaw Addo
Food and Nutrition Bulletin.2025; 46(2-3): 78. CrossRef - Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
Sung-Mi Cha, Soo-Youn Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 541. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary behavior and investigation of the affecting factors among preschoolers in Busan and Gyeongnam area using nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P)
Soo-Youn Kim, Sung-Mi Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 596. CrossRef - Psychoactive substance use among Chinese non-engaged youth: The application of the Health Belief Model
Phoenix Kit-han Mo, Joseph Tak Fai Lau
Children and Youth Services Review.2020; 113: 105008. CrossRef
- The School Food Environment in Ghana is Associated With Dietary Diversity and Anemia: Findings From the 2022 National Nutrition and Health Survey of In-School Adolescents
- 2,545 View
- 47 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Low-carbohydrate and High-fat Diet Supplemented with Ketogenic Drink on Cognitive Function and Physical Performance in the Elderly at High Risk for Dementia
- Eun Ji Kim, Jung Sik Park, Won Sun Choi, Yoo Kyoung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):525-534. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.525
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Reduced glucose utilization in the main parts of the brain involved in memory is a major cause of Alzheimer's disease, in which ketone bodies are used as the only and effective alternative energy source of glucose. This study examined the effects of a low-carbohydrate and high-fat (LCHF) diet supplemented with a ketogenic nutrition drink on cognitive function and physical activity in the elderly at high risk for dementia.
METHODS
The participants of this study were 28 healthy elderly aged 60-91 years showing a high risk factor of dementia or whose Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) score was less than 24 points. Over 3 weeks, the case group was given an LCHF diet with nutrition drinks consisting of a ketone/non-ketone ratio of 1.73:1, whereas the control group consumed well-balanced nutrition drinks while maintaining a normal diet. After 3 weeks, K-MMSE, body composition, urine ketone bodies, and physical ability were all evaluated.
RESULTS
Urine ketone bodies of all case group subjects were positive, and K-MMSE score was significantly elevated in the case group only (p=0.021). Weight and BMI were elevated in the control group only (p<0.05). Grip strength was elevated in all subjects (p<0.01), and measurements of gait speed and one leg balance were improved only in the case group (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
We suggest that adherence to the LCHF diet supplemented with a ketogenic drink could possibly influence cognitive and physical function in the elderly with a high risk factor for dementia. Further, we confirmed the applicability of this dietary intervention in the elderly based on its lack of any side effects or changes in nutritional status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- To Keto or Not to Keto? A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Assessing the Effects of Ketogenic Therapy on Alzheimer Disease
Maria G Grammatikopoulou, Dimitrios G Goulis, Konstantinos Gkiouras, Xenophon Theodoridis, Kalliopi K Gkouskou, Athanasios Evangeliou, Efthimis Dardiotis, Dimitrios P Bogdanos
Advances in Nutrition.2020; 11(6): 1583. CrossRef
- To Keto or Not to Keto? A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Assessing the Effects of Ketogenic Therapy on Alzheimer Disease
- 1,658 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Development and Application of an Education Program for Healthy Dietary Life for Elementary School Aftercare Class Children
- Jung Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, In Young Park, Young Sim Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):497-511. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.497
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to develop a school-centered healthy eating environment for children in elementary care classrooms and prevent incorrect eating habits and obesity through the development and application of standardized healthy eating habit-forming educational materials.
METHODS
Ten schools in eight districts of Gyeonggi-do and 400 students from 19 care classes were selected. Based on the developed educational materials, the program was applied to students once in two weeks. ‘Notices for Parents’ forms were also sent to the students' home to educate their parents. Pre and post-surveys were conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the education. The pre-education, education, and aftercare were conducted from September 28 to September 31, 2016, from October 3 to November 30, 2016, and from December 5 to December 9, 2016, respectively.
RESULTS
The healthy eating program for elementary care classes was designed to develop a school-centered healthy eating environment and provide standardized educational material for healthy eating habits. Twelve educational topics were developed: 〈Eat Evenly〉, 〈Eat Breakfast〉, 〈Eat vegetables and Fruits〉, 〈Clean Body, Strong Body〉, 〈Healthy and Tasty Snacks〉, 〈Keep Healthy Weight〉, 〈Food that enters our body〉, 〈What is safe food?〉, 〈Food selection and Storage〉, 〈Our land, Our grain〉, 〈Enjoy Traditional Food〉, and 〈Food manners〉. Moreover, the materials were produced in four forms: for students, for after school caring teachers, for external specialists, and for parents. The effectiveness evaluation was conducted to confirm the application of the program. The average eating habits score was 3.3 ± 0.6, with no significant difference between before and after application. The score of overall satisfaction of the education was 3.9 ± 0.9. The most satisfying content was ‘Did you get to know how to eat evenly?’. Significant increases were observed in two contents for parents regarding their children's knowledge changes after the education: ‘Five nutrients needed for growing children’ and ‘Knowing sugar foods and sugar-containing foods’. On the other hand, their educational satisfaction was 3.6 ± 0.6, which was lower than the children's satisfaction. This might be because their education was conducted only through the ‘Notices for Parents’ form.
CONCLUSIONS
In the long term, the healthy eating habit-formation education for lower elementary school children is expected to be beneficial. To prevent obesity and establish healthy eating habits of children, it is important to develop healthy eating education programs centered on elementary school aftercare classes, including the development of educational materials and an application system through connection with the home and community. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
Jiyoung Park, Sein Hwang, Seolhyang Baek, Gill A. Ten Hoor
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2389. CrossRef
- An Interactive Live and Online Cooking Program for Children in Vulnerable Families—An Exploratory Study
- 1,492 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Home Meal Replacement Use and Eating Habits of Adults in One-Person Households
- Mi Kyeong Choi, Eun Sun Park, Mi Hyun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):476-484. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.476
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The rise of one-person households may have consequences for food consumption patterns, and eating habits. This study investigated the home meal replacement (HMR) use and eating habits among adults in their 20s-30s living in one-person households.
METHODS
A total of 247 adults aged 26–39 years participated in this study. The subjects were divided into three group according to the household type; one-person households (n=80), two-person households (n=49), and multi-family (three and more members) households (n=118). Their use of HMRs (classified as ready-to-eat, ready-to-cook, and fresh convenience foods) and their eating habits were all compared.
RESULTS
The mean age of the subjects was 30.5 years, 47.8% were male, and there was no significant difference in age, gender, occupation, and monthly income according to the type of household. The intake frequency of total HMR and ready-to-eat foods was significantly higher in one-person households among the three groups. People in one-person households consumed more HMRs alone, and spent more money to buy HMRs. Undesirable dietary habit scores like unbalanced eating (p<0.05) and eating salty foods (p<0.05) were significantly higher in the one-person households. Among the total subjects, the unbalanced eating scores showed a significant positive correlation with the intake frequency of ready-toeat foods, while the unbalanced eating scores showed negative correlation with the preference of fresh convenience foods. The scores for eating salty foods showed a significant positive correlation with the intake frequency and preference of ready-to-eat foods and ready-to-cook foods, while there was negative correlation with the intake frequency and preference of fresh convenience foods.
CONCLUSIONS
Adults in their 20s–30s in one-person households consumed more ready-to-eat foods than those in multi-family households. In addition, people with one-person households had more unbalanced diets and ate more salty foods, and these undesirable eating habits showed a significant positive correlation with the use of ready-to-eat or ready-to-cook foods. These results should be addressed for producing healthier ready-to-eat/ready-to-cook foods and implementing nutrition education for making healthy food choices of one-person households, which are steadily increasing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 53. CrossRef - Dietary status and the relationship between dietary competencies, cooking skills, and nutrition quotient of middle-aged adults living alone in Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Yun-Jung Bae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 257. CrossRef - Maternal home meal replacement use and attitudes, and young children’s preferences by usage frequency in meals for young children: a cross-sectional study
Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 163. CrossRef - Comparative study on eating habits and health of single-person and multi-person households
Haerang Lee, Seon-Jip Kim, Minji Kang, Mi-So Shim
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0327763. CrossRef - Eating behaviors, home meal replacement consumption, and nutrition quotient: a comparative study of male shift and non-shift workers in Chungcheong, Korea
Yeon Jin Lee, Munkyong Pae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 758. CrossRef - 광주 · 전라지역 성인의 식생활 라이프스타일 유형별 식품안전에 대한 인식
의진 박, 복미 정
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2025; 41(1): 50. CrossRef - 가정간편식 수산 제품 인식정도에 따른 가정간편식 수산 제품 이용실태 조사
정은 이, 복미 정
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 284. CrossRef - Diabetes Nutritional Management for Single-Person Households
Min Young Noh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(4): 236. CrossRef - Development of Functional Material by Using Bacillus
subtilis Harboring α-Amylase and Protease
Enzyme Activity
Jae-Hyuk Lee, Gi-Seong Moon
Current Topic in Lactic Acid Bacteria and Probiotics.2023; 9(2): 81. CrossRef - The frequency of convenience food consumption and attitude of sodium and sugar reduction among middle and high school students in Seoul: a descriptive study
Seoyeon Park, Yeonhee Shin, Seoyeon Lee, Heejung Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 269. CrossRef - Problems Encountered in Analyzing the Market Size, Purchase, and Consumption of HMR in the Republic of Korea
Sung Ok Kwon, Injoo Choi, Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 480. CrossRef - Qualities of rice-based home meal replacement products upon
microwave cooking
Gi-Un Seong, Yu Mi Kim, Jun-Hyeon Cho, Ji-Yoon Lee, Sais-Beul Lee, Dongjin Shin, Dong-Soo Park, Kwang-Sup Youn, Ju-Won Kang
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2022; 29(5): 715. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behaviors and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Single- and Multi-Person Households among Korean Adults
Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Healthcare.2021; 9(9): 1116. CrossRef - Relationship between Eating Behavior and Healthy Eating Competency of Single-Person and Multi-Person Households by Age Group
Seung-Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 337. CrossRef - Analysis of Contamination of Total Aerobic Bacteria and Foodborne
Pathogens in Home Meal Replacement (HMR) and the Importance of Food Hygiene
Management
Hyun Jin Cho, Jeeyeon Lee
Resources Science Research.2021; 3(2): 63. CrossRef - Studies of Selection Attributes for Lunch Boxes (Dosirak) Using Conjoint Analysis among Single Men
A Reum Han, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(8): 884. CrossRef - Healthy Eating Capability of One-person Households-The Effects of Eating Alone, Meal Types, and Dietary Lifestyles
Seonglim Lee, Ilsook Choi, Junghoon Kim
Family and Environment Research.2020; 58(4): 483. CrossRef
- Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
- 1,944 View
- 17 Download
- 18 Crossref

- [English]
- The Effect of Consumers' Factors of Food Choices on Replacing Soft Drinks with Carbonated Water
- Seoyoung Park, Dongmin Lee, Jaeseok Jeong, Junghoon Moon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(4):300-308. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.4.300
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This research was conducted to identify the consumers' food choice factors that affect the consumers' replacement of soft drinks with carbonated water.
METHODS
The present study used secondary data from a consumer panel survey conducted by the Rural Development Administration of Korea, and the data included the panel members' purchase records based on their monthly spending receipts. The survey asked the participants about their food choice factors and their personal responsibility for their health. This survey included independent variables for the consumers' food purchase factors. As a dependent variable, two types of groups were defined. The replacement group included those people who increased their purchase of carbonated water and decreased their purchase of soft drinks. The non-replacement group included those people who did not change their purchase patterns or they increased their purchase of soft drinks and they decreased their purchase of carbonated water. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to determine the consumers' food choice factors that were associated with replacing soft drinks with carbonated water.
RESULTS
The replacement group was significantly associated with (1) a younger age (OR=0.953), (2) being a housewife (OR=2.03), (3) higher income (OR=1.001) and (4) less concern about price (OR=0.819) when purchasing food. This group also showed (5) higher enjoyment (OR=1.328) when choosing food and (6) they took greater responsibly for their personal health (OR=1.233).
CONCLUSIONS
This research is the first study to mainly focus on soft drinks and carbonated water. The result of this research showed that young, health-conscious consumers with a higher income and who are more interested in food have more possibilities to replace soft drinks with carbonated water. These research findings may be applied to consumers who have characteristics that are similar to the young health-conscious consumers and the results can help to suggest ways to reduce sugar intake and improve public health. However, this research has a limitation due to the application of secondary data. Therefore, a future study is needed to develop detailed survey questions about food choice factors and to extend these factors to all beverages, including soft drinks made with sugar substitutes, so as to reflect the growth of alternative industries that use artificial sweeteners or different types of sugar to make commercially available drinks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Dietary Behavior-Related Consumer Competency on the Purchase Satisfaction of Fresh Food via Early-Morning Delivery Service
Soon-Ok Lee, Ji-Young Kim, Seung-Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(6): 612. CrossRef
- Effects of the Dietary Behavior-Related Consumer Competency on the Purchase Satisfaction of Fresh Food via Early-Morning Delivery Service
- 1,485 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



