Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- [Korean]
- Research trends in dietary behaviors and nutrition education among individuals with developmental disabilities in Korea: a scoping review (2015–2025)
- Nakyung Kwak, Wonyeong Park, Yu-Ri Kim, Jieun Oh
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):1-20. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
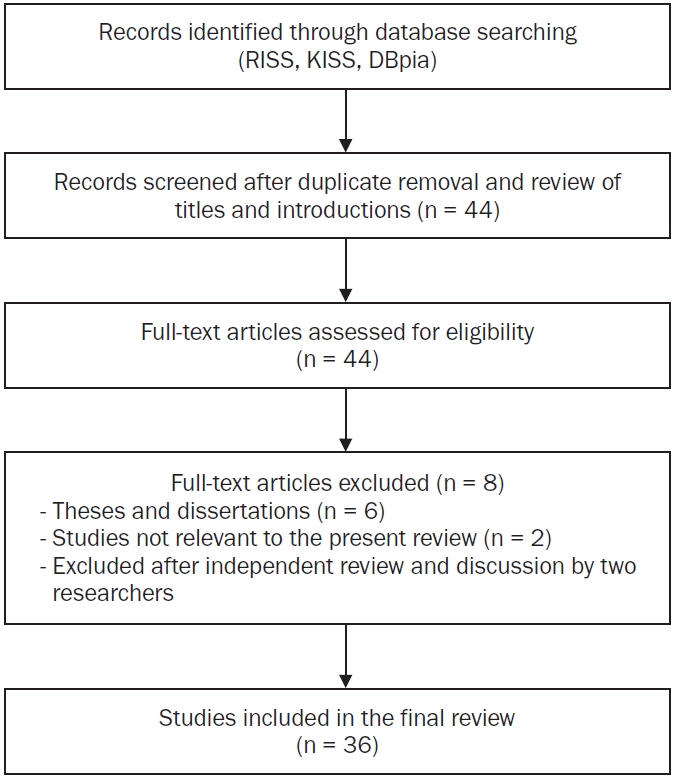
We mapped trends in studies on dietary behaviors, nutritional status, and nutrition-related education among individuals with developmental disabilities in Korea over the past decade to identify research gaps and inform future research and policy development.
Methods
A scoping review was conducted using three major Korean academic databases (RISS, KISS, and DBpia). Studies published between 2015 and September 2025 were identified using combinations of keywords related to developmental disabilities, dietary behavior, nutrition, and health-related interventions. Eligible studies included empirical studies and secondary research (e.g., systematic or scoping reviews) conducted in Korea that focused on dietary behaviors, nutrition, health promotion, or nutrition-related education for individuals with developmental disabilities. Thirty-six studies met our inclusion criteria and were analyzed based on study design, study population, disability type, research topic, and publication period.
Results
Observational quantitative, qualitative, intervention-based experimental, and evidence synthesis accounted for 27.8%, 13.9%, 22.2%, and 36.1% of all included studies, respectively. Children and adolescents (27.8%) and adults (25.0%) were the most frequently studied populations, with limited studies focusing on professionals or teachers. Most studies targeted individuals with developmental disabilities as a combined group (61.1%), followed by those specifically targeting autism spectrum disorder. Research topics included dietary behaviors and nutritional status, nutrition-related education and interventions, health promotion, and medical or clinical issues, with many small-scale and shortterm intervention studies.
Conclusion
Although research on dietary and nutrition-related issues among individuals with developmental disabilities in Korea has expanded in scope and methodology, significant limitations remain. Future research should adopt longitudinal and community-based approaches, incorporate diverse populations, and strengthen policy-oriented nutrition support systems to promote sustainable health and quality of life for individuals with developmental disabilities.
- 80 View
- 6 Download

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Effects of senior-friendly foods on health, nutritional status, and dietary intake among rural elderly women in Korea: a quasi-experimental study
- Sang-ju Lee, Ji-hyeon Kim, Jin-suk Han
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):101-113. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00353
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
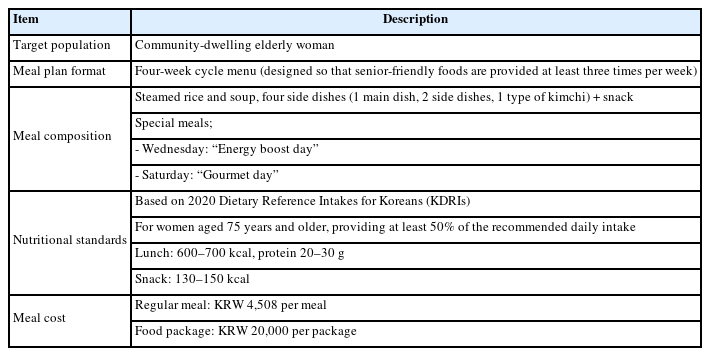
We evaluated the impacts on health, nutritional status, and dietary intake of providing senior-friendly foods to community-dwelling elderly women in a rural area in Korea.
Methods
A pretest–posttest nonequivalent control group design with repeated measures was conducted among 71 rural-dwelling elderly women. Changes in health indicators, nutritional status, and dietary intake were assessed at three time points: baseline, post-intervention, and two months after intervention.
Results
Immediately after a three month intervention, significant differences were observed between the intervention and control groups in frailty score, Dysphagia Handicap Index, Mini Nutritional Assessment, social isolation, resilience, quality of life, and depression (P < 0.05). Significant group-by-time interaction effects were found for muscle mass, hemoglobin A1c, and energy, protein, and micronutrient intake, all of which showed significant improvements in the intervention group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Providing senior-friendly foods effectively improved physical and physiological health and emotional well-being among rural older adults. This intervention also contributed broadly to improved dietary intake. These findings provide empirical evidence to support the development of community-based integrated care models and tailored nutrition intervention programs for rural elderly populations in Korea. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0011666.
- 47 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Impact of a foodservice establishment manager’s willingness to perform duties on hygiene management levels and the mediating effects of extrinsic motivations: a cross-sectional study
- Tae Yang Kim, Mi Young Lee, Young Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):36-49. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Consumer demand is growing for more rigorous hygiene management within foodservice establishments. The aim of this study was to provide customized data specific to each foodservice establishment, thereby informing policy formulation to improve hygiene management levels.
Methods
We surveyed 310 managers of directly managed foodservice establishments (excluding franchises) that were subject to hygiene inspections by the Chungbuk Provincial Office in Korea between September 1 and 27, 2023. Additionally, 30 investigators trained in methods for evaluating the hygiene management levels of foodservice establishments objectively assessed 310 establishments using evaluation sheets. All 310 managers provided consent and personally completed the questionnaires. Data from 277 managers were included in the analysis. General characteristics were analyzed with descriptive statistics in IBM SPSS Statistics 28 (IBM Corp.). Univariate normality verification, measurement model verification, structural model verification, and mediation effect significance analysis were conducted using R’s lavaan package (version 4.3.2.).
Results
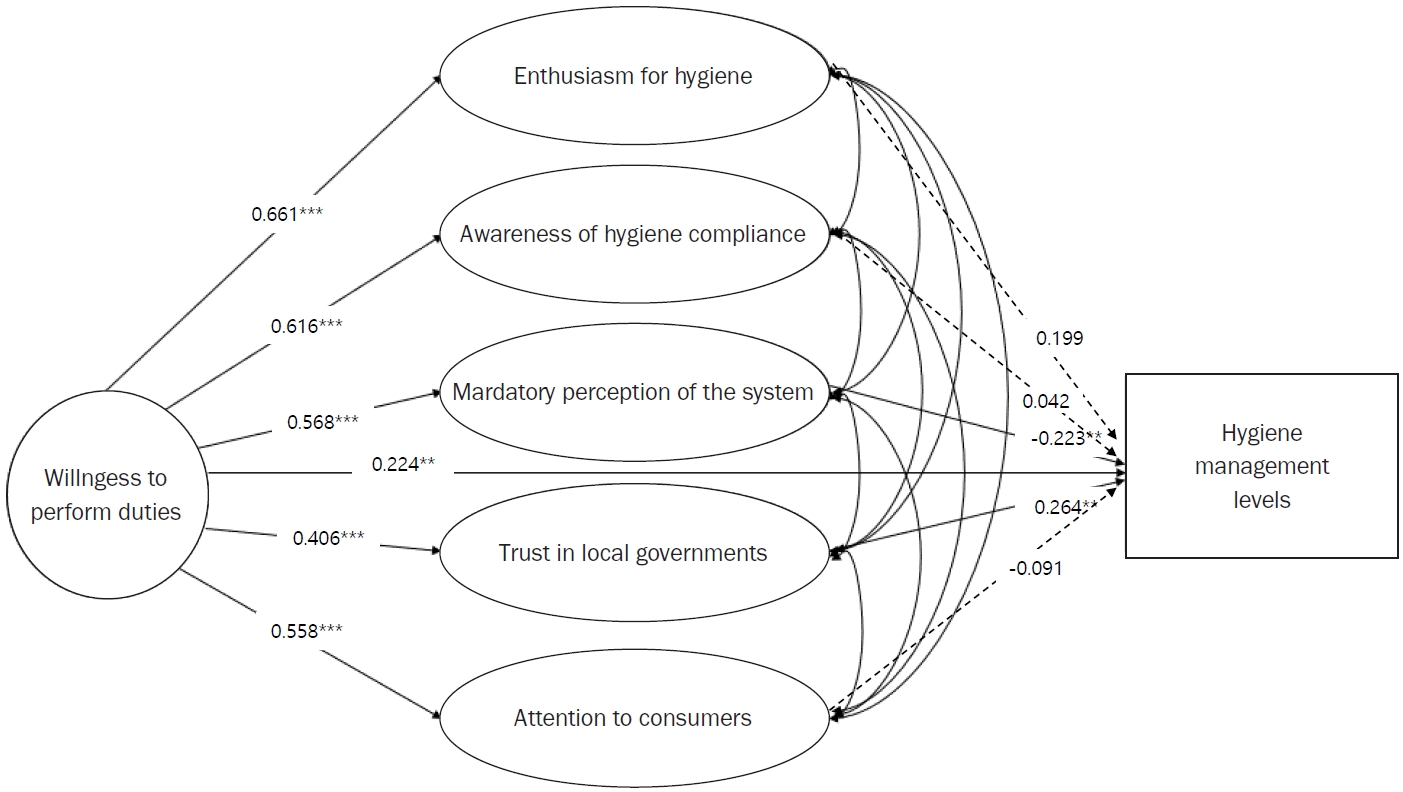
Managers’ willingness to perform duties had a positive influence on hygiene management level (0.224), enthusiasm for hygiene (0.661), awareness of hygiene compliance (0.616), mandatory perception of the system (0.568), trust in local governments (0.406), and attention to consumers (0.558). In the relationship between managers’ willingness to perform duties and hygiene management level, mandatory perception of the system had a negative mediating effect (–0.223), while trust in local governments had a positive mediating effect (0.264).
Conclusion
Structural equation modeling was used to identify the complex pathways by which foodservice establishment managers’ willingness to perform duties, mediated by their human factors, influences their hygiene management level. Accordingly, policy implications were presented, suggesting that the hygiene management level of foodservice establishments could be enhanced by increasing managers’ willingness to perform their duties, and that a shift from mandatory regulations by local governments to support-oriented systems that foster trust in local governments is necessary.
- 56 View
- 3 Download

- [Korean]
- Evaluation of young children’s dietary behaviors by parental growth concern levels in Gyeonggi area: a descriptive study
- Youn-Rok Kang, Hyung-Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):75-86. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00269
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated differences in dietary habits, lifestyle patterns, and feeding- related developmental issues among Korean preschool children based on their parents’ levels of growth concern, and examined the associations between parental growth concern and children’s eating behaviors.
Methods
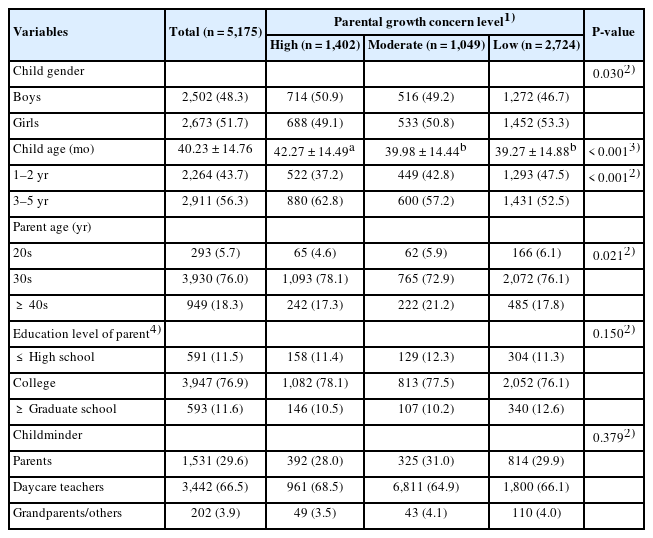
A cross-sectional study was conducted with parents of children aged 1–5 years residing in Gyeonggi Province, Korea. Participants were classified into high, moderate, and low growth concern groups using the children’s dietary screening test. Data were collected on the children’s anthropometric status, lifestyle routines, dietary intake patterns, eating behaviors, and mealtime media exposure.
Results
Children in the high growth concern group showed a higher prevalence of underweight; irregular sleep and mealtime routines; and more frequent eating difficulties, including picky eating, slow eating, and oral processing problems. Mealtime media exposure was associated with lower fruit and vegetable intake and higher consumption of processed and sugar-rich foods. Higher parental growth concern did not correlate with healthier dietary or lifestyle outcomes.
Conclusion
Preschool children’s dietary behaviors and routines differed according to the parents’ levels of growth concern. Higher levels of parental concern were associated with increased feeding difficulties and greater mealtime media exposure. These findings suggest that excessive concern may contribute to maladaptive eating patterns in children. Evidence- based parental guidance and structured nutrition education are essential to promote healthy growth and eating behaviors during early childhood.
- 54 View
- 3 Download

- [Korean]
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):441-456. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
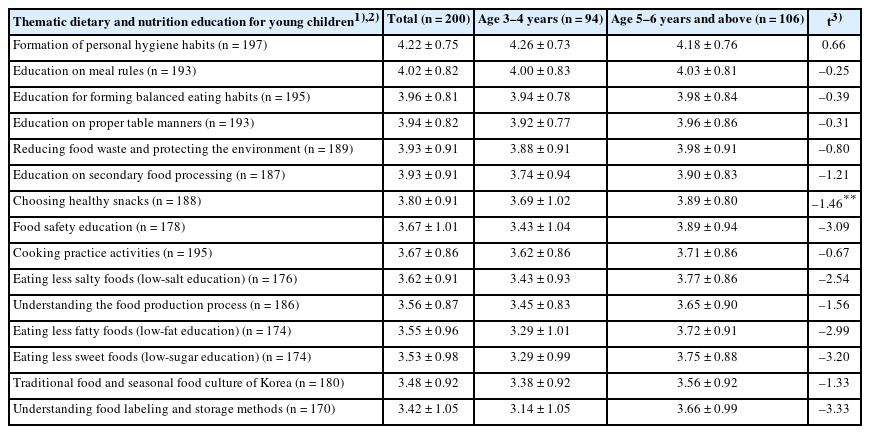
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to clarify parental perceptions of dietary and nutritional education provided to young children, identify parental support needs, and suggest directions for improvement.
Methods
A mixed-method sequential explanatory design was followed. Quantitative data were collected through an online survey conducted nationwide that included 200 parents of children aged three to six years in South Korea. Qualitative data were subsequently obtained through focus group interviews with fifteen parents to explore their contextual insights and experiences.
Results
Needs ratings prioritized expanding activity-based/experiential education (3.65 ± 0.88), followed by strengthening home-school communication and connectivity (3.59 ± 0.84), diversifying topics and content (3.55 ± 0.88), and increasing instructional time (3.39 ± 0.94). Integrated with the focus group interview findings, multilevel barriers were revealed—individual level: strong preferences of children for sweet/processed foods; interpersonal level: strong parental modeling and peer effects counterbalancing limited teacher expertise/time; organizational level: insufficient effective event-based experiential activities, and resource gaps across institutions; community/policy level: infrequent external support, uneven access to local resources, lack of standardized guidance, and limited opportunities for parental participation. Parents favored short, interactive digital content and expressed concerns about overexposure. These convergent findings indicate needs to 1) formalize and extend experiential programs within the regular curriculum, 2) provide standardized guidelines and home resource kits, and 3) institutionalize parental involvement.
Conclusion
These findings reveal that dietary and nutritional education for young children should move beyond fragmented, event-based programs toward an integrated three-tiered model incorporating (1) a structured, experiential curriculum, (2) home-linked educational packages, and (3) safe and interactive digital content. Establishing standardized guidelines, enhancing educational infrastructure, and institutionalizing parental participation are essential for sustainable improvement of early childhood dietary education.
- 460 View
- 37 Download

- [English]
- Nutrition Quotient and nutrient intake among older adults in a rural Korean community: a cross-sectional study
- Ji-Sook Park, Hyeon-Mi Bae, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):397-409. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00283

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Korea is experiencing rapid population aging, with older adults forming a large proportion of rural communities. Aging leads to physiological and functional declines, resulting in lower physical activity, poor diet quality, and higher risk of chronic diseases. Although the Nutrition Quotient for the Elderly (NQ-E) is a validated tool to assess dietary quality, few studies have applied it to rural populations. This study aimed to compare nutrient intake and NQ-E scores by age and sex and examine their associations with lifestyle factors.
Methods
This study investigated the relationship between nutrient intake and NQ-E scores among older adults in rural Korean community, considering age, sex, and lifestyle factors. A cross-sectional study was conducted with 79 community-dwelling older adults (24 male and 55 female; mean age: 76.3 years) residing in Geochang-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. Participants were recruited from community centers and health posts between June 2024 and December 2024. Data collection included general characteristics, 24-hour dietary recalls, and NQ-E questionnaires.
Results
Female aged > 75 years had significantly lower intakes of energy, protein, fat, vitamin E, riboflavin, folate, and zinc than their male counterparts (P < 0.05). The mean NQ-E score was 55.01, which was lower than the national average reported for urban older adults (57.6). Participants with higher NQ-E grades had significantly higher intakes of dietary fiber, vitamin A, thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, potassium, and magnesium, and regular physical activity and dietary supplement use were positively associated with higher NQ-E grades (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
These findings suggest that older female in rural communities are particularly vulnerable to inadequate nutrient intake and lower dietary quality, and that the NQ-E is a useful screening tool for identifying nutritional risk in this population. Community-based nutrition interventions promoting physical activity, supplement use, and dietary diversity are warranted to improve dietary quality and support healthy aging.
- 471 View
- 24 Download

Educational Material
- [Korean]
- Development and evaluation of play-based food and nutrition education materials for early childhood through sensory experiences: a pre-post observational study
- Hyunjoo Ryou, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):471-483. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00276

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop play-based nutrition education (PBNE) materials for young children and to evaluate their applicability and effectiveness.
Methods
An online survey of 1,253 primary caregivers of preschool children was conducted, and the findings were used to develop age-specific utilization guides, slides, activity sheets, activity cards, posters, educational videos, and parent newsletters. Selected materials were implemented in child-care centers through the Children’s Foodservice Management Centers between October and November 2023. The effectiveness of the PBNE program was assessed by examining changes in mushroom consumption as well as food awareness and preferences, before and after the intervention.
Results
A total of eight media formats and 320 educational contents were developed, and mushrooms were as the pilot theme among the 12 possible food items. Following the intervention, children’s positive awareness of mushrooms increased, and > 96% of participants attempted to consume them. Teachers in child-care centers rated the appropriateness and applicability of the content, its contribution to behavioral improvement, and their overall satisfaction at > 4.9 out of 5 points.
Conclusion
This study developed experiential, PBNE materials aligned with the national standard child- and play-centered curriculum. The materials were effective in enhancing food awareness and promoting attempts at consumption. Future efforts should focus on developing additional experiential teaching tools that incorporate teacher feedback and on strengthening home-linked programs to support healthy seasonal food intake and positive dietary experiences in young children.
- 416 View
- 16 Download

Research Articles
- [English]
- Self-reported weight change and diet quality in relation to metabolic syndrome among Korean cancer survivors: a cross-sectional study using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019–2021
- Hye Won Kim, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):341-351. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
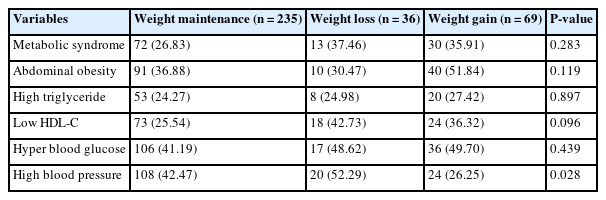
Using data from the 2019‒2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, we examined the association between dietary quality and metabolic syndrome by self-reported weight change among adult Korean cancer survivors.
Methods
We analyzed 340 cancer survivors (≥ 5 years post-diagnosis) by one-year weight change (stable, loss, and gain). Dietary quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI), and metabolic syndrome was defined according to standard criteria. Relative risks (RR) were estimated using a modified Poisson regression.
Results
The weight loss group was older than the weight gain group (P < 0.001). Females were more prevalent in the loss and gain than in the maintenance group (P = 0.008). Hypertension prevalence was highest in the loss and lowest in the gain group (P = 0.028); other risk factors were similar. The gain group had the highest body mass index (P = 0.011). KHEI scores were highest in the maintenance (66.59 ± 0.76) and lowest in the gain group (60.42 ± 1.77; P = 0.006), with significantly lower whole grain (P = 0.036) and fruit intake (P = 0.014). Compared with the maintenance group, the gain group demonstrated higher risks of metabolic syndrome (RR: 2.07, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.40–3.06; P < 0.001), abdominal obesity (RR: 1.93, 95% CI: 1.36–2.74; P < 0.001), and impaired fasting glucose (RR: 1.70, 95% CI: 1.23–2.34; P < 0.01). Within the gain group, participants in the lowest KHEI quartile had increased risks of metabolic syndrome (RR: 2.81, 95% CI: 1.06–7.43; P < 0.05) and hypertriglyceridemia (RR: 7.29, 95% CI: 1.54–34.61; P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Accordingly, weight change and dietary quality may critically affect the metabolic health of cancer survivors. Lifestyle management, including weight control and tailored diets, may help prevent metabolic disorders and support long-term health.
- 1,158 View
- 27 Download

- [Korean]
- A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Kyoung-Min Lee, Woo-jeong Kim, So-young Kim, Young-mi Park, Hwa-young Yoon, Min-Sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):376-388. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
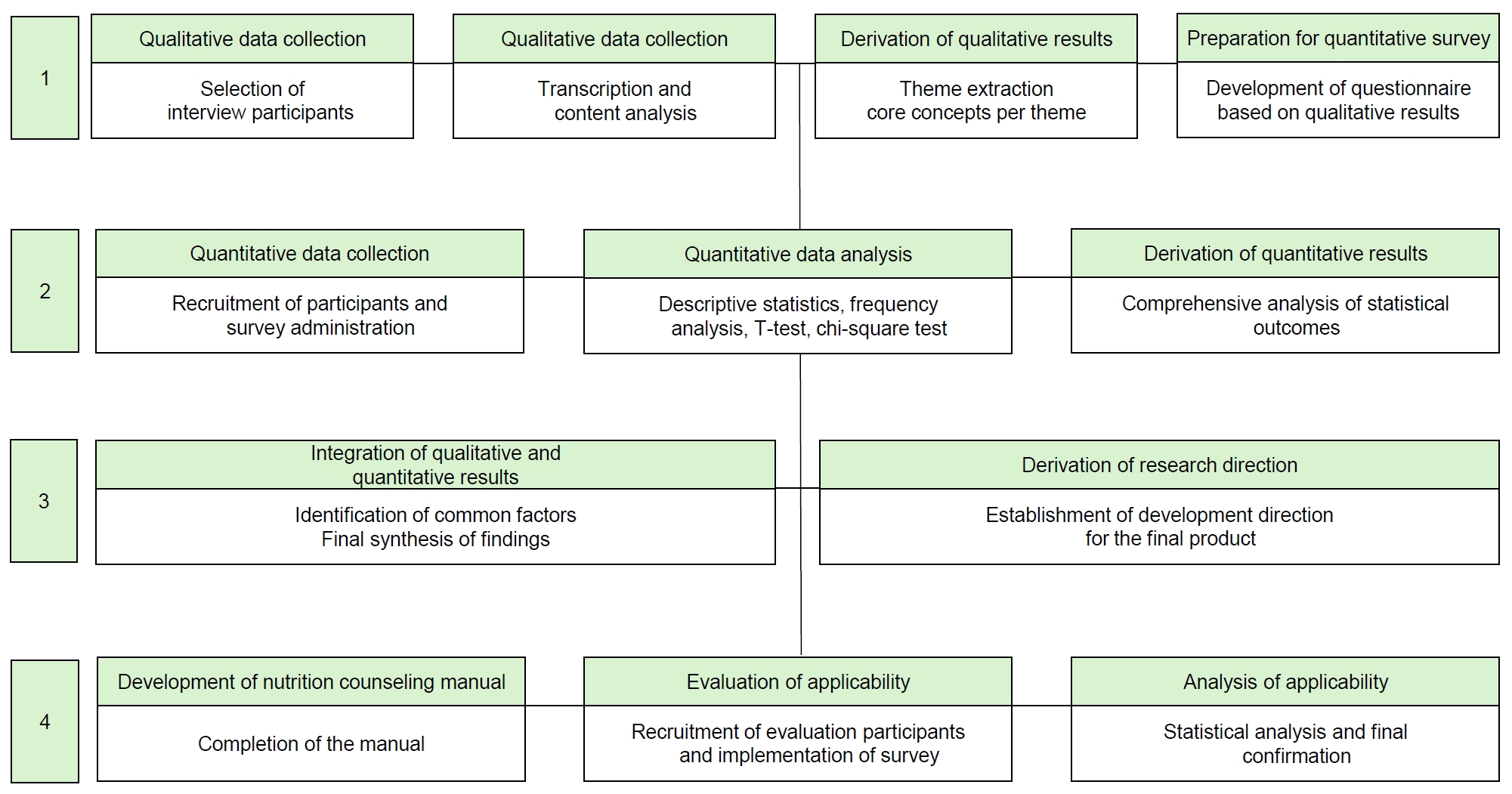
PDF - Objectives
Individuals with disabilities require targeted interventions to ameliorate disability-related conditions and improve overall health status. Nutritional challenges and counseling needs vary according to the type of disability, necessitating comprehensive assessments of dietary habits, physical activity, and food intake. Compared to traditional education, nutrition counseling offers a more sustainable and environmentally adaptable approach that effectively addresses individualized nutritional issues. Therefore, this study aimed to develop and evaluate a practical nutrition counseling manual and meal guidelines for people with disabilities in Korea, addressing their diverse dietary needs and improving nutritional care in social welfare facilities.
Methods
A four-stage integrated research design was employed. Stage 1 involved qualitative research through in-depth interviews with 11 facility staff. In Stage 2, a nationwide survey (n = 249) was conducted based on the results of the interviews. Stage 3 integrated both qualitative and quantitative findings. Stage 4 focused on developing and evaluating a nutrition counseling manual and five types of meal guidelines through feedback from 26 nutritionists at 24 Korean Centers for Social Welfare Foodservice Management.
Results
Six major nutrition counseling topics were identified: healthy eating, managing salt and sugar intake, dysphagia diet, appropriate intake, and hygiene. The manual and guidelines demonstrated high field usability, with average satisfaction scores of 3.98 and 3.99, respectively.
Conclusion
The integrated study resulted in the development of a specialized nutrition counseling manual and handbook for individuals with disabilities in Korean social welfare facilities. The materials were revised and improved based on practical evaluations by dietitians, enhancing their field applicability. These tools are expected to contribute to better dietary management and health promotion among facility residents. The developed materials reflect the real-world needs of people with disabilities and offer practical tools for effective nutrition counseling and dietary management in institutional settings.
- 506 View
- 24 Download

- [English]
- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
- Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):274-285. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00157

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Although diet quality is known to be associated with environment and individuals’ characteristics, these have not been studied together. We determined the association of diet quality with regional factors stratified by individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics.
Methods
This study used nationally representative survey data on regional factors (2010–2020) and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data on individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics (2013–2018). Community-dwelling Koreans aged ≥ 20 were included (n = 26,853). Regions were categorized into metropolitan cities or provinces and subsequently according to regional factors (level of educational attainment, income per capita, food security status, physical activity facilities, time to the nearest large retailer, and internet use of the region). Individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics included age, education status, income, and number of household members. Diet quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI).
Results
In the entire population, education status of metropolitan cities was positively associated with the KHEI. Shorter time to retailers and higher internet use were positively associated with the KHEI in metropolitan residents with higher income levels but negatively associated with the KHEI in those with lower income status. Among provincial residents with a low education status or income, regional physical activity facilities were positively associated with the KHEI.
Conclusion
The association between diet quality and regional factors varied depending on the resident’s sociodemographic characteristics. Both regional and individual sociodemographic factors must be considered to address gaps in nutritional equity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Among Rural Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Changhee Lee, Kyeongmin Jang
Journal of Ageing and Longevity.2026; 6(1): 22. CrossRef
- Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Among Rural Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,760 View
- 33 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of the relationship between foodservice staffing and foodservice quality in elderly care facilities in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Hyeonjeong Kim, Jinhee Kwon, Jungsuk Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):296-308. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00122

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was performed to investigate the relationship between foodservice staffing and foodservice quality in elderly care facilities.
Methods
Data was obtained from the Korean Long-term Care Institute Database and used to analyze 2,084 elderly care facilities operating on-site foodservice. The presence of dietitians and staffing levels for cooking personnel were analyzed by categorizing size according to staffing criteria. Foodservice quality was assessed using food sanitation management and meal service provision as indicators. Descriptive statistical analysis, chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, and Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test were conducted to analyze relationships between staffing level and foodservice quality.
Results
Presence of a dietitian correlated with food sanitation management and meal service provision in groups with 30 or more recipients (P = 0.027, P = 0.049). Elderly care facilities with dietitians had better foodservice quality. After adjusting for size, the presence of dietitians was also found to correlate with food sanitation management (P = 0.024). Staffing levels for cooking personnel were found to correlate with meal service provision only in groups with 38 to 62 recipients. Institutions with larger staffs provided better meal service quality compared to those with basic staffing.
Conclusion
Inclusion of a dietitian and cooking staff size each contribute to enhanced foodservice quality in elderly care facilities, with dietitian inclusion showing a particularly significant association with food sanitation management. These findings suggest the need to revise current staffing and related regulatory standards to optimize deployment of foodservice personnel in elderly care settings. Future studies should focus on developing effective policies for securing qualified foodservice staff and establishing robust quality management systems to enhance overall foodservice quality in long-term care facilities.
- 1,354 View
- 46 Download

- [English]
- The impact of flash continuous glucose monitoring and nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy and weight management in university students in Korea: a pre-post intervention study
- Soojin Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):183-196. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00073
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
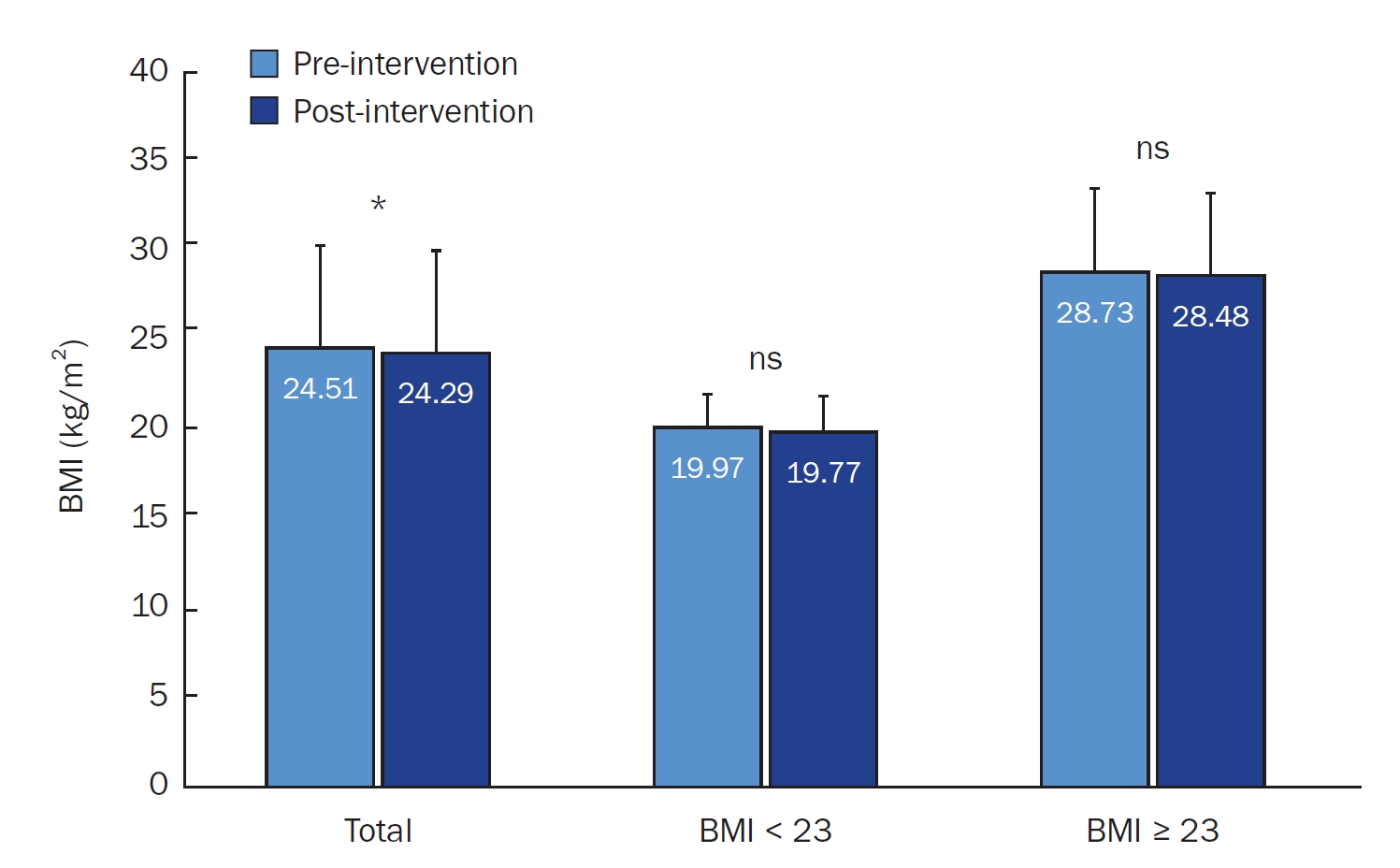
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of a 4-week multicomponent intervention combining flash continuous glucose monitoring (flash-CGM), group nutrition education, and personalized nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy (DSE) and weight management in healthy university students.
Methods
A total of 27 university students participated in a pre-post intervention study. The intervention included a single 4-hour group-based nutrition education session, flash-CGM usage (FreeStyle Libre; Abbott Diabetes Care), and weekly one-on-one nutrition coaching. Participants wore the CGM device for 28 days (replaced after 14 days), and were guided in using the FoodLens app (DoingLab) for dietary tracking and a mobile app-linked digital scale for weight monitoring. Outcomes measured before and after the intervention included DSE, body mass index (BMI), nutrition quotient (NQ) and glycemic indicators. Statistical analyses included Wilcoxon signed-rank and Mann-Whitney U-tests with significance set at P < 0.05.
Results
There was a significant increase in DSE (P < 0.05), particularly in managing eating behavior under stress and fatigue. A modest but significant decrease in BMI was observed in the overall group (P < 0.05), though changes were not significant in the BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2 subgroup. Glycemic indicators showed minimal changes. The overall NQ score improved slightly, with significant increases in fruit intake (P < 0.01) and nutrition label checks (P < 0.05). High satisfaction levels (4.52 ± 0.65 on a 5‑point scale) were reported for device usability and coaching services.
Conclusion
The multicomponent intervention improved DSE, NQ scores, and supported modest weight reduction among university students. The combined effect of CGM, nutrition education, and coaching appears promising; however, further studies are needed to isolate the effects of each component and evaluate long-term outcomes. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010255.
- 2,118 View
- 40 Download

- [English]
- Healthy eating intentions among adults in China: a cross-sectional study of northern and southern regions and city tiers based on the theory of planned behavior
- Yi Jiang, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):114-126. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The theory of planned behavior (TPB) has been widely employed to predict healthy eating intentions. Regional differences may affect dietary habits, health status, and personality traits, whereas variations in urbanization influence accessibility to fresh and healthy food, thereby impacting TPB components. This study aimed to explore whether regional differences between northern and southern China including city-tier development are associated with healthy eating intentions among Chinese adults.
Methods
The study included data from 2,114 Chinese adults aged 19–64 years collected between 2019 and 2023. Participants were categorized by geographic region (north or south) and city-tier status (first-tier or other).
Results
Compared to individuals from northern first-tier cities, those from southern regions exhibited stronger attitudes, perceived behavioral control (PBC), and intention to eat healthily. Participants from other cities in the north had more positive attitudes, subjective norms, PBC, and intentions to participate in healthy eating. Furthermore, residents of southern cities revealed weaker subjective norms than those of cities in the north. The adjusted odds ratio (OR) for compliance with intention to engage in healthy eating was higher among participants from other cities in both the north and south compared to those from northern first-tier cities (northern other cities: OR = 2.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.49–3.97, P < 0.001; southern other cities: OR = 1.95, 95% CI: 1.08–3.51, P = 0.027). No significant differences existed among the subjects from first-tier cities according to their geographic regions. These trends remained consistent even after including the interaction term between geographic regions and city-tier classification.
Conclusion
These findings underscore the complexity of regional variations influencing dietary intentions and indicate that tailored health promotion strategies should incorporate regional characteristics. Future research should explore underlying factors, including regional cultural influences, to better inform policies and interventions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
Md. Asaduzzaman Babu
Food and Humanity.2025; 5: 100779. CrossRef
- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
- 1,947 View
- 32 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of clinical characteristics and dietary intakes according to phenotypes of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Jin Kim, Ji-Sook Park, Sung-Rae Cho, Daeung Yu, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):127-139. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Clinical nutrition treatment is the central part of diabetes management, such as prevention, treatment, and self-management of diabetes, and personalized clinical nutrition treatment, which enables improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study aimed to contribute to the improvement of appropriate nutrition management in personalized treatment for obese and non-obese diabetes patients.
Methods
T2DM patients were recruited as participants, and 36 final participants were assigned to the lean diabetes mellitus group (LDM; body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and the obese diabetes mellitus group (ODM; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). We assessed the dietary intakes, body composition, dietary habits, the Korean version of obesity-related quality of life, and biochemical indices.
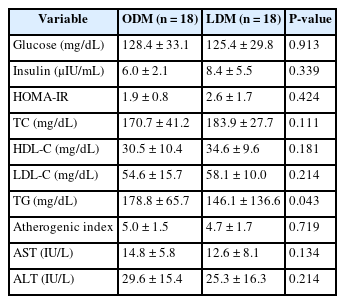
Results
According to the phenotype’s comparison, the ODM group had a high prevalence of T2DM complications and hypertension, had a dietary habit of less than 10 minutes of mealtime duration and preferred fast food intake, and had a low obesity-related quality of life. However, the LDM group had a high choice of Korean dishes at the time of eating out and a high intake of vitamin C, and iodine because of the intake of vegetables and seaweeds.
Conclusion
We observed differences in diet, nutrient intake, and clinical characteristics according to the phenotype of T2DM patients. In particular, obese diabetes patients have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, bad dietary habits, and low obesity-related quality of life. Therefore, personalized nutrition treatment is needed in consideration of the risk of cardiovascular disease and dietary habits for patients in the ODM group, as well as determining the energy requirements of Korean patients with T2DM.
- 2,308 View
- 33 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung–Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):150-162. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00038

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To determine the association between night eating habits and oral health in adolescents.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 were analyzed. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed the frequency of night eating per week, dietary habits, oral health characteristics, and factors affecting the presence of symptoms of poor oral health.
Results
Almost thirty-seven percent (36.6%) of Korean adolescents have eaten at night one to two times per week and 23.0% more than three times per week. An increased frequency of night eating was associated with poor dietary habits. Adolescents who consumed more at night were less likely to have breakfast, drink water, and eat fruit, while their consumption of fast food, sweet drinks, and high-caffeine drinks increased (P < 0.001). An increased frequency of night eating was also associated with poor oral health. In a logistic regression analysis, more frequent night eaters were significantly less likely to brush their teeth at least three times per day (odds ratio [OR], 0.78; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75–0.82; P for trend < 0.001), and brush their teeth before going to sleep (OR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.65–0.75; P for trend < 0.001), while they were more likely to experience sealant (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.13–1.26). More frequent night eaters were significantly more likely to have tooth fracture (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.30–1.53; P for trend < 0.001), tooth pain when eating (OR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.50–1.67; P for trend < 0.001), toothache (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.52–1.70), and bad breath (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.43–1.60).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that frequent night eating is linked to symptomatically poor oral health in adolescents. Therefore, oral health education programs related to dietary habits are necessary to reduce the potential of night eating to negatively influence dietary habits and oral health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Bo Young Park, Eun Bi Sim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(4): 370. CrossRef
- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,676 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
- Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):140-149. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to examine regional differences in dietary behavior and satisfaction between urban and rural residents in Korea, identifying key factors associated with dietary satisfaction in each group to deepen understanding of these variations.
Methods
The data were obtained from the Consumer Behavior Survey for Food 2022 by the Korea Rural Economic Institute. The analysis involved 6,365 adult participants, using the complex survey χ2-test and complex survey t-tests to compare dietary behavior across regions and complex survey regression analysis to explore factors related to dietary satisfaction. Data were analyzed with R 4.3.1 (for macOS; Posit PBC).
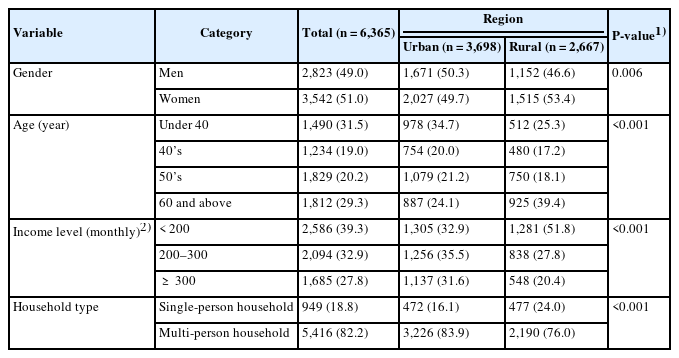
Results
Urban and rural areas differed in consumer characteristics such as gender, age, income, and household type, as well as in food consumption behaviors and in dietary competencies associated with purchasing and intake. Specifically, dining out and processed food consumption were more prevalent in urban areas, whereas home-cooked meals were more frequent in rural areas. Overall, dietary competencies were higher among urban residents. However, there was no significant difference in dietary satisfaction between the two regions. This finding suggests that satisfaction is based on subjective evaluations, with consumers in each region forming satisfaction in ways that align with their environment and lifestyle. Accordingly, the factors contributing to dietary satisfaction differed by region. In urban areas, information utilization competency and maintaining a balanced diet played a significant role in dietary satisfaction, whereas in rural areas, regular mealtimes were more influential. Urban consumers reported higher dietary satisfaction when meals provided a sense of appropriate convenience, whereas rural consumers showed greater satisfaction when meals were shared with family at home.
Conclusion
The findings indicate regional differences in food consumption behaviors and dietary competencies, as well as variations in how consumers achieve dietary satisfaction. These insights provide a foundation for developing dietary policies and programs aimed at improving dietary satisfaction.
- 1,614 View
- 56 Download

- [Korean]
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung Su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):53-63. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To apply a healthy dietary program with reduced sodium intake, developed using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), focusing on the sodium intake level and eating patterns.
Methods
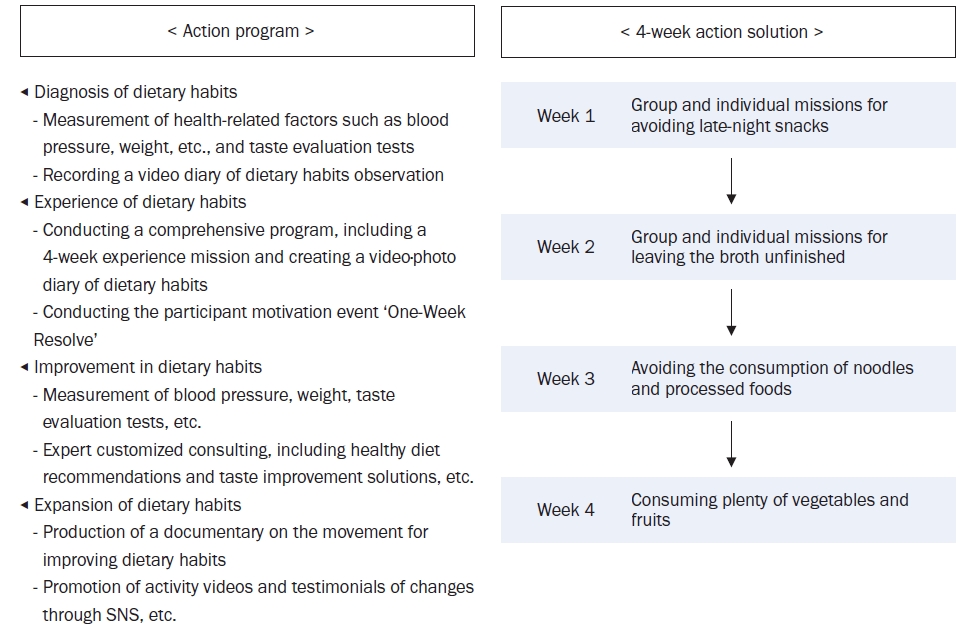
The program was implemented using a living lab model, an open innovation ecosystem for user-centered problem-solving. Analysis of the KNHANES data revealed that older age groups had a low energy intake but a high sodium intake, particularly among those who frequently dined out. The program was designed to improve sodium-reduction literacy and enhance practical competency. Over four weeks, 40 participants tracked their dietary intake and worked with a clinical nutritionist through a process of diagnosis, experience, improvement, and expansion. A self-administered survey was conducted before and after the program to assess effectiveness.
Results
Participants were four teenagers (10%), 26 in their twenties (65%), and 10 aged ≥ 30 years (25%), with eight males (20%) and 32 females (80%). Post-program analysis showed significant improvements in sodium-related nutrition knowledge (P < 0.01), with increased agreement on adopting low-sodium intake practices (e.g., interest in sodium content, choosing lower-sodium foods). Nutrient intake analysis showed a decrease in energy, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (P < 0.001), with sodium intake decreasing from 3,382.37 mg/d to 2,119.05 mg/d (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The community-based, living lab model for the sodium-reduction program effectively improved participant sodium-reduction literacy and practical competency, suggesting that step-by-step, autonomous learning, can reduce sodium intake and promote healthier eating habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
Wonyeong Park, Hae Jin Park, Suah Moon, Jieun Oh
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(6): 917. CrossRef
- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
- 2,036 View
- 64 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
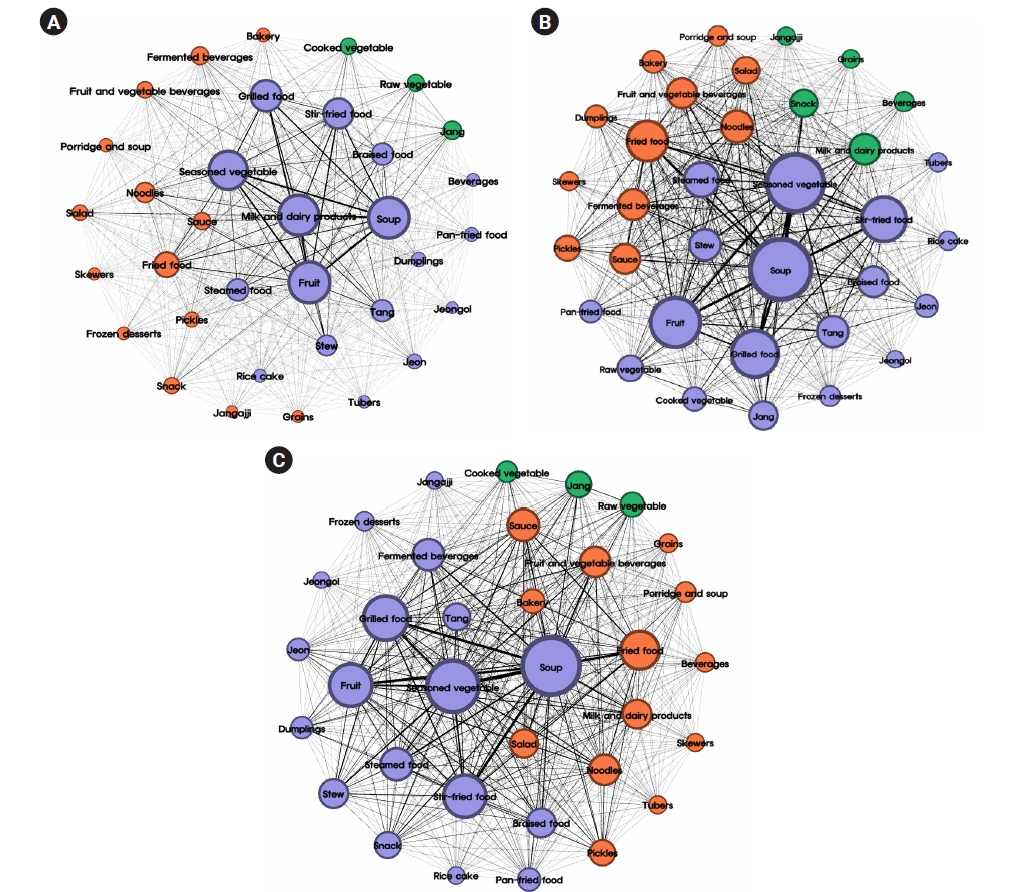
- Co-occurrence network and pattern of school lunch using big data and text-mining using data from the 2021–2023 school meal menu information on the NEIS open educational information portal: an exploratory study
- Hyeyun Kang, Jimi Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):514-527. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study aimed to use big data from elementary, middle, and high school lunches to determine the primary food groups and menu items that contribute to lunch meals through text-mining and investigate the variations in food groups and menu composition patterns across different grade levels.
Methods
Between 2021 and 2023, a total of 7,892,456 lunch menus from 17 cities and provinces in South Korea were analyzed using big data from the National Education Information System (NEIS) system. After undergoing text preprocessing for text-mining, the collected menus were classified into 34 food groups based on primary ingredients and cooking methods, excluding the types of rice and kimchi. Subsequently, analyses of term frequency, term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF), centrality, and co-occurrence networks were performed on the food group and menu data.
Results
According to the TF-IDF, the most frequent food group across all grade levels was soup and seasoned vegetables, whereas milk was the most frequently provided menu. As the grade level increased, the frequency of grilled and fried food increased. In elementary schools, fruits exhibited the highest centrality, whereas soup had the highest centrality in middle and high schools. Co-occurrence frequency revealed that the soup-fruit combination was the most common in elementary schools, whereas soup and seasoned vegetables were most frequently paired in middle and high schools. The co-occurrence network of food groups and menus further indicated that menus regularly provided as standard meals and those frequently offered as special meals formed distinct communities.
Conclusion
This study investigated the food groups and menu provision patterns in school meals through text-mining techniques applied to large-scale school lunch. The findings may contribute in enhancing the quality of nutritional management, school foodservice, and menu composition of school meal programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary patterns and diet quality among adults in their 20s according to rice consumption: a co-occurrence network analysis using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2019–2021
Eun-kyung Kim, Jin-Young Lee, Yong-Seok Kwon, Minji Kang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(6): 571. CrossRef
- Dietary patterns and diet quality among adults in their 20s according to rice consumption: a co-occurrence network analysis using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2019–2021
- 2,206 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
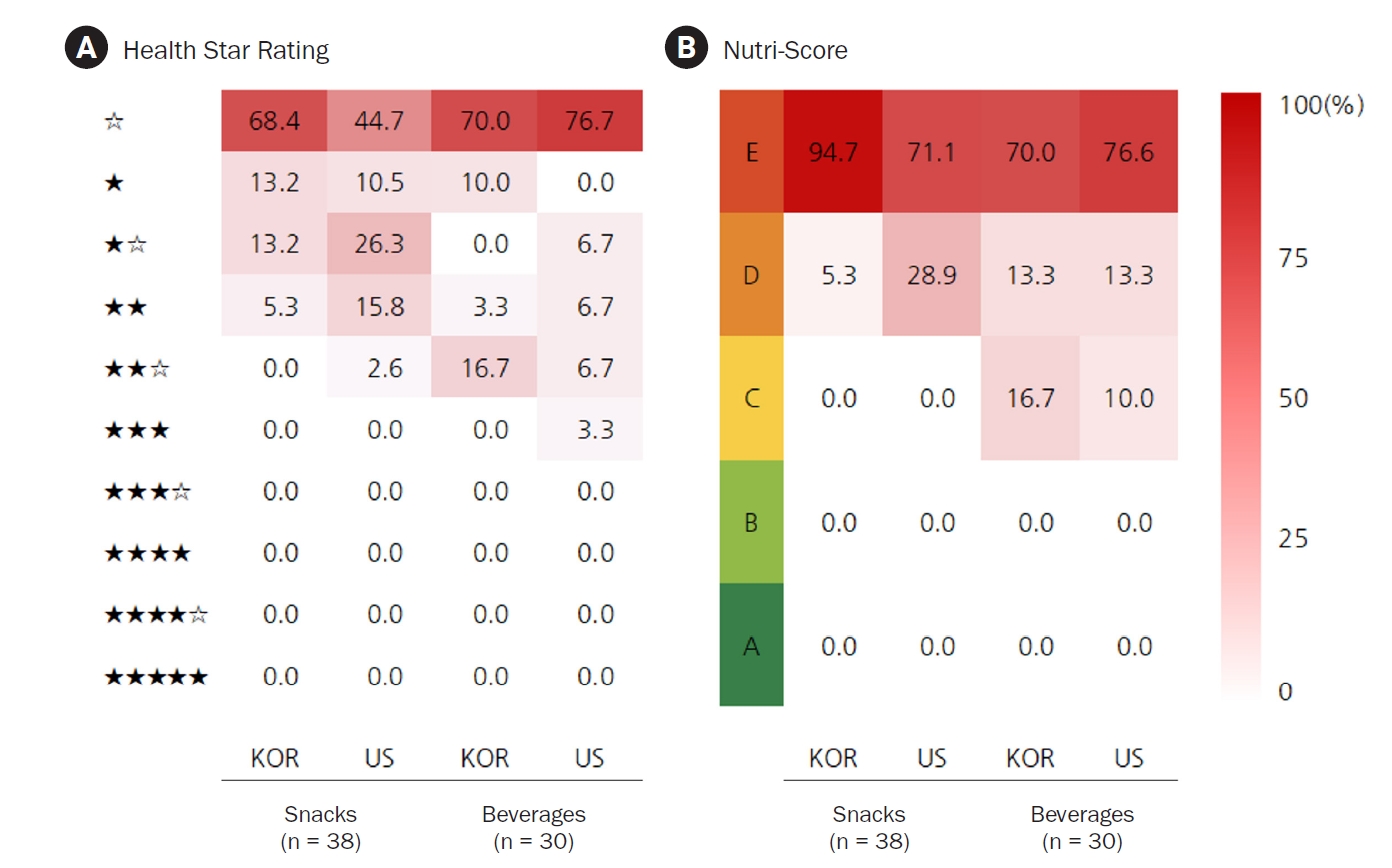
- Nutritional content and healthiness in sweet and salty snacks and beverages popular in South Korea and the United States assessed by nutrition labels: a cross-sectional comparative study
- Bo Jeong Gong, Segovia Lucas, Diewo Camara, Pauline E. Jolly, Chandrika Piyathilake, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):467-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the nutritional differences between sweet and salty snacks and beverages in South Korea (Korea) and the United States (US). Nutritional content and healthiness were determined using back- and front-of-package nutrition labeling (FoPNL) systems.
Methods
Three snack and three beverage categories popular in Korea and the US were selected. Statistical data were used to determine the top 10–15 best-selling products in each category in each country. The selected products included chips (n = 15), cookies (n = 10), chocolate (n = 13), carbonated drinks (n = 10), fruit juices/drinks (n = 10, 5/5), and energy drinks (n = 10). The study excluded products that were artificially sweetened. Nutritional information and percentages of fruit and vegetable content in each product were collected from brand websites and grocery stores in each country. The FoPNL system was used to assess the healthiness of the products, which included multiple traffic light labels, a Health Star Rating, and a Nutri-Score.
Results
Overall, Korean snacks contained significantly more protein, total fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol than US snacks. However, the US chips and carbonated drinks contained more sodium, while the US energy drinks contained more caffeine than Korean products. The serving size of US carbonated drinks was significantly larger than that of Korean drinks, whereas the serving size of US chips was smaller than that of Korean products. The FoPNL system classified the majority of products as ‘less healthy.’
Conclusion
Our results suggest that Korean and US food manufacturers should improve the nutritional quality and/or serving size of commonly consumed food products. Policymakers in both countries should work to improve the presentation of ingredient and nutrient information on nutritional labels to assist consumers in making healthier food choices.
- 6,913 View
- 58 Download

- [English]
- Associations between the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease and dietary and lifestyle behavior among young Korean adults: a preliminary cross-sectional study
- Soheun Shim, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):396-405. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00011

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a clinical condition caused by esophageal tissue damage resulting from the reflux of stomach or duodenal contents. An increasing number of GERD cases have been reported recently; however, research on this population, especially young adults, is lacking. This study aimed to investigate the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Methods: A total of 202 individuals (19–34 years old) living in Gwangju were surveyed using a questionnaire to examine their general characteristics, lifestyle, and dietary behaviors. GERD symptoms were investigated using the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GerdQ). The participants were grouped into normal (GerdQ score ≤ 4) and caution (GerdQ score ≥ 5), and their characteristics were analyzed according to the group. Results: The findings suggested 15 participants (7.4%) belonged to the GERD caution group. More non-office workers were in the caution group than in the normal group (P < 0.05). The participants’ smoking, physical activity, sleep duration, and pillow height were not significantly different between the GERD phenotypes; however, the caution group consumed alcohol more frequently than the normal group (P < 0.001). The analyses of the participants’ eating behaviors revealed that the frequency of overeating, late-night snacking and chocolate consumption was significantly higher in the caution group (P < 0.001). Conclusion: Lifestyle and dietary behaviors were associated with GERD symptoms in young Korean adults. Further studies with larger cohorts are required to confirm these findings.
- 5,994 View
- 77 Download

- [English]
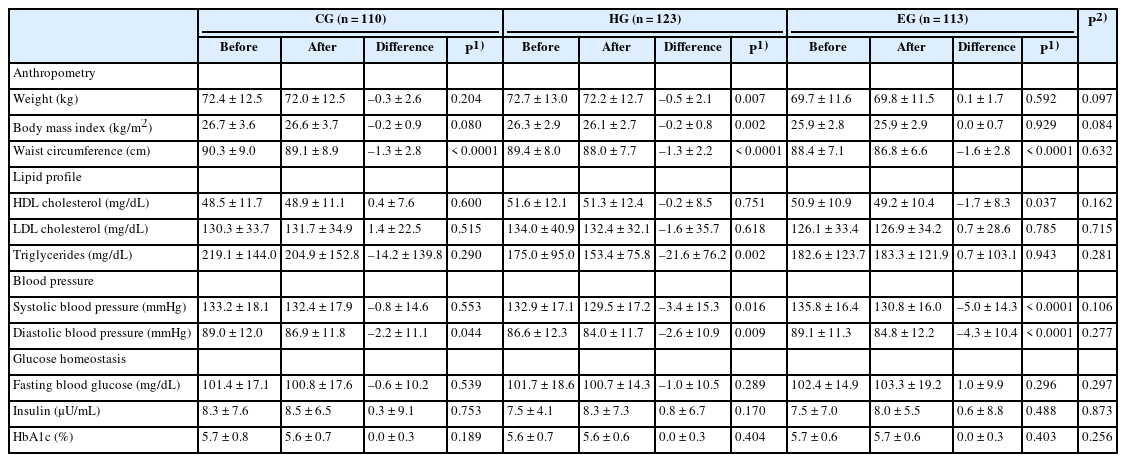
- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middle-aged Korean adults: an intervention study
- Minji Kang, Young-Hee Park, Subeen Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Hyun Wook Baik, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):265-277. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 411 Korean adults 30–59 years of age were allocated randomly into three groups: the nutrition education group for promoting Han-sik consumption (HG), the nutrition education group for eating balanced diet (EG), and the control group (CG). The HG and EG received four face-to-face nutrition education sessions over 16 weeks to improve nutritional problems based on the individual’ usual diet. Effectiveness of the program was evaluated with the differences of self-reported dietary behaviors, dietary intakes, anthropometric measurements and biochemical indices between the baseline and the end of the nutrition education program. The changes within groups were analyzed using paired t-test and McNemar test and effectiveness among three groups was analyzed by repeated analysis of variance.
Results
After the nutrition education, the percentages of participants who achieved the recommended food group consumption in the Korean Food Guidance Systems significantly increased in HG (P = 0.022). Body weight (P = 0.007), body mass index (P = 0.002), and triglycerides (P = 0.002) significantly decreased in HG. Waist circumference and diastolic blood pressure decreased in all three groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
This study found that tailored nutrition education program for middle aged Korean adults showed beneficial effects on improving dietary behaviors and metabolic syndrome risk factors. Further studies are needed to assess the long-term effects of the nutrition education programs on metabolic syndrome risks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multicomponent intervention increases nutrition knowledge scores in rural China
Zhifan He, Ming Feng, Lu Li, Jing Li, Xiaohui Li
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Multicomponent intervention increases nutrition knowledge scores in rural China
- 4,544 View
- 88 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
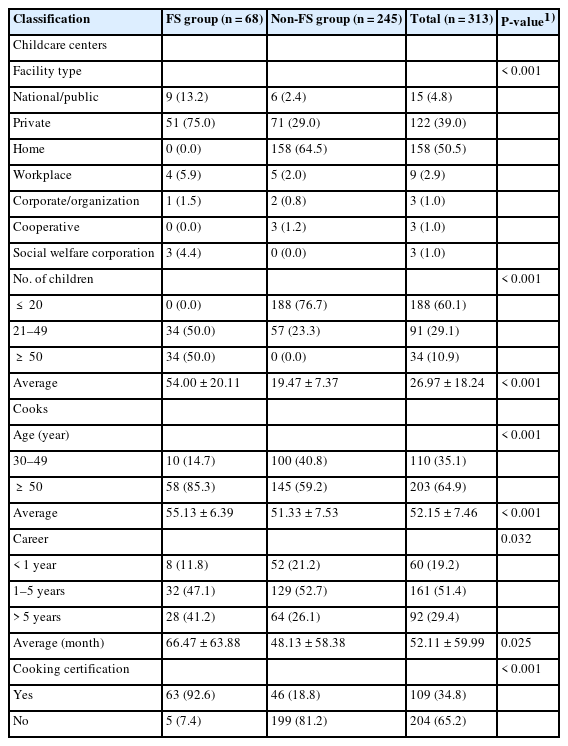
- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
- Jiwoo Min, Youngmi Lee, Yunhee Chang, Yujin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):304-317. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the importance and performance of sodium reduction practices among childcare center cooks in the Yongin area before and after a 3-month salinometer support program.
Methods
In total, 313 cooks employed in childcare centers in Yongin were surveyed before and after participating in a salinometer support program. The survey included questions on general information, sodium-related dietary habits, and perceived importance and performance levels of sodium reduction approaches in the purchasing, cooking, and serving areas. The centers were divided into childcare centers registered as group-feeding facilities (FS group, n = 68) and those not registered as such (non-FS group, n = 245). The differences between the two groups were analyzed.
Results
The overall importance levels increased significantly after the program in both the FS-group (P < 0.001) and non-FS group (P = 0.005). The overall performance levels also increased significantly in both groups (P < 0.001 for all). Consequently, the significant difference between the importance and performance levels disappeared in both groups after the program. However, unlike the FS group, which showed no significant differences between the importance and performance levels after the program in all three areas, the non-FS group still demonstrated lower performance levels than importance levels in the purchasing (P = 0.011) and serving (P = 0.034) areas after the program.
Conclusions
The use of salinometers significantly enhanced the performance and importance of low-sodium management practices among cooks in childcare centers, especially in the FS group. The continuous monitoring of salinity measurements and tailored education specialized for the FS and non-FS groups are recommended.
- 1,827 View
- 28 Download

- [English]
- The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
- Minji Kim, Meera Jang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):278-287. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00002
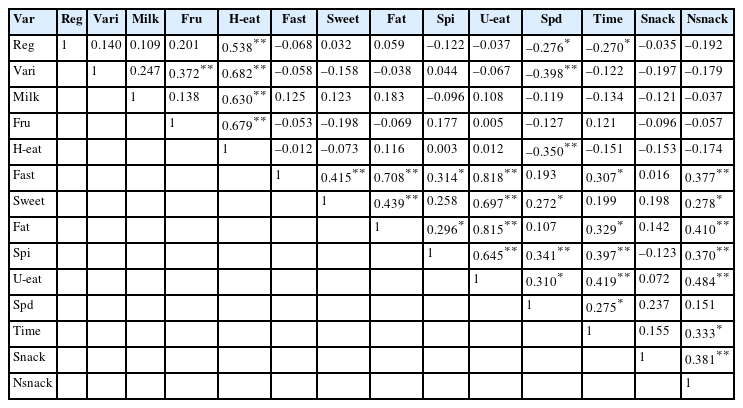
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigates the relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior among elementary school students. Methods: This survey was conducted on 4th- to 6th-grade students at elementary schools in Gangneung from September 6th to September 15th, 2023. Of the 129 copies of the questionnaire that were distributed to 5 schools, 66 copies (51.2%) were returned. Results: Compared to the nationwide statistics, the smartphone ownership rate of elementary school students in Gangneung was lower, but the rate of smartphone overdependence was higher. Smartphone dependence was 21.12 points for study subjects and 26.00 points for the overdependence risk group (Org). Compared to national statistics, the self-control failure factor was higher, so study participants in Gangneung City are thought to have great difficulty with self-control. The Org’s weekend smartphone use time of 7.54 hours was significantly more than the general user group (Gug)’s 4.06 hours. The number of days in which the Org consumed late-night snacks per week was 2.92 days, and the Gug had 2.15 days, but the difference was not significant. Eating fast food showed a positive correlation with eating sweet food, eating fatty food, and eating heavily seasoned food. It was found that frequent consumption of fast food is closely correlated with unhealthy eating behavior. Weekend smartphone use time showed a significant positive correlation with smartphone dependence and the number of days late-night snacks consumed per week. Conclusions: Study participants in Gangneung are more dependent on smartphones than national statistics. Smartphone dependence had a negative correlation with healthy eating behavior and a correlation with average unhealthy eating behavior.
- 3,785 View
- 55 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung-Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(2):156-170. Published online April 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the association between how often Korean adolescents watch Mukbang and Cookbang videos and their dietary habits.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 was analyzed for this study. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed various aspects, including demographics, frequency of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos per week, dietary habits, health behaviors, and mental health factors.
Results
Nearly a third (29.3%) of Korean adolescents watched Mukbang and Cookbang videos one to four times a week, while 13.5% watched them more than five times weekly. Females, those with lower academic achievement, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds were significantly more likely to be frequent viewers (P < 0.001). Increased viewing frequency was associated with poorer dietary habits. Adolescents who watched more frequently were less likely to eat breakfast and consume fruits and milk, while their consumption of fast food, high-caffeine drinks, sugary drinks, and late-night snacks increased (P < 0.001). Higher viewing frequency correlated with increased feelings of stress, depression, and loneliness (P < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis confirmed these associations. More frequent viewers were significantly less likely to eat breakfast (odds ratio (OR), 0.63; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.58–0.68), and more likely to consume fast food (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.69–2.02), high-caffeine drinks (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30–1.56), sugary drinks (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.41–1.67), and late-night snacks (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.25–1.51).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that frequent exposure to Mukbang and Cookbang content is linked to unhealthy dietary habits in adolescents. Educational programs may be necessary to mitigate the potential for these videos to negatively influence dietary choices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
Seung Jae Lee, Yeseul Na, Kyung Won Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2652. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Mukbang and Cookbang Viewing on the Association Between SNS Use and Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyle
Soo Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(11): 986. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef
- Association Between the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and High-Caffeine Drinks and Self-Reported Mental Health Conditions Among Korean Adolescents
- 3,950 View
- 110 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
- Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):51-64. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between ultra-processed food (UPF) consumption and chronic diseases in elderly Koreans.
Methods
Data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were analyzed. Dietary intake and UPF consumption were assessed using the NOVA food classification based on 24-hour recall data from 3,790 participants (aged 65+ years). Participants were divided into 4 groups based on the quartile of energy intake from UPFs. Regions were classified as urban or rural. Multivariable logistic regression was employed to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) after controlling for potential confounders.
Results
Among the participants, 71.3% resided in urban and 28.7% in rural areas. Compared to the urban elderly, rural participants tended to be older, have lower education and income levels, be more likely to live in single-person households, and have a higher smoking rate (P < 0.05). Urban elderly consumed more UPFs daily (146.1 g) compared to rural residents (126.6 g; P < 0.05). “Sugar-sweetened beverages” were the most consumed category in both regions. “Sweetened milk and its products” and “traditional sauces” were prominent in urban areas, while rural elderly consumed more “traditional sauces” and “distilled alcoholic beverages.” Rural areas also had a higher carbohydrate-to-calorie ratio than urban areas. Compared to the lowest quartile of UPF intake, the highest quartile was significantly associated with impaired fasting glucose only in rural areas (AOR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.00–2.19; P for trend = 0.0014). No significant associations were observed for diabetes in either urban or rural areas.
Conclusions
This study suggests that high intake of UPFs is associated with increased odds of impaired fasting glucose in rural elderly. Further research is needed to elucidate the specific negative health effects of UPFs in different populations, and targeted efforts should promote healthy diets in both urban and rural areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
Nazlıcan Erdoğan Gövez, Eda Köksal
Current Nutrition Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study of the Chemosensory Properties of Commercial Processed Foods Using Electronic Sensors
Hyeonjin Park, Younglan Ban, Sojeong Yoon, Hyangyeon Jeong, Seong Jun Hong, Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 805. CrossRef - Analysis of Flavor and Taste Patterns of Various Processed Animal Foods: Using the Electronic Tongue and Nose
Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Younglan Ban, Hyeonjin Park, Sojeong Yoon, Na Eun Yang, Seong Jun Hong, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(12): 1267. CrossRef
- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
- 2,419 View
- 76 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Effectiveness of NQ-E index-based individual nutrition counseling for community-care elderly: an intervention study on improving nutritional status, complex chronic diseases, and quality of life
- Yoonjeong Choi, Jihyun Lee, Heesook Lim, Yoo Kyoung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):480-494. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.480
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study sought to assess the effectiveness of community-based nutrition counseling on improving nutritional status, managing complex chronic diseases, and enhancing the quality of life for elderly individuals with chronic conditions, particularly in older adults with high levels of food insecurity and multiple chronic illnesses.
Methods
Thirty elderly subjects with diabetes and hypertension who were registered at local Senior Welfare Center received individualized nutrition counseling, based on their Nutrition Quotient for the Elderly (NQ-E) index. Over a 16-week period, they received tailored counseling and underwent various health and nutritional assessments. The final analysis included 28 participants after two dropped out. Data analysis was conducted using the SPSS v28.0.
Results
The subjects were over 70, with multiple chronic diseases including diabetes and hypertension and predominantly female. After 16 weeks, significant improvements were observed in the subjects’ grip strength, and HbA1c levels, as well as in their NQ-E scores, indicating improved dietary balance and diversity. There were no significant improvements in the ‘Moderation’ subdomain of the NQ-E index, suggesting that this aspect requires further attention in nutritional counseling. The subjects' nutritional risk scores (NSI) were also significantly decreased, indicating less nutritional risk. Lastly, as measured by the SF-36K, the subjects’ quality of life showed significant improvement in several domains including physical role performance and social function.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that tailored nutrition counseling, based on the NQ-E index, can improve elderly health, manage chronic diseases, and enhance quality of life. This approach potentially broadens the scope of community nutritionists' roles within an aging society. However, additional research is necessary to evaluate these interventions' long-term effects and sustainability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related Quality of Life in Multimorbid Adults: A Random Forest Cross-sectional Analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moonchang You, Geun-Myun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(3): 349. CrossRef - A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
Kyoung-Min Lee, Woo-jeong Kim, So-young Kim, Young-mi Park, Hwa-young Yoon, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 376. CrossRef - A Basic Study to Establish a Nutrition Education System for Welfare Facilities for the Elderly at Home Using Body Composition Analysis and Nutritional Management Cards
Sun Hee Lee, Seung-Lim Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 471. CrossRef
- Health-related Quality of Life in Multimorbid Adults: A Random Forest Cross-sectional Analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,858 View
- 70 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
- Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):466-479. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.466
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A mobile health intervention program was provided for employees with overweight and obesity for 12 weeks, and a process evaluation was completed at the end of the program. We investigated participant engagement based on app usage data, and whether engagement was associated with the degree of satisfaction with the program.
Methods
The program involved the use of a dietary coaching app and a wearable device for monitoring physical activity and body composition. A total of 235 employees participated in the program. App usage data were collected from a mobile platform, and a questionnaire survey on process evaluation and needs assessment was conducted during the post-test.
Results
The engagement level of the participants decreased over time. Participants in their 40s, high school graduates or lower education, and manufacturing workers showed higher engagement than other age groups, college graduates, and office workers, respectively. The overall satisfaction score was 3.6 out of 5. When participants were categorized into three groups according to their engagement level, the upper group was more satisfied than the lower group. A total of 71.5% of participants answered that they wanted to rejoin or recommend the program, and 71.9% answered that the program was helpful in improving their dietary habits. The most helpful components in the program were diet records and a 1:1 chat with the dietary coach from the dietary coaching app. The barriers to improving dietary habits included company dinners, special occasions, lack of time, and eating out. The workplace dietary management programs were recognized as necessary with a need score of 3.9 out of 5.
Conclusions
Participants were generally satisfied with the mobile health intervention program, particularly highly engaged participants. Feedback from a dietary coach was an important factor in increasing satisfaction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 53. CrossRef
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- 1,425 View
- 64 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A comparison of serum lipid concentration by drinking habits based on the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII) : a cross-sectional study
- Chang–Yun Park, Hyung-Sook Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):404-413. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.404
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study compared serum lipid concentration according to drinking habits.
Methods
We analyzed data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII). The study included 8,525 adults (3,651 males and 4,874 females), aged 30 – 59 years.
Results
There were differences in age, gender, education level, smoking status, physical activity, and waist circumference between drinkers and abstainers. The serum low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) level of the drinkers was lower than those of the abstainers (P < 0.05). The serum triglyceride (TG) and high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) concentrations were highest in the group that consumed alcohol ‘more than twice a week’ relative to the other groups (P < 0.001). The LDL-C and atherogenic index (AI) levels were lowest in the ‘more than twice a week’ drinking group compared to the other groups (P < 0.001). The serum TG and HDL-C concentrations were the highest in the ‘7 glasses/time’ group (P < 0.001). The serum LDL-C concentration was the lowest in the ‘7 glasses/time’ group (P < 0.001). Notably, the higher the frequency of binge drinking (7 glasses or more), the higher the concentration of TG (P < 0.001). The serum HDL-C concentration was significantly higher in the ‘no binge’ and ‘more than once a week’ groups compared to the other groups (P < 0.001). The serum LDL-C concentration and AI score were the lowest in the ‘more than once a week’ group (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
As the quantity and frequency of drinking increased, the serum TC concentration increased. Moreover, an increase in the serum HDL-C concentration led to a decrease in AI. The factors exacerbating cardiovascular disease increased simultaneously due to drinking. Our results suggest that for individuals with hypertriglyceridemia and patients with low HDL-cholesterolemia, separate guidelines based on the quantity and frequency of alcohol consumption are warranted.
- 1,769 View
- 22 Download

- [Korean]
- Health behaviors and eating habits in people’s 20s and 30s according to food content usage level on social media: a cross-sectional study
- Seo-Yeon Bang, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):392-403. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.392
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was intended to investigate adults’ health behaviors and eating habits according to their levels of social media use.
Methods
From May 27 to July 11, 2022, an online survey was conducted of 452 male and female social media users in their 20s and 30s, and their eating habits and health behaviors were compared and analyzed according to their degree of social media use. For each of the three levels of food content use, the frequency of social media content use, and the total score range of average social media viewing time per day were divided into three parts, and a group with a score of less than 2 points was classified as low-use; a group with a score of 2 or more and less than 3 points was classified as middle-use; and a group with a score of 3 points or more was classified as high-use.
Results
The use of food content was higher in women than in men (P < 0.001), and higher in those in their 20s than in those in their 30s (P < 0.001). The group with a high level of food content use showed a higher rate of post-use hunger than the group with a low level (P < 0.01). The experience of eating after using food content was also higher in the group with a high level of use than in the group with a low level of use (P < 0.001). The group with a normal or high level of food content use had more negative eating habits than the group with a low level.
Conclusions
The study highlighted the need to provide desirable food content to people in their 20s and 30s with negative eating habits and to promote them so that they can use the right healthy nutrition–related content. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Eating Habits and Health Behaviors According to Long-Form and Short-Form Mukbang Viewing of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
Seogyong Go, Bok-Mi Jung, Yun-Jung Bae, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(6): 597. CrossRef - The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
Minji Kim, Meera Jang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 278. CrossRef
- Eating Habits and Health Behaviors According to Long-Form and Short-Form Mukbang Viewing of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
- 4,163 View
- 111 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Gender differences in dessert satisfaction and purchase behaviors among university students in Gwangju: a preliminary study
- Hyun-Jeong Na, Hyun-Young Jung, Joomin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):293-301. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.293
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the effect of eating habits and dietary attitudes on dessert consumption among university students in Gwangju Province, South Korea.
Methods
A survey was conducted from May to June 2022. Out of 300 distributed questionnaires, 261 valid responses were included in the analysis. The survey assessed dessert selection, satisfaction, consumer attitudes and behaviors, as well as factors influencing satisfaction.
Results
Both genders reported purchasing desserts 2 to 3 times per week, primarily after lunch, due to the convenience of dessert accessibility. Males favored ice cream, bakery items, and fruits, while females preferred bakery items, ice cream, and fruits in that sequence. ‘Having fun’ was identified as the most common motivation for dessert consumption post-meal. Notable gender disparities emerged regarding perceptions of dessert consumption, including its role in stress relief, potential for nutritional imbalance, positive effects, and preferences for seasonal menus. Significant gender-based differences also manifested in intentions to purchase dessert, responsiveness to price changes, and inclination to recommend desserts to others.
Conclusions
This study offers foundational data on university students’ dessert purchasing behaviors, perceptions, and satisfaction levels, intending to inform strategies promoting healthier dietary habits.
- 2,048 View
- 42 Download

- [English]
- Effectiveness of a mobile health intervention on weight loss and dietary behavior changes among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
- Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young-Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):141-159. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.141
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to determine whether a mobile health (mhealth) intervention is effective in reducing weight and changing dietary behavior among employees with overweight and obesity. The study also investigated whether engagement with the intervention affected its effectiveness.
Methods
The intervention involved the use of a dietary coaching app, a wearable device for monitoring physical activity and body composition, and a messenger app for communicating with participants and an intervention manager. A total of 235 employees were recruited for a 12-week intervention from eight workplaces in Korea. Questionnaire surveys, anthropometric measurements, and 24-h dietary recalls were conducted at baseline and after the intervention.
Results
After the intervention, significant decreases in the mean body weight, body mass index, body fat percentage, and waist circumference were observed. Furthermore, the consumption frequencies of multigrain rice and legumes significantly increased, whereas those of pork belly, instant noodles, processed meat, carbonated beverages, and fast food significantly decreased compared with those at baseline. The mean dietary intake of energy and most nutrients also decreased after the intervention. When the participants were categorized into three groups according to their engagement level, significant differences in anthropometric data, dietary behaviors, and energy intake were observed following the intervention, although there were no differences at baseline, indicating that higher engagement level led to greater improvements in weight loss and dietary behavior.
Conclusions
The intervention had positive effects on weight loss and dietary behavior changes, particularly among employees with higher engagement levels. These results indicate the importance of increasing the level of engagement in the intervention to enhance its effectiveness. The mhealth intervention is a promising model for health promotion for busy workers with limited time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Process evaluation of a mobile healthcare program among employees with overweight and obesity: a 12-week intervention study investigating the role of engagement
Imhuei Son, Jiyoun Hong, Young Hee Han, Bo Jeong Gong, Meng Yuan Zhang, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 466. CrossRef - Systematic Review on the Study of the Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in Korea: Dietary Risk Factors
Eun Jeong Heo, Jae Eun Shim, Eun Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 191. CrossRef
- Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
- 2,135 View
- 69 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Examination of explicit and implicit emotions and relationship with the intention to support breastfeeding in public: a descriptive study
- Katilin D. Overgaard, Lauren M. Dinour, Adrian L. Kerrihard, Yeon K. Bai
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):114-123. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Current social norms in the United States do not favor breastfeeding in public. This study examined associations between college students’ explicit and implicit emotions of breastfeeding in public and their intention to support public breastfeeding.
Methods
Twenty-two student participants viewed images of a breastfeeding woman with a fully-covered, fully-exposed, or partially-exposed breast in a public setting. After viewing each image, participants’ explicit emotions (self-reported) of the image were measured using a questionnaire and their implicit emotions (facial expression) were measured using FaceReader technology. We examined if a relationship exists between both emotions [toward images] and intention to support breastfeeding in public using correlation techniques. We determined the relative influence of two emotions on the intention to support breastfeeding in public using regression analyses.
Results
The nursing images depicting a fully-covered breast (r = 0.425, P = 0.049 vs. r = 0.271, P = 0.222) and fully-exposed breast (r = 0.437, P = 0.042 vs. r = 0.317, P = 0.150) had stronger associations with explicit emotions and intention to support breastfeeding in public compared to implicit emotions and intention. Breastfeeding knowledge was associated with a positive explicit emotion for images with partial- (β = 0.60, P = 0.003) and full-breast exposure (β = 0.65, P = 0.002).
Conclusions
Explicit emotions appear to drive stated intentions to support public breastfeeding. Further research is needed to understand the disconnect between explicit and implicit emotions, the factors that influence these emotions, and whether stated intentions lead to consistent behavior.
- 847 View
- 11 Download

- [Korean]
- Association between eating habits, sweet taste assessment, and high-sugar food consumption among elementary school students in Daegu: a descriptive study
- Min-Jung Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):104-113. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to analyze high-sugar food consumption habits frequency among elementary school students, and their correlations with eating habits and sweet taste assessment.
Methods
The participants of the study were 164 elementary school students in Daegu, in the fifth or sixth grade, along with their parents. A questionnaire investigated eating habits, high-sugar food consumption habits and frequency, and sweet taste assessment.
Results
The average eating habits score for elementary school students was determined to be 71.7 out of 100. Students with higher eating habits scores had lower high-sugar food consumption habits and frequency compared to those with lower eating habits scores. Sweet taste assessment revealed that students who preferred less sweetness chose a 5% sugar concentration, those with a preference for normal sweetness chose a 10% sugar concentration, and those who preferred sweeter tastes chose a 20% sugar concentration. Sweet taste assessment showed that students who tended to prefer less sweetness had the highest eating habits scores and the lowest scores for high-sugar food consumption habits and frequency. In addition, eating habits scores were found to be negatively correlated with high-sugar food consumption habits, high-sugar food consumption frequency, and sweet taste assessment. The sweet taste assessment was positively correlated with high-sugar food consumption habits and frequency.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that students with good eating habits had more desirable overall sugar intake habits, and when the preference for sweetness was high, the frequency of high-sugar food consumption was also high. Our study highlights the importance of educating elementary school students and their parents about the harmful effects of excessive sugar consumption, as well as the benefits of adopting healthy eating habits and creating supportive environments.
- 1,217 View
- 33 Download

- [Korean]
- Nutrition teacher’s perception and current status of nutrition education for free learning semester program: a preliminary study
- Mi Joo Park, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(1):24-37. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the current status of nutrition education via a free learning semester program (NE). The understanding of the program, the potential difficulties, and future initiatives for NE improvement were also investigated.
Methods
A total number of 161 nutrition teachers from Gwangju and Jeonnam filled in a questionnaire and participated in this survey, which was performed from July to August 2019.
Results
Our results showed that 8.1% of the nutrition teachers had taught nutrition education in free learning semester programs. The most frequently implemented model was subject selection, followed by club activities. Most of the nutrition teachers comprehended the purpose of NE. The attitude of nutrition teachers to NE differed by the understanding of its purpose. Positive attitude was evident due to a better understanding of the purpose by nutrition teachers. Nutrition teachers reported the most common difficulties of NE were the lack of preparation due to the heavy workload and the lack of a standard running program. The most effective method of NE was the activity classes. The experience of practicing NE influenced the choice of contents for each operating model. Nutrition teachers that were experienced in NE conducted via free learning semester programs preferred the selected topics model, but those without experience chose the career search model.
Conclusions
Although some obstacles exist, nutrition teachers had a positive attitude and perceived well the importance of NE. Therefore, the awareness for the significance of NE of nutrition teachers needs to be improved. For better NE practice, it is necessary to reduce/ manage the workload of general food service. Furthermore, the development of standard running and promotion programs, and teacher training programs should be ensured. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef
- An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
- 1,680 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Problems Encountered in Analyzing the Market Size, Purchase, and Consumption of HMR in the Republic of Korea
- Sung Ok Kwon, Injoo Choi, Yoojeong Joo, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):480-491. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.480
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the problems encountered when analyzing the market size, purchase, and consumption of HMR (home meal replacements) in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
The macro data relevant to the market size and purchase status of HMR were critically summarized. The micro data retrieved from the 2019 & 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) were analyzed to understand the consumption of HMR.
Results
The Korea Agro-Fisheries & Food Trade Corporation and the Ministry of Food and Drug Administration reported the market size of HMR, whereas the Korean Rural Economic Institute and the Rural Development Administration reported the purchase expense and frequencies of HMR. Since the values on the market size and purchase status were calculated or surveyed using different scopes of HMR, there have been reliability issues for the data presented. Additionally, lack of consensus on the use of Korean terms corresponding to HMR was found to be a problem. To examine the consumption of HMR, analysis of the food intake data from KNHANES presented results with very low validity due to the inappropriate survey and coding scheme not reflecting the inclusion of new food types.
Conclusions
Several problematic discrepancies were encountered in the statistics on HMR. The fundamental cause of these problems was the absence of agreement on the scope of HMR and the Korean terms corresponding to it. Considering the increasing importance of HMR in Korean diets, urgent cooperative efforts are required between the government and academia to derive an agreed Korean term and establish the scope of HMR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Human Resource Management in Emergencies: The Case of the Lithuanian Logistics Sector
Kristina Čižiūnienė, Gabrielė Voronavičiūtė, Dragan Marinkovic, Jonas Matijošius
Sustainability.2025; 17(6): 2591. CrossRef - Evaluation of Thermal Resistance in Geobacillus thermodenitrificans subsp. Calidus and Ureibacillus suwonensis Spores Isolated in Korea
Ju-Hee Nam, Du-Yeong Jung, Zi-On Choi, Hyun-Jung Jung, Jung-Beom Kim
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2025; 40(1): 13. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties and Quality Analysis of Miichthys miiuy Products Processed by Drying and Smoking
Yu-Jin Heo, Hayoun Kim, Hae-In Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(7): 629. CrossRef - Survey on consumer perceptions, health benefits and preferences of kindergarten and school foodservices in Korea, including related keywords reported in newspaper: a mixed-methods study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 309. CrossRef - Eating behaviors, home meal replacement consumption, and nutrition quotient: a comparative study of male shift and non-shift workers in Chungcheong, Korea
Yeon Jin Lee, Munkyong Pae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 758. CrossRef - Usage and Quality Satisfaction of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores according to the Eating Behavior of University Students in Southern Gyeonggi Province
Se-In Oh, Ok-Sun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 492. CrossRef
- Sustainable Human Resource Management in Emergencies: The Case of the Lithuanian Logistics Sector
- 6,017 View
- 142 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Effect of Type of Nutrition Labeling on the Healthfulness Evaluation and Purchase Intentions of Home Meal Replacements (HMR) in South Korea
- Mee-Young Joe
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):387-396. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.387
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of the types of nutrition labeling on the processing fluency, health evaluation and purchase intentions of home meal replacements.
Methods
This online experimental study was conducted from December 29 to 31, 2019 and included 134 participants. The research design was 2 (Objective nutrition labeling: present vs. absent) X 2 (Evaluative nutrition labeling: present vs. absent) and each participant was randomly assigned to one of four groups. As stimuli, five types of ready-to-heat foods sold in the market were used.
Results
Processing fluency (4.91 points) and purchase intention (4.13 points) were significantly high when both evaluative nutrition labeling and objective nutrition labeling were presented, and healthfulness evaluation (4.47 points) was significantly high when only evaluative nutrition labeling was presented. All three variables were measured to be high when evaluative nutrition labeling was presented. The evaluative nutrition labeling that visually represented nutritional values was found to be more effective for processing fluency, healthfulness evaluation, and purchase intention than the objective nutrition labeling representing the nutritional value of the product in numbers and proportions.
Conclusions
These results show that it is necessary to develop various types of evaluative nutrition labeling to enable consumers to choose and purchase healthful home meal replacements. Also, consumer education and public campaigns are needed to encourage consumers to select healthier home-cooked meals using nutrition labeling. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Sustainable Dietary Life Competency in Families According to Parents’ Dietary Lifestyle: Using the 2021 Korea Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1179. CrossRef - Study on the consumption practices and Importance-Satisfaction Analysis of meal-kit selection attributes among adults in their 20s and 30s
Se-Eun Kim, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 315. CrossRef
- Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Sustainable Dietary Life Competency in Families According to Parents’ Dietary Lifestyle: Using the 2021 Korea Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
- 1,227 View
- 18 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of the STEAM Education Program on Food Groups for Kindergarteners
- Jinkyeong Ahn, Seyoen Kim, Donghyuk Kim, Jounghee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(5):361-372. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.5.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to explore the effectiveness of the STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) education program on the use of specific food groups in improving nutrition-related knowledge and attitude, dietary behavior, creative problem solving, and STEAM attitude.
Methods
We selected two classes at a kindergarten in Jeollabuk-do, South Korea. A total of 44 kindergarteners from the two classrooms participated in this study. The experimental group and the control group were formed with 22 students each. The experimental group attended 11 STEAM classes on the use of the grain, fruit, and milk food groups. First, we performed the paired t-test to examine changes from pre-to-post classes for both groups. Then, we used ANCOVA to compare post-test scores between the experimental and control groups with the adjustment of pre-test scores.
Results
The results demonstrate that the STEAM education program on the use of the food groups significantly improved (1) nutrition-related knowledge and attitude, and dietary behavior (P < 0.001), (2) creative problem solving (P < 0.001), and (3) STEAM attitude (P < 0.001) in the intervention group when compared with the control group.
Conclusions
The STEAM education program on the use of food groups is effective in enhancing nutrition knowledge and attitude, dietary behavior, creative problem solving, and STEAM attitudes among kindergarten students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and evaluation of play-based food and nutrition education materials for early childhood through sensory experiences: a pre-post observational study
Hyunjoo Ryou, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 471. CrossRef
- Development and evaluation of play-based food and nutrition education materials for early childhood through sensory experiences: a pre-post observational study
- 1,622 View
- 42 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- [Republished study] Assessing Nutritional Status in Outpatients after Gastric Cancer Surgery: A Comparative Study of Five Nutritional Screening Tools
- Jae Won Cho, Jiyoung Youn, Min-Gew Choi, Mi Young Rha, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(3):205-222. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.3.205
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the characteristics of patients according to nutritional status assessed by five nutritional screening tools: Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA), NUTRISCORE, Nutritional Risk Index (NRI), Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI), and Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) and to compare the agreement, sensitivity, and specificity of these tools.
Methods
A total of 952 gastric cancer patients who underwent gastrectomy and chemotherapy from January 2009 to December 2012 were included. The patients were categorized into malnutrition and normal status according to five nutritional screening tools one month after surgery. The Spearman partial correlation, Cohen’s Kappa coefficient, the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity of each two screening tools were calculated.
Results
Malnutrition was observed in 86.24% of patients based on the PG-SGA and 85.82% based on the NUTRISCORE. When NRI or CONUT were applied, the proportions of malnutrition were < 30%. Patients with malnutrition had lower intakes of energy and protein than normal patients when assessed using the PG-SGA, NUTRISCORE, or NRI. Lower levels of albumin, hemoglobin, total lymphocyte count, and total cholesterol and longer postoperative hospital stays were observed among patients with malnutrition compared to normal patients when NRI, PNI, or CONUT were applied. Relatively high agreement for NUTRISCORE relative to PG-SGA was found; the sensitivity was 90.86%, and the AUC was 0.78. When NRI, PNI, and CONUT were compared, the sensitivities were 23.72% for PNI relative to NRI, 44.53% for CONUT relative to NRI, and 90.91% for CONUT relative to PNI. The AUCs were 0.95 for NRI relative to PNI and 0.91 for CONUT relative to PNI.
Conclusions
NUTRISCORE had a high sensitivity compared to PG-SGA, and CONUT had a high sensitivity compared to PNI. NRI had a high specificity compared to PNI. This relatively high sensitivity and specificity resulted in 77.00% agreement between PNI and CONUT and 77.94% agreement between NRI and PNI. Further cohort studies will be needed to determine if the nutritional status assessed by PG-SGA, NUTRISCORE, NRI, PNI, and CONUT predicts the gastric cancer prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Report on the Current Trend of Commercial Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition in Outpatient
Hyun Ji Lee, Hyo Jung Park, Seon Young Chung, Myung Sook Min, Ok Soon Jeong, Ja Kyung Min
Journal of Korean Society of Health-System Pharmacists.2023; 40(2): 211. CrossRef
- Report on the Current Trend of Commercial Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition in Outpatient
- 1,522 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association Between Health Literacy and Health Promoting Behavior (Eating Habits, Physical Activity, and Stress) of University Students
- Yoon-Sun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):94-104. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.94
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study attempted to examine the association between health literacy and health-promoting behavior, and identify the major variables that affect the health-promoting behavior of university students.
Methods
This was a descriptive correlation study that identified the degree of health literacy and health-promoting behavior of 248 university students (119 male and 129 female) and examined the correlation between the two and factors influencing them. The questionnaire covering health literacy comprised 66 questions, and that for health-promoting behavior comprised 10 questions covering eating habits, 3 questions about physical activity, and 10 questions involving stress.
Results
The score for health literacy was 41.56 ± 18.38 out of 66 points, and that for health-promoting behavior was 65.27 ± 11.21 points (27.61 ± 6.72 points for eating habits, 7.23 ± 2.56 points for physical activity, and 30.44 ± 5.61 points for stress). Health literacy and health-promoting behavior had a significant positive correlation (r = 0.175, P < 0.01). The perceived health status (β = 0.391,P < 0.001) was the most important variable in healthpromoting behavior, followed by health literacy (β = 0.236, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
It is necessary to develop a systematic educational strategy and implement educational programs to improve health literacy as well as encourage health-promoting behavior and thus increase the perceived health levels of university students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(2): 207. CrossRef
- Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
- 1,592 View
- 45 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Development and Validation of a Questionnaire on the Feasibility of a Mobile Dietary Self-Monitoring Application
- Heejin Lee, Jeong Sun Ahn, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):146-157. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.146
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop and assess the content validity and internal consistency of a questionnaire on the feasibility of mobile dietary self-monitoring applications.
Methods
We developed a feasibility questionnaire to assess the overall usage, convenience, usefulness, and satisfaction of mobile dietary applications. The initial draft of the questionnaire contained 17 items with yes/no, multiple-choice, and open-ended questions and 52 items on 5-point Likert scales. To validate the content, ten experts evaluated the relevance of the items for each subscale using a 5-point scale. We calculated the item-level content validity index (I-CVI) and scale-level content validity index (S-CVI). A total of 102 adults answered the questionnaires which reflected the experts' reviews. We conducted an exploratory factor analysis to determine the underlying structure of responses and categorized convenience, usefulness, and satisfaction. We also calculated Cronbach's alpha coefficient to examine the internal consistency of items in each subscale.
Results
The S-CVI score of the items was 0.86, and we removed items with an I-CVI score of < 0.80. We combined, revised, or separated some remaining items and added one item as per the experts' comments. As a result, we included 16 items about overall usage and 42 sub-questions. Based on the responses of the 102 adults, we performed exploratory factor analysis using the principal axis method. We retained items with a factor loading of > 0.40, resulting in a final set of 35 questions (convenience: 15, usefulness: 12, satisfaction: 8 items). The Cronbach's alpha values of the three scales were 0.93, 0.91, and 0.91 for 1) usefulness, 2) convenience, and 3) satisfaction, respectively.
Conclusions
We developed a feasibility questionnaire for mobile dietary self-monitoring applications and examined its content validity and internal consistency. Our questionnaire has the potential to measure the feasibility of mobile dietary self-monitoring applications.
- 1,656 View
- 29 Download

- [Korean]
- The Consumption Pattern of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and its Comparison with Body Composition Change from a Four-Week Time-Restricted Eating Intervention in Korean Young Adults
- SuJeong Park, YoonJu Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(1):36-46. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.1.36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the consumption pattern of sugarsweetened beverages (SSB) and compare body composition changes by SSB consumption based on 28 days of dietary records from a four-week time-restricted eating intervention among young adults in Korea.
Methods
A total of 33 participants completed the four-week dietary intervention with 8-hour time-restricted eating (TRE). The body composition was measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis at baseline, and daily dietary records were collected for 28 days during the intervention after 4 weeks.
Results
Based on 924 days of dietary records, the average eating occasion of SSB was 0.9 times per day, and the average amount of SSB was 205.8 g/times. Based on an individual’s usual intake of 28 days, the average eating frequency of SSB was 16.6 times out of 28 days, and the average amount of SSB was 184.0 g/day. The average energy intake from SSB was 131.0 kcal /day (8.7% of energy), and sugar intake from SSB was 18.2 g/day (4.9% of energy). The sugar intake was 2.6% of energy from sweetened dairy products, followed by 2.0% from coffee drinks, 0.5% from soda and juice and 0.2% from others. When subjects were divided into high (14 days or more) and low (less than 14 days) SSB groups based on eating frequency, the weight change in the low SSB group was -2.0 kg over 4 weeks, which was significantly lower than -0.7 kg in the high SSB group. However, no significant difference was found in muscle mass, fat mass and body fat percent between the two groups.
Conclusions
This study suggests that low consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages is more desirable in weight management despite having the dietary intervention of timerestricted eating without counting calories. Thus, further longitudinal studies on the association between SSB and obesity in Korean adults are necessary. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitude, and Dietary Behavior among Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Na-Yeon Noh, So-Young Nam, Hee-Suk Kang, Ji-Eun Lee, Soo-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(2): 101. CrossRef - Needs Assessment for Web-based Self-management Program by the Nutrition Knowledge Levels of Diabetic Patients
Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Jung Eun Youn, Hee-Seon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(1): 155. CrossRef
- Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitude, and Dietary Behavior among Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
- 1,695 View
- 18 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Away-from-Home Eating and Dietary Patterns of Ugandan Adults: a Web-based- Survey
- Anthony Kityo, Pil-Sook Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(1):1-11. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Away-from-home (AFH) eating has been associated with poor diet quality and health outcomes like obesity in developed countries. AFH eating is also emerging in lowincome countries, but its influence on overall diet quality is under-researched. We examined the prevalence of AFH eating and its influence on the dietary patterns of Ugandan adults.
Methods
This cross-sectional study employed a web-based survey to interview Ugandan adults aged 18 ~ 65 years. A qualitative food frequency questionnaire was used to assess the food group intake, which was then converted into daily intake frequencies. Principal component analysis was used to derive dietary patterns. The participants were then classified based on the tertiles (T) of dietary pattern scores.
Results
About 75% of the 375 participants reported eating AFH. The young men, food insecure, and urban dwellers were more likely to eat AFH 5 times/week. Three dietary patterns emerged; the animal-based, beverage pattern; the high fat, sweet pattern; and the traditional, plant-based pattern. Participants who frequently ate AFH were 2.85 times and 5.64 times more likely to be in the second and third tertiles, respectively, of the animalbased, beverage pattern compared to the rare eaters (OR = 2.85, 95% CI: 1.35-6.06 for T2 vs T1; and OR = 5.64, 95% CI: 2.50-12.73 for T3 vs T1). The odds of being in the second tertile of the high fat, sweet pattern was significantly higher for frequent AFH eaters compared to the rare eaters (OR = 2.61, 95% CI:1.23-5.52).
Conclusions
The prevalence of AFH eating was high. Frequent AFH eating was common among the young, male, food insecure, and urban dwellers, and was associated with unhealthy dietary patterns. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Difficulties in eating out of home while diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease: A qualitative interview study from China
Tingting Yin, Ran Ye, Qiuqin Wang, Lulu Wang, Wenjing Xu, Wenjing Tu, Guihua Xu, Yogesh Kumar Jain
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(12): e0288908. CrossRef
- Difficulties in eating out of home while diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease: A qualitative interview study from China
- 1,706 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):467-481. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.467
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to examine the biochemical characteristics, intake of energy, and nutrients by household income levels of Korean adolescents aged 12 to 18 years.
Methods
Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES) were used for the study. A total of 1,839 (966 boys, 873 girls) subjects were included, and they were divided into four income groups according to their household income level. We examined general characteristics (gender, region of residence, skipping or not-skipping breakfast, lunch, dinner, frequency of eating-out), anthropometric characteristics (height, weight, weight status), biochemical characteristics (fasting plasma glucose, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, triglycerides, cholesterol, HDLcholesterol, hemoglobin, and hematocrit), the quantitative intake of energy and nutrients using the Korean Dietary Reference Intakes (KDRI), and the qualitative intake evaluated by the nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean nutrition adequacy ratio (MAR) of the four groups.
Results
There were significant differences by income group within the region of residence and the rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, and dinner. The low-income group had a higher rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, and dinner. According to the income group, there was a difference in the height of boys, and there was no difference in the weight and obesity of boys and girls. In the biochemical characteristics, only the hematocrit of girls showed differences by income group. The quantitative intake of energy and nutrients compared with KDRI differed by income group. There were differences in energy, carbohydrates, proteins, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and phosphorus levels in boys and protein, vitamin A, niacin, and sodium levels in girls. The qualitative intake of energy and nutrients examined using NAR and MAR also differed according to the income group. The NAR showed differences in calcium in boys and vitamin C and calcium in girls. The MAR revealed differences in both boys and girls by income group.
Conclusions
Among adolescents in the low-income group, the rate of skipping meals was high, and the quantitative and qualitative intake of energy and some nutrients was low. It is suggested that the nutritional intake can be improved by lowering the rate of skipping breakfast, lunch, dinner. We suggest that even just providing breakfast in schools can be considered highly effective in improving the rate of avoidance of skipping meals and improving nutrient intake. Also, we suggest that it is necessary to improve the food environment, food availability, and food accessibility through national and social support for low-household income adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(1): 55. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency and value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using dietary area: a descriptive study
Yunhwa Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 317. CrossRef - 제한적인 등교 상황에서 중고등학생의 신체적·정신적 건강 및 식생활 행태 변화:
민지 손, 은주 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 213. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of Changes in Adolescent Dietary Behavior during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Improvement Strategies for School-Provided Nutrition Counseling
Yeseul Na, Jieun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2023; 61(1): 39. CrossRef
- Dietary Behaviors and Health Status by Income Level in Single-Adult Households in Korea: An Analysis of Data From the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,524 View
- 8 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between Eating Alone Patterns and Mental Health Conditions by Region among Korean Adults
- Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):441-454. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the association between the frequency and pattern of eating alone and the mental health status according to region in Korean adults.
Methods
The data of 10,040 Korean adults aged ≥ 19 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2017 and 2019 were used. Participants were divided into 4 groups based on their frequency of eating alone: none (all meals together), 1, 2, and 3 meals/day alone. The regions were divided into urban and rural areas. Mental health status was assessed by stress recognition, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation. Multivariable logistic regressions were conducted to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) on the association of the frequency and pattern of eating alone with poor mental health after controlling for covariates.
Results
Among Korean adults, 74.1% ate more than one meal a day alone. Individuals having 3 meals a day alone tended to be less educated, single, single person households, or living in urban areas (all P < 0.05). In rural areas, those having 3 meals/ day alone had higher odds of stress recognition (AOR: 1.55, 95% CI: 1.02-2.35) than those having all meals together. In urban areas, individuals eating alone 3 times/day had higher odds of stress recognition (AOR: 1.60, 95% CI: 1.31-1.96), depressive symptoms (AOR: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.23-2.12), and suicidal ideation (AOR: 2.14, 95% CI: 1.42-3.22) compared to those having all meals together. Urban residents having dinner alone had higher odds of depressive symptoms (AOR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.05-1.58) and suicidal ideation (AOR: 1.66, 95% CI: 1.19-2.33) than those having dinner with others.
Conclusions
Our findings showed that the frequency and patterns of eating alone were differentially associated with increased odds of poor mental health according to region of residence. Nutrition education is needed for those frequently eating alone, particularly those living in urban areas, to highlight the advantages of eating together and to ensure that they have balanced and healthy meals even if they eat alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Social Activity Restrictions on Depression in Young Single-Person Households: The Moderating Effect of Eating Alone
Jiwon Kim, Youngye Park
Journal of Social Science.2025; 36(3): 27. CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - How Does the Frequency of Eating-Alone among Older People in Korea Affect Their Health and Dietary Behavior?
Yongseok Kwon, Kyung Hee Hong, Yoo-Kyung Park, Sohye Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2085. CrossRef - Impact assessment of a primary care physician counseling program for youth population
Yun-Su Kim, Shin-Ae Kim
Medicine.2022; 101(46): e31916. CrossRef
- The Impact of Social Activity Restrictions on Depression in Young Single-Person Households: The Moderating Effect of Eating Alone
- 2,477 View
- 41 Download
- 4 Crossref

Research Note
- [Korean]
- Basic Concepts and Detailed Dimensions of Food Security and Related Indicators for Policy Development and Evaluation
- Sohyun Park, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(6):429-440. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.6.429
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Standardized guidelines and reference points for a food security policy are necessary to guarantee that basic social safety nets work properly. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the basic concepts and detailed dimensions of food security, including the potential relevant indicators, and sought to establish standardized well-being baselines.
Methods
A literature review and 14 expert roundtable discussions were carried out to analyze and extract the key concepts of food security. After determining these concepts and detailed dimensions of food security, a conceptual framework was modeled. Then, indicators for each local government that could be monitored and evaluated for each sub-area were suggested.
Results
The concept of food security was defined as follows: Individuals should be provided with sufficient, safe, and quality food, which should be accessible to the community and available for use to achieve health and well-being. In addition, food security should be ensured sustainably in a changing environment. Four dimensions were suggested while conceptualizing food security. First, sufficient food, which means sufficient food supply in quantity, quality, and safety. Second, equitable food which includes creating environments in which high-quality and safe food can be purchased at an appropriate price and can be provided regardless of the socioeconomic gap. Third, healthy food which should be provided to promote people’s health and happiness through the eco-friendly consumption of food. Fourth, sustainable food, which can be supplied in a sustainable manner and as part of an eco-friendly food system that considers the conservation of natural environments.
Conclusions
The basic concepts and detailed areas of food security including the potential indicators proposed in this study, may be useful for developing and implementing various policies and programs to support food and nutrition security in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Achieving National Food Security in Sub‐Saharan African Countries: The Role of Foreign Agricultural Aid
Mehmet Balcilar, Godwin Olasehinde‐Williams, Berkan Tokar
Food and Energy Security.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction model for identifying a high-risk group for food insecurity among elderly South Koreans
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Achieving National Food Security in Sub‐Saharan African Countries: The Role of Foreign Agricultural Aid
- 1,570 View
- 26 Download
- 2 Crossref

Research Article
- [Korean]
- Relationship between Eating Behavior and Healthy Eating Competency of Single-Person and Multi-Person Households by Age Group
- Seung-Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):337-349. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.337
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to analyse the relationship between eating behaviour and healthy dietary competency of single and multi-person households, to improve healthy eating behavior.
Methods
This study was conducted on 6,355 adult household members who participated in the Food Consumption Behavior Survey 2020. The subjects were divided into age groups comprising young people in their 20s and 30s, middle-aged people in their 40s and 50s, and the elderly in their 60s and above. The eating behavior and healthy dietary competency of single-person and multi-person households were then analyzed.
Results
The average age of the members in the single-person households was found to be higher. Single-person households were also found to have a lower marriage rate and lower monthly household income than multi-person households across the age groups of young, middle-aged, and elderly people (P < 0.05). Among each of the age groups, single-person households had significantly higher rates of skipping breakfast and eating breakfast, lunch, and dinner alone than multi-person households (P < 0.05). Young single-person households had lower average scores on healthy dietary competency than multi-person households (P = 0.032). When adjusted for age, gender, marriage, education, occupation, and household income, single-person households had a higher risk of delivery/take-out, eating out, or skipping meals compared to multi-person households (P < 0.05). In multi-person households, the risk of skipping meals, eating alone, eating out, or delivery/take-out decreased as healthy dietary competency improved (P< 0.05). On the other hand, in single-person households, as healthy dietary competency increased, the risk of delivery/take-out or eating alone decreased (P< 0.05).
Conclusions
The results of this study suggest that healthy dietary competency and eating practices can be improved by providing customized dietary education by age group for single and multi-person households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
Soyean Kang, Hae Sagong, Juyoung Lee
Public Health Nursing.2025; 42(3): 1182. CrossRef - Understanding the charactersitics and types of single-person households based on food purchase frequencies in Korea: a cross-sectional study using the 2023 Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods
So-Yun Kim, Youngmin Nam, Jong-Youn Rha, Haerang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - Dietary status and the relationship between dietary competencies, cooking skills, and nutrition quotient of middle-aged adults living alone in Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Yun-Jung Bae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(2): 257. CrossRef - A study on regional differences in dietary behaviors and satisfaction in Korea focusing on urban and rural comparisons: a cross-sectional study
Jong-Youn Rha, Sohyun Kim, Hae-Rang Lee, Juhyeon Kil
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 140. CrossRef - Antioxidant and Nutrition Facts Analysis of Konjac Jelly Stick Containing Pinus koraiensis Leaf Powder
Eunbin Park, Soo-In Ryu, Kyung Tae Jang, Jean Kyung Paik
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(5): 402. CrossRef - Comparative study on eating habits and health of single-person and multi-person households
Haerang Lee, Seon-Jip Kim, Minji Kang, Mi-So Shim
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0327763. CrossRef - The impact of flash continuous glucose monitoring and nutrition coaching on dietary self-efficacy and weight management in university students in Korea: a pre-post intervention study
Soojin Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 183. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics and Antioxidant Activities of Morning Bread with the Addition of Whole Citron (Citrus junos seib) Powder
Eun Jung Kwak, Hyun-Joo Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2025; 36(3): 417. CrossRef - Association between food-related media content and the eating behaviors of Korean adults according to household type
Ahyoung Yun, Hyein Jung, Byungmi Kim, Yoonjoo Choi
Frontiers in Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-Person Households: Insights from a Household Survey of Fruit and Vegetable Purchases
Andres Silva, Maripaz Rivera, Samuel Durán-Agüero, Maria Isabel Sactic
Nutrients.2024; 16(17): 2851. CrossRef - Association of delivered food consumption with dietary behaviors and obesity among young adults in Jeju
Minjung Ko, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 336. CrossRef - Comparison of Food and Nutrient Intake according to the Income Level in Korean Adult Single-Person Households: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Min-Hee Han, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(3): 445. CrossRef - Hazardous alcohol use is associated with food insecurity in adults living alone: Findings from a nationwide study in Korea
Seong-Uk Baek, Yu-Min Lee, Jin-Ha Yoon, Jong-Uk Won
Social Science & Medicine.2024; 362: 117468. CrossRef - Malnutrition risk, nutritional knowledge, and dietary intake in chronic kidney disease patients on hemodialysis: comparison according to coexisting diabetes
HyunJung Yoo, Sang Cheol Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(5): 481. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Associations of cooking practices and healthy eating habits among young Korean adults in their 20s
So-Young Kim, Ji Yu Choi
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2023; 31: 100644. CrossRef - 밀키트 이용 고객의 식생활 양식과 밀키트 선택속성이 밀키트 제품의 만족도에 미치는 영향 분석
세은 김, 현주 배
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 187. CrossRef - The relationship between the prevalence of anemia and dietary intake among adults according to household types based on data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Won Kim, Ji-Myung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 510. CrossRef - Improving the nutrition quotient and dietary self-efficacy through personalized goal setting and smartphone-based nutrition counseling among adults in their 20s and 30s
Dahyeon Kim, Dawon Park, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 419. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Perception to the dietary guidelines for Koreans among Korean adults based on sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle
Yejin Yoon, Soo Hyun Kim, Hyojee Joung, Seoeun Ahn
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 742. CrossRef - Association between Healthy Eating Index and Mental Health in Middle-Aged Adults Based on Household Size in Korea
Ji-Myung Kim, EunJung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4692. CrossRef
- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
- 2,497 View
- 96 Download
- 22 Crossref

Research Note
- [Korean]
- Development of 3D Printed Snack-dish for the Elderly with Dementia
- Ji-Yeon Lee, Cheol-Ho Kim, Kug-Weon Kim, Kyong-Ae Lee, Kwangoh Koh, Hee-Seon Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(5):327-336. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.5.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to create a 3D printable snack dish model for the elderly with low food or fluid intake along with barriers towards eating. Methods: The decision was made by the hybrid-brainstorming method for creating the 3D model. Experts were assigned based on their professional areas such as clinical nutrition, food hygiene and chemical safety for the creation process. After serial feedback processes, the grape shape was suggested as the final model. After various concept sketching and making clay models, 3D-printing technology was applied to produce a prototype. Results: 3D design modeling process was conducted by SolidWorks program. After considering Dietary reference intakes for Koreans (KDRIs) and other survey data, appropriate supplementary water serving volume was decided as 285 mL which meets 30% of Adequate intake. To consider printing output conditions, this model has six grapes in one bunch with a safety lid. The FDM printer and PLA filaments were used for food hygiene and safety. To stimulate cognitive functions and interests of eating, numbers one to six was engraved on the lid of the final 3D model. Conclusions: The newly-developed 3D model was designed to increase intakes of nutrients and water in the elderly with dementia during snack time. Since dementia patients often forget to eat, engraving numbers on the grapes was conducted to stimulate cognitive function related to the swallowing and chewing process. We suggest that investigations on the types of foods or fluids are needed in the developed 3D model snack dish for future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 3D Printing Technology : Food Tech Analysis
Yuri Kim, Hyun-Jung Yun, Bum-Keun Kim, Hee-Don Choi, Yun-Sang Choi
Resources Science Research.2022; 4(1): 1. CrossRef
- 3D Printing Technology : Food Tech Analysis
- 1,303 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Crossref

Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Assessing Nutritional Status in Outpatients after Gastric Cancer Surgery : A Comparative Study of Five Nutritional Screening Tools
- Jae Won Cho, Jiyoung Youn, Min-Gew Choi, Mi Young Rha, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(4):280-295. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.4.280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the characteristics of patients according to their nutritional status as assessed by five nutritional screening tools: Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA), NUTRISCORE, Nutritional Risk Index (NRI), Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI), and Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) and to compare the agreement, sensitivity, and specificity of these tools. Methods: A total of 952 gastric cancer patients who underwent gastrectomy and chemotherapy from January 2009 to December 2012 at the Samsung Medical Center were included. We categorized patients into malnourished and normal according to the five nutritional screening tools 1 month after surgery and compared their characteristics. We also calculated the Spearman partial correlation, Cohen’s Kappa coefficient, the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity of each pair of screening tools. Results: We observed 86.24% malnutrition based on the PG-SGA and 85.82% based on the NUTRISCORE among gastric cancer patients in our study. When we applied NRI or CONUT, however, the malnutrition levels were less than 30%. Patients with malnutrition as assessed by the PG-SGA, NUTRISCORE, or NRI had lower intakes of energy and protein compared to normal patients. When NRI, PNI, or CONUT were used to identify malnutrition, lower levels of albumin, hemoglobin, total lymphocyte count, total cholesterol, and longer postoperative hospital stays were observed among patients with malnutrition compared to those without malnutrition. We found relatively high agreement between PG-SGA and NUTRISCORE; sensitivity was 90.86% and AUC was 0.78. When we compared NRI and PNI, sensitivity was 99.64% and AUC was 0.97. AUC ranged from 0.50 to 0.67 for comparisons between CONUT and each of the other nutritional screening tools. Conclusions: Our study suggests that PG-SGA and NRI have a relatively high agreement with the NUTRISCORE and PNI, respectively. Further cohort studies are needed to examine whether the nutritional status assessed by PG-SGA, NUTRISCORE, NRI, PNI, and CONUT predicts the gastric cancer prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Continuous Nutrition Care on Nutritional Status and Dietary Habits of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Surgery
Jina Son, Ha I Kang, Eun young Jung, Hae won Ryu, Kyung-Ha Lee
Clinical Nutrition Research.2023; 12(2): 99. CrossRef
- Effects of Continuous Nutrition Care on Nutritional Status and Dietary Habits of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Surgery
- 1,521 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Analysis of Surveys to Determine the Real Prices of Ingredients used in School Foodservice
- Seo-Hyun Lee, Min A Lee, Jae-Yoon Ryoo, Sanghyo Kim, Soo-Youn Kim, Hojin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):188-199. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose was to identify the ingredients that are usually surveyed for assessing real prices and to present the demand for such surveys by nutrition teachers and dietitians for ingredients used by school foodservice.
Methods
A survey was conducted online from December 2019 to January 2020. The survey questionnaire was distributed to 1,158 nutrition teachers and dietitians from elementary, middle, and high schools nationwide, and 439 (37.9% return rate) of the 1,158 were collected and used for data analysis.
Results
The ingredients which were investigated for price realities directly by schools were industrial products in 228 schools (51.8%), fruits in 169 schools (38.4%), and specialty crops in 166 schools (37.7%). Moreover, nutrition teachers and dietitians in elementary, middle, and high schools searched in different ways for the real prices of ingredients. In elementary schools, there was a high demand for price information about grains, vegetables or root and tuber crops, special crops, fruits, eggs, fishes, and organic and locally grown ingredients by the School Foodservice Support Centers. Real price information about meats, industrial products, and pickled processed products were sought from the external specialized institutions. In addition, nutrition teachers and dietitians in middle and high schools wanted to obtain prices of all of the ingredients from the Offices of Education or the District Office of Education.
Conclusions
Schools want to efficiently use the time or money spent on research for the real prices of ingredients through reputable organizations or to co-work with other nutrition teachers and dietitians. The results of this study will be useful in understanding the current status of the surveys carried out to determine the real price information for ingredients used by the school foodservice.
- 946 View
- 16 Download

- [Korean]
- Can Dining Alone Lead to Healthier Menu Item Decisions than Dining with Others? The Roles of Consumption Orientation and Menu Nutrition Information
- EunSol Her, Carl Behnke, Barbara Almanza
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):155-166. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.155
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Driven by a growth of single-person households and individualized lifestyles, solo dining in restaurants is an increasingly recognizable trend. However, a research gap exists in the comparison of solo and group diners’ menu-decision making processes. Based on the self-control dilemma and the temporal construal theory as a theoretical framework, this study compared the ordering intentions of solo vs. group diners with healthy vs. indulgent (less healthy) entrées. The mediating role of consumption orientation and the moderating role of amount of menu nutrition information were further explored to understand the mechanism and a boundary condition.
Methods
A scenario-based online survey was developed using a 2 (dining social context: solo vs. with others) × 3 (amount of menu nutrition information: no nutrition information vs. calories vs. calories/fat/sodium), between-subjects, experimental design. Consumers’ level of nutrition involvement was controlled. A nationwide survey data (n = 224) were collected from a crowdsourcing platform in the U.S. Data were analyzed using multivariate analysis of covariance, independent t-test, univariate analysis of covariance, and moderated mediation analyses.
Results
Findings reveal that solo (vs. group) diners have less (vs. more) intentions to order indulgent menu items due to a more utilitarian (vs. more hedonic) consumption orientation in restaurant dining. Findings also show that solo (vs. group) diners have more (vs. less) intentions to order healthy menu items when the restaurant menu presented nutrition information including calories, fat, and sodium.
Conclusions
The findings contribute to the literature of foodservice management, healthy eating, and consumer behavior by revealing a mechanism and an external stimuli of solo vs. group diners’ healthy menu-decision making process in restaurants. Furthermore, the findings provide restauranteurs and health professionals with insights into the positive and negative impacts of menu nutrition labelling on consumers’ menu-decisions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Eating contexts encourage sustainable food choices: The mediating role of the symbolic meanings of foods
Chujun Wang, Xiaoang Wan
Appetite.2025; 207: 107896. CrossRef - A systematic review of solo dining research
Huiling Huang, Scarlett Sijia Feng, IpKin Anthony Wong
International Journal of Hospitality Management.2025; 130: 104226. CrossRef
- Eating contexts encourage sustainable food choices: The mediating role of the symbolic meanings of foods
- 1,954 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



